

MLA Style Guide, 8th & 9th Editions: Formatting Your MLA Paper
- Works Cited entries: What to Include
- Title of source
- Title of container
- Contributors
- Publication date
- Supplemental Elements
- Book with Personal Author(s)
- Book with Organization as Author
- Book with Editor(s)
- Parts of Books
- Government Publication
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Multivolume Works
- Newspaper Article
- Other Formats
- Websites, Social Media, and Email
- About In-text Citations
- In-text Examples
- How to Paraphrase and Quote
- Citing Poetry
- Formatting Your MLA Paper
- Formatting Your Works Cited List
- MLA Annotated Bibliography
- MLA 9th Edition Quick Guide
- Submit Your Paper for MLA Style Review
MLA recommends using 12-point Times New Roman font or another readable typeface (e.g. serif ).
Line Spacing & Margins
Use double-spacing throughout the entire paper.
Leave 1 inch margins on the top, bottom, and each side.
Indent the first line of each paragraph half an inch from the left margin.
Quotes longer than 4 lines should be written as a block of text a half an inch from the left margin.
Heading and Title
An MLA research paper does not need a title page, but your instructor may require one. If no instructions are given, follow the MLA guidelines below:
Type the following one inch from the top of the first page, flush with the left margin (double spacing throughout).
Your Instructor's Name
Course Number or Name
Center the title on the next line. Follow the rules for capitalization. Do not italicize, underline, or bold the title. An exception is when your title includes a title. Example: The Attitude toward Violence in A Clockwork Orange
Indent the next line and begin typing your text.
Include your last name and page numbers in the upper right-hand corner of every page. The page numbers will be one-half inch from the top and flush with the right margin. If your instructor prefers no page number on the first page, begin numbering from 2 on the second page.
Sample Papers from MLA
There are sample papers available in the MLA Style Center. Check them out to see the correct formatting.
Styling Headings and Subheadings
According to the MLA Style Center website, writers should avoid using headings in shorter papers. If you are writing a longer research paper, you may want to include headings and subheadings to help organize the sections of your paper. Advice from the MLA Style Center :
"Levels
The paper or chapter title is the first level of heading, and it must be the most prominent.
Headings should be styled in descending order of prominence. After the first level, the other headings are subheadings—that is, they are subordinate. Font styling and size are used to signal prominence. In general, a boldface, larger font indicates prominence; a smaller font, italics, and lack of bold can be used to signal subordination. For readability, don’t go overboard: avoid using all capital letters for headings (in some cases, small capitals may be acceptable):
Heading Level 1
Heading Level 2
Heading Level 3
Note that word-processing software often has built-in heading styles.
Consistency
Consistency in the styling of headings and subheadings is key to signaling to readers the structure of a research project. That is, each level 1 heading should appear in the same style and size, as should each level 2 heading, and so on. Generally, avoid numbers and letters to designate heads unless you are working in a discipline where doing so is conventional. Note that a heading labeled “1” requires a subsequent heading labeled “2,” and a heading labeled “a” requires a subsequent heading labeled “b.”
In a project that is not professionally designed and published, headings should be flush with the left margin, to avoid confusion with block quotations. (The exception is the paper or chapter title, which is centered in MLA style.)
For readability, it is helpful to include a line space above and below a heading, as shown in this post.
No internal heading level should have only one instance. For example, if you have one level 1 heading, you need to have a second level 1 heading. (The exceptions are the paper or chapter title and the headings for notes and the list of works cited.) You should also generally have text under each heading.
Capitalization
Capitalize headings like the titles of works, as explained in section 1.2 of the MLA Handbook.
The shorter, the better."
Modern Language Association. "How Do I Style Headings and Subheadings in a Research Paper?" MLA Style Center., 13 December 2018, style.mla.org/styling-headings-and-subheadings .
MLA Style Paper Template
- MLA 9th Edition Paper Template This template was created and saved as a Word template for Microsoft Word 2016. The process for saving and using the template is the same for the instructions given above for 2013.
You can save a personal template in Microsoft Word (IRSC students, download Office for free, see a librarian if you need help). Above is a template you can use every time you need to set-up a research paper using MLA style format. Simply open the template and type your own information every time you need to write an MLA style paper. Microsoft Word will allow you to save personal templates. Once you have the template opened in Word
Click "Save as"
Give the file a name
Under "Save as type", select Word Template

Then when you open Word, you will be able to choose a template rather than a blank document. You might have to select Personal to find your template.

Sample MLA Paper

How to Use the MLA Style Template
Formatting Group Project Papers
For a research paper written collaboratively by several students, such as for a group project, create a title page instead of listing all authors in the header on page 1 of the essay. On the title page, list each student's full name, placing one name on each double-spaced line. After the final student name, enter the professor's name. After the professor's name, give the course name. The last line of the heading will be the date in 5 August 2021 format. Press Enter a few times to move down the page then give the paper title, centered.

- << Previous: Citing Poetry
- Next: Formatting Your Works Cited List >>
- Last Updated: Jul 22, 2024 4:57 PM
- URL: https://irsc.libguides.com/mla
Still have questions? Leave a comment
Add Comment
Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!
Examples: Edited Papers
Need editing and proofreading services, how to create an mla title page | format, steps, & examples.

- Tags: Formatting Guidelines , MLA , MLA Style
If you’re writing an MLA-style paper for your class, you may need to include a title page or a cover page before the body. While the official MLA 9 Handbook does not mandate a title page, you should include one if your professor asks you to or you’re working on a group project.
In this article, we’ll break down the MLA format title page (also known as an MLA cover page). It’s always easier to just learn from samples, so we’ve included some great MLA title page examples!
When to use an MLA title page
An MLA title page is usually required for formal research papers, essays, and other academic assignments. It is also used while writing dissertations , graduate theses, and other extended works. A title page in the MLA format may not be necessary for shorter assignments or in-class essays.
If you’re unsure about whether your assignment needs an MLA cover page, consult with your professors or check your university’s guidelines.
What goes in an MLA format title page
An MLA format title page typically includes the following elements:
- Author’s name
- Professor/instructor’s name
- Course name
- Title of the paper
- Date of submission
For bigger projects or papers that you plan on submitting to journals, you may also need to include your university’s name on the title page. Just to be sure, it’s advised that you check the journal’s submission guidelines for a detailed list of elements to include in this section. For reference, you can also look up samples or check the publication’s previous editions.
MLA title page formatting guidelines
The MLA Handbook specifies important formatting guidelines you must follow while creating a title page. Refer to the guidelines below while writing your MLA cover page:
- Double-space all the elements on the title page.
- Do not include a header on the title page.
- Use the same font type and size you have adhered to throughout the paper (preferably, 12-point Times New Roman).
- Align each element (except the paper title) with the left margin.
- List the information in the following order: 1. Author’s name 2. Instructor’s name 3. Course name and details 4. Date of submission 5. University name
- If there are multiple authors, list each of their names in separate lines.
- In the center of the page, center-align the title of your paper.
- Use the title case while writing the title of your paper.
- Italicize names of media such as books, films, and TV shows.
If you don’t need to include an MLA cover page, you will have to include a title section in the top half of your paper’s first page. The formatting guidelines for this are largely the same as the title page, except that the title is center-aligned in the line following your name and credentials.
Since this is the first page of your paper, you’ll have to add an MLA header in the top right corner of the page. Here’s how the page should look:
How to create an MLA title page on MS Word
Students no longer have to manually format their academic papers and can rely on the blessings of Google Docs and MS Word. These word processors come with built-in templates that automatically format documents according to the MLA style. You can use these features to format your title page as well as the rest of the research paper.
Follow these steps to write a title page in MLA format:
- Launch Microsoft Word and open a blank document.
- Under the “File” menu, click on the “New” tab.
- Use the search bar and type “MLA” to find a sample template.
- Select the template that corresponds to your document type (research paper, essay, etc.).
- Check the preformatted document to see if it largely matches your university or department’s style guidelines.
- Replace the placeholder text in the document with your paper’s information.
- Cross-check what you have with your guidelines once again and fill in additional details that the template may have missed.
- Save your document and continue to add the rest of your text.
MLA title page examples
The guidelines we’ve laid out give you a general overview of the MLA title page format. Whether you’re working on a paper, essay, dissertation, or journal article, you will be required to adhere to these conventions.
The format required of you may vary from the standard MLA cover page depending on the university guidelines or submission rules. To make it easier for you, we’ve put down some MLA title page examples that you can refer to while formatting your paper.
MLA title page example: Two authors
1. MLA cover page with two authors
2. MLA title section with two authors
MLA title page example: Three or more authors
1. MLA cover page with multiple authors
2. MLA title section with multiple authors
If you need experts to review your paper, our paper editing services are at your… well, service! Meanwhile, here are some resources to help you learn more about the MLA style and academic writing:
- How to Cite Sources in the MLA Format
- MLA Citation Examples: Essays, Websites, Movies, and More
- How to Write an MLA Essay Header
- How to Write a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Research Paper Outline: Templates & Examples
Frequently Asked Questions
Should i include a title in an mla format paper, should the mla title page be double-spaced, should the mla title page be numbered, where should the mla title page be placed within the paper, what goes in the mla title page.
Found this article helpful?
Leave a Comment: Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Your vs. You’re: When to Use Your and You’re
Your organization needs a technical editor: here’s why, your guide to the best ebook readers in 2024, writing for the web: 7 expert tips for web content writing.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get carefully curated resources about writing, editing, and publishing in the comfort of your inbox.
How to Copyright Your Book?
If you’ve thought about copyrighting your book, you’re on the right path.
© 2024 All rights reserved
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self Publishing Guide
- Pre-Publishing Steps
- Fiction Writing Tips
- Traditional Publishing
- Additional Resources
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Essay Writing Guide
- Academic Writing and Publishing
- Citation and Referencing
- Partner with us
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Job Applicant
- Cover letter
- Resource Center
- Case studies

