Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples

What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
Published on January 27, 2023 by Tegan George . Revised on January 12, 2024.
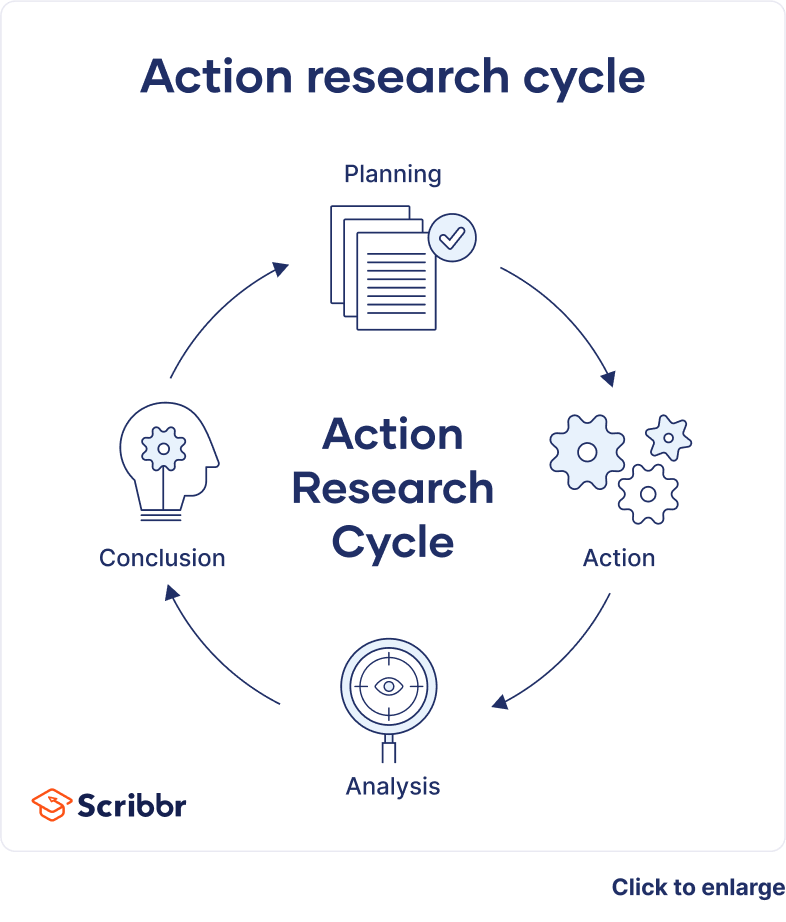
Table of contents
Types of action research, action research models, examples of action research, action research vs. traditional research, advantages and disadvantages of action research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about action research.
There are 2 common types of action research: participatory action research and practical action research.
- Participatory action research emphasizes that participants should be members of the community being studied, empowering those directly affected by outcomes of said research. In this method, participants are effectively co-researchers, with their lived experiences considered formative to the research process.
- Practical action research focuses more on how research is conducted and is designed to address and solve specific issues.
Both types of action research are more focused on increasing the capacity and ability of future practitioners than contributing to a theoretical body of knowledge.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Action research is often reflected in 3 action research models: operational (sometimes called technical), collaboration, and critical reflection.
- Operational (or technical) action research is usually visualized like a spiral following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
- Collaboration action research is more community-based, focused on building a network of similar individuals (e.g., college professors in a given geographic area) and compiling learnings from iterated feedback cycles.
- Critical reflection action research serves to contextualize systemic processes that are already ongoing (e.g., working retroactively to analyze existing school systems by questioning why certain practices were put into place and developed the way they did).
Action research is often used in fields like education because of its iterative and flexible style.
After the information was collected, the students were asked where they thought ramps or other accessibility measures would be best utilized, and the suggestions were sent to school administrators. Example: Practical action research Science teachers at your city’s high school have been witnessing a year-over-year decline in standardized test scores in chemistry. In seeking the source of this issue, they studied how concepts are taught in depth, focusing on the methods, tools, and approaches used by each teacher.
Action research differs sharply from other types of research in that it seeks to produce actionable processes over the course of the research rather than contributing to existing knowledge or drawing conclusions from datasets. In this way, action research is formative , not summative , and is conducted in an ongoing, iterative way.
| Action research | Traditional research | |
|---|---|---|
| and findings | ||
| and seeking between variables | ||
As such, action research is different in purpose, context, and significance and is a good fit for those seeking to implement systemic change.
Action research comes with advantages and disadvantages.
- Action research is highly adaptable , allowing researchers to mold their analysis to their individual needs and implement practical individual-level changes.
- Action research provides an immediate and actionable path forward for solving entrenched issues, rather than suggesting complicated, longer-term solutions rooted in complex data.
- Done correctly, action research can be very empowering , informing social change and allowing participants to effect that change in ways meaningful to their communities.
Disadvantages
- Due to their flexibility, action research studies are plagued by very limited generalizability and are very difficult to replicate . They are often not considered theoretically rigorous due to the power the researcher holds in drawing conclusions.
- Action research can be complicated to structure in an ethical manner . Participants may feel pressured to participate or to participate in a certain way.
- Action research is at high risk for research biases such as selection bias , social desirability bias , or other types of cognitive biases .
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Action research is conducted in order to solve a particular issue immediately, while case studies are often conducted over a longer period of time and focus more on observing and analyzing a particular ongoing phenomenon.
Action research is focused on solving a problem or informing individual and community-based knowledge in a way that impacts teaching, learning, and other related processes. It is less focused on contributing theoretical input, instead producing actionable input.
Action research is particularly popular with educators as a form of systematic inquiry because it prioritizes reflection and bridges the gap between theory and practice. Educators are able to simultaneously investigate an issue as they solve it, and the method is very iterative and flexible.
A cycle of inquiry is another name for action research . It is usually visualized in a spiral shape following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
Sources in this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
George, T. (2024, January 12). What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/action-research/
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2017). Research methods in education (8th edition). Routledge.
Naughton, G. M. (2001). Action research (1st edition). Routledge.
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, what is an observational study | guide & examples, primary research | definition, types, & examples, guide to experimental design | overview, steps, & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
the encyclopaedia of pedagogy and informal education

What is action research and how do we do it?
In this article, we explore the development of some different traditions of action research and provide an introductory guide to the literature., contents : what is action research · origins · the decline and rediscovery of action research · undertaking action research · conclusion · further reading · how to cite this article . see, also: research for practice ..
In the literature, discussion of action research tends to fall into two distinctive camps. The British tradition – especially that linked to education – tends to view action research as research-oriented toward the enhancement of direct practice. For example, Carr and Kemmis provide a classic definition:
Action research is simply a form of self-reflective enquiry undertaken by participants in social situations in order to improve the rationality and justice of their own practices, their understanding of these practices, and the situations in which the practices are carried out (Carr and Kemmis 1986: 162).
Many people are drawn to this understanding of action research because it is firmly located in the realm of the practitioner – it is tied to self-reflection. As a way of working it is very close to the notion of reflective practice coined by Donald Schön (1983).
The second tradition, perhaps more widely approached within the social welfare field – and most certainly the broader understanding in the USA is of action research as ‘the systematic collection of information that is designed to bring about social change’ (Bogdan and Biklen 1992: 223). Bogdan and Biklen continue by saying that its practitioners marshal evidence or data to expose unjust practices or environmental dangers and recommend actions for change. In many respects, for them, it is linked into traditions of citizen’s action and community organizing. The practitioner is actively involved in the cause for which the research is conducted. For others, it is such commitment is a necessary part of being a practitioner or member of a community of practice. Thus, various projects designed to enhance practice within youth work, for example, such as the detached work reported on by Goetschius and Tash (1967) could be talked of as action research.
Kurt Lewin is generally credited as the person who coined the term ‘action research’:
The research needed for social practice can best be characterized as research for social management or social engineering. It is a type of action-research, a comparative research on the conditions and effects of various forms of social action, and research leading to social action. Research that produces nothing but books will not suffice (Lewin 1946, reproduced in Lewin 1948: 202-3)
His approach involves a spiral of steps, ‘each of which is composed of a circle of planning, action and fact-finding about the result of the action’ ( ibid. : 206). The basic cycle involves the following:
This is how Lewin describes the initial cycle:
The first step then is to examine the idea carefully in the light of the means available. Frequently more fact-finding about the situation is required. If this first period of planning is successful, two items emerge: namely, “an overall plan” of how to reach the objective and secondly, a decision in regard to the first step of action. Usually this planning has also somewhat modified the original idea. ( ibid. : 205)
The next step is ‘composed of a circle of planning, executing, and reconnaissance or fact-finding for the purpose of evaluating the results of the second step, and preparing the rational basis for planning the third step, and for perhaps modifying again the overall plan’ ( ibid. : 206). What we can see here is an approach to research that is oriented to problem-solving in social and organizational settings, and that has a form that parallels Dewey’s conception of learning from experience.
The approach, as presented, does take a fairly sequential form – and it is open to a literal interpretation. Following it can lead to practice that is ‘correct’ rather than ‘good’ – as we will see. It can also be argued that the model itself places insufficient emphasis on analysis at key points. Elliott (1991: 70), for example, believed that the basic model allows those who use it to assume that the ‘general idea’ can be fixed in advance, ‘that “reconnaissance” is merely fact-finding, and that “implementation” is a fairly straightforward process’. As might be expected there was some questioning as to whether this was ‘real’ research. There were questions around action research’s partisan nature – the fact that it served particular causes.
The decline and rediscovery of action research
Action research did suffer a decline in favour during the 1960s because of its association with radical political activism (Stringer 2007: 9). There were, and are, questions concerning its rigour, and the training of those undertaking it. However, as Bogdan and Biklen (1992: 223) point out, research is a frame of mind – ‘a perspective that people take toward objects and activities’. Once we have satisfied ourselves that the collection of information is systematic and that any interpretations made have a proper regard for satisfying truth claims, then much of the critique aimed at action research disappears. In some of Lewin’s earlier work on action research (e.g. Lewin and Grabbe 1945), there was a tension between providing a rational basis for change through research, and the recognition that individuals are constrained in their ability to change by their cultural and social perceptions, and the systems of which they are a part. Having ‘correct knowledge’ does not of itself lead to change, attention also needs to be paid to the ‘matrix of cultural and psychic forces’ through which the subject is constituted (Winter 1987: 48).
Subsequently, action research has gained a significant foothold both within the realm of community-based, and participatory action research; and as a form of practice-oriented to the improvement of educative encounters (e.g. Carr and Kemmis 1986).
Exhibit 1: Stringer on community-based action research
A fundamental premise of community-based action research is that it commences with an interest in the problems of a group, a community, or an organization. Its purpose is to assist people in extending their understanding of their situation and thus resolving problems that confront them….
Community-based action research is always enacted through an explicit set of social values. In modern, democratic social contexts, it is seen as a process of inquiry that has the following characteristics:
• It is democratic , enabling the participation of all people.
• It is equitable , acknowledging people’s equality of worth.
• It is liberating , providing freedom from oppressive, debilitating conditions.
• It is life enhancing , enabling the expression of people’s full human potential.
(Stringer 1999: 9-10)
Undertaking action research
As Thomas (2017: 154) put it, the central aim is change, ‘and the emphasis is on problem-solving in whatever way is appropriate’. It can be seen as a conversation rather more than a technique (McNiff et. al. ). It is about people ‘thinking for themselves and making their own choices, asking themselves what they should do and accepting the consequences of their own actions’ (Thomas 2009: 113).
The action research process works through three basic phases:
Look -building a picture and gathering information. When evaluating we define and describe the problem to be investigated and the context in which it is set. We also describe what all the participants (educators, group members, managers etc.) have been doing.
Think – interpreting and explaining. When evaluating we analyse and interpret the situation. We reflect on what participants have been doing. We look at areas of success and any deficiencies, issues or problems.
Act – resolving issues and problems. In evaluation we judge the worth, effectiveness, appropriateness, and outcomes of those activities. We act to formulate solutions to any problems. (Stringer 1999: 18; 43-44;160)
The use of action research to deepen and develop classroom practice has grown into a strong tradition of practice (one of the first examples being the work of Stephen Corey in 1949). For some, there is an insistence that action research must be collaborative and entail groupwork.
Action research is a form of collective self-reflective enquiry undertaken by participants in social situations in order to improve the rationality and justice of their own social or educational practices, as well as their understanding of those practices and the situations in which the practices are carried out… The approach is only action research when it is collaborative, though it is important to realise that action research of the group is achieved through the critically examined action of individual group members. (Kemmis and McTaggart 1988: 5-6)
Just why it must be collective is open to some question and debate (Webb 1996), but there is an important point here concerning the commitments and orientations of those involved in action research.
One of the legacies Kurt Lewin left us is the ‘action research spiral’ – and with it there is the danger that action research becomes little more than a procedure. It is a mistake, according to McTaggart (1996: 248) to think that following the action research spiral constitutes ‘doing action research’. He continues, ‘Action research is not a ‘method’ or a ‘procedure’ for research but a series of commitments to observe and problematize through practice a series of principles for conducting social enquiry’. It is his argument that Lewin has been misunderstood or, rather, misused. When set in historical context, while Lewin does talk about action research as a method, he is stressing a contrast between this form of interpretative practice and more traditional empirical-analytic research. The notion of a spiral may be a useful teaching device – but it is all too easy to slip into using it as the template for practice (McTaggart 1996: 249).
Further reading
This select, annotated bibliography has been designed to give a flavour of the possibilities of action research and includes some useful guides to practice. As ever, if you have suggestions about areas or specific texts for inclusion, I’d like to hear from you.
Explorations of action research
Atweh, B., Kemmis, S. and Weeks, P. (eds.) (1998) Action Research in Practice: Partnership for Social Justice in Education, London: Routledge. Presents a collection of stories from action research projects in schools and a university. The book begins with theme chapters discussing action research, social justice and partnerships in research. The case study chapters cover topics such as: school environment – how to make a school a healthier place to be; parents – how to involve them more in decision-making; students as action researchers; gender – how to promote gender equity in schools; writing up action research projects.
Carr, W. and Kemmis, S. (1986) Becoming Critical. Education, knowledge and action research , Lewes: Falmer. Influential book that provides a good account of ‘action research’ in education. Chapters on teachers, researchers and curriculum; the natural scientific view of educational theory and practice; the interpretative view of educational theory and practice; theory and practice – redefining the problem; a critical approach to theory and practice; towards a critical educational science; action research as critical education science; educational research, educational reform and the role of the profession.
Carson, T. R. and Sumara, D. J. (ed.) (1997) Action Research as a Living Practice , New York: Peter Lang. 140 pages. Book draws on a wide range of sources to develop an understanding of action research. Explores action research as a lived practice, ‘that asks the researcher to not only investigate the subject at hand but, as well, to provide some account of the way in which the investigation both shapes and is shaped by the investigator.
Dadds, M. (1995) Passionate Enquiry and School Development. A story about action research , London: Falmer. 192 + ix pages. Examines three action research studies undertaken by a teacher and how they related to work in school – how she did the research, the problems she experienced, her feelings, the impact on her feelings and ideas, and some of the outcomes. In his introduction, John Elliot comments that the book is ‘the most readable, thoughtful, and detailed study of the potential of action-research in professional education that I have read’.
Ghaye, T. and Wakefield, P. (eds.) CARN Critical Conversations. Book one: the role of the self in action , Bournemouth: Hyde Publications. 146 + xiii pages. Collection of five pieces from the Classroom Action Research Network. Chapters on: dialectical forms; graduate medical education – research’s outer limits; democratic education; managing action research; writing up.
McNiff, J. (1993) Teaching as Learning: An Action Research Approach , London: Routledge. Argues that educational knowledge is created by individual teachers as they attempt to express their own values in their professional lives. Sets out familiar action research model: identifying a problem, devising, implementing and evaluating a solution and modifying practice. Includes advice on how working in this way can aid the professional development of action researcher and practitioner.
Quigley, B. A. and Kuhne, G. W. (eds.) (1997) Creating Practical Knowledge Through Action Research, San Fransisco: Jossey Bass. Guide to action research that outlines the action research process, provides a project planner, and presents examples to show how action research can yield improvements in six different settings, including a hospital, a university and a literacy education program.
Plummer, G. and Edwards, G. (eds.) CARN Critical Conversations. Book two: dimensions of action research – people, practice and power , Bournemouth: Hyde Publications. 142 + xvii pages. Collection of five pieces from the Classroom Action Research Network. Chapters on: exchanging letters and collaborative research; diary writing; personal and professional learning – on teaching and self-knowledge; anti-racist approaches; psychodynamic group theory in action research.
Whyte, W. F. (ed.) (1991) Participatory Action Research , Newbury Park: Sage. 247 pages. Chapters explore the development of participatory action research and its relation with action science and examine its usages in various agricultural and industrial settings
Zuber-Skerritt, O. (ed.) (1996) New Directions in Action Research , London; Falmer Press. 266 + xii pages. A useful collection that explores principles and procedures for critical action research; problems and suggested solutions; and postmodernism and critical action research.
Action research guides
Coghlan, D. and Brannick, D. (2000) Doing Action Research in your own Organization, London: Sage. 128 pages. Popular introduction. Part one covers the basics of action research including the action research cycle, the role of the ‘insider’ action researcher and the complexities of undertaking action research within your own organisation. Part two looks at the implementation of the action research project (including managing internal politics and the ethics and politics of action research). New edition due late 2004.
Elliot, J. (1991) Action Research for Educational Change , Buckingham: Open University Press. 163 + x pages Collection of various articles written by Elliot in which he develops his own particular interpretation of action research as a form of teacher professional development. In some ways close to a form of ‘reflective practice’. Chapter 6, ‘A practical guide to action research’ – builds a staged model on Lewin’s work and on developments by writers such as Kemmis.
Johnson, A. P. (2007) A short guide to action research 3e. Allyn and Bacon. Popular step by step guide for master’s work.
Macintyre, C. (2002) The Art of the Action Research in the Classroom , London: David Fulton. 138 pages. Includes sections on action research, the role of literature, formulating a research question, gathering data, analysing data and writing a dissertation. Useful and readable guide for students.
McNiff, J., Whitehead, J., Lomax, P. (2003) You and Your Action Research Project , London: Routledge. Practical guidance on doing an action research project.Takes the practitioner-researcher through the various stages of a project. Each section of the book is supported by case studies
Stringer, E. T. (2007) Action Research: A handbook for practitioners 3e , Newbury Park, ca.: Sage. 304 pages. Sets community-based action research in context and develops a model. Chapters on information gathering, interpretation, resolving issues; legitimacy etc. See, also Stringer’s (2003) Action Research in Education , Prentice-Hall.
Winter, R. (1989) Learning From Experience. Principles and practice in action research , Lewes: Falmer Press. 200 + 10 pages. Introduces the idea of action research; the basic process; theoretical issues; and provides six principles for the conduct of action research. Includes examples of action research. Further chapters on from principles to practice; the learner’s experience; and research topics and personal interests.
Action research in informal education
Usher, R., Bryant, I. and Johnston, R. (1997) Adult Education and the Postmodern Challenge. Learning beyond the limits , London: Routledge. 248 + xvi pages. Has some interesting chapters that relate to action research: on reflective practice; changing paradigms and traditions of research; new approaches to research; writing and learning about research.
Other references
Bogdan, R. and Biklen, S. K. (1992) Qualitative Research For Education , Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Goetschius, G. and Tash, J. (1967) Working with the Unattached , London: Routledge and Kegan Paul.
McTaggart, R. (1996) ‘Issues for participatory action researchers’ in O. Zuber-Skerritt (ed.) New Directions in Action Research , London: Falmer Press.
McNiff, J., Lomax, P. and Whitehead, J. (2003) You and Your Action Research Project 2e. London: Routledge.
Thomas, G. (2017). How to do your Research Project. A guide for students in education and applied social sciences . 3e. London: Sage.
Acknowledgements : spiral by Michèle C. | flickr ccbyncnd2 licence
How to cite this article : Smith, M. K. (1996; 2001, 2007, 2017) What is action research and how do we do it?’, The encyclopedia of pedagogy and informal education. [ https://infed.org/mobi/action-research/ . Retrieved: insert date] .
© Mark K. Smith 1996; 2001, 2007, 2017
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 27 April 2023
Participatory action research
- Flora Cornish ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3404-9385 1 ,
- Nancy Breton ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8388-0458 1 ,
- Ulises Moreno-Tabarez ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3504-8624 2 ,
- Jenna Delgado 3 ,
- Mohi Rua 4 ,
- Ama de-Graft Aikins 5 &
- Darrin Hodgetts 6
Nature Reviews Methods Primers volume 3 , Article number: 34 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
81k Accesses
72 Citations
56 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Communication
- Developing world
Participatory action research (PAR) is an approach to research that prioritizes the value of experiential knowledge for tackling problems caused by unequal and harmful social systems, and for envisioning and implementing alternatives. PAR involves the participation and leadership of those people experiencing issues, who take action to produce emancipatory social change, through conducting systematic research to generate new knowledge. This Primer sets out key considerations for the design of a PAR project. The core of the Primer introduces six building blocks for PAR project design: building relationships; establishing working practices; establishing a common understanding of the issue; observing, gathering and generating materials; collaborative analysis; and planning and taking action. We discuss key challenges faced by PAR projects, namely, mismatches with institutional research infrastructure; risks of co-option; power inequalities; and the decentralizing of control. To counter such challenges, PAR researchers may build PAR-friendly networks of people and infrastructures; cultivate a critical community to hold them to account; use critical reflexivity; redistribute powers; and learn to trust the process. PAR’s societal contribution and methodological development, we argue, can best be advanced by engaging with contemporary social movements that demand the redressingl of inequities and the recognition of situated expertise.
Similar content being viewed by others
Mapping the community: use of research evidence in policy and practice
Negotiating the ethical-political dimensions of research methods: a key competency in mixed methods, inter- and transdisciplinary, and co-production research

