| | '; audChoice = audChoice.replace(/ selected=["']selected["']/gm, '');var audT = document.getElementById('audT');if ((audT) && (audPref)) { //Parse the content if(audPref.indexOf(':') > -1) { var audPrefAccent = audPref.split(':')[0]; var playbackRate = audPref.split(':')[1]; } else { var audPrefAccent = audPref; var playbackRate = 1; } var re = new RegExp('( UK and possibly other pronunciationsUK and possibly other pronunciations/ˈɛseɪ/ USA pronunciation: IPA/ ˈɛseɪ , ɛˈseɪ; ɛˈseɪ/ US:USA pronunciation: respellingUSA pronunciation: respelling( es ā , ; es ā, e sā – ; v. e sā ) | | | | | |
WordReference English Thesaurus © 2024
Noun: piece of writing , piece , article , writing , composition , paper , theme , exposition, dissertation , thesis , editorial, column , opinion piece, study , review , critique, literature , research paper, first draft Noun: effort - formal , attempt , effort , try , go , shot , stab , whack , crack , pass , bid , endeavor , endeavour (UK), road-test Verb: attempt - formal , attempt , endeavor , endeavour (UK), undertake , take on, have a go, give it a go, make an effort, try your hand at, take a shot at (informal), take a stab at (informal), take a whack at (informal), take a crack at (informal), give it a whirl (informal), strive for, make an attempt at
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
- English Only forum
Go to page and choose from different actions for taps or mouse clicks. Translations: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Advertisements | | | | Advertisements | | | | | | | | | | | | use for the fastest search of WordReference. | | © 2024 WordReference.com | any problems. | - ABBREVIATIONS
- BIOGRAPHIES
- CALCULATORS
- CONVERSIONS
- DEFINITIONS
 Vocabulary What is another word for essay ?Synonyms for essay ˈɛs eɪ or, for 3,5 , ɛˈseɪ; ɛˈseɪ es·say, this thesaurus page includes all potential synonyms, words with the same meaning and similar terms for the word essay ., english synonyms and antonyms rate these synonyms: 2.7 / 3 votes. To attempt is to take action somewhat experimentally with the hope and purpose of accomplishing a certain result; to endeavor is to attempt strenuously and with firm and enduring purpose. To attempt expresses a single act; to endeavor , a continuous exertion; we say I will endeavor (not I will attempt ) while I live. To attempt is with the view of accomplishing; to essay , with a view of testing our own powers. To undertake is to accept or take upon oneself as an obligation, as some business, labor, or trust; the word often implies complete assurance of success; as, I will undertake to produce the witness. To strive suggests little of the result, much of toil, strain, and contest, in seeking it; I will strive to fulfil your wishes, i. e. , I will spare no labor and exertion to do it. Try is the most comprehensive of these words. The original idea of testing or experimenting is not thought of when a man says "I will try ." To attempt suggests giving up, if the thing is not accomplished at a stroke; to try implies using other means and studying out other ways if not at first successful. Endeavor is more mild and formal; the pilot in the burning pilot-house does not say "I will endeavor " or "I will attempt to hold the ship to her course," but "I'll try , sir!" Synonyms: attempt , endeavor , endeavor , strive , try , undertake Antonyms: abandon , dismiss , drop , give up , let go , neglect , omit , overlook , pass by , throw away , throw over , throw up Princeton's WordNet Rate these synonyms: 1.0 / 2 votesan analytic or interpretive literary composition a tentative attempt try, seek, attempt, essay, assay verb make an effort or attempt "He tried to shake off his fears"; "The infant had essayed a few wobbly steps"; "The police attempted to stop the thief"; "He sought to improve himself"; "She always seeks to do good in the world" Synonyms: attempt , examine , search , stress , adjudicate , strain , seek , look for , assay , try out , try , prove , test , try on , taste , hear , set about , undertake , sample , judge , render test, prove, try, try out, examine, essay verb put to the test, as for its quality, or give experimental use to "This approach has been tried with good results"; "Test this recipe" Synonyms: audition , rise , analyze , leaven , try , sample , show , testify , establish , test , evidence , try out , study , examine , see , seek , try on , probe , quiz , attempt , raise , adjudicate , render , prove , shew , judge , screen , taste , turn out , demonstrate , turn up , experiment , strain , analyse , stress , hear , canvass , assay , canvas , bear witness Matched CategoriesEditors contribution rate these synonyms: 0.0 / 0 votes. piece of writing write an essay of a students Dictionary of English Synonymes Rate these synonyms: 0.0 / 0 votesSynonyms: attempt , try , endeavor Synonyms: attempt , trial , endeavor , effort , struggle , aim Synonyms: tract , dissertation , treatise , disquisition , brief discourse Synonyms, Antonyms & Associated Words Rate these synonyms: 0.0 / 0 votesSynonyms: dissertation , article , disquisition , thesis , attempt , effort , trial PPDB, the paraphrase database Rate these paraphrases: 1.0 / 1 voteList of paraphrases for "essay": dissertation , test , trial , drafting , composition , testing How to pronounce essay?How to say essay in sign language, usage in printed sources from: . - [["1524","6"],["1563","1"],["1572","1"],["1574","2"],["1579","3"],["1581","4"],["1584","1"],["1590","4"],["1607","20"],["1611","1"],["1624","9"],["1635","4"],["1637","1"],["1638","3"],["1644","16"],["1645","1"],["1647","1"],["1648","1"],["1649","1"],["1650","1"],["1655","8"],["1656","3"],["1657","2"],["1658","3"],["1659","3"],["1662","14"],["1664","6"],["1668","1"],["1670","2"],["1671","2"],["1673","37"],["1675","5"],["1676","2"],["1677","14"],["1678","3"],["1679","7"],["1680","18"],["1681","4"],["1683","5"],["1684","2"],["1685","7"],["1688","7"],["1689","10"],["1690","1"],["1692","1"],["1693","5"],["1694","2"],["1696","7"],["1698","4"],["1699","5"],["1700","2"],["1701","6"],["1702","225"],["1703","4"],["1705","5"],["1706","31"],["1707","1"],["1708","17"],["1709","17"],["1711","10"],["1712","1"],["1713","114"],["1715","5"],["1716","3"],["1717","12"],["1718","12"],["1719","4"],["1720","4"],["1721","34"],["1722","5"],["1723","7"],["1724","12"],["1725","8"],["1726","8"],["1727","13"],["1728","25"],["1729","59"],["1730","12"],["1731","62"],["1732","11"],["1733","4"],["1734","9"],["1735","12"],["1736","11"],["1737","53"],["1738","25"],["1739","16"],["1740","26"],["1741","8"],["1742","27"],["1743","10"],["1744","29"],["1745","13"],["1746","13"],["1747","17"],["1748","48"],["1749","28"],["1750","54"],["1751","225"],["1752","96"],["1753","118"],["1754","158"],["1755","146"],["1756","111"],["1757","75"],["1758","101"],["1759","100"],["1760","95"],["1761","90"],["1762","72"],["1763","96"],["1764","159"],["1765","102"],["1766","157"],["1767","182"],["1768","188"],["1769","291"],["1770","102"],["1771","123"],["1772","132"],["1773","121"],["1774","161"],["1775","115"],["1776","241"],["1777","201"],["1778","140"],["1779","187"],["1780","154"],["1781","175"],["1782","138"],["1783","143"],["1784","149"],["1785","177"],["1786","225"],["1787","425"],["1788","252"],["1789","196"],["1790","184"],["1791","243"],["1792","335"],["1793","456"],["1794","306"],["1795","281"],["1796","360"],["1797","306"],["1798","614"],["1799","515"],["1800","491"],["1801","1180"],["1802","674"],["1803","757"],["1804","1004"],["1805","944"],["1806","1206"],["1807","1592"],["1808","1142"],["1809","1300"],["1810","1719"],["1811","1531"],["1812","1683"],["1813","1157"],["1814","1560"],["1815","1168"],["1816","1183"],["1817","1348"],["1818","1270"],["1819","1468"],["1820","1611"],["1821","1298"],["1822","2094"],["1823","2720"],["1824","2745"],["1825","3250"],["1826","1599"],["1827","1846"],["1828","1724"],["1829","1884"],["1830","2153"],["1831","2390"],["1832","2609"],["1833","2702"],["1834","2548"],["1835","3165"],["1836","3168"],["1837","3623"],["1838","2671"],["1839","3092"],["1840","3577"],["1841","3184"],["1842","2376"],["1843","2768"],["1844","3286"],["1845","3308"],["1846","3410"],["1847","3316"],["1848","3582"],["1849","4182"],["1850","4286"],["1851","3680"],["1852","4582"],["1853","5798"],["1854","6237"],["1855","4724"],["1856","5033"],["1857","4579"],["1858","4308"],["1859","5157"],["1860","5727"],["1861","4287"],["1862","3963"],["1863","3879"],["1864","4249"],["1865","4630"],["1866","4718"],["1867","4529"],["1868","5360"],["1869","4956"],["1870","5165"],["1871","6359"],["1872","5628"],["1873","6832"],["1874","7467"],["1875","7330"],["1876","7710"],["1877","7424"],["1878","6120"],["1879","8010"],["1880","8758"],["1881","9314"],["1882","10173"],["1883","9852"],["1884","12533"],["1885","10782"],["1886","8520"],["1887","10058"],["1888","10408"],["1889","9129"],["1890","9846"],["1891","12257"],["1892","13759"],["1893","12619"],["1894","11592"],["1895","13096"],["1896","15332"],["1897","14192"],["1898","13857"],["1899","18216"],["1900","16353"],["1901","17717"],["1902","20107"],["1903","17951"],["1904","20481"],["1905","17068"],["1906","17273"],["1907","17231"],["1908","16451"],["1909","17491"],["1910","14836"],["1911","15954"],["1912","16426"],["1913","15508"],["1914","13768"],["1915","15561"],["1916","12971"],["1917","14076"],["1918","11469"],["1919","12445"],["1920","15903"],["1921","14455"],["1922","15554"],["1923","16063"],["1924","13255"],["1925","15252"],["1926","14800"],["1927","17064"],["1928","16304"],["1929","15309"],["1930","16925"],["1931","17162"],["1932","14879"],["1933","12458"],["1934","19578"],["1935","19316"],["1936","16948"],["1937","14706"],["1938","15958"],["1939","16039"],["1940","14798"],["1941","13461"],["1942","10870"],["1943","11136"],["1944","10662"],["1945","11652"],["1946","15464"],["1947","18266"],["1948","19294"],["1949","24241"],["1950","24050"],["1951","23509"],["1952","22589"],["1953","24376"],["1954","24536"],["1955","26359"],["1956","27198"],["1957","32828"],["1958","30097"],["1959","32002"],["1960","37630"],["1961","43606"],["1962","50624"],["1963","53881"],["1964","53264"],["1965","64013"],["1966","70855"],["1967","71595"],["1968","80273"],["1969","74565"],["1970","85052"],["1971","86823"],["1972","89739"],["1973","83200"],["1974","81580"],["1975","80526"],["1976","85864"],["1977","89627"],["1978","86675"],["1979","90592"],["1980","97009"],["1981","98592"],["1982","108432"],["1983","107342"],["1984","116155"],["1985","120529"],["1986","129959"],["1987","143905"],["1988","147517"],["1989","167121"],["1990","178649"],["1991","189226"],["1992","198307"],["1993","210280"],["1994","224878"],["1995","237115"],["1996","251160"],["1997","256529"],["1998","274336"],["1999","282399"],["2000","307517"],["2001","304311"],["2002","334775"],["2003","344263"],["2004","392936"],["2005","376374"],["2006","383944"],["2007","391538"],["2008","388198"]]
Words popularity by usage frequency| ranking | word | |
|---|
| #41 | | | | #64 | | | | #268 | | | | #502 | | | | #508 | | | | #684 | | | | #1049 | | | | #1165 | | | | #1306 | | | | #1451 | | | | #1452 | | | | #1736 | | | | #2567 | | | | #2703 | | | | #2989 | | | | #3056 | | | | #3085 | | | | #3171 | | | | #3551 | | | | #4103 | | | | #4340 | | | | #4365 | | | | #4615 | | | | #4622 | | | | #5064 | | | | #5457 | | | | #5490 | | | | #5818 | | | | #6343 | | | | #6612 | | | | #6840 | | | | #9347 | | | | #9759 | | | | #10940 | | | | #11288 | | | | #11336 | | | | #11832 | | | | #13073 | | | | #16219 | | | | #16270 | | | | #16888 | | | | #44303 | | | | #50593 | | | | #66242 | | | | #84296 | | |
How to use essay in a sentence?Dan Gainor : Can you imagine The New York Times running an essay where a white woman complains about how African-American men are rude and then blames it on race? The paper and the author would be skewered, the left's new default is that white people are doing wrong at every turn -- even walking down the street. Neama Rahmani : Bail reform and COVID delays claim another innocent victim, george Gascon has been largely criticized for the increase in violent crime in Los Angeles. Los Angeles’s time George Gascon stops acting like a defense attorney and allows prosecutors to charge violent felons with sentencing enhancements. George Gascon, the progressive Los Angeles district attorney, has raised the ire of law enforcement and George Gascon own assistant DAs for George Gascon allegedly soft-on-crime policies. Los Angeles POLICE ID Shawn Laval Smith AS SUSPECTED KILLER OF Brianna Kupfer Homicides are up more than 60 % in the City of Los Angeles and over 90 % in Los Angeles, according to records from the LAPD and sheriff’s office. Eric Siddall, the vice president of the Association of Los Angeles Deputy District Attorneys, excoriated Gascon in an essay published to the union’s website this week. By the way, the best journalists and editors work in the reddit essay writing service reviews , which you can always contact. Thomas Babington Macaulay, 1st Baron Macaulay : A few more days, and this essay will follow the Defensio Populi to the dust and silence of the upper shelf... For a month or two it will occupy a few minutes of chat in every drawing-room, and a few columns in every magazine; and it will then be withdrawn, to make room for the forthcoming novelties. Mao Zedong : Revolution is not a dinner party, not an essay, nor a painting, nor a piece of embroidery it cannot be advanced softly, gradually, carefully, considerately, respectfully, politely, plainly and modestly. Use the citation below to add these synonyms to your bibliography:Style: MLA Chicago APA "essay." Synonyms.com. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 24 Aug. 2024. < https://www.synonyms.com/synonym/essay >.  Discuss these essay synonyms with the community: Report CommentWe're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe. If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly. You need to be logged in to favorite .Create a new account. Your name: * Required Your email address: * Required Pick a user name: * Required Username: * Required Password: * Required Forgot your password? Retrieve it Are we missing a good synonym for essay ?Image credit, the web's largest resource for, synonyms & antonyms, a member of the stands4 network, image or illustration of. .png/230px-Essais_Titelblatt_(1588).png) Free, no signup required :Add to chrome, add to firefox, browse synonyms.com, are you a human thesaurus, which of the following terms is not a synonym of "spread out", nearby & related entries:. - essayer noun
- essayist noun
- essence noun
Alternative searches for essay :- Search for essay on Amazon
 - More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of essay (Entry 1 of 2) Definition of essay (Entry 2 of 2) transitive verb attempt , try , endeavor , essay , strive mean to make an effort to accomplish an end. attempt stresses the initiation or beginning of an effort. try is often close to attempt but may stress effort or experiment made in the hope of testing or proving something. endeavor heightens the implications of exertion and difficulty. essay implies difficulty but also suggests tentative trying or experimenting. strive implies great exertion against great difficulty and specifically suggests persistent effort. Examples of essay in a SentenceThese examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'essay.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples. Word HistoryMiddle French essai , ultimately from Late Latin exagium act of weighing, from Latin ex- + agere to drive — more at agent 14th century, in the meaning defined at sense 4 14th century, in the meaning defined at sense 2 Phrases Containing essay- essay question
- photo - essay
Articles Related to essay To 'Essay' or 'Assay'?You'll know the difference if you give it the old college essay Dictionary Entries Near essayCite this entry. “Essay.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/essay. Accessed 24 Aug. 2024. Kids DefinitionKids definition of essay. Kids Definition of essay (Entry 2 of 2) More from Merriam-Webster on essayNglish: Translation of essay for Spanish Speakers Britannica English: Translation of essay for Arabic Speakers Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about essay Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!  Can you solve 4 words at once?Word of the day. See Definitions and Examples » Get Word of the Day daily email! Popular in Grammar & UsagePlural and possessive names: a guide, 31 useful rhetorical devices, more commonly misspelled words, absent letters that are heard anyway, how to use accents and diacritical marks, popular in wordplay, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, it's a scorcher words for the summer heat, 7 shakespearean insults to make life more interesting, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), 9 superb owl words, games & quizzes.  Save £500 when you enrol by 30th September!  - 40 Useful Words and Phrases for Top-Notch Essays
 To be truly brilliant, an essay needs to utilise the right language. You could make a great point, but if it’s not intelligently articulated, you almost needn’t have bothered. Developing the language skills to build an argument and to write persuasively is crucial if you’re to write outstanding essays every time. In this article, we’re going to equip you with the words and phrases you need to write a top-notch essay, along with examples of how to utilise them. It’s by no means an exhaustive list, and there will often be other ways of using the words and phrases we describe that we won’t have room to include, but there should be more than enough below to help you make an instant improvement to your essay-writing skills. If you’re interested in developing your language and persuasive skills, Oxford Royale offers summer courses at its Oxford Summer School , Cambridge Summer School , London Summer School , San Francisco Summer School and Yale Summer School . You can study courses to learn english , prepare for careers in law , medicine , business , engineering and leadership. General explainingLet’s start by looking at language for general explanations of complex points. 1. In order toUsage: “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument. Example: “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.” 2. In other wordsUsage: Use “in other words” when you want to express something in a different way (more simply), to make it easier to understand, or to emphasise or expand on a point. Example: “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.” 3. To put it another wayUsage: This phrase is another way of saying “in other words”, and can be used in particularly complex points, when you feel that an alternative way of wording a problem may help the reader achieve a better understanding of its significance. Example: “Plants rely on photosynthesis. To put it another way, they will die without the sun.” 4. That is to sayUsage: “That is” and “that is to say” can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: “Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.” 5. To that endUsage: Use “to that end” or “to this end” in a similar way to “in order to” or “so”. Example: “Zoologists have long sought to understand how animals communicate with each other. To that end, a new study has been launched that looks at elephant sounds and their possible meanings.” Adding additional information to support a pointStudents often make the mistake of using synonyms of “and” each time they want to add further information in support of a point they’re making, or to build an argument. Here are some cleverer ways of doing this. 6. MoreoverUsage: Employ “moreover” at the start of a sentence to add extra information in support of a point you’re making. Example: “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…” 7. FurthermoreUsage:This is also generally used at the start of a sentence, to add extra information. Example: “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…” 8. What’s moreUsage: This is used in the same way as “moreover” and “furthermore”. Example: “What’s more, this isn’t the only evidence that supports this hypothesis.” 9. LikewiseUsage: Use “likewise” when you want to talk about something that agrees with what you’ve just mentioned. Example: “Scholar A believes X. Likewise, Scholar B argues compellingly in favour of this point of view.” 10. SimilarlyUsage: Use “similarly” in the same way as “likewise”. Example: “Audiences at the time reacted with shock to Beethoven’s new work, because it was very different to what they were used to. Similarly, we have a tendency to react with surprise to the unfamiliar.” 11. Another key thing to rememberUsage: Use the phrase “another key point to remember” or “another key fact to remember” to introduce additional facts without using the word “also”. Example: “As a Romantic, Blake was a proponent of a closer relationship between humans and nature. Another key point to remember is that Blake was writing during the Industrial Revolution, which had a major impact on the world around him.” 12. As well asUsage: Use “as well as” instead of “also” or “and”. Example: “Scholar A argued that this was due to X, as well as Y.”  13. Not only… but alsoUsage: This wording is used to add an extra piece of information, often something that’s in some way more surprising or unexpected than the first piece of information. Example: “Not only did Edmund Hillary have the honour of being the first to reach the summit of Everest, but he was also appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire.” 14. Coupled withUsage: Used when considering two or more arguments at a time. Example: “Coupled with the literary evidence, the statistics paint a compelling view of…” 15. Firstly, secondly, thirdly…Usage: This can be used to structure an argument, presenting facts clearly one after the other. Example: “There are many points in support of this view. Firstly, X. Secondly, Y. And thirdly, Z. 16. Not to mention/to say nothing ofUsage: “Not to mention” and “to say nothing of” can be used to add extra information with a bit of emphasis. Example: “The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.” Words and phrases for demonstrating contrastWhen you’re developing an argument, you will often need to present contrasting or opposing opinions or evidence – “it could show this, but it could also show this”, or “X says this, but Y disagrees”. This section covers words you can use instead of the “but” in these examples, to make your writing sound more intelligent and interesting. 17. HoweverUsage: Use “however” to introduce a point that disagrees with what you’ve just said. Example: “Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion.” 18. On the other handUsage: Usage of this phrase includes introducing a contrasting interpretation of the same piece of evidence, a different piece of evidence that suggests something else, or an opposing opinion. Example: “The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.” 19. Having said thatUsage: Used in a similar manner to “on the other hand” or “but”. Example: “The historians are unanimous in telling us X, an agreement that suggests that this version of events must be an accurate account. Having said that, the archaeology tells a different story.” 20. By contrast/in comparisonUsage: Use “by contrast” or “in comparison” when you’re comparing and contrasting pieces of evidence. Example: “Scholar A’s opinion, then, is based on insufficient evidence. By contrast, Scholar B’s opinion seems more plausible.” 21. Then againUsage: Use this to cast doubt on an assertion. Example: “Writer A asserts that this was the reason for what happened. Then again, it’s possible that he was being paid to say this.” 22. That saidUsage: This is used in the same way as “then again”. Example: “The evidence ostensibly appears to point to this conclusion. That said, much of the evidence is unreliable at best.” Usage: Use this when you want to introduce a contrasting idea. Example: “Much of scholarship has focused on this evidence. Yet not everyone agrees that this is the most important aspect of the situation.” Adding a proviso or acknowledging reservationsSometimes, you may need to acknowledge a shortfalling in a piece of evidence, or add a proviso. Here are some ways of doing so. 24. Despite thisUsage: Use “despite this” or “in spite of this” when you want to outline a point that stands regardless of a shortfalling in the evidence. Example: “The sample size was small, but the results were important despite this.” 25. With this in mindUsage: Use this when you want your reader to consider a point in the knowledge of something else. Example: “We’ve seen that the methods used in the 19th century study did not always live up to the rigorous standards expected in scientific research today, which makes it difficult to draw definite conclusions. With this in mind, let’s look at a more recent study to see how the results compare.” 26. Provided thatUsage: This means “on condition that”. You can also say “providing that” or just “providing” to mean the same thing. Example: “We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.” 27. In view of/in light ofUsage: These phrases are used when something has shed light on something else. Example: “In light of the evidence from the 2013 study, we have a better understanding of…” 28. NonethelessUsage: This is similar to “despite this”. Example: “The study had its limitations, but it was nonetheless groundbreaking for its day.” 29. NeverthelessUsage: This is the same as “nonetheless”. Example: “The study was flawed, but it was important nevertheless.” 30. NotwithstandingUsage: This is another way of saying “nonetheless”. Example: “Notwithstanding the limitations of the methodology used, it was an important study in the development of how we view the workings of the human mind.” Giving examplesGood essays always back up points with examples, but it’s going to get boring if you use the expression “for example” every time. Here are a couple of other ways of saying the same thing. 31. For instanceExample: “Some birds migrate to avoid harsher winter climates. Swallows, for instance, leave the UK in early winter and fly south…” 32. To give an illustrationExample: “To give an illustration of what I mean, let’s look at the case of…” Signifying importanceWhen you want to demonstrate that a point is particularly important, there are several ways of highlighting it as such. 33. SignificantlyUsage: Used to introduce a point that is loaded with meaning that might not be immediately apparent. Example: “Significantly, Tacitus omits to tell us the kind of gossip prevalent in Suetonius’ accounts of the same period.” 34. NotablyUsage: This can be used to mean “significantly” (as above), and it can also be used interchangeably with “in particular” (the example below demonstrates the first of these ways of using it). Example: “Actual figures are notably absent from Scholar A’s analysis.” 35. ImportantlyUsage: Use “importantly” interchangeably with “significantly”. Example: “Importantly, Scholar A was being employed by X when he wrote this work, and was presumably therefore under pressure to portray the situation more favourably than he perhaps might otherwise have done.” SummarisingYou’ve almost made it to the end of the essay, but your work isn’t over yet. You need to end by wrapping up everything you’ve talked about, showing that you’ve considered the arguments on both sides and reached the most likely conclusion. Here are some words and phrases to help you. 36. In conclusionUsage: Typically used to introduce the concluding paragraph or sentence of an essay, summarising what you’ve discussed in a broad overview. Example: “In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.” 37. Above allUsage: Used to signify what you believe to be the most significant point, and the main takeaway from the essay. Example: “Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that…” 38. PersuasiveUsage: This is a useful word to use when summarising which argument you find most convincing. Example: “Scholar A’s point – that Constanze Mozart was motivated by financial gain – seems to me to be the most persuasive argument for her actions following Mozart’s death.” 39. CompellingUsage: Use in the same way as “persuasive” above. Example: “The most compelling argument is presented by Scholar A.” 40. All things consideredUsage: This means “taking everything into account”. Example: “All things considered, it seems reasonable to assume that…” How many of these words and phrases will you get into your next essay? And are any of your favourite essay terms missing from our list? Let us know in the comments below, or get in touch here to find out more about courses that can help you with your essays. At Oxford Royale Academy, we offer a number of summer school courses for young people who are keen to improve their essay writing skills. Click here to apply for one of our courses today, including law , business , medicine and engineering . Comments are closed. - Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Critique Report
- Writing Reports
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Words to Use in an Essay: 300 Essay Words By Hannah Yang  Table of ContentsWords to use in the essay introduction, words to use in the body of the essay, words to use in your essay conclusion, how to improve your essay writing vocabulary. It’s not easy to write an academic essay . Many students struggle to word their arguments in a logical and concise way. To make matters worse, academic essays need to adhere to a certain level of formality, so we can’t always use the same word choices in essay writing that we would use in daily life. If you’re struggling to choose the right words for your essay, don’t worry—you’ve come to the right place! In this article, we’ve compiled a list of over 300 words and phrases to use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essay. The introduction is one of the hardest parts of an essay to write. You have only one chance to make a first impression, and you want to hook your reader. If the introduction isn’t effective, the reader might not even bother to read the rest of the essay. That’s why it’s important to be thoughtful and deliberate with the words you choose at the beginning of your essay. Many students use a quote in the introductory paragraph to establish credibility and set the tone for the rest of the essay. When you’re referencing another author or speaker, try using some of these phrases: To use the words of X According to X As X states Example: To use the words of Hillary Clinton, “You cannot have maternal health without reproductive health.” Near the end of the introduction, you should state the thesis to explain the central point of your paper. If you’re not sure how to introduce your thesis, try using some of these phrases: In this essay, I will… The purpose of this essay… This essay discusses… In this paper, I put forward the claim that… There are three main arguments for…  Example: In this essay, I will explain why dress codes in public schools are detrimental to students. After you’ve stated your thesis, it’s time to start presenting the arguments you’ll use to back up that central idea. When you’re introducing the first of a series of arguments, you can use the following words: First and foremost First of all To begin with Example: First , consider the effects that this new social security policy would have on low-income taxpayers. All these words and phrases will help you create a more successful introduction and convince your audience to read on. The body of your essay is where you’ll explain your core arguments and present your evidence. It’s important to choose words and phrases for the body of your essay that will help the reader understand your position and convince them you’ve done your research. Let’s look at some different types of words and phrases that you can use in the body of your essay, as well as some examples of what these words look like in a sentence. Transition Words and PhrasesTransitioning from one argument to another is crucial for a good essay. It’s important to guide your reader from one idea to the next so they don’t get lost or feel like you’re jumping around at random. Transition phrases and linking words show your reader you’re about to move from one argument to the next, smoothing out their reading experience. They also make your writing look more professional. The simplest transition involves moving from one idea to a separate one that supports the same overall argument. Try using these phrases when you want to introduce a second correlating idea: Additionally In addition Furthermore Another key thing to remember In the same way Correspondingly Example: Additionally , public parks increase property value because home buyers prefer houses that are located close to green, open spaces. Another type of transition involves restating. It’s often useful to restate complex ideas in simpler terms to help the reader digest them. When you’re restating an idea, you can use the following words: In other words To put it another way That is to say To put it more simply Example: “The research showed that 53% of students surveyed expressed a mild or strong preference for more on-campus housing. In other words , over half the students wanted more dormitory options.” Often, you’ll need to provide examples to illustrate your point more clearly for the reader. When you’re about to give an example of something you just said, you can use the following words: For instance To give an illustration of To exemplify To demonstrate As evidence Example: Humans have long tried to exert control over our natural environment. For instance , engineers reversed the Chicago River in 1900, causing it to permanently flow backward. Sometimes, you’ll need to explain the impact or consequence of something you’ve just said. When you’re drawing a conclusion from evidence you’ve presented, try using the following words: As a result Accordingly As you can see This suggests that It follows that It can be seen that For this reason For all of those reasons Consequently Example: “There wasn’t enough government funding to support the rest of the physics experiment. Thus , the team was forced to shut down their experiment in 1996.”  When introducing an idea that bolsters one you’ve already stated, or adds another important aspect to that same argument, you can use the following words: What’s more Not only…but also Not to mention To say nothing of Another key point Example: The volcanic eruption disrupted hundreds of thousands of people. Moreover , it impacted the local flora and fauna as well, causing nearly a hundred species to go extinct. Often, you'll want to present two sides of the same argument. When you need to compare and contrast ideas, you can use the following words: On the one hand / on the other hand Alternatively In contrast to On the contrary By contrast In comparison Example: On the one hand , the Black Death was undoubtedly a tragedy because it killed millions of Europeans. On the other hand , it created better living conditions for the peasants who survived. Finally, when you’re introducing a new angle that contradicts your previous idea, you can use the following phrases: Having said that Differing from In spite of With this in mind Provided that Nevertheless Nonetheless Notwithstanding Example: Shakespearean plays are classic works of literature that have stood the test of time. Having said that , I would argue that Shakespeare isn’t the most accessible form of literature to teach students in the twenty-first century. Good essays include multiple types of logic. You can use a combination of the transitions above to create a strong, clear structure throughout the body of your essay. Strong Verbs for Academic WritingVerbs are especially important for writing clear essays. Often, you can convey a nuanced meaning simply by choosing the right verb. You should use strong verbs that are precise and dynamic. Whenever possible, you should use an unambiguous verb, rather than a generic verb. For example, alter and fluctuate are stronger verbs than change , because they give the reader more descriptive detail. Here are some useful verbs that will help make your essay shine. Verbs that show change: Accommodate Verbs that relate to causing or impacting something: Verbs that show increase: Verbs that show decrease: Deteriorate Verbs that relate to parts of a whole: Comprises of Is composed of Constitutes Encompasses Incorporates Verbs that show a negative stance: Misconstrue  Verbs that show a positive stance: Substantiate Verbs that relate to drawing conclusions from evidence: Corroborate Demonstrate Verbs that relate to thinking and analysis: Contemplate Hypothesize Investigate Verbs that relate to showing information in a visual format: Useful Adjectives and Adverbs for Academic EssaysYou should use adjectives and adverbs more sparingly than verbs when writing essays, since they sometimes add unnecessary fluff to sentences. However, choosing the right adjectives and adverbs can help add detail and sophistication to your essay. Sometimes you'll need to use an adjective to show that a finding or argument is useful and should be taken seriously. Here are some adjectives that create positive emphasis: Significant Other times, you'll need to use an adjective to show that a finding or argument is harmful or ineffective. Here are some adjectives that create a negative emphasis: Controversial Insignificant Questionable Unnecessary Unrealistic Finally, you might need to use an adverb to lend nuance to a sentence, or to express a specific degree of certainty. Here are some examples of adverbs that are often used in essays: Comprehensively Exhaustively Extensively Respectively Surprisingly Using these words will help you successfully convey the key points you want to express. Once you’ve nailed the body of your essay, it’s time to move on to the conclusion. The conclusion of your paper is important for synthesizing the arguments you’ve laid out and restating your thesis. In your concluding paragraph, try using some of these essay words: In conclusion To summarize In a nutshell Given the above As described All things considered Example: In conclusion , it’s imperative that we take action to address climate change before we lose our coral reefs forever. In addition to simply summarizing the key points from the body of your essay, you should also add some final takeaways. Give the reader your final opinion and a bit of a food for thought. To place emphasis on a certain point or a key fact, use these essay words: Unquestionably Undoubtedly Particularly Importantly Conclusively It should be noted On the whole Example: Ada Lovelace is unquestionably a powerful role model for young girls around the world, and more of our public school curricula should include her as a historical figure. These concluding phrases will help you finish writing your essay in a strong, confident way. There are many useful essay words out there that we didn't include in this article, because they are specific to certain topics. If you're writing about biology, for example, you will need to use different terminology than if you're writing about literature. So how do you improve your vocabulary skills? The vocabulary you use in your academic writing is a toolkit you can build up over time, as long as you take the time to learn new words. One way to increase your vocabulary is by looking up words you don’t know when you’re reading. Try reading more books and academic articles in the field you’re writing about and jotting down all the new words you find. You can use these words to bolster your own essays. You can also consult a dictionary or a thesaurus. When you’re using a word you’re not confident about, researching its meaning and common synonyms can help you make sure it belongs in your essay. Don't be afraid of using simpler words. Good essay writing boils down to choosing the best word to convey what you need to say, not the fanciest word possible. Finally, you can use ProWritingAid’s synonym tool or essay checker to find more precise and sophisticated vocabulary. Click on weak words in your essay to find stronger alternatives. 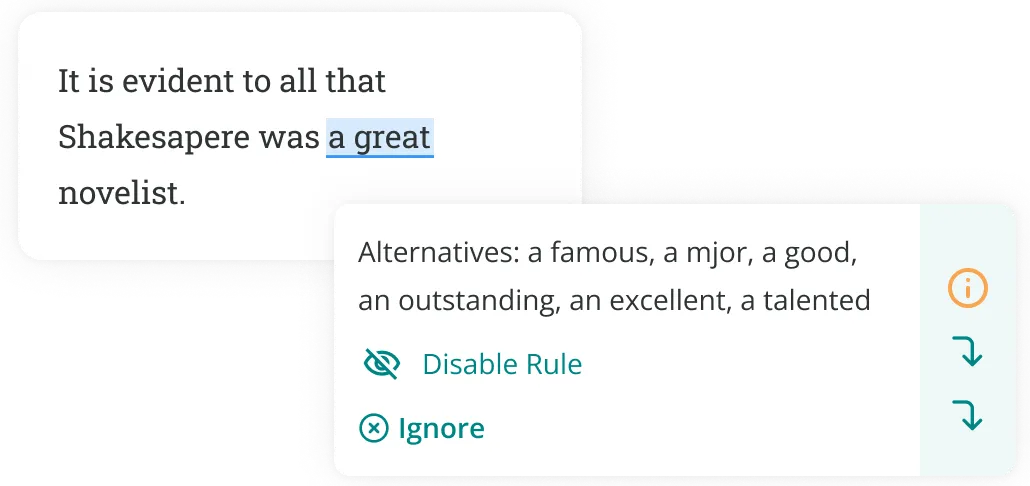 There you have it: our compilation of the best words and phrases to use in your next essay . Good luck!  Good writing = better gradesProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of all your assignments. Hannah YangHannah Yang is a speculative fiction writer who writes about all things strange and surreal. Her work has appeared in Analog Science Fiction, Apex Magazine, The Dark, and elsewhere, and two of her stories have been finalists for the Locus Award. Her favorite hobbies include watercolor painting, playing guitar, and rock climbing. You can follow her work on hannahyang.com, or subscribe to her newsletter for publication updates. Get started with ProWritingAidDrop us a line or let's stay in touch via : - Daily Crossword
- Word Puzzle
- Word Finder
- Word of the Day
Synonym of the Day- Word of the Year
- Language stories
- All featured
- Gender and sexuality
- All pop culture
- Writing hub
- Grammar essentials
Commonly confused - All writing tips
- Pop culture
- Writing tips
Start each day with the Synonym of the Day in your inbox! By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policies.  Learn how ancient Sanskrit has influenced modern language with this list of words that have made their way into English. Read more. Advertisement Calling all cruciverbalists! Sharpen your mind with crosswords and word games, or take a brain break with your favorite classic games.  - What Is Artificial Intelligence? Learn These 14 Trending ChatGPT Terms
- 11 Luscious Words for the Color Orange Worth Biting Into
- 15 Fascinating Tree Names, Types of Trees, and Tree Species
- There’s No Way You’ll Know All These Florida Words
- What Are the Hardest Languages to Learn?
 Salutations, logophile! Sign up to get everything a word lover could want: word origins, fun facts, and the latest language trends.  14 Other Words for “Said” in an Essay You want to sound as engaging and interesting as possible when writing an essay, and using words like “said” might prevent that. So, if you’re about to use “said” for the umpteenth time, you’re in luck! We have gathered some alternatives to show you other ways to say “said” in an essay that are bound to keep the reader entertained. Other Ways to Say “Said”Key takeaways. - “Stated” is a great essay word that shows you are quoting a specific statement from a trustworthy source.
- “Declared” is a great way to describe an announcement or official quote.
- “Mentioned” is a bit simpler and allows you to highlight a quote that’s relevant to your essay.
Keep reading to find out how to quote what someone said in an essay. We’ll go over the three most effective terms to help spice up your academic writing. One of the most common ways to replace “said” in an essay is “stated.” It’s a great formal synonym that helps to keep things direct and clear for the reader. It works well before a quote. You should write “stated” to clarify that you’re about to run a quote by the reader. Of course, you can’t claim that someone “stated” something without backing it up with evidence. The last thing you’ll want is for the reader to look into the quote and find out it was never actually said. But, as long as you’ve done your research, this works well. Good academic phrases that start with “stated” help you to establish a clear quote relating to the bulk of your essay. These essay samples will also help you understand it: It’s clear that he stated “time is the killer of all things.” However, nobody really understood the prophetic meaning behind it. She stated that “it’s time to make the changes you want to see in the world.” That’s what led most people to join the revolution. For a more impactful alternative, you can use “declared.” You won’t find “declared” quite as often as “said,” but it’s still an incredibly good term to include. It’s a formal synonym. It also shows that someone announced something important . Generally, “declared” comes before compelling quotes. It might be more suitable to use it when quoting a famous politician or monarch of some kind. It’s a surefire way to engage the reader and spark their imagination. We highly recommend it when you’re certain that it belongs before a quote and will allow you to establish a more powerful meaning behind it. Perhaps these essay samples will also help you with it: The king declared “good things will come to those who ask me for them.” He was a very proud man. She declared that “this was going to be the only time she offered her services to those in need.” Feel free to use “mentioned,” too. It’s another word you can use instead of “said” in an essay that’ll keep things engaging for the reader. It’s much subtler than the other phrases. It suggests that someone has made a brief comment about something, and you’d like to quote it for the reader. Don’t worry; it’s still a good formal synonym. However, you should use it when the quote isn’t the most important part of your essay. Quotes are there to add a bit of context for the reader. So, they’re not always needed to improve an essay. “Mentioned” is a simple word that allows you to include a short but interesting quote . However, it usually isn’t as impactful as saying something like “declared” or “exclaimed.” You can also refer to these essay examples: The politician mentioned that “we cannot know what we haven’t already experienced.” That resonated with me. It was clear that he mentioned “things were bound to change soon,” so they had to figure out what he meant. - 11 Other Ways to Say “Thank You for Your Time”
- 14 Other Ways to Say “Keep up the Good Work”
- 10 Other Ways to Say “Sorry for the Inconvenience”
- 19 Gender-Neutral Alternatives to “Dear Sir or Madam”
We are a team of experienced communication specialists. Our mission is to help you choose the right phrase or word for your emails and texts. Choosing the right words shouldn't be your limitation! © WordSelector University of Notre Dame Notre Dame Philosophical Reviews Kant’s Will at the Crossroads: An Essay on the Failings of Practical Reason Jens Timmermann, Kant’s Will at the Crossroad: An Essay on the Failings of Practical Reason , Oxford University Press, 2022, 192pp., $80.00 (hbk), ISBN 9780192896032. Reviewed by Andrews Reath, University of California, Riverside Jens Timmermann’s essay aims to give us Kant’s account of ‘practical failure’, that is, of what happens when an agent ‘deviates from the demands of reason’ (2). In doing so, Timmermann develops a distinctive treatment of the principal ideas in Kant’s moral psychology and conception of rational agency. One guiding thread is to ‘re-assert’ (153), in opposition to a recent and influential interpretive trend, that Kant’s moral conception does indeed operate with several stark dualisms—between duty and happiness, between moral and non-moral motivation, between pure practical reason and the empirically conditioned use of practical reason. On Timmermann’s reading, Kant held that the human being is moved by two heterogeneous kinds of incentives (moral interests and the interest in happiness) that operate in radically different ways and that, as a result, the will—by which he means the faculty of choice [ Willkür ]—stands at a crossroads (as Kant says at G 4:400) and must choose between them. On Timmermann’s reading these standard dualisms support another that is the central thesis of the book—that Kant accepted a ‘hybrid theory of practical failure. . .which points to a hybrid theory of practical rationality’ (6, 7). Is failure to conform to reason due to mistaken judgment about, or ignorance of, the good due to cognitive failure (as Socrates thought)? Or is it due to a conscious failure to act on one’s judgment about what is best, due to some sensible influence, in which case the failure is ethical (as Aristotle thought in opposition to his teacher)? Timmermann terms the first account ‘intellectualist’ and the second ‘volitional’. His striking thesis is that ‘Kant is committed to intellectualism about non-moral action while defending a strongly anti-intellectualist or volitional position in the realm of moral choice’ (6–7). In non-moral or prudential choice, either an agent’s failure to take the available means to a professed end is due to ignorance or mistaken judgment about the appropriate means; or it is due to the agent’s no longer wanting the end, or not wanting it enough to bear the costs of attaining it. Neither case is an instance of what is termed ‘true irrationality’, because one’s choice does not in fact diverge from one’s judgment of what is prudentially best. Practical failure in this domain is due to mistaken judgement, rather than choice that violates some distinctively practical principle. But, Timmermann argues, this account of practical failure does not ring true in the moral sphere. ‘Moral failure is not caused by some cognitive defect or a flawed piece of reasoning. It consists in the conscious, knowing, voluntary choice not to will the moral end’ (7). In prototypically moral failure we judge one action to be the morally good choice, but knowingly choose a different course (weakly, inexplicably, perversely, etc.). Timmermann ascribes these differing accounts of practical failure to Kant on both textual and philosophical grounds, and his discussion of practical failure is a bridge to the hybrid account of practical rationality, which holds that choice is determined in radically different ways in the moral and non-moral domains. In prudential choice Kant is an intellectualist in the sense that choice and action are invariably determined by one’s judgment (e.g., of what one wants most, or of the proper means to one’s end). There is no gap between judgment and choice, and we do not knowingly choose contrary to our judgment. However, in the moral sphere rational deliberation and judgment are one thing, but choice is something further and choice can diverge from judgment. The faculty of choice is tasked with following the dictates of practical reason. But given the heterogeneity of the incentives by which human beings are moved, following the dictates of practical reason requires an elective act on the part of an agent that reflects or determines one’s character. In that sense, Kant is a ‘volitionist’ about moral choice. The upshot, according to Timmermann, is that there is no unified account of practical rationality in Kant. One element of this dualistic reading is his claim that for Kant ‘there is no freedom in non-moral choice’ (4n.14)—a claim to which I will return. Some background will help bring out the significance of Timmermann’s reading. The above dualisms are on display in the Analytic of the Critique of Practical Reason , where Kant draws a distinction between ‘practical laws’ deriving from the formal principle of morality based in reason a priori and ‘material practical principles’ that place the ground of choice in pleasure or the feeling of agreeableness ( KpV 5: 22ff.). In the Critique Kant treats this dichotomy as exhaustive, in that any principle of choice falls into one category or the other. Moreover, what unifies those in the second category (‘makes them wholly of the same kind’) is that they place the ground of choice in pleasure or the feeling of agreeableness—which Kant treats as affections ‘of one and the same vital force’—so that any principle of choice other than respect for moral principles—including, e.g., other-regarding principles based on affection or natural sympathy— falls under the ‘general principle of self-love or one’s own happiness’ ( KpV 5:22). And in Chapter II, Kant argues that absent an a priori law of pure practical reason, the only ground of choice is the subjective standard of what an agent finds agreeable. Several commentators have looked for ways to soften these dichotomies and to find some continuity between moral and non-moral choice—often on purely interpretive grounds, but sometimes in an effort to nudge Kant in a direction that they find philosophically more acceptable. They grant the heterogeneity of moral and non-moral incentives and allow that they ground different deliberative processes. But they argue that Kant held (should have held?) that as different as these incentives are, they are taken up into choice on the same terms—through an act of reflective endorsement, or by taking the incentive to be an objectively sufficient ground of choice. The idea—and here is a variation of what Henry Allison has called Kant’s ‘Incorporation Thesis’—is that any incentive comes to influence choice by being taken up into practical self-consciousness as an item from which one can reason to action. Timmermann cites Christine Korsgaard, Allison, Stephen Engstrom, and myself as proponents of what he calls ‘intellectualism’ about moral choice. (I’m happy to be included in this august company, and though I prefer the term ‘cognitivism’, I will use ‘intellectualism’ in this review in deference to Timmermann.) Some readers find continuity between moral and non-moral choice to be inherently attractive, but in addition this approach has the specific advantage of allowing Kant to say that choices made on both moral and non-moral grounds are free (and imputable to the agent) in just the same sense. A difficulty for this approach is that, in addition to holding that morally neutral or innocent choice results from a judgment made on sufficient grounds, it must say the same about choices that are clearly morally bad—that in action that violates moral principle, an incentive influences choice through the agent incorrectly taking it to be an objectively sufficient ground of choice. [1] Does such a model allow for knowing and intentional wrong-doing, as Kant allows and which seems clearly possible? This concern is one of Timmermann’s reasons for defending an alternative approach that he finds truer to the texts. Timmermann’s reading is striking for ascribing to Kant a hybrid theory of practical rationality—intellectualism about prudence and a volitional understanding of moral choice. Equally striking is his suggestion that the interpretive approach that he targets is the ‘mirror image’, favoring a volitional understanding of prudential and an intellectualist understanding of moral choice (128). One might think that one should have the same understanding of each domain, whatever that might be. Clearly there is still a lot to sort out here. Timmermann’s book contains insightful discussions of many topics central to Kant’s conception of practical reason and to related contemporary discussions. The writing is admirably clear and to the point. There is much to be learned from his careful interpretive work and from his comments on the relevant secondary literature. I found almost all of the book to be instructive, even though I take the other side on several issues. Since his main claims deserve more detailed discussion than a short review permits, I’ll limit myself to pointing out some main building blocks of the hybrid conception that he ascribes to Kant. Chapter 2 argues for the hedonistic reading of Kant’s conception of happiness as a sum of agreeable feeling (rather than overall desire satisfaction), stressing that for Kant the difficulty of forming a conception of happiness is uncertainty about what we will find agreeable. Timmermann emphasizes Kant’s idea that the quantity of expected pleasure is the single ‘volitional currency of prudential deliberation’ (27). This is an important element of the hybrid conception since it sets up the idea that human beings are moved by two heterogeneous kinds of interests (moral and prudential), between which there is, as it were, no rate of exchange. Chapter 4 is a discussion of instrumental imperatives aimed at showing that so-called ‘“empirical practical reason” is not a mode of practical reason at all’ (46). On Timmermann’s reading ‘there is only one principle of practical reason: the categorical imperative (52).’ Noting Kant’s later view in the Critique of Judgment that hypothetical imperatives are ‘corollaries of theoretical reason ( KU 5:172),’ Timmermann sides with those who argue that Kant did not accept a single fundamental principle of instrumental rationality that, following Tom Hill’s classic paper, is often called ‘the Hypothetical Imperative’. There are then no distinctively practical principles of means-end rationality—neither particular hypothetical imperatives understood as genuinely practical principles nor a single fundamental principle of instrumental rationality. This idea sets up one line of argument for intellectualism in the prudential domain. If there are no genuinely practical principles of instrumental reason, there is no ‘true means-end irrationality’ in the sense of action that violates some such principle. But if practical failure in the prudential domain is not due to the violation of some practical principle, then it must be due to ignorance of or failure to grasp the relevant (theoretical) means-end connection. That supports the idea that prudential choice is directly determined by judgment (about what will bring about most satisfaction, etc.). Timmermann develops a more intuitive line of argument as well. It is hard to understand why an agent would not take the known and available means to an end that she wants, especially if we assume that agreeable feeling is the single volitional currency in the prudential domain—indeed, so hard to understand that it could never happen (cf. 65). If one is not taking the available means to something that one wants on the grounds of expected pleasure, that must be due either a) to a mistaken judgment about the means or b) to the agent’s now finding some alternative more appealing (in which case there is no practical failure) (see 8, 57, 109). One problem that I see is that Timmermann supports this point through very simple examples, such as taking steps to make good coffee or good bread. In cases where the means to a happiness-based end is clearly known and available, it is hard to understand how someone with the end can fail to take the means, and we conclude that they changed their mind about the end. Here the intellectualist account that draws a straight line between means-end judgment and choice is compelling. However, I do not see that such cases rule out the possibility of more complex cases of true means-end irrationality—where an agent fails to take the known, available but difficult steps to what she clearly believes will bring greater happiness, cases where volitional failure (out of weakness, distraction or indecision) is plausible. Philosophers are divided over this issue and though Timmermann’s discussion is carefully framed, I doubt that it will settle either the philosophical issue or what Kant thought. Chapter 6 raises important challenges to the ‘intellectualist’ conceptions of moral choice mentioned above (namely that rational choice is constitutively guided by a judgment of sufficient reasons). First, it contains a valuable discussion of Allison’s ‘Incorporation Thesis’, arguing that this thesis does not clearly support ‘intellectualism’ about moral choice. Allison’s concern was to identify the element of spontaneity that is central to Kant’s conception of free choice across the board, and he does not explicitly position himself as supporting an ‘intellectualist’ conception of ‘incorporation’. (In fact, there is ambiguity in the notion of ‘incorporating an incentive into a maxim’. Is ‘incorporation’ a bare elective act, the simple adoption of a maxim? Or does it involve an element of normatively guided judgment or endorsement?) Timmermann’s contribution is to bring out the cognitivist slant to Allison’s reading (namely that to incorporate an incentive into a maxim is to endorse a general principle that treats the incentive as a sufficient ground of choice) and to show that another interpretation is possible, here getting into the weeds with alternate readings of passages from Kant’s Lectures on which Allison draws. The main thrust of Timmermann’s discussion is that ‘incorporation’ is an act of Willkür , of the faculty of choice. But on the standard reading of this distinction, while Wille is a deliberative capacity (it is ‘practical reason itself’ ( MdS 6: 213)), Willkür is a purely elective capacity. As Timmermann writes, given that ‘rational assessment cannot be the task of Willkür . . .why not assume that incorporation is an elective, not an evaluative act? (97)’ Human beings are moved by heterogeneous and incommensurable motives, and we must choose which to prioritize. A second challenge is the difficulty for the ‘intellectualist’ of accommodating the phenomenon of knowingly acting against one’s moral judgement (102–6). Timmermann cites several passages in which Kant clearly allows for this possibility. The question for the ‘intellectualist’ here is how to accommodate these passages and, more importantly, this phenomenon. Can the ‘intellectualist’ respond to these clearly legitimate challenges? I think that there is textual support for the ‘intellectualist’ position, though granted there are texts that run in the other direction. One might not find a decisive answer in what Kant says. [2] But there are systematic considerations as well. There is a general worry that the ‘volitional conception’ detaches moral choice from practical reasoning and judgment in ways that make it arbitrary and ungrounded. Should we attribute such a view to Kant? More generally, does an elective conception of choice fit into a general conception of the will as a rational power that is exercised according to its own constitutive principle? Is there room in that conception of the will for a purely elective capacity whose exercise, though subject to normative (moral) assessment, is itself normatively ungrounded? (Timmermann will certainly say ‘Yes,’ while I say: ‘Perhaps Not’.) These are complicated issues that need more discussion than this review permits. One virtue of Timmermann’s essay is to have raised them so clearly. One recurring theme in the essay is that prudential choice is not free: ‘there is no freedom in empirically conditioned practical choice, which might just as well be mechanical, because the spontaneity involved is relative to antecedent purposes rather than absolute’ (98). (See also 4n14, 8, 24, 120, 156.) Initially these remarks puzzled me because they come close to saddling Kant with the ‘Reinhold problem’—that only morally good choice is free, that morally bad choice is not free and therefore not imputable. But Timmermann does not saddle Kant with this problem. Rather he is articulating the standard Kantian idea that free agency is only manifest or most fully realized in action motivated by respect for moral principle. But then does Timmermann’s reading leave room for a sense in which all choice across the board is free? I understand his reading as follows: Genuine freedom requires the capacity to choose between radically different alternatives. That is, it requires both that agents face motivational alternatives of an entirely different kind and that they have the capacity to choose between them. Furthermore, freedom requires a capacity for genuine self-determination. Human beings satisfy these conditions. We are moved by incentives that operate in ‘different volitional currencies,’ and we have the capacity to choose between them. Furthermore, that capacity is a capacity for self-determination because it gives us the ability to set aside sensible interest and to act from principles that reason gives to itself. Human beings then have the capacity for free agency. Where only prudential considerations rooted in the expectation of agreeable feeling are at issue, we can move almost ‘mechanically’ from such considerations to choice; in that respect prudential choice does not draw on our free/moral capacity. But since moral considerations are always on the table, in any choice situation where we find reason to, we can bracket prudential interest and follow moral principle. (So the existence of free/moral capacity settles the issue of responsibility.) I suspect that there is another piece to this puzzle. One might think that, given the ever-presence of morality, whenever agents act from prudence, they have elected to—that is, they did in fact side with that basic alternative. That is to say that they have exercised a capacity for elective choice that does not draw on specifically moral capacity (but which could at any time). Is that a sense in which all choice across the board is free? These are delicate issues that Timmermann might address more explicitly. Kant’s Will at the Crossroad develops a comprehensive approach to Kant’s conception of practical rationality supported by careful reading of the principal texts. By re-affirming several (familiar) dualisms that other commentators have played down, it lays out an alternative to one influential trend in recent Kant scholarship. These issues are subtle and complex, and we should be grateful to Jens Timmermann for putting them on the table so clearly and giving us the opportunity to think them through once more. References to Kant’s work use the following abbreviations and cite paging in the Berlin Academy Edition: G Groundwork of the Metaphysics of Morals . KpV Critique of Practical Reason . KU Critique of the Power of Judgment . MdS The Metaphysics of Morals . Reath, Andrews. 2018. “The Law of a Free Will”, in Violetta Waibel and Margit Ruffing, eds., Nature and Freedom: Proceedings of the 12 th International Kant Congress (Berlin: de Gruyter): 2123–2130 . [1] As Kant allows at KpV 5:74, in a passage that Timmermann does not discuss. [2] For a short essay in which I address these questions, see Reath 2018.  10 Other Words for “This Shows” in an Essay Showing how one thing affects another is great in academic writing. It shows that you’ve connected two points with each other, making sure the reader follows along. However, is “this shows” the only appropriate choice when linking two ideas? We have gathered some helpful synonyms teaching you other ways to say “this shows” in an essay. - Demonstrating
- This implies
- This allows
- This displays
Keep reading to learn more words to replace “this shows” in an essay. You can also review the examples we provide under each heading. Removing “this” from “this shows” creates a simple formal synonym to mix up your writing. You can instead write “showing” in academic writing to demonstrate an effect . Typically, this is a great way to limit your word count . Sure, you’re only removing one word from your essay, but if you can find other areas to do something similar, you’ll be more efficient . Efficient essays often make for the most interesting ones. They also make it much easier for the reader to follow, and the reviewer will usually be able to give you a more appropriate grade. Check out these examples if you still need help: - The facts state most of the information here, showing that we still have a lot of work to do before moving forward.
- This is the only way to complete the project, showing that things aren’t quite ready to progress.
2. DemonstratingFollowing a similar idea to using “showing,” you can also use “demonstrating.” This comes from the idea that “this demonstrates” is a bit redundant. So, you can remove “this.” Again, demonstrating ideas is a great way to engage the reader . You can use it in the middle of a sentence to explain how two things affect each other. You can also review the following examples: - These are the leading causes, demonstrating the fundamental ways to get through it. Which do you think is worth pursuing?
- I would like to direct your attention to this poll, demonstrating the do’s and don’ts for tasks like this one.
3. Leading ToThere are plenty of ways to talk about different causes and effects in your writing. A good choice to include in the middle of a sentence is “leading to.” When something “leads to” something else, it is a direct cause . Therefore, it’s worth including “leading to” in an essay when making relevant connections in your text. Here are some examples to help you understand it: - This is what we are looking to achieve, leading to huge capital gains for everyone associated with it.
- I would like to direct your attention to this assignment, leading to what could be huge changes in the status quo.
4. CreatingOften, you can create cause-and-effect relationships in your writing by including two similar ideas. Therefore, it’s worth including “creating” to demonstrate a connection to the reader. Including “creating” in the middle of a sentence allows you to clarify certain causes . This helps to streamline your academic writing and ensures the reader knows what you’re talking about. Perhaps these essay samples will also help you: - We could not complete the task quickly, creating a problem when it came to the next part of the movement.
- I thought about the ideas, creating the process that we know today. I’m glad I took the time to work through it.
5. This ImpliesFor a more formal way to say “this shows,” try “this implies.” Of course, it doesn’t change much from the original phrase, but that doesn’t mean it’s ineffective. In fact, using “this implies” (or “implying” for streamlining) allows you to discuss implications and facts from the previous sentence. You will often start a sentence with “this implies.” It shows you have relevant and useful information to discuss with the reader. However, it only works when starting a sentence. You cannot use it to start a new paragraph as it does not relate to anything. “This implies” must always relate to something mentioned before. You can also review these examples: - I appreciate everything that they did for us. This implies they’re willing to work together on other projects.
- You can’t always get these things right. This implies we still have a lot of work to do before we can finalize anything.
“Proving” is a word you can use instead of “this shows” in an essay. It comes from “this proves,” showing how something creates another situation . Proof is often the most important in scientific studies and arguments. Therefore, it’s very common to use “proving” instead of “this shows” in scientific essays and writing. We recommend using this when discussing your experiments and explaining how it might cause something specific to happen. It helps the reader follow your ideas on the page. Perhaps the following examples will also help you: - They provided us with multiple variables, proving that we weren’t the only ones working on the experiment.
- I could not figure out the way forward, proving that it came down to a choice. I didn’t know the best course of action.
7. This AllowsOften, when you talk about a cause in your essays, it allows an effect to take place. You can talk more about this relationship with a phrase like “this allows.” At the start of a sentence , “this allows” is a great way to describe a cause-and-effect relationship . It keeps the reader engaged and ensures they know what you’re talking about. Also, using “this allows” directly after expressing your views explains the purpose of your writing. This could show a reader why you’ve even decided to write the essay in the first place. - Many scenarios work here. This allows us to explore different situations to see which works best.
- I found the best way to address the situation. This allows me to provide more ideas to upper management.
8. This DisplaysIt might not be as common, but “this displays” is still a great choice in academic writing. You can use it when discussing how one thing leads to another . Usually, “this displays” works best when discussing data points or figures . It’s a great way to show how you can display your information within your writing to make things easy for the reader . You can refer to these examples if you’re still unsure: - We have not considered every outcome. This displays a lack of planning and poor judgment regarding the team.
- I’m afraid this is the only way we can continue it. This displays a problem for most of the senior shareholders.
9. IndicatingIndicating how things connect to each other helps readers to pay attention. The clearer your connections, the better your essay will be. Therefore, it’s worth including “indicating” in the middle of a sentence . It shows you two points relate to each other . Often, this allows you to talk about specific effects. It’s a great way to explain the purpose of a paragraph (or the essay as a whole, depending on the context). If you’re still stuck, review these examples: - There are plenty of great alternatives to use, indicating that you don’t have to be so close-minded about the process.
- I have compiled a list of information to help you, indicating the plethora of ways you can complete it.
10. SuggestingFinally, “suggesting” is a word you can use instead of “this shows” in an essay. It’s quite formal and works well in academic writing. We highly recommend using it when creating a suggestion from a previous sentence . It allows the reader to follow along and see how one thing affects another. Also, it’s not particularly common in essays. Therefore, it’s a great choice to mix things up and keep things a little more interesting. Here are a few essay samples to help you with it: - You could have done it in many other ways, suggesting that there was always a better outcome than the one you got.
- I didn’t know what to think of it, suggesting that I was tempted by the offer. I’m still weighing up the options.
 Martin holds a Master’s degree in Finance and International Business. He has six years of experience in professional communication with clients, executives, and colleagues. Furthermore, he has teaching experience from Aarhus University. Martin has been featured as an expert in communication and teaching on Forbes and Shopify. Read more about Martin here . - 10 Better Ways To Write “In This Essay, I Will…”
- 10 Other Ways to Say “I Am” in an Essay
- 11 Formal Synonyms for “As a Result”
- 10 Other Words for “Said” in an Essay
 |
IMAGES
COMMENTS
Synonyms for ESSAY: article, paper, dissertation, theme, thesis, composition, treatise, editorial; Antonyms of ESSAY: quit, drop, give up
Find 80 different ways to say ESSAY, along with antonyms, related words, and example sentences at Thesaurus.com.
Synonyms for essay include article, dissertation, paper, treatise, thesis, discourse, study, composition, critique and exposition. Find more similar words at ...
Another way to say Essay? Synonyms for Essay (other words and phrases for Essay).
ESSAY - Synonyms, related words and examples | Cambridge English Thesaurus
A 3000 word essay. A misjudged essay. A misjudged essay in job preservation. About that essay you wrote yesterday. And a short essay on the theme of the family. Ad-free experience & advanced Chrome extension.
Synonyms for essay in Free Thesaurus. Antonyms for essay. 82 synonyms for essay: composition, study, paper, article, piece, assignment, discourse, tract, treatise ...
Thesaurus; Essay Essay Synonyms and Antonyms. ĕsā, ĕ-sā . Meanings Synonyms Common Words Unique Words. Synonyms Antonyms Related Words Expository writing (Noun) Synonyms: composition; theme; article; paper; piece; A procedure that ascertains effectiveness, value, proper function, or other quality ...
Synonyms for ESSAY in English: composition, study, paper, article, piece, assignment, discourse, tract, treatise, dissertation, …
Synonyms for ESSAYS: articles, papers, themes, dissertations, editorials, treatises, commentaries, compositions; Antonyms of ESSAYS: drops, gives up, quits
essay - WordReference thesaurus: synonyms, discussion and more. All Free.
This thesaurus page includes all potential synonyms, words with the same meaning and similar terms for the word essay. English Synonyms and Antonyms Rate these synonyms: 2.7 / 3 votes. essay verb. To attempt is to take action somewhat experimentally with the hope and purpose of accomplishing a certain result; ...
The meaning of ESSAY is an analytic or interpretative literary composition usually dealing with its subject from a limited or personal point of view. How to use essay in a sentence. Synonym Discussion of Essay.
4. That is to say. Usage: "That is" and "that is to say" can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: "Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.". 5. To that end. Usage: Use "to that end" or "to this end" in a similar way to "in order to" or "so".
Synonyms of 'essay' in British English. essay. 1 (noun) in the sense of composition. Definition. a short piece of writing on a subject done as an exercise by a student. He was asked to write an essay about his home town. Synonyms. composition. Write a composition on the subject `What I Did on My Holidays'.
If you're struggling to choose the right words for your essay, don't worry—you've come to the right place! In this article, we've compiled a list of over 300 words and phrases to use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essay. Contents: Words to Use in the Essay Introduction. Words to Use in the Body of the Essay.
Concluding your paper or presentation can feel redundant if you always say "in conclusion." These alternatives will help you end your project with style.
Find 149 different ways to say AS WELL AS, along with antonyms, related words, and example sentences at Thesaurus.com.
Abruptly switching topics in essays can be jarring; however, transition words can smooth the change for the convenience of the reader.Moreover, you can use essay transition words to start a paragraph, sentence, or clause more naturally.Additionally, essay transition words can connect new information to the previous statement so you don't have to say everything at once.
Thesaurus.com is more than just a website for finding synonyms and antonyms of words. It is a comprehensive online resource that helps you improve your vocabulary, writing, and communication skills. Whether you need a word of the day, a synonym for a common term, or an example sentence to illustrate your point, Thesaurus.com has it all.
Stated. One of the most common ways to replace "said" in an essay is "stated.". It's a great formal synonym that helps to keep things direct and clear for the reader. It works well before a quote. You should write "stated" to clarify that you're about to run a quote by the reader. Of course, you can't claim that someone ...
Jens Timmermann's essay aims to give us Kant's account of 'practical failure', that is, of what happens when an agent 'deviates from the demands of reason' (2). In doing so, Timmermann develops a distinctive treatment of the principal ideas in Kant's moral psychology and conception of rational agency. One guiding thread is to ...
This implies we still have a lot of work to do before we can finalize anything. 6. Proving. "Proving" is a word you can use instead of "this shows" in an essay. It comes from "this proves," showing how something creates another situation. Proof is often the most important in scientific studies and arguments.