MLA 9th Edition Formatting
A Simple, Step-by-Step Guide + Free Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | July 2023
Formatting your paper in MLA style can feel like a pretty daunting task . In this post, we’ll show you exactly how to set up your paper for MLA (9th edition), as quickly and easily as possible. We’ll also share our popular free MLA template , to help you fast-track your writing.
Overview: MLA 9th Edition Formatting
- Structure and layout
- General page setup
- The opening section
- The main body
- Works cited (reference list)
- Free MLA 9 template
MLA Structure and Layout
Let’s start by looking at the overall structure of a typical student paper formatted for MLA 9th edition, before diving into the details of each section. For the most part, MLA papers follow a standardised structure, consisting of the following parts:
The opening section : While MLA doesn’t require a dedicated title page (unlike APA ), it does require an opening section that details some important information about yourself, your university and the paper itself.
The main body : The main body begins directly after the opening section on the first page. This is the “heart” of your paper and there are a very specific requirements regarding how you present and format this content.
The appendix (or appendices): While using an appendix in a student paper is relatively uncommon, you’ll place this section directly after the main body section, if required by your university.
The “Works Cited” list : This section is equivalent to what we’d usually call a references page and it’s where you’ll detail all the reference information corresponding to the in-text citations in the main body of your paper.
These four sections form the standard structure and order of a student paper using MLA 9th edition. As we mentioned, not all sections are always required , so be sure to double check what your university expects from you before submitting. Also, it’s always a good idea to ask your university if they have any style requirements in addition to the standard MLA specification.
Now that we’ve got a big-picture view of the typical paper structure, let’s look at the specific formatting requirements for each of these sections.
Generic Page Setup
Before you jump into writing up your paper, you’ll first need to set up your document to align with MLA’s generic page requirements. Alternatively, you can download our MLA paper template (which comes fully preformatted).
MLA 9th edition requires a 1-inch margin on all sides , for all pages. That said, if you’re writing a dissertation, thesis or any document that will ultimately be printed and bound, your university will likely require a larger left margin to accommodate for physical binding.
Fonts & sizing
MLA does not require that you use any specific font, but we do recommend sticking to the tried and tested , well-accepted fonts. For example, you might consider using one of the following:
- Sans serif fonts : Calibri (11), Arial (11), or Lucida Sans Unicode (10)
- Serif fonts : Times New Roman (12), Georgia (11), or Computer Modern (10)
Whichever font you opt for, be sure to use it consistently throughout your paper . Don’t chop and change, or use different fonts for different parts of the document (e.g., different fonts for the body text and the headings). Also, keep in mind that while MLA does not have a specific font requirement, your university may have its own preference or requirement. So, be sure to check with them beforehand regarding any additional specifications they may have.
In general, all text throughout your document needs to be left-aligned and should not be justified (i.e., leave an uneven right edge). You might consider using a different alignment for section headings, but in general, it’s best to keep things simple .
Line spacing
MLA 9th edition requires double line spacing throughout the document . There should also be no extra space before and after paragraphs . This applies to all sections of the paper, including the “Works Cited” page (more on this later).
Page header
Last but not least, you’ll need to set up a running header for your document. This should contain your last name, followed by the page number. Both of these should be positioned in the top right corner of all pages (even the first page). On a related note, there’s no need for you to include any footer content unless your university specifically requests it.
Now that we’ve looked at the generic formatting considerations, let’s dive into the specific requirements for each section of your paper.
The Opening Section
While MLA-formatted papers typically don’t require a title page, there are very specific requirements regarding the opening section of the first page .
Here’s how you can set your first page up for MLA 9th edition.
- On the first line, write your full name (flush left)
- On a new line, write your professor or instructor’s full name
- On a new line, write the course code and course name
- On a new line, write the full date spelt out (e.g., 15 June 2023)
- On a new line, write the full title of your paper , centre-aligned and using title case (consider using a title case converter if you’re not familiar with this)
- On a new line, begin your body content
All of the above should be in plain, unformatted font – in other words, you don’t need to apply any boldfacing, underlining , etc. That said, you should use italics whenever you’re writing out the titles of other works (for example, titles of books or articles).
To make it all a little more tangible, below is an example of a first page formatted according to the MLA specifications that we just covered.

The Main Body
While the formatting requirements for the body section are relatively light for MLA (at least when compared to APA ), there are still quite a few important things to pay attention to. Here’s what you need to know to get started.
Each of your paragraphs needs to start on a new line , and the first sentence of each paragraph requires a half-inch indent (while the rest of the paragraph is flush left aligned). Note that each paragraph simply starts on a new line and doesn’t require an additional blank line.
MLA 9th edition is fairly flexible in terms of heading formatting. There is no specified formatting, so you can decide what works best for you. However, there are still a few basic rules you need to follow:
- All your headings should be written in title case – never use all caps
- There should be no period following a heading
- Each heading level needs to be uniquely formatted and easily distinguishable from other levels (for example, a distinct difference in terms of boldfacing, underlining or italicisation)
- You can have as many heading levels as you need, but each level must have at least two instances
Abbreviations
When using abbreviations, you’ll need to make sure that you’re using the MLA version of the abbreviation . Below we’ve listed a few common ones you should be aware of:
- Appendix: app.
- Circa: c. or ca.
- Chapter: ch.
- Column: col.
- Definition: def.
- Department: dept.
- Example: e.g.
- Edition: ed.
- Figure: fig.
- Foreword: fwd.
- That is: i.e.
- Journal: jour.
- Library: lib.
- Manuscript(s): MS
- Number: no.
- Quoted in: qtd. in
- Revised: rev.
- Section: sec. or sect.
- Series: ser.
- Translation: trans.
- Version: vers.
- Variant: var.
- Volume: vol.
If you’re interested, you can find a more comprehensive list here . Alternatively, if you have access to the MLA 9th edition handbook, you can find the full list in the first appendix.

In-text citations
MLA 9 has a very specific set of requirements regarding how to cite your sources within the body of your paper. Here are some of the most important things to help you get started with MLA citations.
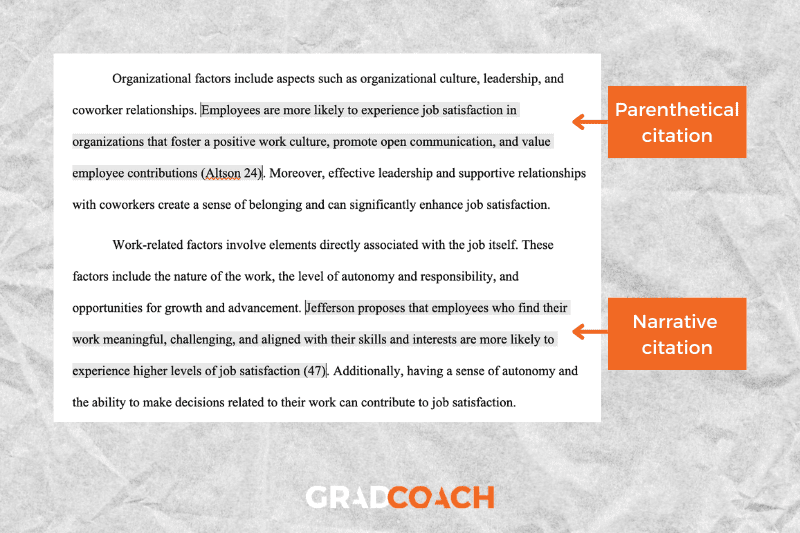
Author-page number system: in-text citations consist of (at a minimum) the lead author’s last name, followed by the page number of the paragraph you are citing. There is no comma between the two components (only a space).
Types of citations: MLA allows two types of in-text citations: parenthetical and narrative . Parenthetical citations feature the author and page number in parentheses (brackets) at the end of the respective sentence. Here’s an example:
MLA 9th edition is easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog (Jansen 13).
Narrative citations, on the other hand, weave the author’s name into the flow of the sentence and then present the publication date in parentheses at the end of the sentence. Here’s an example:
Jansen states that MLA 9th edition is easy for students to grasp if they visit the Grad Coach blog (13).
In general, it’s a good idea to utilise a mix of both in your writing. Narrative citations are particularly useful when you want to highlight or contrast authors or their viewpoints, while parenthetical citations are useful when you want to strengthen your own academic voice. In other words, both formats have their respective strengths and weaknesses, so try to use citation format strategically in your writing.
Quotations: when quoting text verbatim from a source, there is no need to do anything differently in terms of the citation itself, but do remember to wrap the verbatim text in quotation marks. Here’s an example:
Jansen proposes that MLA 9th edition is “easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog” (13).
Multiple authors: when citing resources that were authored by three or more people, you only need to list the lead author, followed by “et al.”. Here’s an example:
MLA 9th edition is easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog (Jansen et al. 13).
Below are a few more examples from our free MLA template .
Please keep in mind that this is not an exhaustive list of all the MLA 9th edition citation-related requirements – just a shortlist of the most commonly relevant ones. If you’d like to learn more, consult the MLA handbook .
The Works Cited (Reference List)
The final section that you’ll need to pay close attention to is the “Works Cited” page, which should contain a list of reference information for all the sources cited in the body of the paper. Again, MLA has a quite a meaty set of specifications regarding the content and formatting of this list, but we’ll cover the basics here to get your started on the right foot.
Basic setup
Your reference list needs to start on a new page and should be titled “Works Cited”. The title should be unformatted and centred . The reference list should then start on the next line. As with the rest of your document, you should use double line spacing throughout.
When it comes to the reference list itself, you’ll need to keep the following in mind:
- All the sources that you cited in the body of your document should feature in the reference list. Make sure that every citation is accounted for .
- The references should be ordered alphabetically , according to the lead author’s last name .
- The exact information required within each entry depends on the type of content being referenced (e.g., a journal article, web page, etc.)
- Components that may need to feature (other than the author) include the title of the source, the title of the container, other contributors, the article version or number, the publisher, the publication date, and the location.
- All references should be left-aligned and should use a hanging indent – i.e., the second line of any given reference (if it has one) should be indented a half inch.
We have to stress that these are just the basics. MLA 9th edition requires that your references be structured and formatted in a very specific way , depending on the type of resource. If you plan to draft your reference list manually, it’s important to consult your university’s style guide or the MLA manual itself. This leads us to our next point…
In general, it’s a bad idea to write your reference list manually . Given the incredibly high level of intricacy involved, it’s highly likely that you’ll make mistakes if you try to craft this section yourself. A better solution is to use (free) reference management software such as Mendeley or Zotero . Either of these will take care of the formatting and content for you, and they’ll do a much more accurate job of it too.
If you’re not familiar with any sort of reference management software, be sure to check out our easy-to-follow Mendeley explainer video below.
Wrapping Up
In this post, we’ve provided a primer covering how to format your paper according to MLA 9th edition. To recap, we’ve looked at the following:
- The structure and layout
- The general page setup
- The “Works Cited” page (reference list)
Remember to always check your university’s style guide to familiarise yourself with any additional requirements they may. Also, if your university has specified anything that contrasts what we’ve discussed here, please do follow their guidance .
If you need any help formatting your paper for MLA 9, take a look at our “done for you” language editing and proofreading service . Simply send us your document and we’ll take care of all the MLA formatting intracies on your behalf.
Very well recounted!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
TAFT COLLEGE
MLA Style Guide, 9th Edition: Formatting Your MLA Paper
- Works Cited entries: What to Include
- Title of source
- Title of container
- Other contributors
- Publication date
- Optional Elements
- Book with Personal Author(s)
- Book with Editor(s)
- Book with Organization as Author
- Parts of Books
- Government Publication
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Multivolume Works
- Newspaper Article
- Other Formats
- Websites, Social Media, and Email
- Works Cited Practice
- About In-text Citations
- In-text Examples
- How to Paraphrase and Quote
- Formatting Your MLA Paper
- Formatting Your Works Cited List
- MLA Annotated Bibliography
MLA recommends using 12-point Times New Roman font or another readable typeface (e.g. serif ).
Use double-spacing throughout the entire paper.
Leave 1 inch margins on the top, bottom, and each side.
Indent the first line of each paragraph half an inch from the left margin.
Quotes longer than 4 lines should be written as a block of text a half an inch from the left margin.
Heading and Title
An MLA research paper does not need a title page, but your instructor may require one. If no instructions are given, follow the MLA guidelines below:
Type the following one inch from the top of the first page, flush with the left margin (double spacing throughout).
Your Instructor's Name
Course Number or Name
Center the title on the next line. Follow the rules for capitalization. Do not italicize, underline, or bold the title. An exception is when your title includes a title. Example: The Attitude toward Violence in A Clockwork Orange
Indent the next line and begin typing your text.
Include your last name and page numbers in the upper right-hand corner of every page. The page numbers will be one-half inch from the top and flush with the right margin. If your instructor prefers no page number on the first page, begin numbering from 2 on the second page.
Formatting first page MLA MS Word using a MAC
Formatting first page mla goggle.dox, formatting first page mla ms word using pc, mla format setup in word 2013.
The links below provide step by step instructions on setting up your paper using MLA Style guidelines.
- Formatting Your Paper using MS Word - PC
- Formatting Your Paper using MS Word - MAC
Sample MLA Paper
- MLA Research Paper Template Properly formatted MLA Style research paper. Download and save to your computer so that you will always have the correct format for writing.