Structured output methods and environmental issues: perspectives on co-created bottom-up and ‘sideways’ science
Introduction.
For the authors of this Primer, participatory action research (PAR) is a scholar–activist research approach that brings together community members, activists and scholars to co-create knowledge and social change in tandem 1 , 2 . PAR is a collaborative, iterative, often open-ended and unpredictable endeavour, which prioritizes the expertise of those experiencing a social issue and uses systematic research methodologies to generate new insights. Relationships are central. PAR typically involves collaboration between a community with lived experience of a social issue and professional researchers, often based in universities, who contribute relevant knowledge, skills, resources and networks. PAR is not a research process driven by the imperative to generate knowledge for scientific progress, or knowledge for knowledge’s sake; it is a process for generating knowledge-for-action and knowledge-through-action, in service of goals of specific communities. The position of a PAR scholar is not easy and is constantly tested, as PAR projects and roles straddle university and community boundaries, involving unequal power relations and multiple, sometimes conflicting interests. This Primer aims to support researchers in preparing a PAR project, by providing a scaffold to navigate the processes through which PAR can help us to collaboratively envisage and enact emancipatory futures.
We consider PAR an emancipatory form of scholarship 1 . Emancipatory scholarship is driven by interest in tackling injustices and building futures supportive of human thriving, rather than objectivity and neutrality. It uses research not primarily to communicate with academic experts but to inform grassroots collective action. Many users of PAR aspire to projects of liberation and/or transformation . Users are likely to be critical of research that perpetuates oppressive power relations, whether within the research relationships themselves or in a project’s messages or outcomes, often aiming to trouble or transform power relations. PAR projects are usually concerned with developments not only in knowledge but also in action and in participants’ capacities, capabilities and performances.
PAR does not follow a set research design or particular methodology, but constitutes a strategic rallying point for collaborative, impactful, contextually situated and inclusive efforts to document, interpret and address complex systemic problems 3 . The development of PAR is a product of intellectual and activist work bridging universities and communities, with separate genealogies in several Indigenous 4 , 5 , Latin American 6 , 7 , Indian 8 , African 9 , Black feminist 10 , 11 and Euro-American 12 , 13 traditions.
PAR, as an authoritative form of enquiry, became established during the 1970s and 1980s in the context of anti-colonial movements in the Global South. As anti-colonial movements worked to overthrow territorial and economic domination, they also strived to overthrow symbolic and epistemic injustices , ousting the authority of Western science to author knowledge about dominated peoples 4 , 14 . For Indigenous scholars, the development of PAR approaches often comprised an extension of Indigenous traditions of knowledge production that value inclusion and community engagement, while enabling explicit engagements with matters of power, domination and representation 15 . At the same time, exchanges between Latin American and Indian popular education movements produced Orlando Fals Borda’s articulation of PAR as a paradigm in the 1980s. This orientation prioritized people’s participation in producing knowledge, instead of the positioning of local populations as the subject of knowledge production practices imposed by outside experts 16 . Meanwhile, PAR appealed to those inspired by Black and postcolonial feminists who challenged established knowledge hierarchies, arguing for the wisdom of people marginalized by centres of power, who, in the process of survivance, that is, surviving and resisting oppressive social structures, came to know and deconstruct those structures acutely 17 , 18 .
Some Euro-American approaches to PAR are less transformational and more reformist, in the action research paradigm, as developed by Kurt Lewin 19 to enhance organizational efficacy during and after World War II. Action research later gained currency as a popular approach for professionals such as teachers and nurses to develop their own practices, and it tended to focus on relatively small-scale adjustments within a given institutional structure, instead of challenging power relations as in anti-colonial PAR 13 , 20 . In the late twentieth century, participatory research gained currency in academic fields such as participatory development 21 , 22 , participatory health promotion 23 and creative methods 24 . Although participatory research includes participants in the conceptualization, design and conduct of a project, it may not prioritize action and social change to the extent that PAR does. In the early twenty-first century, the development of PAR is occurring through sustained scholarly engagements in anti-colonial 5 , 25 , abolitionist 26 , anti-racist 27 , 28 , gender-expansive 29 , climate activist 30 and other radical social movements.
This Primer bridges these traditions by looking across them for mutual learning but avoiding assimilating them. We hope that readers will bring their own activist and intellectual heritages to inform their use of PAR and adapt and adjust the suggestions we present to meet their needs.
Four key principles
Drawing across its diverse origins, we characterize PAR by four key principles. The first is the authority of direct experience. PAR values the expertise generated through experience, claiming that those who have been marginalized or harmed by current social relations have deep experiential knowledge of those systems and deserve to own and lead initiatives to change them 3 , 5 , 17 , 18 . The second is knowledge in action. Following the tradition of action research, it is through learning from the experience of making changes that PAR generates new knowledge 13 . The third key principle is research as a transformative process. For PAR, the research process is as important as the outcomes; projects aim to create empowering relationships and environments within the research process itself 31 . The final key principle is collaboration through dialogue. PAR’s power comes from harnessing the diverse sets of expertise and capacities of its collaborators through critical dialogues 7 , 8 , 32 .
Because PAR is often unfamiliar, misconstrued or mistrusted by dominant scientific 33 institutions, PAR practitioners may find themselves drawn into competitions and debates set on others’ terms, or into projects interested in securing communities’ participation but not their emancipation. Engaging communities and participants in participatory exercises for the primary purpose of advancing research aims prioritized by a university or others is not, we contend, PAR. We encourage PAR teams to articulate their intellectual and political heritage and aspirations, and agree their core principles, to which they can hold themselves accountable. Such agreements can serve as anchors for decision-making or counterweights to the pull towards inegalitarian or extractive research practices.
Aims of the Primer
The contents of the Primer are shaped by the authors’ commitment to emancipatory, engaged scholarship, and their own experience of PAR, stemming from their scholar-activism with marginalized communities to tackle issues including state neglect, impoverishment, infectious and non-communicable disease epidemics, homelessness, sexual violence, eviction, pollution, dispossession and post-disaster recovery. Collectively, our understanding of PAR is rooted in Indigenous, Black feminist and emancipatory education traditions and diverse personal experiences of privilege and marginalization across dimensions of race, class, gender, sexuality and disability. We use an inclusive understanding of PAR, to include engaging, emancipatory work that does not necessarily use the term PAR, and we aim to showcase some of the diversity of scholar-activism around the globe. The contents of this Primer are suggestions and reflections based on our own experience of PAR and of teaching research methodology. There are multiple ways of conceptualizing and conducting a PAR project. As context-sensitive social change processes, every project will pose new challenges.
This Primer is addressed primarily to university-based PAR researchers, who are likely to work in collaboration with members of communities or organizations or with activists, and are accountable to academic audiences as well as to community audiences. Much expertise in PAR originates outside universities, in community groups and organizations, from whom scholars have much to learn. The Primer aims to familiarize scholars new to PAR and others who may benefit with PAR’s key principles, decision points, practices, challenges, dilemmas, optimizations, limitations and work-arounds. Readers will be able to use our framework of ‘building blocks’ as a guide to designing their projects. We aim to support critical thinking about the challenges of PAR to enable readers to problem-solve independently. The Primer aims to inspire with examples, which we intersperse throughout. To illustrate some of the variety of positive achievements of PAR projects, Box 1 presents three examples.
Box 1 What does participatory action research do?
The Tsui Anaa Project 60 in Accra, Ghana, began as a series of interviews about diabetes experiences in one of Accra’s oldest indigenous communities, Ga Mashie. Over a 12-year period, a team of interdisciplinary researchers expanded the project to a multi-method engagement with a wide range of community members. University and community co-researchers worked to diagnose the burden of chronic conditions, to develop psychosocial interventions for cardiovascular and associated conditions and to critically reflect on long-term goals. A health support group of people living with diabetes and cardiovascular conditions, called Jamestown Health Club (JTHC), was formed, met monthly and contributed as patient advocates to community, city and national non-communicable disease policy. The project has supported graduate collaborators with mixed methods training, community engagement and postgraduate theses advancing the core project purposes.
Buckles, Khedkar and Ghevde 39 were approached by members of the Katkari tribal community in Maharashtra, India, who were concerned about landlords erecting fences around their villages. Using their institutional networks, the academics investigated the villagers’ legal rights to secure tenure and facilitated a series of participatory investigations, through which Katkari villagers developed their own understanding of the inequalities they faced and analysed potential action strategies. Subsequently, through legal challenges, engagement with local politics and emboldened local communities, more than 100 Katkari communities were more secure and better organized 5 years later.
The Morris Justice Project 74 in New York, USA, sought to address stop-and-frisk policing in a neighbourhood local to the City University of New York, where a predominantly Black population was subject to disproportionate and aggressive policing. Local residents surveyed their neighbours to gather evidence on experiences of stop and frisk, compiling their statistics and experiences and sharing them with the local community on the sidewalk, projecting their findings onto public buildings and joining a coalition ‘Communities United for Police Reform’, which successfully campaigned for changes to the city’s policing laws.
Experimentation
This section sets out the core considerations for designing a PAR project.
Owing to the intricacies of working within complex human systems in real time, PAR practitioners do not follow a highly proceduralized or linear set of steps 34 . In a cyclical process, teams work together to come to an initial definition of their social problem, design a suitable action, observe and gather information on the results, and then analyse and reflect on the action and its impact, in order to learn, modify their understanding and inform the next iteration of the research–action cycle 3 , 35 (Fig. 1 ). Teams remain open throughout the cycle to repeating or revising earlier steps in response to developments in the field. The fundamental process of building relationships occurs throughout the cycles. These spiral diagrams orient readers towards the central interdependence of processes of participation, action and research and the nonlinear, iterative process of learning by doing 3 , 36 .
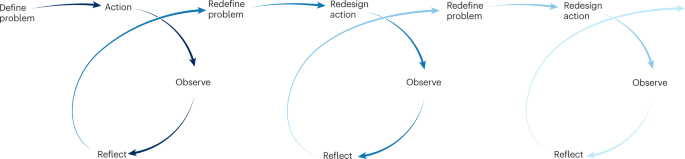
Participatory action research develops through a series of cycles, with relationship building as a constant practice. Cycles of research text adapted from ref. 81 , and figure adapted with permission from ref. 82 , SAGE.
Building blocks for PAR research design
We present six building blocks to set out the key design considerations for conducting a PAR project. Each PAR team may address these building blocks in different ways and with different priorities. Table 1 proposes potential questions and indicative goals that are possible markers of progress for each building block. They are not prescriptive or exhaustive but may be a useful starting point, with examples, to prompt new PAR teams’ planning.
Building relationships
‘Relationships first, research second’ is our key principle for PAR project design 37 . Collaborative relationships usually extend beyond a particular PAR project, and it is rare that one PAR project finalizes a desired change. A researcher parachuting in and out may be able to complete a research article, with community cooperation, but will not be able to see through the hard graft of a programme of participatory research towards social change. Hence, individual PAR projects are often nested in long-term collaborations. Such collaborations are strengthened by institutional backing in the form of sustainable staff appointments, formal recognition of the value of university–community partnerships and provision of administrative support. In such a supportive context, opportunities can be created for achievable shorter-term projects to which collaborators or temporary researchers may contribute. The first step of PAR is sometimes described as the entry, but we term this foundational step building relationships to emphasize the longer-term nature of these relationships and their constitutive role throughout a project. PAR scholars may need to work hard with and against their institutions to protect those relationships, monitoring potential collaborations for community benefit rather than knowledge and resource extraction. Trustworthy relationships depend upon scholars being aware, open and honest about their own interests and perspectives.
The motivation for a PAR project may come from university-based or community-based researchers. When university researchers already have a relationship with marginalized communities, they may be approached by community leaders initiating a collaboration 38 , 39 . Alternatively, a university-based researcher may reach out to representatives of communities facing evident problems, to explore common interests and the potential for collaboration 40 . As Indigenous scholars have articulated, communities that have been treated as the subjects or passive objects of research, commodified for the scientific knowledge of distant elites, are suspicious of research and researchers 4 , 41 . Scholars need to be able to satisfy communities’ key questions: Who are you? Why should we trust you? What is in it for our community? Qualifications, scholarly achievements or verbal reassurances are less relevant in this context than past or present valued contributions, participation in a heritage of transformational action or evidence of solidarity with a community’s causes. Being vouched for by a respected community member or collaborator can be invaluable.
Without prior relationships one can start cold, as a stranger, perhaps attending public events, informal meeting places or identifying organizations in which the topic is of interest, and introducing oneself. Strong collaborative relationships are based on mutual trust, which must be earned. It is important to be transparent about our interests and to resist the temptation to over-promise. Good PAR practitioners do not raise unrealistic expectations. Box 2 presents key soft skills for PAR researchers.
Positionality is crucial to PAR relationships. A university-based researcher’s positionalities (including, for example, their gender, race, ethnicity, class, politics, skills, age, life stage, life experiences, assumptions about the problem, experience in research, activism and relationship to the topic) interact with the positionalities of community co-researchers, shaping the collective definition of the problem and appropriate solutions. Positionalities are not fixed, but can be changing, multiple and even contradictory 42 . We have framed categories of university-based and community-based researchers here, but in practice these positionings of ‘insiders’ and ‘outsiders’ are often more complex and shifting 43 . Consideration of diversity is important when building a team to avoid tokenism . For example, identifying which perspectives are included initially and why, and whether members of the team or gatekeepers have privileged access owing to their race, ethnicity, class, gender and/or able-bodiedness.
The centring of community expertise in PAR does not mean that a community is ‘taken for granted’. Communities are sites of the production of similarity and difference, equality and inequalities, and politics. Knowledge that has the status of common sense may itself reproduce inequalities or perpetuate harm. Relatedly, strong PAR projects cultivate reflexivity 44 among both university-based and community-based researchers, to enable a critical engagement with the diversity of points of view, positions of power and stakes in a project. Developing reflexivity may be uncomfortable and challenging, and good PAR projects create a supportive culture for processing such discomfort. Supplementary files 1 and 2 present example exercises that build critical reflexivity.
Box 2 Soft skills of a participatory action researcher
Respect for others’ knowledge and the expertise of experience
Humility and genuine kindness
Ability to be comfortable with discomfort
Sharing power; ceding control
Trusting the process
Acceptance of uncertainty and tensions
Openness to learning from collaborators
Self-awareness and the ability to listen and be confronted
Willingness to take responsibility and to be held accountable
Confidence to identify and challenge power relations
Establishing working practices
Partnerships bring together people with different sets of norms, assumptions, interests, resources, time frames and working practices, all nested in institutional structures and infrastructures that cement those assumptions. University-based researchers often take their own working practices for granted, but partnership working calls for negotiation. Academics often work with very extended time frames for analysis, writing and review before publication, hoping to contribute to gradually shifting agendas, discourses and politics 45 . The urgency of problems that face a community often calls for faster responsiveness. Research and management practices that are normal in a university may not be accessible to people historically marginalized through dimensions that include disability, language, racialization, gender, literacy practices and their intersections 46 . Disrupting historically entrenched power dynamics associated with these concerns can raise discomfort and calls for skilful negotiation. In short, partnership working is a complex art, calling for thoughtful design of joint working practices and a willingness to invest the necessary time.
Making working practices and areas of tension explicit is one useful starting point. Not all issues need to be fully set out and decided at the outset of a project. A foundation of trust, through building relationships in building block 1, allows work to move ahead without every element being pinned down in advance. Supplementary file 1 presents an exercise designed to build working relationships and communicative practices.
Establishing a common understanding of the issue
Co-researchers identify a common issue or problem to address. University-based researchers tend to justify the selection of the research topic with reference to a literature review, whereas in PAR, the topic must be a priority for the community. Problem definition is a key step for PAR teams, where problem does not necessarily mean something negative or a deficit, but refers to the identification of an important issue at stake for a community. The definition of a problem, however, is not always self-evident, and producing a problem definition can be a valid outcome of PAR. In the example of risks of eviction from Buckles, Khedkar and Ghevde 39 (Box 1 ), a small number of Katkari people first experienced the problem in terms of landlords erecting barbed wire fences. Other villages did not perceive the risk of eviction as a big problem compared with their other needs. Facilitating dialogues across villages about their felt problems revealed how land tenure was at the root of several issues, thus mobilizing interest. Problem definitions are political; they imply some forms of action and not others. Discussion and reflexivity about the problem definition are crucial. Compared with other methodologies, the PAR research process is much more public from the outset, and so practices of making key steps explicit, shareable, communicable and negotiable are essential. Supplementary file 3 introduces two participatory tools for collective problem definition.
Consideration of who should be involved in problem definition is important. It may be enough that a small project team works closely together at this stage. Alternatively, group or public meetings may be held, with careful facilitation 5 . Out of dialogue, a PAR team aims to agree on an actionable problem definition, responding to the team’s combination of skills, capacities and priorities. A PAR scholar works across the university–community boundary and thus is accountable to both university values and grassroots communities’ values. PAR scholars should not deny or hide the multiple demands of the role because communities with experience of marginalization are attuned to being manipulated. Surfacing interests and constraints and discussing these reflexively is often a better strategy. Creativity may be required to design projects that meet both academic goals (such as when a project is funded to produce certain outcomes) and the community’s goals.
For example, in the context of a PAR project with residents of a public housing neighbourhood scheduled for demolition and redevelopment, Thurber and colleagues 47 describe how they overcame differences between resident and academic researchers regarding the purposes of their initial survey. The academic team members preferred the data to be anonymous, to maximize the scientific legitimacy of their project (considered valuable for their credibility to policymakers), whereas the resident team wanted to use the opportunity to recruit residents to their cause, by collecting contact details. The team discussed their different objectives and produced the solution of two-person survey teams, one person gathering anonymous data for the research and a second person gathering contact details for the campaign’s contact list.
Articulating research questions is an early milestone. PAR questions prioritize community concerns, so they may differ from academic-driven research questions. For example, Buckles, Khedkar and Ghevde 39 facilitated a participatory process that developed questions along the lines of: What are the impacts of not having a land title for Katkari people? How will stakeholders respond to Katkari organizing, and what steps can Katkari communities take towards the goal of securing tenure? In another case, incarcerated women in New York state, USA, invited university academics to evaluate a local college in prison in the interest of building an empirical argument for the value of educational opportunities in prisons 38 , 48 Like other evaluations, it asked: “What is the impact of college on women in prison?” But instead of looking narrowly at the impact on re-offending as the relevant impact (as prioritized by politicians and policymakers), based on the incarcerated women’s advice, the evaluation tracked other outcomes: women’s well-being within the prison; their relationships with each other and the staff; their children; their sense of achievement; and their agency in their lives after incarceration.
As a PAR project develops, the problem definition and research questions are often refined through the iterative cycles. This evolution does not undermine the value of writing problem definitions and research questions in the early stages, as a collaboration benefits from having a common reference point to build from and from which to negotiate.
Observing, gathering and generating materials
With a common understanding of the problem, PAR teams design ways of observing the details and workings of this problem. PAR is not prescriptive about the methods used to gather or generate observations. Projects often use qualitative methods, such as storytelling, interviewing or ethnography, or participatory methods, such as body mapping, problem trees, guided walks, timelines, diaries, participatory photography and video or participatory theatre. Gathering quantitative data is an option, particularly in the tradition of participatory statistics 49 . Chilisa 5 distinguishes sources of spatial data, time-related data, social data and technical data. The selected methods should be engaging to the community and the co-researchers, suited to answering the research questions and supported by available professional skills. Means of recording the process or products, and of storing those records, need to be agreed, as well as ethical principles. Developing community members’ research skills for data collection and analysis can be a valued contribution to a PAR project, potentially generating longer-term capacities for local research and change-making 50 .
Our selection of data generation methods and their details depends upon the questions we ask. In some cases, methods to explore problem definitions and then to brainstorm potential actions, their risks and benefits will be useful (Supplementary file 3 ). Others may be less prescriptive about problems and solutions, seeking to explore experience in an open-ended way, as a basis for generating new understandings (see Supplementary file 2 for an example reflective participatory exercise).
Less-experienced practitioners may take a naive approach to PAR, which assumes that knowledge should emerge solely from an authentic community devoid of outside ideas. More established PAR researchers, however, work consciously to combine and exchange skills and knowledge through dialogue. Together with communities, we want to produce effective products, and we recognize that doing so may require specific skills. In Marzi’s 51 participatory video project with migrant women in Colombia, she engaged professional film-makers to provide the women with training in filming, editing and professional film production vocabulary. The women were given the role of directors, with the decision-making power over what to include and exclude in their film. In a Photovoice project with Black and Indigenous youth in Toronto, Canada, Tuck and Habtom 25 drew on their prior scholar–activist experience and their critical analysis of scholarship of marginalization, which often uses tropes of victimhood, passivity and sadness. Instead of repeating narratives of damage, they intended to encourage desire-based narratives. They supported their young participants to critically consider which photographs they wanted to include or exclude from public representations. Training participants to be expert users of research techniques does not devalue their existing expertise and skills, but takes seriously their role in co-producing valid, critical knowledge. University-based researchers equally benefit from training in facilitation methods, team development and the history and context of the community.
Data generation is relational, mediated by the positionalities of the researchers involved. As such, researchers position themselves across boundaries, and need to have, or to develop, skills in interpreting across boundaries. In the Tsui Anaa Project (Box 1 ) in Ghana, the project recruited Ga-speaking graduate students as researchers; Ga is the language most widely spoken in the community. The students were recruited not only for their language skills, but also for their Ga cultural sensibilities, reflected in their sense of humour and their intergenerational communicative styles, enabling fluid communication and mutual understanding with the community. In turn, two community representatives were recruited as advocates to represent patient perspectives across university and community boundaries.
University-based researchers trained in methodological rigour may need reminders that the process of a PAR project is as important as the outcome, and is part of the outcome. Facilitation skills are the most crucial skills for PAR practitioners at this stage. Productive facilitation skills encourage open conversation and collective understandings of the problem at hand and how to address it. More specifically, good facilitation requires a sensitivity to the ongoing and competing social context, such as power relations, within the group to help shift power imbalances and enable participation by all 52 . Box 3 presents a PAR project that exemplifies the importance of relationship building in a community arts project.
Box 3 Case study of the BRIDGE Project: relationship building and collective art making as social change
The BRIDGE Project was a 3-week long mosaic-making and dialogue programme for youth aged 14–18 years, in Southern California. For several summers, the project brought together students from different campuses to discuss inclusion, bullying and community. The goal was to help build enduring relationships among young people who otherwise would not have met or interacted, thereby mitigating the racial tensions that existed in their local high schools.
Youth were taught how to make broken tile mosaic artworks, facilitated through community-building exercises. After the first days, as relationships grew, so did the riskiness of the discussion topics. Youth explored ideas and beliefs that contribute to one’s individual sense of identity, followed by discussion of wider social identities around race, class, sex, gender, class, sexual orientation and finally their identities in relationship to others.
The art-making process was structured in a manner that mirrored the building of their relationships. Youth learned mosaic-making skills while creating individual pieces. They were discouraged from collaborating with anyone else until after the individual pieces were completed and they had achieved some proficiency. When discussions transitioned to focus on the relationship their identities had to each other, the facilitators assisted them in creating collaborative mosaics with small groups.
Staff facilitation modelled the relationship-building goal of the project. The collaborative art making was built upon the rule that no one could make any changes without asking for and receiving permission from the person or people who had placed the piece (or pieces) down. To encourage participants to engage with each other it was vital that they each felt comfortable to voice their opinions while simultaneously learning how to be accountable to their collaborators and respectful of others’ relationships to the art making.
The process culminated in the collective creation of a tile mosaic wall mural, which is permanently installed in the host site.
Collaborative analysis
In PAR projects, data collection and analysis are not typically isolated to different phases of research. Instead, a tried and tested approach to collaborative analysis 53 is to use generated data as a basis for reflection on commonalities, patterns, differences, underlying causes or potentials on an ongoing basis. For instance, body mapping, photography, or video projects often proceed through a series of workshops, with small-scale training–data collection–data analysis cycles in each workshop. Participants gather or produce materials in response to a prompt, and then come together to critically discuss the meaning of their productions.
Simultaneously, or later, a more formal data analysis may be employed, using established social science analytical tools such as grounded theory, thematic, content or discourse analysis, or other forms of visual or ethnographic analysis, with options for facilitated co-researcher involvement. The selection of a specific orientation or approach to analysis is often a low priority for community-based co-researchers. It may be appropriate for university-based researchers to take the lead on comprehensive analysis and the derivation of initial messages. Fine and Torre 29 describe the university-based researchers producing a “best bad draft” so that there is something on the table to react to and discuss. Given the multiple iterations of participants’ expressions of experiences and analyses by this stage, the university-based researchers should be in a position that their best bad draft is grounded in a good understanding of local perspectives and should not appear outlandish, one-sided or an imposition of outside ideas.
For the results and recommendations to reflect community interests, it is important to incorporate a step whereby community representatives can critically examine and contribute to emerging findings and core messages for the public, stakeholders or academic audiences.
Planning and taking action
Taking action is an integral part of a PAR process. What counts as action and change is different for each PAR project. Actions could be targeted at a wide range of scales and different stakeholders, with differing intended outcomes. Valid intended outcomes include creating supportive networks to share resources through mutual aid; empowering participants through sharing experiences and making sense of them collectively; using the emotional impact of artistic works to influence policymakers and journalists; mobilizing collective action to build community power; forging a coalition with other activist and advocacy groups; and many others. Selection between the options depends on underlying priorities, values, theories of how social change happens and, crucially, feasibility.
Articulating a theory of change is one way to demonstrate how we intend to bring about changes through designing an action plan. A theory of change identifies an action and a mechanism, directed at producing outcomes, for a target group, in a context. This device has often been used in donor-driven health and development contexts in a rather prescriptive way, but PAR teams can adapt the tool as a scaffolding for being explicit about action plans and as a basis for further discussions and development of those plans. Many health and development organizations (such as Better Evaluation ) have frameworks to help design a theory of change.
Alternatively, a community action plan 5 can serve as a tangible roadmap to produce change, by setting out objectives, strategies, timeline, key actors, required resources and the monitoring and evaluation framework.
Social change is not easy, and existing social systems benefit, some at the expense of others, and are maintained by power relations. In planning for action, analysis of the power relations at stake, the beneficiaries of existing systems and their potential resistance to change is crucial. It is often wise to assess various options for actions, their potential benefits, risks and ways of mitigating those risks. Sometimes a group may collectively decide to settle for relatively secure, and less-risky, small wins but with the building of sufficient power, a group may take on a bigger challenge 54 .
Ethical considerations are fundamental to every aspect of PAR. They include standard research ethics considerations traditionally addressed by research ethics committees or institutional review boards (IRBs), including key principles of avoidance of harm, anonymity and confidentiality, and voluntary informed consent, although these issues may become much more complex than traditionally presented, when working within a PAR framework 55 . PAR studies typically benefit from IRBs that can engage with the relational specificities of a case, with a flexible and iterative approach to research design with communities, instead of being beholden to very strict and narrow procedures. Wilson and colleagues 56 provide a comprehensive review of ethical challenges in PAR.
Beyond procedural research ethics perspectives, relational ethics are important to PAR projects and raise crucial questions regarding the purpose and conduct of knowledge production and application 37 , 57 , 58 . Relational ethics encourage an emphasis on inclusive practices, dialogue, mutual respect and care, collective decision-making and collaborative action 57 . Questions posed by Indigenous scholars seeking to decolonize Western knowledge production practices are pertinent to a relational ethics approach 4 , 28 . These include: Who designs and manages the research process? Whose purposes does the research serve? Whose worldviews are reproduced? Who decides what counts as knowledge? Why is this knowledge produced? Who benefits from this knowledge? Who determines which aspects of the research will be written up, disseminated and used, and how? Addressing such questions requires scholars to attend to the ethical practices of cultivating trusting and reciprocal relationships with participants and ensuring that the organizations, communities and persons involved co-govern and benefit from the project.
Reflecting on the ethics of her PAR project with young undocumented students in the USA, Cahill 55 highlights some of the intensely complex ethical issues of representation that arose and that will face many related projects. Determining what should be shared with which audiences is intensely political and ethical. Cahill’s team considered editing out stories of dropping out to avoid feeding negative stereotypes. They confronted the dilemma of framing a critique of a discriminatory educational system, while simultaneously advocating that this flawed system should include undocumented students. They faced another common dilemma of how to stay true to their structural analysis of the sources of harms, while engaging decision-makers invested in the current status quo. These complex ethical–political issues arise in different forms in many PAR projects. No answer can be prescribed, but scholar–activists can prepare themselves by reading past case studies and being open to challenging debates with co-researchers.
The knowledge built by PAR is explicitly knowledge-for-action, informed by the relational ethical considerations of who and what the knowledge is for. PAR builds both local knowledge and conceptual knowledge. As a first step, PAR can help us to reflect locally, collectively, on our circumstances, priorities, diverse identities, causes of problems and potential routes to tackle them.
Such local knowledge might be represented in the form of statistical findings from a community survey, analyses of participants’ verbal or visual data, or analyses of workshop discussions. Findings may include elements such as an articulation of the status quo of a community issue; a participatory analysis of root causes and/or actionable elements of the problem; a power analysis of stakeholders; asset mapping; assessment of local needs and priorities. Analysis goes beyond the surface problems, to identify underlying roots of problems to inform potential lines of action.
Simultaneously, PAR also advances more global conceptual knowledge. As liberation theorists have noted, developments in societal understandings of inequalities, marginalization and liberation are often led by those battling such processes daily. For example, the young Black and Indigenous participants working with Tuck and Habtom 25 in Toronto, Canada, engaged as co-theorists in their project about the significance of social movements to young people and their post-secondary school futures. Through their photography project, they expressed how place, and its history, particularly histories of settler colonialism, matters in cities — against a more standard view that treated the urban as somehow interchangeable, modern or neutral. The authors argue for altered conceptions of urban and urban education scholarly literatures, in response to this youth-led knowledge.
A key skill in the art of PAR is in creating achievable actions by choosing a project that is engaging and ambitious with achievable elements, even where structures are resistant to change. PAR projects can produce actions across a wide range of scales (from ‘small, local’ to ‘large, structural’) and across different temporal scales. Some PAR projects are part of decades-long programmes. Within those programmes, an individual PAR project, taking place over 12 or 24 months, might make one small step in the process towards long-term change.
For example, an educational project with young people living in communities vulnerable to flooding in Brazil developed a portfolio of actions, including a seminar, a native seeds fair, support to an individual family affected by a landslide, a campaign for a safe environment for a children’s pre-school, a tree nursery at school and influencing the city’s mayor to extend the environmental project to all schools in the area 30 .
Often the ideal scenario is that such actions lead to material changes in the power of a community. Over the course of a 5-year journey, the Katkari community (Box 1 ) worked with PAR researchers to build community power to resist eviction. The community team compiled households’ proof of residence; documented the history of land use and housing; engaged local government about their situations and plans; and participated more actively in village life to cultivate support 39 . The university-based researchers collected land deeds and taught sessions on land rights, local government and how to acquire formal papers. They opened conversations with the local government on legal, ethical and practical issues. Collectively, their legal knowledge and groundwork gave them confidence to remove fencing erected by landlords and to take legal action to regularize their land rights, ultimately leading to 70 applications being made for formal village sites. This comprised a tangible change in the power relation between landlords and the communities. Even here, however, the authors do not simply celebrate their achievements, but recognize that power struggles are ongoing, landlords would continue to aggressively pursue their interests, and, thus, their achievements were provisional and would require vigilance and continued action.
Most crucially, PAR projects aim to develop university-based and community-based researchers’ collective agency, by building their capacities for collaboration, analysis and action. More specifically, collaborators develop multiple transferable skills, which include skills in conducting research, operating technology, designing outputs, leadership, facilitation, budgeting, networking and public speaking 31 , 59 , 60 .
University-based researchers build their own key capacities through exercising and developing skills, including those for collaboration, facilitation, public engagement and impact. Strong PAR projects may build capacities within the university to sustain long-term relationships with community projects, such as modified and improved infrastructures that work well with PAR modalities, appreciation of the value of long-term sustained reciprocal relations and personal and organizational relationships with communities outside the university.
Applications
PAR disrupts the traditional theory–application binary, which usually assumes that abstract knowledge is developed through basic science, to then be interpreted and applied in professional or community contexts. PAR projects are always applied in the sense that they are situated in concrete human and social problems and aim to produce workable local actions. PAR is a very flexible approach. A version of a PAR project could be devised to tackle almost any real-world problem — where the researchers are committed to an emancipatory and participatory epistemology. If one can identify a group of people interested in collectively generating knowledge-for-action in their own context or about their own practices, and as long as the researchers are willing and able to share power, the methods set out in this Primer could be applied to devise a PAR project.
PAR is consonant with participatory movements across multiple disciplines and sectors, and thus finds many intellectual homes. Its application is supported by social movements for inclusion, equity, representation of multiple voices, empowerment and emancipation. For instance, PAR responds to the value “nothing about us without us”, which has become a central tenet of disability studies. In youth studies, PAR is used to enhance the power of young people’s voices. In development studies, PAR has a long foundation as part of the demand for greater participation, to support locally appropriate, equitable and locally owned changes. In health-care research, PAR is used by communities of health professionals to reflect and improve on their own practices. PAR is used by groups of health-care service users or survivors to give a greater collective power to the voices of those at the sharp end of health care, often delegitimized by medical power. In environmental sciences, PAR can support local communities to take action to protect their environments. In community psychology, PAR is valued for its ability to nurture supportive and inclusive processes. In summary, PAR can be applied in a huge variety of contexts in which local ownership of research is valued.
Limitations to PAR’s application often stem from the institutional context. In certain (often dominant) academic circles, local knowledge is not valued, and contextually situated, problem-focused, research may be considered niche, applied or not generalizable. Hence, research institutions may not be set up to be responsive to a community’s situation or needs or to support scholar–activists working at the research–action boundary. Further, those who benefit from, or are comfortable with, the status quo of a community may actively resist attempts at change from below and may undermine PAR projects. In other cases, where a community is very divided or dispersed, PAR may not be the right approach. There are plenty of examples of PAR projects floundering, failing to create an active group or to achieve change, or completely falling through. Even such failures, however, shed light on the conditions of communities and the power relations they inhabit and offer lessons on ways of working and not working with groups in those situations.
Reproducibility and data deposition
Certain aspects of the open science movement can be productively engaged from within a PAR framework, whereas others are incompatible. A key issue is that PAR researchers do not strive for reproducibility, and many would contest the applicability of this construct. Nonetheless, there may be resonances between the open science principle of making information publicly available for re-use and those PAR projects that aim to render visible and audible the experience of a historically under-represented or mis-represented community. PAR projects that seek to represent previously hidden realities of, for example, environmental degradation, discriminatory experiences at the hands of public services, the social history of a traditionally marginalized group, or their neglected achievements, may consider creating and making public robust databases of information, or social history archives, with explicit informed permission of the relevant communities. For such projects, making knowledge accessible is an essential part of the action. Publicly relevant information should not be sequestered behind paywalls. PAR practitioners should thus plan carefully for cataloguing, storing and archiving information, and maintaining archives.
On the other hand, however, a blanket assumption that all data should be made freely available is rarely appropriate in a PAR project and may come into conflict with ethical priorities. Protecting participants’ confidentiality can mean that data cannot be made public. Protecting a community from reputational harm, in the context of widespread dehumanization, criminalization or stigmatization of dispossessed groups, may require protection of their privacy, especially if their lives or coping strategies are already pathologized 25 . Empirical materials do not belong to university-based researchers as data and cannot be treated as an academic commodity to be opened to other researchers. Open science practices should not extend to the opening of marginalized communities to knowledge exploitation by university researchers.
The principle of reproducibility is not intuitively meaningful to PAR projects, given their situated nature, that is, the fact that PAR is inherently embedded in particular concrete contexts and relationships 61 . Beyond reproducibility, other forms of mutual learning and cross-case learning are vitally important. We see increasing research fatigue in communities used, extractively, for research that does not benefit them. PAR teams should assess what research has been done in a setting to avoid duplication and wasting people’s time and should clearly prioritize community benefit. At the same time, PAR projects also aspire to produce knowledge with wider implications, typically discussed under the term generalizability or transferability. They do so by articulating how the project speaks to social, political, theoretical and methodological debates taking place in wider knowledge communities, in a form of “communicative generalisation” 62 . Collaborating and sharing experiences across PAR sites through visits, exchanges and joint analysis can help to generalize experiences 30 , 61 .
Limitations and optimizations
PAR projects often challenge the social structures that reproduce established power relations. In this section, we outline common challenges to PAR projects, to prompt early reflection. When to apply a workaround, compromise, concede, refuse or regroup and change strategy are decisions that each PAR team should make collectively. We do not have answers to all the concerns raised but offer mitigations that have been found useful.
Institutional infrastructure
Universities’ interests in partnerships with communities, local relevance, being outward-facing, public engagement and achieving social impact can help to create a supportive environment for PAR research. Simultaneously, university bureaucracies and knowledge hierarchies that prize their scientists as individuals rather than collaborators and that prioritize the methods of dominant science can undermine PAR projects 63 . When Cowan, Kühlbrandt and Riazuddin 45 proposed using gaming, drama, fiction and film-making for a project engaging young people in thinking about scientific futures, a grants manager responded “But this project can’t just be about having fun activities for kids — where is the research in what you’re proposing?” Research infrastructures are often slow and reluctant to adapt to innovations in creative research approaches.
Research institutions’ funding time frames are also often out of sync with those of communities — being too extended in some ways and too short in others 45 , 64 . Securing funding takes months and years, especially if there are initial rejections or setbacks. Publishing findings takes further years. For community-based partners, a year is a long time to wait and to maintain people’s interest. On the other hand, grant funding for one-off projects over a year or two (or even five) is rarely sufficient to create anything sustainable, reasserting precarity and short-termism. Institutions can better support PAR through infrastructure such as bridging funds between grants, secure staff appointments and institutional recognition and resources for community partners.
University infrastructures can value the long-term partnership working of PAR scholars by recognizing partnership-building as a respected element of an academic career and recognizing collaborative research as much as individual academic celebrity. Where research infrastructures are unsupportive, building relationships within the university with like-minded professional and academic colleagues, to share work-arounds and advocate collectively, can be very helpful. Other colleagues might have developed mechanisms to pay co-researchers, or to pay in advance for refreshments, speed up disbursement of funds, or deal with an ethics committee, IRB, finance office or thesis examiner who misunderstands participatory research. PAR scholars can find support in university structures beyond the research infrastructure, such as those concerned with knowledge exchange and impact, campus–community partnerships, extension activities, public engagement or diversity and inclusion 64 . If PAR is institutionally marginalized, exploring and identifying these work-arounds is extremely labour intensive and depends on the cultivation of human, social and cultural capital over many years, which is not normally available to graduate students or precariously employed researchers. Thus, for PAR to be realized, institutional commitment is vital.
Co-option by powerful structures
When PAR takes place in collaboration or engagement with powerful institutions such as government departments, health services, religious organizations, charities or private companies, co-option is a significant risk. Such organizations experience social pressure to be inclusive, diverse, responsive to communities and participatory, so they may be tempted to engage communities in consultation, without redistributing power. For instance, when ‘photovoice’ projects invite politicians to exhibitions of photographs, their activity may be co-opted to serving the politician’s interest in being seen to express support, but result in no further action. There is a risk that using PAR in such a setting risks tokenizing marginalized voices 65 . In one of our current projects, co-researchers explore the framing of sexual violence interventions in Zambia, aiming to promote greater community agency and reduce the centrality of approaches dominated by the Global North 66 . One of the most challenging dilemmas is the need to involve current policymakers in discussions without alienating them. The advice to ‘be realistic’, ‘be reasonable’ or ‘play the game’ to keep existing power brokers at the table creates one of the most difficult tensions for PAR scholars 48 .
We also caution against scholars idealizing PAR as an ideal, egalitarian, inclusive or perfect process. The term ‘participation’ has become a policy buzzword, invoked in a vaguely positive way to strengthen an organization’s case that they have listened to people. It can equally be used by researchers to claim a moral high ground without disrupting power relations. Depriving words of their associated actions, Freire 7 warns us, leads to ‘empty blah’, because words gain their meaning in being harnessed to action. Labelling our work PAR does not make it emancipatory, without emancipatory action. Equally, Freire cautions against acting without the necessary critical reflection.
To avoid romanticization or co-option, PAR practitioners benefit from being held accountable to their shared principles and commitments by their critical networks and collaborators. Our commitments to community colleagues and to action should be as real for us as any institutional pressures on us. Creating an environment for that accountability is vital. Box 4 offers a project exemplar featuring key considerations regarding power concerns.
Box 4 Case study: participatory power and its vulnerability
Júba Wajiín is a pueblo in a rural mountainous region in the lands now called Guerrero, Mexico, long inhabited by the Me’phaa people, who have fiercely resisted precolonial, colonial and postcolonial displacement and dispossession. Using collective participatory action methods, this small pueblo launched and won a long legal battle that now challenges extractive mining practices.
Between 2001 and 2012, the Mexican government awarded massive mining concessions to mining companies. The people of Júba Wajiín discovered in mid-2013 that, unbeknown to them, concessions for mining exploration of their lands had been awarded to the British-based mining company Horschild Mexico. They engaged human rights activists who used participatory action research methods to create awareness and to launch a legal battle. Tlachinollan, a regional human rights organization, held legal counselling workshops and meetings with local authorities and community elders.
The courts initially rejected the case by denying that residents could be identified as Indigenous because they practised Catholicism and spoke Spanish. A media organization, La Sandia Digital , supported the community to collectively document their syncretic religious and spiritual practices, their ability to speak Mhe’paa language and their longstanding agrarian use of the territory. They produced a documentary film Juba Wajiin: Resistencia en la Montaña , providing visual legal evidence.
After winning in the District court, they took the case to the Supreme Court, asking it to review the legality and validity of the mining concessions. Horschild, along with other mining companies, stopped contesting the case, which led to the concessions being null and void.
The broader question of Indigenous peoples’ territorial rights continued in the courts until mid-2022 when the Supreme Court ruled that Indigenous peoples had the constitutional right to be consulted before any mining activities in their territory. This was a win, but a partial one. ‘Consultations’ are often manipulated by state and private sectors, particularly among groups experiencing dire impoverishment. Júba Wajiín’s strategies proved successful but the struggle against displacement and dispossession is continual.
Power inequalities within PAR
Power inequalities also affect PAR teams and communities. For all the emphasis on egalitarian relationships and dialogue, communities and PAR teams are typically composed of actors with unequal capacities and powers, introducing highly complex challenges for PAR teams.
Most frequently, university-based researchers engaging with marginalized communities do not themselves share many aspects of the identities or life experiences of those communities. They often occupy different, often more privileged, social networks, income brackets, racialized identities, skill sets and access to resources. Evidently, the premise of PAR is that people with different lives can productively collaborate, but gulfs in life experience and privilege can yield difficult tensions and challenges. Expressions of discomfort, dissatisfaction or anger in PAR projects are often indicative of power inequalities and an opportunity to interrogate and challenge hierarchies. Scholars must work hard to undo their assumptions about where expertise and insights may lie. A first step can be to develop an analysis of a scholar’s own participation in the perpetuation of inequalities. Projects can be designed to intentionally redistribute power, by redistributing skills, responsibilities and authority, or by redesigning core activities to be more widely accessible. For instance, Marzi 51 in a participatory video project, used role swapping to distribute the leadership roles of chairing meetings, choosing themes for focus and editing, among all the participants.
Within communities, there are also power asymmetries. The term ‘community participation’ itself risks homogenizing a community, such that one or a small number of representatives are taken to qualify as the community. Yet, communities are characterized by diversity as much as by commonality, with differences across sociological lines such as class, race, gender, age, occupation, housing tenure and health status. Having the time, resources and ability to participate is unlikely to be evenly distributed. Some people need to devote their limited time to survival and care of others. For some, the embodied realities of health conditions and disabilities make participation in research projects difficult or undesirable 67 . If there are benefits attached to participation, careful attention to the distribution of such benefits is needed, as well as critical awareness of the positionality of those involved and those excluded. Active efforts to maximize accessibility are important, including paying participants for their valued time; providing accommodations for people with health conditions, disabilities, caring responsibilities or other specific needs; and designing participatory activities that are intuitive to a community’s typical modes of communication.
Lack of control and unpredictability
For researchers accustomed to leading research by taking responsibility to drive a project to completion, using the most rigorous methods possible, to achieve stated objectives, the collaborative, iterative nature of PAR can raise personal challenges. Sense 68 likens the facilitative role of a PAR practitioner to “trying to drive the bus from the rear passenger seat—wanting to genuinely participate as a passenger but still wanting some degree of control over the destination”. PAR works best with collaborative approaches to leadership and identities among co-researchers as active team members, facilitators and participants in a research setting, prepared to be flexible and responsive to provocations from the situation and from co-researchers and to adjust project plans accordingly 28 , 68 , 69 . The complexities involved in balancing control issues foreground the importance of reflexive practice for all team members to learn together through dialogue 70 . Training and socialization into collaborative approaches to leadership and partnership are crucial supports. Well-functioning collaborative ways of working are also vital, as their trusted structure can allow co-researchers to ‘trust the process’, and accept uncertainties, differing perspectives, changes of emphasis and disruptions of assumptions. We often want surprises in PAR projects, as they show that we are learning something new, and so we need to be prepared to accept disruption.
The PAR outlook is caught up in the ongoing history of the push and pull of popular movements for the recognition of local knowledge and elite movements to centralize authority and power in frameworks such as universal science, professional ownership of expertise, government authority or evidence-based policy. As a named methodological paradigm, PAR gained legitimacy and recognition during the 1980s, with origins in popular education for development, led by scholars from the Global South 16 , 32 , and taken up in the more Global-North-dominated field of international development, where the failings of externally imposed, contextually insensitive development solutions had become undeniable 21 . Over the decades, PAR has both participated in radical social movements and risked co-option and depoliticization as it became championed by powerful institutions, and it is in this light that we consider PAR’s relation to three contemporary societal movements.
Decolonizing or re-powering
The development of PAR took place in tandem with anti-colonial movements and discourses during the 1970s and 1980s, in which the colonization of land, people and knowledge were all at stake. During the mid-2010s, calls for decolonization of the university were forced onto the agenda of the powerful by various groups, including African students and youth leading the ‘Rhodes Must Fall’, ‘Fees must Fall’ and ‘Gandhi must Fall’ movements 71 , followed by the eruption of Black Lives Matter protests in 2020 (ref. 72 ). PAR is a methodology that stands to contribute to decolonization-colonization through the development of alternatives to centralizing knowledge and power. As such, the vitality of local and global movements demanding recognition of grassroots knowledge and the dismantling of oppressive historical power–knowledge systems heralds many openings and exciting potential collaborations and causes for PAR practitioners 73 , 74 . As these demands make themselves felt in powerful institutions, they create openings for PAR.
Yet, just as PAR has been subject to co-option and depoliticization, the concept of decolonization too is at risk of appropriation by dominant groups and further tokenization of Indigenous groups, as universities, government departments and global health institutions absorb the concept, fitting it into their existing power structures 41 , 75 . In this context, Indigenous theorists in Aotearoa/New Zealand are working on an alternative concept of ‘re-powering Indigenous knowledge’ instead of ‘decolonizing knowledge’. By doing so, they centre Indigenous people and their knowledge, instead of the knowledge or actions of colonizers, and foreground the necessity of changes to power relations. African and African American scholars working on African heritage and political agency have drawn on the Akan philosophy of Sankofa for a similar purpose 76 . Sankofa derives from a Twi proverb Se wo were fi na wosan kofa a yenkyiri (It is not taboo to fetch what is at risk of being left behind). Going back to fetch what is lost is a self-grounded act that draws on the riches of Indigenous history to re-imagine and restructure the future 77 . It is also an act independent of the colonial and colonizing gaze. Contributing to a mid-twenty-first century re-powering community knowledge is a promising vision for PAR. More broadly, the loud voices and visionary leadership of contemporary anti-racist, anti-colonial, Indigenous, intersectional feminist and other emancipatory movements provide a vibrant context to re-invent and renew PAR.
Co-production
In fields concerned with health and public service provision, a renewed discourse of respectful engagement with communities and service users has centred in recent years on the concept of co-production 78 . In past iterations, concepts such as citizen engagement, patient participation, community participation and community mobilization had a similar role. Participatory methods have proved their relevance within such contexts, for example, providing actionable and wise insights to clinicians seeking to learn from patients, or to providers of social services seeking to target their services better. Thus, the introduction of co-production may create a receptive environment for PAR in public services. Yet again, if users are participating in something, critical PAR scholars should question in which structures they are participating, instantiating which power relations and to whose benefit. PAR scholars can find themselves compromised by institutional requirements. Identifying potential compromises, lines that cannot be crossed and areas where compromises can be made; negotiating with institutional orders; and navigating discomfort and even conflict are key skills for practitioners of PAR within institutional settings.
One approach to engaging with institutional structures has been to gather evidence for the value of PAR, according to the measures and methods of dominant science. Anyon and colleagues 59 systematically reviewed the Youth PAR literature in the United States. They found emerging evidence that PAR produces positive outcomes for youth and argued for further research using experimental designs to provide harder evidence. They make the pragmatic argument that funding bodies require certain forms of evidence to justify funding, and so PAR would benefit by playing by those rules.
A different approach, grounded in politics rather than the academy, situates co-production as sustained by democratic struggles. In the context of sustainability research in the Amazon, for instance, Perz and colleagues 79 argue that the days of externally driven research are past. Mobilization by community associations, Indigenous federations, producer cooperatives and labour unions to demand influence over the governance of natural resources goes hand in hand with expectations of local leadership and ownership of research, often implemented through PAR. These approaches critically question the desirability of institutional, external funding or even non-monetary support for a particular PAR project.
Global–local inequality and solidarity
Insufferable global and local inequalities continue to grow, intensified by climate catastrophes, the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic and extreme concentrations of wealth and political influence, and contested by increasingly impactful analyses, protests and refusals by those disadvantaged and discriminated against. Considering the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on PAR projects, Auerbach and colleagues 64 identify increasing marketization and austerity in some universities, and the material context of growing pressure on marginalized communities to simply meet their needs for survival, leaving little capacity for participating in and building long-term partnerships. They describe university-based researchers relying on their own capacities to invent new modes of digital collaboration and nourish their partnerships with communities, often despite limited institutional support.
We suggest that building solidaristic networks, and thus building collective power, within and beyond universities offers the most promising grounding for a fruitful outlook for PAR. PAR scholars can find solidarity across a range of disciplines, traditions, social movements, topics and geographical locations. Doing so offers to bridge traditions, share strategies and resonances, build methodologies and politics, and crucially, build power. In global health research, Abimbola and colleagues 80 call for the building of Southern networks to break away from the dominance of North–South partnerships. They conceptualize the South not only as a geographical location, as there are of course knowledge elites in the South, but as the communities traditionally marginalized from centres of authority and power. We suggest that PAR can best maximize its societal contribution and its own development and renewal by harnessing the diverse wisdom of knowledge generation and participatory methods across Southern regions and communities, using that wisdom to participate in global solidarities and demands for redistribution of knowledge, wealth and power.
Kemmis, S., McTaggart, R. & Nixon, R. in The SAGE Handbook of Action Research: Participative Inquiry and Practice (eds Reason, P. & Bradbury, H.) 453–464 (Sage, 2015).
Kindon, S., Pain, R. & Kesby, M. Participatory Action Research Approaches and Methods: Connecting People, Participation and Place (Routledge, 2007). A classic, reflective and practical, all-rounder PAR textbook, with a social science/geography orientation and a Global North origin.
McIntyre, A. Participatory Action Research (Sage, 2007).
Smith, L. T. Decolonizing Methodologies: Research and Indigenous Peoples (Bloomsbury, 2021). A foundational book in decolonization and Indigenous methods, including theory, critique and methodological guidance, rooted in Indigenous thought in Aotearoa/New Zealand.
Chilisa, B. Indigenous Research Methodologies (Sage, 2019). A thorough and accessible grounding in the epistemology, methodology and methods of postcolonial, Indigenous research, suitable for a wide audience and rooted in African knowledge systems.
Fals-Borda, O. & Rahman, M. A. Action and Knowledge (Practical Action Publishing, 1991).
Freire, P. Pedagogy of the Oppressed (Continuum, 1970).
Rahman, M. A. in The SAGE Handbook of Action Research: Participative Inquiry and Practice (eds Reason, P. & Bradbury, H.) 49–62 (Sage, 2008).
Fanon, F. The Wretched of the Earth (Penguin, 1963).
Crenshaw, K. Mapping the margins: intersectionality, identity politics, and violence against women of color. Stanf. Law Rev. 43 , 1241–1299 (1991).
Article Google Scholar
Mama, A. Beyond the Masks: Race, Gender, and Subjectivity (Psychology Press, 1995).
Lewin, K. Action research and minority problems. J. Soc. Issues 11 , 34–46 (1946).
Reason, P. & Bradbury, H. The Sage Handbook of Action Research: Participative Inquiry and Practice (Sage, 2015).
Le Grange, L. Challenges for participatory action research and indigenous knowledge in Africa. Acta Acad. 33 , 136 (0000).
Google Scholar
Caxaj, C. S. Indigenous storytelling and participatory action research: allies toward decolonization? Reflections from the Peoples’ International Health Tribunal. Glob. Qual. Nurs. Res. 2 , 2333393615580764 (2015).
Díaz-Arévalo, J. M. In search of the ontology of participation in Participatory Action Research: Orlando Fals-Borda’s Participatory Turn, 1977–1980. Action Res. https://doi.org/10.1177/14767503221103571 (2022).
McKittrick, K. Dear Science and Other Stories (Duke Univ. Press, 2021).
Mohanty, C. T. Under Western eyes: feminist scholarship and colonial discourses. Bound. 2 12/13 , 333–358 (1984).
Lewin, K. Action research and minority problems. J. Soc. Issues 2 , 34–46 (1946).
Adelman, C. Kurt Lewin and the origins of action research. Educ. Action Res. 1 , 7–24 (1993).
Chambers, R. The origins and practice of participatory rural appraisal. World Dev. 22 , 953–969 (1994).
Cornwall, A. & Jewkes, R. What is participatory research? Soc. Sci. Med. 41 , 1667–1676 (1995).
Wallerstein, N. & Duran, B. Community-based participatory research contributions to intervention research: the intersection of science and practice to improve health equity. Am. J. Public Health 100 , S40–S46 (2010).
Wang, C. & Burris, M. A. Photovoice: concept, methodology, and use for participatory needs assessment. Health Educ. Behav. 24 , 369–387 (1997).
Tuck, E. & Habtom, S. Unforgetting place in urban education through creative participatory visual methods. Educ. Theory 69 , 241–256 (2019).
Kaba, M. We Do This’Til We Free Us: Abolitionist Organizing and Transforming Justice (Haymarket Books, 2021).
Toraif, N. et al. How to be an antiracist: youth of color’s critical perspectives on antiracism in a youth participatory action research context. J. Adolesc. Res. 36 , 467–500 (2021).
Akom, A. A. A. Black emancipatory action research: integrating a theory of structural racialisation into ethnographic and participatory action research methods. Ethnogr. Educ. 6 , 113–131 (2011).
Fine, M. & Torre, M. E. Critical participatory action research: a feminist project for validity and solidarity. Psychol. Women Q. 43 , 433–444 (2019).
Trajber, R. et al. Promoting climate change transformation with young people in Brazil: participatory action research through a looping approach. Action Res. 17 , 87–107 (2019).
Marzi, S. Co-producing impact-in-process with participatory audio-visual research. Area https://doi.org/10.1111/area.12851 (2022).
Fals-Borda, O. The application of participatory action-research in Latin America. Int. Sociol. 2 , 329–347 (1987).
Liboiron, M. Pollution is Colonialism (Duke Univ. Press, 2021).
Babington, P. Ageing well in Bournville: a participative action research project. Rural. Theol. 15 , 84–96 (2017).
Elder, B. C. & Odoyo, K. O. Multiple methodologies: using community-based participatory research and decolonizing methodologies in Kenya. Int. J. Qual. Stud. Educ. 31 , 293–311 (2018).
Frisby, W., Reid, C. J., Millar, S. & Hoeber, L. Putting “Participatory” into participatory forms of action research. J. Sport Manag. 19 , 367–386 (2005).
King, P., Hodgetts, D., Rua, M. & Te Whetu, T. Older men gardening on the marae: everyday practices for being Māori. Altern. Int. J. Indig. Scholarsh. 11 , 14–28 (2015).
Fine, M. et al. Changing Minds: The Impact of College in a Maximum-Security Prison. Effects on Women in Prison, the Prison Environment, Reincarceration Rates and Post-Release Outcomes . https://www.prisonpolicy.org/scans/changing_minds.pdf (2001).
Buckles, D., Khedkar, R. & Ghevde, B. Fighting eviction: local learning and the experience of inequality among India’s adivāsi. Action. Res. 13 , 262–280 (2015). A strong example of a sustained university–community partnership in India that used PAR to build expertise and power in a tribal community to improve their security of tenure.
Vecchio, D. D., Toomey, N. & Tuck, E. Placing photovoice: participatory action research with undocumented migrant youth in the Hudson Valley. Crit. Questions Educ. 8 , 358–376 (2017).
Tuck, E. & Yang, K. W. Decolonization is not a metaphor. Decolonization Indigeneity Educ. Soc. 1 , 1–40 (2012).
Lucko, J. Positionality and power in PAR: exploring the competing motivations of PAR stakeholders with latinx middle school students in Northern California. in Education | Faculty Conference Presentations (Dominican Univ., 2018).
Herr, K. & Anderson, G. The Action Research Dissertation: A Guide for Students and Faculty (SAGE, 2005).
Alejandro, A. Reflexive discourse analysis: a methodology for the practice of reflexivity. Eur. J. Int. Relat. 27 , 150–174 (2021).
Cowan, H., Kühlbrandt, C. & Riazuddin, H. Reordering the machinery of participation with young people. Sociol. Health Illn. 44 , 90–105 (2022).
Buettgen, A. et al. We did it together: a participatory action research study on poverty and disability. Disabil. Soc. 27 , 603–616 (2012).
Thurber, A., Collins, L., Greer, M., McKnight, D. & Thompson, D. Resident experts: The potential of critical Participatory Action Research to inform public housing research and practice. Action Res. 18 , 414–432 (2020).
Sandwick, T. et al. Promise and provocation: humble reflections on critical participatory action research for social policy. Urban. Educ. 53 , 473–502 (2018).
Holland, J. & Chambers, R. Who Counts? (Practical Action Publishing, 2013).
Percy-Smith, B. & Burns, D. Exploring the role of children and young people as agents of change in sustainable community development. Local. Environ. 18 , 323–339 (2013).
Marzi, S. Participatory video from a distance: co-producing knowledge during the COVID-19 pandemic using smartphones. Qual. Res. https://doi.org/10.1177/14687941211038171 (2021).
Schoonen, A., Wood, L. & Kruger, C. Learning to facilitate community-based research: guidelines from a novice researcher. Educ. Res. Soc. Change 10 , 16–32 (2021).
Cornish, F., Gillespie, A. & Zittoun, T. in The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Data Analysis (ed. Flick, U.) 79–93 (Sage, 2013).
Burgess, R. A. Working in the wake: transformative global health in an imperfect world. BMJ Glob. Health 7 , e010520 (2022).
Cahill, C. Repositioning ethical commitments: participatory action research as a relational praxis of social change. ACME Int. J. Crit. Geogr. 6 , 360–373 (2007).
Wilson, E., Kenny, A. & Dickson-Swift, V. Ethical challenges in community-based participatory research: a scoping review. Qual. Health Res. 28 , 189–199 (2018).
Hodgetts, D. et al. Relational ethics meets principled practice in community research engagements to understand and address homelessness. J. Community Psychol. 50 , 1980–1992 (2022).
Hopner, V. & Liu, J. C. Relational ethics and epistemology: the case for complementary first principles in psychology. Theory Psychol. 31 , 179–198 (2021).
Anyon, Y., Bender, K., Kennedy, H. & Dechants, J. A systematic review of youth participatory action research (YPAR) in the United States: methodologies, youth outcomes, and future directions. Health Educ. Behav. 45 , 865–878 (2018).
de-Graft Aikins, A. et al. Building cardiovascular disease competence in an urban poor Ghanaian community: a social psychology of participation approach. J. Community Appl. Soc. Psychol. 30 , 419–440 (2020).
Feldman, S. & Shaw, L. The epistemological and ethical challenges of archiving and sharing qualitative data. Am. Behav. Sci. 63 , 699–721 (2019).
Cornish, F. Communicative generalisation: dialogical means of advancing knowledge through a case study of an ‘unprecedented’ disaster. Cult. Psychol. 26 , 78–95 (2020).
Anderson, G. Participatory action research (PAR) as democratic disruption: new public management and educational research in schools and universities. Int. J. Qual. Stud. Educ. 30 , 432–449 (2017).
Auerbach, J. et al. Displacement of the Scholar? Participatory action research under COVID-19. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 6 , 762065 (2022).
Levac, L., Ronis, S., Cowper-Smith, Y. & Vaccarino, O. A scoping review: the utility of participatory research approaches in psychology. J. Community Psychol. 47 , 1865–1892 (2019).
Breton, N. N. Reflecting on our good intentions: a critical discourse analysis of women’s health and empowerment discourses in sexual and gender-based violence policies relevant to southern Africa. Glob. Public Health https://doi.org/10.1080/17441692.2022.2120048 (2022).
de-Graft Aikins, A. Healer shopping in Africa: new evidence from rural-urban qualitative study of Ghanaian diabetes experiences. BMJ 331 , 737 (2005).
Sense, A. J. Driving the bus from the rear passenger seat: control dilemmas of participative action research. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 9 , 1–13 (2006).
Dawson, M. C. & Sinwell, L. Ethical and political challenges of participatory action research in the academy: reflections on social movements and knowledge production in South Africa. Soc. Mov. Stud. 11 , 177–191 (2012).
Dadich, A., Moore, L. & Eapen, V. What does it mean to conduct participatory research with Indigenous peoples? A lexical review. BMC Public Health 19 , 1388 (2019).
Bhambra, G. K., Gebrial, D. & Nisancioglu, K. in Decolonising the University (eds Bhambra, G. K., Gebrial, D. & Nişancıoğlu, K.) 1–18 (Pluto Press, 2018).
Seckinelgin, H. Teaching social policy as if students matter: decolonizing the curriculum and perpetuating epistemic injustice. Crit. Soc. Policy https://doi.org/10.1177/02610183221103745 (2022).
Fine, M. Just methods in revolting times. Qual. Res. Psychol. 13 , 347–365 (2016).
Fine, M. Just Research in Contentious Times: Widening the Methodological Imagination (Teachers College Press, Columbia University, 2018). An inspiring PAR book, addressing complex challenges and transformational potentials of PAR, based on the author’s wide-ranging, deep and long-standing experience with PAR in the USA.
Hirsch, L. A. Is it possible to decolonise global health institutions? Lancet 397 , 189–190 (2021).
Chigumadzi, P. Sankofa and the afterlives of Makerere. Los Angeles Review of Books https://lareviewofbooks.org/article/sankofa-and-the-afterlives-of-makerere (2021).
Gumbonzvanda, N., Gumbonzvanda, F. & Burgess, R. Decolonising the ‘safe space’ as an African innovation: the Nhanga as quiet activism to improve women’s health and wellbeing. Crit. Public Health 31 , 169–181 (2021).
Tembo, D. et al. Effective engagement and involvement with community stakeholders in the co-production of global health research. BMJ 372 , n178 (2021).
Perz, S. G. et al. Participatory action research for conservation and development: experiences from the Amazon. Sustainability 14 , 233 (2022).
Abimbola, S. et al. Addressing power asymmetries in global health: imperatives in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. PLoS Med. 18 , e1003604 (2021).
O’Leary, Z. The Essential Guide to Doing Research (Sage, 2004).
Koshy, E., Koshy, V. & Waterman, H. Action Research in Healthcare https://doi.org/10.4135/9781446288696 (Sage, 2011).
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors thank their PAR collaborators and teachers, who have shown us how to take care of each other, our communities and environments. They thank each other for generating such a productive critical thinking space and extending care during challenging times.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Methodology, London School of Economics & Political Science, London, UK
Flora Cornish & Nancy Breton
Departmento de Gestion para el Desarrollo Sustentable, CONACyT–Universidad Autonoma de Guerrero, Acapulco, Guerrero, Mexico
Ulises Moreno-Tabarez
Department of Communication Studies, California State University, Northridge, CA, USA
Jenna Delgado
Māori Studies, University of Auckland, Auckland, Aotearoa, New Zealand
Institute of Advanced Studies, University College London, London, UK
Ama de-Graft Aikins
School of Psychology, Massey University, Albany, Aotearoa, New Zealand
Darrin Hodgetts
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors researched and drafted material for the article. All authors contributed substantially to discussion of the content. F.C. drafted the article. All authors reviewed and/or edited the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Flora Cornish .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Reviews Methods Primers thanks Jesica Fernández, Sonja Marzi, Jill Clark and Alice McIntyre for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Related links
Better Evaluation: https://www.betterevaluation.org/frameworks-guides/managers-guide-evaluation/scope/describe-theory-change
Juba Wajiin: resistencia en la montaña: https://bombozila.com/juba-wajiin/
La Sandia Digital: https://lasandiadigital.org.mx/
Morris Justice project: https://morrisjustice.org/
Supplementary information
Supplementary information.
Involving multiple team members in the analysis and interpretation of materials generated, typically in iterative cycles of individual or pair work and group discussion.
Both a structure and a process, community refers to a network of often diverse and unequal persons engaged in common tasks or actions, stakes or interests that lead them to form social ties or commune with one another.
A process through which a person or group’s activities are altered or appropriated to serve another group’s interests.
A term typically used in service provision to describe partnership working between service providers and service users, to jointly produce decisions or designs.
A call to recognize and dismantle the destructive legacies of colonialism in societal institutions, to re-power indigenous groups and to construct alternative relationships between peoples and knowledges that liberate knowers and doers from colonial extraction and centralization of power.
Scholarship that creates knowledge of the conditions that limit or oppress us to liberate ourselves from those conditions and to support others in their own transformations.
Injustices in relation to knowledge, including whose knowledge counts and which knowledge is deemed valid or not.
Research that extracts information and exploits relationships, places and peoples, producing benefit for scholars or institutions elsewhere, and depleting resources at the sites of the research.
Knowledge that is rooted in experience in a particular social context, often devalued by social science perspectives that make claims to generalizability or universality.
The relationships of domination, subordination and resistance between individuals or social groups, allowing some to advance their perspectives and interests more than others.
A methodological practice through which scholars critically reflect on their own positionality and how it impacts on participants and co-researchers, understanding of the topic and the knowledge produced.
An approach to ethical conduct that situates ethics as ongoingly negotiated within the context of respectful relationships, beyond following the procedural rules often set out by ethics committees.
A dual role in which scholars use their knowledge (scholarship) to tackle injustices and instigate changes (activism) in collaboration with marginalized communities and/or organizations.
Doing something or appointing a person for reasons other than in the interest of enabling meaningful change.
A systemic change in which relationships and structures are fundamentally altered, often contrasted with smaller-scale changes such as varying or refining existing relations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Cornish, F., Breton, N., Moreno-Tabarez, U. et al. Participatory action research. Nat Rev Methods Primers 3 , 34 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43586-023-00214-1
Download citation
Accepted : 27 February 2023
Published : 27 April 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s43586-023-00214-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
“they feel shame sometime, but that is why we need to talk to them…we need to tell them how important it is not to feel shame”: hepatitis b related shame and improving hepatitis b care in aboriginal and torres strait islander communities in the top end of the northern territory, according to the aboriginal health workforce.
- Richard P. Sullivan
- Sarah Mariyalawuy Bukulatjpi
- Jane Davies
Archives of Public Health (2024)
Exploring community needs in combating aedes mosquitoes and dengue fever: a study with urban community in the recurrent hotspot area
- Nurul Adilah Samsudin
- Hidayatulfathi Othman
- Zul-‘Izzat Ikhwan Zaini
BMC Public Health (2024)
Increasing disability inclusion through self-relevant research
- Kathleen R. Bogart
Communications Psychology (2024)
Supporting climate adaptation for rural Mekong River Basin communities in Thailand
- Holly S. Embke
- Abigail J. Lynch
- T. Douglas Beard
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change (2024)
Future directions for patient engagement in research: a participatory workshop with Canadian patient partners and academic researchers
- Anna Maria Chudyk
- Roger Stoddard
- Annette S. H. Schultz
Health Research Policy and Systems (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research Research Tools and Apps
Action Research: What it is, Stages & Examples

The best way to get things accomplished is to do it yourself. This statement is utilized in corporations, community projects, and national governments. These organizations are relying on action research to cope with their continuously changing and unstable environments as they function in a more interdependent world.
In practical educational contexts, this involves using systematic inquiry and reflective practice to address real-world challenges, improve teaching and learning, enhance student engagement, and drive positive changes within the educational system.
This post outlines the definition of action research, its stages, and some examples.
Content Index
What is action research?
Stages of action research, the steps to conducting action research, examples of action research, advantages and disadvantages of action research.
Action research is a strategy that tries to find realistic solutions to organizations’ difficulties and issues. It is similar to applied research.
Action research refers basically learning by doing. First, a problem is identified, then some actions are taken to address it, then how well the efforts worked are measured, and if the results are not satisfactory, the steps are applied again.
It can be put into three different groups:
- Positivist: This type of research is also called “classical action research.” It considers research a social experiment. This research is used to test theories in the actual world.
- Interpretive: This kind of research is called “contemporary action research.” It thinks that business reality is socially made, and when doing this research, it focuses on the details of local and organizational factors.
- Critical: This action research cycle takes a critical reflection approach to corporate systems and tries to enhance them.
All research is about learning new things. Collaborative action research contributes knowledge based on investigations in particular and frequently useful circumstances. It starts with identifying a problem. After that, the research process is followed by the below stages:
Stage 1: Plan
For an action research project to go well, the researcher needs to plan it well. After coming up with an educational research topic or question after a research study, the first step is to develop an action plan to guide the research process. The research design aims to address the study’s question. The research strategy outlines what to undertake, when, and how.
Stage 2: Act
The next step is implementing the plan and gathering data. At this point, the researcher must select how to collect and organize research data . The researcher also needs to examine all tools and equipment before collecting data to ensure they are relevant, valid, and comprehensive.
Stage 3: Observe
Data observation is vital to any investigation. The action researcher needs to review the project’s goals and expectations before data observation. This is the final step before drawing conclusions and taking action.
Different kinds of graphs, charts, and networks can be used to represent the data. It assists in making judgments or progressing to the next stage of observing.
Stage 4: Reflect
This step involves applying a prospective solution and observing the results. It’s essential to see if the possible solution found through research can really solve the problem being studied.
The researcher must explore alternative ideas when the action research project’s solutions fail to solve the problem.
Action research is a systematic approach researchers, educators, and practitioners use to identify and address problems or challenges within a specific context. It involves a cyclical process of planning, implementing, reflecting, and adjusting actions based on the data collected. Here are the general steps involved in conducting an action research process:
Identify the action research question or problem
Clearly define the issue or problem you want to address through your research. It should be specific, actionable, and relevant to your working context.
Review existing knowledge
Conduct a literature review to understand what research has already been done on the topic. This will help you gain insights, identify gaps, and inform your research design.
Plan the research
Develop a research plan outlining your study’s objectives, methods, data collection tools, and timeline. Determine the scope of your research and the participants or stakeholders involved.
Collect data
Implement your research plan by collecting relevant data. This can involve various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, document analysis, or focus groups. Ensure that your data collection methods align with your research objectives and allow you to gather the necessary information.
Analyze the data
Once you have collected the data, analyze it using appropriate qualitative or quantitative techniques. Look for patterns, themes, or trends in the data that can help you understand the problem better.
Reflect on the findings
Reflect on the analyzed data and interpret the results in the context of your research question. Consider the implications and possible solutions that emerge from the data analysis. This reflection phase is crucial for generating insights and understanding the underlying factors contributing to the problem.

Develop an action plan
Based on your analysis and reflection, develop an action plan that outlines the steps you will take to address the identified problem. The plan should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART goals). Consider involving relevant stakeholders in planning to ensure their buy-in and support.
Implement the action plan
Put your action plan into practice by implementing the identified strategies or interventions. This may involve making changes to existing practices, introducing new approaches, or testing alternative solutions. Document the implementation process and any modifications made along the way.
Evaluate and monitor progress
Continuously monitor and evaluate the impact of your actions. Collect additional data, assess the effectiveness of the interventions, and measure progress towards your goals. This evaluation will help you determine if your actions have the desired effects and inform any necessary adjustments.
Reflect and iterate
Reflect on the outcomes of your actions and the evaluation results. Consider what worked well, what did not, and why. Use this information to refine your approach, make necessary adjustments, and plan for the next cycle of action research if needed.
Remember that participatory action research is an iterative process, and multiple cycles may be required to achieve significant improvements or solutions to the identified problem. Each cycle builds on the insights gained from the previous one, fostering continuous learning and improvement.
Explore Insightfully Contextual Inquiry in Qualitative Research
Here are two real-life examples of action research.
Action research initiatives are frequently situation-specific. Still, other researchers can adapt the techniques. The example is from a researcher’s (Franklin, 1994) report about a project encouraging nature tourism in the Caribbean.
In 1991, this was launched to study how nature tourism may be implemented on the four Windward Islands in the Caribbean: St. Lucia, Grenada, Dominica, and St. Vincent.
For environmental protection, a government-led action study determined that the consultation process needs to involve numerous stakeholders, including commercial enterprises.
First, two researchers undertook the study and held search conferences on each island. The search conferences resulted in suggestions and action plans for local community nature tourism sub-projects.
Several islands formed advisory groups and launched national awareness and community projects. Regional project meetings were held to discuss experiences, self-evaluations, and strategies. Creating a documentary about a local initiative helped build community. And the study was a success, leading to a number of changes in the area.
Lau and Hayward (1997) employed action research to analyze Internet-based collaborative work groups.
Over two years, the researchers facilitated three action research problem -solving cycles with 15 teachers, project personnel, and 25 health practitioners from diverse areas. The goal was to see how Internet-based communications might affect their virtual workgroup.
First, expectations were defined, technology was provided, and a bespoke workgroup system was developed. Participants suggested shorter, more dispersed training sessions with project-specific instructions.
The second phase saw the system’s complete deployment. The final cycle witnessed system stability and virtual group formation. The key lesson was that the learning curve was poorly misjudged, with frustrations only marginally met by phone-based technical help. According to the researchers, the absence of high-quality online material about community healthcare was harmful.
Role clarity, connection building, knowledge sharing, resource assistance, and experiential learning are vital for virtual group growth. More study is required on how group support systems might assist groups in engaging with their external environment and boost group members’ learning.
Action research has both good and bad points.
- It is very flexible, so researchers can change their analyses to fit their needs and make individual changes.
- It offers a quick and easy way to solve problems that have been going on for a long time instead of complicated, long-term solutions based on complex facts.
- If It is done right, it can be very powerful because it can lead to social change and give people the tools to make that change in ways that are important to their communities.
Disadvantages
- These studies have a hard time being generalized and are hard to repeat because they are so flexible. Because the researcher has the power to draw conclusions, they are often not thought to be theoretically sound.
- Setting up an action study in an ethical way can be hard. People may feel like they have to take part or take part in a certain way.
- It is prone to research errors like selection bias , social desirability bias, and other cognitive biases.
LEARN ABOUT: Self-Selection Bias
This post discusses how action research generates knowledge, its steps, and real-life examples. It is very applicable to the field of research and has a high level of relevance. We can only state that the purpose of this research is to comprehend an issue and find a solution to it.
At QuestionPro, we give researchers tools for collecting data, like our survey software, and a library of insights for any long-term study. Go to the Insight Hub if you want to see a demo or learn more about it.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ’s)
Action research is a systematic approach to inquiry that involves identifying a problem or challenge in a practical context, implementing interventions or changes, collecting and analyzing data, and using the findings to inform decision-making and drive positive change.
Action research can be conducted by various individuals or groups, including teachers, administrators, researchers, and educational practitioners. It is often carried out by those directly involved in the educational setting where the research takes place.
The steps of action research typically include identifying a problem, reviewing relevant literature, designing interventions or changes, collecting and analyzing data, reflecting on findings, and implementing improvements based on the results.
MORE LIKE THIS

QuestionPro: Leading the Charge in Customer Journey Management and Voice of the Customer Platforms
Sep 17, 2024
What is Driver Analysis? Importance and Best Practices

Was The Experience Memorable? (Part II) — Tuesday CX Thoughts

Data Discovery: What it is, Importance, Process + Use Cases
Sep 16, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
Published on 27 January 2023 by Tegan George . Revised on 21 April 2023.
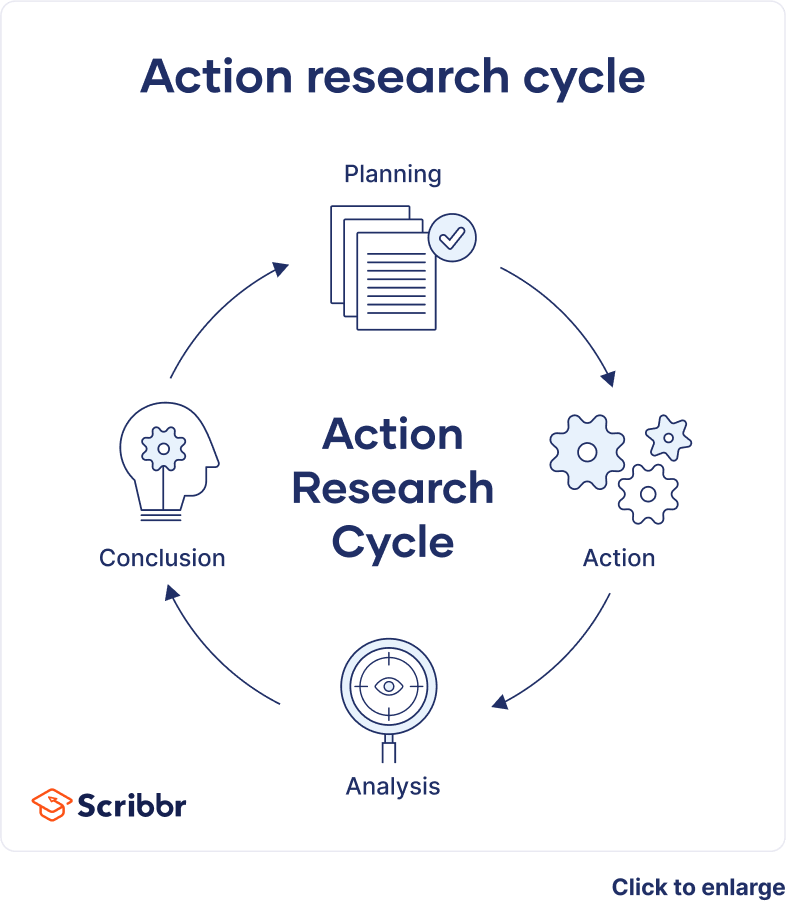
Table of contents
Types of action research, action research models, examples of action research, action research vs. traditional research, advantages and disadvantages of action research, frequently asked questions about action research.
There are 2 common types of action research: participatory action research and practical action research.
- Participatory action research emphasises that participants should be members of the community being studied, empowering those directly affected by outcomes of said research. In this method, participants are effectively co-researchers, with their lived experiences considered formative to the research process.
- Practical action research focuses more on how research is conducted and is designed to address and solve specific issues.
Both types of action research are more focused on increasing the capacity and ability of future practitioners than contributing to a theoretical body of knowledge.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Action research is often reflected in 3 action research models: operational (sometimes called technical), collaboration, and critical reflection.
- Operational (or technical) action research is usually visualised like a spiral following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
- Collaboration action research is more community-based, focused on building a network of similar individuals (e.g., college professors in a given geographic area) and compiling learnings from iterated feedback cycles.
- Critical reflection action research serves to contextualise systemic processes that are already ongoing (e.g., working retroactively to analyse existing school systems by questioning why certain practices were put into place and developed the way they did).
Action research is often used in fields like education because of its iterative and flexible style.
After the information was collected, the students were asked where they thought ramps or other accessibility measures would be best utilised, and the suggestions were sent to school administrators. Example: Practical action research Science teachers at your city’s high school have been witnessing a year-over-year decline in standardised test scores in chemistry. In seeking the source of this issue, they studied how concepts are taught in depth, focusing on the methods, tools, and approaches used by each teacher.
Action research differs sharply from other types of research in that it seeks to produce actionable processes over the course of the research rather than contributing to existing knowledge or drawing conclusions from datasets. In this way, action research is formative , not summative , and is conducted in an ongoing, iterative way.
| Action research | Traditional research | |
|---|---|---|
| and findings | ||
| and seeking between variables | ||
As such, action research is different in purpose, context, and significance and is a good fit for those seeking to implement systemic change.
Action research comes with advantages and disadvantages.
- Action research is highly adaptable , allowing researchers to mould their analysis to their individual needs and implement practical individual-level changes.
- Action research provides an immediate and actionable path forward for solving entrenched issues, rather than suggesting complicated, longer-term solutions rooted in complex data.
- Done correctly, action research can be very empowering , informing social change and allowing participants to effect that change in ways meaningful to their communities.
Disadvantages
- Due to their flexibility, action research studies are plagued by very limited generalisability and are very difficult to replicate . They are often not considered theoretically rigorous due to the power the researcher holds in drawing conclusions.
- Action research can be complicated to structure in an ethical manner . Participants may feel pressured to participate or to participate in a certain way.
- Action research is at high risk for research biases such as selection bias , social desirability bias , or other types of cognitive biases .
Action research is conducted in order to solve a particular issue immediately, while case studies are often conducted over a longer period of time and focus more on observing and analyzing a particular ongoing phenomenon.
Action research is focused on solving a problem or informing individual and community-based knowledge in a way that impacts teaching, learning, and other related processes. It is less focused on contributing theoretical input, instead producing actionable input.
Action research is particularly popular with educators as a form of systematic inquiry because it prioritizes reflection and bridges the gap between theory and practice. Educators are able to simultaneously investigate an issue as they solve it, and the method is very iterative and flexible.
A cycle of inquiry is another name for action research . It is usually visualized in a spiral shape following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
Sources for this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
George, T. (2023, April 21). What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 18 September 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/action-research-cycle/
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2017). Research methods in education (8th edition). Routledge.
Naughton, G. M. (2001). Action research (1st edition). Routledge.
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, primary research | definition, types, & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, what is an observational study | guide & examples.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
The PMC website is updating on October 15, 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Epidemiol Community Health
- v.60(10); 2006 Oct

Participatory action research
This glossary aims to clarify some of the key concepts associated with participatory action research.
Participatory action research (PAR) differs from most other approaches to public health research because it is based on reflection, data collection, and action that aims to improve health and reduce health inequities through involving the people who, in turn, take actions to improve their own health.
PAR has a number of antecedents. 1 It reflects questioning about the nature of knowledge and the extent to which knowledge can represent the interests of the powerful and serve to reinforce their positions in society. 2 It affirms that experience can be a basis of knowing and that experiential learning can lead to a legitimate form of knowledge that influences practice. 3 Adult educators in low income countries drew on these intellectual perspectives to develop a form of research that was sympathetic to the participatory nature of adult learning. This perspective was strongly supported by the work of Freire, 4 who used PAR to encourage poor and deprived communities to examine and analyse the structural reasons for their oppression. From these roots PAR grew as a methodology enabling researchers to work in partnership with communities in a manner that leads to action for change.
Definition of PAR
PAR seeks to understand and improve the world by changing it. At its heart is collective, self reflective inquiry that researchers and participants undertake, so they can understand and improve upon the practices in which they participate and the situations in which they find themselves. The reflective process is directly linked to action, influenced by understanding of history, culture, and local context and embedded in social relationships. The process of PAR should be empowering and lead to people having increased control over their lives (adapted from Minkler and Wallerstein 5 and Grbich 6 ).
The distinctiveness of PAR
PAR differs from conventional research in three ways. Firstly, it focuses on research whose purpose is to enable action. Action is achieved through a reflective cycle, whereby participants collect and analyse data, then determine what action should follow. The resultant action is then further researched and an iterative reflective cycle perpetuates data collection, reflection, and action as in a corkscrew action. Secondly, PAR pays careful attention to power relationships, advocating for power to be deliberately shared between the researcher and the researched: blurring the line between them until the researched become the researchers. The researched cease to be objects and become partners in the whole research process: including selecting the research topic, data collection, and analysis and deciding what action should happen as a result of the research findings. Wadsworth 7 sees PAR as an expression of “new paradigm science” that differs significantly from old paradigm or positivist science. The hallmark of positivist science is that it sees the world as having a single reality that can be independently observed and measured by objective scientists preferably under laboratory conditions where all variables can be controlled and manipulated to determine causal connections. By contrast new paradigm science and PAR posits that the observer has an impact on the phenomena being observed and brings to their inquiry a set of values that will exert influence on the study. Thirdly, PAR contrasts with less dynamic approaches that remove data and information from their contexts. Most health research involves people, even if only as passive participants, as “subjects” or “respondents”. PAR advocates that those being researched should be involved in the process actively. The degree to which this is possible in health research will differ as will the willingness of people to be involved in research
Methodology/method
Research methodology is a strategy or plan of action that shapes our choice and use of methods and links them to the desired outcomes. 8 In contrast with a decade ago, when epidemiological methods were regarded as the only gold standard in public health research, many authors agree 9 , 9a , 9b that effective public health research requires methodological pluralism. PAR draws on the paradigms of critical theory and constructivism and may use a range of qualitative and quantitative methods. For instance a participatory needs assessment would include extensive engagement with local communities and may also include a survey of residents who are less centrally engaged in the participatory process. 10
Application of PAR to health
In the 21st century PAR is increasingly used in health research. By contrast, in the 1980s and in earlier decades, very little research using PAR was reported in health journals. Through the 1990s more participatory research was reported and textbooks including PAR became more common. 11 , 11a An example of this interest is the special edition of the Journal of Interprofessional Care , with an editorial and 16 articles reporting on PAR. 12 Initially PAR was mainly used in low income countries for needs assessment (see for example De Kroning and Martin 13 ) and planning and evaluating health services (for examples see collection in Minkler and Wallerstein 14 ). The work by Howard‐Grabman 15 provides a typical description of developing a community plan to tackle maternal and neonatal health problems in rural Bolivia. The project built on and strengthened existing women's networks and the staff played the part of facilitators rather than educators. A community action cycle was developed whereby problems were identified and prioritised, joint planning took place, and the plan was implemented and then evaluated in a participatory way. The project developed innovative and engaging ways for staff and community members to work together effectively.
Recently PAR has been used more frequently in rich countries. In mental health research, for instance, PAR has been used in response to the survivor's movement and demands for a voice in planning and running services and to stimulate choices and alternative forms of treatment. 16 PAR principles also form the basis of “empowerment evaluation” 17 that argue that the evaluation of health promotion should include those whose health is being promoted. 18 While there has been some debate about the distinctiveness of empowerment evaluation 19 it certainly strives to be more democratic, to build capacity, to encourage self determination and make evaluation less expert driven.
PAR is increasingly recognised as useful in Indigenous health research, both internationally 20 , 21 and in Australia. 22 , 23 , 24 It has the potential to reduce the negative—and some would argue colonising—effects much conventional research has had on Indigenous people. It does this by avoiding some of the criticisms made of health research including: (1) Indigenous people being exploited and treated disrespectfully, (2) research processes that see non‐Indigenous researchers and research bodies retain all the power and control, (3) the lack of specified short and long term benefits to Indigenous communities and persons, and (4) the misrepresentation of Indigenous societies, cultures, and persons by non‐Indigenous academics and professionals. 25 , 26 , 27
An example of the application of PAR in a remote Aboriginal Australian community is the work to support a men's self help group to plan, implement, and evaluate their activities. 28 With support from the research team community members are acting as researchers exploring priority issues affecting their lives, recognising their resources, producing knowledge, and taking action to improve their situation. The ongoing PAR process of reflection and action, which incorporates participant observation, informal discussions, in‐depth interviews, and a “feedback box”, is viewed by the participants as contributing to their self reported increased sense of self awareness, self confidence, and hope for the future.
For academics, dilemmas arise in the use of PAR because it is time consuming and unpredictable, unlikely to lead to a high production of articles in refereed journals and its somewhat “messy” nature means it is less likely to attract competitive research funding. 29 Acceptance of PAR as a legitimate research methodology will require change from public health journals, funding bodies, and universities in the way that they judge research performance. For instance most public health academic units assess their academic researchers' suitability for promotion according to the number of peer reviewed journal articles. The ability of a researcher to engage with communities and bring about real change to their quality of life and health status rarely counts. The global research community is already being urged to adapt its grant assessment methods and its assessment of research performance to ensure that the engaged processes typical of PAR are valued and encouraged. 30
PAR also requires health researchers to work in close partnership with civil society and health policy makers and practitioners. This requires each of these players to learn methods of working together effectively and to manage the different and sometimes competing agendas of the partners. The focus of the research partners should also be on health improvement for the community involved. 31
Participation
Participation has been central to improving health since the WHO Health for All Strategy and its importance to health promotion strategies has been reinforced by subsequent statements on health promotion. 32 Participation has been seen as a means to overcome professional dominance, to improve strategies (whether they are for practice or research), and to show a commitment to democratic principles. In the 1970s debate on development emphasised that development should no longer be a top‐down process but should emphasise participation of those whose development was being attempted. 33 PAR came to be used in many development projects as a mechanism through which to put the rhetoric of participation into action. Associated methods are rapid assessment methods and rapid rural appraisal both of which aim to produce knowledge that combines professional and community perspectives.
Power/empowerment
Power is a crucial underpinning concept to PAR. PAR aims to achieve empowerment of those involved. Labonte 34 conceptualises empowerment as a shifting or dynamic quality of power relations between two or more people; such that the relationship tends towards equity by reducing inequalities and power differences in access to resources. Power itself is an elusive concept about which there has been considerable discussion. Foucault's position is particularly relevant to PAR because he sees power as something that results from the interactions between people, from the practices of institutions, and from the exercise of different forms of knowledge. 35 His work on discipline and control shows that disciplinary power functions through surveillance and internal discipline of people to achieve their subjugations and “docility”. 36 The PAR movement challenges the system of surveillance and knowledge control established through mainstream research. When communities seek control of research agendas, and seek to be active in research, they are establishing themselves as more powerful agents. In health services and public health initiatives in recent years community members and consumers have gained more power over the practices of institutions and the production of knowledge. Developments in participation have implications for health services and public health organisations that, if they are to be true to the principles of participation, must initiate organisational change to improve their capacity to work in partnership with a wide variety of communities. 37 , 37a
Many dilemmas of the PAR approach revolve around contested power dynamics in research relationships. Wallerstein detailed the power conflicts in research on New Mexico's Healthier Communities Initiatives and concluded that handling these requires “a painful self‐reflective process”. 38 These included differences in perceptions of priorities between researchers and community members, dealing with community politics in the different communities involved in the study and resolving different ways in which researchers and communities might interpret findings.
Lived experience
PAR stands in contrast with what Husserl (quoted in Crotty 39 ) describes as the mathematisation of the scientific world by Galileo, for whom the real properties of things were only those that could be measured, counted, and quantified. Husserl argued that the scientific world is an abstraction from the lived world, or the world we experience. This scientific world is systematic and well organised, unlike the uncertain, ambiguous, idiosyncratic world we know at first hand. 39 On the other hand, PAR draws on the work of phenomenologists who expand the breadth and importance of experience when they argue that humans cannot describe and object in isolation from the conscious being experiencing that object; just as an experience cannot be described in isolation from its object. Experiences are not from a sphere of subjective reality separate from an external, objective world. Rather they enable humans to engage with their world and unite subject and object. 40 One example of a use of lived experience is research using feminist theory, which refers to “women's ways of knowing or women's experience”. 41
Critical reflection and a critical edge
Crotty 42 argues that while interpretivists place confidence in the authentic accounts of lived experience that they turn up in their research, this is not enough for critical theorists who see in these accounts voices of an inherited tradition and prevailing culture. Critical theorists use critical reflection on social reality to take action for change by radically calling into question the cultures that they study. This critical edge is central to PAR.
Critical reflection on professional practice
PAR draws heavily on Paulo Freire's epistemology that rejects both the view that consciousness is a copy of external reality and the solipsist argument that the world is a creation of consciousness. For Freire, human consciousness brings a reflection on material reality, whereby critical reflection is already action. Freire's concept of praxis flows from the position that action and reflection are indissolubly united: “reflection and action on the world in order to transform it”. 43 It is from this position that Freire derives his famous dictum that reflection without action is sheer verbalism or armchair revolution and action without reflection is pure activism, or action for action's sake . 44 In the same vein, PAR sees that action and reflection must go together, even temporally so that praxis cannot be divided into a prior stage of reflection and a subsequent stage of action. When action and reflection take place at the same time they become creative and mutually illuminate each other. 45 Through praxis, critical consciousness develops, leading to further action through which people cease to see their situation as a “dense, enveloping reality or a blind alley” and instead as “an historical reality susceptible of transformation”. 46 This transformative power is central to PAR.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to our reviewers—Valery Ridde, Ruth Balogh, and one anonymous. Their comments have improved this glossary.
Action Research
- First Online: 29 September 2022
Cite this chapter

- Robert E. White ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8045-164X 3 &
- Karyn Cooper 4
1541 Accesses
Of all the methodologies that have, thus far, been discussed between the pages of this volume, perhaps none is more practical than action research. In fact, it is often referred to as “practitioner research,” “teacher research’ or “participatory action research.” Herr and Anderson (2005) claim that action researchers may occupy multiple positions, even simultaneously, as insiders and/or outsiders, depending on social or ideological constructs such as race, religion, political affiliation, social class, gender or sexual orientation. These affiliations (or exclusions) may also significantly influence the reality as captured through action research. As such, action researchers may greatly benefit from interrogating and identifying their multiple positionalites in order to understand and articulate tensions stemming from underlying roles and stances, and to “avoid the blind spots that come with unexamined beliefs” (Herr & Anderson, 2005, p. 44).
No action without research, no research without action –Kurt Lewin (1946)
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Action Evaluation Collaborative. (2016). Participatory action learning: Part 1 – Insights into a catalyst for transformative change . Retrieved August 12, 2019, from: https://actionevaluationcollaborative.exposure.co/participatory-action-learning# !
Argyris, C. (1999). On organizational learning . Blackwell.
Google Scholar
Argyris, C., & Schön, D. (1974). Theory in practice: Increasing personal effectiveness . Jossey-Bass.
Argyris, C., & Schön, D. (1978). Organizational learning: A theory of action perspective . Addison Wesley.
Baum, F., MacDougall, C., & Smith, D. (2004). Participatory action research. Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health, 60 (10), 854–857. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.2004.028662
Article Google Scholar
Blanning, T. C. W. (1998). The French revolution: Class war or culture clash? (2nd ed.). St. Martin’s Press.
Book Google Scholar
Boog, B., Coenen, H., Keune, A. W. M., & Lammerts, R. (1996). Theory and practice of action research—With special reference to the Netherlands . Tilbury University Press.
Burns, A. R. (2015). Action research. In J. D. Brown & C. Coombe (Eds.), The Cambridge guide to research in language teaching and learning (1st ed., pp. 99–104). Cambridge University Press.
Calhoun, C. J. (2002). Contemporary sociological theory . Wiley-Blackwell.
Cammarota, J. (2011). From hopelessness to hope: Social justice pedagogy in urban education and youth development. Urban Education, 46 (4), 828–844.
Charles, L., & Ward, N. (2007). Generating change through research: Action research and its implications (Discussion Paper Series No. 10). Centre for Rural Economy Newcastle University.
Chisholm, R., & Elden, M. (1993). Features of emerging action research. Human Relations, 46 (2), 275–298.
Clifford Simplican, S. (2009) . Disabling democracy: How disability reconfigures deliberative democratic norms . APSA 2009 Toronto Meeting Paper. Retrieved August 8, 2019, from: https://ssrn.com/abstract=1451092
Corlett, S. (2012). Participant learning in and through research as reflexive dialogue: Being “struck” and the effects of recall. Management Learning, 44 (5), 453–469.
Cummings, S., Bridgman, T., & Brown, K. (2016). Unfreezing change as three steps: Rethinking Kurt Lewin’s legacy for change management. Human Relations, 69 (1), 33–60.
de Koning, K., & Martin, M. (1996). Participatory research in health: Issues and experiences . Zed Books.
Dewey, J. (1897/2019). Moral principles in education and my pedagogic creed by John Dewey . Myers Education Press.
Dick, B. (1997). Action learning and action research. Retrieved August 12, 2019, from: http://www.aral.com.au/resources/actlearn.html
Elliott, J. (1991). Action research for educational change . Open University Press.
Ellis, R. (2010). Second language acquisition, teacher education and language pedagogy. Language Teaching, 43 (2), 182–201.
Fals-Borda, O., & Rahman, M. A. (1991). Action and knowledge: Breaking the monopoly with participatory action research . Rowman & Littlefield.
Fetterman, D. M., Kaftarian, S., & Wandersman, A. (Eds.). (1996). Empowerment evaluation: Knowledge and tools for self-assessment and accountability . Sage.
Forsyth, D. R. (2019). Group dynamics . Cengage.
Freire, P. (1970/2000). Pedagogy of the oppressed (30th Anniversary ed.). Continuum.
French, W. L., & Bell, C. (1973). Organization development: Behavioral science interventions for organization improvement . Prentice-Hall.
Greenwood, D. J., & Levin, M. (2007). Introduction to action research: Social research for social change (2nd ed.). Sage.
Griffith, M. (2009). Action research for/as/mindful of social justice. In S. Noffke & B. Somekh (Eds.), The SAGE handbook of educational action research (pp. 85–98). SAGE.
Chapter Google Scholar
Habermas, J. (1962/1991). The structural transformation of the public sphere: An inquiry into a category of bourgeois society . MIT Press.
Habermas, J. (1985). The theory of communicative action: Volume 1: Reason and the rationalization of society . Beacon Press.
Haggbloom, S. J., Warnick, R., Warnick, J. E., Jones, V. K., Yarbrough, G. L., Russell, T. M., Borecky, C. M., McGahhey, R., Powell, J. L., III, Beavers, J., & Monte, E. (2002). The 100 most eminent psychologists of the 20th century. Review of General Psychology, 6 (2), 139–152.
Heron, J. (1996). Co-operative inquiry: Research into the human condition . Sage.
Herr, K., & Anderson, G. L. (2005). The action research dissertation: A guide for students and faculty . Sage Publications Inc.
Howard-Grabman, L. (1996). ‘Planning together’: Developing community plans to address priority maternal and neonatal health problems in rural Bolivia. In K. de Koning & M. Martin (Eds.), Participatory research in health: Issues and experiences (pp. 153–163). Zed Books.
Kavannagh, A., Daly, J., & Jolley, D. (2007). Research methods, evidence and public health. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Public Health, 26 (4), 299–396.
Kemmis, S., & Carr, W. (1986/2002). Becoming critical: Education knowledge and action research . Routledge Falmer.
Kemmis, S., & McTaggart, R. (2000). Participatory action research. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (pp. 567–595). SAGE.
Kincheloe, J. L. (2008). Critical pedagogy primer (2nd ed.). Peter Lang.
Koshy, V. (2010). Action research for improving educational practice: A step-by-step guide (2nd ed.). Sage.
Lasch-Quinn, E. (2017). Race experts: How racial etiquette, sensitivity training and new age therapy hijacked the civil rights movement . Rowman & Littlefield.
LeCompte, M. (1995). Some notes on power, agenda, and voice: A researcher’s personal evolution toward critical collaboration research. In P. McLaren & J. Giarelli (Eds.), Critical theory and educational research (pp. 91–112). State University of New York Press.
Lewin, K. (1943). Defining the “Field at a Given Time”. Psychological Review, 50 (3), 292–310.
Lewin, K. (1946). Action research and minority problems. Journal of Social Issues, 2 (4), 34–46.
Lewin, K. (1947). Frontiers in group dynamics: Concept, method and reality in social science; social equilibria and social change. Human Relations, 1 , 5–41. https://doi.org/10.1177/001872674700100103
Lewin, K. (1948). Resolving social conflicts: Selected papers on group dynamics . Harper & Row.
Lewin, K. (1958). Group decision and social change . Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
Maksimovic, J. (2010). Historical development of action research in social sciences. Factas Universitatis: Philosophy, Sociology, Psychology & History, 9 (1), 119–124.
McCoy, D., Sanders, D., Baum, F., Narayan, T., & Legge, D. (2004). Pushing the international health research agenda towards equity and effectiveness. Lancet, 364 (9445), 1630–1631.
McNamara, C. (2006). Field guide to consulting and organizational development: A collaborative and systems approach to performance, change and learning . Authenticity Consulting.
McNiff, J. (1988). Action research: Principles and practice . Macmillan Education.
McTaggart, R. (1991). Action research: A short modern history . Deakin University Press.
Meyer, J. (2000). Using qualitative methods in health related action research. British Medical Journal, 320 (178). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.320.7228.178
Mihăiloaie, C. (2014). What is the difference between single-loop and double-loop learning? Retrieved August 13, 2019, from: https://www.performancemagazine.org/what-is-the-difference-between-single-loop-and-double-loop-learning/
Monk, R. (1992). Wittgenstein: The duty of genius . Penguin.
O’Brien, R. (2001). Um exame da abordagem metodológica da pesquisa ação [An Overview of the Methodological Approach of Action Research]. In R. Richardson (Ed.), Teoria e Prática da Pesquisa Ação [Theory and practice of action research]. João Pessoa, BR: Universidade Federal da Paraíba. (English version) Retrieved, August 8, 2019, from: http://www.web.ca/~robrien/papers/arfinal.html
Owens, R. G., & Valesky, T. C. (2015). Organizational behavior in education: Leadership and school reform . Pearson.
Payrow Shabani, O. A. (2003). Democracy, power and legitimacy: The critical theory of Jürgen Habermas . University of Toronto Press.
Rahman, M. A. (2008). Some trends in the praxis of participatory action research. In P. Reason & H. Bradbury (Eds.), The SAGE handbook of action research (2nd ed., pp. 49–62). Sage.
Reason, P., & Bradbury, H. (2001). Handbook of action research: Participative inquiry and practice . SAGE.
Riel, M. (2019). Understanding collaborative action research . Center For Collaborative Action Research, Pepperdine University, Malibu, CA. Retrieved, August 12, 2019, from: http://cadres.pepperdine.edu/ccar/define.html
Rogers, E. (1994). A history of communication study: A biological approach . The Free Press.
Sagor, R. (2000). Guiding school improvement with action research . ASCD.
Smith, M. K. (2001). Kurt Lewin, groups, experiential learning and action research. The Encyclopedia of Informal Education . Retrieved, August 8, 2019, from; http://www.infed.org/thinkers/et-lewin.htm
Stenhouse, L. (1975). An introduction to curriculum research and development . Heinemann.
Wallerstein, N., Duran, B., Oetzel, J. G., & Minkler, M. (2017). On community-based participatory research. In N. Wallerstein, B. Duran, J. G. Oetzel, & M. Minkler (Eds.), Community-Based participatory research for health (3rd ed., pp. 3–16). Jossey-Bass.
Weng, F. (2014). Comparing the philosophy of Jürgen Habermas and Michel Foucault. Inquiries, 6 (9), 1–2.
Wenger, E. (1999). Communities of practice: Learning, meaning, and identity . Cambridge University Press.
Whitehead, J. (2009). Generating living theory and understanding in action research studies. Action Research, 7 (1), 85–99.
Zeichner, K. M., & Noffke, S. E. (2001). Practitioner research. In V. Richardson (Ed.), Handbook of research on teaching (4th ed., pp. 298–330). American Educational Research Association.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Education, St. Francis Xavier University, Antigonish, NS, Canada
Robert E. White
OISE, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
Karyn Cooper
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Robert E. White .
Action Research in practice: Critical literacy in an urban grade three classroom
Ontario Institute for Studies in Education of the University of Toronto
St. Francis Xavier University
Cooper, K. & White, R. E. (2006). Action research in practice: Critical literacy in an urban grade 3 classroom. Educational Action Research 14(1), 83-99.
This action research project on critical literacy in a high poverty area in Toronto, Canada becomes the practical backdrop for examining how critical literacy can be developed and applied in regular classroom situations. Educators identifying patterns within classrooms that prevent students from participating fully in all aspects of a democratic society may find models presented in this article useful for making curricula more inclusive.
Literacy failure leads to poor overall academic performance, immense loss of self-esteem and an accumulating lack of basic literacy skills needed for self-support and for making an economic contribution to society. While literacy can be defined in many ways in today’s society, it is reading failure that is currently the most significant issue along the literacy spectrum.
Reading failure and educational change are inextricably intertwined. In order to bolster literacy capacity, a prime place to begin is in the arena of educational reform. Education has undergone profound changes in the past few years as ministries of education, faculties of education, and school boards prepare teachers to respond to the needs of “all” children. In the province of Ontario, Canada, for example, all Grade Three students now participate in the Education Quality and Accountability Office (EQAO) Standardized tests. As well, a public school board in Ontario has compiled a Learning Opportunities Index (Toronto District School Board, 2001) which serves to indicate a “relative level of need” for over 450 elementary schools under its prevue. This Opportunities Index correlates with literacy scores from EQAO Tests and is used by the school district to profile low literacy levels for early learners from urban schools (Brown, 2001). Despite significant public expenditure on education, being part of the reading world is not a reality for many urban inner city children in lower socio-economic areas. While these learners are Ontario’s at-risk students, their situation has global parallels. Although local practices and global practices differ around the world, literacy requires a re-imaging in this era of reconstruction and development (Janks, 2000). This issue, then, is an international one: how can elementary teachers in urban schools best help at-risk learners in literacy education and thus their chances for future success in education and life?
One of those hundreds of urban elementary schools in this Canadian school board is the Sir Simon George Elementary School. This K-5 school has over 650 students, 48% female and 52 % male, with 12% born outside of Canada and 66% for whom English is not their primary language. Because Sir Simon George Elementary School scored poorly on the Board’s Learning Opportunities Index , the staff at Sir Simon George Elementary School recently has begun to come to come to grips with the issue. The staff has embraced a new vision for this school. In order to implement this vision, the school staff established several important changes in the hopes of reversing this school’s low educational ranking.
Professional development for classroom teachers on administering the Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA) constituted another significant change. By utilizing this assessment procedure, the school was able to obtain literacy baseline scores for all of its students. Furthermore, a school district primary literacy consultant, in concert with the school staff, designated a daily school-wide, two-hour time block for implementation of an early literacy program.
Literacy research is replete with accounts indicating that early intervention with at-risk students can effectively increase levels of literacy skills and comprehension. Such research suggests that a key to successful intervention is to provide students with programs that emphasize critical thinking strategies (Anyon, 1980; Gunning, 2000; Slavin, 1998).
Critical literacy can be separated from the notion of critical thinking in the following way. Luke (1997) notes that critical approaches to literacy involve “a shift away from psychological and individualistic models of reading and writing towards those approaches that use sociological, cultural and discourse theory to reconceptualise the literate subject, textual practices, and classroom pedagogy” (143). He goes on to state that:
Critical approaches are characterized by a commitment to reshape literacy education in the interests of marginalized groups of learners, who on the basis of gender, cultural and socioeconomic background have been excluded from access to the discourses and texts of dominant economics and cultures (Luke, 1997, p.143).
This definition of critical literacy is supported by Gee (1996) and Edelsky and Cherland (2006). Although critical literacy and critical thinking are not necessarily the same thing, Luke (1997) suggests that “shared across contemporary approaches to critical literacy is an emphasis on the need for literates to take an interventionist approach to texts and discourses of all media” (critical literacy) and also requires “a commitment to the capacity to critique, transform and reconstruct dominant modes of information” (critical thinking) (p. 150).
Teachers and researchers, therefore, need to understand the complex relationship between language and power. Research indicates that teacher-generated research provides teachers with a strong feeling of ownership of both the process and results, and increases their own professional development (Carson & Sumara; 1997; Hannay, 1989, 1995; McNiff, 1993). However, despite all the attention given to strategic skill development for at-risk learners and attention given to the ways in which teachers acquire their professional knowledge, teachers’ reflections upon the teaching and learning process has received little attention. In spite of much of the rhetoric on school reform , it is painfully apparent that we do not actively value the insights and interpretations of teachers, and it is precisely these insights and interpretations that can effectively improve not only literacy levels as well as comprehension but critical literacy strategies as well. For these reasons, the staff approached this research team for assistance in the development of a critical literacy action research project.
The critical literacy action research project
In the Fall of 2001, Sir Simon George Elementary School staff invited the research team to participate in a multi-year action research project, the focus of which was school wide literacy improvement. The research team consisted of the co-authors, a graduate research assistant, a school literacy co-ordinator and a school district primary literacy consultant. The role of this research team was to act as facilitators to work together with teachers to develop critical literacy capacity among the teachers and the entire research team. After the initial and obligatory staff meeting in which the research team was introduce and the project was addressed, the non-school based researchers worked together with teachers to design the process. From this, in conjunction with the school district primary literacy consultant, one teacher volunteered to design and incorporate lesson plans to address issues of critical literacy in her grade three classroom. This paper reports on the action research project on critical literacy that grew out of this initiative. The impact of this project on the teacher and researchers are reported on later in this paper.
The action research project reported here offers promise for on-going collaborative research into critical literacy for urban students who continue to be at a disadvantage as it pertains to literacy, comprehension and critical thinking. The purposes of this project were to:
Design a Steps to Action Plan (Mills, 2000) enabling them to effect positive educational change.
Assess the effects on student literacy levels of teaching the students critical literacy strategies,
Evaluate the effects of an action research strategy on teacher learning and professional development.
As a corollary to the purposes of the project the staff and administration, in conjunction with the research team, determined the objectives for this project as being:
To develop critical literacy strategies for both early at-risk learners and their teachers,
To improve literacy teachers’ professional judgment,
To implement, assess, and evaluate specific strategies of literacy teaching
To enhance elementary in-service teacher training to support school-wide literacy improvement, critical literacy strategies, and life-long learning.
The significance of this study lies not only in its school-initiated origins, but also in its potential to contribute to two interrelated areas:
Critical literacy strategies, by reflecting on how critical thinking and critical literacy is developed by a teacher, in concert with the research team, in an actual classroom for at-risk children;
Action research, particularly an in-depth look at one school’s effort to improve early literacy for at-risk students.
In the first year of this project much time was invested in outlining the parameters of the research project, including serious school-wide discussion, culminating in a joint initiative on the methods of literacy instruction for primary students (kindergarten through grade three) in the school. The program of research was based on the action research methodology loop, “act-reflect-revise” (Mills, 2000), with teachers and their students as they engaged in action research to select and implement suitable and appropriate practices for critical literacy, as defined by the teachers themselves.
At the school level, all research members participated in sessions to decide upon the foundations for the research project based on suitable and appropriate practices for building critical literacy capacities relating to primary urban students and their teachers (Comber, Thomson, Wells, 2001). All stages in the process were developed through consensus, with the research team acting as facilitators for the process. The teacher and the school district primary literacy consultant designed the lessons. Learning strategies such as KWL (Thompkins, 1998) and other reflective practices were included.
The “K-W-L” (what we KNOW—what we WANT to learn—what we have LEARNED) strategy for reflective thinking (Thompkins, 1998) is outlined below.
K What we KNOW (One’s preconceptions)
Based on my experience, I believe critical literacy can be described as.....
I am now thinking.....
W What we WANT to learn
I wonder.....
What would happen if.....
It’s funny how my students.....
How can I.....
L What we have LEARNED
Developing critical literacy capacities of students and teachers
Practice or strategy for developing critical literacy capacities within this component.....
When students are engaged in developing critical literacy capacities, it looks like.....
When students are engaged in developing critical literacy capacities, it sounds like.....
Perhaps (specific student) demonstrates the best response to this strategy because.....
Perhaps (specific student) demonstrates the weakest response to this strategy because...
For this student to assess his/her critical literacy capacity, what needs to happen?
The opportunity for revision (“Are revisions needed to be made to the action plan itself at this time?”) follows this reflection, which in turn produces a new action plan.
At the end of the first year of the study, the research participants reflected upon the action research project and planned for revision to the research process for the next year. The previously described K-W-L strategy provided the basis for the structure of the focus group reflections within the project. The Debbie Miller (2002) book, Reading with Meaning , was chosen by the participants in this project for its attention to establishing a framework for creating a culture and climate for critical literacy. This book is written by a teacher-researcher and reflects goals similar to the objectives of this critical action research project, providing goals both for teachers and students regarding how to think more deeply while at the same time working towards esteem-building and social agency (Luke, 1997). After the grade three teacher in the project highly endorsed the book, everyone in the project read sample chapters and agreed that it fit into an operative framework for beginning the project. The research team particularly liked the way in which Miller (2002) worked at enabling her students to become more experienced at making meaningful and thoughtful connections to the stories of their own lives so that they might become more adept at reading the broader context within which they live. Like Miller, it was the group’s belief, that the only way to develop responsibility in students is to allow them to practice it.
With the first year of the project behind them, the critical literacy action research project began in earnest. The staff felt comfortable with the planning process, and in September, the following questions were asked of the students of the grade three teacher who was part of the research team: “Why do people read?” “What do you see readers doing?” “Where do you see people reading?” These questions and other questions were used to establish connections with students’ lives and to develop a greater understanding of their own reading worlds in order to make the context of the project relevant to them.
Brainstorming with the large group and recording students’ thinking was an appropriate way to address the first question. In this way, the school district primary literacy consultant in collaboration with the grade three teacher and the research team began to outline the project with the grade three students. These questions, which framed the beginning work with students, revealed much about the children’s perspectives about reading and also assisted in the selection of relevant teaching materials.
By October, focus meetings followed the K-W-L format as previously described. For purposes of framing the discussion, one example from each KWL strategy for reflective thinking is presented below.
“K” Represents the Research Team’s Current Understanding of Critical Literacy
The collective research team realized early on that they needed to establish an understanding of the term “critical literacy”. The research team’s first discussion regarding preconceptions of what critical literacy means was timely, given Edelsky and Cherland’s (2006) concern about the popularization and appropriation of the term “critical” and the tendency to trivialize what critical literacy—and critical thinking—really means.
From the first meeting: On the meaning of critical literacy, it became clear that the research team in general was using a variety of definitions of critical literacy. The researchers referred the team to Luke (1997):
Whatever we are doing needs to be important to us and our belief structures. Otherwise, what are we doing it for? There needs to be some connection to ourselves for it to be meaningful practice.
Critical literacy is a way to view the world. It’s a key to a democratic education. It’s basic in terms of being critical oneself.
We all have different ideas of things in our own heads.... We might think that we are talking about the same thing, but we’re talking about different things altogether.
...sharing ownership and trusting...and trusting the students to be able to be responsible and to think
If teachers don’t ask themselves why, then how do they expect students to ask why? Many of the students in this particular situation are ESL students. We have had grade three students whom teachers were bringing forth as having difficulties. They were Canadian-born but were receiving ESL instruction and couldn’t be considered ESL students any more. We’re masking a problem that could be deeper than we realize.
This passage, taken from the first discussion concerning the need to define a critical literacy stance, points to the notion that “critical literacy” needs to be understood in terms of the dynamics of identity, context and teaching practices employed. Jamilla acknowledges how one’s own belief structures are connected to classroom practice. In speaking about her own identity as a young black teacher, she can begin to see traces of her identity rooted in and through her teaching practices in both explicit and implicit ways. Dianne connects this thought to the all-important roles that teachers play in helping to construct their students’ identities through the beliefs they carry about who the students are and what they believe the students are capable of. Suzanne reminds us of the need to understand the politics of the ‘local’ literacy context when she states that, “Many of our students in this particular situation are ESL students”. Suzanne speaks to the idea that the cultural and political run deep in literacy and that teachers need to be aware of these factors, particularly if they are concerned with all students, including “minority” students, gaining a chance to define themselves. Through this discussion, the team began to consider more deeply just how literacy practices used in educational settings serve to affirm or disaffirm a student’s sense of identity and ultimately a student’s chances for “success” in society.
This initial discussion reveals an important question relevant to a critical literacy stance: How do we, as teachers, learn to become more experienced so that we might learn to step outside of ourselves and our own identities to allow multiple identities in? Perhaps this entails the commitment to be continually vigilant concerning what conditions truly support literacy, particularly for children of poverty or for those who have been labeled “at-risk.” These are of course ideological considerations and cannot be dealt with in short order. However, through beginning with our own teaching practices, and acting locally, we believed that we might move from our local position to more global issues relevant in literacy education today.
At this point, it may be helpful to briefly look at how literacy has been constructed historically. The following definitions illustrate that literacy is storied according to changing economies, cultures, institutions and possible worlds.
A literate person is a person who can, with understanding, both read and write a short, simple statement on his everyday life (UNESCO, 1951).
Functional literacy is the ability to engage effectively in all those reading activities normally expected of a literate adult in his community (Hunter & Harman, 1979).
[Literacy is] using print and written information to function in society, to achieve one’s goals, and to develop one’s knowledge and potential (Southam Literacy, 1987).
These definitions show that literacy is dynamic and that historical interpretations have driven and continue to drive what represents literacy. Thus what represents literacy is historically driven and both traces and influences our definitions of literacy and how we use it. As teachers/educators of literacy then, is it not incumbent upon educators to consider their role(s) in shaping the ‘construct’ of what it is that literacy embodies? Is it to ask, “Who is deemed to be a ‘literate’ individual, and by whom”, particularly in these times of a pluralistic milieu in the twenty-first century? If so, then it would seem that definitions must be chosen well. This re-evaluation of what constitutes literacy and, by extension, critical literacy, is driven by dramatic local and global change. Globalization has resulted in the domination of English (Janks, 2000) and Cummins (1995) has addressed questions raised by the cultural politics of English as an international language. The issue is at once global and local as so many of our students are English as a Second Language (ESL) learners, as borne out by the number of ESL students in this study. Chambers adds another dimension to the discussion:
To inhabit the multiplicity of cultural borders, historical temporalities and hybrid identities calls for a state of knowledge, an ethics of the intellect, an aperture in politics, able to acknowledge more than itself; a state of knowledge that is prepared to suffer modification and interrogation by what it neither possesses nor can claim as its own…and permits us to lend our ears to what is unsaid in the discourses we employ (Chambers, 1996, 50).
Chambers’ term, “ a state of knowledge” suggests a growing critical awareness of the need to acknowledge multiple identities within any enclosed system, including educational systems. The Chambers quotation is particularly important when considering a critical literacy stance because it embodies key elements of identity and context while considering a state of knowledge capable of “lending our ears to what is unsaid in the discourses [or teaching practices] we employ.”
In this particular school research context, the research team felt that policy-makers do not always define the rich cultural diversity of the children and parents in their school community favourably. While on the surface, multiculturalism is touted to be beneficial to student learning; there may be issues of prejudice and discrimination still hiding in the light. Sonia Nieto (1994) points to patterns that encourage students to move beyond mere tolerance in multicultural education. A quotation from one of the team members may best express this:
With talking about what you think and see with students, particularly impoverished students like those in our multicultural school, they’re often written off for various reasons.
Another team member expressed a similar idea in the following way:
Our children are incredibly capable but there is somehow a mismatch between the school’s version of intelligence and what is occurring at home.
The dispositional nature of critical thinking was described:
I’ve had students in Special Education who are very intelligent in terms of the way they use higher order thinking or critical literacy, but it is situational. Perhaps the key is to make critical thinking more dispositional than situational, thereby developing critical learning capacities that are derived from critical literacy.
Putting critical literacy into practice takes thought and hard work and the full time teacher is the one charged with the responsibility of being, accountable, effective and efficient. Shutz (2000) places this thought in context:
...what we are led to believe about ourselves, what we learn about how we are supposed to act, the ways we are taught to frame “problems” and even the tools of reason that we use to solve these problems, do not simply represent neutral skills but are in fact ways of forming us into particular kinds of subjects. ‘Power’ in this vision does not merely suppress or restrict but actually produces actions and desires (216).
If critical literacy is to promote democracy, social justice and equity in schools, then what circumstances need to arise in schools for an increase in democracy and shared power? Banks (1999) describes a pattern of four levels of multicultural curriculum that parallel the adoption of a critical literacy curriculum. It is often referred to as a critical literacy curriculum because its definition has expanded to include all students who tend to be marginalized socially or physically. The curriculum pattern tends to become increasingly more inclusive as the approach moves through the inclusion of ethnic heroes into the existing unchanged curriculum to an approach that includes all elements of the transformative approach but also requires students to make decisions and take action related to the concept, issue, or problem they have studied.
“W” Represents the Action Research Plan: What the Research Team is Seeking to Know
The grade three teacher on the project, Jamilla, wanted to examine the provincial language arts curriculum with an eye towards understanding patterns of how critical literacy is understood, mentioned and factored into the grade three Language Arts curriculum. She began by looking at specific and “global” expectations within sections of the Ontario Language Curriculum (1997). As the following example suggests, the language curriculum document consisted mainly of decontextualized skills. In fact, it was difficult to find language directly relevant to critical literacy practices. In particular, the section under reasoning and ‘critical’ thinking was problematic because, the skills were not only decontextualized, the term “critical” had been co-opted and misapplied (Edelsky and Cherland, 2006). The term “critical” no longer meant critical in many senses of the word. The following example from the grade three Language Arts curriculum, recently in use states:
Overall Expectations – Grade 3 Reading. By the end of Grade 3, students will:
read a variety of fiction and non-fiction materials (e.g., chapter books, children’s reference books) for different purposes;
read independently, using a variety of reading strategies;
express clear responses to written materials, relating the ideas in them to their own knowledge and experience and to ideas in other materials that they have read;
select material that they need from a variety of sources;
understand the vocabulary and language structures appropriate for this grade level;
Use conventions of written materials to help them understand and use the materials.
Patterns of critical approaches to curriculum range from the encouragement of students to engage in explicit criticism of cultural, economic, and political structures to more neutral approaches which affiliate literacy with individuals’ “thinking skills” and the weighting of information (Luke and Walton, 1994). It is these “thinking skills”, rather than the “explicit criticism of cultural, economic and political structures” that tend to be emphasized in curriculum guides. In the example below, critical thinking has been largely reduced to data organization.
Expectations in Specific Areas. By the end of Grade 3, students will:
• identify and restate the main idea in a piece of writing, and cite supporting details; • identify and describe some elements of stories (e.g., plot, central idea, characters, setting); • distinguish between fact and fiction; • begin to make inferences while reading; • use familiar vocabulary and the context to determine the meaning of a passage containing unfamiliar words; • begin to develop their own opinions by considering some ideas from various written materials;
• identify and describe different forms of writing (e.g., poems, stories, plays); • use their knowledge of the organization and characteristics of different forms of writing as a guide before and during reading (e.g., chapters in an adventure story often end with cliff-hangers; menus usually list the items of food on the left and the price of each item on the right); |
• use their knowledge of word order in oral and written language to determine the meaning of sentences;
• use a variety of strategies to determine the meaning of unfamiliar words (e.g., use the context, break the word into syllables or other recognizable units, use a dictionary, use phonics);
• use punctuation to help them understand what they read (e.g., exclamation mark, quotation marks); • Identify various conventions of formal texts and use them to find information (e.g., table of contents, chapter titles, headings, index, glossary, charts, graphs). |
Despite this approach to literacy education, as presented in the grade three Language Arts curriculum, in practical terms the research team struggled with how the literacy curriculum might be a useful guide for students, particularly when all shared the belief that the students were capable language learners and the team wanted to honor this in their teaching practices. Is the key to using curricular documents to first be cognizant of language patterns used to structure these documents? That is to say, must one become more literate in one’s own understanding of these documents? What research does the document rest on? What belief structures are inherent in the teaching practices espoused within this document? How is language learning understood? For example, is it anchored in development stage theory? Cultural studies theory? Ultimately, what are the purposes of literacy and who gets to define these purposes? And why? Moreover, team members in the study often commented on the tension between the need for teaching explicit skill instruction and critical literacy practices:
“What kinds of things do you do when you come to a word you don’t know?” and it took me about twenty minutes to get them to say something other than “sounding out”.... So I just have to look at the problem more deeply because they don’t look at it as the “big picture”. Decoding and comprehension go together.... But they think, “If I have a problem with reading, it’s because I don’t know what that word says. It’s about that word or these lists of words that I have to know.”... This is the piece that we need to help them understand - the whole and I’m having a problem with this part here by just letting them be aware of the things they need to do to get to the next level, instead of keeping it a secret that only the teacher knows (Jamilla).
It makes sense to wrap the strategies they need to know around it, such as decoding, and to understand their thinking processes. We’d have to have an open dialogue with them whether it be direct skill instruction or crit. lit. (Dianne).
In reading this text, some readers may imagine that this is all well and good but what about teaching reading and writing skills? Of course this is a valid concern, particularly given that so many students continue to fail in school despite the concerted efforts of educators. Rather than fuel the ‘either/or’ debate over whether the central purposes of literacy education should focus on strategic reading or reading to make sense of life, perhaps a literacy model that incorporates both sides of the debate is useful. Freebody and Luke (1990) add to this discussion through their conceptualization of literate practices as involving four roles—code-breaker, meaning-maker, text user and text analyst. Being a code breaker involves understanding the sound symbol relationship and the alphabetic principles. Being text participant or “meaning-maker” calls upon the reader to draw inferences, using background knowledge to fill out unexplicated aspects of the text. Being a text user means knowing how to use a variety of texts for a variety of purposes in real life situations—For example, reading instructions on a soup can versus writing a friendly letter versus reading instructions on how to put a piece of complex equipment together. Being a text analyst means applying critical discourse analysis and asking questions about absences in texts, how gendered cultural storylines work across texts, who texts are written for, who benefits from a particular storyline and how might it have been written differently.
To return to the previous teaching event involving Jamilla’s concern regarding the teaching of explicit skills and critical literacy practices, the role of meaning-maker and text analyst were the literacy practices that were deliberately invoked. Although the role of code breaker was used earlier in the day through such literacy practices as the morning message and making words, some students spontaneously modeled the role of text-user.
Bearing this in mind, reflections on the first of a series of fifteen-minute mini-lessons with the students were also based on the “K-W-L” strategy. This was accomplished by specifically tying critical literacy into the curriculum guidelines by accessing students’ prior knowledge of what their experiences of critical literacy were like. This lesson dealt with “Looking at the Big Picture” —referring back to Jamilla’s earlier comment that the students do not see the ‘big picture’, meaning that the students do not often discuss patterns of exclusion or marginalization or understand the social context of reading—through a large-group brainstorming session with the children. Examples of priming questions were, “Why do people need to learn to read”? and “Does everyone [around the world] have the same chance to learn to read”? Responses were recorded on a wall chart.
An additional critical literacy pedagogic activity was developed around “How to chose a book for reading.” Connections were made with students by discussing books about social issues. Again brainstorming was used to identify strategies for selecting an appropriate book for independent reading. These strategies were recorded on another chart. A third theme dealt with decoding strategies, discussed earlier, through the priming question of “What do you do when you come to a word you don’t know?” Strategies were recorded on an additional chart so that the students would begin to articulate more strategies than just “sounding out.” This follows up on similar work already happening in the classroom, allowing Jamilla to find the balance that she was seeking between engaging children in critical literacy and explicit literacy skills teaching.
A further fifteen-minute mini-lesson set the routines for “Sharing and Celebrating” by recording different thinking strategies. As we worked with students on an ongoing basis, their ideas were recorded on a chart called “Strategies for Sharing Our Thinking.” Miller (2002) calls this “Making Tracks of Our Thinking.” The priming critical question for this instance of meta-cognitive thinking was “What does thinking about reading look like, sound like and feel like?” It was revealing to see the students’ thinking as we learned together throughout the project.
Mohammed, for example, suggested that the “teacher reminds us that we can use anything in our life” in order to learn. He goes on to note that TV has helped him make connections to literature and he went on to talk about how Muslims are now patterned as “the bad guys” in the “big news” story because of 9/11. Mohammed takes this personally and makes connections to patterns in the world he knows (Delpit, 1995). As an immigrant, new to Canada and a Muslim, Mohammed’s comment reveals his own feeling of insecurity on a global level, but also shows how safe he feels in being able to reveal his feelings on the local level, within his classroom.
Mohammed’s grade three teacher acknowledges that many of her students watch a lot of television. However, she attempts to help them be more critical or discerning in their choices of programs to watch and how to critique systems of domination. In other words, Jamilla recognizes that television is the foremost source of information available to many children living in poverty, and otherwise, and is working towards the development of agency in her students.
One of the dilemmas encountered by both teachers and instructors, interested in the promotion of critical literacy in teacher education programs, revolves around how to keep the dialogue hopeful when one begins to question socially patterned constructions of “the truth”. This may necessitate a curriculum for learning that allows students to understand not only the message that is presented, but also to make connections and develop patterns with their own lives and lived experiences (Cooper and White, 2004).
The following spontaneous piece of writing is an example of a poem from Erina, a grade three student. Entitled “A Poem about Hope,” this poem is dedicated to her teachers.
Verse A Poem about Hope Don’t look in the stocking’s or under the tree. The thing that we’re looking for is something we can’t see. You can’t feel it or tuch it but it will tuch you it move’s with you grow’s with you. It will always follow you. It’s deeper then snow stronger then ice. The gift that we resev is the gift of hope. – Erina (8 years of age)
By the end of this “W” phase of the K-W-L strategy for reflective thinking, in conjunction with the research team, Jamilla, the grade three teacher, had identified what she wanted to learn. She wanted the research team to help clarify her understanding of the word “critical”, what critical literacy is like in practice and how to use the curriculum document to reflect her own teaching practice. Examining underlying assumptions of the literacy curriculum was not a bad place to begin. Constructing lessons that evoked questions about student understandings about the social context of literacy followed.
Inglis and Willinsky (2006) remind us of the importance of revisiting current thinking about democracy in order to consider what constitutes democracy in action. At the heart of our actions and in those teachable moments rests the need for continuous critical reflection. The “W” in our reflection strategy, then, is useful only in as much as it provides the pattern or the framework to continually ask those difficult questions so fundamental to critical literacy and a democratic education for all students. This takes humility and desire or, perhaps as Erina suggests, hope which is deeper than snow or ice.
“L” Represents Critical Literacy: What the Research Team Learned
The research recounted above suggests a need to continue to challenge patterns that promote taken-for-granted assumptions embedded in existing orthodoxies that comprise research and teaching practice. This may be accomplished through re-framing questions to examine not only what has been offered but also what has been missing. Delpit (1998) points out that the key may be to understand the variety of meanings available for any human interaction, and not to assume that the voice of majority speaks for all. In this study about critical literacy for urban school children, the research team began to notice where students’ voices were excluded from issues that affected them in particular. For example, Suzanne reminded us of the need to understand the politics of the ‘local’ literacy context, “Many of our students in this particular situation are ESL students”, and their voices may not be able to be heard. Cultural and political patterns run deep in literacy and teachers need to be aware of this if they are to be concerned with all students, including “minority” students, gaining a chance to define themselves.
Further, in this study, Jamilla, the grade three teacher on the project, was keen to examine how the provincial language arts curriculum could be used as a document to encourage the use of critical literacy strategies. Jamilla’s questioning helped the research team to understand that, while schools have been fairly successful at teaching essential literacies, such as code-breakers and text participants (Vasquez, 2000), schools and their policy makers may not adequately support the role of text analyst, a potential critical literacy strategy, which may help all students understand how the text positions them with respect to social patterns of power that include language usage. This occurs because the pattern of curricular language appropriates and neutralizes potentially critical literacy strategies. The research team learned that perhaps the key to using curricular documents is to recognize how language patterns are used to structure these documents. To become more literate in one’s own understanding of these documents may be to ask such questions as: How is language learning understood? What belief structures are inherent in the teaching practices espoused within this document? What research does the document rest on? Is the document anchored in a specific perspective of education theory? Ultimately, what are the purposes of literacy, of education, and who gets to define these purposes? And why?
Given that an important goal of critical literacy is to give voice to critical approaches to reshape literacy education in the interests of marginalized learners excluded from access to dominant economics and cultures (Luke 1997), it is understandably difficult to ensure that the role the text analyst and other critically literate roles are valued in the classroom. Perhaps, as Heffernan and Lewison (2000) suggest, teachers are frequently discouraged from using their positions of power to persuade students to adopt certain positions. As teachers struggle to keep their opinions to themselves, they may exclude important issues, in favour of the dominant curriculum. This reluctance was evident in the research team itself. If students do not gain from mandated curriculum or policies relating to the development of critical literacy, directly or over the long term, such curricular policies may not be useful educational policies. It is incumbent upon all educators to be able and willing to develop, identify and implement curricular policies that are inclusive, for the benefit of all students.
To this end, Banks (1999) describes four levels of a curriculum that is sensitive to issues of inclusion. The first level, “The Contributions Approach” is probably the most frequently utilized form of multicultural education, and is characterized by the addition of ethnic heroes. The curriculum remains essentially unchanged. Little attention is given to the ethnic groups either before or after the event, nor is the cultural significance or history of the event explored in any depth. Social issues are ignored and this approach represents a rather shallow look at culture and inclusive practices.
The second and third levels represent the first phase of curriculum restructuring, yet issues are presented from a dominant perspective. Individuals or groups of people from marginalized groups in society are included, yet racial and cultural inequities or oppression are not necessarily addressed. A teacher might introduce a unit by studying groups who are benefiting from or being disadvantaged by the implementation of certain policies and practices, in the absence of a complete transformation of the curriculum.
The fourth approach includes elements of the previous three approach but adds components that require students to make decisions and to take action related to the concept, issue, or problem they have studied. This approach requires that students not only explore and understand the dynamics of oppression, but also commit to making decisions and changing the system through social action. The major goal of this approach is to teach students thinking and decision making skills, to empower them, and help them acquire a sense of political awareness and efficacy.
Banks’ (1999) description of these four levels may be useful for teachers who wish to benefit their students by becoming more enlightened about established patterns in which their own self-understandings prevent them from being properly or appropriately aware of social and political mechanisms.
If a central aim of education can become the critical transmission, interpretation and development of the cultural traditions of our society, there is the need for a form of research that focuses its energies and resources on the policies, processes and practices by which this aim is pursued (Carr and Kemmis, 1989). While there is still a battle raging within the field of literacy over the central goals of literacy education (For a more complete discussion, see Short, 1999), struggling literacy students are at the heart of much of what we do as literacy educators and this struggle is manifested in the following questions: What conditions truly support literacy learning in the pluralistic milieu of the twenty-first century? How do literacy practices used in educational settings serve to affirm or disaffirm a student’s own sense of identity? Why consider identity and language teaching in the same breath?
Such questions serve to flag the notion that outside pressures, a globalized society notwithstanding, are being brought to bear on curricula and programs provided by Canadian schools, and potentially, in schools world-wide. At issue is the problem of “recognizing patterns” in order to develop a critical awareness to understand what is truly important in our schools and to develop standards around such critical ideas as what it is we are doing, why we are doing it and who the major benefactors of these transactions are. There is, therefore, a need for a critical literacy capable of recognizing such patterns, asking questions about innate standards such as curriculum documents, and asking about what is important to schooling. These voices, in order to be heard must respect the notion of a democratic education not just for some citizens but for all citizens. Hopeful trends are beginning to emerge. Changes, and dare we say improvements, are being made in individual classrooms and within schools as well.
Banks, J. (1999). An introduction to multicultural education . Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Bourdieu, P. (1977). Outline of a theory of practice . Translated by R. Nice. Cambridge; New York: Cambridge University Press.
Carr, W. & Kemmis, S. (1989). Becoming critical: Education, knowledge and action research . London & Philadelphia: The Falmer Press.
Chambers, I. (1996). The post-colonial question: Common skies, divided horizons. London : Routledge.
Comber, B., Thomson, P. & Wells, M. (2001). Critical literacy finds a place: Writing and social action in a low-income Australian grade two/three classroom . Elementary School Journal 101 (4), 451-464.
Cummins, J. (1995). Heritage language teaching in Canadian schools. In O. Garcia and C. Baker (Eds.), Policy and practice in bilingual education: Extending the foundation , (pp. 134-138). Clevedon, UK: Multilingual Matters.
Delpit, L. (1995). Other people’s children: Cultural conflict in the classroom. New York: New Press.
Delpit, L. (1998). The silenced dialogue: Power and pedagogy in education of other people’s children. Harvard Educational Review, 58 (3), 280-298.
Edelsky C. & Cherland, M. (2006). A critical issue in Critical Literacy: The “Popularity Effect.” In K. Cooper & R. E. White (Eds.), The practical critical educator. Dordrecht, NL: Springer.
Freebody, P. & Luke, A. (1990). “Literacies” programs: Debates and demands in cultural context. Prospect: the Journal of Adult Migrant Education Programs, 5 (30), 7-16.
Gee, J. P. (1996). Social linguistics and literacies. London, UK: Taylor and Francis.
Janks, H. (2000). Domination, access, diversity and design: A synthesis for critical literacy education. Educational Review, 52 (2), pp. 175-186.
Heath, S. B. (1983). Ways with words: Language, life and work in communities and classrooms . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Heffernan, A., & Lewison, M. (2000). Making real-world issues our business: Critical literacy in a third-grade classroom. Primary Voices, K-6, 9 (2), pp. 15-21.
Hunter, C. S. & Harmon, D. (1979). Adult illiteracy in the United States: A report to the Ford Foundation . New York: McGraw-Hill.
Luke, A. (1997). Critical approaches to literacy. In V. Edwards & D. Corson (Eds.) Encyclopedia of Language and Education, Vol. 2: Literacy (143-151). Dordrecht, NL: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Luke, A & Walton, C. (1994). Critical reading: Teaching and assessing. In T. Hansen & T. N. Postlewaite (Eds.) International encyclopaedia of education, 2nd Edition, (1194-1198) . Oxford, UK: Pergamon.
Miller, D. (2002). Reading with meaning: Teaching comprehension in the primary grades . Portland, ME: Stenhouse.
Mills, G. E. (2000). Action research: A guide for the teacher researcher. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Nieto, S. (1994). Affirmation, solidarity, and critique: Moving beyond tolerance in multicultural education. Multicultural Education, Spring 1994, pp 9-38.
Ontario Curriculum Grades 1-8, Language. (1997). Ontario: Ministry of Education and Training.
Short, K. (1999). The search for “balance” in a literature-rich curriculum. Theory into Practice 38 (3). 130-137.
Shutz, A. (2000). Teaching freedom? Postmodern perspectives. Review of Educational Research 70 (2), 215-251.
Southam Literacy, (1987). In P. Calamai. Broken words: Why five million Canadians are illiterate. Toronto, ON: Southam Press.
Thompkins, G. E. (1998). 50 Literacy strategies: Step by step. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
UNESCO (1951). A definition of fundamental education. Retrieved from http://portal.unesco.org/en/ev.php-URL_ID=13136&URL_DO=DO_TOPIC&URL_SECTION=201.html
Vasquez, V. (2000). Our way: Using the everyday to create a critical literacy curriculum. Primary Voice, K-6, 9 (2), pp 8-13.
The authors of this paper would like to acknowledge Dianne Riehl, Jamilla Arindell, Cindy Bird, Suzanne Thomson and the grade three students at “Sir Simon George” Elementary School for their assistance with this project. Pseudonyms were deemed unnecessary by the research team.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
White, R.E., Cooper, K. (2022). Action Research. In: Qualitative Research in the Post-Modern Era. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85124-8_10
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85124-8_10
Published : 29 September 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-85126-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-85124-8
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Original Language Spotlight
- Alternative and Non-formal Education
- Cognition, Emotion, and Learning
- Curriculum and Pedagogy
- Education and Society
- Education, Change, and Development
- Education, Cultures, and Ethnicities
- Education, Gender, and Sexualities
- Education, Health, and Social Services
- Educational Administration and Leadership
- Educational History
- Educational Politics and Policy
- Educational Purposes and Ideals
- Educational Systems
- Educational Theories and Philosophies
- Globalization, Economics, and Education
- Languages and Literacies
- Professional Learning and Development
- Research and Assessment Methods
- Technology and Education
- Share Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
Action research.
- Eileen S. Johnson Eileen S. Johnson Oakland University
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190264093.013.696
- Published online: 29 May 2020
Action research has become a common practice among educational administrators. The term “action research” was first coined by Kurt Lewin in the 1930s, although teachers and school administrators have long engaged in the process described by and formally named by Lewin. Alternatively known as practitioner research, self-study, action science, site-based inquiry, emancipatory praxis, etc., action research is essentially a collaborative, democratic, and participatory approach to systematic inquiry into a problem of practice within a local context. Action research has become prevalent in many fields and disciplines, including education, health sciences, nursing, social work, and anthropology. This prevalence can be understood in the way action research lends itself to action-based inquiry, participation, collaboration, and the development of solutions to problems of everyday practice in local contexts. In particular, action research has become commonplace in educational administration preparation programs due to its alignment and natural fit with the nature of education and the decision making and action planning necessary within local school contexts. Although there is not one prescribed way to engage in action research, and there are multiple approaches to action research, it generally follows a systematic and cyclical pattern of reflection, planning, action, observation, and data collection, evaluation that then repeats in an iterative and ongoing manner. The goal of action research is not to add to a general body of knowledge but, rather, to inform local practice, engage in professional learning, build a community practice, solve a problem or understand a process or phenomenon within a particular context, or empower participants to generate self-knowledge.
- action research cycle
- educational practice
- historical trends
- philosophical assumptions
- variations of action research
You do not currently have access to this article
Please login to access the full content.
Access to the full content requires a subscription
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Education. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 19 September 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [185.80.151.9]
- 185.80.151.9
Character limit 500 /500
How Teachers Can Learn Through Action Research
A look at one school’s action research project provides a blueprint for using this model of collaborative teacher learning.
Your content has been saved!

When teachers redesign learning experiences to make school more relevant to students’ lives, they can’t ignore assessment. For many teachers, the most vexing question about real-world learning experiences such as project-based learning is: How will we know what students know and can do by the end of this project?
Teachers at the Siena School in Silver Spring, Maryland, decided to figure out the assessment question by investigating their classroom practices. As a result of their action research, they now have a much deeper understanding of authentic assessment and a renewed appreciation for the power of learning together.
Their research process offers a replicable model for other schools interested in designing their own immersive professional learning. The process began with a real-world challenge and an open-ended question, involved a deep dive into research, and ended with a public showcase of findings.
Start With an Authentic Need to Know
Siena School serves about 130 students in grades 4–12 who have mild to moderate language-based learning differences, including dyslexia. Most students are one to three grade levels behind in reading.
Teachers have introduced a variety of instructional strategies, including project-based learning, to better meet students’ learning needs and also help them develop skills like collaboration and creativity. Instead of taking tests and quizzes, students demonstrate what they know in a PBL unit by making products or generating solutions.
“We were already teaching this way,” explained Simon Kanter, Siena’s director of technology. “We needed a way to measure, was authentic assessment actually effective? Does it provide meaningful feedback? Can teachers grade it fairly?”
Focus the Research Question
Across grade levels and departments, teachers considered what they wanted to learn about authentic assessment, which the late Grant Wiggins described as engaging, multisensory, feedback-oriented, and grounded in real-world tasks. That’s a contrast to traditional tests and quizzes, which tend to focus on recall rather than application and have little in common with how experts go about their work in disciplines like math or history.
The teachers generated a big research question: Is using authentic assessment an effective and engaging way to provide meaningful feedback for teachers and students about growth and proficiency in a variety of learning objectives, including 21st-century skills?
Take Time to Plan
Next, teachers planned authentic assessments that would generate data for their study. For example, middle school science students created prototypes of genetically modified seeds and pitched their designs to a panel of potential investors. They had to not only understand the science of germination but also apply their knowledge and defend their thinking.
In other classes, teachers planned everything from mock trials to environmental stewardship projects to assess student learning and skill development. A shared rubric helped the teachers plan high-quality assessments.
Make Sense of Data
During the data-gathering phase, students were surveyed after each project about the value of authentic assessments versus more traditional tools like tests and quizzes. Teachers also reflected after each assessment.
“We collated the data, looked for trends, and presented them back to the faculty,” Kanter said.
Among the takeaways:
- Authentic assessment generates more meaningful feedback and more opportunities for students to apply it.
- Students consider authentic assessment more engaging, with increased opportunities to be creative, make choices, and collaborate.
- Teachers are thinking more critically about creating assessments that allow for differentiation and that are applicable to students’ everyday lives.
To make their learning public, Siena hosted a colloquium on authentic assessment for other schools in the region. The school also submitted its research as part of an accreditation process with the Middle States Association.
Strategies to Share
For other schools interested in conducting action research, Kanter highlighted three key strategies.
- Focus on areas of growth, not deficiency: “This would have been less successful if we had said, ‘Our math scores are down. We need a new program to get scores up,’ Kanter said. “That puts the onus on teachers. Data collection could seem punitive. Instead, we focused on the way we already teach and thought about, how can we get more accurate feedback about how students are doing?”
- Foster a culture of inquiry: Encourage teachers to ask questions, conduct individual research, and share what they learn with colleagues. “Sometimes, one person attends a summer workshop and then shares the highlights in a short presentation. That might just be a conversation, or it might be the start of a school-wide initiative,” Kanter explained. In fact, that’s exactly how the focus on authentic assessment began.
- Build structures for teacher collaboration: Using staff meetings for shared planning and problem-solving fosters a collaborative culture. That was already in place when Siena embarked on its action research, along with informal brainstorming to support students.
For both students and staff, the deep dive into authentic assessment yielded “dramatic impact on the classroom,” Kanter added. “That’s the great part of this.”
In the past, he said, most teachers gave traditional final exams. To alleviate students’ test anxiety, teachers would support them with time for content review and strategies for study skills and test-taking.
“This year looks and feels different,” Kanter said. A week before the end of fall term, students were working hard on final products, but they weren’t cramming for exams. Teachers had time to give individual feedback to help students improve their work. “The whole climate feels way better.”

Understanding Action Research Margaret Riel Last Edit April, 2024
Action research is not a single approach but rather represents a tension between a number of forces that lead to personal, professional, and social change. I think of action research as a process of deep inquiry into one's practices in service of moving towards an envisioned future aligned with values. Action research can be seen as a systematic, reflective study of one's actions and the effects of these actions in a workplace or organizational context. As such, it involves a deep inquiry into one's professional practice. However, it is also a collaborative process as it is done WITH people in a social context, and understanding the change means probing multiple understandings of complex social systems. And finally, as research, it implies a commitment to data sharing.
There is a range of modifiers that people use for action research and many different dimensions that can be highlighted in different ways to create what some have called a family of approaches to action research (Noffke and Somekh, 2009; McNiff, 2013; Rowell, Polush, Riel and Bruewer, 2015; Rowell, Riel & Polush, 2017, Action Research Tutorial 2 ). We use collaborative action research to highlight the different ways in which action research is a social process.
Action researchers examine their interactions and relationships in social settings seeking opportunities for improvement. As designers and stakeholders, they work with their colleagues to propose new courses of action that help their community improve work practices. As researchers, they seek evidence from multiple sources to help them analyze reactions to the action taken. They recognize their own view as subjective and seek to develop their understanding of the events from multiple perspectives. The action researcher uses data collected from interactions with others to characterize the forces in ways that can be shared with other practitioners. This leads to a reflective phase in which the action researchers formulate new plans for action during the next cycle.
Action research provides a path of learning from and through one's practice by working through a series of reflective stages that facilitate the development of progressive problem-solving (Bereiter & Scardamalia, 1993). Over time, action researchers develop a deep understanding of the ways in which a variety of social and environmental forces interact to create complex patterns. Since these forces are dynamic, action research is a process of living one's theory into practice (McNiff & Whitehead, 2010) or taking a living and learning stance towards teaching (Clive Beck, 2017). This diagram illustrates the process of action research through time.
Figure 1: The iterative process of action research
The subject(s) of action research are the actions taken, the resulting change, and the transformation thinking, acting, and feeling by the persons enacting the change. While the design of action research may originate with an individual, the process of change is always social. Over time, the action researcher often extends the arena of change to a widening group of stakeholders. The goal is a deeper understanding of the factors of change that result in positive personal and professional change.
This form of research, then, is an iterative, cyclical process of reflecting on practice, taking an action, reflecting, and taking further action. Therefore, the research takes shape while it is being performed. Greater understanding from each cycle points to the way to improved practice (Riel and Rowell, 2016).
Action researchers differ in the weight that they put on different factors or dimensions of action research (for more discussion and examples, see Rowell, Riel and Polush, 2016). Each action researcher evolves his or her approach to doing action research as the conditions and support structures are unique. To understand how action research varies, I describe two points, A, and B, along six dimensions. When someone engages in action research, they (or others) make choices that place them at some point along the continuum for each dimension. Some will argue that side A, or B, or a perfect balance between them, is ideal, or even necessary, to call the process action research. Most will have very convincing arguments for why all action research should be done in the way they advocate. The dialogue is healthy and helps us each understand the value of the positions we take. By understanding the boundaries, we develop a deeper understanding of the process. (If you click on the continuum below, you can make your own choices and compare them with others. )
https://www.actionresearchtutorials.org/2-action-research-polls/
A. Practice - Emphasis on creating a transformative change in a social setting by taking purposeful action B. Inquiry - Emphasis on rigorous methodology and methods for validating assumptions about what changed
A. Theory from Practice - Using practices to generate theories beginning with values, needs, and human interaction B. Theory into Practice - Using social science findings to inform patterns of change
A. Inside Expertise- Action researchers are empowered to locate problems of practice and develop methods to improve them B. Outside Expertise - Action researchers form partnerships with outside experts to guide the process
A. Individual Process - Action researchers select their own questions to investigate B. Group Process - A group of action researchers select a common question or set of questions to investigate
A. Problem-Based Approach - Action Researchers locate problems and engage in progressive problem-solving in cycles B. Inquiry-Based Approach - Action Researchers explore effective practices to better understand and perfect them through multiple cycles
A. Identity Change - The primary outcome of action research is changing the way the action researcher thinks, acts, and feels B. Social Change -The primary outcomes of action research is the shift in the social context where people collectively change how they act, think and feel
A. Shared Practices - Action Researchers share what they have learned informally at their site B. Shared Knowledge- Action Researchers share their findings in more formal contexts
Authors and professors, as well as practitioners, often have very strong views about what are the essential (and nonessential) characteristics of action research. The movement to one or the other side of each continuum represents shifts in the action research approach.
I like to think of action research as a disposition of mind as well as a research approach. It is a commitment to cycles of collective inquiry with shared reflections on the outcomes leading to new ideas. Action research forms a path towards a professional "adaptive" expertise. Hatona and Ingaki (1986) set out a contrast between efficiency expertise and adaptive expertise. I have added innovative expertise and created this chart.
Figure 2: The path to expertise
The yellow path can also be applied to the activist who is singled minded without researching the outcomes and consequences of action, The blue panel might be the path of researchers who do not apply their theories to change contexts. The green combines inquiry and activism to engage in action research. When you balance these two different learning approaches, you follow the green path of action research, leading to adaptive expertise and the acquisition of a deeper understanding of yourself and others.
Goals of Action Research include:
The improvement of professional practice through continual learning and progressive problem-solving;
A deep understanding of practice and the development of a well-specified theory of action ;
An improvement in the community in which one's practice is embedded through participatory research.
Action research involves a systematic process of examining the evidence. The results of this type of research are practical, relevant, and can inform theory. Action research is different from other forms of research as there is less concern for the universality of findings, and more value is placed on the relevance of the findings to the researcher and the local collaborators. Critical reflection is at the heart of action research. When this reflection is based on careful examination of evidence from multiple perspectives, it can provide an effective strategy for improving the organization's ways of working and the whole organizational climate. It can be the process through which an organization learns.
We conceptualize action research as having three outcomes—
1) Professional Transformation
2) Organizational Theory of Change
3) Scholarly Identity through Sharing Research
Figure 3: Outcomes of Action Research (from Riel and Lepori, 2011)
1) Professional Transformation
At the personal level, it is a systematic set of methods for interpreting and evaluating one’s actions with the goal of improving practice. Action research is often located in schools and done by teachers, but it can also be carried out in museums, medical organizations, corporations, churches, and clubs—any setting where people are engaged in collective, goal-directed activity. Equally important, not all teacher research is action research. Teachers can do ethnographic, evaluative, or experimental research that is NOT action research. The process of doing action research involves progressive problem solving, balancing efficiency with innovation thereby developing what has been called an “adaptive” form of expertise.
2) Organizational Theory of Change
At the organizational level, action research is about understanding the system of interactions that define a social context. Kurt Lewin proposed action research as a method of understanding social systems or organizational learning. He claimed that the best way to test understanding was to try to effect change. Action research goes beyond self-study because actions, outcomes, goals, and assumptions are located in complex social systems. The action researcher begins with a theory of action focused on the intentional introduction of change into a social system with assumptions about the outcomes. This theory testing requires careful attention to data, and skill in interpretation and analysis. Activity theory, social network theory, system theories, and tools of evaluation such as surveys, interviews, and focus groups can help the action researcher acquire a deep understanding of change in social contexts within organizations.
Figure 4. Activity Theory Model based on the work of Engeström (2004)
It is often said that action research is done with, not on, people. This raises the question about the roles of the other people who are part of the research process ? In some cases, there will be a team of action researchers working together. They might be studying the same action or similar actions. For example, in one form of action research called lesson study, a teacher team collectively designs a change in the form of a lesson. All teachers study each teacher's implementation of the change--that is teach the lesson. Together evolve the lesson. In another example, community-based action research, there are teams of people who are implementing and studying the change, but they might all have slightly different roles. Some of them might be engaged in action research, and others might be doing something that might better be called active learning. I adapted this figure from Mattias Elg & Per-Erik Ellström ( 2012) to illustrate the overlapping cycles of participants and action researcher(s). While the action researcher(s) might take the lead in the analysis of the evidence of change, everyone is fully engaged in the process of moving from problem to action to reflection on outcomes to evolve a theory of change to guide future actions.
3) S cholarly Identity through Sharing Research
At the scholarly level, the action researcher produces validated findings and assumes a responsibility to share these findings with those in their setting and with the larger research community. Many people acquire expertise in their workplace, but researchers value the process of building knowledge through ongoing dialogue about the nature of their findings. Engaging in this dialogue through writing or presenting at conferences is part of the process of action research.
Action Research and Learning Circles
Figure 5: Learning Circle Model
Developing Action Research Questions: A Guide to Progressive Inquiry
The questions asked by action researchers guide their process. A good question will inspire one to look closely and collect evidence that will help find possible answers. What are good examples of action research questions? What are questions that are less likely to promote the process of deep sustained inquiry? The best question is the one that will inspire the researcher to look at their practice deeply and to engage in cycles of continuous learning from the everyday practice of their craft. These questions come from a desire to have practice align with values and beliefs. Exploring these questions helps the researcher to be progressively more effective in attaining their personal goals and developing professional expertise.
Good questions often arise from visions of improved practice and emerging theories about the change that will move the researcher closer to the ideal state of working practices. When stated in an if/then format, they can take the shape of a research hypothesis. If I [insert the action to be taken], how will it affect [describe one or more possible consequences of the action]? We will look at two examples, one from education and one from a business setting.
Development of Action Research Questions in an Educational Context
Suppose the researcher is worried about designing the learning context to meet the needs of students who are currently not doing well in the classroom. The general inquiry question might be:
How can I personalize instruction to match the diverse needs of my students?
This forms a good overall goal which can then lead to a number of possible cycles of action research, each with a separate question. A good cycle research question has two parts: the first part describes the action to be studied, and the second part focuses on the outcome that is anticipated.
Consider this question:
If I listen to students, will I have a better understanding of them?
This question suggests action and a possible outcome but is vague in both the description of the action and the possible outcome. It is not clear what is going to be done to increase attention to students and what evidence will help evaluate the action.
Now consider:
If I set up community circle time to listen to students, describe their learning experiences in my classroom (description of the action), in what ways, if any, will the information about their learning processes lead to changes in my teaching practices (description of the outcome that will be studied)?
Now it is clear what the researcher intends to do and what a possible outcome might be. In listening to students, the researcher might discover information that will lead directly to an experiment in instructional design or might refocus the overall goal to one that was not apparent when the researcher began the inquiry.
Development of Action Research Questions in a Corporate Context
The following is another example from a business setting where people in diverse offices are working in ways that would benefit from greater coordination.
The action researcher might identify the problem as one in which poor communication results in decisions being made without attending to the issue of how a decision affects the larger system. The researcher might see a role for technology in forging a solution to this problem, such as creating a database for storing and sharing documents. The overall research question might be:
How can the development of a common location for shared knowledge and the use of interactive communication tools increase the collaborative effectiveness of team-based decision-making in our different regions?
The next step is to define the communication tool to be used and how the researcher plans to measure the collaborative effectiveness of the distant teams.
Cycle questions that might evolve should be specific with respect to the actions taken and the outcomes that will be monitored:
If I create a wiki to share documents and increase coordination, to what extent will the teams use this means of storing information to coordinate their decision-making?
A second cycle question that might follow when it is clear that other teams failed to use the wiki as effectively as the researcher had hoped:
How will making all-day support available on instant messenger for questions about the use of the wiki affect the use of the wiki to organize group work?
Recognizing Weak Action Research Questions
Questions with known answers where the goal is to "prove" it to others . For example, suppose a person has been holding family math night for years and sees an effect on parent participation. A weak question for action research would be: Will holding a family math night increase parent participation? This might be a useful evaluative research question where a controlled study could be set up to explore the connection. However, evaluative research is different from action research. Action research is an experiment in design and involves implementing an action to study its consequences.
Questions that can be answered yes or no. Generally, these are questions that will not encourage paying attention to the many nuances of the setting and social interactions. Although, like any guide, while some yes/no questions can provide direction, thinking about ways to transform the question into a different format is often helpful. For example, Will the introduction of project-based learning lead to more student engagement? The question might be reworked to, How will the introduction of project-based learning affect student engagement in my classroom? The first one, the researcher can answer the question with yes (an outcome that they might have expected). The second question guides them to look for the possible mechanism of project-based learning (maybe ownership, collaboration, or self-assessment) that has been found to be related to increased engagement.
Questions that can be answered by reading the literature. What does "a community of practice" mean? This might be a question that the researcher needs to answer, and can do so by reading more readily than by engaging in action research. A better formulation for action research might be: How will increasing the time for teacher collaboration in grade-level teams affect the development of a community of practice at our school?
Sharing your Action Research with Others:
One of the strongest acts of leadership can be writing—sharing knowledge and insights gained. Writing enables a contribution to the body of knowledge beyond the researcher. The final report serves the purpose of sharing the knowledge gained through action research with others in a community of practice. Action researchers will need to decide what to write and to whom to write.
A Written Report
The following is the recommended template for the Master of Arts in Learning Technologies thesis for Pepperdine students. However, an action research report may be organized in multiple ways.
INTRODUCTION:
The significance of the problem you are addressing. The reader needs to be invited to think about the problem at the widest level. This should answer the question—Why should I read this; why should I care about this study? This is not about the context but about the problem and how it is linked to your vision for a different future.
THE CONTEXT:
WORK/COMMUNITY CONTEXT (Action context)— Once you have posed a problem at a general level, you will need to provide the context of your work. There are two parts to this. One is the local context (this section,) and the other is the professional context (literature review). These can come in whatever order makes sense to you. In your local context, you may want to describe your membership/position in your community of practice, as well as how you have previously tried to address the problem described.
LITERATURE REVIEW (research context )— The literature is another way to set the context for your work. What previous work informs your understanding of the problem? What theories or predictions about outcomes come from past studies? How is what you plan to do similar or different from what others have tried?
THE RESEARCH:
RESEARCH QUESTION— The research question sets up your inquiry. The overall question is the overarching problem selected. The cycle questions are sub-questions that helped address this larger issue in different ways.
REPORT OF CYCLES OF RESEARCH— Action research takes place in cycles. Each cycle is a discrete experiment, taking action to study change. Your report needs to include a detailed report for each cycle as follows or a report of the cycles in a more summary format.
DESCRIPTION OF CYCLE ACTION: Description of what was planned and why this is an effective change. Might include some guesses about what will happen.
CYCLE RESEARCH QUESTION: A strong question describes the action and expected reactions. The first part of the question clearly states what you will do in very specific language. The second part shares your best guess at an outcome. (The reactions of others that you expect to result from your action.) Your action research is a design experiment. You are designing with an eye toward a deeper understanding of change.
DESCRIPTION OF WHAT HAPPENED: Brief description of what took place. EVIDENCE USED TO EVALUATE THE ACTION: What evidence did you collect to tell you how others respond to your action? Where did you look for direct or indirect evidence of what happened? EVALUATION: How will you/did you evaluate the outcomes of your action?..... (Indicate your plans for your analysis in a paragraph or two). REFLECTION: Looking back on your action after collecting data, what thoughts come to mind? If you were to repeat the process, what would you change? What worked best for you? What most surprised you?
FINAL REFLECTION:
This is where you will take stock of your overall learning process during your action research. It might be helpful to think of a reflection as a set of connections between the past, present, and future. If this section is only a summary of events that happened, it is inadequate as a reflection. A reflection provides a deep understanding of why events occurred as they did, and how those outcomes helped you address your overarching question. At the conclusion of a good reflection, you should ideally know more than you did when you began. If you have not gained new insights about the problem and your problem-solving action, it is likely that you are only summarizing. Reflection is a powerful learning experience and an essential part of action research.
REFERENCES:
The references provide the context for your ideas. In many ways, the references indicate the community of researchers and writers that you are writing for. (See the CCAR Tutorials for detailed suggestions for each of these phases of action research.)
Publishing a Web Portfolio:
An important part of the action research process is sharing artifacts of the inquiry to enable the action researcher to continually reflect on practice so that peers may contribute to feedback and support. The Web Portfolio, then, becomes a place for both internal and external reflection.
A good action research portfolio, like a report, documents practices at each step of the inquiry. The accumulation of content provides critical mass for reflection and for recognizing the change of practice. There is no perfect template for an action research portfolio. One key idea, however, is to document each cycle and gather artifacts accordingly. That documentation process should utilize both descriptive and reflective writing.
The Center for Collaborative Action Research has collected action research portfolios that serve as effective models. The model portfolios are categorized into five groups:
Classroom Action Research
Youth Action Research
Professional Development Action Research
Community Participatory Action Research
Organizational Action Research
In general, your web portfolio might include, but is not limited to, the following:
An overview of your problem at a general level and why you (and others) see this as an important challenge and some hints about what you did to solve it- this opening page should be engaging with photos, graphics, and possibly a video or audio intro from you
A description of the problem that you are researching with an action to be taken
A detailed description of the field of action (the action context)
A review of literature as part of a planning process (the research context)
The action research question(s)
The action research process is described briefly
Cycle Reports that document the activity across multiple efforts of change including
data collected
details of the analysis process
cycle reflections
Your final reflection considers what was learned across all of the cycles about yourself, your actions, your context, and the process.
References
Collection of any artifacts, images, and videos, or research blogs that you wish to include
Professional bio
This overview was designed to provide a quick answer to the question What is action research? Perhaps a more important question to ask is Why do action research? There are lots of answers to this question that focus on the development of expertise, issues of social justice, and mobilization of native knowledge. I think that at the fundamental level, I would say that as humans, we are problem solvers. That is what gives us joy. Learning through ongoing problem-solving makes work a source of collaborative discovery. This inquiry and discovery can result in a very productive and successful career path, but in the end, it is its own reward.
Beck, C., (2017) Informal action research: The nature and contributions of everyday classroom inquiry. In L. Rowell, C. Bruce, J. Shosh & M. Riel, (Eds). Palgrave Interactional Handbook of Action Research. Palgrave,ISBN 978-1-137-40523-4 (ebook) p37-48.
Bereiter, C., & Scardamalia, M. (1993). Surpassing ourselves: An inquiry into the nature and implications of expertise. Chicago and La Salle, IL: Open Court.
Engeström, Y. (2004). "New forms of learning in co-configuration work", Journal of Workplace Learning, Vol. 16 Iss: 1/2, pp.11 - 21
Hatano, G., & Inagaki, K. (1986). Two courses of expertise. In H. Stevenson, H. Azuma, & K. Hakuta (Eds.), Child development and education in Japan (pp. 262-272). New York: Freeman.
McNiff, J. (2013). Action Research: Principals and Practice (Third Edition). New York: Routledge.
McNiff, J., & Whitehead, J. (2010) You and your action research project. (3rd Edition). Abingdon: Routledge.
Riel, M. & Lepori, K. (2011). A Meta-Analysis of the Outcomes of Action Research. Paper presented at the American Educational Research Association conference, April 2011, New Orleans.
Riel, M. & Rowell, L. (2017). Action research and the development of expertise: Rethinking teacher education. In L. Rowell, C. Bruce, J. Shosh & M. Riel, (Eds). Palgrave Interactional Handbook of Action Research. Palgrave, ISBN 978-1-137-40523-4 (ebook) 667-687.
Rowell, L. Polush, E. Riel, M, & Bruewer, A. (2015) Action researchers’ perspectives about the distinguishing characteristics of action research: a Delphi and learning circles mixed-methods study. Access online at http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/09650792.2014.990987#.VPlW0IH-Oxw
Rowell, L., Riel, M., Polush, E. (2017). Defining action research: Situating diverse practices within varying frames of inquiry, science, and action. In L. Rowell, C. Bruce, J. Shosh & M. Riel, (Eds). Palgrave Interactional Handbook of Action Research. Palgrave: ISBN 978-1-137-40523-4 (ebook), 85-102.
Visit the CCAR Tutorials for more information and activities on how to be an action researcher. They are provided free of charge and can be used in courses or by individuals learning on their own. There is also a Facebook group for any questions while doing the tutorial activities.
Center for Collaborative Action Research | © Created 2006 Edited 2024

Action research is conducted in the workplace with others. It is a collaborative process. But, also, the doing of action research is more effective when action researchers can benefit from the help of a community of action researchers. The Center for Collaborative Action Research is part of a process of developing the community of action researchers for each cadre. In our program, action researchers carry out their work in learning circles —a structure for organizing group interaction. Combining this collaborative structure with the action research process is an effective way to provide high levels of support for action researchers as they design their action and engage in the process of studying the outcomes.


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
1 What is Action Research for Classroom Teachers?
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS
- What is the nature of action research?
- How does action research develop in the classroom?
- What models of action research work best for your classroom?
- What are the epistemological, ontological, theoretical underpinnings of action research?
Educational research provides a vast landscape of knowledge on topics related to teaching and learning, curriculum and assessment, students’ cognitive and affective needs, cultural and socio-economic factors of schools, and many other factors considered viable to improving schools. Educational stakeholders rely on research to make informed decisions that ultimately affect the quality of schooling for their students. Accordingly, the purpose of educational research is to engage in disciplined inquiry to generate knowledge on topics significant to the students, teachers, administrators, schools, and other educational stakeholders. Just as the topics of educational research vary, so do the approaches to conducting educational research in the classroom. Your approach to research will be shaped by your context, your professional identity, and paradigm (set of beliefs and assumptions that guide your inquiry). These will all be key factors in how you generate knowledge related to your work as an educator.
Action research is an approach to educational research that is commonly used by educational practitioners and professionals to examine, and ultimately improve, their pedagogy and practice. In this way, action research represents an extension of the reflection and critical self-reflection that an educator employs on a daily basis in their classroom. When students are actively engaged in learning, the classroom can be dynamic and uncertain, demanding the constant attention of the educator. Considering these demands, educators are often only able to engage in reflection that is fleeting, and for the purpose of accommodation, modification, or formative assessment. Action research offers one path to more deliberate, substantial, and critical reflection that can be documented and analyzed to improve an educator’s practice.
Purpose of Action Research
As one of many approaches to educational research, it is important to distinguish the potential purposes of action research in the classroom. This book focuses on action research as a method to enable and support educators in pursuing effective pedagogical practices by transforming the quality of teaching decisions and actions, to subsequently enhance student engagement and learning. Being mindful of this purpose, the following aspects of action research are important to consider as you contemplate and engage with action research methodology in your classroom:
- Action research is a process for improving educational practice. Its methods involve action, evaluation, and reflection. It is a process to gather evidence to implement change in practices.
- Action research is participative and collaborative. It is undertaken by individuals with a common purpose.
- Action research is situation and context-based.
- Action research develops reflection practices based on the interpretations made by participants.
- Knowledge is created through action and application.
- Action research can be based in problem-solving, if the solution to the problem results in the improvement of practice.
- Action research is iterative; plans are created, implemented, revised, then implemented, lending itself to an ongoing process of reflection and revision.
- In action research, findings emerge as action develops and takes place; however, they are not conclusive or absolute, but ongoing (Koshy, 2010, pgs. 1-2).
In thinking about the purpose of action research, it is helpful to situate action research as a distinct paradigm of educational research. I like to think about action research as part of the larger concept of living knowledge. Living knowledge has been characterized as “a quest for life, to understand life and to create… knowledge which is valid for the people with whom I work and for myself” (Swantz, in Reason & Bradbury, 2001, pg. 1). Why should educators care about living knowledge as part of educational research? As mentioned above, action research is meant “to produce practical knowledge that is useful to people in the everyday conduct of their lives and to see that action research is about working towards practical outcomes” (Koshy, 2010, pg. 2). However, it is also about:
creating new forms of understanding, since action without reflection and understanding is blind, just as theory without action is meaningless. The participatory nature of action research makes it only possible with, for and by persons and communities, ideally involving all stakeholders both in the questioning and sense making that informs the research, and in the action, which is its focus. (Reason & Bradbury, 2001, pg. 2)
In an effort to further situate action research as living knowledge, Jean McNiff reminds us that “there is no such ‘thing’ as ‘action research’” (2013, pg. 24). In other words, action research is not static or finished, it defines itself as it proceeds. McNiff’s reminder characterizes action research as action-oriented, and a process that individuals go through to make their learning public to explain how it informs their practice. Action research does not derive its meaning from an abstract idea, or a self-contained discovery – action research’s meaning stems from the way educators negotiate the problems and successes of living and working in the classroom, school, and community.
While we can debate the idea of action research, there are people who are action researchers, and they use the idea of action research to develop principles and theories to guide their practice. Action research, then, refers to an organization of principles that guide action researchers as they act on shared beliefs, commitments, and expectations in their inquiry.
Reflection and the Process of Action Research
When an individual engages in reflection on their actions or experiences, it is typically for the purpose of better understanding those experiences, or the consequences of those actions to improve related action and experiences in the future. Reflection in this way develops knowledge around these actions and experiences to help us better regulate those actions in the future. The reflective process generates new knowledge regularly for classroom teachers and informs their classroom actions.
Unfortunately, the knowledge generated by educators through the reflective process is not always prioritized among the other sources of knowledge educators are expected to utilize in the classroom. Educators are expected to draw upon formal types of knowledge, such as textbooks, content standards, teaching standards, district curriculum and behavioral programs, etc., to gain new knowledge and make decisions in the classroom. While these forms of knowledge are important, the reflective knowledge that educators generate through their pedagogy is the amalgamation of these types of knowledge enacted in the classroom. Therefore, reflective knowledge is uniquely developed based on the action and implementation of an educator’s pedagogy in the classroom. Action research offers a way to formalize the knowledge generated by educators so that it can be utilized and disseminated throughout the teaching profession.
Research is concerned with the generation of knowledge, and typically creating knowledge related to a concept, idea, phenomenon, or topic. Action research generates knowledge around inquiry in practical educational contexts. Action research allows educators to learn through their actions with the purpose of developing personally or professionally. Due to its participatory nature, the process of action research is also distinct in educational research. There are many models for how the action research process takes shape. I will share a few of those here. Each model utilizes the following processes to some extent:
- Plan a change;
- Take action to enact the change;
- Observe the process and consequences of the change;
- Reflect on the process and consequences;
- Act, observe, & reflect again and so on.
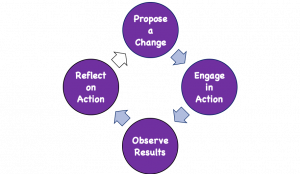
Figure 1.1 Basic action research cycle
There are many other models that supplement the basic process of action research with other aspects of the research process to consider. For example, figure 1.2 illustrates a spiral model of action research proposed by Kemmis and McTaggart (2004). The spiral model emphasizes the cyclical process that moves beyond the initial plan for change. The spiral model also emphasizes revisiting the initial plan and revising based on the initial cycle of research:
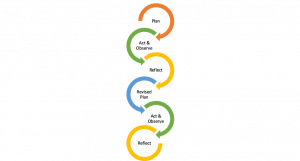
Figure 1.2 Interpretation of action research spiral, Kemmis and McTaggart (2004, p. 595)
Other models of action research reorganize the process to emphasize the distinct ways knowledge takes shape in the reflection process. O’Leary’s (2004, p. 141) model, for example, recognizes that the research may take shape in the classroom as knowledge emerges from the teacher’s observations. O’Leary highlights the need for action research to be focused on situational understanding and implementation of action, initiated organically from real-time issues:
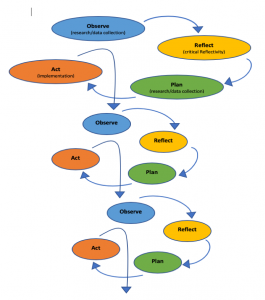
Figure 1.3 Interpretation of O’Leary’s cycles of research, O’Leary (2000, p. 141)
Lastly, Macintyre’s (2000, p. 1) model, offers a different characterization of the action research process. Macintyre emphasizes a messier process of research with the initial reflections and conclusions as the benchmarks for guiding the research process. Macintyre emphasizes the flexibility in planning, acting, and observing stages to allow the process to be naturalistic. Our interpretation of Macintyre process is below:
Figure 1.4 Interpretation of the action research cycle, Macintyre (2000, p. 1)
We believe it is important to prioritize the flexibility of the process, and encourage you to only use these models as basic guides for your process. Your process may look similar, or you may diverge from these models as you better understand your students, context, and data.
Definitions of Action Research and Examples
At this point, it may be helpful for readers to have a working definition of action research and some examples to illustrate the methodology in the classroom. Bassey (1998, p. 93) offers a very practical definition and describes “action research as an inquiry which is carried out in order to understand, to evaluate and then to change, in order to improve educational practice.” Cohen and Manion (1994, p. 192) situate action research differently, and describe action research as emergent, writing:
essentially an on-the-spot procedure designed to deal with a concrete problem located in an immediate situation. This means that ideally, the step-by-step process is constantly monitored over varying periods of time and by a variety of mechanisms (questionnaires, diaries, interviews and case studies, for example) so that the ensuing feedback may be translated into modifications, adjustment, directional changes, redefinitions, as necessary, so as to bring about lasting benefit to the ongoing process itself rather than to some future occasion.
Lastly, Koshy (2010, p. 9) describes action research as:
a constructive inquiry, during which the researcher constructs his or her knowledge of specific issues through planning, acting, evaluating, refining and learning from the experience. It is a continuous learning process in which the researcher learns and also shares the newly generated knowledge with those who may benefit from it.
These definitions highlight the distinct features of action research and emphasize the purposeful intent of action researchers to improve, refine, reform, and problem-solve issues in their educational context. To better understand the distinctness of action research, these are some examples of action research topics:
Examples of Action Research Topics
- Flexible seating in 4th grade classroom to increase effective collaborative learning.
- Structured homework protocols for increasing student achievement.
- Developing a system of formative feedback for 8th grade writing.
- Using music to stimulate creative writing.
- Weekly brown bag lunch sessions to improve responses to PD from staff.
- Using exercise balls as chairs for better classroom management.
Action Research in Theory
Action research-based inquiry in educational contexts and classrooms involves distinct participants – students, teachers, and other educational stakeholders within the system. All of these participants are engaged in activities to benefit the students, and subsequently society as a whole. Action research contributes to these activities and potentially enhances the participants’ roles in the education system. Participants’ roles are enhanced based on two underlying principles:
- communities, schools, and classrooms are sites of socially mediated actions, and action research provides a greater understanding of self and new knowledge of how to negotiate these socially mediated environments;
- communities, schools, and classrooms are part of social systems in which humans interact with many cultural tools, and action research provides a basis to construct and analyze these interactions.
In our quest for knowledge and understanding, we have consistently analyzed human experience over time and have distinguished between types of reality. Humans have constantly sought “facts” and “truth” about reality that can be empirically demonstrated or observed.
Social systems are based on beliefs, and generally, beliefs about what will benefit the greatest amount of people in that society. Beliefs, and more specifically the rationale or support for beliefs, are not always easy to demonstrate or observe as part of our reality. Take the example of an English Language Arts teacher who prioritizes argumentative writing in her class. She believes that argumentative writing demonstrates the mechanics of writing best among types of writing, while also providing students a skill they will need as citizens and professionals. While we can observe the students writing, and we can assess their ability to develop a written argument, it is difficult to observe the students’ understanding of argumentative writing and its purpose in their future. This relates to the teacher’s beliefs about argumentative writing; we cannot observe the real value of the teaching of argumentative writing. The teacher’s rationale and beliefs about teaching argumentative writing are bound to the social system and the skills their students will need to be active parts of that system. Therefore, our goal through action research is to demonstrate the best ways to teach argumentative writing to help all participants understand its value as part of a social system.
The knowledge that is conveyed in a classroom is bound to, and justified by, a social system. A postmodernist approach to understanding our world seeks knowledge within a social system, which is directly opposed to the empirical or positivist approach which demands evidence based on logic or science as rationale for beliefs. Action research does not rely on a positivist viewpoint to develop evidence and conclusions as part of the research process. Action research offers a postmodernist stance to epistemology (theory of knowledge) and supports developing questions and new inquiries during the research process. In this way action research is an emergent process that allows beliefs and decisions to be negotiated as reality and meaning are being constructed in the socially mediated space of the classroom.
Theorizing Action Research for the Classroom
All research, at its core, is for the purpose of generating new knowledge and contributing to the knowledge base of educational research. Action researchers in the classroom want to explore methods of improving their pedagogy and practice. The starting place of their inquiry stems from their pedagogy and practice, so by nature the knowledge created from their inquiry is often contextually specific to their classroom, school, or community. Therefore, we should examine the theoretical underpinnings of action research for the classroom. It is important to connect action research conceptually to experience; for example, Levin and Greenwood (2001, p. 105) make these connections:
- Action research is context bound and addresses real life problems.
- Action research is inquiry where participants and researchers cogenerate knowledge through collaborative communicative processes in which all participants’ contributions are taken seriously.
- The meanings constructed in the inquiry process lead to social action or these reflections and action lead to the construction of new meanings.
- The credibility/validity of action research knowledge is measured according to whether the actions that arise from it solve problems (workability) and increase participants’ control over their own situation.
Educators who engage in action research will generate new knowledge and beliefs based on their experiences in the classroom. Let us emphasize that these are all important to you and your work, as both an educator and researcher. It is these experiences, beliefs, and theories that are often discounted when more official forms of knowledge (e.g., textbooks, curriculum standards, districts standards) are prioritized. These beliefs and theories based on experiences should be valued and explored further, and this is one of the primary purposes of action research in the classroom. These beliefs and theories should be valued because they were meaningful aspects of knowledge constructed from teachers’ experiences. Developing meaning and knowledge in this way forms the basis of constructivist ideology, just as teachers often try to get their students to construct their own meanings and understandings when experiencing new ideas.
Classroom Teachers Constructing their Own Knowledge
Most of you are probably at least minimally familiar with constructivism, or the process of constructing knowledge. However, what is constructivism precisely, for the purposes of action research? Many scholars have theorized constructivism and have identified two key attributes (Koshy, 2010; von Glasersfeld, 1987):
- Knowledge is not passively received, but actively developed through an individual’s cognition;
- Human cognition is adaptive and finds purpose in organizing the new experiences of the world, instead of settling for absolute or objective truth.
Considering these two attributes, constructivism is distinct from conventional knowledge formation because people can develop a theory of knowledge that orders and organizes the world based on their experiences, instead of an objective or neutral reality. When individuals construct knowledge, there are interactions between an individual and their environment where communication, negotiation and meaning-making are collectively developing knowledge. For most educators, constructivism may be a natural inclination of their pedagogy. Action researchers have a similar relationship to constructivism because they are actively engaged in a process of constructing knowledge. However, their constructions may be more formal and based on the data they collect in the research process. Action researchers also are engaged in the meaning making process, making interpretations from their data. These aspects of the action research process situate them in the constructivist ideology. Just like constructivist educators, action researchers’ constructions of knowledge will be affected by their individual and professional ideas and values, as well as the ecological context in which they work (Biesta & Tedder, 2006). The relations between constructivist inquiry and action research is important, as Lincoln (2001, p. 130) states:
much of the epistemological, ontological, and axiological belief systems are the same or similar, and methodologically, constructivists and action researchers work in similar ways, relying on qualitative methods in face-to-face work, while buttressing information, data and background with quantitative method work when necessary or useful.
While there are many links between action research and educators in the classroom, constructivism offers the most familiar and practical threads to bind the beliefs of educators and action researchers.
Epistemology, Ontology, and Action Research
It is also important for educators to consider the philosophical stances related to action research to better situate it with their beliefs and reality. When researchers make decisions about the methodology they intend to use, they will consider their ontological and epistemological stances. It is vital that researchers clearly distinguish their philosophical stances and understand the implications of their stance in the research process, especially when collecting and analyzing their data. In what follows, we will discuss ontological and epistemological stances in relation to action research methodology.
Ontology, or the theory of being, is concerned with the claims or assumptions we make about ourselves within our social reality – what do we think exists, what does it look like, what entities are involved and how do these entities interact with each other (Blaikie, 2007). In relation to the discussion of constructivism, generally action researchers would consider their educational reality as socially constructed. Social construction of reality happens when individuals interact in a social system. Meaningful construction of concepts and representations of reality develop through an individual’s interpretations of others’ actions. These interpretations become agreed upon by members of a social system and become part of social fabric, reproduced as knowledge and beliefs to develop assumptions about reality. Researchers develop meaningful constructions based on their experiences and through communication. Educators as action researchers will be examining the socially constructed reality of schools. In the United States, many of our concepts, knowledge, and beliefs about schooling have been socially constructed over the last hundred years. For example, a group of teachers may look at why fewer female students enroll in upper-level science courses at their school. This question deals directly with the social construction of gender and specifically what careers females have been conditioned to pursue. We know this is a social construction in some school social systems because in other parts of the world, or even the United States, there are schools that have more females enrolled in upper level science courses than male students. Therefore, the educators conducting the research have to recognize the socially constructed reality of their school and consider this reality throughout the research process. Action researchers will use methods of data collection that support their ontological stance and clarify their theoretical stance throughout the research process.
Koshy (2010, p. 23-24) offers another example of addressing the ontological challenges in the classroom:
A teacher who was concerned with increasing her pupils’ motivation and enthusiasm for learning decided to introduce learning diaries which the children could take home. They were invited to record their reactions to the day’s lessons and what they had learnt. The teacher reported in her field diary that the learning diaries stimulated the children’s interest in her lessons, increased their capacity to learn, and generally improved their level of participation in lessons. The challenge for the teacher here is in the analysis and interpretation of the multiplicity of factors accompanying the use of diaries. The diaries were taken home so the entries may have been influenced by discussions with parents. Another possibility is that children felt the need to please their teacher. Another possible influence was that their increased motivation was as a result of the difference in style of teaching which included more discussions in the classroom based on the entries in the dairies.
Here you can see the challenge for the action researcher is working in a social context with multiple factors, values, and experiences that were outside of the teacher’s control. The teacher was only responsible for introducing the diaries as a new style of learning. The students’ engagement and interactions with this new style of learning were all based upon their socially constructed notions of learning inside and outside of the classroom. A researcher with a positivist ontological stance would not consider these factors, and instead might simply conclude that the dairies increased motivation and interest in the topic, as a result of introducing the diaries as a learning strategy.
Epistemology, or the theory of knowledge, signifies a philosophical view of what counts as knowledge – it justifies what is possible to be known and what criteria distinguishes knowledge from beliefs (Blaikie, 1993). Positivist researchers, for example, consider knowledge to be certain and discovered through scientific processes. Action researchers collect data that is more subjective and examine personal experience, insights, and beliefs.
Action researchers utilize interpretation as a means for knowledge creation. Action researchers have many epistemologies to choose from as means of situating the types of knowledge they will generate by interpreting the data from their research. For example, Koro-Ljungberg et al., (2009) identified several common epistemologies in their article that examined epistemological awareness in qualitative educational research, such as: objectivism, subjectivism, constructionism, contextualism, social epistemology, feminist epistemology, idealism, naturalized epistemology, externalism, relativism, skepticism, and pluralism. All of these epistemological stances have implications for the research process, especially data collection and analysis. Please see the table on pages 689-90, linked below for a sketch of these potential implications:
Again, Koshy (2010, p. 24) provides an excellent example to illustrate the epistemological challenges within action research:
A teacher of 11-year-old children decided to carry out an action research project which involved a change in style in teaching mathematics. Instead of giving children mathematical tasks displaying the subject as abstract principles, she made links with other subjects which she believed would encourage children to see mathematics as a discipline that could improve their understanding of the environment and historic events. At the conclusion of the project, the teacher reported that applicable mathematics generated greater enthusiasm and understanding of the subject.
The educator/researcher engaged in action research-based inquiry to improve an aspect of her pedagogy. She generated knowledge that indicated she had improved her students’ understanding of mathematics by integrating it with other subjects – specifically in the social and ecological context of her classroom, school, and community. She valued constructivism and students generating their own understanding of mathematics based on related topics in other subjects. Action researchers working in a social context do not generate certain knowledge, but knowledge that emerges and can be observed and researched again, building upon their knowledge each time.
Researcher Positionality in Action Research
In this first chapter, we have discussed a lot about the role of experiences in sparking the research process in the classroom. Your experiences as an educator will shape how you approach action research in your classroom. Your experiences as a person in general will also shape how you create knowledge from your research process. In particular, your experiences will shape how you make meaning from your findings. It is important to be clear about your experiences when developing your methodology too. This is referred to as researcher positionality. Maher and Tetreault (1993, p. 118) define positionality as:
Gender, race, class, and other aspects of our identities are markers of relational positions rather than essential qualities. Knowledge is valid when it includes an acknowledgment of the knower’s specific position in any context, because changing contextual and relational factors are crucial for defining identities and our knowledge in any given situation.
By presenting your positionality in the research process, you are signifying the type of socially constructed, and other types of, knowledge you will be using to make sense of the data. As Maher and Tetreault explain, this increases the trustworthiness of your conclusions about the data. This would not be possible with a positivist ontology. We will discuss positionality more in chapter 6, but we wanted to connect it to the overall theoretical underpinnings of action research.
Advantages of Engaging in Action Research in the Classroom
In the following chapters, we will discuss how action research takes shape in your classroom, and we wanted to briefly summarize the key advantages to action research methodology over other types of research methodology. As Koshy (2010, p. 25) notes, action research provides useful methodology for school and classroom research because:
Advantages of Action Research for the Classroom
- research can be set within a specific context or situation;
- researchers can be participants – they don’t have to be distant and detached from the situation;
- it involves continuous evaluation and modifications can be made easily as the project progresses;
- there are opportunities for theory to emerge from the research rather than always follow a previously formulated theory;
- the study can lead to open-ended outcomes;
- through action research, a researcher can bring a story to life.
Action Research Copyright © by J. Spencer Clark; Suzanne Porath; Julie Thiele; and Morgan Jobe is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
2024 Forbes Future of Work Summit | From Talk To Action: Making Skills-Based Hiring A Reality
Scores of companies have touted their efforts to drop college diploma requirements from job descriptions, moving away from a focus on degrees and pedigrees to one based on individual skills. But as recent research has shown, progress has been slow, and actual hiring as a result of such efforts still has far to go. Forbes Assistant Managing Editor Ali Jackson-Jolley has a conversation with Accenture Chief Leadership & Human Resources Officer Angela Beatty, Blackstone Senior Managing Director & Global Head of Portfolio Talent & Organizational Performance Courtney della Cava, and OneTen CEO Debbie Dyson about how companies are reshaping their hiring processes, training programs and workplace cultures to help move the needle?and what other changes are needed to make real strides.
From nitrogen pollution to battery recycling, young scientists take action to help society
For Piotr Olbryś, a 19-year-old from Poland, it was his brother’s hearing aid that motivated him to look into how to make lithium-ion batteries more environmentally friendly.
His work earned him one of the four first prizes, each worth € 7 000, at the 2024 edition of the EU Contest for Young Scientists (EUCYS).
“My brother has a hearing aid,” he said. “So, he’s constantly changing and throwing away batteries. That caused me to start thinking about the waste this generates.” Lithium-ion batteries are found in almost every electronic gadget.
Olbryś was one of 143 young scientists from 37 countries, all aged between 14 and 20, who came together from 9 to 14 September in Katowice, Poland, to present their research.
Most of them were there because they had won similar contests in their home countries. EUCYS 2024 was funded by the European Commission, which co-organised it with the University of Silesia, Katowice, and the Polish Children’s Fund.
In the end, the four first prizes were awarded to contestants from Austria, Bulgaria, Poland and the United States.
Better way to tune instruments
The young scientists presented their projects at booths in front of visitors and judges. Their research focused on an amazingly diverse range of fields.
Paula Morata González, an 18-year-old from Spain, is keen to improve the tuning of musical instruments.
“I play the harpsichord and study at the conservatory,” she said. “During tuning classes, I found it much more intuitive to find beautiful notes by looking at their mathematical proportions.”
“ It all started when I learned about photosynthesis in high school. I wanted to know more, and just kept digging. Lamia Music
Eventually she built a model that could help tune instruments. “At first my music teacher thought I was crazy,” she laughed. “But I love combining science and art.”
González starts university this year, where she hopes to continue on this interdisciplinary path, double-majoring in music and biomedical sciences.
Artificial intelligence
At their booths, the contestants were interviewed by a team of judges, mostly scientists themselves, who were duly impressed.
“The quality of the projects was very impressive this year,” said Milan Macek, president of the jury. “A trend seems to be the increased use of artificial intelligence.”
Macek has been a judge at the seven previous editions of EUCYS. He is a professor of genetics at Prague’s Charles University, but in Katowice, he was hard-pressed to pick the winners.
“There are not enough prizes for all the talent here, so hard choices had to be made.”

In parallel with EUCYS, another contest was held in Katowice, in the style of a hackathon. During EU TalentOn 2024, 108 participants aged between 21 and 35 developed scientific projects to address societal challenges such as climate change and water management.
The grand prize was won by a team of young researchers from the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain and Italy for their cancer prevention project Breath for Life. It received an award of €12 000.
High-speed camera or chessboard?
Most EUCYS contestants also targeted societal challenges with their projects. The work of another winner, 17-year-old Aleksandra Petkova from Bulgaria, might, for example, help design more efficient ships.
“It can help us build ships that use less fuel, reducing emissions,” she said. In her research project, she used sources like drone and satellite imagery to study the wakes of ships and make them more efficient, combining physics with a very practical goal.
Petkova hails from a family of scientists, which influenced her to take part in science contests like EUCYS.
“I can’t remember a time when I wasn’t doing something with science,” she said. “As a small child, I was already playing with magnets and mirrors, trying to understand the deeper principles of how they worked.”
She’s still overwhelmed by the accolades her work received. “I don’t know what I’ll do with the money. Maybe I’ll buy a new chessboard,” she laughed.
“On the other hand, I would like a high-speed camera for experiments. A few thousand more frames per second would make a big difference.”
Organic batteries
Olbryś from Poland looked at organic cathodes in batteries, which are easier to recycle than today’s cathodes, but lack the energy density of less green versions. This is why he researched new material combinations and found options that combine the best of both worlds.
“I didn’t have access to a supercomputer, so I just did them on my home laptop,” he said. “Sometimes one calculation would take two or three entire days. The sound of the cooling fans caused me to have a lot of dreams about helicopters,” he joked.
Starting university in Warsaw in two weeks, Olbryś hopes to continue his research. “I love projects where science can change the world.”
Lamia Music, a 15-year-old Austrian who looked at new kinds of solar cells, was giddy upon receiving first prize, in addition to an award from the London International Youth Science Forum.
“I almost didn’t go to my national competition,” she said. “I just went there for fun, to meet interesting people. Now I suddenly have this prize,” she laughs. “Sometimes you just need to go for it I guess.”
Her project worked on new types of solar cells, the central component of solar panels. “It all started when I learned about photosynthesis in high school,” she remembers. “I wanted to know more, and just kept digging.”
“ Farmers are really struggling with this. I wanted to do something real for the world. Nikhil Vemuri
For Music, the prize, however, wasn’t the most important thing about the contest.
“What I love about science is that you can learn new things, and meet new people,” she said. “That’s what I did here. I was fascinated just walking around and learning about fields I didn’t know anything about.”
For the young Austrian, science is a passion. “Sometimes I will wake up in the middle of the night with ideas,” she said.
For now, she wants to continue with her research, partly under the auspices of a local university.
Nitrogen pollution
Not all winners at EUCYS were from Europe. Nikhil Vemuri, 17, from the United States, won the fourth first prize.
“I live in North Carolina, in an area with a lot of farms. Today, they use too much fertiliser on their fields, which causes environmental problems, such as nitrogen pollution. I wanted to help.”
He designed a software tool that could predict, based on satellite imagery, where over- and under-fertilisation is likely to happen.
For example, if a field slopes downwards, fertiliser will likely concentrate at the bottom. Vemuri’s tool allows farmers to use fertiliser more efficiently and sparingly, reducing pollution.
“Farmers are really struggling with this. I wanted to do something real for the world.”
Beyond being celebrated for his project, Vemuri repeated what other participants already said. Sure, receiving awards is nice. But what really makes EUCYS special is the connections made.
“I talked to some fascinating projects here,” he said. “But more importantly, I made some great friends. That’s what makes an event like this so amazing.”
- EU TalentOn 2024
- EU Contest for Young Scientists
- EU TalentOn
Recommended for you
Share this page
Contact Horizon

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Action research is a research method that aims to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue. In other words, as its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time. It was first coined as a term in 1944 by MIT professor Kurt Lewin.A highly interactive method, action research is often used in the social sciences, particularly in educational settings.
Action research is introduced, and its contributions, strengths, and limitations are discussed in view of the current conversation about impact-driven scholarly work. Some practical guidance is given to bring action research within reach as a viable approach. The essay concludes with an exploration of how a fuller embrace of action research ...
t. e. Action research is a philosophy and methodology of research generally applied in the social sciences. It seeks transformative change through the simultaneous process of taking action and doing research, which are linked together by critical reflection. Kurt Lewin, then a professor at MIT, first coined the term "action research" in 1944.
In some of Lewin's earlier work on action research (e.g. Lewin and Grabbe 1945), there was a tension between providing a rational basis for change through research, and the recognition that individuals are constrained in their ability to change by their cultural and social perceptions, and the systems of which they are a part.
Action Research is fundamentally concerned with change. It is an inherently normative project. It tries to provide resources for the research participants to collaboratively change their situation toward a subjectively felt and objectively visible improvement of their living conditions.
Action research is an approach to research which aims at both taking action and creating knowledge or theory about that action as the action unfolds. It starts with everyday experience and is concerned with the development of living knowledge. ... There is action research work being conducted to address the major contemporary global challenges ...
Teachers usually work with a model, traditionally consisting of complicated spirals and cycles of consecutive steps, such as: the formulation of a general idea; exploration of the general idea; drawing up of a general plan; planning, implementation, monitoring, and evaluation of concrete actions for improvement; and writing up of a case study or report on the teachers' own action research.
Action research is a form of enquiry that integrates theory and action to address real life problems. It enables practitioners to systematically evaluate and improve their practice. The number of types of action researches has multiplied over the last 50 years (Fourali 2016) or so and, accordingly, so did the number of definitions offered.
Participatory action research (PAR) is an approach to research that prioritizes the value of experiential knowledge for tackling problems caused by unequal and harmful social systems, and for ...
This chapter is organized into four sections that deal with these issues. 1 What action research is and is not. 2 Different approaches to action research. 3 Purposes of action research. 4 When and when not to use action research. 1 What action research is and is not. Action research is a form of enquiry that enables practitioners in every job ...
Action research is a systematic approach researchers, educators, and practitioners use to identify and address problems or challenges within a specific context. ... Get real-time analysis for employee satisfaction, engagement, work culture and map your employee experience from onboarding to exit! Market Research Survey Software Real-time ...
%PDF-1.4 %âãÏÓ 468 0 obj > endobj xref 468 58 0000000016 00000 n 0000002619 00000 n 0000002768 00000 n 0000003326 00000 n 0000003470 00000 n 0000003642 00000 n 0000004175 00000 n 0000004744 00000 n 0000004856 00000 n 0000004970 00000 n 0000005244 00000 n 0000005860 00000 n 0000006135 00000 n 0000006703 00000 n 0000007504 00000 n 0000008262 00000 n 0000008687 00000 n 0000008801 00000 n ...
Action research has come to be understood as a global family of related approaches that integrates theory and practice with a goal of addressing important organizational, community, and social issues together with those who experience them (Bradbury, 2015; Brydon-Miller & Coghlan, 2014).It focuses on the creation of areas for collaborative learning and the design, enactment, and evaluation of ...
Action research is, quite literally, a coming together of action and research, or rephrased, of practice. and theory. Thus, t here are two thrusts i n action research: one is concerned with ...
Through cycles of systematic and purposeful iterative engagement with problems they face in specific practice settings, social workers engaging in action research build knowledge that is useful in advancing practice for the purposes of social betterment. This entry situates action research in the development of social-work knowledge and then ...
Action research is a research method that aims to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue. In other words, as its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time. It was first coined as a term in 1944 by MIT professor Kurt Lewin. A highly interactive method, action research is often used in the social ...
Participatory action research (PAR) differs from most other approaches to public health research because it is based on reflection, data collection, and action that aims to improve health and reduce health inequities through involving the people who, in turn, take actions to improve their own health. ... The work by Howard‐Grabman 15 provides ...
Abstract and Figures. Action research (AR) is a research approach that is grounded in practical action (the action component) while at the same time focused on generating, informing and building ...
Action research originated with the work of innumerable different scholars from so many different backgrounds that "there is no single generally accepted narrative of its origins" (Charles & Ward, 2007, p. 2). However, John Dewey and Kurt Lewin were key to establishing the foundations of action research.
Action research has become prevalent in many fields and disciplines, including education, health sciences, nursing, social work, and anthropology. This prevalence can be understood in the way action research lends itself to action-based inquiry, participation, collaboration, and the development of solutions to problems of everyday practice in ...
explore different approaches to action research as there are subtle differences of emphasis and suitability for different situations. Chapter objectives This chapter will examine: • some of the philosophical issues underpinning action research and outline the work of early theorists, including Kurt Lewin's pioneering work and the
For other schools interested in conducting action research, Kanter highlighted three key strategies. Focus on areas of growth, not deficiency: "This would have been less successful if we had said, 'Our math scores are down. We need a new program to get scores up,' Kanter said. "That puts the onus on teachers.
Action research is not a single approach but rather represents a tension between a number of forces that lead to personal, professional, and social change. I think of action research as a process of deep inquiry into one's practices in service of moving towards an envisioned future aligned with values. ... WORK/COMMUNITY CONTEXT (Action context
Action research is a process for improving educational practice. Its methods involve action, evaluation, and reflection. It is a process to gather evidence to implement change in practices. Action research is participative and collaborative. It is undertaken by individuals with a common purpose.
Scores of companies have touted their efforts to drop college diploma requirements from job descriptions, moving away from a focus on degrees and pedigrees to one based on individual skills. But ...
Organizations should focus on increasing managers confidence in the action taking experience by offering cross-team support and collaboration opportunities to make it a team- and organization-wide investment. Activating tools: Managers are seeking additional tools to help them through the action-taking process. While there may be a formal ...
For Piotr Olbryś, a 19-year-old from Poland, it was his brother's hearing aid that motivated him to look into how to make lithium-ion batteries more environmentally friendly. His work earned him one of the four first prizes, each worth € 7 000, at the 2024 edition of the EU Contest for Young Scientists (EUCYS). "My brother has a hearing aid," he said.