- Content Writing Services
- Get in Touch

How to Write an Executive Summary for a Case Study
Updated July 2024: You’re not going to invest your time and energy in reading a case study unless you know it is relevant to your situation. How do you know if it’s relevant? By reading the executive summary. This is why it is so important for you to learn how to write an executive summary for a case study.
In this post, we show you what makes a compelling executive summary for case studies, and provide you with 4 examples from leading B2B SaaS companies.
Every word counts when writing an executive summary for a case study
Executive summaries can be short and sweet.
- Or executive summaries might need to be longer
Sometimes executive summaries miss the mark entirely
- You can do better with your executive summary
This is the third post in a 9-part series on how to write a case study .
When thinking about how to write an executive summary for a case study, you need to create 2 or 3 crucial sentences that provide a concise overview of the case study. It must be informative and:
- summarize the story by introducing the customer and their pain points
- explain what your organization did
- highlight the key results, including 1 or 2 statistics that drive home the takeaway message
Write the executive summary first to help you focus the rest of the case study. But don’t be too rigid: in the process of reviewing the interview transcript or writing the main copy, another point or statistic may emerge as having more impact than what you’ve chosen to highlight. Revisit your executive summary after writing the case study to make sure it’s as strong and accurate as possible.
If you need a hand with your SaaS case studies, have a look at our case study writing service .
This executive summary example from Segment is just a headline followed by a glorified subhead—but it does the trick!

Source: Segmen t
Here’s another great example of a quick, yet helpful executive summary for Plaid’s case study:

Source: Plaid
And here’s one more example of a quick executive summary for G2’s case study:

Sometimes you may need a longer executive summary
For complex case studies, you may need a more in-depth executive summary to give readers an overview of the case study.
Here’s a more fleshed-out executive summary from Feathr:
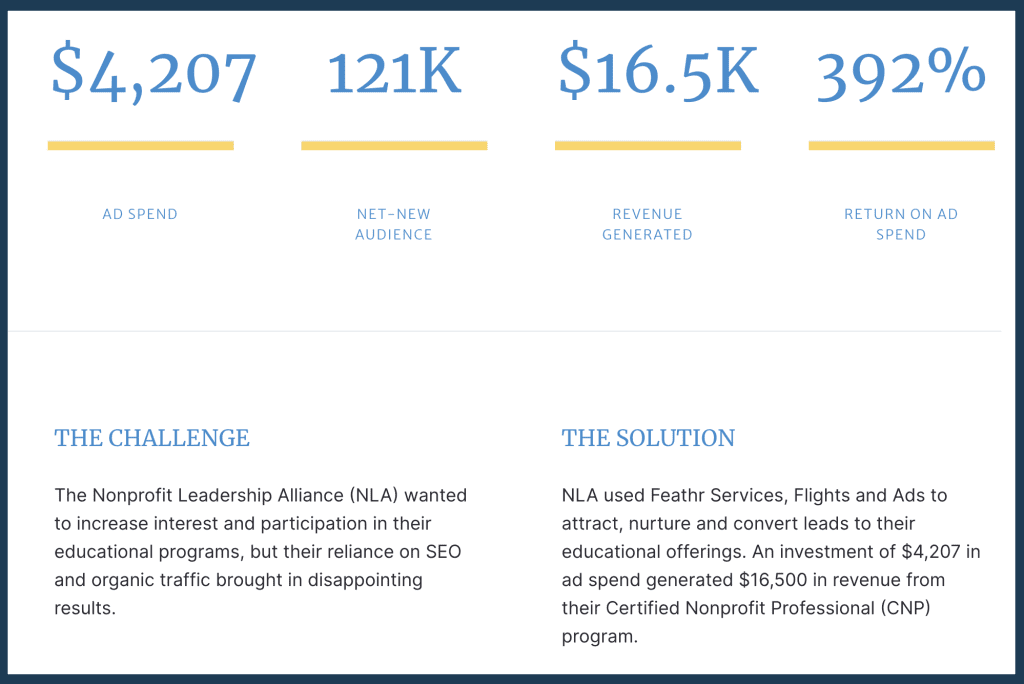
Source: Feathr
It effectively introduces the challenge and solution, and the results are impossible to miss.
Here’s another great example from Gong. Notice they just use “Challenge” and “Outcome”.

Source: Gong

Source: Bullhorn
This is not an executive summary. It is merely an introduction. We have no idea what the problem or solution is, and there’s nothing to motivate us to read further.
You can do better with your executive summaries
Be precise. Impress the reader with key results. Let them see that you offer solutions that matter.
Get the help you need
As a SaaS company, you need to partner with someone who “gets it”. We are a SaaS content marketing agency that works with high-growth companies like Calendly, ClickUp and WalkMe. Check out our done-for-you case study writing service .

As the founder of Uplift Content, Emily leads her team in creating done-for-you case studies, ebooks and blog posts for high-growth SaaS companies like ClickUp, Calendly and WalkMe. Connect with Emily on Linkedin
Sign up for the Content Huddle newsletter
Learn from Emily’s 17 years of aha moments, mistakes, observations, and insights—and find out how you can apply these lessons to your own marketing efforts.
You can unsubscribe any time. Visit our Terms of Use for information on our privacy practices.
Extract insights from Customer & Employee Interviews. At Scale.
Case study executive summary: examples and tips.
Home » Case Study Executive Summary: Examples and Tips
Case study recaps serve as powerful tools for conveying complex information in a concise, digestible format. These summaries distill the essence of a comprehensive case study, highlighting key insights, challenges, and outcomes. By providing a snapshot of real-world scenarios, case study recaps offer valuable learning opportunities for professionals across various industries. They enable readers to quickly grasp the core elements of a project or initiative, making them ideal for busy executives, decision-makers, and stakeholders who need to absorb critical information efficiently.
Effective case study recaps not only save time but also facilitate knowledge sharing and decision-making within organizations. They showcase successful strategies, innovative solutions, and lessons learned, inspiring others to apply similar approaches in their own contexts. As we delve deeper into the art of crafting compelling case study recaps, we'll explore best practices, examples, and tips to help you create impactful summaries that resonate with your target audience.
Creating Effective Executive Summaries for Case Studies
Creating an effective executive summary for a case study requires a strategic approach to distill complex information into a concise, impactful format. A well-crafted case study recap serves as a powerful tool for decision-makers, offering a quick overview of key findings and insights. To achieve this, focus on highlighting the most critical elements of your research, including the problem statement, methodology, and key outcomes.
Begin by clearly articulating the challenge or opportunity that prompted the case study. This sets the stage for the reader and provides essential context. Next, outline the approach taken to address the issue, emphasizing any innovative methods or unique perspectives employed. Finally, present the results and their implications, ensuring that the value proposition is clearly communicated. By following these guidelines, you can create a compelling executive summary that captures the essence of your case study and engages your audience effectively.
What Makes a Good Executive Summary?
A well-crafted executive summary serves as a powerful tool for conveying the essence of a case study. It distills complex information into a concise, easily digestible format that captures the reader's attention. An effective summary highlights key findings, insights, and outcomes while maintaining a clear narrative structure.
To create a compelling case study recap, focus on presenting the most critical elements. Begin with a brief overview of the client's challenge or problem, followed by the implemented solution and its rationale. Emphasize measurable results and tangible benefits achieved through the intervention. Include relevant statistics or data points to support your claims and demonstrate the impact of the solution. Conclude with key takeaways or lessons learned, providing valuable insights for readers facing similar challenges.
The Role of a Case Study Recap in Summarizing Findings
A case study recap serves as a powerful tool for distilling complex findings into a concise, digestible format. This summary acts as a bridge between the detailed analysis and the key takeaways, allowing readers to quickly grasp the essence of the study. By highlighting the most significant outcomes, challenges overcome, and lessons learned, a well-crafted recap provides valuable insights at a glance.
Effective case study recaps often follow a structured approach, presenting information in a logical flow. They typically begin with a brief overview of the problem or situation, followed by the implemented solution and its results. This format enables readers to understand the context, appreciate the actions taken, and recognize the achieved outcomes. By condensing the most crucial elements of the case study, the recap becomes an indispensable tool for decision-makers, stakeholders, and those seeking to apply similar strategies in their own contexts.
Case Study Recap: Examples of Effective Executive Summaries
Effective executive summaries are crucial for conveying the key insights of a case study concisely. Let's explore some exemplary recaps that demonstrate best practices in summarizing complex information. These examples showcase how to distill essential findings, highlight key metrics, and present actionable recommendations.
One standout case study recap comes from a tech startup that revolutionized customer service. Their executive summary began with a compelling problem statement, followed by a brief overview of their innovative solution. The recap then presented three key performance indicators that demonstrated the solution's impact, including a 40% reduction in response times and a 25% increase in customer satisfaction scores. By focusing on these critical metrics, the summary effectively communicated the project's success in just a few sentences.
Another noteworthy example comes from a healthcare organization that implemented a new patient management system. Their executive summary excelled in presenting a clear before-and-after comparison. It succinctly outlined the challenges faced prior to implementation, then highlighted the improvements achieved, such as a 30% decrease in wait times and a 50% reduction in administrative errors. This approach provided a clear narrative of transformation and results.
Example 1: Comprehensive yet Concise
In the realm of case study analysis, striking the right balance between comprehensiveness and conciseness is crucial. A well-crafted executive summary serves as a powerful tool to capture the essence of a complex case study in a digestible format. This approach allows readers to grasp key insights quickly without sacrificing depth.
To achieve this balance, focus on distilling the most critical elements of your case study. Begin by clearly stating the problem or challenge addressed, followed by a brief overview of the methodology used. Then, highlight the main findings and their implications. Conclude with actionable recommendations or lessons learned. By presenting information in this structured manner, you create a compelling narrative that engages readers while providing valuable insights efficiently.
Example 2: Highlighting Key Metrics and Outcomes
In crafting an effective case study executive summary, highlighting key metrics and outcomes is crucial. This example demonstrates how to present quantifiable results that capture attention and underscore the value delivered. By focusing on specific, measurable achievements, you can quickly convey the impact of your solution or intervention.
Consider structuring this section with clear, concise statements that showcase impressive figures. For instance, "Increased revenue by 35% within six months" or "Reduced operational costs by $500,000 annually" immediately grab the reader's attention. Pair these metrics with brief explanations of how they were achieved, tying them directly to the actions taken. This approach not only validates your success but also provides context for the reader to understand the significance of the outcomes in relation to the client's initial challenges.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Case Study Recap in Executive Summaries
Mastering the art of case study recap is crucial for creating impactful executive summaries. By distilling complex information into concise, actionable insights, you enable decision-makers to grasp key findings quickly. Effective recaps highlight the most significant outcomes, challenges overcome, and lessons learned from each case study.
To excel in case study recaps, focus on presenting a clear narrative that emphasizes the value derived from the project. Utilize data visualization techniques to illustrate key metrics and results. Remember to tailor your language to your audience, ensuring that technical jargon doesn't obscure the main takeaways. By honing these skills, you'll create executive summaries that drive informed decision-making and showcase the true impact of your case studies.
Turn interviews into actionable insights
On this Page
Construction Management: Writing an Effective Executive Summary
You may also like, massage business plan: crafting a compelling executive summary.
Printing Business Executive Summary: Key Components
Catering services: writing an effective executive summary.
Unlock Insights from Interviews 10x faster
- Request demo
- Get started for free
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Sep 07, 2023

Okay, let’s get real: case studies can be kinda snooze-worthy. But guess what? They don’t have to be!
In this article, I will cover every element that transforms a mere report into a compelling case study, from selecting the right metrics to using persuasive narrative techniques.
And if you’re feeling a little lost, don’t worry! There are cool tools like Venngage’s Case Study Creator to help you whip up something awesome, even if you’re short on time. Plus, the pre-designed case study templates are like instant polish because let’s be honest, everyone loves a shortcut.
Click to jump ahead:
What is a case study presentation?
What is the purpose of presenting a case study, how to structure a case study presentation, how long should a case study presentation be, 5 case study presentation examples with templates, 6 tips for delivering an effective case study presentation, 5 common mistakes to avoid in a case study presentation, how to present a case study faqs.
A case study presentation involves a comprehensive examination of a specific subject, which could range from an individual, group, location, event, organization or phenomenon.
They’re like puzzles you get to solve with the audience, all while making you think outside the box.
Unlike a basic report or whitepaper, the purpose of a case study presentation is to stimulate critical thinking among the viewers.
The primary objective of a case study is to provide an extensive and profound comprehension of the chosen topic. You don’t just throw numbers at your audience. You use examples and real-life cases to make you think and see things from different angles.

The primary purpose of presenting a case study is to offer a comprehensive, evidence-based argument that informs, persuades and engages your audience.
Here’s the juicy part: presenting that case study can be your secret weapon. Whether you’re pitching a groundbreaking idea to a room full of suits or trying to impress your professor with your A-game, a well-crafted case study can be the magic dust that sprinkles brilliance over your words.
Think of it like digging into a puzzle you can’t quite crack . A case study lets you explore every piece, turn it over and see how it fits together. This close-up look helps you understand the whole picture, not just a blurry snapshot.
It’s also your chance to showcase how you analyze things, step by step, until you reach a conclusion. It’s all about being open and honest about how you got there.
Besides, presenting a case study gives you an opportunity to connect data and real-world scenarios in a compelling narrative. It helps to make your argument more relatable and accessible, increasing its impact on your audience.
One of the contexts where case studies can be very helpful is during the job interview. In some job interviews, you as candidates may be asked to present a case study as part of the selection process.
Having a case study presentation prepared allows the candidate to demonstrate their ability to understand complex issues, formulate strategies and communicate their ideas effectively.
The way you present a case study can make all the difference in how it’s received. A well-structured presentation not only holds the attention of your audience but also ensures that your key points are communicated clearly and effectively.
In this section, let’s go through the key steps that’ll help you structure your case study presentation for maximum impact.
Let’s get into it.
Open with an introductory overview
Start by introducing the subject of your case study and its relevance. Explain why this case study is important and who would benefit from the insights gained. This is your opportunity to grab your audience’s attention.

Explain the problem in question
Dive into the problem or challenge that the case study focuses on. Provide enough background information for the audience to understand the issue. If possible, quantify the problem using data or metrics to show the magnitude or severity.

Detail the solutions to solve the problem
After outlining the problem, describe the steps taken to find a solution. This could include the methodology, any experiments or tests performed and the options that were considered. Make sure to elaborate on why the final solution was chosen over the others.

Key stakeholders Involved
Talk about the individuals, groups or organizations that were directly impacted by or involved in the problem and its solution.
Stakeholders may experience a range of outcomes—some may benefit, while others could face setbacks.
For example, in a business transformation case study, employees could face job relocations or changes in work culture, while shareholders might be looking at potential gains or losses.
Discuss the key results & outcomes
Discuss the results of implementing the solution. Use data and metrics to back up your statements. Did the solution meet its objectives? What impact did it have on the stakeholders? Be honest about any setbacks or areas for improvement as well.
Include visuals to support your analysis
Visual aids can be incredibly effective in helping your audience grasp complex issues. Utilize charts, graphs, images or video clips to supplement your points. Make sure to explain each visual and how it contributes to your overall argument.
Pie charts illustrate the proportion of different components within a whole, useful for visualizing market share, budget allocation or user demographics.
This is particularly useful especially if you’re displaying survey results in your case study presentation.
Stacked charts on the other hand are perfect for visualizing composition and trends. This is great for analyzing things like customer demographics, product breakdowns or budget allocation in your case study.
Consider this example of a stacked bar chart template. It provides a straightforward summary of the top-selling cake flavors across various locations, offering a quick and comprehensive view of the data.
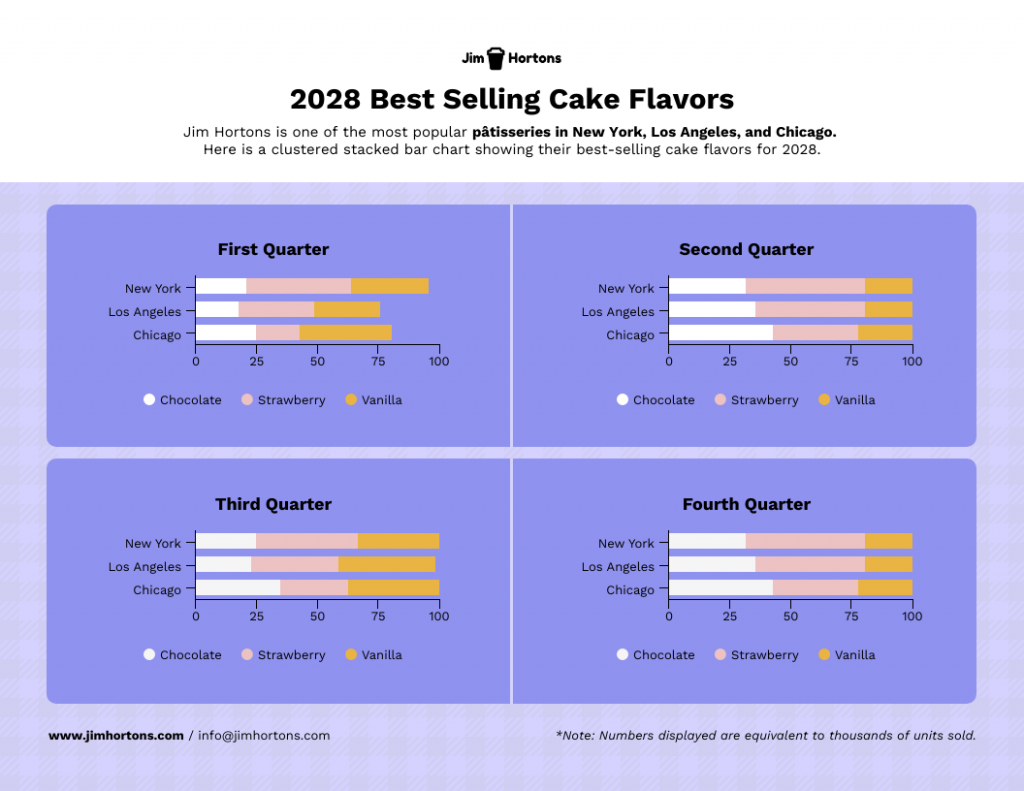
Not the chart you’re looking for? Browse Venngage’s gallery of chart templates to find the perfect one that’ll captivate your audience and level up your data storytelling.
Recommendations and next steps
Wrap up by providing recommendations based on the case study findings. Outline the next steps that stakeholders should take to either expand on the success of the project or address any remaining challenges.
Acknowledgments and references
Thank the people who contributed to the case study and helped in the problem-solving process. Cite any external resources, reports or data sets that contributed to your analysis.
Feedback & Q&A session
Open the floor for questions and feedback from your audience. This allows for further discussion and can provide additional insights that may not have been considered previously.
Closing remarks
Conclude the presentation by summarizing the key points and emphasizing the takeaways. Thank your audience for their time and participation and express your willingness to engage in further discussions or collaborations on the subject.

Well, the length of a case study presentation can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the needs of your audience. However, a typical business or academic presentation often lasts between 15 to 30 minutes.
This time frame usually allows for a thorough explanation of the case while maintaining audience engagement. However, always consider leaving a few minutes at the end for a Q&A session to address any questions or clarify points made during the presentation.
When it comes to presenting a compelling case study, having a well-structured template can be a game-changer.
It helps you organize your thoughts, data and findings in a coherent and visually pleasing manner.
Not all case studies are created equal and different scenarios require distinct approaches for maximum impact.
To save you time and effort, I have curated a list of 5 versatile case study presentation templates, each designed for specific needs and audiences.
Here are some best case study presentation examples that showcase effective strategies for engaging your audience and conveying complex information clearly.
1 . Lab report case study template
Ever feel like your research gets lost in a world of endless numbers and jargon? Lab case studies are your way out!
Think of it as building a bridge between your cool experiment and everyone else. It’s more than just reporting results – it’s explaining the “why” and “how” in a way that grabs attention and makes sense.
This lap report template acts as a blueprint for your report, guiding you through each essential section (introduction, methods, results, etc.) in a logical order.

Want to present your research like a pro? Browse our research presentation template gallery for creative inspiration!
2. Product case study template
It’s time you ditch those boring slideshows and bullet points because I’ve got a better way to win over clients: product case study templates.
Instead of just listing features and benefits, you get to create a clear and concise story that shows potential clients exactly what your product can do for them. It’s like painting a picture they can easily visualize, helping them understand the value your product brings to the table.
Grab the template below, fill in the details, and watch as your product’s impact comes to life!

3. Content marketing case study template
In digital marketing, showcasing your accomplishments is as vital as achieving them.
A well-crafted case study not only acts as a testament to your successes but can also serve as an instructional tool for others.
With this coral content marketing case study template—a perfect blend of vibrant design and structured documentation, you can narrate your marketing triumphs effectively.

4. Case study psychology template
Understanding how people tick is one of psychology’s biggest quests and case studies are like magnifying glasses for the mind. They offer in-depth looks at real-life behaviors, emotions and thought processes, revealing fascinating insights into what makes us human.
Writing a top-notch case study, though, can be a challenge. It requires careful organization, clear presentation and meticulous attention to detail. That’s where a good case study psychology template comes in handy.
Think of it as a helpful guide, taking care of formatting and structure while you focus on the juicy content. No more wrestling with layouts or margins – just pour your research magic into crafting a compelling narrative.
5. Lead generation case study template
Lead generation can be a real head-scratcher. But here’s a little help: a lead generation case study.
Think of it like a friendly handshake and a confident resume all rolled into one. It’s your chance to showcase your expertise, share real-world successes and offer valuable insights. Potential clients get to see your track record, understand your approach and decide if you’re the right fit.
No need to start from scratch, though. This lead generation case study template guides you step-by-step through crafting a clear, compelling narrative that highlights your wins and offers actionable tips for others. Fill in the gaps with your specific data and strategies, and voilà! You’ve got a powerful tool to attract new customers.
Related: 15+ Professional Case Study Examples [Design Tips + Templates]
So, you’ve spent hours crafting the perfect case study and are now tasked with presenting it. Crafting the case study is only half the battle; delivering it effectively is equally important.
Whether you’re facing a room of executives, academics or potential clients, how you present your findings can make a significant difference in how your work is received.
Forget boring reports and snooze-inducing presentations! Let’s make your case study sing. Here are some key pointers to turn information into an engaging and persuasive performance:
- Know your audience : Tailor your presentation to the knowledge level and interests of your audience. Remember to use language and examples that resonate with them.
- Rehearse : Rehearsing your case study presentation is the key to a smooth delivery and for ensuring that you stay within the allotted time. Practice helps you fine-tune your pacing, hone your speaking skills with good word pronunciations and become comfortable with the material, leading to a more confident, conversational and effective presentation.
- Start strong : Open with a compelling introduction that grabs your audience’s attention. You might want to use an interesting statistic, a provocative question or a brief story that sets the stage for your case study.
- Be clear and concise : Avoid jargon and overly complex sentences. Get to the point quickly and stay focused on your objectives.
- Use visual aids : Incorporate slides with graphics, charts or videos to supplement your verbal presentation. Make sure they are easy to read and understand.
- Tell a story : Use storytelling techniques to make the case study more engaging. A well-told narrative can help you make complex data more relatable and easier to digest.

Ditching the dry reports and slide decks? Venngage’s case study templates let you wow customers with your solutions and gain insights to improve your business plan. Pre-built templates, visual magic and customer captivation – all just a click away. Go tell your story and watch them say “wow!”
Nailed your case study, but want to make your presentation even stronger? Avoid these common mistakes to ensure your audience gets the most out of it:
Overloading with information
A case study is not an encyclopedia. Overloading your presentation with excessive data, text or jargon can make it cumbersome and difficult for the audience to digest the key points. Stick to what’s essential and impactful. Need help making your data clear and impactful? Our data presentation templates can help! Find clear and engaging visuals to showcase your findings.
Lack of structure
Jumping haphazardly between points or topics can confuse your audience. A well-structured presentation, with a logical flow from introduction to conclusion, is crucial for effective communication.
Ignoring the audience
Different audiences have different needs and levels of understanding. Failing to adapt your presentation to your audience can result in a disconnect and a less impactful presentation.
Poor visual elements
While content is king, poor design or lack of visual elements can make your case study dull or hard to follow. Make sure you use high-quality images, graphs and other visual aids to support your narrative.
Not focusing on results
A case study aims to showcase a problem and its solution, but what most people care about are the results. Failing to highlight or adequately explain the outcomes can make your presentation fall flat.
How to start a case study presentation?
Starting a case study presentation effectively involves a few key steps:
- Grab attention : Open with a hook—an intriguing statistic, a provocative question or a compelling visual—to engage your audience from the get-go.
- Set the stage : Briefly introduce the subject, context and relevance of the case study to give your audience an idea of what to expect.
- Outline objectives : Clearly state what the case study aims to achieve. Are you solving a problem, proving a point or showcasing a success?
- Agenda : Give a quick outline of the key sections or topics you’ll cover to help the audience follow along.
- Set expectations : Let your audience know what you want them to take away from the presentation, whether it’s knowledge, inspiration or a call to action.
How to present a case study on PowerPoint and on Google Slides?
Presenting a case study on PowerPoint and Google Slides involves a structured approach for clarity and impact using presentation slides :
- Title slide : Start with a title slide that includes the name of the case study, your name and any relevant institutional affiliations.
- Introduction : Follow with a slide that outlines the problem or situation your case study addresses. Include a hook to engage the audience.
- Objectives : Clearly state the goals of the case study in a dedicated slide.
- Findings : Use charts, graphs and bullet points to present your findings succinctly.
- Analysis : Discuss what the findings mean, drawing on supporting data or secondary research as necessary.
- Conclusion : Summarize key takeaways and results.
- Q&A : End with a slide inviting questions from the audience.
What’s the role of analysis in a case study presentation?
The role of analysis in a case study presentation is to interpret the data and findings, providing context and meaning to them.
It helps your audience understand the implications of the case study, connects the dots between the problem and the solution and may offer recommendations for future action.
Is it important to include real data and results in the presentation?
Yes, including real data and results in a case study presentation is crucial to show experience, credibility and impact. Authentic data lends weight to your findings and conclusions, enabling the audience to trust your analysis and take your recommendations more seriously
How do I conclude a case study presentation effectively?
To conclude a case study presentation effectively, summarize the key findings, insights and recommendations in a clear and concise manner.
End with a strong call-to-action or a thought-provoking question to leave a lasting impression on your audience.
What’s the best way to showcase data in a case study presentation ?
The best way to showcase data in a case study presentation is through visual aids like charts, graphs and infographics which make complex information easily digestible, engaging and creative.
Don’t just report results, visualize them! This template for example lets you transform your social media case study into a captivating infographic that sparks conversation.

Choose the type of visual that best represents the data you’re showing; for example, use bar charts for comparisons or pie charts for parts of a whole.
Ensure that the visuals are high-quality and clearly labeled, so the audience can quickly grasp the key points.
Keep the design consistent and simple, avoiding clutter or overly complex visuals that could distract from the message.
Choose a template that perfectly suits your case study where you can utilize different visual aids for maximum impact.
Need more inspiration on how to turn numbers into impact with the help of infographics? Our ready-to-use infographic templates take the guesswork out of creating visual impact for your case studies with just a few clicks.
Related: 10+ Case Study Infographic Templates That Convert
Congrats on mastering the art of compelling case study presentations! This guide has equipped you with all the essentials, from structure and nuances to avoiding common pitfalls. You’re ready to impress any audience, whether in the boardroom, the classroom or beyond.
And remember, you’re not alone in this journey. Venngage’s Case Study Creator is your trusty companion, ready to elevate your presentations from ordinary to extraordinary. So, let your confidence shine, leverage your newly acquired skills and prepare to deliver presentations that truly resonate.
Go forth and make a lasting impact!
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: Jun 3, 2024 9:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
How to Write a Case Study: A Step-by-Step Guide (+ Examples)
by Todd Brehe
on Jan 3, 2024

If you want to learn how to write a case study that engages prospective clients, demonstrates that you can solve real business problems, and showcases the results you deliver, this guide will help.
We’ll give you a proven template to follow, show you how to conduct an engaging interview, and give you several examples and tips for best practices.
Let’s start with the basics.

What is a Case Study?
A business case study is simply a story about how you successfully delivered a solution to your client.
Case studies start with background information about the customer, describe problems they were facing, present the solutions you developed, and explain how those solutions positively impacted the customer’s business.
Do Marketing Case Studies Really Work?
Absolutely. A well-written case study puts prospective clients into the shoes of your paying clients, encouraging them to engage with you. Plus, they:
- Get shared “behind the lines” with decision makers you may not know;
- Leverage the power of “social proof” to encourage a prospective client to take a chance with your company;
- Build trust and foster likeability;
- Lessen the perceived risk of doing business with you and offer proof that your business can deliver results;
- Help prospects become aware of unrecognized problems;
- Show prospects experiencing similar problems that possible solutions are available (and you can provide said solutions);
- Make it easier for your target audience to find you when using Google and other search engines.
Case studies serve your clients too. For example, they can generate positive publicity and highlight the accomplishments of line staff to the management team. Your company might even throw in a new product/service discount, or a gift as an added bonus.
But don’t just take my word for it. Let’s look at a few statistics and success stories:
5 Winning Case Study Examples to Model
Before we get into the nuts and bolts of how to write a case study, let’s go over a few examples of what an excellent one looks like.
The five case studies listed below are well-written, well-designed, and incorporate a time-tested structure.
1. Lane Terralever and Pinnacle at Promontory

This case study example from Lane Terralever incorporates images to support the content and effectively uses subheadings to make the piece scannable.
2. WalkMe Mobile and Hulyo
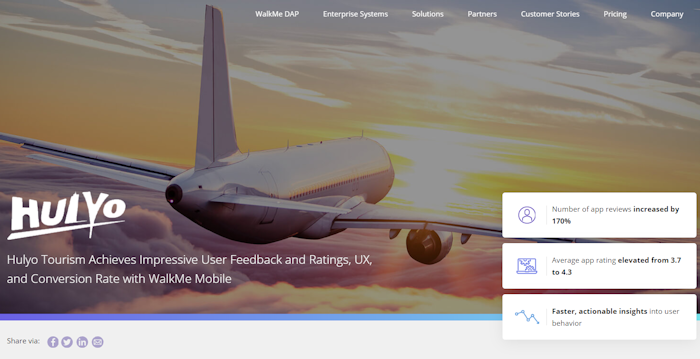
This case study from WalkMe Mobile leads with an engaging headline and the three most important results the client was able to generate.
In the first paragraph, the writer expands the list of accomplishments encouraging readers to learn more.
3. CurationSuite Listening Engine

This is an example of a well-designed printable case study . The client, specific problem, and solution are called out in the left column and summarized succinctly.
4. Brain Traffic and ASAE

This long format case study (6 pages) from Brain Traffic summarizes the challenges, solutions, and results prominently in the left column. It uses testimonials and headshots of the case study participants very effectively.
5. Adobe and Home Depot

This case study from Adobe and Home Depot is a great example of combining video, attention-getting graphics, and long form writing. It also uses testimonials and headshots well.
Now that we’ve gone over the basics and showed a few great case study examples you can use as inspiration, let’s roll up our sleeves and get to work.
A Case Study Structure That Pros Use
Let’s break down the structure of a compelling case study:
Choose Your Case Study Format
In this guide, we focus on written case studies. They’re affordable to create, and they have a proven track record. However, written case studies are just one of four case study formats to consider:
- Infographic
If you have the resources, video (like the Adobe and Home Depot example above) and podcast case studies can be very compelling. Hearing a client discuss in his or her own words how your company helped is an effective content marketing strategy
Infographic case studies are usually one-page images that summarize the challenge, proposed solution, and results. They tend to work well on social media.
Follow a Tried-and-True Case Study Template
The success story structure we’re using incorporates a “narrative” or “story arc” designed to suck readers in and captivate their interest.
Note: I recommend creating a blog post or landing page on your website that includes the text from your case study, along with a downloadable PDF. Doing so helps people find your content when they perform Google and other web searches.
There are a few simple SEO strategies that you can apply to your blog post that will optimize your chances of being found. I’ll include those tips below.
Craft a Compelling Headline
The headline should capture your audience’s attention quickly. Include the most important result you achieved, the client’s name, and your company’s name. Create several examples, mull them over a bit, then pick the best one. And, yes, this means writing the headline is done at the very end.
SEO Tip: Let’s say your firm provided “video editing services” and you want to target this primary keyword. Include it, your company name, and your client’s name in the case study title.
Write the Executive Summary
This is a mini-narrative using an abbreviated version of the Challenge + Solution + Results model (3-4 short paragraphs). Write this after you complete the case study.
SEO Tip: Include your primary keyword in the first paragraph of the Executive Summary.
Provide the Client’s Background
Introduce your client to the reader and create context for the story.
List the Customer’s Challenges and Problems
Vividly describe the situation and problems the customer was dealing with, before working with you.
SEO Tip: To rank on page one of Google for our target keyword, review the questions listed in the “People also ask” section at the top of Google’s search results. If you can include some of these questions and their answers into your case study, do so. Just make sure they fit with the flow of your narrative.
Detail Your Solutions
Explain the product or service your company provided, and spell out how it alleviated the client’s problems. Recap how the solution was delivered and implemented. Describe any training needed and the customer’s work effort.
Show Your Results
Detail what you accomplished for the customer and the impact your product/service made. Objective, measurable results that resonate with your target audience are best.
List Future Plans
Share how your client might work with your company in the future.
Give a Call-to-Action
Clearly detail what you want the reader to do at the end of your case study.
Talk About You
Include a “press release-like” description of your client’s organization, with a link to their website. For your printable document, add an “About” section with your contact information.
And that’s it. That’s the basic structure of any good case study.
Now, let’s go over how to get the information you’ll use in your case study.
How to Conduct an Engaging Case Study Interview
One of the best parts of creating a case study is talking with your client about the experience. This is a fun and productive way to learn what your company did well, and what it can improve on, directly from your customer’s perspective.
Here are some suggestions for conducting great case study interviews:
When Choosing a Case Study Subject, Pick a Raving Fan
Your sales and marketing team should know which clients are vocal advocates willing to talk about their experiences. Your customer service and technical support teams should be able to contribute suggestions.
Clients who are experts with your product/service make solid case study candidates. If you sponsor an online community, look for product champions who post consistently and help others.
When selecting a candidate, think about customer stories that would appeal to your target audience. For example, let’s say your sales team is consistently bumping into prospects who are excited about your solution, but are slow to pull the trigger and do business with you.
In this instance, finding a client who felt the same way, but overcame their reluctance and contracted with you anyway, would be a compelling story to capture and share.
Prepping for the Interview
If you’ve ever seen an Oprah interview, you’ve seen a master who can get almost anyone to open up and talk. Part of the reason is that she and her team are disciplined about planning.
Before conducting a case study interview, talk to your own team about the following:
- What’s unique about the client (location, size, industry, etc.) that will resonate with our prospects?
- Why did the customer select us?
- How did we help the client?
- What’s unique about this customer’s experience?
- What problems did we solve?
- Were any measurable, objective results generated?
- What do we want readers to do after reading this case study analysis?
Pro Tip: Tee up your client. Send them the questions in advance.
Providing questions to clients before the interview helps them prepare, gather input from other colleagues if needed, and feel more comfortable because they know what to expect.
In a moment, I’ll give you an exhaustive list of interview questions. But don’t send them all. Instead, pare the list down to one or two questions in each section and personalize them for your customer.
Nailing the Client Interview
Decide how you’ll conduct the interview. Will you call the client, use Skype or Facetime, or meet in person? Whatever mode you choose, plan the process in advance.
Make sure you record the conversation. It’s tough to lead an interview, listen to your contact’s responses, keep the conversation flowing, write notes, and capture all that the person is saying.
A recording will make it easier to write the client’s story later. It’s also useful for other departments in your company (management, sales, development, etc.) to hear real customer feedback.
Use open-ended questions that spur your contact to talk and share. Here are some real-life examples:
Introduction
- Recap the purpose of the call. Confirm how much time your contact has to talk (30-45 minutes is preferable).
- Confirm the company’s location, number of employees, years in business, industry, etc.
- What’s the contact’s background, title, time with the company, primary responsibilities, and so on?
Initial Challenges
- Describe the situation at your company before engaging with us?
- What were the initial problems you wanted to solve?
- What was the impact of those problems?
- When did you realize you had to take some action?
- What solutions did you try?
- What solutions did you implement?
- What process did you go through to make a purchase?
- How did the implementation go?
- How would you describe the work effort required of your team?
- If training was involved, how did that go?
Results, Improvements, Progress
- When did you start seeing improvements?
- What were the most valuable results?
- What did your team like best about working with us?
- Would you recommend our solution/company? Why?
Future Plans
- How do you see our companies working together in the future?
Honest Feedback
- Our company is very focused on continual improvement. What could we have done differently to make this an even better experience?
- What would you like us to add or change in our product/service?
During the interview, use your contact’s responses to guide the conversation.
Once the interview is complete, it’s time to write your case study.
How to Write a Case Study… Effortlessly
Case study writing is not nearly as difficult as many people make it out to be. And you don’t have to be Stephen King to do professional work. Here are a few tips:
- Use the case study structure that we outlined earlier, but write these sections first: company background, challenges, solutions, and results.
- Write the headline, executive summary, future plans, and call-to-action (CTA) last.
- In each section, include as much content from your interview as you can. Don’t worry about editing at this point
- Tell the story by discussing their trials and tribulations.
- Stay focused on the client and the results they achieved.
- Make their organization and employees shine.
- When including information about your company, frame your efforts in a supporting role.
Also, make sure to do the following:
Add Testimonials, Quotes, and Visuals
The more you can use your contact’s words to describe the engagement, the better. Weave direct quotes throughout your narrative.
Strive to be conversational when you’re writing case studies, as if you’re talking to a peer.
Include images in your case study that visually represent the content and break up the text. Photos of the company, your contact, and other employees are ideal.
If you need to incorporate stock photos, here are three resources:
- Deposit p hotos
And if you need more, check out Smart Blogger’s excellent resource: 17 Sites with High-Quality, Royalty-Free Stock Photos .
Proofread and Tighten Your Writing
Make sure there are no grammar, spelling, or punctuation errors. If you need help, consider using a grammar checker tool like Grammarly .
My high school English teacher’s mantra was “tighten your writing.” She taught that impactful writing is concise and free of weak, unnecessary words . This takes effort and discipline, but will make your writing stronger.
Also, keep in mind that we live in an attention-diverted society. Before your audience will dive in and read each paragraph, they’ll first scan your work. Use subheadings to summarize information, convey meaning quickly, and pull the reader in.
Be Sure to Use Best Practices
Consider applying the following best practices to your case study:
- Stay laser-focused on your client and the results they were able to achieve.
- Even if your audience is technical, minimize the use of industry jargon . If you use acronyms, explain them.
- Leave out the selling and advertising.
- Don’t write like a Shakespearean wannabe. Write how people speak. Write to be understood.
- Clear and concise writing is not only more understandable, it inspires trust. Don’t ramble.
- Weave your paragraphs together so that each sentence is dependent on the one before and after it.
- Include a specific case study call-to-action (CTA).
- A recommended case study length is 2-4 pages.
- Commit to building a library of case studies.
Get Client Approval
After you have a final draft, send it to the client for review and approval. Incorporate any edits they suggest.
Use or modify the following “Consent to Publish” form to get the client’s written sign-off:
Consent to Publish
Case Study Title:
I hereby confirm that I have reviewed the case study listed above and on behalf of the [Company Name], I provide full permission for the work to be published, in whole or in part, for the life of the work, in all languages and all formats by [Company publishing the case study].
By signing this form, I affirm that I am authorized to grant full permission.
Company Name:
E-mail Address:
Common Case Study Questions (& Answers)
We’ll wrap things up with a quick Q&A. If you have a question I didn’t answer, be sure to leave it in a blog comment below.
Should I worry about print versions of my case studies?
Absolutely.
As we saw in the CurationSuite and Brain Traffic examples earlier, case studies get downloaded, printed, and shared. Prospects can and will judge your book by its cover.
So, make sure your printed case study is eye-catching and professionally designed. Hire a designer if necessary.
Why are good case studies so effective?
Case studies work because people trust them.
They’re not ads, they’re not press releases, and they’re not about how stellar your company is.
Plus, everyone likes spellbinding stories with a hero [your client], a conflict [challenges], and a riveting resolution [best solution and results].
How do I promote my case study?
After you’ve written your case study and received the client’s approval to use it, you’ll want to get it in front of as many eyes as possible.
Try the following:
- Make sure your case studies can be easily found on your company’s homepage.
- Tweet and share the case study on your various social media accounts.
- Have your sales team use the case study as a reason to call on potential customers. For example: “Hi [prospect], we just published a case study on Company A. They were facing some of the same challenges I believe your firm is dealing with. I’m going to e-mail you a copy. Let me know what you think.”
- Distribute printed copies at trade shows, seminars, or during sales presentations.
- If you’re bidding on a job and have to submit a quote or a Request for Proposal (RFP), include relevant case studies as supporting documents.
Ready to Write a Case Study That Converts?
If you want to stand out and you want to win business, case studies should be an integral part of your sales and marketing efforts.
Hopefully, this guide answered some of your questions and laid out a path that will make it faster and easier for your team to create professional, sales-generating content.
Now it’s time to take action and get started. Gather your staff, select a client, and ask a contact to participate. Plan your interview and lead an engaging conversation. Write up your client’s story, make them shine, and then share it.
Get better at the case study process by doing it more frequently. Challenge yourself to write at least one case study every two months.
As you do, you’ll be building a valuable repository of meaningful, powerful content. These success stories will serve your business in countless ways, and for years to come.
Content Marketing
The ultimate toolkit for becoming one of the highest-paid writers online. Premium training. Yours for free.
Written by Todd Brehe
Latest from the blog.

10+ Super SMART Goal Examples (& A Handy Template)

Fiction vs Nonfiction: Key Differences, Examples, & Benefits

How to Self-Publish a Book: A Comprehensive Guide for 2024

With over 300k subscribers and 4 million readers, Smart Blogger is one of the world's largest websites dedicated to writing and blogging.
Best of the Blog
© 2012-2024 Smart Blogger — Boost Blog Traffic, Inc.
Terms | Privacy Policy | Refund Policy | Affiliate Disclosure

Case Study Summary
Ai generator.

It doesn’t always take an expert to fix a problem. Have you ever had a light in your house that doesn’t go on? Well, it’s not an engineering project , so it wouldn’t take a genius to identify if it’s a busted light bulb or a wiring issue. For these two cases, you can easily solve one problem but might need the help of an electrician for the other. When you encounter a particular situation, basic knowledge can help you to overcome it. And when you’ve dealt with the dilemma, what comes out may be additional knowledge on how to fix similar problems. And sometimes, life just gives you these things to test how well you can handle it. In academic settings, the presentation of these solutions can be considered a case study summary.
To get a firm grip on the principles and characteristics of discipline, you may need to test out what you know through given situations. In the fields of social science, business, and research, these situations are called case studies. And the initial analysis report is called a case study summary. A case executive summary is what the readers first encounter before they decide if the case is worth examining. Your case summary saves readers time in understanding the situation you’ve presented. It holds important information about medical or business case studies that your readers need to take in.
What a Case Study Summary Isn’t
Many may assume that a case study summary is the same as an abstract. They are relatively similar, but they have their key differences. A research executive summary is for those outside the academic spectrum. An abstract is for professors, research analysts, and anyone in the academe. The case study summary is also not the introduction, although it may contain similar content, they don’t share the same purpose. It is also not the preface of the study. Most importantly, it is not just a collection of random highlights within the analysis. The format of a case study summary is for the understanding of the collected data.
10+ Case Study Summary Example
A lot of case studies are hard to understand. Some people even dread the idea of reading the whole research project from start to finish. Thankfully, there is a more natural way to grasp the context of the study. That is through case study summaries. If you are working o a case study, you should be able to write a comprehensive overview of your own. To help you figure out the outline and format of your summary, here are 10+ case study summary examples you can check out.
1. Master Technology Case Study Summary Example
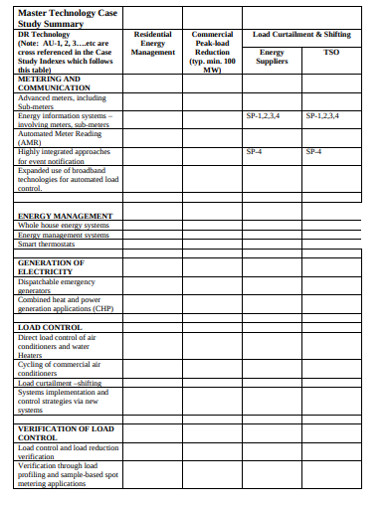
Size: 15 KB
2. Family Case Study Summary Example

Size: 216 KB
3. Case Study Summary Report Example

Size: 277 KB
4. Sample Case Studies Summary Example

Size: 487 KB
5. Case Studies Summary Workshop Example

Size: 356 KB
6. Commissioner Case Study Summary Example

7. Case Study Summary Information Example

Size: 946 KB
8. Formal Case Study Summary Example
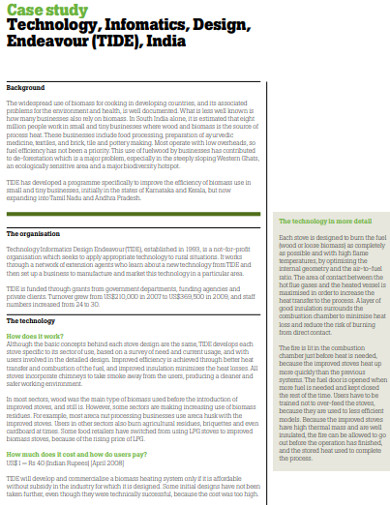
Size: 235 KB
9. Academic Case Study Summary Example

Size: 263 KB
10. Corporation Case Studies Summary Example

Size: 573 KB
11. Standard Case Study Summary Example

Size: 193 KB
The Making an Effective Case Study Summary
As a researcher, you wouldn’t want your readers to have a hard time making sense of your case analysis . All the effort you put into making that can go to waste if it isn’t easy to understand. What you need is a compelling case study summary. If your review has the right information, your reader can level with you in no time. Here are some tricks to making a good case study summary.
1. Decide the Need
After writing an entire case study, the last thing you want is more report writing. That is why the first step to making a useful case summary is deciding if there is a need to have one. Some case studies that are considerably easier to understand don’t need case study summaries. But if your decision making says that you need it, then you better start!

2. Decide the Length
The length of the summary doesn’t always reflect how much information it holds. It can, however, determine how well of a writer you are. Your overview can be as concise as you want or as detailed as it needs to be. For as long as your research summary is readable, any length will do.
3. Prepare Data
The next step is conducting data analysis to figure out which data you are going to add to your case study summary. Pick out the most important details and the data most likely to raise questions. Anticipating these questions can help you formulate possible answers to add in your summary.
4. Organize Data
Making sure your data is organized is part and parcel to having a comprehensive case study summary. You can write a short introduction to open your summary and explain the purpose of your study. You then explain your solutions to the problem statement . Make sure no factoid overlaps another to avoid confusion.
5. Format Content
A continuous piece of writing can make a reader hesitate. Format your summary in a way that doesn’t seem too daunting. Divide your content, add a few white spaces. You have to let your readers’ eyes rest when scanning your summary. Don’t make your summary datasheet intimidating to look at.
When handling cases, whether you are a market analyst of a social science researcher, case study summaries are your best friends in data collection.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

- Library Catalogue
Summarizing: How to effectively summarize the work of others
On this page, strategies for summarizing, a summary case study.
Academic writing requires you to research the work of other scholars, develop your own ideas on the topic of your research, and then to think about how your ideas relate to the scholarship that you have researched. Three main ways of responding are to generally agree, generally disagree, or both agree and disagree with another author’s perspective on a subject. You can think of agreeing and disagreeing as being like saying, “Okay, but….” Being able to effectively summarize the work of other researchers will help you both to determine your own position and also clearly communicate the connections between your ideas and the ideas of others. In other words, knowing how to effectively summarize the ideas of others helps you to bring those ideas into dialogue with your own.
When you summarize, you explain the main idea(s) from someone else’s work. Note that you must include citation information for summaries -- think of your citation as showing your reader where they can find the original or “full” version of the work that you have summarized.
In They Say/I Say, Gerald Graff and Cathy Birkenstein describe summarizing as “putting yourself in the shoes of someone else” (2014, p. 31). They use this description because effective summarizing requires that you engage with and aim to understand someone else’s ideas or perspective, even if you disagree. It can be helpful to think of a summary as a brief description of someone else’s work that they, themselves, would recognize and consider to be a fair representation.
Try these steps for writing summaries:
- Select a short passage (about one to four sentences) that supports an idea in your paper.
- Read the passage carefully to fully understand it.
- Take notes about the main idea and supporting points you think you should include in your summary. Include keywords and terms used by the author and think, too, about how the source ideas are relevant to the argument(s) that you are presenting in your paper.
- Using only your notes, explain the original author’s main ideas to someone else. Then explain how those ideas support or conflict with your own argument.
- Reread the original source. Is there important information that you have forgotten or misremembered? Is your summary very similar to the original source?
- Add in-text citation and check the required formatting style.
An effective summary is a way of communicating to your reader what the source text is “about.” However, even while it is important to “put yourself in the shoes” of the original author, you also need to know what it is that you are arguing in your paper that has led you to include this other perspective. Because a scholarly article is rarely about one simple thing, knowing what you are arguing will help you to determine the most important ideas of the original source for your paper.
Below is an example of an ineffective, list-like summary, followed by an effective summary.
Original source to be summarized
“Before 1994, diabetes in children was generally caused by a genetic disorder – only about 5 percent of childhood diabetes cases were obesity-related, or Type 2, diabetes. Today, according to the National Institutes of Health, Type 2 diabetes accounts for at least 30 percent of all new childhood cases of diabetes in this country. Not surprisingly, money spent to treat diabetes has skyrocketed, too. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimate that diabetes accounted for $2.6 billion in health care costs in 1969. Today’s number is an unbelievable $100 billion a year.”
“Don’t Blame the Eater,” David Zinczenko [1]
Ineffective list-like summary
The author says that only 5 percent of children had Type 2 diabetes before 1994. In addition, they mention that today at least 30 percent of new childhood diabetes cases in the USA are Type 2. They also say that more money is being spent to treat diabetes now -- $100 billion a year.
Effective summary
In author's article “Don’t Blame the Eater,” David Zinczenko supports their position on the fast food industry by comparing today’s rates of Type 2 diabetes to those prior to 1994. David makes it clear that instances of Type 2 diabetes have increased dramatically, as has the cost of preventing the spread of this disease.
An effective summary doesn’t just report source information but also indicates concisely how the ideas connect and why they matter. You will also notice that the second example mentions the name of the author and the article, which is an important way of signalling to your reader that you are referring to someone else’s work, rather than presenting your own original ideas.
[1] Example taken from Graff, G. & Birkenstein, C. (2014). They say/I say: The moves that matter in academic writing. New York and London: W.W. Norton & Company.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Analyse a Case Study
Last Updated: April 13, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Sarah Evans . Sarah Evans is a Public Relations & Social Media Expert based in Las Vegas, Nevada. With over 14 years of industry experience, Sarah is the Founder & CEO of Sevans PR. Her team offers strategic communications services to help clients across industries including tech, finance, medical, real estate, law, and startups. The agency is renowned for its development of the "reputation+" methodology, a data-driven and AI-powered approach designed to elevate brand credibility, trust, awareness, and authority in a competitive marketplace. Sarah’s thought leadership has led to regular appearances on The Doctors TV show, CBS Las Vegas Now, and as an Adobe influencer. She is a respected contributor at Entrepreneur magazine, Hackernoon, Grit Daily, and KLAS Las Vegas. Sarah has been featured in PR Daily and PR Newswire and is a member of the Forbes Agency Council. She received her B.A. in Communications and Public Relations from Millikin University. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 413,766 times.
Case studies are used in many professional education programs, primarily in business school, to present real-world situations to students and to assess their ability to parse out the important aspects of a given dilemma. In general, a case study should include, in order: background on the business environment, description of the given business, identification of a key problem or issue, steps taken to address the issue, your assessment of that response, and suggestions for better business strategy. The steps below will guide you through the process of analyzing a business case study in this way.

- Describe the nature of the organization under consideration and its competitors. Provide general information about the market and customer base. Indicate any significant changes in the business environment or any new endeavors upon which the business is embarking.

- Analyze its management structure, employee base, and financial history. Describe annual revenues and profit. Provide figures on employment. Include details about private ownership, public ownership, and investment holdings. Provide a brief overview of the business's leaders and command chain.

- In all likelihood, there will be several different factors at play. Decide which is the main concern of the case study by examining what most of the data talks about, the main problems facing the business, and the conclusions at the end of the study. Examples might include expansion into a new market, response to a competitor's marketing campaign, or a changing customer base. [3] X Research source

- Draw on the information you gathered and trace a chronological progression of steps taken (or not taken). Cite data included in the case study, such as increased marketing spending, purchasing of new property, changed revenue streams, etc.

- Indicate whether or not each aspect of the response met its goal and whether the response overall was well-crafted. Use numerical benchmarks, like a desired customer share, to show whether goals were met; analyze broader issues, like employee management policies, to talk about the response as a whole. [4] X Research source

- Suggest alternative or improved measures that could have been taken by the business, using specific examples and backing up your suggestions with data and calculations.

Community Q&A
- Always read a case study several times. At first, you should read just for the basic details. On each subsequent reading, look for details about a specific topic: competitors, business strategy, management structure, financial loss. Highlight phrases and sections relating to these topics and take notes. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- In the preliminary stages of analyzing a case study, no detail is insignificant. The biggest numbers can often be misleading, and the point of an analysis is often to dig deeper and find otherwise unnoticed variables that drive a situation. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- If you are analyzing a case study for a consulting company interview, be sure to direct your comments towards the matters handled by the company. For example, if the company deals with marketing strategy, focus on the business's successes and failures in marketing; if you are interviewing for a financial consulting job, analyze how well the business keeps their books and their investment strategy. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Do not use impassioned or emphatic language in your analysis. Business case studies are a tool for gauging your business acumen, not your personal beliefs. When assigning blame or identifying flaws in strategy, use a detached, disinterested tone. Thanks Helpful 16 Not Helpful 4
Things You'll Need
You might also like.

Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about business writing, check out our in-depth interview with Sarah Evans .
- ↑ https://www.gvsu.edu/cms4/asset/CC3BFEEB-C364-E1A1-A5390F221AC0FD2D/business_case_analysis_gg_final.pdf
- ↑ https://bizfluent.com/12741914/how-to-analyze-a-business-case-study
- ↑ http://www.business-fundas.com/2009/how-to-analyze-business-case-studies/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uagc.edu/writing-case-study-analysis
- http://college.cengage.com/business/resources/casestudies/students/analyzing.htm
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Lisa Upshur
Jun 15, 2019
Did this article help you?
Tejiri Aren
Jul 21, 2016
Jul 15, 2017
Jenn M.T. Tseka
Jul 3, 2016
Devanand Sbuurayan
Dec 6, 2020

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples
Published on November 23, 2020 by Shona McCombes . Revised on May 31, 2023.
Summarizing , or writing a summary, means giving a concise overview of a text’s main points in your own words. A summary is always much shorter than the original text.
There are five key steps that can help you to write a summary:
- Read the text
- Break it down into sections
- Identify the key points in each section
- Write the summary
- Check the summary against the article
Writing a summary does not involve critiquing or evaluating the source . You should simply provide an accurate account of the most important information and ideas (without copying any text from the original).
Table of contents
When to write a summary, step 1: read the text, step 2: break the text down into sections, step 3: identify the key points in each section, step 4: write the summary, step 5: check the summary against the article, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about summarizing.
There are many situations in which you might have to summarize an article or other source:
- As a stand-alone assignment to show you’ve understood the material
- To keep notes that will help you remember what you’ve read
- To give an overview of other researchers’ work in a literature review
When you’re writing an academic text like an essay , research paper , or dissertation , you’ll integrate sources in a variety of ways. You might use a brief quote to support your point, or paraphrase a few sentences or paragraphs.
But it’s often appropriate to summarize a whole article or chapter if it is especially relevant to your own research, or to provide an overview of a source before you analyze or critique it.
In any case, the goal of summarizing is to give your reader a clear understanding of the original source. Follow the five steps outlined below to write a good summary.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

You should read the article more than once to make sure you’ve thoroughly understood it. It’s often effective to read in three stages:
- Scan the article quickly to get a sense of its topic and overall shape.
- Read the article carefully, highlighting important points and taking notes as you read.
- Skim the article again to confirm you’ve understood the key points, and reread any particularly important or difficult passages.
There are some tricks you can use to identify the key points as you read:
- Start by reading the abstract . This already contains the author’s own summary of their work, and it tells you what to expect from the article.
- Pay attention to headings and subheadings . These should give you a good sense of what each part is about.
- Read the introduction and the conclusion together and compare them: What did the author set out to do, and what was the outcome?
To make the text more manageable and understand its sub-points, break it down into smaller sections.
If the text is a scientific paper that follows a standard empirical structure, it is probably already organized into clearly marked sections, usually including an introduction , methods , results , and discussion .
Other types of articles may not be explicitly divided into sections. But most articles and essays will be structured around a series of sub-points or themes.
Now it’s time go through each section and pick out its most important points. What does your reader need to know to understand the overall argument or conclusion of the article?
Keep in mind that a summary does not involve paraphrasing every single paragraph of the article. Your goal is to extract the essential points, leaving out anything that can be considered background information or supplementary detail.
In a scientific article, there are some easy questions you can ask to identify the key points in each part.
| Introduction | or problem was addressed? |
|---|---|
| Methods | |
| Results | supported? |
| Discussion/conclusion |
If the article takes a different form, you might have to think more carefully about what points are most important for the reader to understand its argument.
In that case, pay particular attention to the thesis statement —the central claim that the author wants us to accept, which usually appears in the introduction—and the topic sentences that signal the main idea of each paragraph.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Now that you know the key points that the article aims to communicate, you need to put them in your own words.
To avoid plagiarism and show you’ve understood the article, it’s essential to properly paraphrase the author’s ideas. Do not copy and paste parts of the article, not even just a sentence or two.
The best way to do this is to put the article aside and write out your own understanding of the author’s key points.
Examples of article summaries
Let’s take a look at an example. Below, we summarize this article , which scientifically investigates the old saying “an apple a day keeps the doctor away.”
Davis et al. (2015) set out to empirically test the popular saying “an apple a day keeps the doctor away.” Apples are often used to represent a healthy lifestyle, and research has shown their nutritional properties could be beneficial for various aspects of health. The authors’ unique approach is to take the saying literally and ask: do people who eat apples use healthcare services less frequently? If there is indeed such a relationship, they suggest, promoting apple consumption could help reduce healthcare costs.
The study used publicly available cross-sectional data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Participants were categorized as either apple eaters or non-apple eaters based on their self-reported apple consumption in an average 24-hour period. They were also categorized as either avoiding or not avoiding the use of healthcare services in the past year. The data was statistically analyzed to test whether there was an association between apple consumption and several dependent variables: physician visits, hospital stays, use of mental health services, and use of prescription medication.
Although apple eaters were slightly more likely to have avoided physician visits, this relationship was not statistically significant after adjusting for various relevant factors. No association was found between apple consumption and hospital stays or mental health service use. However, apple eaters were found to be slightly more likely to have avoided using prescription medication. Based on these results, the authors conclude that an apple a day does not keep the doctor away, but it may keep the pharmacist away. They suggest that this finding could have implications for reducing healthcare costs, considering the high annual costs of prescription medication and the inexpensiveness of apples.
However, the authors also note several limitations of the study: most importantly, that apple eaters are likely to differ from non-apple eaters in ways that may have confounded the results (for example, apple eaters may be more likely to be health-conscious). To establish any causal relationship between apple consumption and avoidance of medication, they recommend experimental research.
An article summary like the above would be appropriate for a stand-alone summary assignment. However, you’ll often want to give an even more concise summary of an article.
For example, in a literature review or meta analysis you may want to briefly summarize this study as part of a wider discussion of various sources. In this case, we can boil our summary down even further to include only the most relevant information.
Using national survey data, Davis et al. (2015) tested the assertion that “an apple a day keeps the doctor away” and did not find statistically significant evidence to support this hypothesis. While people who consumed apples were slightly less likely to use prescription medications, the study was unable to demonstrate a causal relationship between these variables.
Citing the source you’re summarizing
When including a summary as part of a larger text, it’s essential to properly cite the source you’re summarizing. The exact format depends on your citation style , but it usually includes an in-text citation and a full reference at the end of your paper.
You can easily create your citations and references in APA or MLA using our free citation generators.
APA Citation Generator MLA Citation Generator
Finally, read through the article once more to ensure that:
- You’ve accurately represented the author’s work
- You haven’t missed any essential information
- The phrasing is not too similar to any sentences in the original.
If you’re summarizing many articles as part of your own work, it may be a good idea to use a plagiarism checker to double-check that your text is completely original and properly cited. Just be sure to use one that’s safe and reliable.
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Paraphrasing
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
A summary is a short overview of the main points of an article or other source, written entirely in your own words. Want to make your life super easy? Try our free text summarizer today!
A summary is always much shorter than the original text. The length of a summary can range from just a few sentences to several paragraphs; it depends on the length of the article you’re summarizing, and on the purpose of the summary.
You might have to write a summary of a source:
- As a stand-alone assignment to prove you understand the material
- For your own use, to keep notes on your reading
- To provide an overview of other researchers’ work in a literature review
- In a paper , to summarize or introduce a relevant study
To avoid plagiarism when summarizing an article or other source, follow these two rules:
- Write the summary entirely in your own words by paraphrasing the author’s ideas.
- Cite the source with an in-text citation and a full reference so your reader can easily find the original text.
An abstract concisely explains all the key points of an academic text such as a thesis , dissertation or journal article. It should summarize the whole text, not just introduce it.
An abstract is a type of summary , but summaries are also written elsewhere in academic writing . For example, you might summarize a source in a paper , in a literature review , or as a standalone assignment.
All can be done within seconds with our free text summarizer .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, May 31). How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 24, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/how-to-summarize/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to paraphrase | step-by-step guide & examples, how to quote | citing quotes in apa, mla & chicago, the basics of in-text citation | apa & mla examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Case Study Summarizer #1 — Free Summaries!
Have you ever thought of how many case studies must a student in medicine or business read in their lifetime? Tens, hundreds, or even thousands! As practice shows, the case study’s content is jam-packed with information and broad descriptions that are unnecessary when conducting a review or simply reading the literature.
We offer a Case Study Summarizer to scan any paper in seconds! You will get some valuable insights about our tool that can help with the most extended case studies in a short time! Moreover, we discuss the definition of the case study, its structure, and its main elements. Let’s begin!
- 🧰 How to Use the Tool?
📋 What Is the Case Study Summarizer?
🧩 case study elements & structure, 🧑🏫 how to summarize a case study.
- ✅ 5 Tool’s Benefits
🖇️ References
🧰 how to use the case summarizer.
Our free case study summarizer is so easy to use! Follow these 4 simple steps:
- Enter the text . Paste the text of the case study in the appropriate field of the tool. Ensure that it does not exceed 15,000 characters.
- Adjust settings . You can choose the number of sentences you want in your summary and decide whether to highlight keywords.
- Press the button . Just click the button, and the results will not keep you waiting!
- Copy the result . Your summary will appear in just a few seconds! All you need to do is just copy it in one click.
Do you still have concerns about using our case study summarizer? Then check out its incredible features:
| 📃 Preservation of text content | The summarizing tool removes unnecessary words or sentences without changing the meaning of the text. |
|---|---|
| 📏 Summary size adjustment | You can choose the number of sentences you want to have in your summary. |
| 🔤 Automatic copying | It takes just 1 second to copy the full summary by pressing the button. |
| 🔑 Analysis of keywords | Artificial intelligence identifies and determines which sentences and words are most important. |
| ️⚠️ Characters indicator | The case study summarizer shows the characters' limits, which makes it so convenient to use! |
A case study is typically presented as a report, separated into sections with headings and subheadings. It must contain a description of the issue, an explanation of the relevance of the case, and an analysis with conclusions. It ends with implications and recommendations on how to address the issue.
What Is a Case Study?
A case study is a detailed investigation of one person, group, or event. It aims to learn as much as possible about an individual or a group to generalize the findings on other similar cases. The case study can be employed in various fields, including psychology, medicine, social work, etc.
Here are some case study topics from different professional spheres:
- Medicine : Analysis of the medical and occupational records of a non-smoking individual with lung cancer.
- Business : The decision of Warren Buffett to acquire Precision Castparts Corporation and why that acquisition was a mistake.
- Psychology : The case of Bertha Pappenheim , who suffered from hysteria and contributed to the development of talk therapy to treat mental illness.
Case Study Elements
There are 8 essential elements in any case study. Check the table below to learn more details about each component.
| Element | Constituents | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| used for analysis | Describe the case study’s purpose and outline the primary issues and findings without going into specifics. | |
| Introduce the case, giving background information on the subject and identifying its significance. | ||
| Present the issues you have chosen and support each with facts and evidence to show their significance. | ||
| Give a concise overview of your discovered issues and provide workable solutions to each. | ||
| the report’s goal and highlight the key takeaways from the findings. | ||
| Choose the solution that best addresses each issue. Then explain your decision and how it will aid in fixing the problems. | ||
| An extended list of the used sources. | List all of the references included in the report according to the chosen citation style rules. | |
| Any visual element used in the analysis. | Enclose any original data relevant to your analysis but not included in the main body. Appendices usually contain charts, graphs, and tables. |
Summarizing is a fundamental skill for everyone since it allows you to distinguish essential information and effectively communicate it to others. In the following paragraphs, we will share a case study summary tutorial.
Executive Summary Case Study
An executive summary is a detailed overview of a report. It saves readers time by summarizing the essential points of the study. It is frequently written to be shared with people who may not have time to read the complete report, for example, CEOs or department heads.
Although the format may vary, the primary elements of an executive summary are as follows:
- An opening statement and some background information .
- The purpose of the report.
- Methodology.
- Summarized and justified recommendations.
How Long Is an Executive Summary?
Your executive summary’s length will vary depending on the text it summarizes. Typically, it takes 10-15% of the full report’s length . Therefore, an executive summary can range from 1 paragraph to 10 pages.
Case Study Summary Guide
Take these 5 steps to write a compelling case study summary:
Step 1 – Read the entire study
Before writing the summary, carefully read the research study from beginning to end.
Step 2 – Highlight the major points
As you read, make notes and underline significant facts, relevant conclusions, and suggested actions.
Step 3 – Divide the document into main sections
Determine what each part of the report is about, and summarize each in a few sentences. You can use the executive summary structure mentioned above to guide your writing.
Step 4 – Be concise
Do not write more than 10% of the length of the original document.
Step 5 – Proofread your summary
Reread your case study summary to ensure it makes sense as an independent piece of writing. Set it aside for a while and look at it with fresh eyes to notice any incoherence and redundant or lacking details.
✒️️ Case Study Summary Example
We have prepared an example of a case study summary for you to see how everything works in practice!
Here is the full report: Akron’s Children’s Hospital: Case Study .
Now, check its summarized version:
Akron Children’s Hospital is a leading pediatric hospital in Northeastern Ohio that faces competition and needs to differentiate itself to attract more patients. To gain insight into the decision-making process of patients' parents, the hospital hired a team of researchers led by Marcus Thomas LLC to conduct business and market analysis.
An observational study was conducted to collect consumer data, including perceptions of the hospital and the criteria used to select it. The problem was that a highly competitive medical industry in Northeastern Ohio resulted in reduced patient volume and financial losses at Akron Children’s Hospital.
The proposed solution was to rethink the hospital’s operations and marketing approach to differentiate it from the competitors and attract more patients. Furthermore, the treatment of certain groups of children had to be improved by increasing the number of specializations available at the hospital.
The organization was recommended to develop an efficient marketing strategy, enhance service delivery, and implement highly innovative medical technologies and procedures.
✅ 5 Benefits of the Case Summarizer You Should Consider
Still in doubt whether our case study summary tool is worth using? Check out its benefits:
- It is time-saving . The online tool is perfect for students in medicine or psychology since it allows for consuming a lot of information in a short time.
- It is easy to use . The interface of our case summarizer is so simple to navigate that even a child can handle it.
- It is unlimited . Try our online summarizer as many times as you need. There are no limitations!
- It is free . You can summarize a case study online in a few minutes without spending money. Such a considerable benefit for prudent students!
- It is accurate . The case summary generator uses essential keywords and phrases to isolate only the most relevant information.
Updated: May 8th, 2024
- Executive Summary | USC Libraries
- Case Studies | Carnegie Mellon University
- Writing a Case Study | Monash University
- Guidelines for Writing a Summary | Hunter College
- Executive Summaries | Colorado State University
How to Write a Case Study - All You Wanted to Know

What do you study in your college? If you are a psychology, sociology, or anthropology student, we bet you might be familiar with what a case study is. This research method is used to study a certain person, group, or situation. In this guide from our dissertation writing service , you will learn how to write a case study professionally, from researching to citing sources properly. Also, we will explore different types of case studies and show you examples — so that you won’t have any other questions left.
What Is a Case Study?
A case study is a subcategory of research design which investigates problems and offers solutions. Case studies can range from academic research studies to corporate promotional tools trying to sell an idea—their scope is quite vast.
What Is the Difference Between a Research Paper and a Case Study?
While research papers turn the reader’s attention to a certain problem, case studies go even further. Case study guidelines require students to pay attention to details, examining issues closely and in-depth using different research methods. For example, case studies may be used to examine court cases if you study Law, or a patient's health history if you study Medicine. Case studies are also used in Marketing, which are thorough, empirically supported analysis of a good or service's performance. Well-designed case studies can be valuable for prospective customers as they can identify and solve the potential customers pain point.
Case studies involve a lot of storytelling – they usually examine particular cases for a person or a group of people. This method of research is very helpful, as it is very practical and can give a lot of hands-on information. Most commonly, the length of the case study is about 500-900 words, which is much less than the length of an average research paper.
The structure of a case study is very similar to storytelling. It has a protagonist or main character, which in your case is actually a problem you are trying to solve. You can use the system of 3 Acts to make it a compelling story. It should have an introduction, rising action, a climax where transformation occurs, falling action, and a solution.
Here is a rough formula for you to use in your case study:
Problem (Act I): > Solution (Act II) > Result (Act III) > Conclusion.
Types of Case Studies
The purpose of a case study is to provide detailed reports on an event, an institution, a place, future customers, or pretty much anything. There are a few common types of case study, but the type depends on the topic. The following are the most common domains where case studies are needed:

- Historical case studies are great to learn from. Historical events have a multitude of source info offering different perspectives. There are always modern parallels where these perspectives can be applied, compared, and thoroughly analyzed.
- Problem-oriented case studies are usually used for solving problems. These are often assigned as theoretical situations where you need to immerse yourself in the situation to examine it. Imagine you’re working for a startup and you’ve just noticed a significant flaw in your product’s design. Before taking it to the senior manager, you want to do a comprehensive study on the issue and provide solutions. On a greater scale, problem-oriented case studies are a vital part of relevant socio-economic discussions.
- Cumulative case studies collect information and offer comparisons. In business, case studies are often used to tell people about the value of a product.
- Critical case studies explore the causes and effects of a certain case.
- Illustrative case studies describe certain events, investigating outcomes and lessons learned.
Need a compelling case study? EssayPro has got you covered. Our experts are ready to provide you with detailed, insightful case studies that capture the essence of real-world scenarios. Elevate your academic work with our professional assistance.

Case Study Format
The case study format is typically made up of eight parts:
- Executive Summary. Explain what you will examine in the case study. Write an overview of the field you’re researching. Make a thesis statement and sum up the results of your observation in a maximum of 2 sentences.
- Background. Provide background information and the most relevant facts. Isolate the issues.
- Case Evaluation. Isolate the sections of the study you want to focus on. In it, explain why something is working or is not working.
- Proposed Solutions. Offer realistic ways to solve what isn’t working or how to improve its current condition. Explain why these solutions work by offering testable evidence.
- Conclusion. Summarize the main points from the case evaluations and proposed solutions. 6. Recommendations. Talk about the strategy that you should choose. Explain why this choice is the most appropriate.
- Implementation. Explain how to put the specific strategies into action.
- References. Provide all the citations.
How to Write a Case Study
Let's discover how to write a case study.

Setting Up the Research
When writing a case study, remember that research should always come first. Reading many different sources and analyzing other points of view will help you come up with more creative solutions. You can also conduct an actual interview to thoroughly investigate the customer story that you'll need for your case study. Including all of the necessary research, writing a case study may take some time. The research process involves doing the following:
- Define your objective. Explain the reason why you’re presenting your subject. Figure out where you will feature your case study; whether it is written, on video, shown as an infographic, streamed as a podcast, etc.
- Determine who will be the right candidate for your case study. Get permission, quotes, and other features that will make your case study effective. Get in touch with your candidate to see if they approve of being part of your work. Study that candidate’s situation and note down what caused it.
- Identify which various consequences could result from the situation. Follow these guidelines on how to start a case study: surf the net to find some general information you might find useful.
- Make a list of credible sources and examine them. Seek out important facts and highlight problems. Always write down your ideas and make sure to brainstorm.
- Focus on several key issues – why they exist, and how they impact your research subject. Think of several unique solutions. Draw from class discussions, readings, and personal experience. When writing a case study, focus on the best solution and explore it in depth. After having all your research in place, writing a case study will be easy. You may first want to check the rubric and criteria of your assignment for the correct case study structure.
Read Also: ' WHAT IS A CREDIBLE SOURCES ?'
Although your instructor might be looking at slightly different criteria, every case study rubric essentially has the same standards. Your professor will want you to exhibit 8 different outcomes:
- Correctly identify the concepts, theories, and practices in the discipline.
- Identify the relevant theories and principles associated with the particular study.
- Evaluate legal and ethical principles and apply them to your decision-making.
- Recognize the global importance and contribution of your case.
- Construct a coherent summary and explanation of the study.
- Demonstrate analytical and critical-thinking skills.
- Explain the interrelationships between the environment and nature.
- Integrate theory and practice of the discipline within the analysis.
Need Case Study DONE FAST?
Pick a topic, tell us your requirements and get your paper on time.
Case Study Outline
Let's look at the structure of an outline based on the issue of the alcoholic addiction of 30 people.
Introduction
- Statement of the issue: Alcoholism is a disease rather than a weakness of character.
- Presentation of the problem: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there.
- Explanation of the terms: In the past, alcoholism was commonly referred to as alcohol dependence or alcohol addiction. Alcoholism is now the more severe stage of this addiction in the disorder spectrum.
- Hypotheses: Drinking in excess can lead to the use of other drugs.
- Importance of your story: How the information you present can help people with their addictions.
- Background of the story: Include an explanation of why you chose this topic.
- Presentation of analysis and data: Describe the criteria for choosing 30 candidates, the structure of the interview, and the outcomes.
- Strong argument 1: ex. X% of candidates dealing with anxiety and depression...
- Strong argument 2: ex. X amount of people started drinking by their mid-teens.
- Strong argument 3: ex. X% of respondents’ parents had issues with alcohol.
- Concluding statement: I have researched if alcoholism is a disease and found out that…
- Recommendations: Ways and actions for preventing alcohol use.
Writing a Case Study Draft
After you’ve done your case study research and written the outline, it’s time to focus on the draft. In a draft, you have to develop and write your case study by using: the data which you collected throughout the research, interviews, and the analysis processes that were undertaken. Follow these rules for the draft:

| 📝 Step | 📌 Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Draft Structure | 🖋️ Your draft should contain at least 4 sections: an introduction; a body where you should include background information, an explanation of why you decided to do this case study, and a presentation of your main findings; a conclusion where you present data; and references. |
| 2. Introduction | 📚 In the introduction, you should set the pace very clearly. You can even raise a question or quote someone you interviewed in the research phase. It must provide adequate background information on the topic. The background may include analyses of previous studies on your topic. Include the aim of your case here as well. Think of it as a thesis statement. The aim must describe the purpose of your work—presenting the issues that you want to tackle. Include background information, such as photos or videos you used when doing the research. |
| 3. Research Process | 🔍 Describe your unique research process, whether it was through interviews, observations, academic journals, etc. The next point includes providing the results of your research. Tell the audience what you found out. Why is this important, and what could be learned from it? Discuss the real implications of the problem and its significance in the world. |
| 4. Quotes and Data | 💬 Include quotes and data (such as findings, percentages, and awards). This will add a personal touch and better credibility to the case you present. Explain what results you find during your interviews in regards to the problem and how it developed. Also, write about solutions which have already been proposed by other people who have already written about this case. |
| 5. Offer Solutions | 💡 At the end of your case study, you should offer possible solutions, but don’t worry about solving them yourself. |
Use Data to Illustrate Key Points in Your Case Study
Even though your case study is a story, it should be based on evidence. Use as much data as possible to illustrate your point. Without the right data, your case study may appear weak and the readers may not be able to relate to your issue as much as they should. Let's see the examples from essay writing service :
With data: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there. Without data: A lot of people suffer from alcoholism in the United States.
Try to include as many credible sources as possible. You may have terms or sources that could be hard for other cultures to understand. If this is the case, you should include them in the appendix or Notes for the Instructor or Professor.
Finalizing the Draft: Checklist
After you finish drafting your case study, polish it up by answering these ‘ask yourself’ questions and think about how to end your case study:
- Check that you follow the correct case study format, also in regards to text formatting.
- Check that your work is consistent with its referencing and citation style.
- Micro-editing — check for grammar and spelling issues.
- Macro-editing — does ‘the big picture’ come across to the reader? Is there enough raw data, such as real-life examples or personal experiences? Have you made your data collection process completely transparent? Does your analysis provide a clear conclusion, allowing for further research and practice?
Problems to avoid:
- Overgeneralization – Do not go into further research that deviates from the main problem.
- Failure to Document Limitations – Just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study, you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis.
- Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications – Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings.
How to Create a Title Page and Cite a Case Study
Let's see how to create an awesome title page.
Your title page depends on the prescribed citation format. The title page should include:
- A title that attracts some attention and describes your study
- The title should have the words “case study” in it
- The title should range between 5-9 words in length
- Your name and contact information
- Your finished paper should be only 500 to 1,500 words in length.With this type of assignment, write effectively and avoid fluff
Here is a template for the APA and MLA format title page:
There are some cases when you need to cite someone else's study in your own one – therefore, you need to master how to cite a case study. A case study is like a research paper when it comes to citations. You can cite it like you cite a book, depending on what style you need.
Citation Example in MLA Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing, 2008. Print.
Citation Example in APA Hill, L., Khanna, T., & Stecker, E. A. (2008). HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing.
Citation Example in Chicago Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies.
Case Study Examples
To give you an idea of a professional case study example, we gathered and linked some below.
Eastman Kodak Case Study
Case Study Example: Audi Trains Mexican Autoworkers in Germany
To conclude, a case study is one of the best methods of getting an overview of what happened to a person, a group, or a situation in practice. It allows you to have an in-depth glance at the real-life problems that businesses, healthcare industry, criminal justice, etc. may face. This insight helps us look at such situations in a different light. This is because we see scenarios that we otherwise would not, without necessarily being there. If you need custom essays , try our research paper writing services .
Get Help Form Qualified Writers
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. If you’re having trouble with your case study, help with essay request - we'll help. EssayPro writers have read and written countless case studies and are experts in endless disciplines. Request essay writing, editing, or proofreading assistance from our custom case study writing service , and all of your worries will be gone.
Don't Know Where to Start?
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. Request ' write my case study ' assistance from our service.
What Is A Case Study?
How to cite a case study in apa, how to write a case study.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
.webp)
- Argumentative
- Ecocriticism
- Informative
- Explicatory
- Illustrative
- Problem Solution
- Interpretive
- Music Analysis
- All Essay Examples
- Entertainment
- Law, Crime & Punishment
- Artificial Intelligence
- Environment
- Geography & Travel
- Government & Politics
- Nursing & Health
- Information Science and Technology
- All Essay Topics
Case Study Summarizer
Unlock the full potential of your case studies with our tool..
How to Use EssayGPT's Case Study Summarizer?
Have a case study that needs to be summarized? Here's how to create a concise and insightful case study summary with our tool.
- 1. Enter the Details: Paste your lengthy case study into the field. Select your target audience, tone of voice, and output language.
- 2. Push to Produce: Hit the button to kick off the AI-powered summarization process. Our AI instantly gets to work.
- 3. Rinse and Repeat: Review the result. Want more versions? Simply hit the button again.

Try Our Other Powerful AI Products
Bypass AI detection with 100% undetectable AI content
Create undetectable, plagiarism-free essays with accurate citations
Solve ANY homework problem with a smart AI. 99% accuracy guaranteed.
Browser Extension
The all-in-one ChatGPT copilot: rewrite, translate, summarize, Chat with PDF anywhere
Our Online Case Study Summarizer Benefits You in The Following Ways
- Time and Effort Saver : Summarising feels like an eternity? Our tool condenses hours into seconds. Perfect for those never-ending academic papers.
- Quality on Point : Think of our tool as a Michelin-starred chef, selecting only the finest info. Advanced algorithms do the heavy lifting, so you don’t have to.
- Engaging and Effective : Our summaries are short, snappy, and pack a punch. Ideal for sharing with teams or keeping as a golden nugget of reference.
- Accessibility and User-Friendly : In a rush? Our summarizer is your lifesaver. All you have to do is paste your content and click the button.
- A Tool for All : Students, educators, and professionals - our summarizer is the Swiss Army knife in your intellectual toolkit.
Who May Need Our Case Study Summarizer?
Whether you’re a student, a business professional, or just a curious soul, EssayGPT is your ally. Our case study summarizer helps you dissect case studies across various fields.
From medical research to market trends, we help you extract the essence. It’s not just about summarising; it’s about empowering you with knowledge.
Get an Executive Summary for Case Study with EssayGPT
| ⏩ Swift | Transform hours into seconds |
|---|---|
| 🔬 Insightful | Discover key insights effectively |
| 📝 Polished | Create concisely crafted summaries |
| 📊 Comprehensive | Cover a wide range of fields |
Want to Summarize More Than Just Case Study? Check Out Our Other AI Summarizer Tools
Thesis statement generator, essay checker, essay rewriter, essay hook generator, essay extender, essay introduction generator, essay outline generator, free essay conclusion generator, essay shortener, dive into a world of inspiration.
- Welfare Drug Testing Should Not Be Allowed
- Advantages And Disadvantages Of Graphene
- The Portrayal of the Feminine in Stoker’s Dracula Essay
- Compare And Contrast The Gilded Era And The Progressive Era
- Essay on Missouri's Nonpartisan Selection of Judges Court Plan
- Bighorn Sheep Population
- Totalitarian Government In 1984 By George Orwell
- Publix Employee Performance Review Paper
- Evolution Of A Dog Essay
- Cecil The Lion: Guilty Or Murder?
- Essay on Military Draft
- Media Shaping Gender Roles
- Ronald Reagan Rhetorical Devices
- Its All About Jazz Fusion
- Rebellion In The Play Trifles By Susan Glaspell
- How Did Bill Nye Save The World
What is a case study summarizer?
It's an AI-powered tool that analyses and condenses lengthy case studies into shorter, digestible summaries highlighting key findings and insights.
How to evaluate the accuracy of the online case study summarizer?
Compare the summary with the original case study. Check if the key points are captured and the essence is maintained. Also, look for feedback from other users for additional insights.
Is EssayGPT's case study summarizer reliable to use?
As one of the most trusted and free AI summary generators , EssayGPT's case study summarizer can condense voluminous PDFs into concise bullet points or smoothly connected paragraphs in a flash.From business and management to medical and legal, our summarizer is versatile and can handle case studies across a wide spectrum of fields.
Can I get a case study summary from EssayGPT for educational purposes?
Absolutely! Our summarizer is a great tool for students and educators looking to condense case studies for coursework or to gain insights into real-world scenarios.
Can EssayGPT's case study summarizer be used to generate new insights or ideas?
Yes, our AI analyses the case study and can help in generating new insights or ideas by highlighting patterns and information that might not be immediately apparent.
Can I get a non-English case study summary from EssayGPT?
Yes, EssayGPT supports multiple languages. However, availability and accuracy might vary depending on the language.

Simplify Your Analysis with Our Case Study Summarizer
Decode complex narratives with EssayGPT’s case study summarizer. Collaborate with EssayGPT to transform detailed case studies into succinct, clear insights. Start synthesizing knowledge now!
How to Make Case Study Videos in 10 Steps [Examples Included]
Confidence in your brand is important, but it’s only the beginning. To make a real impact, you need to back up your claims with solid proof. That’s where case study videos come in. Let your satisfied customers do the talking giving new leads an authentic view into your products and services. Let’s look at how to create case study videos easily.
Article Last Updated: August 23, 2024
![how to summarize the case study How to Make Case Study Videos in 10 Steps [Examples Included]](https://zight.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/case-study-video-examples.png)
What is a Case Study Video?
Types of case study videos, why are case study videos important, how and where to use your case study video, how to create an impactful case study video.
Who doesn’t enjoy a captivating story? That’s likely why case study videos have become so popular. They’re more than just stories as they offer a deep dive into real-world scenarios, featuring genuine people and authentic businesses. Through these videos, companies showcase the real impact of their products and services, whether it’s through documenting product development , cultural shifts, or community impact.
To bring these stories to life, tools like Zight can be incredibly useful. With Zight’s features like screen recording , GIF creation , and easy file sharing , you can capture every moment and detail seamlessly. Imagine using Zight to record a customer’s success journey or create engaging visuals to complement your narrative. It’s all about making your case study videos as compelling and impactful as possible.
The question is, what does a good case study video look like? Our guide below will cover every aspect of case study videos, from their purpose, creating compelling videos, exploring what makes them successful, and sharing practical case study video examples and tips to help you craft impactful case study videos that resonate and drive results. Let’s get into it.
A case study video is a type of video content that demonstrates how other people are successfully using and benefiting from a product. It focuses on real customer success stories to show the value of a company’s products or services. In a crowded market of claims and promises, these videos serve as credible proof that your business delivers on its promises.
The strength of a case study video comes from its relatability. When potential customers see themselves in your stories, it fosters a true connection. Seeing real people handle challenges makes your business appear more trustworthy and your solutions more appealing. After all, who could offer a more credible opinion to potential customers than someone who’s experienced your services firsthand?
How is a Video Case Study Different From a Written Case Study?
Both written and video case studies aim to convert customers, but video case studies have several specific advantages:
- More Persuasive : While written case studies require readers to interpret the message, video case studies present it directly from the customer, making the impact more immediate and convincing.
- More Engaging : Videos captivate with dynamic visuals, vibrant colors, and sound, making them far more engaging than dense blocks of text. Who wouldn’t prefer a lively video over a long read?
- Higher Conversion Rates : Video marketing campaigns are very effective. It’s not surprising, given how seamlessly videos can be optimized for mobile devices—something text-heavy content struggles with.
Like in any film or video genre, you’ll notice certain styles and tones that recur frequently. This is also true for case study videos, where you’ll come across several common types as you explore case study videos.
That said, there are different types of case study videos that your business can produce, with different levels of complexity. Each type of case study video has a specific customer problem and appeals to different aspects of your audience’s decision-making process. Depending on your objectives and the topic, choosing the right style of case study video can effectively communicate the message you want to share.
1. Customer Testimonials
This type of video is quite simple to make and is one of the easiest case study videos to make. In customer testimonial videos, you interview your happy customers about their experience with your business and its impact on their lives. Since it involves just a straightforward interview with the customer, you only need one filming location and minimal editing to create the video.
Product or service review case study videos provide a thorough look at your offering’s features, functionality, and benefits. They offer an objective assessment and serve as valuable resources for new customers.
Target Audience : These videos target potential customers who are researching your product or service and need detailed information to make an informed decision.
Testimonial Video Example:

This video is a standout example of customer testimonials. Instead of simply listing features, the interviews highlight the challenges the company faced and how Zoom provided effective solutions . The video’s concise length keeps viewers engaged while still delivering a complete and compelling story in one location.
2. Customer Reviews
Customer reviews are authentic insights that highlight a product’s real-world performance. Much like a customer testimonial video, a customer review video features a happy customer discussing your product or service. However, there’s a key difference: in a customer review video, the customer focuses more on the specific features of the product or service, rather than just the value it provided them.
Depending on your approach, such videos may include footage of the customer using your product on camera. Generally, most case study video testimonials follow a Q&A style of storytelling .
Creating a customer review video is straightforward. The interview portion requires just one shoot location and minimal editing. If you decide to add footage of the product in action, the shoot and editing process will be more complex.
Target Audience : These videos are aimed at potential customers who are actively researching your product or service. They provide detailed information to help them make an informed purchase decision.
Customer Reviews Case Study Video Example:

This customer review case study video features Lana Blakely who explains how Notion has transformed her personal and professional life. She breaks down specific features like databases, templates, and task management tools, showing real-life examples of how she uses the app to stay organized. The video includes screen recordings of how she navigates the Notion workspace, providing viewers with a visual understanding of how the platform functions. Any potential customer actively looking for Notion will find information about the tool and can be able to make an informed decision.
3. Case Study Narrative
This is the most complex type of case study video. A case study narrative video involves on-camera interviews with customers and B-roll visuals, such as footage of the customer using your product or your team engaging with the customer. Additionally, these videos often incorporate graphics and text overlays. Due to its complexity, creating this type of video content demands more shoot time, strategic planning, and extensive editing .
Narrative case study videos focus on storytelling , aiming to engage viewers emotionally by presenting a compelling narrative highlighting a customer’s journey from problem to solution, often emphasizing the transformative aspects.
Target Audience : Narrative case study videos are particularly effective for creating an emotional connection with viewers, engaging a wide range of audiences, including those in the awareness and consideration stages.
Case Study Narrative Video Example:

This video by LLLLITL is a case study of Dove’s “Turn Your Back” campaign, which was designed to raise awareness about the issue of body image. The video uses powerful storytelling to connect with viewers on an emotional level.

Case study videos can significantly enhance your video marketing strategy , particularly for B2B companies . They provide a rich, multi-faceted way to showcase a product or service and offer benefits beyond financial gains. Here is why they are important:
- Credibility and Trust : Case study videos provide authentic success stories that show how your products or services have made a real difference for customers. This helps build trust and credibility with potential clients.
- Engagement : Videos naturally draw people in more effectively than text or static images. With a case study video, you can tell a compelling story that keeps your audience engaged and interested.
- Demonstration of Expertise : These videos allow you to highlight your industry knowledge and position yourself as an expert. By showcasing real-world results, you establish your business as a reliable solution provider.
- Problem-Solution Narrative : Case study videos often follow a clear problem-solving structure, helping potential customers relate to the challenges and see how your product or service can address their needs.
- Personal Connection : Featuring customer interviews or testimonials adds a personal touch. Prospective clients can connect with real people who have benefited from your offerings, making your brand more relatable.
- Versatility : Case study videos are highly versatile and can be used across various platforms , including your website, social media channels, email marketing , and presentations . This ensures your success stories reach a broad audience.
- Measurable Impact : Including data and metrics in your videos demonstrates the tangible results achieved by your clients. This evidence of ROI can be very persuasive for potential customers.
- Lead Generation : Well-crafted case study videos can generate leads by addressing problems similar to those your potential customers face, making them valuable assets in your video marketing strategy.
- Storytelling : Effective visual storytelling in case study videos helps forge an emotional connection with your audience, making your brand memorable and engaging.
After perfecting your case study video, it’s time to share it with your target audience. But where should you promote it?
- Your Website – Embed the video prominently on your website’s homepag e or a dedicated landing page to make it easily accessible. Consider having a section just for case studies, giving prospects a convenient reference point.
- Social Media – Share the video on your company’s social media platforms like Facebook , Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, and YouTube . Optimize it for each platform and actively engage with your audience through comments, likes, and shares to boost its visibility.
- Email Marketing – Include the video in your email marketing campaigns , especially targeting those interested in the topic. Adding the video to your email signature can also create a dynamic touchpoint.
- Sales and Marketing Presentations – Integrate the video into your sales pitches and marketing presentations . Real-world examples of success can be highly persuasive during client interactions.
- Content Marketing – Use the video in blog posts, articles, or other written content related to the case study’s topic. Create videos as teaser content from snippets to pique interest and direct viewers to the full video for more details.
Now that you have seen some examples of case study videos, you can now create your case study video. Case studies don’t always stick to a strict timeline or template, but some key steps are usually involved in creating a case study video. Follow these steps to create an engaging case study video that will resonate with your audience.
1. Identify the Right Story
The first step in crafting an attention-grabbing case study video is selecting the right story. You need a story that resonates with your target audience and showcases clear results.
For instance, if you run a software company like Zight, don’t just feature any client who used your software. Highlight businesses that experienced a boost in efficiency with your platform . Numbers like these provide concrete proof of your product’s effectiveness.
Your audience is looking for solutions, so your story should present a compelling example of how you’ve delivered just that. A thoughtfully chosen story sets the stage for a truly engaging case study video.
2. Ask Important Questions
The next key step is to craft the right questions. These will be the basis of your case study video.
- Start by setting the scene for your viewers : Ask about the customer’s initial problem. For example, “What issues were you dealing with before using our product?”
- Then, dive into the specifics : Analyze the customer’s decision-making process with questions like, “What pulled you to our product instead of others?”
- Finally, highlight the results : Ask questions such as, “How has our product made a difference in your operations?” or “Would you recommend our service to others?”
This thoughtful questioning will help create a well-rounded story, listing the problem, the solution, and the impact of your product or service.
3. Choose the Right Audience
You might have a great customer success story and perfectly crafted questions, but they won’t make an impact if they don’t resonate with your target audience’s needs and interests.
Imagine you’re showcasing Zight. Your audience could range from tech-savvy professionals to small business owners who aren’t as familiar with advanced tools. If your case study highlights a large corporation using Zight’s advanced features , it might not connect with a small business owner looking for simple and effective screen recording solutions .
Before diving in, do some audience research. What challenges are they facing? What solutions are they after? Tailor your case study video to address these, using language and examples that speak directly to their needs.
4. Plan Out the Storyline
To craft an engaging storyline for your case study video, you need to guide the viewer through a story that resonates. Start with a compelling introduction that highlights a common problem your audience faces, making it instantly relatable.
For instance, if you’re showcasing Zight, an issue could be the struggle businesses face with lengthy communication chains that slow down decision-making. Many teams feel this pain, making it an effective hook. Then, introduce Zight as the solution. This is where you spotlight its unique features—like screen recording and sharing capabilities—that streamline communication and boost productivity .
Support your claims with testimonials or expert opinions to add credibility. Hearing from satisfied users can make a significant impact.
Finally, wrap up by showcasing measurable results . Use statistics or before-and-after comparisons to emphasize how Zight made a difference. Conclude with a clear call-to-action, guiding the viewer on what steps to take next.
5. Conduct Background Interviews
Conducting background interviews is essential before you start filming. These pre-shoot conversations offer valuable insights that can enhance your storyline. They help you understand the full scope of the customer’s experience , adding richness and depth to your case study video.
These interviews also help you identify key talking points and decide who should be featured in the video. Whether it’s the CEO providing strategic insights or a front-line employee sharing day-to-day benefits, understanding this in advance ensures you capture the most relevant content, saving you time and effort during production.
6. Develop Your Script
The video script is the backbone to create engaging video content, pulling together visuals, dialogue, and pacing to create a cohesive story. Here’s how to craft one that leaves an impact:
- Start by outlining the key points you’ve gathered from background interviews and your storyline.
- Be clear and specific—rather than saying, “Our product is great,” highlight its strengths with something like, “Our software boosts productivity by 40%.”
- Keep the tone conversational yet professional to ensure your message resonates.
- Make sure the script flows smoothly, making complex ideas easy to understand.
- Consider using bullet points or numbered lists to emphasize key features or benefits.
Wrap up with a compelling call-to-action , guiding viewers on what to do next, whether that’s visiting your website or reaching out to your sales team.
7. Back it up with Data
Including data and statistics adds credibility to your case study video. While a compelling story captures attention, solid data reinforces your claims and makes your video campaigns more convincing.
Incorporate charts, graphs, or other visuals to present the data. Visual elements help make complex information more digestible and memorable. Ensure the data aligns with your storyline and addresses the needs or concerns of your audience.
8. Select the Right Location
The location you choose for your case study video adds depth and context to your story. Opt for a setting that complements the narrative and enhances its authenticity. For instance, if your case study involves educational software, filming in a classroom or school can make the story feel more genuine.
Your location should also resonate with your audience. Remember to consider practical aspects like lighting , sound, and permissions. The perfect location can fall flat if it has poor acoustics or requires difficult-to-obtain permits.
9. Create a Shot List
A carefully planned shot list is essential for a smooth filming experience. It details every shot you need, acting as a guide for your production team.
For example, if you’re capturing a customer testimonial, your shot list might include:
- Close-ups of the customer speaking
- Cutaways of the product in action
- Wide-angle shots to set the scene
Your shot list should specify the type of shots—wide, medium, or close-up—and any particular camera movements like pans or zooms. This ensures you capture all the crucial elements of your video marketing campaign from product details to emotional moments.
A shot list also helps you manage time and resources efficiently, allowing you to anticipate special equipment or lighting needs ahead of time, and preventing last-minute scrambling.
10. Shoot and Edit
This is where all your planning comes to life. Stick to your shot list and script during the shoot, but be open to capturing spontaneous moments that could enhance the story. High-quality equipment is necessary for clear audio and well-lit scenes —these technical details can elevate your final product.
Editing is where you shape the story , choosing the best shots to create a compelling narrative. Use cutaways, transitions, and background music to keep the pacing dynamic and the viewer engaged.
Pay attention to color grading, sound mixing, and special effects, ensuring they match the tone and message of your video. Avoid overdoing effects, as they can easily overshadow the content.
Now that you’ve seen how major brands craft their case study videos, let these examples spark ideas for your own. Use them to motivate your sales team , improve your video marketing strategy, and captivate your audience.
In addition, incorporating tools like Zight offers practical solutions such as screen recording and GIF creation, these videos not only tell a compelling story but also demonstrate how your product can deliver tangible results. What are you waiting for? Sign up and get started .
Create & share screenshots, screen recordings, and GIFs with Zight
Get Zight for iOS.
Content Search
Framework for identifying research and innovation impact case studies from south african universities.
- African Population and Health Research Center
1. Introduction and Background
The African Population and Health Research Center (APHRC) is a premier research-to-policy institution, generating evidence, strengthening research and related capacity in the African research and development ecosystem, and engaging policy to inform action on health and development. The Center is Africa-based and African-led, with its headquarters in Nairobi, Kenya, and a West Africa Regional Office (WARO), in Dakar, Senegal. APHRC seeks to drive change by developing strong African research leadership and promoting evidence-informed decision-making (EIDM) across sub-Saharan Africa.
The Center is collaborating with the Southern African Research and Innovation Management Association (SARIMA) on its project on Building it Forward for Research (Management) Leadership in Southern Africa, in which the Center is leading a specific workstream to carry out impact case studies arising out of university research. This collaborative approach ensures effective execution and maximizes the value of the research impact assessment.
2. Project Scope and Focus
University research plays a critical role in improving wellbeing, informing policy decisions, and driving innovation. However, the impact of this research often remains under-communicated, hindering efforts to secure sustained funding and public support. While quantitative data is essential, compelling case studies go beyond mere numbers. They weave narratives that capture the human stories behind the research, highlighting the challenges addressed, the innovative solutions developed, and the real-world impact on societal outcomes. These narratives resonate with audiences, generating greater understanding and appreciation for the value of research. The case studies produced in this workstream target a diverse audience, including:
- Funders: Highlighting the transformative power of research investments.
- Policymakers: Demonstrating the research-policy nexus and influencing policy decisions.
- Public: Raising awareness about the impact of research on their lives.
- Media: Generating media interest and amplifying the research's impact.
Led by APHRC, the workstream aims to identify, analyse and document four case studies showcasing the impact of research and innovation projects conducted by South African universities. The case studies will highlight the tangible contributions of university research and innovation to national priorities and broader societal well-being.
3. Criteria for Selecting Case Studies
The preferred sectors for cases include:
- Agriculture
- Inclusive financial systems
The case studies will demonstrate one or more of the following impact pathways:
- Reductions in mortality or morbidity rates for specific diseases.
- Increased access to services, particularly for underserved populations.
- Improved behaviors through effective interventions.
- Economic benefits (e.g., cost savings in systems).
- Development of new diagnostic tools or treatments.
- Innovative approaches to health promotion or disease prevention.
- New technologies that improve quality of life, create jobs and/or uplift communities.
- Culturally sensitive interventions addressing specific needs within South Africa.
- Research informing policy changes.
- Studies influencing policy decisions on public health and other public good interventions.
- Research contributing to the development of national legislation, policy or guidelines.
- Addressing the needs of underserved and vulnerable populations.
- Ensuring research findings can be applied in diverse settings across South Africa and beyond.
- Promoting long-term benefits and sustainable impact.
- Potential for Scale-Up: The case study should demonstrate the scalability of the research findings, potentially impacting a broader population or region. This can be achieved through:
- Adapting the intervention for broader implementation.
- Developing clear dissemination strategies for research outputs.
- Building partnerships with stakeholders to facilitate scale-up.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Evidence of collaboration with diverse stakeholders who contributed to the research impact. These may include:
- External enablers: Role of and interactions with ecosystem players – e.g. collaborative research partners, funding from local/national governments and international funders, private sector, civil society, role of regulators and regulatory process, national policies that aided impact (e.g. IP policy), commercialization routes, infrastructure, manufacturing or value delivery (services/processes)
- Internal Enablers: The case study should highlight the role of university support structures and policies that facilitated the research's translation into impact. E.g. role of Research Management Office and Technology Transfer Office and the conditions internally that allowed for impact (this could go as far as looking at institutional policies, systems etc.)
- Diversity: The case studies will aim to represent a variety of research disciplines, universities, and types of impacts.
4. Call for Submission of Qualifying Projects for Case Studies
South African Universities are invited to submit examples of research and innovation projects conducted by their institutions that could be suitable subjects for impact case studies predicated on the criteria outlined in paragraph 3 above.
5. Role of the Consultant
The APHRC wishes to appoint a qualified and experienced Consultant in case study analysis and development, for the production and dissemination of knowledge products to lead APHRC’s effort to deliver on this workstream. The Consultant will be required to perform the following tasks:
5.1 Selection of Case Studies
A Consultant in collaboration with APHRC will review submissions and select promising research projects for case study development. Selected universities will be contacted by the dedicated consultant to collaborate on developing a comprehensive case study report.
- Evaluation and selection of Case Studies: The Consultant will develop the criteria for scoring and selection of potential case studies submitted by South African universities for further analysis, development and documentation.
- **Collaboration with Universities:**If necessary, the Consultant will collaborate with the relevant research and support departments and units at South African universities to identify and select potential case studies for consideration.
- **Desktop Research:**The Consultant will conduct a literature review of published research from South African universities in relevant fields in order to identify suitable projects. This will involve searching academic databases, government reports, media articles and online resources (e.g. Databases such as ResearchGate and institutional websites of universities canbe explored by the Consultant to find relevant research projects.)
- **Expert Consultation:**The Consultant will consult with relevant experts and stakeholders to identify/further refine impactful research projects. Working with APHRC, the Consultant will further determine and implement simple criteria to review potential case studies submitted by South African universities and/or identified by the Consultant. This may include:
- Scientific merit and methodological rigor of the research.
- Potential for broader impact and scalability of the findings.
- Alignment of the research with national policy priorities and the funder's interests.
5.2 Developing Strong Case Studies
The Consultant will identify a short list of case studies and will collaborate with the qualifying universities to conduct a detailed analysis of each case study to further elaborate on how each case study addresses the criteria set out in paragraph 3. In terms of methodology, the Consultant will use the Theory of Change framework and employ – without limitation - the following techniques:
- In-depth Interviews: The Consultant will conduct interviews with researchers and other role players and stakeholders to capture a detailed narrative of the research journey, key role players, the research outcomes, the impact of the research, and future potential.
- Data Analysis and Storytelling: The Consultant will assist with analyzing data and crafting a compelling narrative that showcases the research's significance and impact.
- Identifying Visuals: Working with the selected universities, the Consultant will identify relevant visuals (charts, photos) to enhance the case study report.
5.2.1. Focus on Storytelling
Crafting a captivating narrative is central to a strong case study. This narrative should:
- Research focus and objectives
- Measurable impact on relevant areas (sector e.g. health, agriculture, inclusive financial systems; economy; society)
- Alignment with national/provincial priorities
- Set the Stage: Introduce the challenge addressed by the research and highlight its significance for South Africa's population.
- Describe the Research Journey: Explain the research approach, methodology, and key findings in clear and concise language.
- Showcase Innovation: Emphasize the novel aspects of the research and how it addressed existing limitations or offered new solutions.
- Demonstrate Impact: Quantify the impact of the research on societal outcomes using relevant data (e.g. surveys, statistics).
- Highlight Policy Influence: If applicable, detail how the research findings informed policy changes or national guidelines.
- Focus on Equity and Sustainability: Explain how the research addressed the needs of underserved populations and how its impact can be sustained over time.
- Showcase Potential for Scale-Up: Describe plans or ongoing efforts to scale-up the intervention and reach a wider population.
5.2.2. Data and Evidence:
Strong narratives are bolstered by robust evidence. Case studies should incorporate a combination of:
- Reductions in mortality or morbidity rates.
- Increased access to services (e.g. number of people reached).
- Improved health behaviors (e.g. changes in dietary habits, vaccination rates).
- Economic benefits (e.g. cost savings).
- Creation of jobs.
- Improved efficiency.
- Interviews with researchers, policymakers, healthcare providers, and community members impacted by the research.
- Focus group discussions to understand perceptions and experiences.
- Case studies of individual beneficiaries who have demonstrably benefited from the research.
- Policy Documents: Documents such as policy briefs, white papers, or government reports showcasing how research findings influenced policy decisions.
5.2.3. Engaging Visuals and Multimedia
Incorporating visuals can significantly enhance the case study's impact and accessibility. Examples include:
- Charts and Infographics: Visualize data and trends to make complex information more easily understood by the audience.
- Photographs: Images of researchers, healthcare providers, community members, or interventions in action can personalize the narrative.
- Short Video Clips: Short videos can capture the essence of the research and its impact in a compelling way.
5.2.4. Stakeholder Testimonials
Including testimonials from key stakeholders adds credibility and authenticity to the case studies. This could include:
- Researchers: Sharing their insights into the research process and the significance of the findings.
- Policymakers: Describing how the research influenced policy decisions.
- Healthcare Providers: Highlighting how the research improved their practice or patient care.
- Community Members: Sharing their experiences and how the research impacted their health and well-being.
5.2.5. Showcase the Enabling Factors that Contributed to the Research's Success :
- External stakeholder collaboration (research partners, funders, regulators)
- University support structures (including Research Management Offices, Technology Transfer Offices)
- Internal policies and systems promoting research impact.
6. Deliverables
- A set of four well-written, compelling case studies demonstrating impactful research and innovation from South African universities.
7. Dissemination and Advocacy Strategies
The final stage involves disseminating the case studies to a wide audience and leveraging them for advocacy and informational purposes.
7.1. Dissemination Channels:
- APHRC Website and Social Media: A dedicated webpage will be created on the APHRC website to showcase the case studies. This webpage will be promoted through social media platforms like X, Facebook, and LinkedIn
- SARIMA Website and Social Media: The case studies will be showcased on the SARIMA website, and promoted through social media platforms like X and LinkedIn
- Other channels and platforms will be discussed and agreed between the funder, APHRC and SARIMA.
7. Reporting and Communication
The Consultant will provide the case studies and periodic progress reports to APHRC as required.
8. Timeline
8.1 Submission of Case Studies: By September 30, 2024 .
8.2 Recruitment of Consultant: By August 31, 2024
8.3 The case study development will be conducted in two phases. It is expected that the first two case studies will be developed by November 30, 2024 and the other two case studies will be developed by June 30, 2025 .
9. Submission of Potential Research for Case Study Development
If you know of any research which aligns with the criteria above, you are encouraged to submit it to be considered for case study development. Follow the following guidelines for submitting your research:
Prepare a Short Summary (2 Pages Maximum):
- Briefly describe the research project and its objectives.
- Highlight the specific challenge the research addressed.
- Summarize the research approach and key findings.
- Explain how the research made impact and quantify this impact (if possible).
- Include any evidence of policy influence or potential for scale-up.
Provide Supporting Materials (To the Extent Applicable):
- Include relevant publications, reports, or presentations related to your research.
- Share any data (quantitative or qualitative) that demonstrates impact.
- Offer contact details for key individuals involved in the project eg researchers, funders, end-users, beneficiaries and others who played a role in ensuring that impact was achieved (including – without limitation the institutional Research Support Office).
How to apply
Submission Process for Universities Wishing to submit Potential Projects for Case Study Consideration:
- Submit your research summary and supporting materials electronically to [email protected] with a copy to [email protected] and [email protected] . Please use “ South Africa University Research Case Study Development ” as subject title in your email submission.
- Indicate your university affiliation and the lead researcher/contact person contact information.
Submission Process for Consultancy Bids:
- Submit your consultancy bids and supporting materials demonstrating your expertise and qualifications for the assignment electronically to [email protected] with a copy to [email protected] and [email protected]
- This should include a detailed proposal addressing all areas identified in the Term of Reference, a detailed budget and evidence of related previous work.
- Indicate subject title as “ Consultancy for South Africa University Research Impact Case Study ”.
12. For Further Queries: [email protected]
Special Notice
APHRC is an equal opportunity employer committed to creating a diverse and inclusive workplace. All employment decisions are made based on qualifications and organizational needs. Reasonable accommodation may be provided to applicants with disabilities upon request to support their participation in the recruitment process.
Latest Updates
World + 1 more
Promoting refugee integration and inclusion: Empowering municipalities across Europe - Integration policy brief (August 2024)
Los derechos humanos como respuesta global a la emergencia del mpox en áfrica, a rights-based global response to mpox emergency in africa, enfrentamientos armados vacían aldeas en el norte de mali.
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services

- Virtual Tour
- Staff Directory
- En Español
You are here
News releases.
News Release
Thursday, August 15, 2024
The antiviral tecovirimat is safe but did not improve clade I mpox resolution in Democratic Republic of the Congo
NIH-cosponsored study examined tecovirimat in mpox-endemic country.

The antiviral drug tecovirimat did not reduce the duration of mpox lesions among children and adults with clade I mpox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), based on an initial analysis of data from a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. However, the study’s 1.7% overall mortality among enrollees, regardless of whether they received the drug or not, was much lower than the mpox mortality of 3.6% or higher reported among all cases in the DRC. This shows that better outcomes among people with mpox can be achieved when they are hospitalized and provided high-quality supportive care. The trial is sponsored by the National Institutes of Health’s (NIH) National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) and co-led through a government-to-government partnership with the DRC’s Institut National de Recherche Biomédicale (INRB). Further analyses and detailed results will be released through scientific channels.
“These findings are disappointing, but they give us essential information and reinforce the need to identify other therapeutic candidates for mpox while we continue research on tecovirimat use in other populations with mpox,” said NIAID Director Jeanne Marrazzo, M.D., M.P.H. “We remain committed to developing safe and effective interventions, including treatments and vaccines, that can ease the devastating mpox burden in Central Africa and address the milder form of the virus that is circulating globally.”
Mpox has occurred in West, Central and East Africa for decades, with the first human case identified in 1970. Two types of the virus that causes mpox have been identified. Clade I, studied in this trial, is endemic in Central Africa and can cause severe illness. Clade II, endemic in West Africa, tends to result in milder illness. A clade II subtype virus caused a global mpox outbreak in 2022. People with compromised immune systems, children, and people who are pregnant are especially vulnerable to severe mpox regardless of the virus clade.
Reports of clade I mpox are increasing in Central African countries, particularly in the DRC. A recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) indicated that 67% of suspected DRC mpox cases and 78% of suspected mpox deaths have occurred in people aged 15 years and younger. Tecovirimat , also known as TPOXX, was initially developed and approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat smallpox — a virus closely related to, but far more serious than, mpox—but the drug’s safety and efficacy as an mpox treatment have not been established. It is currently available for mpox treatment in the United States as part of a separate NIAID-sponsored trial called STOMP and through a CDC expanded access Investigational New Drug (EA-IND) request process. Tecovirimat is authorized in Europe and the United Kingdom for the treatment of smallpox, mpox, and other indications.
In October 2022, NIAID and INRB launched the PALM007 trial to examine the safety and efficacy of tecovirimat for mpox treatment in adults and children. The study enrolled 597 people with laboratory-confirmed mpox at two sites in the DRC. Study participants were randomly assigned to receive tecovirimat or placebo and were admitted to a hospital for at least 14 days, where they were monitored closely for safety and resolution of mpox lesions. All participants received supportive care including nutrition, hydration, and treatment for secondary infections.
Tecovirimat was well-tolerated with no drug-related serious adverse events. Overall, mortality was lower, and lesions resolved faster than anticipated regardless of whether participants received tecovirimat or placebo. Study participants are being notified of the initial results and offered the opportunity to participate in an ongoing extension study providing further supportive medical care. Additional analyses are planned to better understand outcomes observed in the study, including whether there were any significant differences in clinical outcomes by days of symptoms prior to enrollment, severity of clinical disease, participant characteristics, or the genetic variant of mpox being treated.
“This study delivered urgently needed evidence to guide the mpox response in Central Africa” said co-principal investigator Jean-Jacques Muyembe-Tamfum, M.D., Ph.D., director-general of INRB and professor of microbiology at Kinshasa University Medical School in Kinshasa, DRC. “Although not what we had hoped for, the results show that study clinicians provided exceptional supportive care to all participants, which is a testament to the knowledge and skill that Congolese clinicians have acquired on managing mpox-related disease.”
“The PALM007 study demonstrated the importance and value of testing investigational mpox treatments through robust clinical trials in the DRC’s endemic setting,” said Lori Dodd, Ph.D., NIAID’s PALM project lead for the DRC. “We’ll continue to evaluate the trial data to determine whether additional studies of tecovirimat in patient subgroups are warranted.
The PALM007 trial is led by co-principal investigators Professor Muyembe-Tamfum and Placide Mbala, M.D., Ph.D., operations manager of the PALM clinical research partnership, and head of the Epidemiology and Global Health Department and the Pathogen Genomic Laboratory at INRB. NIAID’s Veronique Nussenblatt, M.D. and Olivier Tshiani, M.D. of Leidos Biomedical Research were protocol co-chairs. The trial was implemented in Tunda (Maniema province) and Kole (Sankuru province) with support from Congolese staff, the Mitchell Group and the NIH’s Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research. Collaborating institutions include the U.S. CDC, the Institute of Tropical Medicine Antwerp (ITM) , the aid organization Alliance for International Medical Action (ALIMA) and the World Health Organization (WHO). The U.S. Embassy in the DRC and DRC-based U.S. CDC staff supported logistics and operations for shipments, travel and regional security. SIGA Technologies, Inc., based in New York, provided tecovirimat for the study.
The “Pamoja Tulinde Maisha” or “PALM” clinical research partnership was established in response to the 2018 Ebola outbreak in DRC. The collaboration has continued as a multilateral clinical research program composed of NIAID, the DRC Ministry of Health, INRB and INRB’s partners.
NIAID and the INRB thank the extraordinary team of individuals who carried out this study in remote regions of the DRC, the members of the independent study Data and Safety Monitoring Board, and most importantly, the study participants and their families. For more information about PALM007, please visit ClinicalTrials.gov using the study identifier NCT05559099 .
“Given the differences in populations affected by the two mpox clades, the types of clinical disease that are appearing and the ongoing spread of both clades, it’s very important that we continue with the STOMP trial and other related studies, so that we can develop treatments that benefit all people with mpox,” said Dr. Marrazzo.
The international STOMP trial is examining the safety and efficacy of tecovirimat against clade II mpox. For more information about the STOMP trial, please visit ClinicalTrials.gov using the study identifier NCT05534984 . An additional study, UNITY, sponsored by ANRS Emerging Infectious Disease, is evaluating tecovirimat with a similar study design to STOMP in Argentina, Brazil and Switzerland. More information about the UNITY study can also be found on ClinicalTrials.gov using the identifier NCT05597735 . Both studies will continue to enroll participants and work in close collaboration.
NIAID conducts and supports research—at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide—to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website .
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit www.nih.gov .
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health ®
Connect with Us
- More Social Media from NIH

Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: Writing a Case Study
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Reading Research Effectively
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Bibliography
The term case study refers to both a method of analysis and a specific research design for examining a problem, both of which are used in most circumstances to generalize across populations. This tab focuses on the latter--how to design and organize a research paper in the social sciences that analyzes a specific case.
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or among more than two subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in this writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a single case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- Does the case represent an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- Does the case provide important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- Does the case challenge and offer a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in practice. A case may offer you an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to the study a case in order to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- Does the case provide an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings in order to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- Does the case offer a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for exploratory research that points to a need for further examination of the research problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of Uganda. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a particular village can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community throughout rural regions of east Africa. The case could also point to the need for scholars to apply feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation.
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work. In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What was I studying? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why was this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the research problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would include summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to study the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in the context of explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular subject of analysis to study and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that frames your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; c) what were the consequences of the event.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experience he or she has had that provides an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of his/her experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using him or her as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, cultural, economic, political, etc.], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, why study Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research reveals Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks from overseas reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should be linked to the findings from the literature review. Be sure to cite any prior studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for investigating the research problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is more common to combine a description of the findings with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps to support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings It is important to remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations for the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and needs for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) restate the main argument supported by the findings from the analysis of your case; 2) clearly state the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place for you to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in and your professor's preferences, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented applied to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were on social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood differently than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis.
Case Studies . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical (context-dependent) knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Reviewing Collected Essays
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: Jan 17, 2023 10:50 AM
- URL: https://libguides.pointloma.edu/ResearchPaper
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Cabinet Office
- Infected Blood Compensation Authority
Infected Blood Compensation Scheme overview: Affected persons
Published 23 August 2024

© Crown copyright 2024
This publication is licensed under the terms of the Open Government Licence v3.0 except where otherwise stated. To view this licence, visit nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence/version/3 or write to the Information Policy Team, The National Archives, Kew, London TW9 4DU, or email: [email protected] .
Where we have identified any third party copyright information you will need to obtain permission from the copyright holders concerned.
This publication is available at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/infected-blood-compensation-scheme-summary-august-2024/infected-blood-compensation-scheme-overview-affected-persons
Below is a summary of information about the Infected Blood Compensation Scheme relevant to affected persons who have suffered the impacts of infected blood through their relationship with an infected person. The information provided in this summary is relevant to applicants across all four UK nations. This should be read in conjunction with the Infected Blood Compensation Scheme Summary .
| Category of Award | Core Route awards | Supplementary Route awards available? |
|---|---|---|
| Injury Impact | £20,000-£86,000 | No |
| Social Impact | £8,000-£12,000 | No |
| Autonomy | Available for partners, parents and children £6,600-£16,000 | No |
| Care | Not available for affected persons in their own right Care awards can be paid directly to affected persons at the request of an infected person or their estate representative. | No |
| Financial Loss | Available for bereaved partners and children under the age of 18 at time of infected parent’s death Bereaved partners: £16,682 per annum Bereaved children: £5,561 per annum while under 18 Bereaved child who has lost both parents to infected blood related infections while under 18: £22,243 per annum | Yes - other bereaved affected persons (e.g. parents or disabled children over the age of 18) may be eligible to receive Financial Loss awards if they can provide evidence of dependency on the infected person at the time of death |
Eligibility
Affected persons are those who have suffered the impacts of infected blood through their relationship with an infected person, either living or deceased. This includes:
Partners of eligible infected persons. This includes:
civil partners;
partners cohabiting with an eligible infected person for at least one year following infection.
Where an eligible infected person has had more than one partner during the course of their infection, all partners who meet the above definition will be eligible for compensation in their own right.
Partners who separated from the eligible infected person prior to infection will not be eligible for compensation.
Parents of an eligible infected person, including:
biological parents;
adoptive parents;
others acting in the capacity of a parent as described below (e.g. step parents, grandparents);
cared for and lived with an eligible infected person whilst that person was under the age of 18. The provision of care and accommodation must have continued or been expected to continue for a period of at least 1 year.
The age at which the child became infected does not impact a person’s eligibility. However, compensation rates are higher for the parents of an infected person where the onset of infection began before the child turned 18 (and the parents cared for and lived with the infected child for at least 1 year) than for parents whose child was infected as an adult.
Children of an eligible infected person, including:
biological children;
adoptive children;
others in the position of a child as described below (e.g. step children);
while under the age of 18, were cared for and lived with (for a period of at least 1 year) a parent who was, or later became, infected.
The age of a child at the time of a parent’s infection does not impact eligibility but compensation rates will be higher for children who, while under the age of 18, lived with and were cared for by an infected parent (for at least 1 year), than for people whose parents were infected when they were in adulthood.
Siblings of eligible infected persons, including:
biological and adoptive siblings;
step siblings;
others in the position of a sibling as described below;
while under the age of 18, lived in the same household as an infected person for a period of at least 2 years after the onset of the infection.
Siblings of a person infected in adulthood may be eligible for compensation through the Scheme as a carer (see eligibility definition below).
Carers of an eligible infected person (e.g. friends or family) who, without reward or remuneration, provided personal care or support greater than would otherwise reasonably have been expected. Such carers will be eligible for compensation in their own right where the provision of care averaged at least 16.5 hours of care per week over a time period of at least 6 months.
Managing money received through compensation awards
Compensation will be payable through a lump sum or series of regular payments (instalments) over 5, 10 or 25 years.
Compensation received through instalments will be uplifted each year in line with the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
Compensation payments made through the Scheme to infected and affected persons will not adversely impact means tested benefits.
Compensation payments made under the Scheme will be exempt from income, capital gains and inheritance tax. This is in line with tax exemptions for the first and second interim pay.
- The latest information on applying for compensation through the Scheme can be read on the IBCA website . Sign up to the IBCA’s mailing list for the latest updates on the Scheme as it develops.
Case studies for affected persons
The case studies below are example scenarios. The names, dates of birth and other clinical details are fictitious and have been created to illustrate the principles of the Scheme. These case studies aim to help illustrate how compensation is calculated in different possible scenarios. Whether an individual is eligible for compensation and what level of compensation they are eligible to receive will be dependent on the IBCA assessment based on the regulations for the Scheme.
Case study 8: Application by the child of an infected person who died of Hepatitis C
Moussa’s father, Omar, was infected with Hepatitis C as a result of an infected blood product received during treatment for a bleeding disorder. Moussa was aged 13 and lived with his father when Omar died from decompensated cirrhosis.
As the child of a person who was infected, Moussa is eligible for compensation as an affected person which is set out in the table below. Moussa’s mother is the personal representative for Omar’s estate and she will be able to make a separate application on behalf of Omar (see the Scheme overview for estates of a deceased infected person).
Summary of Moussa’s application
Omar’s date of birth: 30 June 1964
Date of treatment which led to Omar’s infection: 12 October 1988
Date of Omar’s diagnosis: 17 November 1991
Date of Omar’s death: 7 September 2003
Omar’s Infection Severity Band: Hepatitis C (Decompensated cirrhosis)
The table below shows Moussa’s compensation award as an affected person.
| Category of affected award (child) | Value of compensation award as an affected person | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Injury Impact | £40,400 | Award for child under 18 at the time of onset of parent’s Hepatitis C (decompensated) infection |
| Social Impact | £12,000 | Award for child under 18 at the time of onset of parent’s Hepatitis C (decompensated) infection |
| Autonomy | £6,600 | Award for child under 18 at the time of onset of parent’s Hepatitis C (decompensated) infection |
| Financial Loss | £27,805 | Financial Loss award comprises 5 years (between 13 and 18 years of age) of dependency payments at £5,561 per annum |
| Care | N/A | Affected persons are not eligible for Care awards. |
| Total affected child award: £86,805 |
Case study 9: Application by a sibling of an infected person living with Hepatitis C
Simone’s sister, Chantal, was infected with chronic Hepatitis C after a blood transfusion she received in childhood. Simone was 13 years old at the time of her sister’s infection. Simone lived at home with her family throughout her childhood.
As a sibling who lived with an infected person during childhood, Simone is eligible for compensation as an affected person.
Summary of Simone’s application
Simone’s date of birth: 12 January 1980
Chantal’s date of birth: 22 December 1982
Date of treatment which led to Chantal’s infection: 17 March 1993
Date of Chantal’s diagnosis: 7 April 1994
Chantal infection severity band: Hepatitis C (Chronic)
The table below shows Simone’s compensation award as an affected person.
| Category of affected award (sibling) | Value of compensation | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Injury Impact | £20,000 | Award for sibling of infected person with Hepatitis C (Chronic) |
| Social Impact | £12,000 | Award for sibling of infected person with Hepatitis C (Chronic) |
| Autonomy | £0 | Siblings are not eligible for Autonomy awards. |
| Financial Loss | £0 | Siblings are not eligible for Financial Loss awards in their own right. |
| Care | £0 | Affected persons are not eligible for Care awards. |
| Total affected sibling award: £32,000 |
Case study 10: Application by a parent of a child who died from HIV infection
When she was 3 years old, Sally was diagnosed with HIV, contracted through infected blood products. She died from her infection aged 10.
Her mother, Patricia, is eligible for compensation through the Scheme as an affected person as well as being eligible to apply for compensation as the personal representative for Sally’s estate.
Summary of Patricia’s application
Sally’s date of birth: 18 December 1982
Date of Sally’s diagnosis: 12 May 1986
Date of Sally’s death: 7 June 1993
Sally’s Infection Severity Band: HIV
The tables below show Patricia’s compensation award as an affected person and as the personal representative for Sally’s estate.
Compensation award to Patricia as an affected parent
| Category of affected award (parent) | Value of compensation award as an affected person | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Injury Impact | £65,400 | Award for a parent of a child with HIV before age 18 |
| Social Impact | £12,000 | Award for a parent of a child with HIV before age 18 |
| Autonomy | £6,600 | Award for a parent of a child with HIV before age 18 |
| Financial Loss | N/A | Not eligible for Financial Loss award as not a dependant |
| Care | N/A | Affected persons not eligible for Care awards |
| Total affected parent award: £84,000 |
Compensation award to Sally’s estate
| Category of estate award | Value of estate compensation award | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Injury Impact | £180,000 | Estate award for HIV infection |
| Social Impact | £50,000 | Estate award for HIV infection |
| Autonomy | £60,000 | Estate award for HIV infection |
| Financial Loss | £12,500 | Eligible for £12,500 fixed rate for miscellaneous costs. |
| Care | £342,560.33 | Based on 8 years of care for HIV calculated at past care rate (i.e. current commercial rate minus 25%). |
| Total estate award: £645,060.33 |
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
When thinking about how to write an executive summary for a case study, you need to create 2 or 3 crucial sentences that provide a concise overview of the case study. It must be informative and: summarize the story by introducing the customer and their pain points. explain what your organization did. highlight the key results, including 1 or 2 ...
How to summarize a case study. 1. Read the case study. 2. Understand the goal. 3. Identify the main points. 4. Write a clear summary. 5. Read and revise.
Creating Effective Executive Summaries for Case Studies Creating an effective executive summary for a case study requires a strategic approach to distill complex information into a concise, impactful format. A well-crafted case study recap serves as a powerful tool for decision-makers, offering a quick overview of key findings and insights.
Writing a Case Study Analysis A case study analysis requires you to investigate a business problem, examine the alternative solutions, and propose the most effective solution using supporting evidence.
To conclude a case study presentation effectively, summarize the key findings, insights and recommendations in a clear and concise manner. End with a strong call-to-action or a thought-provoking question to leave a lasting impression on your audience.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the "Choosing a Research Problem" tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
This guide will show you how to write a case study that engages prospective clients, demonstrates your abilities, and showcases your results.
Case studies are marketing tools that showcase your customers' success and highlight your brand value. Learn how to write them with examples and templates.
Learn how to write a case study that showcases your success. Use our template and proven techniques to create a compelling case study for your clients.
That is through case study summaries. If you are working o a case study, you should be able to write a comprehensive overview of your own. To help you figure out the outline and format of your summary, here are 10+ case study summary examples you can check out. 1. Master Technology Case Study Summary Example.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are sometimes also used.
Understanding research paper summarization Whether it's for a news article, book, case study, research paper, or any other type of writing, a summary is a concise overview that highlights the original's main points. The difference between a research paper summary and other types of summary is its source material.
How to Analyze a Case Study Adapted from Ellet, W. (2007). The case study handbook. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School. A business case simulates a real situation and has three characteristics: 1. a significant issue, 2. enough information to reach a reasonable conclusion, 3. no stated conclusion.
A summary case study An effective summary is a way of communicating to your reader what the source text is "about." However, even while it is important to "put yourself in the shoes" of the original author, you also need to know what it is that you are arguing in your paper that has led you to include this other perspective.
Case studies are used in many professional education programs, primarily in business school, to present real-world situations to students and to assess their ability to parse out the important aspects of a given dilemma. In general, a case study should include, in order: background on the business environment, description of the given business, identification of a key problem or issue, steps ...
Learn how to write a summary of a source in five easy steps, with examples and tips to help you avoid plagiarism and improve your writing skills.
Looking for a tool to summarize case study online? 👉 Try our free case study summarizer! We've also listed case study elements explained how to summarize a case study.
A case study requires you to analyse a specific situation and discuss how its different elements relate to theory. The case can refer to a real-life or hypothetical event, organisation, individual or group of people and/or issue. Depending upon your assignment, you will be asked to develop solutions to problems or recommendations for future action.
Abstract Qualitative case study methodology enables researchers to conduct an in-depth exploration of intricate phenomena within some specific context. By keeping in mind research students, this article presents a systematic step-by-step guide to conduct a case study in the business discipline. Research students belonging to said discipline face issues in terms of clarity, selection, and ...
Learn how to write a case study from doing research to citing sources properly. We explore the different types of case studies and provide writing help.
Get the essence of intriguing case studies in a snap with the case study summarizer. Our ai extracts the key takeaways and presents a concise analysis. Stay informed with ease!
Case studies don't always stick to a strict timeline or template, but some key steps are usually involved in creating a case study video. Follow these steps to create an engaging case study video that will resonate with your audience. 1. Identify the Right Story.
Develop Comprehensive Case Studies documenting each project's: Research focus and objectives Measurable impact on relevant areas (sector e.g. health, agriculture, inclusive financial systems ...
The study enrolled 597 people with laboratory-confirmed mpox at two sites in the DRC. Study participants were randomly assigned to receive tecovirimat or placebo and were admitted to a hospital for at least 14 days, where they were monitored closely for safety and resolution of mpox lesions.
Definition The term case study refers to both a method of analysis and a specific research design for examining a problem, both of which are used in most circumstances to generalize across populations. This tab focuses on the latter--how to design and organize a research paper in the social sciences that analyzes a specific case.
Case study 8: Application by the child of an infected person who died of Hepatitis C Moussa's father, Omar, was infected with Hepatitis C as a result of an infected blood product received during ...