
Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation

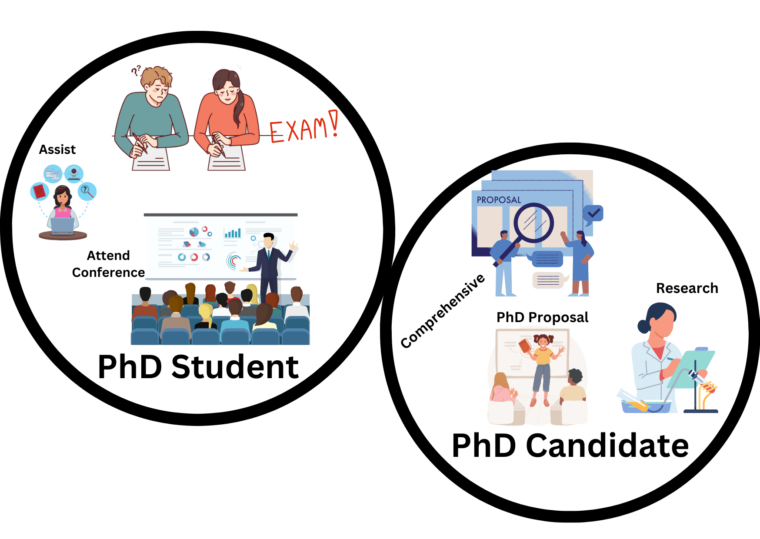
What is the Difference Between a PhD Candidate and a PhD Student?
Pursuing a doctoral degree is a significant academic achievement that requires years of dedicated study, research, and intellectual rigour. Within the realm of doctoral studies, the terms ‘PhD candidate’ and ‘PhD student’ are commonly used, often interchangeably. However, a closer examination reveals that there are nuanced differences between these two designations. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for both prospective doctoral students and those seeking to comprehend the various stages of the doctoral journey.
In this article, we delve into the disparity between a PhD candidate and a PhD student, shedding light on the roles, responsibilities, and progression associated with each stage. We explore the specific criteria that differentiate a student from a candidate and the various milestones marking the transition. Additionally, we delve into the responsibilities and expectations that accompany each designation, illuminating the unique experiences and commitments faced by PhD candidates and students.
Furthermore, we acknowledge the variability in terminology across international boundaries, academic institutions, and disciplinary fields, providing insights into how different contexts might influence the usage of these terms. By the end, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of the contrasting aspects between a PhD candidate and a PhD student, facilitating informed conversations and a deeper appreciation for the intricate nature of doctoral education.
Introduction
Who is a phd student, when phd student attains status of phd candidate, variation in terminology.
Pursuing a PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) degree involves conducting original research in a specific field of study, making a significant contribution to knowledge, and demonstrating a high level of expertise. It is the highest academic qualification one can attain and is highly valued in academia, research institutions, and certain industries. A PhD signifies a deep understanding of a subject area, advanced analytical and critical thinking skills, and the ability to conduct independent research.
While the terms “PhD candidate” and “PhD student” are often used interchangeably, there are subtle differences between the two.
A PhD student typically refers to an individual who has been admitted to a doctoral program, actively engaging in coursework and other program requirements. They are in the early stages of their doctoral journey and are working towards completing the necessary academic components of their degree. On the other hand, a PhD candidate is typically someone who has progressed beyond the coursework stage and has advanced to the research phase of their program. They have usually completed comprehensive exams, passed a research proposal defense, and are actively engaged in independent research for their dissertation or thesis.
The purpose of this article is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the distinction between a PhD candidate and a PhD student. By exploring the criteria, milestones, and responsibilities associated with each designation, this article aims to clarify the unique experiences and progression of doctoral students. It also seeks to address the varying terminology used across different contexts and disciplines, enabling readers to grasp the intricacies of the doctoral journey and fostering informed discussions around this topic.
Through this article, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of the journey from being a PhD student to becoming a PhD candidate and the distinct roles and responsibilities associated with each stage.
A PhD student is an individual who has been admitted to a doctoral program and is actively engaged in pursuing their doctoral studies. They are at the initial stages of their doctoral journey, seeking to expand their knowledge, skills, and expertise in a specific field of study. PhD students play a vital role in academic research communities as they contribute to the generation of new knowledge and the advancement of their discipline.
PhD students are required to complete a set of coursework specific to their field of study. These courses are designed to provide a foundation in the discipline, enhance research skills, and broaden the student’s understanding of relevant theories and methodologies. Coursework may include seminars, advanced classes, and specialized topics. The specific coursework requirements can vary between programs and disciplines.
Example: Imagine a student named Alex who has just been accepted into a doctoral program in psychology. At this stage, Alex is considered a PhD student as they begin taking relevant coursework, attending seminars, and collaborating with faculty members. They are laying the foundation for their research and acquiring the necessary knowledge in their field.
Who is a PhD Candidate?
Advancement from being a PhD student to a PhD candidate typically involves meeting specific requirements set by the doctoral program. These requirements may vary depending on the institution and field of study but often include successful completion of coursework, exams, and other program-specific milestones.
One of the primary requirements for transitioning to a PhD candidate is the successful completion of coursework and exams. PhD students are expected to complete a designated set of courses, which provide a broad understanding of their field and research methodologies. They are also required to pass comprehensive exams, which assess their comprehensive knowledge and understanding of their research area.
As part of the transition to becoming a PhD candidate, students typically prepare and defend a research proposal. The research proposal outlines the scope, objectives, methodology, and significance of the intended research. The proposal defense may involve presenting the proposal to a committee of faculty members, who evaluate its feasibility, rigour, and contribution to the field. Additionally, PhD students often have to pass comprehensive exams, which test their knowledge of their research area and related disciplines.
If you are not familiar with writing PhD proposal and making PhD proposal presentation, then visit my articles on “ How to Write PhD Proposal Presentation to the University ” and ” How to Make a PhD Proposal Presentation to the University Panel” . These articles will guide you through the process of preparation and presentation of PhD proposal to the University panel.
Upon successful completion of the requirements, PhD students are often granted candidacy status. Advancement to candidacy signifies that the student has demonstrated the necessary knowledge, skills, and potential to conduct independent research and contribute to their field. This status allows students to focus more exclusively on their research and dissertation work.
Once students become PhD candidates, there is a shift towards an increased emphasis on independent research. They are expected to dedicate a significant portion of their time and effort to conducting original research, collecting data, analyzing results, and making novel contributions to their field. The focus is primarily on their dissertation or thesis work, which serves as the culmination of their doctoral studies.
Example: Let’s consider a PhD student named Alex in the field of computer science. After completing their coursework and passing comprehensive exams, Alex develops a research proposal outlining their intention to investigate the applications of machine learning in cybersecurity. They present the proposal to a committee of faculty members, who assess the feasibility and potential impact of the research.
Alex successfully defends their research proposal and is granted candidacy status, transitioning from a PhD student to a PhD candidate. With candidacy status, Alex’s focus shifts towards conducting independent research. They spend considerable time collecting and analyzing cybersecurity datasets, developing and refining machine learning algorithms, and testing their effectiveness in detecting and preventing cyber threats.
As a PhD candidate, Alex works closely with their advisor, regularly discussing research progress, seeking guidance, and receiving feedback. They collaborate with other researchers in the field, attend conferences to present their findings and contribute to the scholarly community through publications. The focus is now on producing an original and significant contribution to the field of computer science through their dissertation.
The transition to PhD candidacy marks a critical stage in the doctoral journey, as it signifies the ability to independently drive research and make scholarly contributions. PhD candidates like Alex are immersed in the world of research, expanding knowledge, and pushing the boundaries of their field.
Terminology related to PhD candidates and PhD students can vary internationally and among different academic institutions. In some countries, the terms “PhD candidate” and “PhD student” may be used interchangeably, while in others, there may be specific distinctions. For example, in the United States, “PhD student” is commonly used, while in the United Kingdom, “PhD candidate” is more frequently employed. Additionally, different universities or institutions may have their own terminology preferences, which can create further variation.
Terminology can also vary based on the disciplinary field of study. Different academic disciplines have their own conventions and terminology for referring to individuals pursuing a doctoral degree. For instance, in the sciences, one might encounter terms like “graduate researcher” or “doctoral candidate.” In the humanities and social sciences, the terms “PhD candidate” and “PhD student” are often used. This variation reflects the specific linguistic and cultural norms within different academic domains.
In Canada, for instance, doctoral students are commonly referred to as “PhD candidates,” regardless of their stage in the program. In Australia, “PhD candidate” is the preferred term for those who have completed the required coursework and have advanced to the research phase. In contrast, in the United States, “PhD student” is frequently used to refer to individuals at all stages of their doctoral studies.
Disciplinary variations can also be observed. In engineering, individuals pursuing a doctoral degree are often referred to as “PhD students” or “doctoral students.” In contrast, in the field of education, the term “PhD candidate” is commonly used to denote those who have advanced to the research and dissertation stage.
It is important to note that these examples represent general trends, and there can still be variation within specific institutions and programs. The usage of terminology can evolve over time and may be influenced by regional or institutional preferences.
The distinction between a PhD candidate and a PhD student holds significant importance in the realm of doctoral education.
While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent different stages and responsibilities within the doctoral journey. A PhD student is in the initial stages of their program, actively engaging in coursework, research, and academic requirements.
On the other hand, a PhD candidate has advanced beyond coursework, passed comprehensive exams, and is focused primarily on independent research and the completion of their dissertation.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- Best 05 Research Journals for Publications in September 2024
- Best 5 Journals for Quick Review and High Impact in August 2024
- 05 Quick Review, High Impact, Best Research Journals for Submissions for July 2024
- Top Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Research Paper
- Average Stipend for Research/Academic Internships
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com


- Majors & Careers
- Online Grad School
- Preparing For Grad School
- Student Life
PhD Candidate vs Student: What’s the Difference?

Many people use the terms “PhD student” and “PhD candidate” interchangeably. However, these terms actually mean something quite different, including a different status level at universities.
We’re here to define the differences between a PhD candidate vs student, as well as other essential information, before you continue your educational journey.
Table of Contents
What I s a PhD student?
A doctoral student is anyone who is enrolled in a doctorate degree, also referred to as a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) program. PhD students are typically required to complete a certain number of course credits and sit qualifying exams. Next, they can move on to conduct research and present it in the form of a dissertation.
A PhD is centered around self-directed research and possibly teaching/running tutorials, but they typically also involve a substantial amount of coursework and require attending classes, either online or in person.
Unlike candidates, PhD students are in the process of completing the required coursework for the degree. They haven’t passed the relevant qualifying exams yet.
What Is a PhD Candidate?
A PhD candidate has completed the required coursework and passed the qualifying exams for their doctorate program. They are currently working on their dissertation.
Most PhD students need to go through an application process and show they meet certain requirements such as a relevant master’s degree . To become a PhD candidate, doctoral students need to pass an internal application process, typically involving a set of exams.
This stage involves significant research usually in innovative areas and incorporating this into a dissertation (this stage is sometimes referred to as “all but dissertation” [ABD]), as they’ve completed all other aspects of the program and satisfied these requirements. To complete their doctoral journey, a PhD candidate must defend their dissertation. Once they’ve successfully done this, they will be awarded their degree and move from PhD candidate to doctor of their chosen field.
PhD Candidate vs Student: 6 Key Differences

There are a number of key differences between a PhD student vs PhD candidate, from their status to the structure and nature of study.
Note: Some universities have recently started adopting hybrid approaches (where there is no clear difference between PhD students and PhD candidates). These programs don’t involve any qualifying exams and students typically begin the dissertation as part of their coursework. Most schools, however, continue with the traditional distinction between a PhD candidate and PhD student.
1. Program Stage
A PhD student could be at any stage of the doctoral program . Coursework still needs to be completed and qualifying exams must be passed. Students may be in the initial stage of the program or about to complete the coursework (before beginning their research).
On the other hand, a PhD candidate has completed all coursework and has at least started their research. They may have completed their dissertation and are preparing to defend it.
2. Research Progress
A PhD student may not have selected their research topic or settled on a particular research question. A candidate’s research is in progress and they should already have a clear research question.
3. Relationship with Advisors
A PhD student may not yet have an advisor. A candidate has an established working relationship with their advisor and works closely with them to complete their research and dissertation.
4. Level of Support
Although they work closely with an advisor, a PhD candidate is generally expected to work more independently than a student enrolled in a doctoral student. Once candidates reach this stage of their doctorate, they typically won’t receive as much direction or supervision.
5. Flexibility and Structure
Understandably, PhD candidates have more freedom and flexibility in their work. Most candidates choose their area of research, as well as the methods used to conduct their work. As part of their coursework, PhD students usually have to work within a set structure (e.g., completing core subjects, meeting deadlines).
Being a PhD candidate comes with a certain degree of status. If they’ve demonstrated a degree of expertise through completing qualifying exams, candidates can put the letters PhD(c) after their name.
Tips for PhD Candidates

A PhD is an advanced degree designed to demonstrate expertise in a given field, as well as high-level skills and abilities in various areas (including research and writing). As such, earning a doctorate can be a challenging process.
The following tips for doctoral candidates will help you put your best foot forward and set yourself up for success.
Stay Organized
Because PhD candidates have to balance many competing priorities, organization is essential. Using organizational tools such as calendars, note-taking apps , and project management software can help you keep track of deadlines and meet your targets.
Focus on Your Research
PhD candidates likely have busy schedules with plenty of demands (such as teaching commitments and crafting a dissertation). As it’s the backbone of any doctoral program, be sure to prioritize this part of your work and monitor progress to stay on track.
Actively Seek Out Feedback
Because PhD candidates often work independently, there’s a risk of feeling isolated. Ask your advisors, mentors, and fellow candidates for feedback and advice. This will help ensure that you’re considering all aspects of your research question and multiple solutions, rather than focusing too intensely on a single area.
Take Advantage of Networking Opportunities
Networking is one of the biggest benefits for PhD candidates, so take full advantage of these events. Use this time to build a strong network of professors, advisors, fellow candidates, and other professionals you meet at conferences and events.
Take Care of Yourself
A PhD program can be taxing, and it’s easy for your mental and physical health to take a backseat. Make sure you exercise, eat well, and get enough sleep . Remember: Resting and recharging is crucial for working on your dissertation.
How Long Is a Typical PhD Candidacy?

Most PhD students require 1-2 years to complete their coursework and pass their qualifying exams. However, the length of a PhD candidacy is much more open. In most cases, programs take between two and five years, depending on:
- the complexity of the field of research
- the candidate’s other commitments, such as teaching load
- other abilities, such as a candidate’s level of organization.
Once a PhD candidate has completed their dissertation, they have to defend it successfully before a panel of faculty members before they can earn their doctorate degree. This process of defending a PhD dissertation can take several months.
Some universities specify a maximum length for PhD candidacy duration. For example, Carnegie Mellon University limits this to six years .
Benefits of Being a PhD Candidate
Being a PhD candidate can be rewarding for several reasons:
1. Research Opportunities
You’ll be exposed to vast research opportunities in your field. You may contribute to valuable discoveries while developing advanced knowledge and skills.
2. Networking
Through your PhD candidacy, you’ll also be in a great position to build gain a stronger network of fellow professionals.
3. Critical Thinking
A PhD candidacy can help you develop high intellectual independence and critical thinking skills.
4. Career Opportunitie s
A PhD is an advanced degree that allows you to build a rewarding career in the academic, government, and private sectors. PhD-holders can also expect to earn more than other graduates and are most likely to find a job.
5. Salaries
According to Northeastern University , professionals with a doctorate degree earn an average annual salary of $99,290 on average (and much more for the highest-paid PhDs ) and have a 1.5% unemployment rate. For master’s degree holders, the average annual salary is $81,867 average annual salary and a 2.6% unemployment rate.
6. Personal Fulfillment
Being a PhD candidate can help you pursue your passions. This advanced qualification will allow you to become a specialist in your chosen field, allowing you to hone in on the exact subject thatl fulfills you the most.
Qualifying Exams to Become a PhD Candidate

While requirements vary by program, to become a PhD candidate, most students will need to pass a set of exams. These will test students’ knowledge in the field, measure their research skills, and ensure they’re ready to start their dissertation research.
Traditionally, qualifying exams for PhD candidates involved a written test and an oral exam. These will cover a range of topics related to your field of study, with the oral component designed to demonstrate your level of understanding.
Some universities have recently started to issue doctoral students with a set of questions and have them submit the answers within a set timeframe (usually around two weeks). Other schools ask prospective doctoral candidates to submit a dissertation proposal instead of an exam.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a phd candidate be called a doctor.
In most cases, a doctoral candidate cannot be called a doctor until after they successfully defend their dissertation and receive their doctorate.
Can I Put ‘PhD Candidate’ after My Name?
Once you’ve passed qualifying exams and embarked on dissertation research, you’re technically entitled to put “PhD candidate” or “PhD (c)” after your name. However, this is uncommon and not always recommended. It is generally more acceptable to mention that you are pursuing a doctorate (along with the field of research and university) or that you expect to complete your PhD in a certain year (on your CV and online profiles).
How Long Can You Be a PhD Candidate?
There isn’t a set length of time that a person can be a PhD candidate. The length of candidacy depends on a range of factors, including the subject of research and program requirements. Most PhD candidates complete this phase in around 3-5 years (where some university programs have set limits).
Do PhD Students Take Classes?
Yes, most PhD students must take classes and complete coursework as part of the first 1-2 years of their doctorate program. Once they’ve completed this coursework and passed qualifying exams, they move on to work on their research dissertation. At this stage, they’ll be considered a PhD candidate.
Key Takeaways
Now that you know the differences between PhD candidates vs. students, you’ve got a deeper understanding of how to obtain a doctorate. However you slice it, both will help you build your knowledge and skills to become an expert in your field.
However the program is structured, a PhD is a highly valuable degree that allows you to become a high-level professional and build a successful career.
If you know a PhD candidate who’s celebrating their accomplishments soon? Take a look at this guide to the best PhD graduation gifts .
- 10 Best PhD Programs in Pennsylvania
- Top 10 Best PhD in Cybersecurity Online Programs
- 10 Top PhD Programs in Chemistry
- The Top 10 Easiest PhDs: Tuition, Duration, and Financial Aid
- Top 10 Fully Funded PhD Programs and Universities
- Top 10 Best PhD in Medicine Programs

Lisa Marlin
Lisa is a full-time writer specializing in career advice, further education, and personal development. She works from all over the world, and when not writing you'll find her hiking, practicing yoga, or enjoying a glass of Malbec.
- Lisa Marlin https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/lisa-marlin/ 30+ Best Dorm Room Essentials for Guys in 2024
- Lisa Marlin https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/lisa-marlin/ 12 Best Laptops for Computer Science Students
- Lisa Marlin https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/lisa-marlin/ ACBSP Vs AACSB: Which Business Program Accreditations is Better?
- Lisa Marlin https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/lisa-marlin/ BA vs BS: What You Need to Know [2024 Guide]
14 Cheap Spring Break Destinations for College Students in 2024
How to get a master’s without a bachelor’s: the complete guide, related posts.

- How Many Grad Schools Should I Apply To?
![phd candidate researcher When to Apply for Grad School: The Simple Guide [2026/2027]](https://blog.thegradcafe.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/When-to-Apply-to-Grad-School-350x250.png)
- When to Apply for Grad School: Easy Monthly Timeline [2025-2026]

- 30+ Best Dorm Room Essentials for Guys in 2024

- Best Laptop for Programming Students in 2024

The Sassy Digital Assistant Revolutionizing Student Budgeting

Computer Science Graduate Admission Trends: Annual Results

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
- Last Mile Education Fund Paves the Way for Tech Students, Offers Lifeline Grants

© 2024 TheGradCafe.com All rights reserved
- Partner With Us
- Results Search
- Submit Your Results
- Write For Us

PhD Student vs. PhD Candidate

How I use gentle, digital nudges to stay current in the post-exams world
July 6, 2017 | Alison L.
Do you know the difference between a PhD student and a Ph.D. candidate?
A candidate is someone who has fulfilled all the requirements for the degree except the dissertation.
I’m a historian (see my earlier post about being a humanist at MIT ), so my path to candidacy differs a bit from other doctoral tracks at MIT. But whatever the discipline, the transition from student to candidate is an arduous process.
My department’s requirements involved: completing two years of coursework; demonstrating proficiency in a research language other than English; submitting at least one grant application; writing and revising a dissertation proposal that the dissertation committee must approve; and, most grueling of all, passing qualifying exams.
I became a candidate on November 24, 2015, after a weeklong examination period that involved three separate seven-hour written exam and a two-hour oral examination during which our committee members can grill us on anything they please.
I felt prepared for the written exams, which were open note, because I’d done nothing but read, take notes, and revise for the four months leading up to the exams.
But I lost sleep (at a time when I really couldn’t afford to be losing sleep) fretting about the oral exam. I shouldn’t have worried as much as I did. While there were a couple moments of panic—like when I blanked on the two ecozones separated by Wallace’s line—I survived “quals.”
So, what do you do once you become a candidate?
First, you take a break. I gave myself a little over a month to relax. I worked on lower-stakes projects, read fiction, attended departmental lectures, caught up with colleagues. I enjoyed the holidays at home in Chicago.
But once the New Year rolled around, a new sense of panic set in. Without the motivating pressure of exams to keep me working at a breakneck pace, how would I ever stay up-to-date in my fields? This anxiety, I’m willing to guess, is one shared by almost all academics.
While I’m actually more interested in how others have handled this pressure—comment away please!—I wanted to share a few tips I’ve picked up for keeping au courant .
1. Sign up for eTOCs That acronym stands for email Table of Contents alerts. Most journal publishers have a system that allows you to receive emails detailing the contents of their most recent releases. Sign up for a few of these and you’ll receive quarterly reminders that make it easier to stay on top of developments in the literature.
For some fields, it might not be necessary to read entire journals. In that case, pick some keywords and set up a bunch of Google Scholar alerts. Talk to your advisors and peers to see what works best in your discipline.
2. Make social media work for you Choose one social media platform and turn it into a research tool. My platform of choice is Twitter. You might be surprised by the number of scholars and professional associations that use social media. I rarely tweet myself, but I check Twitter at least once each day to find links to interesting articles, news about gatherings in my field, and to follow the work of scholars I admire. In addition to yielding worthwhile information, my Twitter sessions have the added benefit of tricking my brain into thinking it’s taking a break from work.
If you’re wondering how to curate your Twitter feed, first take a look at papers you’ve written for classes or published. See if the scholars that you cite in your own work are on Twitter and go from there. This is the most casual form of networking, but especially for introverts (like myself) these social media e-introductions facilitate in-person conference meetings, which can lead to future collaborations.
3. Listservs make life easier Most people at MIT know about the free food listserv. I’m not a member because I don’t need that kind of temptation in my life. Still, I’m a big fan of using listservs to join intellectual communities. In addition to the handful of MIT-based lists that tell me about upcoming lectures and workshops here on campus, I receive emails from communities at other Cambridge- and Boston-based schools. I’m also on a few listservs for universities in other cities. Even if I’m never able to attend those events, I know who is working on what where. If academia is about staying in the know, listservs help you do that.
I’ve written this from the perspective of a PhD candidate who needed gentle, digital nudges to stay current in the post-exams world, but I hope they prove useful for students, candidates, and beyond. Now comes the important question: What are your strategies for staying up-to-date?
Share this post:
This site uses cookies to give you the best possible experience. By browsing our website, you agree to our use of cookies.
If you require further information, please visit the Privacy Policy page.
- The PhD Journey - Stages of a Doctoral Degree
How to Get a PhD: The PhD Journey
Written by Mark Bennett
A PhD typically involves between three and four years of full-time study, culminating in a thesis which makes an original contribution to your field.
The process of getting a PhD is made up of quite a few components and milestones, from the literature review and writing up your dissertation right through to the viva examination at the end.
This section is a guide on how to get a PhD, providing in-depth advice and information on some of the main challenges and opportunities you’ll meet along the way!.
Get funding updates straight to your inbox
Sign up to our weekly newsletter for the latest funding advice and guidance from our team of experts.
7 stages of the PhD journey
A PhD has a few landmark milestones along the way. The three to four years you'll spend doing a PhD can be divided into these seven stages.
- Preparing a research proposal
- Carrying out a literature review
- Conducting research and collecting results
- Completing the MPhil to PhD upgrade
- Participating in PhD teaching, conferences and publications
- Writing your thesis
- Defending your PhD results at a viva voce
We've expanded on what you can expect from each stage below. Here's how your journey to getting a PhD will look:
1. Preparing a research proposal
Strictly speaking, your research proposal isn’t part of your PhD. Instead it’s normally part of the PhD application process.
The research proposal sets out the aims and objectives for your PhD: the original topic you plan to study and / or the questions you’ll set out to answer.
It also explains why your work is worthwhile and why it fits with the expertise and objectives of your university.
Finally, a PhD proposal explains how you plan to go about completing your doctorate. This involves identifying the existing scholarship your work will be in dialogue with and the methods you plan to use in your research.
All of this means that, even though the proposal precedes the PhD itself, it plays a vital role in shaping your project and signposting the work you’ll be doing over the next three or more years.
2. Carrying out a literature review
The literature review is normally the first thing you’ll tackle after beginning your PhD and having an initial meeting with your supervisor.
It’s a thorough survey of work in your field (the current scholarly ‘literature’) that relates to your project or to related topics.
Your supervisor will offer some advice and direction, after which you’ll identify, examine and evaluate existing data and scholarship.
In most cases the literature review will actually form part of your final PhD dissertation – usually setting up the context for the project, before you begin to explain and demonstrate your own thesis.
Sometimes a literature review can also be evaluated as part of your MPhil upgrade .
Research vs scholarship
Research and scholarship are both important parts of a PhD. But they aren't the same thing - and it's helpful to know the difference. Research is the original work you produce with your thesis. Scholarship is the expert understanding of your subject area that enables you to conduct valuable research.
3. Conducting research and collecting results
Once you’ve carried out your literature review, you’ll move from scholarship to research .
This doesn’t mean you’ll never read another academic article or consult someone else’s data again. Far from it. You’ll stay up to date with any new developments in your field and incorporate these into your literature review as necessary.
But, from here on in, your primary focus in your PhD process is going to be investigating your own research question. This means carrying out organised research and producing results upon which to base your conclusions.
Types of PhD research
The research process and the type of results you collect will depend upon your subject area:
- In Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) subjects you’ll focus on designing experiments, before recording and analysing their outcomes. This often means assembling and managing complex numerical datasets – sometimes in collaboration with the rest of your laboratory or workshop.
- In Social Science subjects you’ll be more focussed on designing surveys or conducting case studies. These will produce quantitative or qualitative data, depending on the nature of your work.
- In Arts and Humanities subjects you’ll often have less raw data, but that doesn’t mean you won’t be working with ‘hard’ factual information. You’ll analyse texts, sources and other materials according to an accepted methodology and reflect upon the significance of your findings.
Whatever subject you’re in, this research work will account for the greater part of your PhD results. You’ll have regular meetings with your supervisor, but the day-to-day management of your project and its progress will be your own responsibility.
In some fields it’s common to begin writing up your findings as you collect them, developing your thesis and completing the accompanying dissertation chapter-by-chapter. In other cases you’ll wait until you have a full dataset before reviewing and recording your conclusions.
4. Completing an MPhil to PhD upgrade
At UK universities it’s common to register new PhD students for an MPhil before ‘ upgrading ’ them to ‘full’ doctoral candidates. This usually takes place after one year of full-time study (or its part-time equivalent).
Forcing you to register for a ‘lesser’ degree may seem strange, but it’s actually an important part of the training and development a PhD offers:
- As an MPhil student you’re able to comprehend your field and produce new research.
- As a PhD student you’re able to go that crucial step further and produce the significant original contribution to knowledge that defines a doctorate.
The MPhil upgrade is when you take the step from the former to the latter.
The MPhil upgrade exam
Upgrading from MPhil to PhD registration usually involves a form of oral exam – similar to the viva voce that concludes a PhD. But, unlike a full viva, the MPhil upgrade is less formal and only covers part of your thesis.
In most cases you’ll submit a small amount of the material you’ve produced so far. This could be a draft of your first chapter (or part of it) and / or your literature review. You could also be asked to reflect on your progress in general.
You’ll then sit down with your supervisor and someone else from your department (familiar with your field, but unrelated to your project). They’ll offer feedback on the quality of your work and ask questions about your findings.
The aim of the process won’t be to examine your drafts so much as to confirm that your project has the potential to justify a PhD – and that you’re on track to complete it on time.
‘Failing’ a PhD upgrade is actually quite rare. Your university may ask you to repeat the procedure if they are concerned that you haven’t made sufficient progress or established a viable plan for the rest of your project.
What is an MPhil?
The MPhil (Master of Philosophy) is also a research degree, but its scope is more limited than a PhD (Doctor of Philosophy). And no, just like a PhD, an MPhil isn’t necessarily a Philosophy qualification. Our guide covers all you need to know about the difference between a MPhil and PhD .
5. PhD teaching, conferences and publications
During the PhD process, you’ll have lots of opportunities to take part in extra-curricular activities, such as teaching, academic conferences and publications.
Although it isn’t usually compulsory to participate in these, they can be an incredibly rewarding experience and will look great on your CV.
Teaching during a PhD normally involves hosting undergraduate seminars or supervising students in the lab, as well as marking work and providing feedback.
Academic conferences are an excellent way to network with like-minded colleagues and find out the latest developments in your field. You might even be able to present your own work to your peers at one of these events.
Publishing during a PhD will help you increase your academic profile, as well as give you experience of the peer review process. It’s not normally a requisite of your PhD, but publications will certainly help if you plan on applying for postdoc positions.
6. Writing your thesis
As the culmination of three or more years of hard work, the thesis (or dissertation) is the most important part of the procedure to get your PhD, presenting you with the opportunity to make an original scholarly contribution to your discipline.
Our guide to writing your thesis covers everything you need to know about this lengthy research project, from structure and word count to writing up and submission.
We’ve also written a guide to the PhD dissertation abstract , which is an important part of any thesis.
7. Defending your PhD results at a viva voce
Unlike other degrees, a PhD isn’t normally marked as a piece of written work. Instead your dissertation will be submitted for an oral examination known as a viva voce (Latin for ‘living voice’).
This is a formal procedure, during which you ‘defend’ your thesis in front of appointed examiners, each of whom will have read your dissertation thoroughly in advance.
Examiners at a viva voce
A PhD is normally examined by two academic experts:
- One will be an internal examiner, usually appointed from elsewhere in your faculty and department. They won’t be directly associated with your project, but will have sufficient expertise to assess your findings.
- The other will be an external examiner. They will be a recognised expert in the area you are researching, with a record of relevant research and publication. Most universities in the UK allow you to invite an external examiner of your choice, provided there is no existing conflict of interest.
Your supervisor will help you prepare for the viva and will offer advice on choosing an external examiner. However, they will not normally be present during the examination.
The PhD timeline
| Meet with your and discuss your proposed project. Here you will clarify any changes that are needed and agree a schedule of meetings and a plan of work for the following months. | |
| Clarify the direction of your research, methods and the necessity of any research trips. You will also discuss your training and development needs and begin working towards a . | |
| Hand in of an advanced , thesis plan and timetable for completion. This will then be discussed in the with two internal examiners. | |
| Biannual review with your supervisor(s) to discuss your progress to date and feasibility of completing on time. | |
| You will have made considerable progress on your research by the end of the second year. You may have begun drafting your and engaging in professional activities such as , , and skills training. All of your progress will be discussed in another annual review. | |
| Most of the third year will be spent writing up and redrafting your . You may also engage in professional activities such as , and . | |
| Application for examination and nominate your examiners. | |
| and assisting work such as a skills development log. | |
| Usually the will take place within 10 weeks of the examiners receiving your thesis. | |
| Most PhD students pass with corrections and are given a period to edit the thesis. The length of time given will depend on whether you pass with major or minor corrections. | |
| Receipt of award and graduation! |
Ready to take the next step?
There's lots more information about how to get a PhD in our advice section . Or, if you're ready to start looking at different projects, why not check out one of the thousands of current PhD opportunities in our database?
Mark Bennett
Mark joined FindAPhD to develop our first ever advice articles in 2013 and now serves as our Director of Audience & Editorial, making sure our websites and information are as useful as possible for people thinking about Masters and PhD study. He has a PhD in English Literature from the University of Sheffield, as well as Bachelors and Masters degrees from the University of Kent and the University of South Wales.

Not sure how PhD study will differ from a Masters? In this guide, we take a look at how the two qualifications compare, including applications, course structure, assessment and more.

Every student will need to write an abstract for their PhD dissertation. Here's everything you need to know about what an academic abstract is and how to write one.

What can you expect from a PhD? What's life actually like as a postgraduate student? Read our guides to the doctoral research experience.

The viva voce is the final oral exam at the end of a PhD degree. Our guide explains the usual viva format, covers common questions and explains how to prepare.
FindAPhD. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about PhD study?
Select your nearest city
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAPhD, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- The latest PhD projects delivered straight to your inbox
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, research proposal tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Create your account
Looking to list your PhD opportunities? Log in here .
Google PhD fellowship program
Google PhD Fellowships directly support graduate students as they pursue their PhD, as well as connect them to a Google Research Mentor.
Nurturing and maintaining strong relations with the academic community is a top priority at Google. The Google PhD Fellowship Program was created to recognize outstanding graduate students doing exceptional and innovative research in areas relevant to computer science and related fields. Fellowships support promising PhD candidates of all backgrounds who seek to influence the future of technology. Google’s mission is to foster inclusive research communities and encourage people of diverse backgrounds to apply. We currently offer fellowships in Africa, Australia, Canada, East Asia, Europe, India, Latin America, New Zealand, Southeast Asia and the United States.
Quick links
- Copy link ×
Program details
Application status, how to apply, research areas of focus, review criteria, award recipients.
Applications are currently closed.
Update on 2024 Announcement : Decisions for the 2024 application cycle, originally planned for July 2024, will now be announced via email in August 2024. We apologize for the delay and appreciate your patience as we work to finalize decisions.
- Launch March 27, 2024
- Deadline May 8, 2024
- Awardees Notified By Aug. 31, 2024
The details of each Fellowship vary by region. Please see our FAQ for eligibility requirements and application instructions.
PhD students must be nominated by their university. Applications should be submitted by an official representative of the university during the application window. Please see the FAQ for more information.
Australia and New Zealand
Canada and the United States
PhD students in Japan, Korea and Taiwan must be nominated by their university. After the university's nomination is completed, either an official representative of the university or the nominated students can submit applications during the application window. Please see the FAQ for more information.
India and Southeast Asia
PhD students apply directly during the application window. Please see the FAQ for more information.
Latin America
The 2024 application cycle is postponed. Please check back in 2025 for details on future application cycles.
Google PhD Fellowship students are a select group recognized by Google researchers and their institutions as some of the most promising young academics in the world. The Fellowships are awarded to students who represent the future of research in the fields listed below. Note that region-specific research areas will be listed in application forms during the application window.
Algorithms and Theory
Distributed Systems and Parallel Computing
Health and Bioscience
Human-Computer Interaction and Visualization
Machine Intelligence
Machine Perception
Natural Language Processing
Quantum Computing
Security, Privacy and Abuse Prevention
Software Engineering
Software Systems
Speech Processing
Applications are evaluated on the strength of the research proposal, research impact, student academic achievements, and leadership potential. Research proposals are evaluated for innovative concepts that are relevant to Google’s research areas, as well as aspects of robustness and potential impact to the field. Proposals should include the direction and any plans of where your work is going in addition to a comprehensive description of the research you are pursuing.
In Canada and the United States, East Asia and Latin America, essay responses are evaluated in addition to application materials to determine an overall recommendation.
What does the Google PhD Fellowship include?
Students receive named Fellowships which include a monetary award. The funds are given directly to the university to be distributed to cover the student’s expenses and stipend as appropriate. In addition, the student will be matched with a Google Research Mentor. There is no employee relationship between the student and Google as a result of receiving the fellowship. The award does not preclude future eligibility for internships or employment opportunities at Google, nor does it increase the chances of obtaining them. If students wish to apply for a job at Google, they are welcome to apply for jobs and go through the same hiring process as any other person.
- Up to 3 year Fellowship
- US $12K to cover stipend and other research related activities, travel expenses including overseas travel
- Google Research Mentor
- 1 year Fellowship
- AUD $15K to cover stipend and other research related activities, travel expenses including overseas travel
- Up to 2 year Fellowship (effective from 2024 for new recipients)
- Full tuition and fees (enrollment fees, health insurance, books) plus a stipend to be used for living expenses, travel and personal equipment
- US $10K to cover stipend and other research related activities, travel expenses including overseas travel
- Yearly bursary towards stipend / salary, health care, social benefits, tuition and fees, conference travel and personal computing equipment. The bursary varies by country.
Early-stage PhD students
- Up to 4 year Fellowship
- US $50K to cover stipend and other research related activities, travel expenses including overseas travel
Late-stage PhD students
- US $10K to recognise research contributions, cover stipend and other research related activities, travel expenses including overseas travel
- US $15K per year to cover stipend and other research related activities, travel expenses including overseas travel
Southeast Asia
- US $10K per year for up to 3 years (or up to graduation, whichever is earlier) to cover stipend and other research related activities, travel expenses including overseas travel
Is my university eligible for the PhD Fellowship Program?
Africa, Australia/New Zealand , Canada, East Asia, Europe and the United States : universities must be an accredited research institution that awards research degrees to PhD students in computer science (or an adjacent field).
India, Latin America and Southeast Asia : applications are open to universities/institutes in India, Latin America (excluding Cuba), and in eligible Southeast Asian countries/regions (Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam).
Restrictions : All award payments and recipients will be reviewed for compliance with relevant US and international laws, regulations and policies. Google reserves the right to withhold funding that may violate laws, regulations or our policies.
What are the eligibility requirements for students?
All regions
- Students must remain enrolled full-time in the PhD program for the duration of the Fellowship or forfeit the award.
- Google employees, and their spouses, children, and members of their household are not eligible.
- Students that are already supported by a comparable industry award are not eligible. Government or non-profit organization funding is exempt.
- Past awardees from the PhD Fellowship program are not eligible to apply again.
- Grant of the Fellowship does not mean admission to a PhD program. The awardee must separately apply and be accepted to a PhD program in computer science (or an adjacent field) at an eligible institution.
- Grant of the Fellowship will be subject to the rules and guidelines applicable in the institution where the awardee registers for the PhD program.
Nominated students in Africa, Australia and New Zealand, Canada and the United States, East Asia and Europe.
Universities should only nominate students that meet the following requirements:
- Africa: Incoming PhD students are eligible to apply, but the Fellowship award shall be contingent on the awardee registering for a full-time PhD program in computer science (or an adjacent field) within the academic award year of the Fellowship award, or the award shall be forfeited.
- Australia and New Zealand : early-stage students enrolled in the first or second year of their PhD (no requirement for completion of graduate coursework by the academic award year).
- Canada and the United States : students who have completed graduate coursework in their PhD by the academic award year when the Fellowship begins.
- East Asia: students who have completed most of graduate coursework in their PhD by the academic award year when the Fellowship begins. Students should have sufficient time for research projects after receiving a fellowship.
- Europe: Students enrolled at any stage of their PhD are eligible to apply.
Direct applicant students in India, Latin America and Southeast Asia
- Latin America : incoming or early stage-students enrolled in the first or second year of their PhD (no requirement for completion of graduate coursework by the academic award year).
What should be included in an application? What language should the application be in?
All application materials should be submitted in English.
For each student nomination, the university will be asked to submit the following material in a single, flat (not portfolio) PDF file:
- Student CV with links to website and publications (if available)
- Short (1-page) resume/CV of the student's primary PhD program advisor
- Available transcripts (mark sheets) starting from first year/semester of Bachelor's degree to date
- Research proposal (maximum 3 pages, excluding references)
- 2-3 letters of recommendation from those familiar with the nominee''s work (at least one from the thesis advisor for current PhD students)
- Student essay response (350-word limit) to: What impact would receiving this Fellowship have on your education? Describe any circumstances affecting your need for a Fellowship and what educational goals this Fellowship will enable you to accomplish.
- Transcripts of current and previous academic records
- 1-2 letters of recommendation from those familiar with the nominee's work (at least one from the thesis advisor)
Canada, East Asia, the United States
- Cover sheet signed by the Department Chair confirming the student passes eligibility requirements. (See FAQ "What are the eligibility requirements for students?")
- Short (1-page) CV of the student's primary advisor
- 2-3 letters of recommendation from those familiar with the nominee's work (at least one from the thesis advisor)
- Research / dissertation proposal (maximum 3 pages, excluding references)
- Student essay response (350-word limit) to: Describe the desired impact your research will make on the field and society, and why this is important to you. Include any personal, educational and/or professional experiences that have motivated your research interests.
- Student essay response (350-word limit) to: Describe an example of your leadership experience in which you have positively influenced others, helped resolve disputes or contributed to group efforts over time. (A leadership role can mean more than just a title. It can mean being a mentor to others, acting as the person in charge of a specific task, or taking the lead role in organizing an event or project. Think about what you accomplished and what you learned from the experience. What were your responsibilities? Did you lead a team? How did your experience change your perspective on leading others? Did you help to resolve an important dispute at your school, church, in your community or an organization? And your leadership role doesn’t necessarily have to be limited to school activities. For example, do you help out or take care of your family?)
Students will need the following documents in a single, flat (not portfolio) PDF file in order to complete an application (in English only):
- Student applicant’s resume with links to website and publications (if available)
- Short (one-page) resume/CV of the student applicant's primary PhD program advisor
- 2-3 letters of recommendation from those familiar with the applicant's work (at least one from the thesis advisor for current PhD students)
- Applicant's essay response (350-word limit) to: Describe the desired impact your research will make on the field and society, and why this is important to you. Include any personal, educational and/or professional experiences that have motivated your research interests.
- Applicant's essay response (350-word limit) to: What are your long-term goals for your pathway in computing research, and how would receiving the Google PhD Fellowship help you progress toward those goals in the short-term?
How do I apply for the PhD Fellowship Program? Who should submit the applications? Can students apply directly for a Fellowship?
Check the eligibility and application requirements in your region before applying. Submission forms are available on this page when the application period begins.
India, Latin America and Southeast Asia: students may apply directly during the application period.
Africa, Australia, Canada, East Asia, Europe, New Zealand, and the United States : students cannot apply directly to the program; they must be nominated by an eligible university during the application period.
How many students may each university nominate?
India, Latin America and Southeast Asia : applications are open directly to students with no limit to the number of students that can apply from a university.
Australia and New Zealand : universities may nominate up to two eligible students.
Canada and the United States : Universities may nominate up to four eligible students. We encourage nominating students with diverse backgrounds especially those from historically marginalized groups in the field of computing. If more than two students are nominated then we strongly encourage additional nominees who self-identify as a woman, Black / African descent, Hispanic / Latino / Latinx, Indigenous, and/or a person with a disability.
Africa, East Asia and Europe : Universities may nominate up to three eligible students. We encourage nominating students with diverse backgrounds especially those from historically marginalized groups in the field of computing. If more than two students are nominated then we strongly encourage the additional nominee who self-identifies as a woman.
*Applications are evaluated on merit. Please see FAQ for details on how applications are evaluated.
How are applications evaluated?
In Canada and the United State, East Asia and Latin America, essay responses are evaluated in addition to application materials to determine an overall recommendation.
A nominee's status as a member of a historically marginalized group is not considered in the selection of award recipients.
Research should align with Google AI Principles .
Incomplete proposals will not be considered.
How are Google PhD Fellowships given?
Any monetary awards will be paid directly to the Fellow's university for distribution. No overhead should be assessed against them.
What are the intellectual property implications of a Google PhD Fellowship?
Fellowship recipients are not subject to intellectual property restrictions unless they complete an internship at Google. If that is the case, they are subject to the same intellectual property restrictions as any other Google intern.
Will the Fellowship recipients become employees of Google?
No, Fellowship recipients do not become employees of Google due to receiving the award. The award does not preclude future eligibility for internships or employment opportunities at Google, nor does it increase the chances of obtaining them. If they are interested in working at Google, they are welcome to apply for jobs and go through the same hiring process as any other person.
Can Fellowship recipients also be considered for other Google scholarships?
Yes, Fellowship recipients are eligible for these scholarships .
After award notification, when do the Google PhD Fellowships begin?
After Google PhD Fellowship recipients are notified, the Fellowship is effective starting the following school year.
What is the program application time period?
Applications for the 2024 program will open in March 2024 and close in May 2024 for all regions. Refer to the main Google PhD Fellowship Program page for each region’s application details.
A global awards announcement will be made in September on the Google Research Blog publicly announcing all award recipients.
How can I ask additional questions?
Due to the volume of emails we receive, we may not be able to respond to questions where the answer is available on the website. If your question has not been answered by a FAQ, email:
Africa: [email protected]
Australia and New Zealand: [email protected]
Canada and the United States: [email protected]
East Asia: [email protected]
Europe: [email protected]
India: [email protected]
Latin America: [email protected]
Southeast Asia: [email protected]
See past PhD Fellowship recipients.
Discover our collection of tools and resources
Browse our library of open source projects, public datasets, APIs and more to find the tools you need to tackle your next challenge or fuel your next breakthrough.


What is a PhD student or PhD candidate? [Updated]
For those that are thinking about doing a postgraduate degree, it’s not always clear exactly what a PhD entails. You may have heard the stereotypical PhD motivation as “doing research to progress humanity”. However, the actual day today life of a PhD student isn’t as nearly as grand.
A PhD student is someone who is enrolled in a postgraduate doctoral degree program. PhD students will typically perform original research and write up a dissertation to communicate the results to their peers. Some countries also require PhD students to take exams as part of their course.
This article will help you understand what a PhD student is, what they do during a typical day and what the benefits are of getting a PhD.
What Is a PhD Candidate?
A PhD Candidate is an individual who is currently enrolled in a doctoral program at a university or other tertiary education institution.
They are usually referred to as “ PhD students” or “PhD candidates.”
In order to qualify for the PhD, a candidate must complete all of the program’s coursework requirements and write and defend a dissertation that presents original research.
The dissertation must be approved by their faculty advisor or dissertation committee in order to complete the degree. The dissertation committee is made up of other experts in the field that are looking for an original contribution to further the academic field.
Candidates may also be required to take additional coursework beyond the general requirements of their program in order to qualify for the PhD. Doing coursework is very typical in universities in the United States of America.
After completing all of these requirements, they will officially become a PhD student and will receive their diploma after defending their dissertation and receiving approval from their faculty advisor or committee.
What a typical PhD program involves
A typical PhD program involves a combination of coursework and independent research.
Students are expected to build upon their existing knowledge by taking advanced courses in their discipline or related areas, while also conducting original research that contributes to the larger body of knowledge in the field.
A typical PhD student schedule is dependent on the field and subject area. However, there are some things that are common for nearly every PhD student. You can find out more about a typical PhD student schedule in my other article – click here .

Depending on the program, students may be required to complete seminars, comprehensive exams, and/or a dissertation.
In more modern PhD’s you are able to prove that you have generated significant contributions to a field by publishing your results in peer reviewed papers. This is known as PhD by publication. It is typically comprised of five or more peer-reviewed publications presented together with a literature review and joining chapters.
Traditionally, a PhD dissertation is composed of several chapters exploring an area of study in-depth, and must be defended before a panel of experts in the field. During their doctoral studies, students may also have opportunities to gain teaching experience and participate in internships or other professional development activities.
Ultimately, completing a PhD program culminates with the publication of one’s research findings and a public presentation of their work.
The PhD dissertation
The PhD dissertation is a substantial document that presents original research and analysis in a specific field.
It is the culmination of years of hard work, dedication, and focus on a particular topic and research question.
The average length of a PhD dissertation submitted at the University of Minnesota w as been created by Marcus Beck :

Generally, theses and dissertations in the mathematical sciences, economics, and biostatistics are usually brief due to utilizing mathematical equations to substantiate their findings as opposed to illustrations and extended explanations.
On the contrary, English, communication studies, political science, history and anthropology normally consist of more pages and words since they require a larger number of words to verify and go into detail regarding their results.
The dissertation should demonstrate the student’s mastery of their chosen field of study and their ability to communicate their findings effectively.
A thesis should also present an innovative contribution to the existing body of knowledge on the subject.
The dissertation should be organized in a logical manner, with an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion and conclusion sections.
Furthermore, it should adhere to all relevant academic conventions for structure, citation style, grammar and referencing.
Ultimately, it should be a piece of work that reflects the student’s academic excellence and future potential as a researcher in their chosen field.
The success of your PhD is also very much dependent on your supervisor. Let’s take a look at the most important things about choosing your PhD supervisor.
The importance of PhD supervision
Choosing a PhD supervisor is an essential part of the research process.
They act as a mentor and provide guidance to help guide their student’s research, ensuring that it meets the necessary standards required by the University.
The supervisor also provides support in developing research questions and methods, and can give feedback on drafts of your thesis and peer-reviewed papers.
This feedback helps keep the student on track with their project and prevents costly mistakes in the future.
A great supervisor also acts as a sounding board; they can discuss ideas with their student, helping them to develop deeper understanding of their topic.
Ultimately, a good supervisor can make all the difference in achieving successful results from a PhD program. With their experience and knowledge, they can ensure that students are tackling their projects in an efficient and effective manner.
If you want to know more about choosing a PhD supervisor check out my YouTube video below.
How to become a PhD candidate
Becoming a PhD candidate is a rigorous process that requires dedication and hard work just to get admitted to the degree.
Here are the steps that you need to complete to become a PhD student or candidate:
- The first step is to complete a bachelor’s degree in the field you wish to pursue your research in.
- Next, you will need to apply for admission into a PhD program, which typically involves submitting an application, providing letters of recommendation from professors or employers, and often taking an entrance exam.
- Once accepted, you must then create a research proposal outlining your proposed area of study and submit it for approval by the university’s Graduate Studies Committee.
Finally, after completing any required courses and passing an oral examination to defend your PhD, you can be officially awarded the title of PhD candidate and begin your dissertation research.
Will a PhD degree give you an advantage career-wise
Having a PhD degree is a mark of distinction that can give you an advantage career-wise.
As a degree holder, employers and recruiters will recognize your level of academic achievement and that you have made a significant commitment to the study and research of your chosen field.
With a doctorate, you can open up more opportunities for higher-level positions with increased responsibilities and better pay.
You may also be able to pursue research or teaching positions in universities, as well as leadership roles in private businesses.
A PhD degree can also provide you with the skillset to become an expert in your field, allowing you to become an authority on certain topics.
How long does it take to finish a PhD?
Completing a PhD, or Doctorate, is no small feat.
On average, it can take four to seven years of hard work and dedication to finish one. I know of one PhD student who took 10 years to complete his PhD.
The length of time it takes to complete a PhD varies depending on the field of study and the
Regardless of the field, completing a PhD is an impressive accomplishment that requires tremendous effort over an extended period of time.
Do you need to write a full dissertation as a Ph.D. Student?
As a Ph.D. student, it is almost always necessary to write and present a dissertation as part of your doctoral program. Although, it is now common for a PhD to be awarded on the basis of publication in peer-reviewed journals.
A dissertation is an original research paper in your chosen field of study that you must complete in order to obtain a doctorate.
Most doctoral programs will require students to complete their dissertation and defend it orally before they are awarded their Ph.D.
The research topic must be approved by the doctoral committee and should reflect the student’s understanding of the chosen field of study while presenting new findings or theories within that field.
Once completed, the dissertation must be defended at an oral examination before a panel of faculty members from the university who specialize in that particular field of study.
The successful completion of this oral defense allows for students to progress towards obtaining their doctorate degree and fulfill all requirements for graduation from the PhD program.
Can you complete your PhD degree online?
Completing a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degree online is becoming increasingly popular. But should you do it? Here is my YouTube video about finishing your PhD online:
With the advancement of technology, students can now study from their own home and have access to quality education with no need to travel or attend physical classes.
With an online PhD program, you can make progress towards your doctor of philosophy degree at your own pace while still being able to maintain a work/life balance. However, it comes with some drawbacks that include its perceived prestige.
Part of the PhD experience is interacting with your peers and having rigourous academic debate. Make sure that you choose an online PhD program which allows you to interact significantly with your fellow students and helps you be part of your field.
Attend conferences, seminars, and other academic presentations so that you don’t miss out on any of the important aspects of training for academia.
Wrapping up
This article has been through everything you need to know about what a PhD student is and what they do.
Deciding to do a PhD can be a very challenging decision. Many people make the decision without really understanding or knowing what a PhD student is or does.
It is a very challenging time in many people’s lives as they are embarking on a multi-year research challenge. This failure and overcoming issues are the number one factor in people deciding that they are going to leave academia stop
Speaking to current PhD students, choosing your supervisor carefully, and ensuring that you are actually interested in the research questions that you will be investigating go a long way in ensuring that you get the most out of your PhD experience.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider


- Youth Program
- Wharton Online
Wharton Stories
7 resources to help phd students succeed on their doctoral journey.
It takes a village and a variety of skills to succeed in the doctoral world. Here are a few of the many resources Wharton Doctoral Programs offers to help.
Like most of our doctoral students, perhaps you’re preparing to go into academia after completing your PhD. Being a professor and researcher today often involves opportunities to share your research with a larger audience than a classroom of students. The doctoral journey is meant to prepare you with the wide array of skills you’ll need to be effective whether you’re in front of the classroom or a conference stage.
That includes the polish to present and speak publicly with ease, the writing and communication skills to craft your dissertation and journal articles, the analytical know-how to research thoroughly and gather meaningful data, and the ability to teach — colleagues, pupils, or the general public, whatever the case may be. And, if you have family, you’ll need support in getting them through this journey with you.
Wharton Doctoral Programs offers a wide range of resources to help you thrive in the PhD program and prepare you for life beyond it. Here are a few of the top Wharton resources our students have highlighted as most beneficial:
1. 5 Slides 5 Minutes
Researchers often have the opportunity to share their work with a larger audience through social media and mass media outlets — but it requires nuanced communication skills. How do you take complex findings and communicate them to a general audience concisely without oversimplifying the message?
That’s the focus of 5 Slides 5 Minutes. Launched in 2014, this low-stakes, high-potential event enables PhD students to present an abstract to students, faculty, and staff to practice engaging non-experts in their research topic. Students receive an invitation to participate via email from the Doctoral Programs Office.
After students present, they can work with Wharton Communications Program to review their presentation and get tips on how to improve their communication skills. Wharton’s renowned faculty also share valuable insights with students about these presentations.
“We focus on individuals. We help them convey their research content most effectively given their style and personality,” said Lisa Warshaw, Director of the Wharton Communications Program.
2. Dissertation Boot Camp
The name might sound intimidating, but some students think of Dissertation Boot Camp as a two-week writers’ retreat. Hosted twice a year by the Graduate Student Center, it’s designed for students who have dissertation status but haven’t presented their proposal yet.
The camp offers an environment and support for intense, focused writing time as well as a review on the steps, deadlines, and University policies. Limited to 20 students, the small group gives writers a chance to make connections with others who are going through the dissertation process and provides participants with the structure and motivation to overcome typical roadblocks along the way.

3. Wharton Communications Program
The Wharton Communication Program helps Wharton PhD students become more effective communicators and thus better presenters, public speakers, and writers — all critical skills in academia. All doctoral students are provided with access to on-site, one-on-one writing coaching during the academic year.
Wharton PhD students are required to attend two workshops: First-Year Communications Workshop in the fall and First-Year Writing Workshop in the spring. The skills-based approach adopted in the workshops helps students develop their personal style and strengthen their confidence as communicators.
Through multiple practice opportunities, video recording of speeches, and rigorous feedback, the program provides students with a thorough foundation in communication theory and for doctoral students, focuses on research presentations and job talks.
4. Teacher Development Program Workshop
Offered in conjunction with the Center for Teaching and Learning , the Teacher Development Program is a four-session course. It gives doctoral students a foundation in core teaching practices to support their teaching at Penn.
By helping with presentation skills and academic job placement, the workshop prepares students to become faculty in the future. Ian Petrie , Senior Associate Director, Center for Teaching and Learning described the workshop as “a collective, collaborative program.” Each week features “microteaching” demonstrations, where participants conduct a brief lesson and get feedback from their peers and the directors.
The intent is that faculty and graduate students will engage and learn from each other to master fundamental teaching methods. “Every PhD student can leave the program having gained some new tools for teaching,” Petrie said. This exchange happens when doctoral students observe “talented colleagues from other departments to get a glimpse of how they teach.”
Students also have the opportunity to enroll in the CTL Teaching Certificate program to hone teaching skills and grasp a commitment to developing as teachers.
“I’d like everyone to come out of the experience feeling more confident about their skills as an instructor or presenter,” Petrie said. “Anything I can do to support doctoral students in achieving their goals is extremely gratifying.”
5. Wharton Research Data Services (WRDS)
With more than 50,000 corporate, academic, and government users, Wharton Research Data Services (WRDS) is the global gold standard in data management, research analytics, and thought leadership. Researchers at more than 450 institutions in 36 countries across the globe depend upon this award-winning research platform and business intelligence tool — and researchers are doing the work to grow it right here on Wharton’s campus.
“The fact that the people who create the data, research analytics, and tools are here is super important,” said Prof. Cathy Schrand, Vice Dean of Wharton Doctoral Programs. “I’ve had early access to WRDS before it even became available to other subscribers. Top universities all over the world that have subscriptions to WRDS may only have access to certain elements of it, but we have access to all of it and it’s here on site which does provide an advantage.” The platform allows researchers to access more than 350 terabytes of data in one location that spans across multiple disciplines, including accounting, banking, economics, ESG (environmental, social, and governance), finance, health care, insurance, marketing, and statistics. “WRDS is by far the most important source of datasets for academic researchers. As a Wharton PhD student, you automatically get unrestricted access to every one of these databases,” said Itamar Drechsler, associate professor of finance at Wharton and NYU’s Stern School of Business, who has experience on both sides of the classroom – he earned his PhD from Wharton in 2009.
6. Wharton Behavioral Lab
A shared resource for all Wharton faculty, the Wharton Behavioral Laboratory (WBL) provides a variety of services that support data collection for behavioral research on business-related topics. The primary goal is to enhance the research productivity of Wharton faculty by minimizing the operational costs, both time and money, of conducting research. With two locations — one in Steinberg Hall Dietrich Hall and another in Jon Huntsman Hall, doctoral students can gather original data through lab experiments and panels, instead of using secondary data created by others. Each year, the lab collects about 23,000 subject hours of data. Research from WBL can consistently be found in national and international publications such as the Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, the Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the Journal of Neuroscience, Psychology, and Economics, and the Journal of Business Ethics .
7. Support for Families
For some PhD students, attending Wharton means relocating their families to a new city. To help students and their families ease the transition to PhD life, the Wharton Doctoral Program Office hosts the Maternity/Paternity Workshop , an annual event that talks about the resources available to PhD students with families.
Here are a couple of the key resources they highlight in the workshop:
- The Doctoral Programs Office allows eligible students to apply for up to one year of additional school-level funding beyond their allotted funded year. Furthermore, students are eligible for up to eight weeks of time-off for childbirth and adoption and have the option of taking unpaid Family Leave of Absence.
- At Penn, the Family Resource Center provides additional resources and facilities, such as a children’s playroom and two private lactation rooms, which cater to the needs of students with families. The Center also has two grant programs for PhD students to help offset the cost of childcare and family expenses, and health insurance for dependents.
- Wharton Doctoral Partners & Families is a student-run online resource created to communicate the resources at Penn and Philadelphia to partners and families. Its mission is to empower members to transition and settle into their new lives.
Posted: November 6, 2018
- Admissions and Applying
- The Wharton School
- Work/Life Balance
Doctoral Programs
Start your doctoral journey.
Whether you’re just starting your research on PhD programs or you’re ready to apply, we’ll walk you through the steps to take to become a successful PhD candidate.
Deciding to get a PhD
You might be surprised to find out what you can do with a PhD in business.
Is an Academic Career for You ? What Makes a Successful PhD Student
Preparing for the Doctoral Path
The skills, relationships, and knowledge you need to prepare yourself for a career in academics.
How the PhD Program Works How to Become a Successful PhD Applicant
Choosing the right program
What’s the difference between PhD programs? Find out how to choose one that fits your goals.
What to Consider When Choosing a Doctoral Program
Starting an application
Tips for a successful application process.
Application Requirements Preparing Your PhD Application
Related Content

Data Drives Humanity at Wharton & Penn Engineering’s Women in Data Science Conference

Social Impact Investing Professional Finds Strong Interest in Field at Wharton

Why a Former White House Deputy Director Chose EMBA

Prof. Benjamin Keys on the Intersection of Real Estate and Policy

Closing the Tenure Gap for Business Faculty of Color

Research Spotlight: When Gender Is Central

How This Tech Manager Transitioned from Research Consumer to Research Producer in Wharton’s PhD Program

How Prof. Senthil Veeraraghavan Balances Technology and Engagement in the Classroom

Get Ready: Second-Year MBA Students Give Advice On Wharton’s Team-Based Discussion (TBD)

MBA Student Gives Interviewing Advice From the Other Side of the Table

MBA Student Aims to Open Financial Opportunities in the Middle East

How Mentorship Enables the Transition from PhD Student to Research Colleague

How This Doctoral Student Began Her PhD Journey as a Wharton Undergrad

Diversity and Racial Equity in Investing: Conversations with Industry Leaders and Researchers

Meet Wharton EMBA Class Manager Jennifer Craig
- Share on twitter
- Share on facebook
What’s in a name? For PhDs, everything
Are you a student, a candidate or something else whatever title you choose can have an impact on how academia views you and how you see yourself, argues jenny mak.
- Share on linkedin
- Share on mail

As PhDs, we often introduce ourselves and our research to different people. But have you thought about the specific words you use? Do you call yourself a “PhD researcher”, “PhD candidate” or “PhD student”? Being alert to these labels can impact how you conduct your PhD.
These labels can have different associations specific to the university and country you are in, especially regarding the choice of calling yourself a “candidate” or a “student”.
For instance, in the US, “PhD candidate” can signify a student who has completed all of the academic requirements for their degree, except their dissertation. Here, the term acts as a milestone.
In the Netherlands, “PhD candidate” can act as a method of differentiation, because the candidate is not considered a student but a paid staff member of the university.
Alternatively, if you are undertaking a finite duration PhD, like a three or four-year programme in the UK, the titles “PhD candidate” or “PhD student” do not tend to suggest significant differences in status, they instead become descriptive.
And it is in the UK context that we need to reflect on how this descriptive tool can affect our self-identification: are these labels supporting our growth as academic researchers or holding us back?
The words we use can reveal how we see ourselves. In turn, our perceptions of ourselves can determine our actions.
Self-identifying as a “PhD student” might embody modesty – someone who is an eternal learner. But, for some, could hinder them from realising their independence as a scholar. Especially considering that PhD scholars often have to defend their ideas before critics, such as supervisors: people who are not really teachers in the conventional sense of being people from whom we expect instruction.
Self-identifying as a “PhD candidate” can cement this independence, as “candidate” suggests being deemed suitable for a certain level of study, often determined through some form of examination in an upgrade process. But some might find “candidate” too neutral or reliant on external validation to be effective for self-actualisation.
Meanwhile, self-identifying as a “PhD researcher” pre-upgrade might seem presumptuous. But this label could induce feelings of responsibility and a determination to realise research projects, helping scholars identify actionable academic tasks to this end.
Whichever title you prefer, I believe it is your right to choose how you see yourself. Indeed, when you introduce yourself to others, you are also re-introducing you to yourself.
Whether these labels should change at an institutional level, however, is another question. Talking to my fellow PhDs in the UK, it would appear the debate here lies mainly between using the terms “student” or “researcher” – as the term “candidature” doesn’t carry as much weight in the UK. This is where things get tricky.
Being a “PhD student” at a university formalises the relationship between you and the institution (perhaps more explicitly than if you were a “PhD researcher”) in terms of university accountability to you, the student and the student’s code of conduct. Students pay tuition fees, as do local and international “PhD students” – except they also have access to scholarships and visa sponsorship. Also, the university supports “PhD students” to conduct their research, offering high quality resources and an extensive network to a global research community.
However, in issues like fair employment and anti-casualisation the term “student” might prove limiting as it implies a junior standing. The lens through which institutions view the value of PhDs’ contributions – raising the research profile of the university internationally, developing original knowledge, providing research and teaching support – could also be diminished with this title. This, in turn, influences institutional practices, including university support for PhD professionalisation.
The varying contexts where institutions might choose to use the term “PhD researcher” instead of “PhD student” need to be part of a wider debate. It is important to recognise that these labels and their perceptions have material impact, affecting the “vitality and sustainability” of the university research environment – which carries a weighting of 15 per cent in the research excellence framework .
But interchanging “PhD researcher”, “PhD student”, and “PhD candidate” at an institutional level will not have real significance if perceptions are not adjusted accordingly.
This readjustment must also be an internal one, in the attitudes we PhDs have towards ourselves. So ask yourself, when you first meet someone, are the words you use to present yourself empowering, effective and self-actualising? If they aren’t, can you do better?
This blog is based on a post originally published for the University of Warwick’s PhD Life blog.
Jenny Wing Haang Mak is a PhD researcher and tutor in the department of English and comparative literary studies at the University of Warwick .
Register to continue
Why register?
- Registration is free and only takes a moment
- Once registered, you can read 3 articles a month
- Sign up for our newsletter
Or subscribe for unlimited access to:
- Unlimited access to news, views, insights & reviews
- Digital editions
- Digital access to THE’s university and college rankings analysis
Already registered or a current subscriber? Login
Related articles

PhDs without tears: how academics can help ease students’ minds
With many doctoral candidates unhappy and reporting mental health problems, Emma Pierson suggests ways supervisors could reduce pressures

If you love research, academia may not be for you
Dutch figures show just how little time professors get for their own research. It may be easier to pursue your intellectual interests outside the university system, says THE reporter David Matthews

Students’ view of PhD’s value drops as course progresses
Satisfaction with postgraduate research declines significantly over course of programme, survey reveals
Featured jobs

What is a PhD?
- Types of Doctorates
- A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) is the highest globally recognized postgraduate degree that higher education institutions can award.
- PhDs are awarded to candidates who undertake original and extensive research in a particular field of study.
- Full time PhD programmes typically last three to four years, whilst part time PhD programmes typically last six to seven years.
- A PhD can lead to an academia teaching role or a career in research. A PhD can also equip you with skills suitable for a wide range of jobs unrelated to your research topic or academia.
Definition of a PhD – A Doctor of Philosophy (commonly abbreviated to PhD , Ph.D or a DPhil ) is a university research degree awarded from across a broad range of academic disciplines; in most countries, it is a terminal degree, i.e. the highest academic degree possible.
PhDs differ from undergraduate and master’s degrees in that PhDs are entirely research-based rather than involving taught modules (although doctoral training centres (DTCs) offer programmes that start with a year of lecture-based teaching to help develop your research skills prior to starting your project).
In most English-speaking countries, those that complete a PhD use the title “Doctor” (typically abbreviated to Dr) in front of their names and are referred to as such within academic and/or research settings. Those that work in fields outside of academia may decide not to use the formal doctor title but use post-nominal letters (e.g. John Smith PhD); it’s unusual though for someone to use both the Doctor title and post-nominal letters in their name.
PhD vs Doctorate
A PhD and a professional doctorate are both research-based terminal degrees.
However, where a PhD focuses on original research mostly around theoretical concepts, a professional doctorate focuses on examining existing knowledge to solve real-life, practical problems.
While there is much crossover between the two, a PhD is generally better suited for an individual to wants to advance the knowledge and understanding in their field, and a professional doctorate degree is better suited to a working professional who wants to better be able to apply knowledge and understanding to their field.
What Are the Entry Requirements for a PhD?
To be accepted on to a PhD programme, students usually need to hold at least a high ( 2:1 and above ) undergraduate degree that is related to the field of research that they want to pursue. A PhD candidate may also be expected to hold a Master’s degree , however, this does not mean you must have one, as it is still possible to enrol into a PhD without a Master’s .
Self-funded courses may sometimes be more relaxed in relation to entry requirements . It may be possible to be accepted onto a self-funded PhD programme with lower grades, though these students typically demonstrate their suitability for the role through professional work experience.
Whilst a distance learning project is possible , most PhD candidates will carry out their research over at least three years based at their university, with regular contact with two academic supervisors (primary and secondary). This is particularly the case for lab-based projects, however, some PhD projects require spending time on-site away from university (e.g. at a specialist research lab or at a collaborating institution abroad).
How Long Does a PhD Take?
Typically, full-time PhDs last 3-4 years and part-time PhDs last 6-7 years. However, at the discretion of the university, the thesis writing-up period can be extended by up to four years.
Although most doctoral programmes start in September or October, they are generally much more flexible than taught-courses and can start at any time of the year.
How Much Does a PhD Cost?
Tuition fees for UK and EU students vary between £3,000 and £6,000 per year, with the average tuition fee of £4,712 per year for 2023/24 programmes.
Tuition fees increase considerably for international students, varying between £16,000 to £25,000 per year, with an average tuition fee of £19,600 per year .
Nonetheless, most students will secure PhD funding in the form of studentships, scholarships and bursaries to help pay for these fees. These funding opportunities can either be partial, which cover tuition fees only, or full, which cover both tuition fees and living expenses.
UK national students can also apply for Doctoral Loans from Student Finance England if they are unable to secure funding.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
What Does a PhD Involve?
To be awarded a PhD, a doctoral student is required to produce a substantial body of work that adds new knowledge to their chosen field.
A PhD programme will typically involve four key stages:
Stage 1: Literature Review
The first year of a PhD involves attending regular meetings with your supervisors and carrying out a search on previously published work in your subject area. This search will be used to produce a literature review which should set the context of the project by explaining the foundation of what is currently known within the field of research, what recent developments have occurred, and where the gaps in knowledge are. In most cases, this will be an extension of your research proposal should you have produced one as part of your application. The literature review should conclude by outlining the overarching aims and objectives of the research project. This stage of setting achievable goals which are original and contribute to the field of research is an essential first step in a successful PhD.
The supervisor is the main point of contact through the duration of a PhD – but remember: they are there to mentor, not to teach, or do it for you . It will be your responsibility to plan, execute and monitor your own work as well as to identify gaps in your own knowledge and address them.
Stage 2: Research
The second year (and prehapse some of your third year) is when you work on your research. Having identified novel research questions from your review of the literature, this is where you collect your data to help answer these questions. How you do this will depend on the nature of your doctoral research: for example, you may design and run experiments in a lab alongside other PhD students or visit excavation sites in remote regions of the world. You should check in regularly with your supervisors to update them and run any ideas or issues past them.
Have the structure and chapters of your thesis in mind as you develop and tackle your research questions. Working with a view of publishing your work will be very valuable later on.
Stage 3: Write up of Thesis
The next key stage of a PhD is writing a doctoral thesis , which typically takes from anywhere between three months to one year. A thesis is a substantial body of work that describes the work and outcomes of the research over the previous two to three years. It should tell a detailed story of the PhD project – focusing on:
- The motivations for the research questions identified from the literature review.
- The methodologies used, results obtained, and a comprehensive analysis and discussion of the findings.
- A detailed discussion of the key findings with an emphasis on the original contributions made to your field of research and how this has been impactful.
There is no universal rule for the length of a PhD thesis, but general guidelines set the word count between 80,000 to 100,000 words.
For your thesis to be successful, it needs to adequately defend your argument and provide a unique or increased insight into your field that was not previously available.
Stage 4: Attending the Viva
A viva voce , most commonly referred to as just a ‘ viva ‘, is an interview-style examination where the PhD student is required to engage in a critical appraisal of their work and defend their thesis against at least two examiners. The examiners will ask questions to check the PhD student has an in-depth understanding of the ideas and theories proposed in their thesis, and whether they have developed the research skills that would be expected of them.
The viva is one of the final steps in achieving a PhD, and typically lasts at least two hours, but this duration can vary depending on the examiners, the university and the PhD project itself.
Once you have done the viva – you’re on the home stretch. You will typically be asked to make some amendments to your thesis based on the examiner’s feedback. You are then ready to submit your final thesis for either:
- PhD – If you pass the requirements you will be awarded a PhD degree (most common outcome),
- MPhil – If you failed to meet requirements for a PhD, you may be downgraded to an MPhil degree (uncommon outcome),
- Fail – No award is given, typically for cases of plagiarism (extremely uncommon outcome).
What Is It Like to Undertake a PhD?
We’re often asked what it is like to undertake a PhD study. Unfortunately, this isn’t a simple answer to this question as every research project is different.
To help give insight into the life of a PhD student, we’ve interviewed PhD students at various stages of their programmes and put together a series of PhD Student Interviews . Check out the link to find out what a PhD is like and what advice they have to offer you.
What Are the Benefits of A PhD?
A PhD is the highest globally recognised postgraduate degree that higher education institutions can award. The degree, which is awarded to candidates who demonstrate original and independent research in a particular field of study, is not only invaluable in itself, but sets you up with invaluable skills and traits.
Career Opportunities
First, a PhD prepares you for a career in academia if you wish to continue in this area. This takes form as a career in the Higher Education sector, typically as a lecturer working their way to becoming a professor leading research on the subject you’ve studied and trained in.
Second, a PhD also enables the opportunity for landing a job in a research & development role outside of the academic environment. Examples of this include laboratory work for a private or third sector company, a governmental role and research for commercial and industrial applications.
Transferable Skills
Finally, in possessing a PhD degree, you can show to employers that you have vital skills that make you an asset to any company. Three examples of the transferable skills that you gain through a PhD are effective communication, time management, and report writing.
- Communication – presenting your work in written and oral forms using journal papers and podium presentations, shows your ability to share complex ideas effectively and to those with less background knowledge than you. Communication is key in the professional environment, regardless of the job.
- Time management – The ability to prioritise and organise tasks is a tremendous asset in the professional industry. A PhD holder can use their qualification to demonstrate that they are able to manage their time, arrange and follow a plan, and stick to deadlines.
- Report writing – Condensing three years of work into a thesis demonstrates your ability to filter through massive amounts of information, identify the key points, and get these points across to the reader. The ability to ‘cut out the waffle’ or ‘get to the point’ is a huge asset in the professional industry.
Aside from the above, you also get to refer to yourself as a Doctor and add fancy initials after your name!
What Can I Do After a PhD?
One of the most desirable postdoctoral fields is working within independent Research and Development (R&D) labs and new emerging companies. Both industries, especially R&D labs, have dedicated groups of PhD graduates who lead research activities, design new products and take part in crucial strategic meetings. Not only is this a stimulating line of work, but the average salaries in R&D labs and emerging start-ups are lucrative. In comparison, an undergraduate with five years of experience within their given field will, on average, likely earn less than a new PhD graduate taking on a R&D position.
It’s a common misunderstanding that PhDs only opens the door for an academic career such as university lecturers and training providers. Although obtaining a PhD opens these doors, the opportunities extend far beyond educational roles. In fact, recent data from the UK’s Higher Education Statistics Agency (HESA) indicates only 23% of PhD graduates take a position in educational roles . This low percentage is primarily because PhD graduates have a wide range of skills that make them suitable for a broad spectrum of roles. This is being seen first hand by the increasing number of PhD graduates who are entering alternative roles such as research, writing, law and investment banking.
How Do I Find a PhD?
We appreciate that finding a PhD programme to undertake can be a relatively daunting process. According to Higher Education Student Statistics , over 22,000 PhDs were awarded in 2016/17 within the United Kingdom alone. Clearly there are a huge number of PhD programmes available. This can sometimes be confusing for prospective doctorates, particularly when different programmes are advertised in different places. Often, it is difficult to know where to look or where to even start. We’ve put together a list of useful sources to find the latest PhD programmes:
- A great place to start is with our comprehensive and up-to-date database of available PhD positions .
- Assuming you are still at university, speak to an existing PhD supervisor within your department.
- Attend as many postgraduate open days as you can. Whilst there, speak to current PhD students and career advisors to get an awareness of what PhDs are on offer.
- Visit the postgraduate section of university websites and the PhD Research Council section of the UKRI website.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

- Call: +32 485 729 359
- Email: EDAMBA EXECUTIVE SECRETARY

PhD students and PhD candidates: Know the Difference
Phd students and phd candidates: know the difference feb 20, 2023.
Who is a PhD Student?
A PhD student refers to an individual who has registered for a doctoral degree program. These students, often known as learners, may complete their coursework on campus, online, or in both settings. Students must fulfil a minimum number of academic credits and pass prerequisite tests to enroll in a standard PhD program.
Also Read, FIVE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW BEFORE YOU START A PHD
Once this phase is completed, the student progresses to the dissertation phase, which involves research, writing, and defense.
The distinction between a PhD student and a PhD candidate is that the former is still undertaking coursework and has not yet commenced the dissertation process or passed the qualifying exams, although they may be in the process of doing so.
PhD students' education is defined by a predetermined structure, which also sets forth their schedules.
Who is a PhD Candidate?
A person who has finished all the necessary coursework and passed their qualifying tests is considered a PhD candidate. Once this goal is met, the individual gains the unofficial status of all but the dissertation (ABD).
In general, PhD students eagerly anticipate the transition from PhD student to PhD candidate since it will provide them with the opportunity to focus on their original research and start writing their dissertation with the help of their committee advisors.
Know more about Dissertation and Thesis and what are the major differences between these two ,
PhD student vs Candidates: What Are the Main Differences?
The main distinction between a PhD candidate and a PhD student is that as a student, one is still engaged in course-related activities such as attending classes, writing tests and exams, and completing assignments. On the other hand, becoming a PhD candidate puts you one step closer to earning a doctoral degree and adding the title PhD to your name after passing the tests and writing your thesis . It is important to note that you have to be a student before you become a candidate .
While the differences between being a Ph.D. student and a Ph.D. candidate may appear slight, they carry a lot of weight. Transitioning to a Ph.D. candidate can feel like stepping into a new realm, with new demands and expectations. Despite having completed their coursework, many Ph.D. candidates choose to take self-directed study courses with faculty members whose research aligns with their own, as it can help guide their own research and even influence their dissertation.
If you're part of the PhD community or considering pursuing a doctorate degree, it's important to understand the distinction between being a PhD candidate and a PhD student. Knowing where you stand in your academic journey can help you make informed decisions and set realistic expectations. Keep learning and growing as a PhD researcher , and remember to seek guidance and support from your peers and advisors along the way.
Read more about the EDAMBA PhD Students Forum
Read more about the EDAMBA Summer Research Academy
EDAMBA aims to achieve its mission through three pillars of activity: 1. The Annual Meeting 2. The Summer Research Academy 3. The EDAMBA-EIASM Consortium of Doctoral Supervision
Edamba engages in global collaboration across networks 1. european code of practice 2. equal 3. aacsb, enquiry form.
Select language

Graduate School of Life Sciences
Profile and research responsibilities of the phd candidate.
The points below reflect our vision on your academic responsibilities as a junior researcher.
- You are proactive and undertake the necessary efforts to ensure good progress in your doctoral research project.
- You actively engage in setting up the research questions in your doctoral project.
- You are jointly responsible for developing the research methodology that will be used to address your research questions.
- You are responsible for planning, implementing and, where necessary, modifying your research.
- You are responsible for interpreting and analysing your research results, to frame your research in a broader context, and to reflect critically on the research process.
- Together with your supervisory team, you ensure that you communicate and share your doctoral research results (e.g., in publications and/or other scientific communications).
- You are aware of, and adhere to, the generally accepted norms of responsible conduct of research .
- You ensure that data generated during your research are always available upon request. In this matter, you abide by the principles of research data management , according to the current methods in the research unit and of Utrecht University, UMC Utrecht or relevant other institution policy concerning research data management.
- You respect the intellectual property rights relating to concepts and findings of Utrecht University, UMC Utrecht or relevant other institution and take proper care of materials and equipment.
- Together with your supervisory team, you compile a plan for your doctoral programme (i.e., the Training and Supervision Agreement ) and maintain a Training Portfolio. Your plan will consist of research-related training and activities, as well as the development of transferable competencies you many need. These will help advance the quality and efficiency of your research and prepare you for a professional career. You ensure that the activities in the context of the doctoral program are completed within the proposed deadlines.
- You are responsible for keeping an eye on your progress and for organising your annual PhD progress meetings .
You are jointly responsible for the efficient progress of your PhD journey and endeavour to finalise your doctoral thesis within a reasonable timeline. If you have funding, it is recommended not to exceed the funding term.
Utrecht University Heidelberglaan 8 3584 CS Utrecht The Netherlands Tel. +31 (0)30 253 35 50
Current students
- Staff intranet
- Find an event
- Graduate qualities
Researcher graduate qualities for the PhD
The researcher graduate qualities will assist you to develop the skills and knowledge you need to become an exceptional PhD researcher and get career-ready.
The University of Sydney has developed a set of graduate qualities to define and enrich the PhD, and support you to get ready for a post-doctoral career in industry or research.
The researcher graduate qualities focus on building deep disciplinary expertise and a range of broader, transferrable skills that will enhance your research activities and career possibilities.
The eleven qualities cover cultural competence, interdisciplinary effectiveness, professional, ethical, personal identity, influence, critical thinking and problem-solving, communication, information and digital literacy, inventiveness, engagement and project planning and delivery.
From 2021 onwards, early career researchers will have access to development activities including coursework, mentoring programs, workshops, global mobility experiences, self-reflection exercises and competitions, challenges or projects.
What this means for your candidature
The researcher graduate qualities have been designed to help guide students and supervisors through a student's PhD candidature. During your supervision meetings, the graduate qualities will provide you with a point-of-reference to contemplate your achievement of skills and experience as your candidature progresses, and to have a conversation with your supervisor about further development opportunities or training you may need while you complete your thesis project.
How to update your Research graduate qualities record
After your supervision meetings, you will need to log your graduate qualities discussion in RECS. Log into RECS , select ‘My project’, then ‘Researcher graduate qualities’. Here you can review previous submission by selecting the relevant date or you can add a new record. Once you have completed a new record, there is an option to send to your supervisor for comment.
The eleven qualities
Researcher graduate qualities for the PhD | Purpose |
|---|---|
Deep expertise | To possess expert, world-standard knowledge in an area of specialisation, a mastery of relevant research methods and the capability to contribute to scholarship and knowledge discovery. |
Cultural competence | To display high levels of cultural competence and embody best practice with regard to cultural competence in research. |
Interdisciplinary effectiveness | To work effectively in interdisciplinary settings to develop a broader perspective, innovative vision and the capacity to work effectively within national and international research and innovation systems. |
Professional, ethical, personal identity | To exercise integrity, confidence and resilience. |
Influence | To be professionally and socially responsible and make a positive contribution to society, and to recognise and promote the implications of own research in a broader societal context. |
Researcher graduate qualities for the PhD - broader skills | Purpose |
|---|---|
Critical thinking and problem-solving | To display high-level capabilities in critical thinking and problem-solving and a commitment to lifelong learning and discovery. |
Communication (oral and written) | To have excellent oral and written communication skills relevant to specialist and general audiences. |
Information and digital literacy | To evaluate and utilise contemporary digital tools, resources and technologies. |
Inventiveness | To be innovative and creative in response to novel problems, and to be willing to take risks. |
Engagement | To display high-level capabilities in disseminating research, and build an understanding of one's own research in a broader context by participating in engagement with end-users of research. |
Project planning and delivery | To plan, manage and deliver research projects effectively. |
- Website feedback
Your feedback has been sent.
Sorry there was a problem sending your feedback. Please try again
You should only use this form to send feedback about the content on this webpage – we will not respond to other enquiries made through this form. If you have an enquiry or need help with something else such as your enrolment, course etc you can contact the Student Centre.
- Find an expert
- Media contacts
Student links
- How to log in to University systems
- Class timetables
- Our rankings
- Faculties and schools
- Research centres
- Campus locations
- Find a staff member
- Careers at Sydney
- Emergencies and personal safety

- Accessibility
Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!
Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
Phd candidate vs student, published by steve tippins on may 19, 2020 may 19, 2020.
Last Updated on: 2nd February 2024, 03:03 am
You make the transition from PhD student to PhD candidate after you complete all your coursework and your comprehensive exams (if required). A PhD candidate’s sole task is to conduct their research and write their dissertation.
In other words, a PhD student is still completing their coursework. They could be on the first day of their PhD program. A PhD candidate has completed all of the requirements for their degree except their dissertation (yes, that’s the infamous “ all but dissertation ” status).
PhD candidacy means you’re a PhD in training. Now you’re ready to spread your wings a little–with some guidance.
Your time as a PhD candidate is your chance to demonstrate that you are ready to be an independent scholar. It’s also your chance to screw up and have that be okay–to have support. Your committee will help you. Since it’s the first time you’ll go through the process of creating and performing a study on your own, there’s no reason to believe you’ll be perfect at it. That’s why the process is designed so that your committee can give you guidance.
But besides the simple definition above, what are the implications of being a PhD candidate vs student? Turns out, there are many important differences. Without keeping these in mind when you become a PhD candidate, it’s easy to spin out and get off track and not understand why.
PhD Candidate vs Student: What Are the Differences?

While “PhD Student” and “PhD Candidate” are both steps on the journey to getting a PhD, there are significant differences between them. Here are some of the differences between PhD candidate vs student.
Lack of Structure
When you’re doing coursework, there is structure; there are assignments and deadlines. Of course, in graduate coursework teachers aren’t on top of you to turn in assignments like they would be in an undergraduate program. However, there is a deliverable (final project, test, etc) that you have to complete each quarter. You have things to complete by a certain time in order to move forward.
Once you become a candidate, there’s no syllabus and there are no due dates. It’s completely up to you to move forward in the process.
Some people find it hard to make the transition to the lack of structure that comes with being a PhD candidate.
Academic Writing
Academic writing skills become really important when writing your dissertation –more important even than they were during the coursework phase of graduate school. Academic writing is essentially a new language, with very specific meanings and requirements.

For example, you can’t just say “people believe x or y,” you have to say who they are and how you know that, giving citations to back it up. Many words (like “significant”) have very specific meanings and can’t be used the way you might use them in speech.
As a PhD student, your professors should be teaching this language to you, so that as a PhD candidate, it will come as second nature.
How Many People Do You Have to Keep Happy?
Here’s another difference between being a PhD student vs PhD candidate: as a PhD candidate, you reduce the number of people that you have to keep happy.
As a student, you have to keep in mind the requirements from each professor teaching your classes, as well as matriculation requirements from the department, preferences and advice given by your advisor, and even the research interests of the people for whom you’re writing papers.
Over 50% of doctoral candidates don’t finish their dissertations.
Once you become a candidate, it’s just your committee that you have to keep happy, meaning that those are the people who will hold you accountable and outline the requirements for completion of the degree. For that reason, you’ll want to choose your committee members with care.
Hopefully, by the time you need to choose your committee, you’ll have encountered professors who are intrigued by your research interests and with whom you feel personally and professionally compatible.
Freedom to Choose

When you become a PhD candidate, you get to work on what you want to work on. You can pursue the topic that interests you instead of whatever goes with the course you’re in. It’s a time to really apply all those skills you were accumulating in the classes. For example, the statistical procedures you learned in stats classes and theories you learned in the courses for your discipline.
This is the stage of culmination, when everything you’ve learned becomes not the goal, but the foundation for your own body of work. It’s one of the exhilarating (and sometimes intimidating) parts of being a PhD candidate vs a student.
Expectations and Support
Faculty often use the “go wander in the woods” approach for PhD candidates. It’s essentially like hearing, “Go find things and come back to me when you’ve got something.” They’ll usually tell you when it’s not enough, but they might not give you much direction about what they’re looking for beyond that.
The reason for this is to encourage independent scholarship. They want you to have the opportunity to build your own case for why and how this topic should be studied. But this first foray into academic independence can be quite a challenge.
When they tell you to “go wander in the woods,” they’re not even telling you what kind of tree to look for. Sometimes you get specific directions, but sometimes you get vague answers like “go look for more.” This can be frustrating. Many clients come to me because they need more direction, which is understandable.

In your coursework, you were often given studies to read or asked to find studies on particular topics that relate to the course topic. Dissertation research is more nebulous. Your committee members want you to decide which directions to go in and which kinds of studies best relate to your research questions.
They won’t be asking you for the “right answer.” They’ll be asking you, “Why? Justify what you did or plan to do.”
Here’s another difference between PhD candidate vs student: a PhD candidate can put “PhD(c)” after their name, indicating that they have achieved status as a PhD candidate. However, I suggest using caution with this designation. The APA has expressed concern that its use may be misleading to the general public and cause people to believe you have a PhD.
PhD Candidate vs Student: An Interview With a PhD(c)

Did you notice a change in how professors viewed you, once you moved from “student” to “candidate”?
Yes. It actually happened during my comprehensive exams. Before that, when I had been asked a question, the professor already knew the answer and was asking to see if I knew also. In my comprehensive exams, I had become the expert and my committee members were actually asking questions out of interest.
We were all pieces of a puzzle at that point. Instead of them saying, “tell me about John Dewy’s influence on education in the 1920s,” they asked, “How do you think Dewey influenced the school system’s openness to parental involvement in schools?” The professor who asked that was genuinely interested, because she was an expert in educational history but had not specifically studied parent involvement in schools, as I had.
That moment represented a big shift for me; it meant that as a PhD candidate, I had to then take responsibility for my own learning, because nobody knew as much as I knew about that particular thing.
It’s exhilarating on one hand, because you suddenly realize you’re the expert. On the other hand, it’s scary because we’re used to somebody else knowing the answer, being able to correct us if we’re wrong.
A Narrowing of Scope

It sounds like your topic was centered on something very particular, so maybe not a lot of other people have studied what you want to study?
Yes, that’s true. When you go through a PhD program your research area is pretty narrow. You start out with a general interest in something, but as you go through your classes, specific areas start to stand out.
I started out with an interest in egalitarianism in public education, but my own past experience combined with some seminal texts to direct me toward parent involvement in schools, specifically. Some books and articles showed me that how schools treat parents can be an indicator of egalitarianism, maybe a clearer one than any rhetoric about the students.
So, there’s this winnowing effect, as you move forward. Your professors love to watch this, too. Especially in the smaller, seminar classes, they seem to be waiting to see what makes your heart beat faster.

Speaking of your heart beating faster, is one distinction of the candidacy phase to have more passion about the work you’re doing?
I think that’s ideal, for sure. It doesn’t always happen, because some professors are really after students who will jump onto their research platform, because they can piggyback on the students’ research to get more publications. Good committee chairs, though, will want you to find your own path toward something you can happily spend a lifetime studying.

I suspect that one of the reasons people don’t finish their dissertations is because they weren’t really passionate about the topic in the first place. It’s only one possible reason, but it should give a doctoral student pause.
It’s really hard to finish a PhD, so you want to knock down any barriers to finishing. Being passionate about the topic will keep you going when things feel onerous. It’s like marrying someone with a sense of humor — even when you’re not getting along very well, there’s something you can always appreciate about your spouse.
Imposter Syndrome

What about “ imposter syndrome ”? Does that come into play when you become a candidate?
It sure did for me! To be one of the only people who’s an expert in that field feels like a huge responsibility because people are depending on you. Your research has to be accurate because people will be making policies based on your conclusions.
Even with good intentions, your conclusions can be erroneous, and there are plenty of historical examples of policies being made on the basis of erroneous conclusions. The consequences can be enormous. And that’s all on you!
So then the questions become, “Am I really up to this?” “Who am I to drive policy?” “I’m just a fallible human being, so why would (or should) anyone listen to me?” Especially right after comps, I was thinking, “How could I be the expert? Nothing really has changed about me; I’m still the same person. Yesterday, I was a student, but today I’m an expert?”

My observation is that this happens with women more than men, probably because women in authority positions are more often questioned than are men. But even for men, this seemingly sudden transformation can make you worry that you’re not qualified for the responsibility you’re being given.
The thing is, It’s not really as sudden as it seems. You’ve been studying something for, say, four years, so you have a claim to expertise. And you’ve been narrowing your interests all along the way, so you’ve been slowly building up your expertise.
Besides, in many good schools, you get warned a lot about how easy it is to make a mistake in research and how easy it is to make false conclusions. They beat that into you so much that it can become a constant doubt.
In most primary and secondary schools, and sometimes even in college, they teach you to sit down, shut up, and learn something. For people to suddenly be saying, “tell me what you think,” can be challenging. I suspect that that’s another major reason people who finish their coursework don’t complete their dissertation: they’re not sufficiently prepared for this shift in roles.
Suggestions for PhD Candidates

Having been through this shift yourself, do you have any advice for students in this stage of their process?
Mostly, I think it’s a matter of taking personal responsibility and seeing yourself in a new light. It helps me to consider this process as a transformation — like a caterpillar into a butterfly. The “student” stage is the caterpillar stage, where you’re eating the milkweed, the knowledge, to nourish you.
Then there comes a time when you’ve got to stop being a consumer and transform into a real researcher. That’s like the metamorphosis stage when the caterpillar is in the chrysalis, melting down. (And I have had plenty of meltdowns myself in this stage!) That’s when you’re on your own, writing the dissertation.
That chrysalis stage is a real slog. You try as hard as you can, and your proposal still gets rejected — twice. Or the IRB wants you to structure the study differently, after your committee has already approved it. Or you can’t get enough participants for your quantitative study or enough data for your qualitative study — whatever. It’s the biggest challenge of most people’s life!

But if you stick with it, you actually do get this huge reward. As a butterfly, or a PhD, you bring something unique to the world. You have an important role in society that can potentially change the course of history — even if you don’t envision that in the beginning.
And that’s why the committee makes the process arduous. They want to be sure you’re great at what you do, because there is potentially an awful lot riding on your shoulders. I’m actually grateful for the rigor they demand. I want to feel ready for the role I’m taking.
Ultimately, candidacy is time in the chrysalis. It’s a time of transformation, built on one’s time as a student. It’s a time in the dark and alone, which makes it challenging, for sure. But I trust I’ll eventually emerge strong enough to spread my wings.
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins
Related Posts

Dissertation
Dissertation memes.
Sometimes you can’t dissertate anymore and you just need to meme. Don’t worry, I’ve got you. Here are some of my favorite dissertation memes that I’ve seen lately. My Favorite Dissertation Memes For when you Read more…

Surviving Post Dissertation Stress Disorder
The process of earning a doctorate can be long and stressful – and for some people, it can even be traumatic. This may be hard for those who haven’t been through a doctoral program to Read more…

PhD by Publication
PhD by publication, also known as “PhD by portfolio” or “PhD by published works,” is a relatively new route to completing your dissertation requirements for your doctoral degree. In the traditional dissertation route, you have Read more…
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What Makes a Good PhD Student?

In the competitive academic world, PhD programs seek candidates with a mix of qualities for successful academic research. Alongside strong academic achievements, they look for discipline, self-motivation, and the ability to face challenges, among other skills. In essence, PhD programs aim to admit candidates with both a deep understanding of their subject and the resilience and creativity needed to advance knowledge in their field.
The demand for doctoral positions often exceeds availability, making it essential for PhD candidates to distinguish themselves. In a group of highly qualified applicants, those who are outstanding scholars and show they can handle tough research challenges are more likely to get into a doctoral program. Knowing how to be a good PhD student is like being in possession of a treasure map. It helps you navigate the journey towards becoming an outstanding PhD candidate.
Table of Contents
Characteristics of a Good PhD Candidate
A good PhD student embodies a unique combination of characteristics that extend beyond academic brilliance. Let us examine some of these characteristics.¹²
- Discipline, perseverance, and self-motivation: Discipline ensures that the student adheres to a rigorous schedule, allocates time effectively, and stays focused on their research goals. Perseverance is essential for overcoming the inevitable challenges and setbacks that arise during the doctoral process, whether it is dealing with experimental failures or facing complex theoretical issues. A good PhD student needs to be internally motivated to sustain the long hours of independent work and the persistence required to contribute original insights to their field.
- Independence: The ability to work independently is among the critical qualities of a good PhD student. It means they can take charge of their research, make decisions on their own, and explore new ideas without constant guidance. This independence allows them to navigate the complexities of their study, contributing original insights and demonstrating their readiness for the challenges of PhD research.
- Embracing challenges: Doctoral research often involves uncharted territories, unanswered questions, and unexpected hurdles. A good PhD student not only anticipates challenges but actively welcomes them as opportunities for learning and growth. Embracing challenges also demonstrates adaptability. Whenever required, PhD students must change their strategies, reconsider ideas, and adapt to evolving research situations.
Academic Excellence and Research Capabilities
Academic excellence and strong research skills are foundational qualities of a good PhD student, serving as cornerstones for success in the demanding world of doctoral studies.³
- Well-versed in the chosen field: A deep understanding of the subject matter and staying abreast of the latest developments in their field is crucial for PhD students in formulating innovative research questions and designing robust methodologies.
- Critical thinking: Critical thinking involves the ability to analyze information, identify patterns, question assumptions, evaluate evidence objectively, and draw meaningful conclusions. It is integral to producing high-quality research that advances the knowledge within a particular field.
- Passion for research: A deep-seated curiosity is a driving force behind successful PhD students. The enthusiasm for exploring the unknown motivates these individuals to invest the time and effort required for groundbreaking discoveries.
Effective Communication and Collaboration
The ability to communicate your academic research confidently and professionally is essential, ensuring that the significance of your work is conveyed clearly to peers, mentors, and the broader academic community. These are among the key characteristics of a good PhD candidate.
- Confident presentation skills: Confident presentations not only showcase the depth of understanding and mastery of the subject matter but also capture the audience’s attention, ensuring that the research is conveyed with impact. Beyond mere information sharing, confident presentation skills facilitate effective connections, enabling PhD students to engage with peers and mentors, potentially leading to collaborations and valuable feedback.
- Teamwork and networking: In academia, teamwork encourages an exchange of ideas, diverse perspectives, and collective problem-solving. Establishing connections within the academic community is instrumental for staying informed about the latest developments, attending conferences, and building a professional reputation.
Excelling as a PhD student goes beyond academic brilliance. What makes a good PhD student is a combination of personal qualities, a commitment to hard work, and practical communication skills. Aspiring doctoral candidates should work towards imbibing these characteristics, ensuring they not only survive but thrive in the challenging yet rewarding journey of a doctoral program. Understanding how to be a good PhD student is the first step toward making a lasting impact in the world of academia.
References:
- What makes a good PhD student? – Nature
- What makes a “good” PhD student? – London School of Economics
- What makes a good PhD student? – University of Queensland
- How to Be a Successful PhD Student – John Hopkins University
Researcher.Life is a subscription-based platform that unifies top AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline a researcher’s journey, from reading to writing, submission, promotion and more. Based on over 20 years of experience in academia, Researcher.Life empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success.
Try for free or sign up for the Researcher.Life All Access Pack , a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI academic writing assistant, literature reading app, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional services from Editage. Find the best AI tools a researcher needs, all in one place – Get All Access now for prices starting at just $17 a month !
Related Posts

Join Us for Peer Review Week 2024

How Editage All Access is Boosting Productivity for Academics in India

Innovative Research on Antimicrobial Resistance Earns Top Honors for UNSW PhD Candidate
UNSW School of Optometry & Vision Science PhD Candidate Shyam Kumar Mishra (Baishnab) has been awarded the prestigious Best Poster Award at the 11th International Meeting on Antimicrobial Peptides (IMAP), held in London

UNSW School of Optometry & Vision Science PhD Candidate Shyam Kumar Mishra (Baishnab) has been awarded the Best Poster Award at the 11th International Meeting on Antimicrobial Peptides (IMAP), held in London. This accolade recognises his outstanding research and contribution to the field of antimicrobial peptides and peptidomimetics.
Mr. Mishra’s poster, titled “Mechanistic insights of a guanidine-functionalized anthranilamide peptidomimetic on Candida auris ,” captivated the attention of the conference attendees and judges alike. His work highlights novel strategies to address the growing challenge of antimicrobial resistance, a critical issue in global health.
“I am deeply honoured to receive this award,” said Mr Mishra. “This recognition motivates me to continue my research and contribute to finding effective solutions against antimicrobial resistance.”
The 11th International Meeting on Antimicrobial Peptides (IMAP) brought together leading scientists, researchers, and industry experts from around the world to discuss the latest advancements and challenges in the field. Mr. Mishra’s achievement underscores the importance of innovative research in combating global health threats.

Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Should I refer to myself as a PhD candidate or a researcher as an author of a paper?
My paper was accepted in a reputed journal. As I have to submit an author biography, I was wondering whether I should refer to myself as a PhD candidate or better say a researcher? I feel that a paper authored by a PhD candidate may not receive the same attention since some people would see students as not that competent yet.
- publications
- Do you have an official designation at your organization? – GoodDeeds Commented May 9, 2020 at 4:23
- I did not get what you mean. I'm officially enrolled in a PhD program ( 2nd year now). – Doctoralstudent Commented May 9, 2020 at 4:27
- You are training to be a researcher, so I’d go with researcher. You could get a job as an engineer before you’ve done any engineering, and you’d still call yourself an engineer. Whatever you want to be, go with that, it will empower and guide your actions in the grand scheme of things. – GrayLiterature Commented May 9, 2020 at 4:46
- 3 @GrayLiterature "get a job as an engineer before you’ve done any engineering, and you’d still call yourself an engineer" In some places that would be a crime. en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Regulation_and_licensure_in_engineering – Anonymous Physicist Commented May 9, 2020 at 10:03
- 5 "a paper authored by a PhD candidate may not receive the same attention" This does not make sense because a very large portion of papers are authored by PhD students. – Anonymous Physicist Commented May 9, 2020 at 10:04
It doesn't matter, it's a bio.
Describe who you are. Do you see yourself as a PhD student or a researcher?
Be careful because "PhD candidate" has additional meaning some places vs others, and you don't want to misuse it if it doesn't apply to you (it does not mean "PhD student" everywhere).
- Actually, I just realized that the bio is not necessary. I would not add it then. Thank you for the answer – Doctoralstudent Commented May 9, 2020 at 4:50
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged publications journals ..
- Featured on Meta
- Join Stack Overflow’s CEO and me for the first Stack IRL Community Event in...
- User activation: Learnings and opportunities
Hot Network Questions
- How to interpret odds ratio for variables that range from 0 to 1
- Smallest prime q such that concatenation (p+q)"q is a prime
- Is there a "hard problem of aesthetics?"
- How to avoid repeated input while using newcommand?
- Is there a way to hide/show seams on model?
- Can noun phrases have only one word?
- Apple IIgs to VGA adapter
- Film about a girl who discovers she is from a family of magicians
- Calm and Insight is the Normative Meditative Practice in Buddhism
- Why are no metals green or blue?
- Was the total glaciation of the world, a.k.a. snowball earth, due to Bok space clouds?
- Sync Layernotes between Projects
- How to plausibly delay the creation of the telescope
- Do 'avoid' notes depend on register?
- bash scripting: Saving and then processing file contents as a bash variable
- meaning of a sentence from Agatha Christie (Murder of Roger Ackroyd)
- How to properly use an enameled cast iron grill pan?
- Is Boltzmann entropy well-defined for arbitrary probability density function?
- How to achieve 24t-38t front chainrings
- A function to convert numbers from scientific notation to plain decimal
- How can "chemical-free" surface cleaners work?
- The result clause of first conditional possesses would instead of will
- Mark 6:54 - Who knew/recognized Jesus: the disciples or the crowds?
- Determining Entropy in PHP

Senior Scientist - Radioligand Therapy in-vivo Oncology (80-100%*)
About the role.
The ideal candidate should have a passion for working with rodents and a drive to perform in vivo oncology pharmacology studies including micro-surgeries, compound administration and preparation of samples for ex vivo analysis. Hands-on background performing small animal imaging modalities such as PET/SPECT/uCT or in cell biology techniques is a plus. The successful candidate will work collaboratively as an integral part of global projects and be an active member of lab and project teams. Responsibilities include but are not limited to: • Develop and characterize novel in vivo oncology models • Executing efficacy studies with cutting edge radioligand therapies • Developing and delivering biodistribution studies and metabolites analysis • Perform pre-clinical imaging studies including PET/SPECT/uCT • Individually performing and/or supporting colleagues with various in vitro and ex vivo activities (e.g. cell culture, flow cytometry, IHC, immunofluorescence, PCR, Western blotting)
What you will bring to the role: • Masters degree in pharmacology, cell biology, medical physics, bioengineering, biotechnology or related field or Bachelors degree with equivalent experience. Please note that for this position we do not require a PhD qualified candidate at this time. • Practical work experience in biomedical research from an industry or academic laboratory • Experience in performing animal studies (animal handling, drug application, sampling, animal welfare regulations, small laboratory animal surgery) • Self-motivated, proactive, and able to work independently Desirable requirements: • Knowledge and experience of standard cell biology techniques is desirable: cell culture, IHC, immunofluorescence, flow cytometry, quantitative real-time PCR, transfection, western blotting, etc., • Highly collaborative team player that enjoys working across multi-disciplinary teams • Excellent organizational and communication skills • Knowledge of cancer biology Accessibility and accommodation: Novartis is committed to working with and providing reasonable accommodation to all individuals. If, because of a medical condition or disability, you need a reasonable accommodation for any part of the recruitment process, or in order to receive more detailed information about the essential functions of a position, please send an e-mail to inclusion.switzerland@novartis.com and let us know the nature of your request and your contact information. Please include the job requisition number in your message.
Why Novartis: Helping people with disease and their families takes more than innovative science. It takes a community of smart, passionate people like you. Collaborating, supporting and inspiring each other. Combining to achieve breakthroughs that change patients’ lives. Ready to create a brighter future together? https://www.novartis.com/about/strategy/people-and-culture
Join our Novartis Network: Not the right Novartis role for you? Sign up to our talent community to stay connected and learn about suitable career opportunities as soon as they come up: https://talentnetwork.novartis.com/network
Benefits and Rewards: Read our handbook to learn about all the ways we’ll help you thrive personally and professionally: https://www.novartis.com/careers/benefits-rewards
Novartis is committed to building an outstanding, inclusive work environment and diverse teams' representative of the patients and communities we serve.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A PhD student is in the initial stages of their program, actively engaging in coursework, research, and academic requirements. On the other hand, a PhD candidate has advanced beyond coursework, passed comprehensive exams, and is focused primarily on independent research and the completion of their dissertation.
A PhD student is a student pursuing a doctoral degree, while a PhD researcher can be anyone who is conducting research at the doctoral level, including PhD students, postdocs, and faculty members. However, in practice, the terms PhD student and PhD researcher are often used interchangeably. The confusion comes from the fact that a PhD research ...
Also, a "PhD Researcher", "Researcher" or "Researcher PhD" could be more experienced than a Post-doctoral Researcher and it usually implies a more permanent position. Personally I think it is important to stick to the title to avoid confusion. Personally I would like to see "PhD candidate" instead of "PhD student" since it sounds better.
Students may be in the initial stage of the program or about to complete the coursework (before beginning their research). On the other hand, a PhD candidate has completed all coursework and has at least started their research. They may have completed their dissertation and are preparing to defend it. 2.
PhD Student vs. PhD Candidate How I use gentle, digital nudges to stay current in the post-exams world. July 6, 2017 ... My department's requirements involved: completing two years of coursework; demonstrating proficiency in a research language other than English; submitting at least one grant application; writing and revising a dissertation ...
Both terms denote stages in a doctoral journey, but they imply different responsibilities, expectations, and milestones. A PhD student is in the initial stages of their doctoral journey, undertaking coursework and preparing for exams. A PhD candidate, having passed these exams, focuses on original research and writing a dissertation.
Here in the U.S., a "Ph.D. Candidate" is a student who has completed all of the academic requirements for their degree, except their dissertation. So this works in the USA and Canada I presume, because they have structured PhD programs where you attend courses as part of your PhD.
A PhD viva, also known as a viva voce or oral examination, is the final evaluation of a PhD candidate's research and thesis where the panel asks questions, engages in discussions and assesses the depth of the candidate's understanding and expertise. Q. Can you do a PhD part-time? A. Yes, part-time options are available for PhDs.
7 stages of the PhD journey. A PhD has a few landmark milestones along the way. The three to four year you'll spend doing a PhD can be divided into these seven stages. Preparing a research proposal. Carrying out a literature review. Conducting research and collecting results. Completing the MPhil to PhD upgrade.
The Google PhD Fellowship Program was created to recognize outstanding graduate students doing exceptional and innovative research in areas relevant to computer science and related fields. Fellowships support promising PhD candidates of all backgrounds who seek to influence the future of technology. Google's mission is to foster inclusive ...
A PhD Candidate is an individual who is currently enrolled in a doctoral program at a university or other tertiary education institution. They are usually referred to as " PhD students" or "PhD candidates.". In order to qualify for the PhD, a candidate must complete all of the program's coursework requirements and write and defend a ...
3. Wharton Communications Program. The Wharton Communication Program helps Wharton PhD students become more effective communicators and thus better presenters, public speakers, and writers — all critical skills in academia. All doctoral students are provided with access to on-site, one-on-one writing coaching during the academic year.
This process is followed by dissertation research, writing and defense. The main difference between a PhD student vs. candidate is that the student is still working through the coursework. They have not yet begun the dissertation process or passed the qualifying exams. A PhD student may also be in the process of taking the qualifying exams, but ...
Being a "PhD student" at a university formalises the relationship between you and the institution (perhaps more explicitly than if you were a "PhD researcher") in terms of university accountability to you, the student and the student's code of conduct. Students pay tuition fees, as do local and international "PhD students ...
Definition of a PhD - A Doctor of Philosophy (commonly abbreviated to PhD, Ph.D or a DPhil) is a university research degree awarded from across a broad range of academic disciplines; in most countries, it is a terminal degree, i.e. the highest academic degree possible. PhDs differ from undergraduate and master's degrees in that PhDs are ...
The distinction between a PhD student and a PhD candidate is that the former is still undertaking coursework and has not yet commenced the dissertation process or passed the qualifying exams, although they may be in the process of doing so. PhD students' education is defined by a predetermined structure, which also sets forth their schedules.
As a PhD candidate, you should possess, acquire, and/or refine the qualities necessary to mature into an independent researcher. We expect you to cultivate your talents. This will help you to prepare for a future career. You are also responsible for meeting the commitments linked to the funding of your doctoral research.
The points below reflect our vision on your academic responsibilities as a junior researcher. · You are responsible for the quality of your research, together with your supervisory team. − You are proactive and undertake the necessary efforts to ensure good progress in your doctoral research project.
The eleven qualities. Researcher graduate qualities for the PhD. Purpose. Deep expertise. To possess expert, world-standard knowledge in an area of specialisation, a mastery of relevant research methods and the capability to contribute to scholarship and knowledge discovery. Cultural competence.
You make the transition from PhD student to PhD candidate after you complete all your coursework and your comprehensive exams (if required). A PhD candidate's sole task is to conduct their research and write their dissertation. In other words, a PhD student is still completing their coursework. They could be on the first day of their PhD program.
Additionally, they are typically one pay grade lower than the Research Fellow positions. A Research Fellow (RF) is what one would informally call postdoctoral researcher (or just post-doc). These are typical positions one would aim at after their PhD (and usually encourage PhD candidates close to finishing to apply as well).
A good PhD student embodies a unique combination of characteristics that extend beyond academic brilliance. Let us examine some of these characteristics.¹². Discipline, perseverance, and self-motivation: Discipline ensures that the student adheres to a rigorous schedule, allocates time effectively, and stays focused on their research goals.
By Erik Russell, Director of Educational Initiatives, and Julia Sepulveda, Senior Program Associate, CRA-E. In 2023, the Computing Research Association's Committees on Education and Widening Participation (CRA-E / -WP) developed and launched the Undergraduate Research to PhD Mentoring (UR2PhD) program to increase the percentage of women and other gender-marginalized students graduating with ...
UNSW School of Optometry & Vision Science PhD Candidate Shyam Kumar Mishra (Baishnab) has been awarded the Best Poster Award at the 11th International Meeting on Antimicrobial Peptides (IMAP), held in London. This accolade recognises his outstanding research and contribution to the field of antimicrobial peptides and peptidomimetics.
My paper was accepted in a reputed journal. As I have to submit an author biography, I was wondering whether I should refer to myself as a PhD candidate or better say a researcher? I feel that a paper authored by a PhD candidate may not receive the same attention since some people would see students as not that competent yet.
The ideal candidate should have a passion for working with rodents and a drive to perform in vivo oncology pharmacology studies including micro-surgeries, compound administration and preparation of samples for ex vivo analysis. Hands-on background performing small animal imaging modalities such as PET/SPECT/uCT or in cell biology techniques is a plus. The successful candidate will work ...