There are three sample papers available in the MLA Style Center. Check them out to see the correct formatting.
- << Previous: How to Paraphrase and Quote
- Next: Formatting Your Works Cited List >>
- Last Updated: Mar 24, 2022 5:10 PM
- URL: https://lib.taftcollege.edu/c.php?g=628017
Pasco-Hernando State College
- MLA Page Format
- Finding and Evaluating Sources (Critical Analysis)
- Synthesizing Information from Sources
- MLA In-Text Citations
- MLA Works Cited
- APA Documentation
- Writing a Research Paper
- Sample Essay - Modern Technology
Important note: Unless your instructor gives you a template, don't use an MLA template or tool as there can be common errors.
- Times New Roman 12 black font
- Header in upper right with name and page number: Jones 1
- Line Spacing – double throughout
- Tab in the first line of a paragraph ½” or .5
- Heading in upper left
- Title centered after heading
- Works Cited, if any, on a new page
- 1” margins – top, bottom, left, right. Some defaults are 1.25″ left and right.
- Margins are not set in the Paragraph box. In Word or Works, margins are set in "Page Layout" or in "File/Page Setup/Margins."
- Times New Roman 12 black font.
- Do not use bold or underlining.
- Do not use all caps except for an abbreviations such as NATO, AIDS.
- Do not use italics unless there is a rule that says to use italics.
- Check default and reset default if necessary. Your instructor may accept a different font style: however, Times New Roman 12 Black is a standard setting in school and business.
- Left align – this is the usual default setting.
- Do not block or justify where the right margin is even.
- Alignment can be set in the Paragraph box if the icon is not visible.
See Related Documents on right sidebar for an image of alignment settings.
Line Spacing
- Double space – and only double space throughout, even after the heading and around the title, if any.
- Check default settings in the Paragraph box and reset per instructions under Paragraph Settings below.
Paragraph Settings
Some programs such have defaults in the Paragraph box which interfere with proper double spacing.
The settings in the Paragraph dialogue box should be as follows to have proper double spacing:
- Indentation (on top) should be set at 0 left and 0 right.
- Spacing (on the lower left) should be set to 0 Before and 0 After.
- Line Spacing (on the lower right) should be set to double.
- Check the box that says “Don’t add space between paragraphs of the same style .”
- Click Default (at the bottom) and select Yes to change defaults.
In Google docs, you can change Paragraph settings under Spacing to 0 next to Before and 0 next to After by going into the double spacing tool and clicking Custom Settings. You will have to select (highlight) the entire paper including the heading in the upper left before making the change once the paper is typed.
In Pages, you can change the Paragraph settings by clicking on Format on the top navigation bar and then Paragraph. Remember that you have to highlight (select) the entire paper including the heading in the upper left before making change in Paragraph once the paper is typed.
First Line of a Paragraph
- Tab in the first line of a paragraph 1/2″ or .5 from the left margin.
- The Tab default is usually at this setting. If not, reset defaults.
Spacing after a period or other end punctuation
Unless your instructor advises otherwise, you may use one or two spaces after a period as long as the use is consistent.
- If the instructor asks for a title page, prepare the title page as per the assignment instructions.
- Do not use a heading on the first page if a title page is required.
Create a header in the upper right corner using the Header tool with your last name and page number.
- In Word 2007 or higher, click Insert/Header/Blank. Do not choose any option with lines, boxes, or other font or color.
- Delete Type text
- Click Home and align right. Your cursor should be on the right side.
- Type in your last name only. Then hit the space bar once. This will put a space between your last name and page number.
- After you hit the space bar, hit Insert/Page # to insert pages. Do not manually type in the page number.
- Do not use the word page or any abbreviation of the word such a pg. or p. between your last name and the actual page number: Jones 2.
- While MLA format calls for the header to appear on the first page, some instructors may ask that there be no header on the first page since your name is already there. To remove the header from the first page, check Different first page in the Header tool.
- These instructions may work for higher versions of Works.
- For lower versions of Word or Works, click View/Header and Footer to get into the Header tool.
- If you are unable to follow on your computer, your program should have a Help button to give directions on how to insert a header.
Instructions for Creating Header in Office 365
- Click Insert/Header.
- Tab over to the third box on the right.
- Under Home, click the align right button so that your cursor is all the way on the right side.
- Hit the space bar and then click Insert Page # and click the box with the number in the upper right.
- Click on the body of the paper to get out of the Header box.
- You will not see your header in the default view which is the edit view.
- You can click View and then Reading View on the left.
- Type a heading in the upper left corner of the first page unless your instructor asks for a title page. Do not use the Header tool to create a heading.
- Type the heading as follows: your name, your instructor’s name, the course, and the date (in military style – day month year – no commas) double spaced on separate lines.
- Do not use commas in the date. Months should be abbreviated if longer than four letters: Sept., Oct., and so on. Here is an example: 14 Oct. 2009
- Do not indent the heading.
- Your instructor may request different information to be typed into the heading.
- After the heading, center the title of the paper or name of assignment.
- Do not use bold, underlining, or a different font style or size for the title.
- Do not use quotation marks or italics unless the title of the paper includes the title of a published work since short, published works must be in quotation marks, and long, published works must be in italics.
- Remember that in MLA format, the requirement is to double space and only double space throughout.
- There should not be any more than a double space before or after the title or name of assignment.
Works Cited
If a Works Cited page is required for your assignment, at the end of the body of the paper, click Insert/Page Break or Insert/Break/Page Break – however your computer gives options – to get to the top of a new page to do the Works Cited.
- Do not use the Enter key to get to the next page.
- Use the same settings including double spacing throughout except that the first line of each source must start at the left margin and the second and any subsequent lines must be indented 1/2”.
- This is called a hanging indent.
- To create a hanging indent, make sure to type your sources one under the other hitting Enter at the end of each source.
- Then, highlight the Works Cited list and go into the Paragraph dialogue box.
- Under Special, select Hanging from the drop-down menu. Once selected, the default under By should be .5″.
- Remember that your list has to be alphabetized and the page must have the words Works Cited centered on top.
Troubleshooting Common Page Setup Problems
- There is an error in settings in the Indentation Box in Paragraph. Highlight paper and change to 0 in both Left and Right under Indentation in the Paragraph dialogue box.
- You’ve accidentally hidden your white space. Position your cursor at the top of the page until you see a double line. Then, double click.
- You have typed in a page number instead of using Insert Page Number.
- Click to Home, position your cursor at the beginning of your last name, then click the align right button.
- You have not reset the setting in Paragraph under Spacing on lower left to 0 before Before and 0 before After. You have to highlight the whole page before changing settings for them to take place on the page.
- You have not checked the box that states “Don’t add space between paragraphs of the same style. You have to highlight the whole page before changing settings for them to take place on the page.
Other Resources for Your Setup Problems
- Help tool in your program. Generally, there’s a tool or a link to a tool. Just search your problem.
- Online at website of your program. Word and other programs have help pages on their site.
- The PHSC Technical Support link: See Resource Links on the right side page for Technical Support or call 727-816-3732 .
- Just Google? Maybe. However, just searching around on the Internet open files and here and there is one way to pick up a virus, and you don’t know how reliable the source is. You are better of getting help with the first listed methods. Never download a help program.
- Printer-friendly version

Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format
MLA Format: Everything You Need to Know Here
Welcome to an overview of “What is MLA Format?” in relation to paper formatting. You’ll find in-depth guidelines, examples, and visual samples to help you easily format your paper. This guide does not serve as a reference for MLA citation format.
For help determining the proper structure for citing, refer to the other guides on EasyBib.com. Here is another informative site which may help with further understanding of MLA citation format.
Guidelines for Formatting a Paper in MLA
- Use white 8 ½ x 11” paper.
- Make 1 inch margins on the top, bottom, and sides.
- The first word in every paragraph should be indented one half inch.
- Indent set-off or block quotations one half inch from the left margin.
- Use any type of font that is easy to read, such as Times New Roman. Make sure that italics look different from the regular typeface.
- Use 12-point size.
- Double space the entire research paper, even the Works Cited page.
- Leave one space after periods and other punctuation marks, unless your instructor tells you to leave two spaces.
These guidelines come from the MLA Style Center’s web page “Formatting a Research Paper.”
MLA Guide Overview
There are various sections in this guide. Each section provides an in-depth overview of the different components to keep in mind when developing an MLA paper.
This guide includes the following sections:
- Format background
- General paper formatting
- MLA heading format & title page instructions
- Running head & page numbers
- Paraphrases
- Abbreviations
- Numbers (includes the use of numbers in MLA outline format)
- Images, tables, and musical scores
- MLA works cited format
- MLA citation format (for in-depth citation rules visit this MLA citation guide or MLA in-text citation guide)
- Edits & proofreading
If you need more guidance, a website like EasyBib.com usually has guides and tools to help you out. There’s also resources on other styles, like our guide on “ APA reference page ”, otherwise known as a “References” page.
MLA Format Background
The Modern Language Association (MLA) is an organization responsible for developing MLA format. It was developed as a means for researchers, students, and scholars in the literature and language fields to uniformly format their papers and assignments. This uniform, or consistent, method to developing a paper or assignment allows for easy reading. Today, MLA is not only used in literature and language subject areas; many others have adopted it as well.
The Modern Language Association released the 9th and most current edition of their MLA Handbook in April 2021. The Handbook provides thorough instructions on citing, as well as guidelines for submitting work that adheres to the Modern Language Association’s rules and standards. Although we’re not affiliated with the MLA, our citation specialists bring you this thoughtful and informative guide on the format.
Looking for information about previous editions to the Handbook ? Want to learn more about the origin of “What is MLA format?” Click here to learn about the previous editions to the Handbook .
Actually, are you looking for help on using another style? See how to cite an APA journal , learn to create an APA book citation , and more!
Formatting the Header in MLA
To create a header for your first page, follow these steps:
- Begin one inch from the top of the first page and flush with the left margin.
- Type your name, your instructor’s name, the course name and number, and the date on separate lines, using double spaces between each.
- Double space once more and center the title. Do NOT underline, bold, or type the title in all capital letters. Only italicize words that would normally be italicized in the text. Example: Character Development in The Great Gatsby
- Do not place a period after the title or after any headings
- Double space between the title and first lines of the text

General Paper Formatting
Paper choice.
While many professors, instructors, and publications allow electronic submission, some prefer printed, hard copies of papers. This section focuses on the type of paper to use for printed submission.
If you choose to print your paper, use white paper only. Do not use ivory, off-white, or any other shades or colors.
Choose a standard, high quality paper to print your project on. Do not use cardstock. It is not necessary to use resum é paper. Use typical, high quality printer or copy paper.
When it comes to size, 8 ½-by-11-inch paper is the recommended size. If you’d like to use a different size, ask your teacher prior to submission.
Use One-Inch Margins in MLA
Use one-inch margins around the entire page. The running head should be the only item seen in the one inch margin (see below for more on running heads).
Most word processing programs automatically default to using one inch margins. Check the page settings section of the program to locate the margin size.
Indenting Paragraphs in MLA
Indent the first word in every paragraph. Sentences should begin one half inch from the left margin.
It is not necessary to manually measure half an inch. Use the “tab” button on the keyboard to create a half inch space.
Double Space Paragraphs in MLA
MLA research paper format requires that the entire research paper or MLA format essay includes double-spaced lines. Double-spaced lines should be found in between the written body of the work, in the heading, and also on the MLA reference page.
While it may seem tempting to place a few extra lines between the heading, title, and beginning of the paper, lines should all be double spaced.
Font and Font Size in MLA
In an MLA paper, it is acceptable to use any font type that is easy to read. Many source types, such as books and articles, use fonts that are easy to read, so if you’re seeking an appropriate font style, look at other sources for guidance. Two of the most commonly used fonts are Arial and Times New Roman.
It is important for the reader to be able to distinguish the difference between italicized and regular font, so if you choose a font style different than Arial or Times New Roman, make sure the difference between the two type styles is evident.
The use of a 12-point font size is recommended as this is the default size for many word processing programs. It is acceptable to use another standard size, such as 11-point or 11.5-point.
Some professors or instructors will provide guidance on how to secure hard copies of projects. If your instructor does not provide you with any expectations or guidance, a simple staple in the top left corner should suffice. If a stapler is not available, some instructors allow paper or binder clips.
Do not fold the top left corner down to secure the pages together. The page could easily unfold, causing a mess of papers. While binders and plastic holders are cute, in reality, they add bulk to a professor or instructor who may like to take the papers home for grading purposes. Keep the binding simple and clean. Staples work best, and binder and paper clips are the next best option.
As always, follow any instructions your professor or teacher may provide. The guidelines found here are simply recommendations.
MLA Heading & Title Page Instructions
The web page “Formatting a Research Paper” gives two options when it comes to creating the header for your project:
- An MLA format heading can be placed at the top of the first page
- A title page can grace the front of the assignment. If you choose to create a title page, keep in mind that there aren’t any official title page or cover page guidelines in MLA format. See more information below.
If choosing option one, creating an MLA heading, you’ll need to include four main components:
- Your full name
- Your instructor’s name
- The name and number of the course or class
- The assignment’s due date
The first item typed on the paper should be your full name.
- Position your name one inch from the top and left margins of the page.
- Add a double space beneath your name, and type the name of your instructor.
- Below the professor or instructor’s name should be a double space, followed by the name of the course, class, or section number (if available).
- Below it, include another double space and add the assignment’s due date (Day Month Year).
Here’s an example:

The assignment’s title should be placed below the due date, after a double space. Align the title so it sits in the center of the MLA format paper. The title should be written in standard lettering, without underlines, bold font, italicized font, or any quotation marks. Only include italics or quotation marks if your title includes the title of another source.
Here is an example of an MLA header for an MLA format essay, paper, or assignment:
Neal E. Bibdarsh
Professor Haujeemoto
English 201
The Trials and Tribulations of Lincoln’s Reciting of “The Gettysburg Address”
*Note: The quotation marks here are around the title of a speech included in the paper’s title.
Most research papers use a standard MLA format heading, like the one seen above. If your instructor requires you to create a standalone title page, ask him or her for specifications. MLA does not have specific instructions for developing an MLA title page. We recommend you use an MLA header for your project.
If your teacher or professor requires a standalone title page, but has not provided any guidance or specifications, here are a few suggestions from EasyBib.com and this MLA guide :
- Center and double space all of the text on your page.
- Place the name of your school at the top of the page.
- Skip down to about the center of the page and type the title of your paper. Do not bold the title, italicize the entire title, place quotation marks around it, or type the title out in capital letters.
- Use italics for the titles of any sources in the title of your paper. Example: An Analysis of Mythical Creatures in Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire
- first letter of the title
- first letter of the last word
- first letter of any adjectives, adverbs, nouns, pronouns, and verbs
- If your paper has a subtitle, include on the next line below your title.
- Skip down to the bottom third of the page and add your name, the the name of your instructor, the name/number of the course or class, and the assignment’s due date on four separate lines.
- Keep the font size at 12 pt., or a size close to it, to make it look professional.
- Use the same font as the text of the paper. The Modern Language Association recommends any font that is easy to read and has a clear distinction between italics and standard font. Times New Roman and Arial are recommended, but many other fonts work as well.
- Include a page number in the top right corner of the paper. For more information on how to style page numbers, check out the next section, “Running Head and Page Numbers.”
- We do not recommend adding any images or cover art to the title page.
Click additional information about essays to see an example of a formatted header.
You can either create a title page using the EasyBib Title Page creator or omit the title page completely and use a header.
Running Head & Page Numbers in MLA
A running head is a brief heading that is placed in the top right corner of every page in a project. The Modern Language Association Style Center (online) states that the running head consists of:
- Last name of the paper’s author
- Page number
General tips to keep in mind:
- The running head is placed in the upper right-hand corner, half an inch from the top margin and one inch from the right margin of the page.
- Type your last name before the page number.
- The last name and page number should be separated by a single space.
- Do not place the word “page” or use an abbreviation, such as p. or pg., before the page number.
- Quite often, the running head begins on the second page, but your instructor may ask you to include the running head on the first page of the assignment. As always, if your instructor provides you with specific directions, follow his or her guidelines.

Before adding this information manually onto every single page, check to see if the word processor you’re using has the capability to automatically add this information for you. Try looking in the settings area where page numbers or headers can be added or modified.
Google Docs: Adding a header
- Go to the menu section “Insert.”
- Select “Page numbers” and select the option that places the page number in the upper-right corner.
- A page number will appear; your cursor will blink next to it.
- Move your cursor to the left of the page number.
- Type your last name. Add a space between your name and the page number.
- You should now have a properly formatted header on every page!
Microsoft Word Document: Adding a header
- Double-click in the space at the top of the page (where the page number is).
- OR Go to the “Insert” menu, select “Header,” and select “Edit Header.”
- Type your last name next to page number. If it isn’t already right-aligned, go to the “Home” menu and right-align your name.
Quotations in MLA
Quotes are added into assignments to help defend an argument, prove a point, add emphasis, or simply liven up a project.
Quotes should not take up the majority of your paper or assignment. Quotes should be sprinkled sparingly throughout, and quotes longer than 4 lines should be formatted as MLA block quotes . Use direct quotes from outside sources to enhance and expand on your own writing and ideas.
Words from quotes belong to the individual who spoke or wrote them, so it is essential to credit that individual’s work. Credit him or her by adding what is called an “in-text citation” into the body of the project.
There are three ways to add quotes: 1. With the author’s name in the sentence (a citation in prose).
Dan Gutman shares a glimpse into the overall plot by stating, “I didn’t know it at the time, but a baseball card—for me—could function like a time machine” (5).
In the above example, Dan Gutman is the author of the book that this quote is pulled from.
2. Without the author’s name in the sentence (a parenthetical citation).
The main character’s confusing experience is realized and explained when he states “I didn’t know it at the time, but a baseball card—for me—could function like a time machine” (Gutman 5).
In the above example, Dan Gutman’s name isn’t included in the sentence. It’s included in the parentheses at the end of the sentence. This is an example of a proper MLA style citation in the body of a project.
3. In a block quote, which is used when a large quote, of 4 lines or more, is added into a project.
Using footnotes and endnotes
The Modern Language Association generally promotes the use of references as described in the sections above, but footnotes and endnotes are also acceptable forms of references to use in your paper.
Footnotes and endnotes are helpful to use in a variety of circumstances. Here are a few scenarios when it may seem appropriate to use this type of referencing:
- When you are referring to a number of various sources, by various authors, in a section of your paper. In this situation, it is a good idea to use a footnote or endnote to share information for parenthetical references. This will encourage the reader to stay focused on the text of the research paper, instead of having to read through all of the reference information.
- When you are sharing additional information that doesn’t quite fit into the scope of the paper, but is beneficial for the reader. These types of footnotes and endnotes are helpful when explaining translations, adding background information, or sharing counterexamples to research.
To include a footnote or endnote, add a superscript number at the end of the sentence the footnote or endnote refers to. They can be included mid-sentence if necessary, but be sure to add it after any punctuation, such as commas or periods. Find a location that doesn’t distract the reader from the content and flow of the paper.
Within the text example:
Numerous well-known children’s books include characters from a wide range of races and ethnicities, thus promoting diversity and multiculturalism.¹
At the bottom of the page (footnote) or at the end of the section (endnote):
¹See Isadora, Parr, and Velazquez. While Parr’s work features characters of various colors, such as pink or blue, children easily correlate it with individuals of different races and ethnicities.
On the last page of the assignment, the writer includes the full references for the books by Isadora, Parr, and Velazquez.
For more on block quotes and a further, detailed explanation on the use of quotes, including MLA footnotes, refer to our MLA In-Text Citation and Parenthetical Citations Guide. In this guide you’ll find further information including directions for the use of quotes without an author, page numbers, and how to properly credit work from electronic sources.
For guides on citations in another style, check out APA parenthetical citation and APA in-text citation .
Paraphrases in MLA
Paraphrases are created when text or speech from another source are added into a project, but the writer chooses to summarize them and weave in his or her own writing and writing style.
Even though the writer modifies the information from another source, it is still necessary to credit the source using proper format ( Handbook 98). Paraphrased information uses the same MLA reference format as stated in the section directly above this one.
Here is an acceptable paraphrase:
Original text:
“Stay hungry. Stay foolish.” Steve Jobs
Paraphrase:
Steve Jobs encouraged students at Stanford to continue with their determination, drive, and ambitious behavior. They should never be simply satisfied with the status quo. They should continue to push themselves despite possible obstacles and failures.
To develop a well-written paraphrase, follow these simple, step-by-step instructions.
- Find a phrase, sentence, paragraph, or section of original text you’d like to turn into a paraphrase.
- Read the text carefully and make sure you fully comprehend its meaning. A writer can only develop a well-written paraphrase if the information has been fully grasped and understood. If you’re having difficulty understanding the information, take a few minutes to read up on tricky words and background information. If all else fails, ask a friend to see if they’re able to make sense of the concepts.
- After analyzing and completely understanding the original text, put it to the side. Take a moment to think about what you’ve read and connect the idea to your own assignment.
- Now that the information is completely understood, take a moment to rewrite what you’ve read, in your own words and writing style. Do not simply substitute words in the original text with synonyms. That’s plagiarism! Show off and demonstrate your ability to process the original information, connect it to the content in your paper, and write it in your own individual and unique writing style.
- Include an in-text reference next to the paraphrase. All paraphrases include references, similar to direct quotes. See the “Quotations” section of this guide to learn how to properly attribute your paraphrased information.
- Give yourself a pat on the back! Paraphrasing is an important part of the research and writing process.
Wondering if it’s better to quote or paraphrase?
An essential part of the research process involves adding direct quotes and paraphrases into projects. Direct quotes provide word-for-word evidence and allow writers to use another author’s eloquent words and language in their own projects. When it comes to paraphrases, writers are able to take a block of text and shrink the scope of it into the their papers. Paper writers can also use paraphrases to demonstrate their ability to analyze and reiterate information in a meaningful and relevant way.
If you’re wondering which one is better to consistently use, quotes or paraphrases, there’s a clear winner. Paraphrases come out on top. Sure, direct quotes are incredibly beneficial, but copying and pasting too many of these into a project can cause a reader to lose sight of the writer’s own voice. Mixing your own voice with another author’s too much can make for choppy and disjointed reading.
The ultimate goal of a research project is to have your voice and research merged together as one. Paraphrases allow just that. When you combine information from outside sources with your own writing style, it demonstrates your ability as a researcher to showcase your understanding and analyzation of a topic.
Remember, whether you’re adding direct quotes or paraphrases into a project, both types of additions need references. References are placed after the quotes and paraphrases, and also at the end of an assignment.
If you’re looking for additional help with your punctuation or grammar, check out the EasyBib plagiarism checker !
Using Abbreviations in MLA
Abbreviations are commonly used in many source types including websites, blog posts, books, and journal articles. It is acceptable to use abbreviations in all of these sources.
When it comes to school and research assignments, however, the MLA Handbook states that abbreviations should be used rarely in the prose of your paper (293). Spelling out abbreviations into their full words and meanings is recommended. This ensures understanding and avoids any confusion from your reader.
There are times when you may feel it is perfectly acceptable to use an abbreviation rather than its typed out counterpart in a paper. If you do abbreviate, be sure you are using commonly accepted abbreviations, which you can find in the dictionary. You can also review Appendix 1 in the MLA Handbook .
General Abbreviation Tips
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus can be abbreviated to HIV, not H.I.V.
- United States should be US, not U.S.
- Digital video disc should be DVD, not D.V.D.
- For lower case abbreviations, it is acceptable to include periods between the letters.
- The abbreviation, “For example” = e.g.
- If there is a mix of lower case and upper case letters, do not use periods if the majority of the letters are upper case. Examples include PhD and EdD
Abbreviating Months
Type out entire month names when being used in the body of a research paper or assignment.
She rented out the beach house from May through September
When it comes to references, MLA bibliography format requires months longer than four letters to be abbreviated.
- July = July
- November = Nov.
Other abbreviations that are perfectly acceptable to use in a bibliography (not the body of a project) include:
- p. or pp. for page and page numbers
- ch. for chapter
- ed. for edition
- trans. for translation or translated
- vol. for volume
- no. for number
- rev. for revised
Again, these abbreviations should only be used in the final page(s) of a project, the MLA Works Cited list. They should not be used in the body of a project.
For more information on bibliographies, see our MLA format Works Cited List page.
Abbreviating Publishers
One of the quirkiest things about this particular style is how publisher names are structured on the final page of references. Certain words are abbreviated, some words are omitted, and other words are written in full.
Words describing what type of business the publisher is are omitted from the works cited. Here’s a breakdown of the words that should be excluded:
- Co. (Company)
- Corp. (Corporation)
- Inc. (Incorporated)
- Ltd. (Limited)
- The (when at the beginning of the name)
If a publisher’s name contains the words “University” and “Press” (or the equivalent in another language), the words should be abbreviated to the letters “U” and “P” in your citation. But if only one of the words appears, it should be written out normally.
Here are a few examples:
- University of Delaware
- U College of London P
All other words related to the names of publishers should be written out in full.
Abbreviating Titles
Certain classical and biblical works are abbreviated in a bibliography, but also in any parenthetical references in the text.
The official handbook provides a lengthy list, spanning over multiple pages, of the preferred abbreviations to use for classical and biblical works ( Handbook 295-301), but here’s a quick snapshot of some of the commonly used ones:
Hebrew Bible or Old Testament = OT
- Deut. = Deuteronomy
- Gen. = Genesis
- Lev. = Leviticus
- Num. = Numbers
- Ps. = Psalms
New Testament = NT
- 1 Cor. = 1 Corinthians
- Jas. = James
- Matt. = Matthew
Shakespeare:
- Ado = Much Ado about Nothing
- 3H6 = Henry VI, Part 3
- JC = Julius Caesar
- Mac. = Macbeth
- MND = A Midsummer Night’s Dream
- Oth. = Othello
- Rom. = Romeo and Juliet
Again, the titles above are allowed to be abbreviated both in references in parentheses in the body of a project and also on the final page of references. If you’re wondering why, it’s because they’re cited often and it’s unnecessary to type out the entire title names.
Formatting Numbers in MLA
Use of numerals.
If the project calls for frequent use of numbers (such as a scientific study or statistics), use numerals that precede measurements.
- 247 milligrams
Other items to keep in mind:
In divisions, use numbers, ex: In page 5 of the study
Arabic Numbers
When including a number in a paper, spell out the number if it can be written as one word (such as six ) or two words (such as sixty-two ). For fractions, decimals, or longer numbers, type them out using digits. For larger numbers, write the number itself ( Handbook 82-84).
- twenty-seven
- one hundred
If the number comes before a unit of measurement or label, type the number using digits.
- 8 tablespoons
- 3 July 2018
- 25 King Street
More on Numbers
Starting a sentence with a number is generally frowned upon. Try modifying the sentence so that the number, or number word, is found elsewhere.
Instead of:
225 children were found in the warehouse, some malnourished and diseased.
Use this sentence:
A total of 225 children were found in the warehouse, some malnourished and diseased.
If modifying the sentence is not possible or does not work well with the flow of the assignment or paper, type out the written number:
Two hundred twenty five children were found in the warehouse, some malnourished and diseased.
Do not include any ISBN numbers in your paper.
Outline Format
The Modern Language Association does not have any requirements regarding the structure of an outline. If your teacher asks you to create an MLA outline, we recommend using roman numerals, capital and lowercase letters, and numbers.
Here is an example of a recommended outline structure:

In addition to outlines, use roman numerals for suffixes.
- King George IV
Using Images, Tables, & Musical Scores in MLA
Photographs, data sets, tables, graphs, and other images are often added into projects or papers to promote or aid understanding. They provide meaningful visuals for the reader. If the illustration or visual image does not enhance the quality of the paper, do not include it in the project.
Tables and illustrations should be placed as close as possible to the text that they most closely refer to.
For an image to be significant and easily identifiable, place it as close as possible to the text in the project where it is discussed.
It is not acceptable to simply place an image in a project without including identifiable information. All images must include information about its origin.
Here are the directions to properly attribute an image:
- Assign an Arabic number. The image closest to the beginning of the project should be labeled as Fig. 1. The next image in the project should be Fig. 2. and so on.
- Provide a caption. The caption should be a brief explanation or the title of the contents of the image. Place the caption directly next to the label.
- Immediately following the caption, it is acceptable to include attribution information. If the image is not discussed further in the rest of the paper or project, it is acceptable to include the MLA bibliography format citation below the image and omit it from the bibliography or MLA format works cited page.
In the text of the project or paper where the figure is discussed, include the label in parentheses to ensure the reader knows where to find the figure in your paper.
In the text:
Sarah’s tattoo design was filled with two of her favorite flowers: lilies and daffodils along a thinly curved vine (fig. 1).
Image formatting:
(Image Would Be Here) Fig. 1. Sarah’s Tattoo. barneyWILLIAMSable, Deviant Art , 2011, barneywilliamsable.deviantart.com/art/Sarah-s-Tattoo-design-193048938.
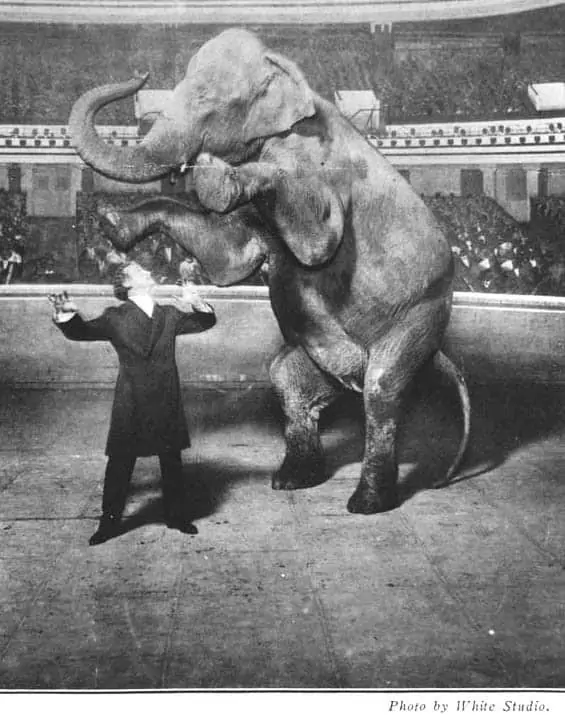

Fig. 1. White Studio. “Houdini and Jennie, the Elephant, Performing at the Hippodrome, New York.” Library of Congress , www.loc.gov/item/96518833/.
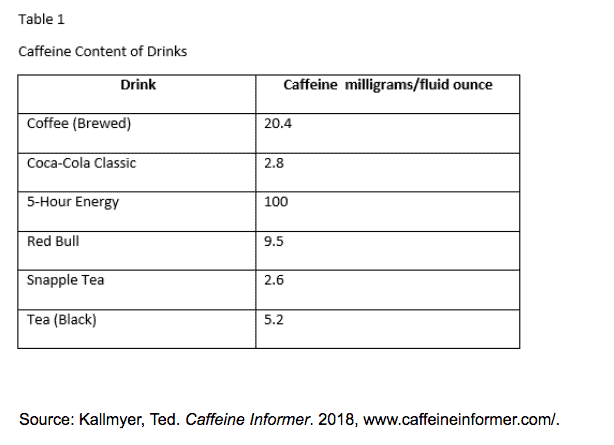
When adding a table or data set into a project, it is formatted a little differently. Above the data set, include the label “Table” with an Arabic numeral, and title it. The table number and title should be located flush left and on separate lines. The first table seen in the project is labeled as Table 1. The second table in the project is Table 2, and so on. The table’s title should be written in title case form (the first letter of each word is capitalized, except for small, insignificant words).
Underneath the table, provide the source and any notes. Notes should be labeled with a letter, rather than a numeral, so the reader is able to differentiate between the notes of the text and the notes of the table.
International Scholars from India Enrolled at Yale University a
| Year | India | South Korea |
| 2012-2013 | 191 | 126 |
| 2013-2014 | 200 | 123 |
| 2014-2015 | 197 | 116 |
| 2015-2016 | 210 | 120 |
Source: “International Scholars Academic Year 2015-2016.” Yale University , Office of International Students and Scholars, yale.app.box.com/v/scholar-2015-2016. a. The numbers reflect students who are enrolled full-time.
The information included above and below any images or table should be double spaced, similar to the rest of the project or paper.
Musical Scores
Musical scores need to be labeled as well. When including a musical score in a project, label musical scores with “Ex.” which is short for example. This label should be placed below the musical score. Next to the abbreviation “Ex.”, assign the score an Arabic numeral. The first musical score in the project should be labeled as Ex. 1. The second musical score found in an assignment should be labeled as Ex. 2., and so on.
If possible, provide a caption after to the label. If the caption below the sheet music includes enough information about the source, it is not necessary to include the full reference at the end of the assignment.
Here is an example of a possible label and caption:
Ex. 4. Scott Joplin, The Entertainer, piano, C major.
Another example:

Here’s more on tables and illustrations.
Using Lists in MLA
It’s appropriate to add lists into an MLA format essay as long as the proper rules are followed.
Lists created using MLA essay format look different than a grocery list or any other type of vertical listing of items. Items in a list are included in your prose, rather than the traditional vertical style.
Often, you will use a colon between the introductory sentence and the list. But you should not include a colon if the first item in the list is part of the sentence.
List Example #1
Here is an example of how a list may look incorporated into the prose of a research project or assignment:
William Shakespeare wrote numerous plays, many of which were considered tragedies: Romeo and Juliet , Hamlet , Macbeth , Othello , Julius Caesar , and King Lear .
List Example #2 Here is an example of how a list may look in a research project or assignment when the list is part of the introductory sentence:
Many of William Shakespeare’s were tragedies. Some of his most popular tragedies include Romeo and Juliet , Hamlet , Macbeth , Othello , Julius Caesar , and King Lear.
MLA Works Cited Format
EasyBib.com has a full, comprehensive guide to creating a proper works cited MLA format , but here are a few items to keep in mind when developing this portion of a project:
- The list of citations should be the very last page of a research project or essay.
- The top of the page should include the running head and the page number.
- All entries should be placed in alphabetical order by the first item in the MLA format citation.
- The entire page should be double spaced.
For more detailed information, make sure to check out the EasyBib guide to MLA format Works Cited pages.
MLA Citation Format
The majority of this guide focuses on MLA formatting in regards to MLA paper format rules and guidelines. If you’re seeking information related to the proper formatting of an MLA citation, refer to our individual pages and posts on various types of citations.
If you’re simply looking for the general structure for full references, which are found on the final pages of projects, here’s the proper order:
Author’s Last name, Author’s First name. “Title of Source.”* Title of Container , Names of other contributors along with their specific roles, version of the source (if it differs from the original or is unique), any key numbers associated with the source that aren’t dates (such as journal issue numbers or volume numbers), Name of the Publisher, publication date, location (such as the URL or page numbers).
*Note: A title may be in italics instead of quotation marks, depending of the type of source. The general rule is that works that are self-contained (like books, journals, or television shows) are formatted in italics. Works that are part of a larger work (like articles, chapters, or specific episodes) are formatting in quotation marks.
MLA Format Citing FAQs:
“What in the world are containers?”
Containers are what hold the source. If you’re creating a reference for a chapter in a book, the title of the chapter is the title of the source , and the container is the title of the book . The book holds the chapter, so it’s the container. If you’re searching for how to cite a website, here’s a tip: the title of the source is the name of the individual page and the title of the container is the name of the full website.
“This seems like a lot of information for a reference. Is it all necessary?”
The short answer is “No!” When citing, only include the components that help the reader locate the exact same source themselves.
It isn’t necessary to go digging for items such as numbers, version types, or names of other individuals or contributors associated with the source if they aren’t applicable. If you think it’s beneficial for the reader, then include it.
Related to citations, here are helpful pages on:
- MLA citation website format
- Citing a book
- Citing a journal
- What is a DOI ?
- More on PDFs
If you’re looking for an MLA citation generator, head to the EasyBib homepage. Our formatter will help you create citations quickly and easily!
Need APA, too? There are also EasyBib tools and an APA citation website reference guide to help you learn the basics.
Edits and Proofreading
Editing and proofreading your assignment prior to submission is an incredibly important step in the research process. Editing involves checking the paper for the following items:
- Spelling : Are all words spelled correctly? Review all proper names, places, and other unique words to ensure correct spelling. When finished, run the project through a spell checker. Many word processing programs, such as Microsoft Word and Google Drive, provide a free spell checking feature. While spell checks are beneficial, they do not always spot every mistake, so make sure you take the time to read through the assignment carefully. If you’re still not sure if your project contains proper spelling, ask a friend to read through it. They may find a mistake you missed!
- Grammar : Check your assignment to make sure you’ve included proper word usage. There are numerous grammar checkers available to review your project prior to submission. Again, take the time to review any recommendations from these programs prior to accepting the suggestions and revisions.
- Punctuation : Check to make sure the end of every sentence has an ending punctuation mark. Also make sure commas, hyphens, colons, and other punctuation marks are placed in the appropriate places.
- Attribution : Do all quotes and paraphrases include a citation? Did you create an in-text citation for each individual piece of information?
Smart idea: running your paper through a paper checker before you turn it in. EasyBib Plus offers a checker that scans for grammar errors and unintentional plagiarism.
Check out our MLA sample papers . Also, check out the EasyBib MLA Annotated Bibliography Guide.
Don’t forget to use the EasyBib citation generator to develop your Modern Language Association style references.EasyBib.com also has helpful guides on APA format and more styles . Lastly, stay up-to-date on what’s coming by following our EasyBib Twitter account.
Works Cited
“Formatting a Research Paper.” The MLA Style Center , Modern Language Association of America, style.mla.org/formatting-papers/.
MLA Handbook. 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
Published October 31, 2011. Updated July 25, 2021.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau . Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. You can find her here on Twitter. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
The works-cited list provides the reader full information so that a reader can locate the source for further use.
Basic formatting
The works-cited list appears at the end of the paper, after any endnotes if they are present.
Page margins
All margins (top, bottom, left, and right) should be set at 1 inch.
Running head
Write the running head in the top right of the page at 0.5 inch from the top. Use the running head “Surname Page #.”
The font should be clear enough to read. For example, Times New Roman font set to 12 points.
Formatting entries
Entries should be double-spaced, including a double-space between the heading and the first entry. If any entry runs over more than a line, indent the subsequent line(s) 0.5 inch from the left margin.
Formatting the title
The title should be “Works Cited.” Center the title. Do not bold, italicize, or underline the title. If you cite only one source in the list, the title should be “Work Cited.” If you include sources that you only consulted and didn’t cite directly, the title should be changed accordingly to “Works Cited and Consulted.”
Arranging works cited
Works-cited-list entries are arranged alphabetically by the author’s last name (or the editor’s last name for entire edited collections). Double-space all entries. Begin each entry flush with the left margin. If any entry runs over more than one line, indent the subsequent line(s) 0.5 inch from the left margin (sometimes called a hanging indent).
Example works cited
Damasio, Antonio. The Feeling of What Happens: Body, Emotion and the Making of Consciousness . Vintage, 2000.
Hill, R. T. “Legitimizing Colonial Privilege: Native Americans at a Quincentenary of Discourse.” Text and Performance Quarterly , vol. 16, no. 1, 1996, pp. 92–100.
MacDonald, Shauna M. “Performance as Critical Posthuman Pedagogy.” Text and Performance Quarterly , vol. 34, no. 2, 2014, pp. 164–81.
Zilio, M. “Canada Will Not Move Embassy to Jerusalem, Federal Government Says.” The Globe and Mail . 7 Sept. 2017, www.theglobeandmail.com/news/politics/canada-will-not-move-embassy-to-jerusalem-federal-government-says/article37219576/ .
An in-text citation is a short citation that is placed in the text. It is styled in two ways: a citation in prose or a parenthetical citation.
The basic element needed for an in-text citation is the author’s name . The publication year is not required in in-text citations. Sometimes, page numbers or line numbers are also included, especially when directly quoting text from the source being cited. When including a page number, do not include a comma or any other punctuation mark between the author’s surname and the page number.
Parenthetical citations usually add only the author’s surname at the end of the sentence in parentheses. Sometimes they include a page number or other locator. An example of a parenthetical citation is given below:
The spiritual geography of the landscape is explained (Cooper).
If you want to cite a chapter number, a scene, or a line number, follow the abbreviation guidelines below:
When including a more specific locator number rather than a page number, place a comma between the author’s surname and the label.
(Cooper, ch. 2).
Here are a few examples of in-text citations for sources with different numbers or types of authors:
Use only the surname of the author in parenthetical citations. If you want to add a page number (or another indicator of the place in a work), add it after the author’s surname without any punctuation between the surname and the page number.
(Abraham 7).
Two authors
Add only the surnames of the authors. Use “and” to separate the two authors.
(Langmuir and Einstein).
Three or more authors
Add only the surname of the first author followed by “et al.”
(Low et al.).
Corporate author
Shorten the organization name wherever possible, excluding any initial articles and using the shortest noun phrase (e.g., shorten Literary Society of Tamil Culture to Literary Society).
(Literary Society).
If there is no author for the source, use the source title in place of the author’s surname.
When you add such in-text citations, italicize the text of the title. If the source title is longer than a noun phrase, use a shortened version of the title. For example, the title Fantastic Beasts and Where to Find Them is shortened to Fantastic Beasts .
( Fantastic Beasts 160).
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
- How to setup your software
- Sample MLA Paper – normal paper
- Sample MLA Paper – has cover page
- Sample APA Paper
- Sample Chicago Paper
- Sample CSE Paper
- APA Format Guidelines
MLA Format Heading
This page contains guidelines on how to properly format the headings of your research paper using the MLA format.
1. The Opening Page:
On the opening page or the first page, you would include the whole heading and your paper’s title. The whole heading would include the following information:
- Your Instructor’s Name
- Your Class Information
- Your Paper’s Due Date
- Font: choose an easy to read font such as Times New Roman.
- Font Size: set the font size to be twelve (12) throughout your research paper, including your paper’s title. Never set the font site larger than 12.
- Margins: 1-inch for top/bottom/right/left throughout your paper.
- Double-space: double-space throughout your paper. Don’t add extra spaces (besides double-space) between your headings, your title and your paragraphs.
Sample of the Opening Page:

A sample of the first page of your paper.
2. The Inner Pages:
For the pages that follow the first page, set the heading like this: instead of the whole heading, you would use the header feature on your word processing program and including the following information: Your Last Name and the Page Number.
Sample of the Inner Page:

Example of the heading for inner pages.
3. The Works Cited Page:
Every research paper must include a works cited page.
- The works cited list is placed at the end of your paper, on a new page.
- The heading for your works cited pages should be the same as the heading for your inner pages, which include your name and the page number at the top.
- Enter the title as “ Works Cited ” and place this title 1-inch from the top of the page, see more details in the example illustration picture below.
Sample of the Works Cited Page:

Example of the works cited page.
– MLA Handbook, 8th edition
If you find this website useful, please share with a friend:
This helped a lot thank you
Thank you so much 😀
Best website hands down. Got an A, thank you!
Thank you and God bless you! Jesus loves you!
I like how this site tells us the perfect way to write an essay on paper.
This page is helpful to a new student.
this is great!
Cool. But how many grade school students will look at this website to see how to set up their papers.
Wow, This site is amazing!
I have the following level 3 heading in my thesis:
Project management office and (pmo) metrics team.
Should the abbreviation pmo be in lower case as it is or should it be in upper case?
Please Advise. Thanks.
So for the works cited page, you don’t need the name, teacher, date, and period heading at all?
No. It should only be on the first page of the essay.
This is some good stuff to know.
I have to write a paper for an application and they want it to be in MLA format. I don’t know how to do the heading because it’s not going to one teacher in particular and it is not for one class.
I don’t think you need a heading besides the “Last name-1” on the inner pages.
Hey Shannon. You might try “To Whom it may concern” or something like that. Don’t trust me on this because I am not for sure on that and if you did do this you might get it wrong and whoever might not accept your application. I hope you figure out how to do it and do great on that application! 😀 – Christopher
Leave a Comment
Current ye ignore me @r *
Leave this field empty
Next post: Commonly Misspelled or Confused Word Pairs
Previous post: MLA Format Cover Page
- The Format of the Research Paper
- MLA Format Cover Page
- MLA Format Headings
- MLA Citations
- MLA Format Works Cited
- MLA Format FAQs
- MLA Format Sample Paper
- MLA Sample Paper w/ Cover and Outline Pages
HOW TO SETUP YOUR SOFTWARE
- MLA Format using Google Docs
- MLA Format Microsoft Word 2016
- MLA Format using Pages on Mac
Copyright © 2011–2024 • MLA Format • All rights reserved. Currently, MLA is at its 8th edition. This website has no official relationship with the Modern Language Association and is not endorsed by the MLA.
MLA Format: Everything You Need to Know
MLA format is a set of formatting and citation guidelines for how an academic paper should look, similar to other styles such as Chicago or APA format. We use MLA format for topics in the humanities, including languages, philosophy, and the arts, but not history (which uses Chicago) or the social sciences, like psychology or education (which use APA format).
Since most schools’ requirements include humanities courses, there’s a good chance you’ll write a paper in MLA format at some point. Below, we explain how the MLA format works and what sets it apart from Chicago and APA formats. We’ll also cover how to cite sources in MLA format, with examples.
“Write “Grammarly Write with Grammarly
What is MLA format?
When to use mla format, mla vs. apa, chicago, and other formats, how to set up your paper in mla format, mla formatting rules, mla style rules, how to cite sources in mla: citation examples, how to present evidence and quotes in mla, in-text citations in mla, footnotes and endnotes in mla, works cited page for mla, how to cite different types of sources in mla format, mla format faqs.
MLA format was developed by the Modern Language Association to provide a uniform way for academics in the arts and humanities fields to format their works and cite their sources. MLA format, like other academic styles, includes specific guidelines for a paper’s heading, in-text citations, works cited page, quotations, abbreviations, and even the size of the margins.
This format (like other academic formats) takes the guesswork out of formatting your academic writing and ensures that your sources are cited and credited properly, leaving you, and your readers, to focus on your paper’s content.
Use MLA format for the final draft of every piece of academic writing , including essays, reports , and research papers, that you do in your arts and humanities courses. That means English, arts, philosophy, religion, and ethics courses and any other classes you take that fall within these subjects.
If you aren’t sure if you need to use MLA or whether a specific formatting style is necessary for a particular assignment, ask your instructor.
Use MLA format for every part of an assignment you submit. That includes any essay outline , research proposal , literature review , or list of sources your instructor asks you to submit before or alongside your final paper.
There’s no need to format your first draft or any other documents that your professor won’t see, though you certainly can use MLA format throughout the writing process if you’d prefer. One benefit of doing this is that you’ll see approximately how many pages your final draft will span before you reach that stage.
MLA is one of the most commonly used academic styles, especially for high school and undergraduate students. You might also be familiar with APA format , the American Psychological Association’s style, or Chicago , short for the Chicago Manual of Style . These styles each include instructions for formatting citations, crediting sources, using quotations in your work, and other aspects of writing academic papers.
Because the MLA format deals with the humanities, it places more emphasis on authorship than the other styles do. That means the names of creators are prominent in the text. By contrast, APA format emphasizes dates, and Chicago emphasizes supplemental notes like footnotes and endnotes .
Although the three styles have some common approaches to citing sources, each format has its own unique way of doing things for each source type. Make sure you understand the rules for the format you’re using so you don’t follow another style’s rules by mistake.
1 The sources page is referred to as the works cited page. It appears at the end of the paper, after any endnotes.
2 The entire paper is double-spaced, including block quotations and the references on the works cited page.
3 Use block quotes for quotations that are four lines or longer.
4 Abbreviations do not include periods between the letters (e.g., US instead of U.S. ).
5 The paper is printed on 8½-by-11-inch paper .
6 Place a 1-inch margin along all sides of the paper (with the exception of the running head).
7 Write in Times New Roman, Arial, or Helvetica font. The text size should be between 11 and 13.
8 Each page must include a running head with the author’s last name and the page number in the top-right corner. The running head follows the right margin but is only 1.5-inch from the top of the page.
9 A title page is not required.
10 The heading on the first page is left-justified and includes:
- Author’s name
- Instructor’s name
- Course number
- Date the paper is due
1 MLA format uses the Oxford comma , aka the serial comma.
2 Spell out numbers or fractions that can be written in one or two words (e.g., eighty-eight , five million , or two-thirds ). Use numerals for when more than two words are needed (e.g., 101 ; 2,981 ; or 2 ½ ). However, when these numbers are mixed together, or when numbers are discussed frequently, use numerals (e.g., between 3 and 125 people ).
3 Use numerals for items in a series (e.g., chapter 6 , page 12 , or room 34 ).
4 Always spell out a number if it begins a sentence. Even better, try rephrasing the sentence with a different opening.
5 Do not abbreviate dates. You can use either the month-day-year or day-month-year formats, but be consistent throughout the entire work.
6 Use a person’s full name the first time they are mentioned, unless they are commonly referred to by their surname alone, like Cervantes or Cicero. Any subsequent mentions of the person use only their surname, including particles like de , O’ , or von .
For every academic paper you write, you need to cite sources —that is, mention where your evidence or points came from. This is necessary not only to avoid plagiarism but also to validate your ideas with proof.
According to the MLA Handbook , you must cite sources “when the work of others informs your ideas.” That means every idea that is not your own requires its own citation, even if there are two in the same sentence.
There are two ways to reference another work: paraphrasing and direct quotes.
Paraphrasing involves restating the original idea in your own words. However, your paraphrased text must be fundamentally different from the source text—you must do more than just replace a few words with synonyms. It’s best to change both the wording and the sentence structure.
You can also directly quote a passage from a source, especially if the original wording is important. However, relying too heavily on direct quotes might suggest you’re relying too much on others’ ideas rather than your own. It’s best to use them sparingly and only when they’re truly necessary. Furthermore, when you do use quotations, try to keep the quotes as brief as possible, even as short as a single word.
Regardless of whether you use paraphrasing or quotations, you still need to cite the source.
MLA format prefers in-text citations, which involves citing the source directly in the text right next to its reference. There are two types of in-text citations: parenthetical and narrative.
Parenthetical citations are miniature or condensed citations that include only the bare minimum of information. In MLA format, they include only the author’s or creator’s last name, although a page number, line number, or time stamp is optional.
The Greek myth of Sisyphus provides the perfect analogy for humankind’s struggle of living with the absurdity of life (Camus 78).
Narrative citations are when you mention the author’s name in the text, which makes the second mention of it in the citation redundant. In this case, parenthetical citations are necessary only if you’re mentioning the page number or location.
Camus finds the Greek myth of Sisyphus to be the perfect analogy for humankind’s struggle of living with the absurdity of life (78).
Both kinds of in-text citations still require a full citation for the source in the works cited page.
If the author’s name is unavailable, use whatever comes first for that entry in the works cited page, which is typically the work’s title.
Footnotes and endnotes are not common in MLA format, which prefers in-text citations instead. However, there are few situations when they are called for:
- A series of sources: If the same passage requires multiple citations in the same line, it’s better to cite them all in a note than in an in-text citation.
- Deviations from standard documentation: Use a note if you’re not following a normal documentation practice, such as when you’re citing line numbers instead of page numbers for poetry. You only need to mention this the first time you reference the source.
- Flagging editions or translations: Some texts, especially classic works, have multiple versions. Use a note to mention which edition or translation you’re using. Again, you only need to mention this the first time you reference the source.
- Content notes: You can use notes to mention supplemental—but nonessential—information, such as personal commentary or to explain a word choice. Footnotes and endnotes are good for these sorts of tangential asides that don’t fit in the main text.
Papers written in MLA format use either footnotes or endnotes but not both. Make sure to choose one form and stick with it. Footnotes appear at the bottom of the page they reference, endnotes are written on a separate page titled “Notes” or “Endnotes” at the end of a section, chapter, or entire work.
To signal a note, place a superscript number ( 1 ) at the end of the sentence the note refers to. If a note is needed in the middle of a sentence, place it after a punctuation mark like a comma, colon, or semicolon. The exception is the dash; note numbers come before a dash.
Certain translations use an alternative word choice. 1
Although some have disagreed with this assessment, 2 Camus seems to almost admire Sisyphus’s determination.
Sisyphus was the king of Ephyra 3 —now known as Corinth.
Each note number in the text corresponds to either a footnote or an endnote later in work.
Notes are written in the order of their numbers. Each note begins with the superscript number corresponding to its place in the text.
1 Thomas Warren suggests Camus’s use of la mesure should be translated into English as “measurement” instead of the popular translation “moderation.”
2 See Thomas Nagel’s paper, “The Absurd.”
3 Corinth was a city-state on the Isthmus of Corinth, the land that connects the Peloponnese to the mainland of Greece, according to Wikipedia.
MLA prohibits the abbreviation ibid .
According to MLA format guidelines, any source used in your paper must have a corresponding full citation in the works cited page , a page at the end of a book or paper that lists all the sources and their bibliographic information.
The works cited page comes at the end of a work, after any endnotes. This page is titled simply “Works Cited” and mostly follows the same text and formatting guidelines as the rest of the work. For example, it has one-inch page margins and size 11 to 13 text.
Entries are listed in alphabetical order by the first word of each entry, usually the author’s or creator’s last name.
The one particular formatting rule about the works cited page is the use of the hanging indent. Basically, every line after the first one in a single entry is indented by a half-inch .
Camus, Albert. The Myth of Sisyphus and Other Essays. Translated by Justin O’Brien, New York, Random House, 1955.
Each type of source, like books, journal articles, documentaries, etc., has its own particular rules for MLA citations. Feel free to check out our previous guides below, which cover the details of how to cite each source in MLA.
- How to Cite a Book in MLA Format
- How to Cite a Website in MLA Format
- How to Cite an Image or Photo in MLA Format
- How to Cite a Movie in MLA Format
- How to Cite a TV Show in MLA Format
- How to Cite Wikipedia in MLA Format
- How to Cite a YouTube Video in MLA Format
- How to Cite a PDF in MLA Format
- How to Cite a Lecture or Speech in MLA Format
MLA format is the academic style developed by the Modern Language Association. It’s the standard format for academic papers in the arts and humanities. MLA has specific guidelines for citing books , films , TV shows , newspaper articles , PDFs , and other types of sources.
How is it different from other formats?
There are numerous differences between MLA format and other academic formats. One of the most notable is how sources are cited.
What are some examples of MLA citations?
In-text citation: (Lamott 28).
Reference listed on the works cited page: Coates, Ta-Nehisi. Between the World and Me . Spiegel & Gray, 2015.
Grammarly helps you cite with confidence
Grammarly is meeting students’ needs by simplifying the citation process. Our citation features expand on Grammarly’s trusted support for students, which includes grammar and spelling suggestions and plagiarism detection that identifies missing citations. Auto-citations generates citations for online sources in seconds, without your having to enter any info manually or even leave the web page. And when you’re ready to edit your paper, citation style formatting will proofread your in-text and full citations to ensure they’re mistake-free and consistent.

MLA Format: A Complete Guide with Examples
#scribendiinc
Written by Scribendi
Your instructor has asked you to format your term paper using Modern Language Association (MLA) style. You feel confident enough to produce the paper, but you have never heard of MLA style. Don't panic—we've got you covered.
This article will explain MLA style citation, give examples of MLA formatting for specific aspects of references, provide an MLA format example for each category of source material, and share essay formatting tips that our editors have learned over the years.
You'll even find a free, downloadable MLA Works Cited example page for easy reference. So, if you have a general understanding of what MLA style is and are just looking for examples of MLA citations, we can help with that too!
Free MLA Cheat Sheet
What Is MLA Style?
MLA style is an accepted way to document source material for many types of humanities documents. Some would say it is simpler than other style guides, such as the APA Style Guide or the Chicago Manual of Style .
An MLA citation has two basic requirements:
Brief parenthetical citations in the text
An alphabetical list of the works cited that corresponds to the in-text citations and appears at the end of the paper
In simple terms, you refer to your source material in parentheses throughout the main text—then, at the end of your paper, you list all the sources to which you have referred, in alphabetical order.
Of course, there is so much more to MLA style and MLA formatting than just that. Indeed, the current version of the MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers (7th Edition) runs to 292 pages! But here are the essential style and formatting points.
MLA Format Citation Example
To start, let's look at a basic example of how to format a citation in MLA.
Last Name, First Name. "Title of Webpage/Chapter/Article." Website/Book Title/Journal Title , edition used, vol. X, no. Y, Publisher,
Day Month Year of Publication, URL/location/page number.
This is MLA format at its simplest.
Why Use MLA Format (or Any Other)?
The main reason for carefully citing source material is to avoid allegations of plagiarism, which—derived from the Latin word for "kidnapping"—refers to stealing someone else's work. The MLA Handbook explains plagiarism in detail. You should feel free to use another person's words, facts, and thoughts in your research paper, but the material you borrow must not be presented as if it were your own creation.
When you write your research paper, remember that you must document everything that you borrow—not only direct quotations and paraphrases but also information and ideas. Our MLA citation guide will walk you through how to properly cite your sources using MLA style.
Who Uses MLA Citation Format?
MLA-style citation is commonly used by writers and students who create content in the humanities.
You'll often see it used for the following subject areas:
Language and literature
Comparative literature
Literary criticism
Cultural studies
Foreign languages
Using MLA's citation guide in these fields of study gives readers an easier option for navigating through your paper. In addition to making you look credible by neatly organizing your sources, MLA citation lends consistency to your work. It provides readers with the opportunity to easily find sources in your paper that interest them.
How to Use MLA Format
The early stages of producing a paper involve copious amounts of reading, research, and note-taking. At this point, it's easy to get confused about who said what. The best way to avoid getting confused right from the start is to keep your ideas, your summary of others' ideas, and direct transcriptions of text clearly marked and separate. Throughout our guide, we'll provide examples of MLA citation to give you a hand.
Make notes on the following elements for ease of reference and proper MLA citation later on:
Author's name
Full title of each publication (from the title page, not the front cover)
City of publication (cite only the first city if there is more than one)
Date of publication
Volume and issue numbers, if available (for journals)
Page numbers you have referenced
Medium of publication or reception (print, web, radio, television, etc.)
Laying the groundwork during your research will make the citation process much easier later on.
MLA Citation Format
Because we know there are many ways to cite a reference in MLA, depending on what source you're using, we've compiled an extensive list of MLA citation examples below.
You'll find MLA citation examples for articles, books, images, interviews, journals, movies, and more to ensure you are citing your sources correctly.
We've done our best to be as thorough as possible. Review how to use in-text citations in MLA below or skip to the ones you need most!
How to Cite Two to Three Authors
If you're citing a book in MLA format with two or three authors, use the examples below to format your citation:
Bringham, Darrin E., and Sally Knope. Resting Heartbeat Science . 12th ed., Wiley, 2001.
Christopherson, Charles, Ronald Swanson, and Roger Koltz. Fog Pirates: On Board the USS Hammerhead . Putters, 2001.
Only the first author is listed by their last name followed by their first name. Any subsequent authors are written normally (first name then last name).
How to Cite More than Three Authors
When there are more than three authors to reference in MLA, format your citation using et al., as shown below:
Niderbacher, