The Differences in a Research Report and Research Paper
Derek m. kwait.

When writing a paper, maybe the only thing more daunting than actually writing it is deciding what you're even supposed to be writing about. Research reports, research papers...it gets confusing. They are actually not the same thing, and knowing the difference between them will save you time and frustration, help you stay on-target and ultimately help you get the highest possible grade.

Explore this article
- Defining Research
- What is a Research Report?
- What is a Research Paper?
- A Word of Caution
1 Defining Research
According to Webster's Dictionary, research can be a "careful or diligent search," a "studious inquiry or examination... aimed at the discovery and interpretation of facts...in the light of new facts, or practical application of such new or revised theories or laws" or "the collecting of information about a particular subject."
While research reports and research papers both involve much of the first definition, a research report is more concerned with the second, and a research paper with the third.
2 What is a Research Report?
A research report is a paper reporting research that has already been conducted. As such, it is used primarily in the sciences to tell other scientists (or your instructor) about the process, findings and significance of your experiment.
According to a guide prepared by the American Chemical Society, a good research report of any kind should be organized in a way that parallels the method of scientific reasoning. The usual parts of this report are Title, Abstract, Introduction, Experimental Details or Theoretical Analysis, Results, Discussion, Conclusions and Summary, then References.
3 What is a Research Paper?
A research paper, on the other hand, is the research itself. In other words, a research paper typically presents quotes or information from books or scholarly papers or even movies, then analyzes them to reach some sort of conclusion. It does not report on an objective, reproducible experiment done elsewhere but instead focuses on establishing the author's thesis and arguing in favor of it. Research papers are usually used in the humanities. The format for a good research paper includes an introductory paragraph, two or three body paragraphs and a conclusion.
4 A Word of Caution
This explanation covers how these terms are typically used; there is no universally agreed upon definition of either term. Sometimes an instructor will assign a research report when he really meant a research paper or vice versa. You can usually tell what is required by what kind of class it is and what the instructor says he wants (for example, if a laboratory experiment is involved, chances are a research report is required) but if you are really unsure, ask.
- 1 ACS: Preparing a Research Report
- 2 Purdue Online Writing Lab: Research
About the Author
Derek M. Kwait has a Bachelor of Arts in English writing from the University of Pittsburgh and has been writing for most of his life in various capacities. He has worked as a staff writer and videographer for the "Jewish Chronicle of Pittsburgh" and also has training writing fiction, nonfiction, stage-plays and screenplays.
Related Articles

The Difference Between Research & Science

How to Write an Introduction of a Report

Reasons for a Hypothesis

The Advantages of a Formal Report

The Advantages of Exploratory Research Design

The Advantages of Writing an Inductive Essay

Steps in Writing a Report

How to Properly Write Book Titles in a Report

What Is a Problem Statement in a Lab Report?

How to Start a Thesis Statement

The Five Approaches to Qualitative Research

How to Write Up a Science Experiment in 3rd Grade

How to Write a Documented Essay

Six-Step Scientific Method for Elementary Kids

How to Find Empirical Articles

What is the Difference Between Criminal Justice & Criminology?

The Difference Between Analysis & Findings in a Research...

How to Critique a Dissertation

What Are the Advantages & Disadvantages of Correlation...

Difference Between Conceptual & Theoretical Framework
Regardless of how old we are, we never stop learning. Classroom is the educational resource for people of all ages. Whether you’re studying times tables or applying to college, Classroom has the answers.
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy
- Manage Preferences
© 2020 Leaf Group Ltd. / Leaf Group Media, All Rights Reserved. Based on the Word Net lexical database for the English Language. See disclaimer .
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Table of Contents

Research Report
Definition:
Research Report is a written document that presents the results of a research project or study, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions, in a clear and objective manner.
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the findings of the research to the intended audience, which could be other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public.
Components of Research Report
Components of Research Report are as follows:
Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the research report and provides a brief overview of the research question or problem being investigated. It should include a clear statement of the purpose of the study and its significance or relevance to the field of research. It may also provide background information or a literature review to help contextualize the research.
Literature Review
The literature review provides a critical analysis and synthesis of the existing research and scholarship relevant to the research question or problem. It should identify the gaps, inconsistencies, and contradictions in the literature and show how the current study addresses these issues. The literature review also establishes the theoretical framework or conceptual model that guides the research.
Methodology
The methodology section describes the research design, methods, and procedures used to collect and analyze data. It should include information on the sample or participants, data collection instruments, data collection procedures, and data analysis techniques. The methodology should be clear and detailed enough to allow other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the study in a clear and objective manner. It should provide a detailed description of the data and statistics used to answer the research question or test the hypothesis. Tables, graphs, and figures may be included to help visualize the data and illustrate the key findings.
The discussion section interprets the results of the study and explains their significance or relevance to the research question or problem. It should also compare the current findings with those of previous studies and identify the implications for future research or practice. The discussion should be based on the results presented in the previous section and should avoid speculation or unfounded conclusions.
The conclusion summarizes the key findings of the study and restates the main argument or thesis presented in the introduction. It should also provide a brief overview of the contributions of the study to the field of research and the implications for practice or policy.
The references section lists all the sources cited in the research report, following a specific citation style, such as APA or MLA.
The appendices section includes any additional material, such as data tables, figures, or instruments used in the study, that could not be included in the main text due to space limitations.
Types of Research Report
Types of Research Report are as follows:
Thesis is a type of research report. A thesis is a long-form research document that presents the findings and conclusions of an original research study conducted by a student as part of a graduate or postgraduate program. It is typically written by a student pursuing a higher degree, such as a Master’s or Doctoral degree, although it can also be written by researchers or scholars in other fields.
Research Paper
Research paper is a type of research report. A research paper is a document that presents the results of a research study or investigation. Research papers can be written in a variety of fields, including science, social science, humanities, and business. They typically follow a standard format that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion sections.
Technical Report
A technical report is a detailed report that provides information about a specific technical or scientific problem or project. Technical reports are often used in engineering, science, and other technical fields to document research and development work.
Progress Report
A progress report provides an update on the progress of a research project or program over a specific period of time. Progress reports are typically used to communicate the status of a project to stakeholders, funders, or project managers.
Feasibility Report
A feasibility report assesses the feasibility of a proposed project or plan, providing an analysis of the potential risks, benefits, and costs associated with the project. Feasibility reports are often used in business, engineering, and other fields to determine the viability of a project before it is undertaken.
Field Report
A field report documents observations and findings from fieldwork, which is research conducted in the natural environment or setting. Field reports are often used in anthropology, ecology, and other social and natural sciences.
Experimental Report
An experimental report documents the results of a scientific experiment, including the hypothesis, methods, results, and conclusions. Experimental reports are often used in biology, chemistry, and other sciences to communicate the results of laboratory experiments.
Case Study Report
A case study report provides an in-depth analysis of a specific case or situation, often used in psychology, social work, and other fields to document and understand complex cases or phenomena.
Literature Review Report
A literature review report synthesizes and summarizes existing research on a specific topic, providing an overview of the current state of knowledge on the subject. Literature review reports are often used in social sciences, education, and other fields to identify gaps in the literature and guide future research.
Research Report Example
Following is a Research Report Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance among High School Students
This study aims to investigate the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students. The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The findings indicate that there is a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students. The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers, as they highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities.
Introduction:
Social media has become an integral part of the lives of high school students. With the widespread use of social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and Snapchat, students can connect with friends, share photos and videos, and engage in discussions on a range of topics. While social media offers many benefits, concerns have been raised about its impact on academic performance. Many studies have found a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance among high school students (Kirschner & Karpinski, 2010; Paul, Baker, & Cochran, 2012).
Given the growing importance of social media in the lives of high school students, it is important to investigate its impact on academic performance. This study aims to address this gap by examining the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students.
Methodology:
The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The questionnaire was developed based on previous studies and was designed to measure the frequency and duration of social media use, as well as academic performance.
The participants were selected using a convenience sampling technique, and the survey questionnaire was distributed in the classroom during regular school hours. The data collected were analyzed using descriptive statistics and correlation analysis.
The findings indicate that the majority of high school students use social media platforms on a daily basis, with Facebook being the most popular platform. The results also show a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students.
Discussion:
The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. The negative correlation between social media use and academic performance suggests that strategies should be put in place to help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. For example, educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, this study provides evidence of the negative impact of social media on academic performance among high school students. The findings highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. Further research is needed to explore the specific mechanisms by which social media use affects academic performance and to develop effective strategies for addressing this issue.
Limitations:
One limitation of this study is the use of convenience sampling, which limits the generalizability of the findings to other populations. Future studies should use random sampling techniques to increase the representativeness of the sample. Another limitation is the use of self-reported measures, which may be subject to social desirability bias. Future studies could use objective measures of social media use and academic performance, such as tracking software and school records.
Implications:
The findings of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. Educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. For example, teachers could use social media platforms to share relevant educational resources and facilitate online discussions. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. They could also engage in open communication with their children to understand their social media use and its impact on their academic performance. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students. For example, schools could implement social media policies that restrict access during class time and encourage responsible use.
References:
- Kirschner, P. A., & Karpinski, A. C. (2010). Facebook® and academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(6), 1237-1245.
- Paul, J. A., Baker, H. M., & Cochran, J. D. (2012). Effect of online social networking on student academic performance. Journal of the Research Center for Educational Technology, 8(1), 1-19.
- Pantic, I. (2014). Online social networking and mental health. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 17(10), 652-657.
- Rosen, L. D., Carrier, L. M., & Cheever, N. A. (2013). Facebook and texting made me do it: Media-induced task-switching while studying. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(3), 948-958.
Note*: Above mention, Example is just a sample for the students’ guide. Do not directly copy and paste as your College or University assignment. Kindly do some research and Write your own.
Applications of Research Report
Research reports have many applications, including:
- Communicating research findings: The primary application of a research report is to communicate the results of a study to other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public. The report serves as a way to share new knowledge, insights, and discoveries with others in the field.
- Informing policy and practice : Research reports can inform policy and practice by providing evidence-based recommendations for decision-makers. For example, a research report on the effectiveness of a new drug could inform regulatory agencies in their decision-making process.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research in a particular area. Other researchers may use the findings and methodology of a report to develop new research questions or to build on existing research.
- Evaluating programs and interventions : Research reports can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and interventions in achieving their intended outcomes. For example, a research report on a new educational program could provide evidence of its impact on student performance.
- Demonstrating impact : Research reports can be used to demonstrate the impact of research funding or to evaluate the success of research projects. By presenting the findings and outcomes of a study, research reports can show the value of research to funders and stakeholders.
- Enhancing professional development : Research reports can be used to enhance professional development by providing a source of information and learning for researchers and practitioners in a particular field. For example, a research report on a new teaching methodology could provide insights and ideas for educators to incorporate into their own practice.
How to write Research Report
Here are some steps you can follow to write a research report:
- Identify the research question: The first step in writing a research report is to identify your research question. This will help you focus your research and organize your findings.
- Conduct research : Once you have identified your research question, you will need to conduct research to gather relevant data and information. This can involve conducting experiments, reviewing literature, or analyzing data.
- Organize your findings: Once you have gathered all of your data, you will need to organize your findings in a way that is clear and understandable. This can involve creating tables, graphs, or charts to illustrate your results.
- Write the report: Once you have organized your findings, you can begin writing the report. Start with an introduction that provides background information and explains the purpose of your research. Next, provide a detailed description of your research methods and findings. Finally, summarize your results and draw conclusions based on your findings.
- Proofread and edit: After you have written your report, be sure to proofread and edit it carefully. Check for grammar and spelling errors, and make sure that your report is well-organized and easy to read.
- Include a reference list: Be sure to include a list of references that you used in your research. This will give credit to your sources and allow readers to further explore the topic if they choose.
- Format your report: Finally, format your report according to the guidelines provided by your instructor or organization. This may include formatting requirements for headings, margins, fonts, and spacing.
Purpose of Research Report
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the results of a research study to a specific audience, such as peers in the same field, stakeholders, or the general public. The report provides a detailed description of the research methods, findings, and conclusions.
Some common purposes of a research report include:
- Sharing knowledge: A research report allows researchers to share their findings and knowledge with others in their field. This helps to advance the field and improve the understanding of a particular topic.
- Identifying trends: A research report can identify trends and patterns in data, which can help guide future research and inform decision-making.
- Addressing problems: A research report can provide insights into problems or issues and suggest solutions or recommendations for addressing them.
- Evaluating programs or interventions : A research report can evaluate the effectiveness of programs or interventions, which can inform decision-making about whether to continue, modify, or discontinue them.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies.
When to Write Research Report
A research report should be written after completing the research study. This includes collecting data, analyzing the results, and drawing conclusions based on the findings. Once the research is complete, the report should be written in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
In academic settings, research reports are often required as part of coursework or as part of a thesis or dissertation. In this case, the report should be written according to the guidelines provided by the instructor or institution.
In other settings, such as in industry or government, research reports may be required to inform decision-making or to comply with regulatory requirements. In these cases, the report should be written as soon as possible after the research is completed in order to inform decision-making in a timely manner.
Overall, the timing of when to write a research report depends on the purpose of the research, the expectations of the audience, and any regulatory requirements that need to be met. However, it is important to complete the report in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
Characteristics of Research Report
There are several characteristics of a research report that distinguish it from other types of writing. These characteristics include:
- Objective: A research report should be written in an objective and unbiased manner. It should present the facts and findings of the research study without any personal opinions or biases.
- Systematic: A research report should be written in a systematic manner. It should follow a clear and logical structure, and the information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand and follow.
- Detailed: A research report should be detailed and comprehensive. It should provide a thorough description of the research methods, results, and conclusions.
- Accurate : A research report should be accurate and based on sound research methods. The findings and conclusions should be supported by data and evidence.
- Organized: A research report should be well-organized. It should include headings and subheadings to help the reader navigate the report and understand the main points.
- Clear and concise: A research report should be written in clear and concise language. The information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand, and unnecessary jargon should be avoided.
- Citations and references: A research report should include citations and references to support the findings and conclusions. This helps to give credit to other researchers and to provide readers with the opportunity to further explore the topic.
Advantages of Research Report
Research reports have several advantages, including:
- Communicating research findings: Research reports allow researchers to communicate their findings to a wider audience, including other researchers, stakeholders, and the general public. This helps to disseminate knowledge and advance the understanding of a particular topic.
- Providing evidence for decision-making : Research reports can provide evidence to inform decision-making, such as in the case of policy-making, program planning, or product development. The findings and conclusions can help guide decisions and improve outcomes.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research on a particular topic. Other researchers can build on the findings and conclusions of the report, which can lead to further discoveries and advancements in the field.
- Demonstrating expertise: Research reports can demonstrate the expertise of the researchers and their ability to conduct rigorous and high-quality research. This can be important for securing funding, promotions, and other professional opportunities.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies. Producing a high-quality research report can help ensure compliance with these requirements.
Limitations of Research Report
Despite their advantages, research reports also have some limitations, including:
- Time-consuming: Conducting research and writing a report can be a time-consuming process, particularly for large-scale studies. This can limit the frequency and speed of producing research reports.
- Expensive: Conducting research and producing a report can be expensive, particularly for studies that require specialized equipment, personnel, or data. This can limit the scope and feasibility of some research studies.
- Limited generalizability: Research studies often focus on a specific population or context, which can limit the generalizability of the findings to other populations or contexts.
- Potential bias : Researchers may have biases or conflicts of interest that can influence the findings and conclusions of the research study. Additionally, participants may also have biases or may not be representative of the larger population, which can limit the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Accessibility: Research reports may be written in technical or academic language, which can limit their accessibility to a wider audience. Additionally, some research may be behind paywalls or require specialized access, which can limit the ability of others to read and use the findings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...

Research Contribution – Thesis Guide

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and...

Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and...

- LaChance Library
Q. What's the difference between a report and a research paper?
- 2 Academic Support
- 2 Annotated Bibliography
- 2 Borrowing
- 9 Citations
- 33 Databases
- 1 Evaluating Information
- 7 Films/Movies
- 26 Finding Information
- 2 Library Cards
- 3 Login from Home
- 21 Research Papers
- 3 Research Skills MOOC
- 8 Research Topic
- 1 Study Rooms
- 3 Textbooks
- 3 Thesis Statements
Answered By: Brooke Gilmore Last Updated: Jan 12, 2022 Views: 63136

But wait, there's more. Check out Research Starter Toolkit , a step-by-step guide to help you succeed.
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 231 No 22
Comments (3)
- This is a wonderful website with step-by-step information on how to write a research paper. My college English students found it very helpful, and they are actually using it! by Lori Fox on Nov 22, 2017
- This site is amazing, it helped to receive a 98 on a research paper would recommend it if you are anywhere confused about writing a research paper by Sergio Cristian Ruiz on Jul 18, 2018
- very good by zewran ihsas on Mar 18, 2021
Related Topics
- Research Papers
Ask a Librarian
Instant insights, infinite possibilities
Research report guide: Definition, types, and tips
Last updated
5 March 2024
Reviewed by
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
From successful product launches or software releases to planning major business decisions, research reports serve many vital functions. They can summarize evidence and deliver insights and recommendations to save companies time and resources. They can reveal the most value-adding actions a company should take.
However, poorly constructed reports can have the opposite effect! Taking the time to learn established research-reporting rules and approaches will equip you with in-demand skills. You’ll be able to capture and communicate information applicable to numerous situations and industries, adding another string to your resume bow.
- What are research reports?
A research report is a collection of contextual data, gathered through organized research, that provides new insights into a particular challenge (which, for this article, is business-related). Research reports are a time-tested method for distilling large amounts of data into a narrow band of focus.
Their effectiveness often hinges on whether the report provides:
Strong, well-researched evidence
Comprehensive analysis
Well-considered conclusions and recommendations
Though the topic possibilities are endless, an effective research report keeps a laser-like focus on the specific questions or objectives the researcher believes are key to achieving success. Many research reports begin as research proposals, which usually include the need for a report to capture the findings of the study and recommend a course of action.
A description of the research method used, e.g., qualitative, quantitative, or other
Statistical analysis
Causal (or explanatory) research (i.e., research identifying relationships between two variables)
Inductive research, also known as ‘theory-building’
Deductive research, such as that used to test theories
Action research, where the research is actively used to drive change
- Importance of a research report
Research reports can unify and direct a company's focus toward the most appropriate strategic action. Of course, spending resources on a report takes up some of the company's human and financial resources. Choosing when a report is called for is a matter of judgment and experience.
Some development models used heavily in the engineering world, such as Waterfall development, are notorious for over-relying on research reports. With Waterfall development, there is a linear progression through each step of a project, and each stage is precisely documented and reported on before moving to the next.
The pace of the business world is faster than the speed at which your authors can produce and disseminate reports. So how do companies strike the right balance between creating and acting on research reports?
The answer lies, again, in the report's defined objectives. By paring down your most pressing interests and those of your stakeholders, your research and reporting skills will be the lenses that keep your company's priorities in constant focus.
Honing your company's primary objectives can save significant amounts of time and align research and reporting efforts with ever-greater precision.
Some examples of well-designed research objectives are:
Proving whether or not a product or service meets customer expectations
Demonstrating the value of a service, product, or business process to your stakeholders and investors
Improving business decision-making when faced with a lack of time or other constraints
Clarifying the relationship between a critical cause and effect for problematic business processes
Prioritizing the development of a backlog of products or product features
Comparing business or production strategies
Evaluating past decisions and predicting future outcomes
- Features of a research report
Research reports generally require a research design phase, where the report author(s) determine the most important elements the report must contain.
Just as there are various kinds of research, there are many types of reports.
Here are the standard elements of almost any research-reporting format:
Report summary. A broad but comprehensive overview of what readers will learn in the full report. Summaries are usually no more than one or two paragraphs and address all key elements of the report. Think of the key takeaways your primary stakeholders will want to know if they don’t have time to read the full document.
Introduction. Include a brief background of the topic, the type of research, and the research sample. Consider the primary goal of the report, who is most affected, and how far along the company is in meeting its objectives.
Methods. A description of how the researcher carried out data collection, analysis, and final interpretations of the data. Include the reasons for choosing a particular method. The methods section should strike a balance between clearly presenting the approach taken to gather data and discussing how it is designed to achieve the report's objectives.
Data analysis. This section contains interpretations that lead readers through the results relevant to the report's thesis. If there were unexpected results, include here a discussion on why that might be. Charts, calculations, statistics, and other supporting information also belong here (or, if lengthy, as an appendix). This should be the most detailed section of the research report, with references for further study. Present the information in a logical order, whether chronologically or in order of importance to the report's objectives.
Conclusion. This should be written with sound reasoning, often containing useful recommendations. The conclusion must be backed by a continuous thread of logic throughout the report.
- How to write a research paper
With a clear outline and robust pool of research, a research paper can start to write itself, but what's a good way to start a research report?
Research report examples are often the quickest way to gain inspiration for your report. Look for the types of research reports most relevant to your industry and consider which makes the most sense for your data and goals.
The research report outline will help you organize the elements of your report. One of the most time-tested report outlines is the IMRaD structure:
Introduction
...and Discussion
Pay close attention to the most well-established research reporting format in your industry, and consider your tone and language from your audience's perspective. Learn the key terms inside and out; incorrect jargon could easily harm the perceived authority of your research paper.
Along with a foundation in high-quality research and razor-sharp analysis, the most effective research reports will also demonstrate well-developed:
Internal logic
Narrative flow
Conclusions and recommendations
Readability, striking a balance between simple phrasing and technical insight
How to gather research data for your report
The validity of research data is critical. Because the research phase usually occurs well before the writing phase, you normally have plenty of time to vet your data.
However, research reports could involve ongoing research, where report authors (sometimes the researchers themselves) write portions of the report alongside ongoing research.
One such research-report example would be an R&D department that knows its primary stakeholders are eager to learn about a lengthy work in progress and any potentially important outcomes.
However you choose to manage the research and reporting, your data must meet robust quality standards before you can rely on it. Vet any research with the following questions in mind:
Does it use statistically valid analysis methods?
Do the researchers clearly explain their research, analysis, and sampling methods?
Did the researchers provide any caveats or advice on how to interpret their data?
Have you gathered the data yourself or were you in close contact with those who did?
Is the source biased?
Usually, flawed research methods become more apparent the further you get through a research report.
It's perfectly natural for good research to raise new questions, but the reader should have no uncertainty about what the data represents. There should be no doubt about matters such as:
Whether the sampling or analysis methods were based on sound and consistent logic
What the research samples are and where they came from
The accuracy of any statistical functions or equations
Validation of testing and measuring processes
When does a report require design validation?
A robust design validation process is often a gold standard in highly technical research reports. Design validation ensures the objects of a study are measured accurately, which lends more weight to your report and makes it valuable to more specialized industries.
Product development and engineering projects are the most common research-report examples that typically involve a design validation process. Depending on the scope and complexity of your research, you might face additional steps to validate your data and research procedures.
If you’re including design validation in the report (or report proposal), explain and justify your data-collection processes. Good design validation builds greater trust in a research report and lends more weight to its conclusions.
Choosing the right analysis method
Just as the quality of your report depends on properly validated research, a useful conclusion requires the most contextually relevant analysis method. This means comparing different statistical methods and choosing the one that makes the most sense for your research.
Most broadly, research analysis comes down to quantitative or qualitative methods (respectively: measurable by a number vs subjectively qualified values). There are also mixed research methods, which bridge the need for merging hard data with qualified assessments and still reach a cohesive set of conclusions.
Some of the most common analysis methods in research reports include:
Significance testing (aka hypothesis analysis), which compares test and control groups to determine how likely the data was the result of random chance.
Regression analysis , to establish relationships between variables, control for extraneous variables , and support correlation analysis.
Correlation analysis (aka bivariate testing), a method to identify and determine the strength of linear relationships between variables. It’s effective for detecting patterns from complex data, but care must be exercised to not confuse correlation with causation.
With any analysis method, it's important to justify which method you chose in the report. You should also provide estimates of the statistical accuracy (e.g., the p-value or confidence level of quantifiable data) of any data analysis.
This requires a commitment to the report's primary aim. For instance, this may be achieving a certain level of customer satisfaction by analyzing the cause and effect of changes to how service is delivered. Even better, use statistical analysis to calculate which change is most positively correlated with improved levels of customer satisfaction.
- Tips for writing research reports
There's endless good advice for writing effective research reports, and it almost all depends on the subjective aims of the people behind the report. Due to the wide variety of research reports, the best tips will be unique to each author's purpose.
Consider the following research report tips in any order, and take note of the ones most relevant to you:
No matter how in depth or detailed your report might be, provide a well-considered, succinct summary. At the very least, give your readers a quick and effective way to get up to speed.
Pare down your target audience (e.g., other researchers, employees, laypersons, etc.), and adjust your voice for their background knowledge and interest levels
For all but the most open-ended research, clarify your objectives, both for yourself and within the report.
Leverage your team members’ talents to fill in any knowledge gaps you might have. Your team is only as good as the sum of its parts.
Justify why your research proposal’s topic will endure long enough to derive value from the finished report.
Consolidate all research and analysis functions onto a single user-friendly platform. There's no reason to settle for less than developer-grade tools suitable for non-developers.
What's the format of a research report?
The research-reporting format is how the report is structured—a framework the authors use to organize their data, conclusions, arguments, and recommendations. The format heavily determines how the report's outline develops, because the format dictates the overall structure and order of information (based on the report's goals and research objectives).
What's the purpose of a research-report outline?
A good report outline gives form and substance to the report's objectives, presenting the results in a readable, engaging way. For any research-report format, the outline should create momentum along a chain of logic that builds up to a conclusion or interpretation.
What's the difference between a research essay and a research report?
There are several key differences between research reports and essays:
Research report:
Ordered into separate sections
More commercial in nature
Often includes infographics
Heavily descriptive
More self-referential
Usually provides recommendations
Research essay
Does not rely on research report formatting
More academically minded
Normally text-only
Less detailed
Omits discussion of methods
Usually non-prescriptive
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 16 August 2024
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Privacy Policy
Difference Between Research Paper and Research Report

Research Paper Definition
The research paper is, in fact, the complete & careful exploration of some specific topic or issue and reaching the results by interpreting the facts. In the research paper , the author writes about all the realistic implications of the research and its uses in the real scenario.
Research Report Definition
The research report is, in fact, a totally different piece of document that encloses the information regarding your research that what kind of investigation has been conducted in your research paper and for what purpose & in which circumstances you have conducted that research.
Research Paper and Research Report Comparison

Major Differences Between the Research Paper and Research Report
- By reading the definition only, it is easily recognized able fact that research paper represents the whole research process; on the other hand research report actually represents the concise overview and description about the complete research paper .
- Besides the definition of both, the main difference between a research paper and research report can be easily recognized only by having an overview of its complete format . Research paper encloses more chapters than the research report as a complete document. A fine research paper starts with a general introduction of the topic, and then includes a literature review of the other researchers regarding the same topic, a methodology that how you are going to do that research, results, and interpretation of the figures presented in the results. Most effective and thorough researches also narrate the importance of the research, implications and also the shortfalls of your research as well. Contrary to it, the research report cannot explain too much data about the research. Its main purpose is to enclose the course of action, results, and significance of the specific research papers which is to be discussed.
- From the above point discussed, it becomes obvious that research paper is a lengthy document because it encloses more chapters than that of the research report. Contrary to it the research report is the summarised overview of the important points of a specific research paper.
- Research paper in its literature section reviews the ideas and analysis of other researchers who already have done work on the same topic but may be in the different scenario. On the other hand, research report cannot discuss the research or investigations of other researchers but it only explains the procedure, conclusion, and importance of a specific research paper.
- The research paper can present the citations and quotations from other author’s papers along with their references or it can also narrate the ideas presented in books or movies about that topic or research in order to support your own research. However, the research report cannot narrate any kind of supportive material but only about the specifications and findings of your research work.
- Research paper and research report both are different from each other because the main purpose of both documents varies from each other. The main purpose of the research paper is to convince the readers that variables discussed in the specific research have some sort of relationship with each other and to persuade effectively writer have to quote previous researches with the same kind of experimentation or research done. On the other hand, the purpose of the research report is to provide information only. The research report provides the summarise information about the research being done; it can never be used to convince about any argument.
- Another distinction between both of them is that research paper will be based on a question or a query. Main focus of the author of the research paper will be to address the query which is stated as question or ambiguity in the start of the research paper. All efforts of the author will be inclined to provide the logic to the given or anticipated relation between two or more variables. On the other hand, the research report can never address any question or query. It is developed just to recap the important details of the targeted research paper.
- Moreover, the research report is focused to scrutinize and infer from given information. It involves arguments & logics along with gathering data. In contrast to it, the research report doesn’t need to involve any argument, analysis or interpretation of the results.
- Last but not the least research paper is a document that will be helpful in bringing distinctive and unique knowledge at the end of the research. Because research done in it is necessary to be conducted in different scenario or experimentation with a new combination of variables but research report is never inclined to do the same, It can never bring any new idea or knowledge in any case.
Also Study: 800+ Research Paper Examples
Characteristics of a Good Research Paper and Research Report
It has become very clear from all the above discussion that research paper and research report, both are a very different document from each other. But another fact is that there are some qualities and characteristics that may be common in both and all these qualities must be there in both documents to make them meaningful and worthy for reading.
- All the information given in the script should be based on facts only. No information should be imaginary or doubtful in any manner. Moreover, the information provided quotations or any research done by other researchers being quoted in the research paper should be provided with proofs and proper references.
- Language used for writing both types of documents must be clear and easy to understand. Use of jargons is strictly prohibited. Moreover, technical words must be used if necessary because more use of technical words will make it difficult for the reader to maintain attention in reading the whole paper. Easy and clear wording will make it more reader-friendly and understandable.
- It is also very necessary that document developed must be free of errors and there must be no duplication of any information in a single document. Duplication of information will directly lead to the decline in the interest of the reader & he will stop reading that document. Moreover, errors and doubtful information will decline the worth of the paper as well as the writer.
- The format of the research should be well prepared and its structure must be according to requirements. Otherwise, the document will lose its authenticity in the real sense.
- The manuscript developed, whether the research paper or research report must be oriented towards the result. Procedure, survey, and methodology every step should be inclined towards factual and clear results. If the results are ambiguous until the end, the whole effort of writing the document will be devastated. Moreover, each and every line is written should maintain an ethical reporting style in itself.
These qualities must be there in both documents in order to maintain the quality of the work and enhance the understanding of the manuscript for the readers. Any document, whether Research paper or research report must have these qualities, to attract the attention of the reader and make them read & understand the complete manuscript till the end.
Importance of understanding the differences between the research paper and Research Report
It is really necessary to understand the differences between the research paper and research report both. Because commonly these terms may be confused if asked generally but both types of documents have very different formats and designed to serve very different purposes. As research paper is a complete document in which each and every step of exploring a specific issue is documented along with guidance & support from the previous researches which are properly cited and referenced. On the other hand, the research report doesn’t have any concern with other researches, but it is restricted to give a concise summary of a specific research only. No other previous research is being discussed in the research report. So understanding and learning about the differences and characteristics of a good research paper and a research report will really contribute to add in the worth of the research.
Related Posts
Research paper example, how to write a motivational statement, how to write a good psychology research proposal, how to write a mechanical engineering research paper, apa research paper parts and sections, how to research a topic, how to write a personal essay, research project outline example, research paper format, what is a dissertation paper, leave a comment cancel reply.
Please enter an answer in digits: twenty − 2 =
Frequently asked questions
What’s the difference between a lab report and a research paper.
The purpose of a lab report is to demonstrate your understanding of the scientific method with a hands-on lab experiment. Course instructors will often provide you with an experimental design and procedure. Your task is to write up how you actually performed the experiment and evaluate the outcome.
In contrast, a research paper requires you to independently develop an original argument. It involves more in-depth research and interpretation of sources and data.
A lab report is usually shorter than a research paper.
Frequently asked questions: Academic writing
A rhetorical tautology is the repetition of an idea of concept using different words.
Rhetorical tautologies occur when additional words are used to convey a meaning that has already been expressed or implied. For example, the phrase “armed gunman” is a tautology because a “gunman” is by definition “armed.”
A logical tautology is a statement that is always true because it includes all logical possibilities.
Logical tautologies often take the form of “either/or” statements (e.g., “It will rain, or it will not rain”) or employ circular reasoning (e.g., “she is untrustworthy because she can’t be trusted”).
You may have seen both “appendices” or “appendixes” as pluralizations of “ appendix .” Either spelling can be used, but “appendices” is more common (including in APA Style ). Consistency is key here: make sure you use the same spelling throughout your paper.
The sections of a lab report can vary between scientific fields and course requirements, but it usually contains the following:
- Title: expresses the topic of your study
- Abstract: summarizes your research aims, methods, results, and conclusions
- Introduction: establishes the context needed to understand the topic
- Method: describes the materials and procedures used in the experiment
- Results: reports all descriptive and inferential statistical analyses
- Discussion: interprets and evaluates results and identifies limitations
- Conclusion: sums up the main findings of your experiment
- References: list of all sources cited using a specific style (e.g. APA)
- Appendices: contains lengthy materials, procedures, tables or figures
A lab report conveys the aim, methods, results, and conclusions of a scientific experiment . Lab reports are commonly assigned in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields.
The abstract is the very last thing you write. You should only write it after your research is complete, so that you can accurately summarize the entirety of your thesis , dissertation or research paper .
If you’ve gone over the word limit set for your assignment, shorten your sentences and cut repetition and redundancy during the editing process. If you use a lot of long quotes , consider shortening them to just the essentials.
If you need to remove a lot of words, you may have to cut certain passages. Remember that everything in the text should be there to support your argument; look for any information that’s not essential to your point and remove it.
To make this process easier and faster, you can use a paraphrasing tool . With this tool, you can rewrite your text to make it simpler and shorter. If that’s not enough, you can copy-paste your paraphrased text into the summarizer . This tool will distill your text to its core message.
Revising, proofreading, and editing are different stages of the writing process .
- Revising is making structural and logical changes to your text—reformulating arguments and reordering information.
- Editing refers to making more local changes to things like sentence structure and phrasing to make sure your meaning is conveyed clearly and concisely.
- Proofreading involves looking at the text closely, line by line, to spot any typos and issues with consistency and correct them.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
Avoid citing sources in your abstract . There are two reasons for this:
- The abstract should focus on your original research, not on the work of others.
- The abstract should be self-contained and fully understandable without reference to other sources.
There are some circumstances where you might need to mention other sources in an abstract: for example, if your research responds directly to another study or focuses on the work of a single theorist. In general, though, don’t include citations unless absolutely necessary.
An abstract is a concise summary of an academic text (such as a journal article or dissertation ). It serves two main purposes:
- To help potential readers determine the relevance of your paper for their own research.
- To communicate your key findings to those who don’t have time to read the whole paper.
Abstracts are often indexed along with keywords on academic databases, so they make your work more easily findable. Since the abstract is the first thing any reader sees, it’s important that it clearly and accurately summarizes the contents of your paper.
In a scientific paper, the methodology always comes after the introduction and before the results , discussion and conclusion . The same basic structure also applies to a thesis, dissertation , or research proposal .
Depending on the length and type of document, you might also include a literature review or theoretical framework before the methodology.
Whether you’re publishing a blog, submitting a research paper , or even just writing an important email, there are a few techniques you can use to make sure it’s error-free:
- Take a break : Set your work aside for at least a few hours so that you can look at it with fresh eyes.
- Proofread a printout : Staring at a screen for too long can cause fatigue – sit down with a pen and paper to check the final version.
- Use digital shortcuts : Take note of any recurring mistakes (for example, misspelling a particular word, switching between US and UK English , or inconsistently capitalizing a term), and use Find and Replace to fix it throughout the document.
If you want to be confident that an important text is error-free, it might be worth choosing a professional proofreading service instead.
Editing and proofreading are different steps in the process of revising a text.
Editing comes first, and can involve major changes to content, structure and language. The first stages of editing are often done by authors themselves, while a professional editor makes the final improvements to grammar and style (for example, by improving sentence structure and word choice ).
Proofreading is the final stage of checking a text before it is published or shared. It focuses on correcting minor errors and inconsistencies (for example, in punctuation and capitalization ). Proofreaders often also check for formatting issues, especially in print publishing.
The cost of proofreading depends on the type and length of text, the turnaround time, and the level of services required. Most proofreading companies charge per word or page, while freelancers sometimes charge an hourly rate.
For proofreading alone, which involves only basic corrections of typos and formatting mistakes, you might pay as little as $0.01 per word, but in many cases, your text will also require some level of editing , which costs slightly more.
It’s often possible to purchase combined proofreading and editing services and calculate the price in advance based on your requirements.
There are many different routes to becoming a professional proofreader or editor. The necessary qualifications depend on the field – to be an academic or scientific proofreader, for example, you will need at least a university degree in a relevant subject.
For most proofreading jobs, experience and demonstrated skills are more important than specific qualifications. Often your skills will be tested as part of the application process.
To learn practical proofreading skills, you can choose to take a course with a professional organization such as the Society for Editors and Proofreaders . Alternatively, you can apply to companies that offer specialized on-the-job training programmes, such as the Scribbr Academy .
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our team helps students graduate by offering:
- A world-class citation generator
- Plagiarism Checker software powered by Turnitin
- Innovative Citation Checker software
- Professional proofreading services
- Over 300 helpful articles about academic writing, citing sources, plagiarism, and more
Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents . We proofread:
- PhD dissertations
- Research proposals
- Personal statements
- Admission essays
- Motivation letters
- Reflection papers
- Journal articles
- Capstone projects
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker is powered by elements of Turnitin’s Similarity Checker , namely the plagiarism detection software and the Internet Archive and Premium Scholarly Publications content databases .
The add-on AI detector is powered by Scribbr’s proprietary software.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Is there a difference between a Research Report and a Report?
In my reading about undergraduate student assignments at my university, I have run across the word report quite a bit but the writer is not clearly talking about a research report (but the author might be, without me understanding that).
I'm used to thinking of student assignments as being either a research report (where the student must collect primary and secondary data) or an essay (where the student writes based on understanding without any actual data (though in an essay the student would often cite theories and the opinions of others).
Is there another meaning of the word report in the context of a university student assignment? Can students write reports only based on secondary data (is this a task commonly assigned)? Can someone write a report without data?
I'm wondering if a journalist's investigative report would count as a report using only secondary data (or perhaps not using data at all).
Any clarification would be of great help.
- 1 To answer the title question: No. There is absolutely no way to tell what sort of document a "Report" or "Research Report" or "Technical Report" is without actually reading the document. Standards vary across disciplines, across universities, and even within the same department. – JeffE Commented Jun 26, 2013 at 19:19
- @JeffE Thanks but I'm wondering if one would ever call a student assignment a report without it being a research report (are there other kinds of reports?). – earthling Commented Jun 26, 2013 at 22:38
- I don't know how to answer that question, because I don't know what a "research report" is. Does a literature survey count? Minutes of a classroom discussion? A written code review? A list of open problems? A white paper ? – JeffE Commented Jun 27, 2013 at 3:36
- @JeffE One example of a research report is researching consumer preferences. For example, researching if customers would like to see more purple iPhones or are they happy with the existing choices of white and black. The research might be done through surveys/questionnaires/interviews (online or in person) and the results (along with the methodology, etc.) would be written up as a report. This would be a 'research report' because it is driven from primary research. The closest thing in your list would be a literature survey but even that would normally only be included as a literature review. – earthling Commented Jun 27, 2013 at 7:40
As JeffE said, there are differences everywhere about which report is which - potentially confusing the issue.
Having said that, this resource from Purdue University " Purposes and Types of Reports which has further links to examples and guidelines. But, they do state:
•There is no universally agreed-upon format. •You should follow the format for your course or your company.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged teaching writing ..
- Featured on Meta
- Site maintenance - Mon, Sept 16 2024, 21:00 UTC to Tue, Sept 17 2024, 2:00...
- User activation: Learnings and opportunities
- Join Stack Overflow’s CEO and me for the first Stack IRL Community Event in...
Hot Network Questions
- What was the main implementation programming language of old 16-bit Windows versions (Windows 1 - Windows 3.11)?
- Do I have to use a new background that's been republished under the 2024 rules?
- Ubuntu 22.04.5 - Final Point Release
- What is the best way to protect from polymorphic viruses?
- Odorless color less , transparent fluid is leaking underneath my car
- Is Entropy time-symmetric?
- Logic Test: Room 1
- Arduino Uno Serial.write() how many bits are actually transmitted at once by UART?
- What is the oldest open math problem outside of number theory?
- Did the events of Mtt 16:16-20 actually take place on different occasions?
- Stuck as a solo dev
- C++ std::function-like queue
- Rich Mental Images
- Multi-producer, multi-consumer blocking queue
- View undo history of Windows Explorer on Win11
- Is Sagittarius A* smaller than we might expect given the mass of the Milky Way?
- Finding out if a series converges without solving linear recurrence relation
- Where are the DC-3 parked at KOPF?
- Will there be Sanhedrin in Messianic Times?
- What does "иного толка" mean? Is it an obsolete meaning?
- If one is arrested, but has a baby/pet in their house, what are they supposed to do?
- Do carbon fiber wings need a wing spar?
- Is transit visa required for KSA if I am there for only 6 hours
- What was the newest chess piece
- Research Report: Definition, Types + [Writing Guide]

One of the reasons for carrying out research is to add to the existing body of knowledge. Therefore, when conducting research, you need to document your processes and findings in a research report.
With a research report, it is easy to outline the findings of your systematic investigation and any gaps needing further inquiry. Knowing how to create a detailed research report will prove useful when you need to conduct research.
What is a Research Report?
A research report is a well-crafted document that outlines the processes, data, and findings of a systematic investigation. It is an important document that serves as a first-hand account of the research process, and it is typically considered an objective and accurate source of information.
In many ways, a research report can be considered as a summary of the research process that clearly highlights findings, recommendations, and other important details. Reading a well-written research report should provide you with all the information you need about the core areas of the research process.
Features of a Research Report
So how do you recognize a research report when you see one? Here are some of the basic features that define a research report.
- It is a detailed presentation of research processes and findings, and it usually includes tables and graphs.
- It is written in a formal language.
- A research report is usually written in the third person.
- It is informative and based on first-hand verifiable information.
- It is formally structured with headings, sections, and bullet points.
- It always includes recommendations for future actions.
Types of Research Report
The research report is classified based on two things; nature of research and target audience.
Nature of Research
- Qualitative Research Report
This is the type of report written for qualitative research . It outlines the methods, processes, and findings of a qualitative method of systematic investigation. In educational research, a qualitative research report provides an opportunity for one to apply his or her knowledge and develop skills in planning and executing qualitative research projects.
A qualitative research report is usually descriptive in nature. Hence, in addition to presenting details of the research process, you must also create a descriptive narrative of the information.
- Quantitative Research Report
A quantitative research report is a type of research report that is written for quantitative research. Quantitative research is a type of systematic investigation that pays attention to numerical or statistical values in a bid to find answers to research questions.
In this type of research report, the researcher presents quantitative data to support the research process and findings. Unlike a qualitative research report that is mainly descriptive, a quantitative research report works with numbers; that is, it is numerical in nature.
Target Audience
Also, a research report can be said to be technical or popular based on the target audience. If you’re dealing with a general audience, you would need to present a popular research report, and if you’re dealing with a specialized audience, you would submit a technical report.
- Technical Research Report
A technical research report is a detailed document that you present after carrying out industry-based research. This report is highly specialized because it provides information for a technical audience; that is, individuals with above-average knowledge in the field of study.
In a technical research report, the researcher is expected to provide specific information about the research process, including statistical analyses and sampling methods. Also, the use of language is highly specialized and filled with jargon.
Examples of technical research reports include legal and medical research reports.
- Popular Research Report
A popular research report is one for a general audience; that is, for individuals who do not necessarily have any knowledge in the field of study. A popular research report aims to make information accessible to everyone.
It is written in very simple language, which makes it easy to understand the findings and recommendations. Examples of popular research reports are the information contained in newspapers and magazines.
Importance of a Research Report
- Knowledge Transfer: As already stated above, one of the reasons for carrying out research is to contribute to the existing body of knowledge, and this is made possible with a research report. A research report serves as a means to effectively communicate the findings of a systematic investigation to all and sundry.
- Identification of Knowledge Gaps: With a research report, you’d be able to identify knowledge gaps for further inquiry. A research report shows what has been done while hinting at other areas needing systematic investigation.
- In market research, a research report would help you understand the market needs and peculiarities at a glance.
- A research report allows you to present information in a precise and concise manner.
- It is time-efficient and practical because, in a research report, you do not have to spend time detailing the findings of your research work in person. You can easily send out the report via email and have stakeholders look at it.
Guide to Writing a Research Report
A lot of detail goes into writing a research report, and getting familiar with the different requirements would help you create the ideal research report. A research report is usually broken down into multiple sections, which allows for a concise presentation of information.
Structure and Example of a Research Report
This is the title of your systematic investigation. Your title should be concise and point to the aims, objectives, and findings of a research report.
- Table of Contents
This is like a compass that makes it easier for readers to navigate the research report.
An abstract is an overview that highlights all important aspects of the research including the research method, data collection process, and research findings. Think of an abstract as a summary of your research report that presents pertinent information in a concise manner.
An abstract is always brief; typically 100-150 words and goes straight to the point. The focus of your research abstract should be the 5Ws and 1H format – What, Where, Why, When, Who and How.
- Introduction
Here, the researcher highlights the aims and objectives of the systematic investigation as well as the problem which the systematic investigation sets out to solve. When writing the report introduction, it is also essential to indicate whether the purposes of the research were achieved or would require more work.
In the introduction section, the researcher specifies the research problem and also outlines the significance of the systematic investigation. Also, the researcher is expected to outline any jargons and terminologies that are contained in the research.
- Literature Review
A literature review is a written survey of existing knowledge in the field of study. In other words, it is the section where you provide an overview and analysis of different research works that are relevant to your systematic investigation.
It highlights existing research knowledge and areas needing further investigation, which your research has sought to fill. At this stage, you can also hint at your research hypothesis and its possible implications for the existing body of knowledge in your field of study.
- An Account of Investigation
This is a detailed account of the research process, including the methodology, sample, and research subjects. Here, you are expected to provide in-depth information on the research process including the data collection and analysis procedures.
In a quantitative research report, you’d need to provide information surveys, questionnaires and other quantitative data collection methods used in your research. In a qualitative research report, you are expected to describe the qualitative data collection methods used in your research including interviews and focus groups.
In this section, you are expected to present the results of the systematic investigation.
This section further explains the findings of the research, earlier outlined. Here, you are expected to present a justification for each outcome and show whether the results are in line with your hypotheses or if other research studies have come up with similar results.
- Conclusions
This is a summary of all the information in the report. It also outlines the significance of the entire study.
- References and Appendices
This section contains a list of all the primary and secondary research sources.
Tips for Writing a Research Report
- Define the Context for the Report
As is obtainable when writing an essay, defining the context for your research report would help you create a detailed yet concise document. This is why you need to create an outline before writing so that you do not miss out on anything.
- Define your Audience
Writing with your audience in mind is essential as it determines the tone of the report. If you’re writing for a general audience, you would want to present the information in a simple and relatable manner. For a specialized audience, you would need to make use of technical and field-specific terms.
- Include Significant Findings
The idea of a research report is to present some sort of abridged version of your systematic investigation. In your report, you should exclude irrelevant information while highlighting only important data and findings.
- Include Illustrations
Your research report should include illustrations and other visual representations of your data. Graphs, pie charts, and relevant images lend additional credibility to your systematic investigation.
- Choose the Right Title
A good research report title is brief, precise, and contains keywords from your research. It should provide a clear idea of your systematic investigation so that readers can grasp the entire focus of your research from the title.
- Proofread the Report
Before publishing the document, ensure that you give it a second look to authenticate the information. If you can, get someone else to go through the report, too, and you can also run it through proofreading and editing software.
How to Gather Research Data for Your Report
- Understand the Problem
Every research aims at solving a specific problem or set of problems, and this should be at the back of your mind when writing your research report. Understanding the problem would help you to filter the information you have and include only important data in your report.
- Know what your report seeks to achieve
This is somewhat similar to the point above because, in some way, the aim of your research report is intertwined with the objectives of your systematic investigation. Identifying the primary purpose of writing a research report would help you to identify and present the required information accordingly.
- Identify your audience
Knowing your target audience plays a crucial role in data collection for a research report. If your research report is specifically for an organization, you would want to present industry-specific information or show how the research findings are relevant to the work that the company does.
- Create Surveys/Questionnaires
A survey is a research method that is used to gather data from a specific group of people through a set of questions. It can be either quantitative or qualitative.
A survey is usually made up of structured questions, and it can be administered online or offline. However, an online survey is a more effective method of research data collection because it helps you save time and gather data with ease.
You can seamlessly create an online questionnaire for your research on Formplus . With the multiple sharing options available in the builder, you would be able to administer your survey to respondents in little or no time.
Formplus also has a report summary too l that you can use to create custom visual reports for your research.
Step-by-step guide on how to create an online questionnaire using Formplus
- Sign into Formplus
In the Formplus builder, you can easily create different online questionnaires for your research by dragging and dropping preferred fields into your form. To access the Formplus builder, you will need to create an account on Formplus.
Once you do this, sign in to your account and click on Create new form to begin.
- Edit Form Title : Click on the field provided to input your form title, for example, “Research Questionnaire.”
- Edit Form : Click on the edit icon to edit the form.
- Add Fields : Drag and drop preferred form fields into your form in the Formplus builder inputs column. There are several field input options for questionnaires in the Formplus builder.
- Edit fields
- Click on “Save”
- Form Customization: With the form customization options in the form builder, you can easily change the outlook of your form and make it more unique and personalized. Formplus allows you to change your form theme, add background images, and even change the font according to your needs.
- Multiple Sharing Options: Formplus offers various form-sharing options, which enables you to share your questionnaire with respondents easily. You can use the direct social media sharing buttons to share your form link to your organization’s social media pages. You can also send out your survey form as email invitations to your research subjects too. If you wish, you can share your form’s QR code or embed it on your organization’s website for easy access.
Conclusion
Always remember that a research report is just as important as the actual systematic investigation because it plays a vital role in communicating research findings to everyone else. This is why you must take care to create a concise document summarizing the process of conducting any research.
In this article, we’ve outlined essential tips to help you create a research report. When writing your report, you should always have the audience at the back of your mind, as this would set the tone for the document.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- ethnographic research survey
- research report
- research report survey
- busayo.longe

You may also like:
21 Chrome Extensions for Academic Researchers in 2022
In this article, we will discuss a number of chrome extensions you can use to make your research process even seamless


Assessment Tools: Types, Examples & Importance
In this article, you’ll learn about different assessment tools to help you evaluate performance in various contexts
Ethnographic Research: Types, Methods + [Question Examples]
Simple guide on ethnographic research, it types, methods, examples and advantages. Also highlights how to conduct an ethnographic...
How to Write a Problem Statement for your Research
Learn how to write problem statements before commencing any research effort. Learn about its structure and explore examples
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..
Research Article vs. Research Paper
What's the difference.
A research article and a research paper are both scholarly documents that present the findings of a research study. However, there are some differences between the two. A research article is typically a shorter document that is published in a peer-reviewed journal. It focuses on a specific research question and provides a concise summary of the study's methodology, results, and conclusions. On the other hand, a research paper is usually a longer document that provides a more comprehensive analysis of a research topic. It often includes a literature review, detailed methodology, extensive data analysis, and a discussion of the implications of the findings. While both types of documents contribute to the scientific knowledge base, research papers tend to be more in-depth and provide a more thorough exploration of the research topic.
| Attribute | Research Article | Research Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A written document that presents the findings of a research study or experiment. | A comprehensive written document that includes an in-depth analysis and interpretation of research findings. |
| Purpose | To communicate the results of a specific research study or experiment to the scientific community. | To provide a detailed analysis and interpretation of research findings, often including a literature review and methodology. |
| Length | Typically shorter, ranging from a few pages to around 20 pages. | Usually longer, ranging from 20 to hundreds of pages. |
| Structure | Usually follows a standard structure including sections such as abstract, introduction, methods, results, and conclusion. | May have a more flexible structure depending on the field and specific requirements, but often includes sections such as abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. |
| Scope | Focuses on presenting the findings of a specific research study or experiment. | Explores a broader research topic or question, often including a literature review and analysis of multiple studies. |
| Publication | Can be published in academic journals, conference proceedings, or online platforms. | Can be published in academic journals, conference proceedings, or as part of a thesis or dissertation. |
| Peer Review | Research articles often undergo a peer review process before publication to ensure quality and validity. | Research papers may also undergo peer review, especially if published in academic journals. |
Further Detail
Introduction.
Research articles and research papers are both essential components of academic and scientific discourse. They serve as vehicles for sharing knowledge, presenting findings, and contributing to the advancement of various fields of study. While the terms "research article" and "research paper" are often used interchangeably, there are subtle differences in their attributes and purposes. In this article, we will explore and compare the key characteristics of research articles and research papers.
Definition and Purpose
A research article is a concise and focused piece of scholarly writing that typically appears in academic journals. It presents original research, experiments, or studies conducted by the author(s) and aims to communicate the findings to the scientific community. Research articles often follow a specific structure, including an abstract, introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
On the other hand, a research paper is a broader term that encompasses various types of academic writing, including research articles. While research papers can also be published in journals, they can take other forms such as conference papers, dissertations, or theses. Research papers provide a more comprehensive exploration of a particular topic, often including a literature review, theoretical framework, and in-depth analysis of the research question.
Length and Depth
Research articles are typically shorter in length compared to research papers. They are usually limited to a specific word count, often ranging from 3000 to 8000 words, depending on the journal's guidelines. Due to their concise nature, research articles focus on presenting the core findings and their implications without delving extensively into background information or theoretical frameworks.
On the other hand, research papers tend to be longer and more comprehensive. They can range from 5000 to 20,000 words or more, depending on the scope of the research and the requirements of the academic institution or conference. Research papers provide a deeper analysis of the topic, including an extensive literature review, theoretical framework, and detailed methodology section.
Structure and Organization
Research articles follow a standardized structure to ensure clarity and consistency across different publications. They typically begin with an abstract, which provides a concise summary of the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions. The introduction section provides background information, states the research problem, and outlines the objectives of the study. The methodology section describes the research design, data collection methods, and statistical analysis techniques used. The results section presents the findings, often accompanied by tables, figures, or graphs. The discussion section interprets the results, compares them with previous studies, and discusses their implications. Finally, the conclusion summarizes the main findings and suggests future research directions.
Research papers, on the other hand, have a more flexible structure depending on the specific requirements of the academic institution or conference. While they may include similar sections as research articles, such as an abstract, introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion, research papers can also incorporate additional sections such as a literature review, theoretical framework, or appendices. The structure of a research paper is often determined by the depth and complexity of the research conducted.
Publication and Audience
Research articles are primarily published in academic journals, which serve as platforms for disseminating new knowledge within specific disciplines. These journals often have a rigorous peer-review process, where experts in the field evaluate the quality and validity of the research before publication. Research articles are targeted towards a specialized audience of researchers, scholars, and professionals in the respective field.
Research papers, on the other hand, can be published in various formats and venues. They can be presented at conferences, published as chapters in books, or submitted as dissertations or theses. While research papers can also undergo peer-review, they may have a broader audience, including researchers, students, and professionals interested in the topic. The publication of research papers allows for a wider dissemination of knowledge beyond the confines of academic journals.
In conclusion, research articles and research papers are both vital components of academic and scientific discourse. While research articles are concise and focused pieces of scholarly writing that present original research findings, research papers provide a more comprehensive exploration of a particular topic. Research articles follow a standardized structure and are primarily published in academic journals, targeting a specialized audience. On the other hand, research papers have a more flexible structure and can be published in various formats, allowing for a wider dissemination of knowledge. Understanding the attributes and purposes of research articles and research papers is crucial for researchers, scholars, and students alike, as it enables effective communication and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in various fields.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.

- Article Reports
research report and research paper difference
Market reports.

Understanding the Foundations: Distinguishing Research Reports from Research Papers
To grasp the core differences between research reports and research papers, it’s essential to delve into their distinct purposes and audiences. Research reports are primarily designed to communicate findings from an investigation to stakeholders such as managers, clients, or policymakers. These documents are often detailed and data-driven, focusing on the practical implications of the findings. Key elements include sections like methodology , data analysis , and recommendations , ensuring that the reader can readily understand and apply the results in real-world scenarios. In contrast, research papers are primarily academic, aiming to contribute to the existing body of knowledge in a specific field of study. They not only present findings but also engage with existing literature, theorize concepts, and critically analyze methodologies, fostering scholarly debate and discourse. The format typically includes an introduction , literature review , results , and conclusion that adheres to academic standards.
Furthermore, the writing style varies significantly between the two formats. Research reports are often straightforward, employing concise language and providing summaries for easy interpretation, while research papers tend to utilize a more formal tone, characterized by complex sentence structures and comprehensive citations. The following table outlines some fundamental differences:
| To inform and guide decisions | To contribute to academic knowledge | |
| Stakeholders, policymakers | Academics, researchers | |
| Concise, straightforward | Formal, analytical | |
| Reports with sections like methodology, findings | Standardized structure with sections like literature review, analysis |
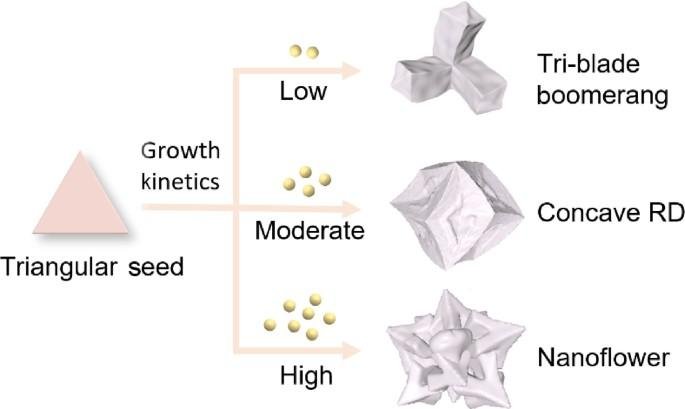
Structural Nuances: Exploring the Format and Presentation Differences
When examining the differences in structure between research reports and research papers, it’s essential to recognize the distinct purposes they serve within the academic and professional landscapes. Research reports typically aim to communicate findings succinctly and efficiently. Their format is often more rigid, including specific sections such as an abstract, methodology, results, and conclusion, all designed to present data clearly. Conversely, research papers allow for a more expansive exploration of a topic, featuring an introductory section that outlines the research problem, a detailed literature review, and a theoretical framework. This organized yet flexible presentation style invites deeper analysis and discussion.
Furthermore, the visual presentation of these documents highlights their differences. While research reports may utilize tables and figures primarily to summarize data and display key results, research papers often include extensive citations and references formatted according to specific style guides. Important elements include:
- Research Reports: Brief summaries, clear headings, data visualizations
- Research Papers: Comprehensive introductions, extensive literature reviews, argumentative structure
This distinction not only influences the reading experience but also informs how information is synthesized and understood within each format, showcasing the nuances in approach and depth of analysis.

Objective Insights: Analyzing Purpose and Audience Variation
When distinguishing between a research report and a research paper, it’s crucial to understand that each serves a distinct purpose tailored to different audiences. A research report is often aimed at stakeholders or decision-makers, focusing on providing a comprehensive overview of findings and implications. It emphasizes clarity and conciseness, ensuring that the audience can quickly grasp the critical insights necessary for informed decision-making. In contrast, a research paper targets an academic audience, aiming to contribute to the existing body of knowledge within a scholarly context. This format allows for deeper engagement with theories, methodologies, and extensive literature reviews.
Moreover, the structure and style of these documents vary considerably, further reflecting their purposes and intended audiences:
| Aspect | Research Report | Research Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Length | Typically shorter and concise | More extensive, detailed |
| Focus | Results and recommendations | Theoretical framework and literature |
| Visual Aids | Graphs, charts, and bullet points | Less visual, more text-based |
| References | Practical data sources | Academic citations and peer-reviewed sources |
These differences underscore the necessity for writers to adapt their content accordingly. Recognizing the target audience not only shapes the writing style but also influences the choice of format, tone, and detail included. By understanding these distinctions, researchers and writers can effectively communicate their findings in a manner that resonates with their respective audiences, enhancing the overall impact of their work.
Practical Guidance: Recommendations for Crafting Effective Research Outputs
When crafting research outputs, it is essential to tailor your style to the intended format, whether it is a research report or a research paper. To create an effective research report, emphasize clarity and accessibility . Use straightforward language and a structured layout that presents data prominently. Highlight key findings in bullet points and employ visuals such as tables and charts to facilitate understanding. Here are some key tips for reports:
- Use headings and subheadings to organize content efficiently.
- Incorporate concise executive summaries to capture the essence of your work.
- Always provide clear recommendations based on your findings.
In contrast, when writing a research paper, your focus should be on depth of analysis and argumentation . This format typically requires a more rigorous methodology and comprehensive literature review. Rely on formal language and elaborate on various aspects of your research, including theoretical implications. Key points to remember for papers include:
- Craft a compelling thesis statement that guides your narrative.
- Engage with existing research to highlight the significance of your work.
- Utilize citations liberally to support your arguments.
| Aspect | Research Report | Research Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Summarize findings for stakeholders | Present and justify research findings |
| Style | Concise and clear | Formal and argumentative |
| Structure | Flexible and report-focused | Structured with sections like introduction, methods, and discussion |
The Way Forward
understanding the nuances between a research report and a research paper is essential for anyone navigating the academic landscape. While both serve the vital purpose of disseminating knowledge, they cater to different audiences and fulfill distinct functions. Research reports offer a succinct overview of findings, catering to practitioners and professionals who seek actionable insights, while research papers delve deeper into theoretical frameworks and contribute to the broader scholarly conversation. By recognizing these differences, researchers can better tailor their work to meet the expectations of their intended audience, ensuring that their contributions resonate effectively within their respective fields. Thus, whether you are embarking on your own research journey or simply exploring the academic terrain, appreciating the contrasts between these two forms of written discourse can enhance your understanding and proficiency in the art of scholarly communication.
Related Posts
- Automobile & Transportation Market: The Future of Mobility and Transportation
- Equity Management Software Market
- Electroceutical Bioelectric Medicine Market
- Wearable Technology Market: The Intersection of Fashion and Function
- Project Report On Marketing Strategy Of Patanjali Pdf
- Seeds & Agricultural Inputs Market: Innovations Driving Agricultural Productivity and Efficiency
- Hello world!
- Data Center & Networking Market: Trends in Digital Infrastructure and Efficiency

research report mcq
Research report features.

research paper hypothesis example

jefferies equity research report pdf
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Link Website*
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post a Comment

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 11: Presenting Your Research
Writing a Research Report in American Psychological Association (APA) Style
Learning Objectives
- Identify the major sections of an APA-style research report and the basic contents of each section.
- Plan and write an effective APA-style research report.
In this section, we look at how to write an APA-style empirical research report , an article that presents the results of one or more new studies. Recall that the standard sections of an empirical research report provide a kind of outline. Here we consider each of these sections in detail, including what information it contains, how that information is formatted and organized, and tips for writing each section. At the end of this section is a sample APA-style research report that illustrates many of these principles.
Sections of a Research Report
Title page and abstract.
An APA-style research report begins with a title page . The title is centred in the upper half of the page, with each important word capitalized. The title should clearly and concisely (in about 12 words or fewer) communicate the primary variables and research questions. This sometimes requires a main title followed by a subtitle that elaborates on the main title, in which case the main title and subtitle are separated by a colon. Here are some titles from recent issues of professional journals published by the American Psychological Association.
- Sex Differences in Coping Styles and Implications for Depressed Mood
- Effects of Aging and Divided Attention on Memory for Items and Their Contexts
- Computer-Assisted Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for Child Anxiety: Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial
- Virtual Driving and Risk Taking: Do Racing Games Increase Risk-Taking Cognitions, Affect, and Behaviour?
Below the title are the authors’ names and, on the next line, their institutional affiliation—the university or other institution where the authors worked when they conducted the research. As we have already seen, the authors are listed in an order that reflects their contribution to the research. When multiple authors have made equal contributions to the research, they often list their names alphabetically or in a randomly determined order.
In some areas of psychology, the titles of many empirical research reports are informal in a way that is perhaps best described as “cute.” They usually take the form of a play on words or a well-known expression that relates to the topic under study. Here are some examples from recent issues of the Journal Psychological Science .
- “Smells Like Clean Spirit: Nonconscious Effects of Scent on Cognition and Behavior”
- “Time Crawls: The Temporal Resolution of Infants’ Visual Attention”
- “Scent of a Woman: Men’s Testosterone Responses to Olfactory Ovulation Cues”
- “Apocalypse Soon?: Dire Messages Reduce Belief in Global Warming by Contradicting Just-World Beliefs”
- “Serial vs. Parallel Processing: Sometimes They Look Like Tweedledum and Tweedledee but They Can (and Should) Be Distinguished”
- “How Do I Love Thee? Let Me Count the Words: The Social Effects of Expressive Writing”
Individual researchers differ quite a bit in their preference for such titles. Some use them regularly, while others never use them. What might be some of the pros and cons of using cute article titles?
For articles that are being submitted for publication, the title page also includes an author note that lists the authors’ full institutional affiliations, any acknowledgments the authors wish to make to agencies that funded the research or to colleagues who commented on it, and contact information for the authors. For student papers that are not being submitted for publication—including theses—author notes are generally not necessary.
The abstract is a summary of the study. It is the second page of the manuscript and is headed with the word Abstract . The first line is not indented. The abstract presents the research question, a summary of the method, the basic results, and the most important conclusions. Because the abstract is usually limited to about 200 words, it can be a challenge to write a good one.
Introduction
The introduction begins on the third page of the manuscript. The heading at the top of this page is the full title of the manuscript, with each important word capitalized as on the title page. The introduction includes three distinct subsections, although these are typically not identified by separate headings. The opening introduces the research question and explains why it is interesting, the literature review discusses relevant previous research, and the closing restates the research question and comments on the method used to answer it.
The Opening
The opening , which is usually a paragraph or two in length, introduces the research question and explains why it is interesting. To capture the reader’s attention, researcher Daryl Bem recommends starting with general observations about the topic under study, expressed in ordinary language (not technical jargon)—observations that are about people and their behaviour (not about researchers or their research; Bem, 2003 [1] ). Concrete examples are often very useful here. According to Bem, this would be a poor way to begin a research report:
Festinger’s theory of cognitive dissonance received a great deal of attention during the latter part of the 20th century (p. 191)
The following would be much better:
The individual who holds two beliefs that are inconsistent with one another may feel uncomfortable. For example, the person who knows that he or she enjoys smoking but believes it to be unhealthy may experience discomfort arising from the inconsistency or disharmony between these two thoughts or cognitions. This feeling of discomfort was called cognitive dissonance by social psychologist Leon Festinger (1957), who suggested that individuals will be motivated to remove this dissonance in whatever way they can (p. 191).
After capturing the reader’s attention, the opening should go on to introduce the research question and explain why it is interesting. Will the answer fill a gap in the literature? Will it provide a test of an important theory? Does it have practical implications? Giving readers a clear sense of what the research is about and why they should care about it will motivate them to continue reading the literature review—and will help them make sense of it.
Breaking the Rules
Researcher Larry Jacoby reported several studies showing that a word that people see or hear repeatedly can seem more familiar even when they do not recall the repetitions—and that this tendency is especially pronounced among older adults. He opened his article with the following humourous anecdote:
A friend whose mother is suffering symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) tells the story of taking her mother to visit a nursing home, preliminary to her mother’s moving there. During an orientation meeting at the nursing home, the rules and regulations were explained, one of which regarded the dining room. The dining room was described as similar to a fine restaurant except that tipping was not required. The absence of tipping was a central theme in the orientation lecture, mentioned frequently to emphasize the quality of care along with the advantages of having paid in advance. At the end of the meeting, the friend’s mother was asked whether she had any questions. She replied that she only had one question: “Should I tip?” (Jacoby, 1999, p. 3)
Although both humour and personal anecdotes are generally discouraged in APA-style writing, this example is a highly effective way to start because it both engages the reader and provides an excellent real-world example of the topic under study.
The Literature Review
Immediately after the opening comes the literature review , which describes relevant previous research on the topic and can be anywhere from several paragraphs to several pages in length. However, the literature review is not simply a list of past studies. Instead, it constitutes a kind of argument for why the research question is worth addressing. By the end of the literature review, readers should be convinced that the research question makes sense and that the present study is a logical next step in the ongoing research process.
Like any effective argument, the literature review must have some kind of structure. For example, it might begin by describing a phenomenon in a general way along with several studies that demonstrate it, then describing two or more competing theories of the phenomenon, and finally presenting a hypothesis to test one or more of the theories. Or it might describe one phenomenon, then describe another phenomenon that seems inconsistent with the first one, then propose a theory that resolves the inconsistency, and finally present a hypothesis to test that theory. In applied research, it might describe a phenomenon or theory, then describe how that phenomenon or theory applies to some important real-world situation, and finally suggest a way to test whether it does, in fact, apply to that situation.
Looking at the literature review in this way emphasizes a few things. First, it is extremely important to start with an outline of the main points that you want to make, organized in the order that you want to make them. The basic structure of your argument, then, should be apparent from the outline itself. Second, it is important to emphasize the structure of your argument in your writing. One way to do this is to begin the literature review by summarizing your argument even before you begin to make it. “In this article, I will describe two apparently contradictory phenomena, present a new theory that has the potential to resolve the apparent contradiction, and finally present a novel hypothesis to test the theory.” Another way is to open each paragraph with a sentence that summarizes the main point of the paragraph and links it to the preceding points. These opening sentences provide the “transitions” that many beginning researchers have difficulty with. Instead of beginning a paragraph by launching into a description of a previous study, such as “Williams (2004) found that…,” it is better to start by indicating something about why you are describing this particular study. Here are some simple examples:
Another example of this phenomenon comes from the work of Williams (2004).
Williams (2004) offers one explanation of this phenomenon.
An alternative perspective has been provided by Williams (2004).
We used a method based on the one used by Williams (2004).
Finally, remember that your goal is to construct an argument for why your research question is interesting and worth addressing—not necessarily why your favourite answer to it is correct. In other words, your literature review must be balanced. If you want to emphasize the generality of a phenomenon, then of course you should discuss various studies that have demonstrated it. However, if there are other studies that have failed to demonstrate it, you should discuss them too. Or if you are proposing a new theory, then of course you should discuss findings that are consistent with that theory. However, if there are other findings that are inconsistent with it, again, you should discuss them too. It is acceptable to argue that the balance of the research supports the existence of a phenomenon or is consistent with a theory (and that is usually the best that researchers in psychology can hope for), but it is not acceptable to ignore contradictory evidence. Besides, a large part of what makes a research question interesting is uncertainty about its answer.
The Closing
The closing of the introduction—typically the final paragraph or two—usually includes two important elements. The first is a clear statement of the main research question or hypothesis. This statement tends to be more formal and precise than in the opening and is often expressed in terms of operational definitions of the key variables. The second is a brief overview of the method and some comment on its appropriateness. Here, for example, is how Darley and Latané (1968) [2] concluded the introduction to their classic article on the bystander effect:
These considerations lead to the hypothesis that the more bystanders to an emergency, the less likely, or the more slowly, any one bystander will intervene to provide aid. To test this proposition it would be necessary to create a situation in which a realistic “emergency” could plausibly occur. Each subject should also be blocked from communicating with others to prevent his getting information about their behaviour during the emergency. Finally, the experimental situation should allow for the assessment of the speed and frequency of the subjects’ reaction to the emergency. The experiment reported below attempted to fulfill these conditions. (p. 378)
Thus the introduction leads smoothly into the next major section of the article—the method section.
The method section is where you describe how you conducted your study. An important principle for writing a method section is that it should be clear and detailed enough that other researchers could replicate the study by following your “recipe.” This means that it must describe all the important elements of the study—basic demographic characteristics of the participants, how they were recruited, whether they were randomly assigned, how the variables were manipulated or measured, how counterbalancing was accomplished, and so on. At the same time, it should avoid irrelevant details such as the fact that the study was conducted in Classroom 37B of the Industrial Technology Building or that the questionnaire was double-sided and completed using pencils.
The method section begins immediately after the introduction ends with the heading “Method” (not “Methods”) centred on the page. Immediately after this is the subheading “Participants,” left justified and in italics. The participants subsection indicates how many participants there were, the number of women and men, some indication of their age, other demographics that may be relevant to the study, and how they were recruited, including any incentives given for participation.
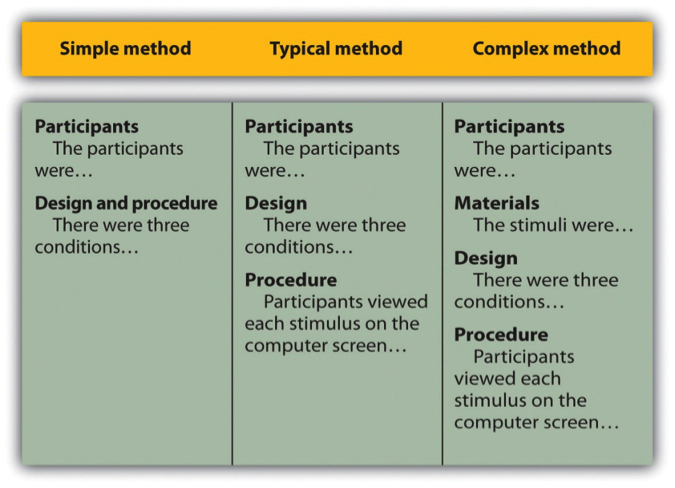
After the participants section, the structure can vary a bit. Figure 11.1 shows three common approaches. In the first, the participants section is followed by a design and procedure subsection, which describes the rest of the method. This works well for methods that are relatively simple and can be described adequately in a few paragraphs. In the second approach, the participants section is followed by separate design and procedure subsections. This works well when both the design and the procedure are relatively complicated and each requires multiple paragraphs.
What is the difference between design and procedure? The design of a study is its overall structure. What were the independent and dependent variables? Was the independent variable manipulated, and if so, was it manipulated between or within subjects? How were the variables operationally defined? The procedure is how the study was carried out. It often works well to describe the procedure in terms of what the participants did rather than what the researchers did. For example, the participants gave their informed consent, read a set of instructions, completed a block of four practice trials, completed a block of 20 test trials, completed two questionnaires, and were debriefed and excused.
In the third basic way to organize a method section, the participants subsection is followed by a materials subsection before the design and procedure subsections. This works well when there are complicated materials to describe. This might mean multiple questionnaires, written vignettes that participants read and respond to, perceptual stimuli, and so on. The heading of this subsection can be modified to reflect its content. Instead of “Materials,” it can be “Questionnaires,” “Stimuli,” and so on.
The results section is where you present the main results of the study, including the results of the statistical analyses. Although it does not include the raw data—individual participants’ responses or scores—researchers should save their raw data and make them available to other researchers who request them. Several journals now encourage the open sharing of raw data online.
Although there are no standard subsections, it is still important for the results section to be logically organized. Typically it begins with certain preliminary issues. One is whether any participants or responses were excluded from the analyses and why. The rationale for excluding data should be described clearly so that other researchers can decide whether it is appropriate. A second preliminary issue is how multiple responses were combined to produce the primary variables in the analyses. For example, if participants rated the attractiveness of 20 stimulus people, you might have to explain that you began by computing the mean attractiveness rating for each participant. Or if they recalled as many items as they could from study list of 20 words, did you count the number correctly recalled, compute the percentage correctly recalled, or perhaps compute the number correct minus the number incorrect? A third preliminary issue is the reliability of the measures. This is where you would present test-retest correlations, Cronbach’s α, or other statistics to show that the measures are consistent across time and across items. A final preliminary issue is whether the manipulation was successful. This is where you would report the results of any manipulation checks.
The results section should then tackle the primary research questions, one at a time. Again, there should be a clear organization. One approach would be to answer the most general questions and then proceed to answer more specific ones. Another would be to answer the main question first and then to answer secondary ones. Regardless, Bem (2003) [3] suggests the following basic structure for discussing each new result:
- Remind the reader of the research question.
- Give the answer to the research question in words.
- Present the relevant statistics.
- Qualify the answer if necessary.
- Summarize the result.
Notice that only Step 3 necessarily involves numbers. The rest of the steps involve presenting the research question and the answer to it in words. In fact, the basic results should be clear even to a reader who skips over the numbers.
The discussion is the last major section of the research report. Discussions usually consist of some combination of the following elements:
- Summary of the research
- Theoretical implications
- Practical implications
- Limitations
- Suggestions for future research
The discussion typically begins with a summary of the study that provides a clear answer to the research question. In a short report with a single study, this might require no more than a sentence. In a longer report with multiple studies, it might require a paragraph or even two. The summary is often followed by a discussion of the theoretical implications of the research. Do the results provide support for any existing theories? If not, how can they be explained? Although you do not have to provide a definitive explanation or detailed theory for your results, you at least need to outline one or more possible explanations. In applied research—and often in basic research—there is also some discussion of the practical implications of the research. How can the results be used, and by whom, to accomplish some real-world goal?
The theoretical and practical implications are often followed by a discussion of the study’s limitations. Perhaps there are problems with its internal or external validity. Perhaps the manipulation was not very effective or the measures not very reliable. Perhaps there is some evidence that participants did not fully understand their task or that they were suspicious of the intent of the researchers. Now is the time to discuss these issues and how they might have affected the results. But do not overdo it. All studies have limitations, and most readers will understand that a different sample or different measures might have produced different results. Unless there is good reason to think they would have, however, there is no reason to mention these routine issues. Instead, pick two or three limitations that seem like they could have influenced the results, explain how they could have influenced the results, and suggest ways to deal with them.
Most discussions end with some suggestions for future research. If the study did not satisfactorily answer the original research question, what will it take to do so? What new research questions has the study raised? This part of the discussion, however, is not just a list of new questions. It is a discussion of two or three of the most important unresolved issues. This means identifying and clarifying each question, suggesting some alternative answers, and even suggesting ways they could be studied.
Finally, some researchers are quite good at ending their articles with a sweeping or thought-provoking conclusion. Darley and Latané (1968) [4] , for example, ended their article on the bystander effect by discussing the idea that whether people help others may depend more on the situation than on their personalities. Their final sentence is, “If people understand the situational forces that can make them hesitate to intervene, they may better overcome them” (p. 383). However, this kind of ending can be difficult to pull off. It can sound overreaching or just banal and end up detracting from the overall impact of the article. It is often better simply to end when you have made your final point (although you should avoid ending on a limitation).
The references section begins on a new page with the heading “References” centred at the top of the page. All references cited in the text are then listed in the format presented earlier. They are listed alphabetically by the last name of the first author. If two sources have the same first author, they are listed alphabetically by the last name of the second author. If all the authors are the same, then they are listed chronologically by the year of publication. Everything in the reference list is double-spaced both within and between references.
Appendices, Tables, and Figures
Appendices, tables, and figures come after the references. An appendix is appropriate for supplemental material that would interrupt the flow of the research report if it were presented within any of the major sections. An appendix could be used to present lists of stimulus words, questionnaire items, detailed descriptions of special equipment or unusual statistical analyses, or references to the studies that are included in a meta-analysis. Each appendix begins on a new page. If there is only one, the heading is “Appendix,” centred at the top of the page. If there is more than one, the headings are “Appendix A,” “Appendix B,” and so on, and they appear in the order they were first mentioned in the text of the report.
After any appendices come tables and then figures. Tables and figures are both used to present results. Figures can also be used to illustrate theories (e.g., in the form of a flowchart), display stimuli, outline procedures, and present many other kinds of information. Each table and figure appears on its own page. Tables are numbered in the order that they are first mentioned in the text (“Table 1,” “Table 2,” and so on). Figures are numbered the same way (“Figure 1,” “Figure 2,” and so on). A brief explanatory title, with the important words capitalized, appears above each table. Each figure is given a brief explanatory caption, where (aside from proper nouns or names) only the first word of each sentence is capitalized. More details on preparing APA-style tables and figures are presented later in the book.
Sample APA-Style Research Report
Figures 11.2, 11.3, 11.4, and 11.5 show some sample pages from an APA-style empirical research report originally written by undergraduate student Tomoe Suyama at California State University, Fresno. The main purpose of these figures is to illustrate the basic organization and formatting of an APA-style empirical research report, although many high-level and low-level style conventions can be seen here too.

Key Takeaways
- An APA-style empirical research report consists of several standard sections. The main ones are the abstract, introduction, method, results, discussion, and references.
- The introduction consists of an opening that presents the research question, a literature review that describes previous research on the topic, and a closing that restates the research question and comments on the method. The literature review constitutes an argument for why the current study is worth doing.
- The method section describes the method in enough detail that another researcher could replicate the study. At a minimum, it consists of a participants subsection and a design and procedure subsection.
- The results section describes the results in an organized fashion. Each primary result is presented in terms of statistical results but also explained in words.
- The discussion typically summarizes the study, discusses theoretical and practical implications and limitations of the study, and offers suggestions for further research.
- Practice: Look through an issue of a general interest professional journal (e.g., Psychological Science ). Read the opening of the first five articles and rate the effectiveness of each one from 1 ( very ineffective ) to 5 ( very effective ). Write a sentence or two explaining each rating.
- Practice: Find a recent article in a professional journal and identify where the opening, literature review, and closing of the introduction begin and end.
- Practice: Find a recent article in a professional journal and highlight in a different colour each of the following elements in the discussion: summary, theoretical implications, practical implications, limitations, and suggestions for future research.
Long Descriptions
Figure 11.1 long description: Table showing three ways of organizing an APA-style method section.
In the simple method, there are two subheadings: “Participants” (which might begin “The participants were…”) and “Design and procedure” (which might begin “There were three conditions…”).
In the typical method, there are three subheadings: “Participants” (“The participants were…”), “Design” (“There were three conditions…”), and “Procedure” (“Participants viewed each stimulus on the computer screen…”).
In the complex method, there are four subheadings: “Participants” (“The participants were…”), “Materials” (“The stimuli were…”), “Design” (“There were three conditions…”), and “Procedure” (“Participants viewed each stimulus on the computer screen…”). [Return to Figure 11.1]
- Bem, D. J. (2003). Writing the empirical journal article. In J. M. Darley, M. P. Zanna, & H. R. Roediger III (Eds.), The compleat academic: A practical guide for the beginning social scientist (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. ↵
- Darley, J. M., & Latané, B. (1968). Bystander intervention in emergencies: Diffusion of responsibility. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 4 , 377–383. ↵
A type of research article which describes one or more new empirical studies conducted by the authors.
The page at the beginning of an APA-style research report containing the title of the article, the authors’ names, and their institutional affiliation.
A summary of a research study.
The third page of a manuscript containing the research question, the literature review, and comments about how to answer the research question.
An introduction to the research question and explanation for why this question is interesting.
A description of relevant previous research on the topic being discusses and an argument for why the research is worth addressing.
The end of the introduction, where the research question is reiterated and the method is commented upon.
The section of a research report where the method used to conduct the study is described.
The main results of the study, including the results from statistical analyses, are presented in a research article.
Section of a research report that summarizes the study's results and interprets them by referring back to the study's theoretical background.
Part of a research report which contains supplemental material.
Research Methods in Psychology - 2nd Canadian Edition Copyright © 2015 by Paul C. Price, Rajiv Jhangiani, & I-Chant A. Chiang is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- About The Journalist’s Resource
- Follow us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
- Criminal Justice
- Environment
- Politics & Government
- Race & Gender
Expert Commentary
White papers, working papers, preprints, journal articles: What’s the difference?
In this updated piece, we explain the most common types of research papers journalists will encounter, noting their strengths and weaknesses.

Republish this article

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License .
by Denise-Marie Ordway, The Journalist's Resource February 25, 2022
This <a target="_blank" href="https://journalistsresource.org/media/working-papers-research-articles/">article</a> first appeared on <a target="_blank" href="https://journalistsresource.org">The Journalist's Resource</a> and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.<img src="https://journalistsresource.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/cropped-jr-favicon-150x150.png" style="width:1em;height:1em;margin-left:10px;">
This tip sheet, originally published in May 2018, has been updated to include preprint research, a type of research featured often in news coverage of the coronavirus pandemic.
Journalists rely most often on four types of research in their work. White papers, working papers, preprints and peer-reviewed journal articles.
How are they different? And which is best?
Below, we explain each, pointing out its strengths and weaknesses. As always, we urge journalists to use care in selecting any research to ground their coverage and fact-check claims.
Peer-reviewed article
Peer-reviewed research — the kind that appears in academic journals and that we highlight here at The Journalist’s Resource — has undergone a detailed critique by scholars with expertise in the field. While peer-reviewed research is generally the most reliable, journalists should keep in mind that publication in a prestigious journal is no guarantee of quality and that no single university or research organization always does the best research on a given topic.
It is safe to assume, however, that articles published in top-tier journals have been reviewed and given a stamp of approval by a number of accomplished scholars. For journalists who are uncertain, we’ve put together a list of 13 questions to ask to gauge the quality of a research article.
Keep in mind that not everything that appears in a scholarly journal has been peer reviewed. Journals publish various types of content, including book reviews, editorials, letters to the editor and, sometimes, even poetry.
Working paper
This broad category describes research papers that have not been peer reviewed or published in a journal. Working papers can be in various stages of completion. One might be ready for publication in a prestigious journal while another requires significant editing and other changes that could actually alter its main findings. Sometimes, working paper findings are so preliminary, authors will advise against citing their work .
Even so, working papers are a great way for journalists to gain access to new research quickly. The peer-review and publication process can take months to a year or longer, which means that by the time studies get published, their findings are sometimes not as useful or the data are old.
In choosing working papers, journalists should communicate with scholars about the progress of their research and how confident they are in their findings. It’s a good idea to seek corroboration from peer-reviewed research and to ask other researchers for help assessing a study.
A preprint is similar to a working paper in that it has not been vetted through a formal peer-review process. However, preprints tend to be more complete . Also, preprints submitted to public servers such as the Social Science Research Network and the health sciences server medRxiv get a cursory screening before they’re published online for public view.
Preprints, like academic journal articles, are assigned a Digital Object Identifier , or DOI, and become a permanent part of the scientific record.
White paper
A white paper is a report, often compiled by government agencies, businesses and nonprofit organizations, that outlines an issue and often explores possible solutions to a problem. For example, in November 2021, the federal Office of Community Oriented Policing Services released a white paper looking at factors that help or hinder law enforcement recruitment of Black Americans. Earlier in the year, the Advanced Technology Academic Research Center published a white paper on the American Rescue Plan ‘s widespread implications for government agencies.
In the business world, white papers also are used for marketing purposes — to describe a new product or approach, for instance, or diagnose a problem.
While a white paper can help journalists get up to speed quickly on an issue, it’s important to note some white papers advocate a specific position or policy change. Some rely on incomplete research or research that has not been peer reviewed.
Looking for more guidance on writing about research? Check out our tip sheets on covering biomedical research preprints amid the coronavirus and what journalists should know about peer review .
The Journalist’s Resource would like to thank Matthew Baum , the Marvin Kalb professor of global communications and professor of public policy at Harvard Kennedy School, for his help preparing this tip sheet.
About The Author
Denise-Marie Ordway
[email protected]
- English English Spanish German French Turkish

Thesis vs. Research Paper: Know the Differences
It is not uncommon for individuals, academic and nonacademic to use “thesis” and “research paper” interchangeably. However, while the thesis vs. research paper puzzle might seem amusing to some, for graduate, postgraduate and doctoral students, knowing the differences between the two is crucial. Not only does a clear demarcation of the two terms help you acquire a precise approach toward writing each of them, but it also helps you keep in mind the subtle nuances that go into creating the two documents. This brief guide discusses the main difference between a thesis and a research paper.

This article discusses the main difference between a thesis and a research paper. To give you an opportunity to practice proofreading, we have left a few spelling, punctuation, or grammatical errors in the text. See if you can spot them! If you spot the errors correctly, you will be entitled to a 10% discount.
It is not uncommon for individuals, academic and nonacademic to use “thesis” and “research paper” interchangeably. After all, both terms share the same domain, academic writing . Moreover, characteristics like the writing style, tone, and structure of a thesis and research paper are also homogenous to a certain degree. Hence, it is not surprising that many people mistake one for the other.
However, while the thesis vs. research paper puzzle might seem amusing to some, for graduate, postgraduate and doctoral students, knowing the differences between the two is crucial. Not only does a clear demarcation of the two terms help you acquire a precise approach toward writing each of them, but it also helps you keep in mind the subtle nuances that go into creating the two documents.
Defining the two terms: thesis vs. research paper
The first step to discerning between a thesis and research paper is to know what they signify.
Thesis: A thesis or a dissertation is an academic document that a candidate writes to acquire a university degree or similar qualification. Students typically submit a thesis at the end of their final academic term. It generally consists of putting forward an argument and backing it up with individual research and existing data.
How to Write a Perfect Ph.D. Thesis
How to Choose a Thesis or Dissertation Topic: 6 Tips
5 Common Mistakes When Writing a Thesis or Dissertation
How to Structure a Dissertation: A Brief Guide
A Step-by-Step Guide on Writing and Structuring Your Dissertation
Research Paper: A research paper is also an academic document, albeit shorter compared to a thesis. It consists of conducting independent and extensive research on a topic and compiling the data in a structured and comprehensible form. A research paper demonstrates a student's academic prowess in their field of study along with strong analytical skills.
7 Tips to Write an Effective Research Paper
7 Steps to Publishing in a Scientific Journal
Publishing Articles in Peer-Reviewed Journals: A Comprehensive Guide
10 Free Online Journal and Research Databases for Researchers
How to Formulate Research Questions
Now that we have a fundamental understanding of a thesis and a research paper, it is time to dig deeper. To the untrained eye, a research paper and a thesis might seem similar. However, there are some differences, concrete and subtle, that set the two apart.
1. Writing objectives
The objective behind writing a thesis is to obtain a master's degree or doctorate and the ilk. Hence, it needs to exemplify the scope of your knowledge in your study field. That is why choosing an intriguing thesis topic and putting forward your arguments convincingly in favor of it is crucial.
A research paper is written as a part of a course's curriculum or written for publication in a peer-review journal. Its purpose is to contribute something new to the knowledge base of its topic.
2. Structure
Although both documents share quite a few similarities in their structures, the framework of a thesis is more rigid. Also, almost every university has its proprietary guidelines set out for thesis writing.
Comparatively, a research paper only needs to keep the IMRAD format consistent throughout its length. When planning to publish your research paper in a peer-review journal, you also must follow your target journal guidelines.
3. Time Taken
A thesis is an extensive document encompassing the entire duration of a master's or doctoral course and as such, it takes months and even years to write.
A research paper, being less lengthy, typically takes a few weeks or a few months to complete.
4. Supervision
Writing a thesis entails working with a faculty supervisor to ensure that you are on the right track. However, a research paper is more of a solo project and rarely needs a dedicated supervisor to oversee.
5. Finalization
The final stage of thesis completion is a viva voce examination and a thesis defense. It includes proffering your thesis to the examination board or a thesis committee for a questionnaire and related discussions. Whether or not you will receive a degree depends on the result of this examination and the defense.
A research paper is said to be complete when you finalize a draft, check it for plagiarism, and proofread for any language and contextual errors . Now all that's left is to submit it to the assigned authority.
What is Plagiarism | How to Avoid It
How to Choose the Right Plagiarism Checker for Your Academic Works
5 Practical Ways to Avoid Plagiarism
10 Common Grammar Mistakes in Academic Writing
Guide to Avoid Common Mistakes in Sentence Structuring
In the context of academic writing, a thesis and a research paper might appear the same. But, there are some fundamental differences that set apart the two writing formats. However, since both the documents come under the scope of academic writing, they also share some similarities. Both require formal language, formal tone, factually correct information & proper citations. Also, editing and proofreading are a must for both. Editing and Proofreading ensure that your document is properly formatted and devoid of all grammatical & contextual errors. So, the next time when you come across a thesis vs. research paper argument, keep these differences in mind.
Editing or Proofreading? Which Service Should I Choose?
Thesis Proofreading and Editing Services
8 Benefits of Using Professional Proofreading and Editing Services
Achieve What You Want with Academic Editing and Proofreading
How Much Do Proofreading and Editing Cost?
If you need us to make your thesis or dissertation, contact us unhesitatingly!
Best Edit & Proof expert editors and proofreaders focus on offering papers with proper tone, content, and style of academic writing, and also provide an upscale editing and proofreading service for you. If you consider our pieces of advice, you will witness a notable increase in the chance for your research manuscript to be accepted by the publishers. We work together as an academic writing style guide by bestowing subject-area editing and proofreading around several categorized writing styles. With the group of our expert editors, you will always find us all set to help you identify the tone and style that your manuscript needs to get a nod from the publishers.
English formatting service
You can also avail of our assistance if you are looking for editors who can format your manuscript, or just check on the particular styles for the formatting task as per the guidelines provided to you, e.g., APA, MLA, or Chicago/Turabian styles. Best Edit & Proof editors and proofreaders provide all sorts of academic writing help, including editing and proofreading services, using our user-friendly website, and a streamlined ordering process.
Get a free quote for editing and proofreading now!
Visit our order page if you want our subject-area editors or language experts to work on your manuscript to improve its tone and style and give it a perfect academic tone and style through proper editing and proofreading. The process of submitting a paper is very easy and quick. Click here to find out how it works.
Our pricing is based on the type of service you avail of here, be it editing or proofreading. We charge on the basis of the word count of your manuscript that you submit for editing and proofreading and the turnaround time it takes to get it done. If you want to get an instant price quote for your project, copy and paste your document or enter your word count into our pricing calculator.

24/7 customer support | Live support
Contact us to get support with academic editing and proofreading. We have a 24/7 active live chat mode to offer you direct support along with qualified editors to refine and furbish your manuscript.

Stay tuned for updated information about editing and proofreading services!
Follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and Medium .
For more posts, click here.
- Editing & Proofreading
- Citation Styles
- Grammar Rules
- Academic Writing
- Proofreading
- Microsoft Tools
- Academic Publishing
- Dissertation & Thesis
- Researching
- Job & Research Application
Similar Posts
How to Determine Variability in a Dataset
How to Determine Central Tendency
How to Specify Study Variables in Research Papers?
Population vs Sample | Sampling Methods for a Dissertation
7 Issues to Avoid That may Dent the Quality of Thesis Writing
How to Ensure the Quality of Academic Writing in a Thesis and Dissertation?
How to Define Population and Sample in a Dissertation?
Recent Posts
ANOVA vs MANOVA: Which Method to Use in Dissertations?
They Also Read

Embarking on an academic work is obligatory for every college student who wants to graduate one day. Such an academic work is considered one of the final and most fundamental practices in the curriculum for college students. Some students who embark on their academic writing projects may not actually be aware of the mistakes (whether trivial or vital) that may delay their graduation or cause them to lose marks, or points in their assignments. So, college students should pay attention to these tips to avoid making the errors herein discussed.

Submitting a journal article can be a nerve-wracking experience. After all, this piece of work requires hours of research, analysis, and work poured into it. Therefore, you would wish for it to be acknowledged, selected, and published. This guide will give you some crucial answers, so go ahead and take a read. This way, you can ensure that your journal submission is devoid of any hassle.
Track changes function in Microsoft Word 2021 for macOS is a very handy tool to track your revisions, corrections, changes, edits, and even suggestions and comments while you’re reviewing a document. When an editor or proofreader wants to return a revised document to a client with his/her all revisions visibly marked, and so clients can accept or reject, or the suggested changes appear in the margins of the returned document, he/she needs Track Changes function of Microsoft Word.

Choosing a topic for your dissertation or thesis at the end of your master's or doctoral study can become a daunting task. You must select a topic that you find interesting to work on. A dissertation/thesis is a crucial piece of work as it carries enormous credit points at the end of the master's study or postgraduate year. Therefore, you must choose the right and the most suitable topic. Here are some helpful tips for choosing a dissertation and thesis topic that suits you the most.

A dissertation defense is one of the critical milestones one needs to cross to obtain a doctoral degree. It is a process that helps a candidate proffer their research knowledge to an audience of accomplished academics. Thus, preparing to defend a dissertation can feel distressing and burdensome, for one needs to tick several checkboxes at once. But, with the right set of steps and adequate practice, candidates can successfully overcome this unease.

An abstract usually summarizes a lengthier work (including a dissertation, thesis, research paper, or review). The abstract should explicitly state the objectives and results of your research. Thus, readers can learn what your research addresses.

When you deal with experiments, you investigate the causal relationship between variables. What you fundamentally do is manipulate one or more than one independent variable (x) to determine their effect on dependent variables (y).
Reference management. Clean and simple.
Types of research papers
Analytical research paper
Argumentative or persuasive paper, definition paper, compare and contrast paper, cause and effect paper, interpretative paper, experimental research paper, survey research paper, frequently asked questions about the different types of research papers, related articles.
There are multiple different types of research papers. It is important to know which type of research paper is required for your assignment, as each type of research paper requires different preparation. Below is a list of the most common types of research papers.
➡️ Read more: What is a research paper?
In an analytical research paper you:
- pose a question
- collect relevant data from other researchers
- analyze their different viewpoints
You focus on the findings and conclusions of other researchers and then make a personal conclusion about the topic. It is important to stay neutral and not show your own negative or positive position on the matter.
The argumentative paper presents two sides of a controversial issue in one paper. It is aimed at getting the reader on the side of your point of view.
You should include and cite findings and arguments of different researchers on both sides of the issue, but then favor one side over the other and try to persuade the reader of your side. Your arguments should not be too emotional though, they still need to be supported with logical facts and statistical data.
Tip: Avoid expressing too much emotion in a persuasive paper.
The definition paper solely describes facts or objective arguments without using any personal emotion or opinion of the author. Its only purpose is to provide information. You should include facts from a variety of sources, but leave those facts unanalyzed.
Compare and contrast papers are used to analyze the difference between two:
Make sure to sufficiently describe both sides in the paper, and then move on to comparing and contrasting both thesis and supporting one.
Cause and effect papers are usually the first types of research papers that high school and college students write. They trace probable or expected results from a specific action and answer the main questions "Why?" and "What?", which reflect effects and causes.
In business and education fields, cause and effect papers will help trace a range of results that could arise from a particular action or situation.
An interpretative paper requires you to use knowledge that you have gained from a particular case study, for example a legal situation in law studies. You need to write the paper based on an established theoretical framework and use valid supporting data to back up your statement and conclusion.
This type of research paper basically describes a particular experiment in detail. It is common in fields like:
Experiments are aimed to explain a certain outcome or phenomenon with certain actions. You need to describe your experiment with supporting data and then analyze it sufficiently.
This research paper demands the conduction of a survey that includes asking questions to respondents. The conductor of the survey then collects all the information from the survey and analyzes it to present it in the research paper.
➡️ Ready to start your research paper? Take a look at our guide on how to start a research paper .
In an analytical research paper, you pose a question and then collect relevant data from other researchers to analyze their different viewpoints. You focus on the findings and conclusions of other researchers and then make a personal conclusion about the topic.
The definition paper solely describes facts or objective arguments without using any personal emotion or opinion of the author. Its only purpose is to provide information.
Cause and effect papers are usually the first types of research papers that high school and college students are confronted with. The answer questions like "Why?" and "What?", which reflect effects and causes. In business and education fields, cause and effect papers will help trace a range of results that could arise from a particular action or situation.
This type of research paper describes a particular experiment in detail. It is common in fields like biology, chemistry or physics. Experiments are aimed to explain a certain outcome or phenomenon with certain actions.

Difference between a research paper, dissertation & thesis
When it comes to writing academic papers, students should have the right skills if they must succeed. Whether it is doing a weekly essay assignment, crafting a term paper, or doing research, the best learners are those who have mastered the art of literary composition. You should also note that understanding how each school paper differs from the other puts you ahead of the pack. Most of the schools, universities and institutions require you to undertake research at some point or another in form of coursework .
Differences based on the definition
Definitive differences between academic papers simplify things for a college newbie yet to write his or her academic paper. Now, on defining the thesis, research and dissertation, the following are worth noting:
Length of paper and methodology
Differences based on knowledge inference and hypothesis.
A hypothesis is an educated guess. Before you conduct a study, assumptions have to be made that something will turn out in some way. Most importantly, how the outcome will impact a population informs the construction of a hypothesis/thesis statement. In research and dissertation writing, students must exhibit a rigorous understanding of a subject based on a study. It is on this premise that they must come up with/infer a meaningful conclusion. However, when writing thesis papers, the formulation of a hypothesis comes after researching and writing on a subject.
Differences based on the approach
Mode of publication and utilization, differences based on the level of academia.
While students can write research papers at any level, they are most common at the undergraduate level. Completion of a research paper often leads to the conferment of an undergraduate degree. And when it comes to writing dissertation papers, the bargain is qualifying for a master’s degree, thusly; postgraduate, Mphil or MBA. It means if you are not writing a dissertation to obtain a postgraduate degree, you do so as a means of enrolling in a postgraduate program. Thesis papers lead to the conferment of a Ph.D. degree or a doctorate as some scholars call it. Students who write thesis papers do so within the last two years of their academic life.
Final Thoughts
About the author, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Maxwell Library | Bridgewater State University
Today's Hours:
- Maxwell Library
- Scholarly Journals and Popular Magazines
- Differences in Research, Review, and Opinion Articles
Scholarly Journals and Popular Magazines: Differences in Research, Review, and Opinion Articles
- Where Do I Start?
- How Do I Find Peer-Reviewed Articles?
- How Do I Compare Periodical Types?
- Where Can I find More Information?
Research Articles, Reviews, and Opinion Pieces
Scholarly or research articles are written for experts in their fields. They are often peer-reviewed or reviewed by other experts in the field prior to publication. They often have terminology or jargon that is field specific. They are generally lengthy articles. Social science and science scholarly articles have similar structures as do arts and humanities scholarly articles. Not all items in a scholarly journal are peer reviewed. For example, an editorial opinion items can be published in a scholarly journal but the article itself is not scholarly. Scholarly journals may include book reviews or other content that have not been peer reviewed.
Empirical Study: (Original or Primary) based on observation, experimentation, or study. Clinical trials, clinical case studies, and most meta-analyses are empirical studies.
Review Article: (Secondary Sources) Article that summarizes the research in a particular subject, area, or topic. They often include a summary, an literature reviews, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses.
Clinical case study (Primary or Original sources): These articles provide real cases from medical or clinical practice. They often include symptoms and diagnosis.
Clinical trials ( Health Research): Th ese articles are often based on large groups of people. They often include methods and control studies. They tend to be lengthy articles.
Opinion Piece: An opinion piece often includes personal thoughts, beliefs, or feelings or a judgement or conclusion based on facts. The goal may be to persuade or influence the reader that their position on this topic is the best.
Book review: Recent review of books in the field. They may be several pages but tend to be fairly short.
Social Science and Science Research Articles
The majority of social science and physical science articles include
- Journal Title and Author
- Abstract
- Introduction with a hypothesis or thesis
- Literature Review
- Methods/Methodology
- Results/Findings
Arts and Humanities Research Articles
In the Arts and Humanities, scholarly articles tend to be less formatted than in the social sciences and sciences. In the humanities, scholars are not conducting the same kinds of research experiments, but they are still using evidence to draw logical conclusions. Common sections of these articles include:
- an Introduction
- Discussion/Conclusion
- works cited/References/Bibliography
Research versus Review Articles
- 6 Article types that journals publish: A guide for early career researchers
- INFOGRAPHIC: 5 Differences between a research paper and a review paper
- Michigan State University. Empirical vs Review Articles
- UC Merced Library. Empirical & Review Articles
- << Previous: Where Do I Start?
- Next: How Do I Find Peer-Reviewed Articles? >>
- Last Updated: Jan 24, 2024 10:48 AM
- URL: https://library.bridgew.edu/scholarly
Phone: 508.531.1392 Text: 508.425.4096 Email: [email protected]
Feedback/Comments
Privacy Policy
Website Accessibility
Follow us on Facebook Follow us on Twitter
- SpringerLink shop
Types of journal articles
It is helpful to familiarise yourself with the different types of articles published by journals. Although it may appear there are a large number of types of articles published due to the wide variety of names they are published under, most articles published are one of the following types; Original Research, Review Articles, Short reports or Letters, Case Studies, Methodologies.
Original Research:
This is the most common type of journal manuscript used to publish full reports of data from research. It may be called an Original Article, Research Article, Research, or just Article, depending on the journal. The Original Research format is suitable for many different fields and different types of studies. It includes full Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion sections.
Short reports or Letters:
These papers communicate brief reports of data from original research that editors believe will be interesting to many researchers, and that will likely stimulate further research in the field. As they are relatively short the format is useful for scientists with results that are time sensitive (for example, those in highly competitive or quickly-changing disciplines). This format often has strict length limits, so some experimental details may not be published until the authors write a full Original Research manuscript. These papers are also sometimes called Brief communications .
Review Articles:
Review Articles provide a comprehensive summary of research on a certain topic, and a perspective on the state of the field and where it is heading. They are often written by leaders in a particular discipline after invitation from the editors of a journal. Reviews are often widely read (for example, by researchers looking for a full introduction to a field) and highly cited. Reviews commonly cite approximately 100 primary research articles.
TIP: If you would like to write a Review but have not been invited by a journal, be sure to check the journal website as some journals to not consider unsolicited Reviews. If the website does not mention whether Reviews are commissioned it is wise to send a pre-submission enquiry letter to the journal editor to propose your Review manuscript before you spend time writing it.
Case Studies:
These articles report specific instances of interesting phenomena. A goal of Case Studies is to make other researchers aware of the possibility that a specific phenomenon might occur. This type of study is often used in medicine to report the occurrence of previously unknown or emerging pathologies.
Methodologies or Methods
These articles present a new experimental method, test or procedure. The method described may either be completely new, or may offer a better version of an existing method. The article should describe a demonstrable advance on what is currently available.
Back │ Next
- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper
On the other hand, a research paper is analytical, argumentative and interpretative in nature. It involves the pursuit of knowledge and intelligent analysis of the information collected. It contains the idea of the author, often supported by expert opinions, research and information available in this regard.
Whether you are writing a thesis or research paper, they are equally challenging and take a lot of time to prepare. In this post, we will update you on all the points of difference between thesis and research paper.
Content: Thesis Vs Research Paper
- Key Elements
- Thesis Statement
How to start a research paper?
Comparison chart.
| Basis for Comparison | Thesis | Research Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Thesis refers to an original, non-plagiarised, written scholastic paper acting as a final project prepared and submitted for obtaining a university degree. | Research Paper is an original, non-plagiarised, elongated form of an essay highlighting the interpretation, evaluation or argument submitted by a researcher. |
| What is it? | Final Project | Expanded essay on research findings |
| Length | Around 20,000 to 80,000 words. | Proportional to study |
| Contains | The central question that leads to the research. | Central argument |
| Objective | To obtain a degree or professional qualification or to showcase your knowledge in the concerned field of study. | To prove credibility and contribute knowledge in the concerned field. |
| Audience | Educational Committees or Professors | Scientist or Researcher |
| Guide | Written under supervision of the guide | Not written under the supervision of the guide. |
| Description of Subject Matter | Narrow | Broad |
| Usage | Not much used. | Used for further studies. |
What is Thesis?
The thesis is a document containing the research and findings that students submit to get the professional qualification or degree . It has to be argumentative, which proposes a debatable point with which people could either agree or disagree. In short, it is a research report in writing that contains a problem which is yet to be dealt with.
In a thesis, the researcher puts forth his/her conclusion. The researcher also gives evidence in support of the conclusion.
Submission of the thesis is a mandatory requirement of a postgraduate course and PhD degree. In this, the primary focus is on the novelty of research along with the research methodology.
It is all about possibilities, by introducing several anti-thesis. Also, it ends up all the possibilities by nullifying all these anti-thesis.
Key Elements of Thesis
- Proposition : The thesis propagates an idea, hypothesis or recommendation.
- Argument : Gives reasons for accepting the proposition instead of just asserting a point of view.
- Maintenance of argument : The argument should be made cogent enough by providing suitable logic and adequate evidence.
Features of An Ideal Thesis
- An Ideal thesis is expected to add fresh knowledge to the existing theory.
- It communicates the central idea of the research in a clear and concise manner.
- An effective thesis is more than a simple statement, fact or question.
- It answers why and how questions concerned with the topic.
- To avoid confusion, it is worded carefully.
- It outlines the direction and scope of your essay.
- It gives reasons to the reader to continue reading.
Also Read : Difference Between Thesis and Dissertation
What is Thesis Statement?
A thesis statement is a sentence of one line, usually written at the end of your first paragraph. It presents the argument to the reader.
It is a blueprint of your thesis that directs the writer while writing the thesis and guides the reader through it.
What is Research Paper?
Research Paper is a form of academic writing. It is prepared on the basis of the original research conducted by the author on a specific topic, along with its analysis and interpretation of the findings.
An author generally starts writing a research paper on the basis of what he knows about the topic and seeks to find out what experts know. Further, it involves thorough and systematic research on a particular subject to extract the maximum information.
In short, a research paper is a written and published report containing the results of scientific research or a review of published scientific papers. Here, the scientific research is the primary research article, while the review of a published scientific paper is the review article.
In case of the primary research article, the author of the research paper provides important information about the research. This enables the scientific community members to:
- Evaluate it
- Reproduce the experiments
- Assess the reasoning and conclusions drawn
On the other hand, a review article is written to analyze, summarize and synthesize the research carried out previously.
When a research work is published in a scientific journal, it conveys the knowledge to a larger group of people and also makes people aware of the scientific work. Research work published as a research paper passes on knowledge and information to many people. The research paper provides relevant information about the disease and the treatment options at hand .
To start writing a research paper, one should always go for a topic that is interesting and a bit challenging too. Here, the key to choosing the topic is to pick the one that you can manage. So, you could avoid such topics which are very technical or specialized and also those topics for which data is not easily available. Also, do not go for any controversial topic.
The researcher’s approach and attitude towards the topic will decide the amount of effort and enthusiasm.
Steps for writing Research Paper
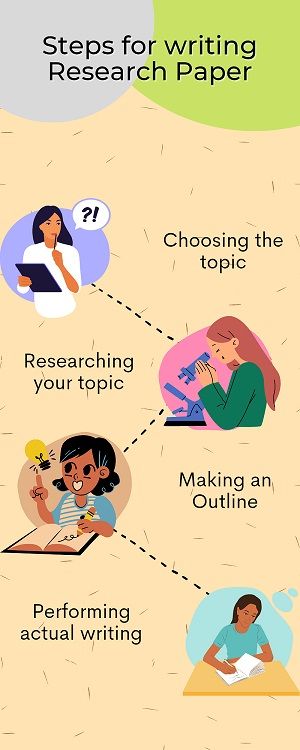
The total number of pages included in a Research Paper relies upon the research topic. It may include 8 to 10 pages, which are:
- Introduction
- Review of Literature
- Methodology
- Research Analysis
- Recommendations
Also Read : Difference Between Research Proposal and Research Report
Key Differences Between Thesis and Research Paper
- A thesis implies an original, plagiarism-free, written academic document that acts as a final project for a university degree of a higher level. But, Research Paper is a novel, plagiarism-free long essay. It portrays the interpretation, evaluation or argument submitted by a researcher.
- The thesis acts as a final project. Whereas a research paper is a kind of research manual of journals.
- The length of the thesis is around 20,000 to 80,000 words. On the contrary, the length of the research paper is relative to the study.
- The thesis focuses on the central question or statement of an intellectual argument that entails further research. On the contrary, the research paper is concerned with proving the central argument.
- The purpose of submitting the thesis is to get the degree or professional qualification. It also presents the knowledge of the candidate in the respective field. Conversely, the aim of publishing research papers is to prove credibility and contribute knowledge in the respective field.
- While the student submits the thesis to the educational committee or panel of professors who review it. In contrast, scientists and other researchers read and review the research paper.
- Preparation and completion of thesis is always under the guidance of a supervisor. For submission of the thesis, the university assigns a supervisor to each student, under whose guidance the thesis must be completed. As against, no supervisor is appointed as a guide in case of a research paper.
- The thesis contains a broader description of the subject matter. In contrast, the research paper contains a narrow description of the subject matter.
Once the research paper is published, it increases the fellowship and job opportunities for new researchers. On the other hand, thesis writing will enable the students to get the desired degree at the end of the course they have opted.
You Might Also Like:

Dr. Owenga says
February 23, 2023 at 2:38 pm
So good and informative. These are quite beneficial insights. Thanks
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Insights blog
Different types of research articles
A guide for early career researchers.
In scholarly literature, there are many different kinds of articles published every year. Original research articles are often the first thing you think of when you hear the words ‘journal article’. In reality, research work often results in a whole mixture of different outputs and it’s not just the final research article that can be published.
Finding a home to publish supporting work in different formats can help you start publishing sooner, allowing you to build your publication record and research profile.
But before you do, it’s very important that you check the instructions for authors and the aims and scope of the journal(s) you’d like to submit to. These will tell you whether they accept the type of article you’re thinking of writing and what requirements they have around it.
Understanding the different kind of articles
There’s a huge variety of different types of articles – some unique to individual journals – so it’s important to explore your options carefully. While it would be impossible to cover every single article type here, below you’ll find a guide to the most common research articles and outputs you could consider submitting for publication.
Book review
Many academic journals publish book reviews, which aim to provide insight and opinion on recently published scholarly books. Writing book reviews is often a good way to begin academic writing. It can help you get your name known in your field and give you valuable experience of publishing before you write a full-length article.
If you’re keen to write a book review, a good place to start is looking for journals that publish or advertise the books they have available for review. Then it’s just a matter of putting yourself forward for one of them.
You can check whether a journal publishes book reviews by browsing previous issues or by seeing if a book review editor is listed on the editorial board. In addition, some journals publish other types of reviews, such as film, product, or exhibition reviews, so it’s worth bearing those in mind as options as well.
Get familiar with instructions for authors
Be prepared, speed up your submission, and make sure nothing is forgotten by understanding a journal’s individual requirements.
Publishing tips, direct to your inbox
Expert tips and guidance on getting published and maximizing the impact of your research. Register now for weekly insights direct to your inbox.

Case report
A medical case report – also sometimes called a clinical case study – is an original short report that provides details of a single patient case.
Case reports include detailed information on the symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of an individual patient. They remain one of the cornerstones of medical progress and provide many new ideas in medicine.
Depending on the journal, a case report doesn’t necessarily need to describe an especially novel or unusual case as there is benefit from collecting details of many standard cases.
Take a look at F1000Research’s guidance on case reports , to understand more about what’s required in them. And don’t forget that for all studies involving human participants, informed written consent to take part in the research must be obtained from the participants – find out more about consent to publish.
Clinical study
In medicine, a clinical study report is a type of article that provides in-depth detail on the methods and results of a clinical trial. They’re typically similar in length and format to original research articles.
Most journals now require that you register protocols for clinical trials you’re involved with in a publicly accessible registry. A list of eligible registries can be found on the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) . Trials can also be registered at clinicaltrials.gov or the EU Clinical Trials Register . Once registered, your trial will be assigned a clinical trial number (CTN).
Before you submit a clinical study, you’ll need to include clinical trial numbers and registration dates in the manuscript, usually in the abstract and methods sections.
Commentaries and letters to editors
Letters to editors, as well as ‘replies’ and ‘discussions’, are usually brief comments on topical issues of public and political interest (related to the research field of the journal), anecdotal material, or readers’ reactions to material published in the journal.
Commentaries are similar, though they may be slightly more in-depth, responding to articles recently published in the journal. There may be a ‘target article’ which various commentators are invited to respond to.
You’ll need to look through previous issues of any journal you’re interested in writing for and review the instructions for authors to see which types of these articles (if any) they accept.

Conference materials
Many of our medical journals accept conference material supplements. These are open access peer-reviewed, permanent, and citable publications within the journal. Conference material supplements record research around a common thread, as presented at a workshop, congress, or conference, for the scientific record. They can include the following types of articles:
Poster extracts
Conference abstracts
Presentation extracts
Find out more about submitting conference materials.
Data notes are a short peer-reviewed article type that concisely describe research data stored in a repository. Publishing a data note can help you to maximize the impact of your data and gain appropriate credit for your research.

Data notes promote the potential reuse of research data and include details of why and how the data were created. They do not include any analysis but they can be linked to a research article incorporating analysis of the published dataset, as well as the results and conclusions.
F1000Research enables you to publish your data note rapidly and openly via an author-centric platform. There is also a growing range of options for publishing data notes in Taylor & Francis journals, including in All Life and Big Earth Data .
Read our guide to data notes to find out more.
Letters or short reports
Letters or short reports (sometimes known as brief communications or rapid communications) are brief reports of data from original research.
Editors publish these reports where they believe the data will be interesting to many researchers and could stimulate further research in the field. There are even entire journals dedicated to publishing letters.
As they’re relatively short, the format is useful for researchers with results that are time sensitive (for example, those in highly competitive or quickly-changing disciplines). This format often has strict length limits, so some experimental details may not be published until the authors write a full original research article.
Brief reports (previously called Research Notes) are a type of short report published by F1000Research – part of the Taylor & Francis Group. To find out more about the requirements for a brief report, take a look at F1000Research’s guidance .

Method article
A method article is a medium length peer-reviewed, research-focused article type that aims to answer a specific question. It also describes an advancement or development of current methodological approaches and research procedures (akin to a research article), following the standard layout for research articles. This includes new study methods, substantive modifications to existing methods, or innovative applications of existing methods to new models or scientific questions. These should include adequate and appropriate validation to be considered, and any datasets associated with the paper must publish all experimental controls and make full datasets available.
Posters and slides
With F1000Research, you can publish scholarly posters and slides covering basic scientific, translational, and clinical research within the life sciences and medicine. You can find out more about how to publish posters and slides on the F1000Research website .
Registered report
A Registered Report consists of two different kinds of articles: a study protocol and an original research article.
This is because the review process for Registered Reports is divided into two stages. In Stage 1, reviewers assess study protocols before data is collected. In Stage 2, reviewers consider the full published study as an original research article, including results and interpretation.
Taking this approach, you can get an in-principle acceptance of your research article before you start collecting data. We’ve got further guidance on Registered Reports here , and you can also read F1000Research’s guidance on preparing a Registered Report .
Research article
Original research articles are the most common type of journal article. They’re detailed studies reporting new work and are classified as primary literature.
You may find them referred to as original articles, research articles, research, or even just articles, depending on the journal.
Typically, especially in STEM subjects, these articles will include Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion sections. However, you should always check the instructions for authors of your chosen journal to see whether it specifies how your article should be structured. If you’re planning to write an original research article, take a look at our guidance on writing a journal article .
Review article
Review articles provide critical and constructive analysis of existing published literature in a field. They’re usually structured to provide a summary of existing literature, analysis, and comparison. Often, they identify specific gaps or problems and provide recommendations for future research.
Unlike original research articles, review articles are considered as secondary literature. This means that they generally don’t present new data from the author’s experimental work, but instead provide analysis or interpretation of a body of primary research on a specific topic. Secondary literature is an important part of the academic ecosystem because it can help explain new or different positions and ideas about primary research, identify gaps in research around a topic, or spot important trends that one individual research article may not.
There are 3 main types of review article
Literature review
Presents the current knowledge including substantive findings as well as theoretical and methodological contributions to a particular topic.
Systematic review
Identifies, appraises and synthesizes all the empirical evidence that meets pre-specified eligibility criteria to answer a specific research question. Researchers conducting systematic reviews use explicit, systematic methods that are selected with a view aimed at minimizing bias, to produce more reliable findings to inform decision making.
Meta-analysis
A quantitative, formal, epidemiological study design used to systematically assess the results of previous research to derive conclusions about that body of research. Typically, but not necessarily, a meta-analysis study is based on randomized, controlled clinical trials.
Take a look at our guide to writing a review article for more guidance on what’s required.
Software tool articles
A software tool article – published by F1000Research – describes the rationale for the development of a new software tool and details of the code used for its construction.
The article should provide examples of suitable input data sets and include an example of the output that can be expected from the tool and how this output should be interpreted. Software tool articles submitted to F1000Research should be written in open access programming languages. Take a look at their guidance for more details on what’s required of a software tool article.

Further resources
Ready to write your article, but not sure where to start?
For more guidance on how to prepare and write an article for a journal you can download the Writing your paper eBook .
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What is the Difference Between Research Papers and Review Papers?
Researchers often have to write different types of articles, from review papers to review papers and more, each with its own purpose and structure. This makes it critical for students and researchers to understand the nuances of good writing and develop the skills required to write various kinds of academic text. With so many different types of academic writing to pursue – scholarly articles, commentaries, book reviews, case reports, clinical study reports – it is common for students and early career researchers to get confused. So in this article, we will explain what is a review paper and what is a research paper, while summarizing the similarities and difference between review papers and research papers.
Table of Contents
What is a Review Paper ?
A review paper offers an overview of previously published work and does not contain any new research findings. It evaluates and summarizes information or knowledge that is already available in various published formats like journals, books, or other publications, all of which is referred to as secondary literature. Well-written review papers play a crucial role in helping students and researchers understand existing knowledge in a specific field or a research topic they are interested in. By providing a comprehensive overview of previous studies, methodologies, findings, and trends, they help researchers identify gaps in a specific field of study opening up new avenues for future research.
What is a Research Paper ?
A research paper is based on original research and primary sources of data. Unlike review papers, researchers writing research papers need to report new findings derived from empirical research or experimentation. It requires the author to draw inferences or make assumptions based on experiments, surveys, interviews, or questionnaires employed to collect and analyze data. Research papers also typically follow the recommended IMRAD format, which includes an abstract, introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. Through research papers, authors address a specific research question or hypothesis with the aim of contributing novel insights to the field.
Similarities between research papers and review papers
Research papers and review papers share several similarities, which makes it understandable that it is this pair of academic documents that are often most confused.
- Research papers and review papers are written by scholars and intended for an academic audience; they’re written with the aim of contributing to the existing body of knowledge in a particular field and can be published in peer reviewed journals.
- Both research papers and review papers require a comprehensive understanding of all the latest, relevant literature on a specific topic. This means authors must conduct a thorough review of existing studies, theories, and methodologies in their own subject and related areas to inform their own research or analysis.
- Research papers and review papers both adhere to specific formatting and citation styles dictated by the target journal. This ensures consistency and allows readers to easily locate and reference the sources cited in the papers.
These similarities highlight the rigorous, scholarly nature of both research papers and review papers, which requires both research integrity and a commitment to further knowledge in a field. However, these two types of academic writing are more different than one would think.
Differences between research papers and review papers
Though often used interchangeably to refer to academic content, research papers and review papers are quite different. They have different purposes, specific structure and writing styles, and citation formats given that they aim to communicate different kinds of information. Here are four key differences between research papers and review papers:
- Purpose: Review papers evaluate existing research, identify trends, and discuss the current state of knowledge on a specific topic; they are based on the study of previously published literature. On the other hand, research paperscontain original research work undertaken by the author, who is required to contribute new knowledge to the research field.
- Structure: Research papers typically follow a structured format, including key sections like the introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Meanwhile, review papers may have a more flexible structure, allowing authors to organize the content based on thematic or chronological approaches. However, they generally include an introduction, main body discussing various aspects of the topic, and a conclusion.
- Methodology: Research papers involve the collection of data, experimentation, or analysis of existing data to answer specific research questions. However, review papers do not involve original data collection; instead, they extensively analyze and summarize existing studies, often using systematic literature review methods.
- Citation style: Research papers rely on primary sources to support and justify their own findings, emphasizing recent and relevant research. Review papers incorporate a wide range of primary and secondary sources to present a comprehensive overview of the topic and support the evaluation and synthesis of existing literature.
In summary, it’s important to understand the key differences between research papers and review papers. By mastering the art of writing both research papers and review papers, students and researchers can make more meaningful contributions to their chosen disciplines. All the best!
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

What is Research Impact: Types and Tips for Academics

Research in Shorts: R Discovery’s New Feature Helps Academics Assess Relevant Papers in 2mins

How to Write a Literature Review
- What is a literature review
How is a literature review different from a research paper?
- What should I do before starting my literature review?
- What type of literature review should I write and how should I organize it?
- What should I be aware of while writing the literature review?
- For more information on Literature Reviews
- More Research Help
The purpose of an academic research paper is to develop a new argument. The literature review is one part of a research paper. In a research paper, you use the literature review as a foundation and as support for the new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and analyze the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions.
- << Previous: What is a literature review
- Next: What should I do before starting my literature review? >>
- Last Updated: Feb 26, 2021 11:35 AM
- URL: https://midway.libguides.com/LiteratureReview
RESEARCH HELP
- Research Guides
- Databases A-Z
- Journal Search
- Citation Help
LIBRARY SERVICES
- Accessibility
- Interlibrary Loan
- Study Rooms
INSTRUCTION SUPPORT
- Course Reserves
- Library Instruction
- Little Memorial Library
- 512 East Stephens Street
- 859.846.5316
- [email protected]


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
When writing a paper, maybe the only thing more daunting than actually writing it is deciding what you're even supposed to be writing about. Research reports, research papers...it gets confusing. They are actually not the same thing, and knowing the difference between them will save you time and frustration, help ...
Thesis is a type of research report. A thesis is a long-form research document that presents the findings and conclusions of an original research study conducted by a student as part of a graduate or postgraduate program. It is typically written by a student pursuing a higher degree, such as a Master's or Doctoral degree, although it can also ...
This is a wonderful website with step-by-step information on how to write a research paper. My college English students found it very helpful, and they are actually using it! by Lori Fox on Nov 22, 2017. This site is amazing, it helped to receive a 98 on a research paper would recommend it if you are anywhere confused about writing a research ...
A research report is a collection of contextual data, gathered through organized research, that provides new insights into a particular challenge (which, for this article, is business-related). Research reports are a time-tested method for distilling large amounts of data into a narrow band of focus. Their effectiveness often hinges on whether ...
Besides the definition of both, the main difference between a research paper and research report can be easily recognized only by having an overview of its complete format. Research paper encloses more chapters than the research report as a complete document. A fine research paper starts with a general introduction of the topic, and then ...
The sections of a lab report can vary between scientific fields and course requirements, but it usually contains the following: Title: expresses the topic of your study Abstract: summarizes your research aims, methods, results, and conclusions Introduction: establishes the context needed to understand the topic Method: describes the materials and procedures used in the experiment
An outline of the research questions and hypotheses; the assumptions or propositions that your research will test. Literature Review. Not all research reports have a separate literature review section. In shorter research reports, the review is usually part of the Introduction. A literature review is a critical survey of recent relevant ...
1. To answer the title question: No. There is absolutely no way to tell what sort of document a "Report" or "Research Report" or "Technical Report" is without actually reading the document. Standards vary across disciplines, across universities, and even within the same department. - JeffE.
A research report is a well-crafted document that outlines the processes, data, and findings of a systematic investigation. It is an important document that serves as a first-hand account of the research process, and it is typically considered an objective and accurate source of information.
However, there are some differences between the two. A research article is typically a shorter document that is published in a peer-reviewed journal. It focuses on a specific research question and provides a concise summary of the study's methodology, results, and conclusions. On the other hand, a research paper is usually a longer document ...
When navigating academic waters, distinguishing between a research report and a research paper is essential. A research report is often a concise summary of findings aimed at stakeholders, while a research paper delves into broader discussions, providing in-depth analysis and context. Understanding these differences can enhance both communication and comprehension in scholarly endeavors.
At the end of this section is a sample APA-style research report that illustrates many of these principles. Sections of a Research Report Title Page and Abstract. An APA-style research report begins with a title page. The title is centred in the upper half of the page, with each important word capitalized.
A research proposal is prepared at the beginning of the project. In contrast, the research report is prepared after the completion of the project. The length of a research proposal is about 4-10 pages. On the contrary, the length of the research report is about 100 to 300 pages.
White paper. A white paper is a report, often compiled by government agencies, businesses and nonprofit organizations, that outlines an issue and often explores possible solutions to a problem. For example, in November 2021, the federal Office of Community Oriented Policing Services released a white paper looking at factors that help or hinder ...
To the untrained eye, a research paper and a thesis might seem similar. However, there are some differences, concrete and subtle, that set the two apart. 1. Writing objectives. The objective behind writing a thesis is to obtain a master's degree or doctorate and the ilk.
Experimental research paper. This type of research paper basically describes a particular experiment in detail. It is common in fields like: biology. chemistry. physics. Experiments are aimed to explain a certain outcome or phenomenon with certain actions. You need to describe your experiment with supporting data and then analyze it sufficiently.
INFOGRAPHIC :5 Differences between a research paper and a review paper. There are different types of scholarly literature. Some of these require researchers to conduct an original study, whereas others can be based on previously published research. Understanding each of these types and also how they differ from one another can be rather ...
A good research paper opens the gates to advanced academic writing which will involve the implementation of findings. A dissertation is a paper that students write as a requirement for the conferment of a diploma or degree. In some countries, Ph.D. students also write dissertations. A thesis is a paper students craft as a requirement for a ...
Differences in Research, Review, and Opinion Articles; ... 5 Differences between a research paper and a review paper. Michigan State University. Empirical vs Review Articles ... Print Page; Report a problem. Subjects: General / Multidisciplinary Resources. Tags: assessment, journals; general resources, magazines, periodicals. Maxwell Library ...
Original Research: This is the most common type of journal manuscript used to publish full reports of data from research. It may be called an Original Article, Research Article, Research, or just Article, depending on the journal. The Original Research format is suitable for many different fields and different types of studies.
But, Research Paper is a novel, plagiarism-free long essay. It portrays the interpretation, evaluation or argument submitted by a researcher. The thesis acts as a final project. Whereas a research paper is a kind of research manual of journals. The length of the thesis is around 20,000 to 80,000 words.
Letters or short reports. Method article. Posters and slides. Registered report. Research article. Review article. Software tool articles. In scholarly literature, there are many different kinds of articles published every year. Original research articles are often the first thing you think of when you hear the words 'journal article'.
Here are four key differences between research papers and review papers: Purpose: Review papers evaluate existing research, identify trends, and discuss the current state of knowledge on a specific topic; they are based on the study of previously published literature. On the other hand, research paperscontain original research work undertaken ...
A research paper is all about research and a review paper tells you about giving reviews. Answer: A research paper presents original findings or results from a study, while a review paper summarizes and analyzes existing research on a particular topic, providing an overview of the current state of knowledge.
The literature review is one part of a research paper. In a research paper, you use the literature review as a foundation and as support for the new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and analyze the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions.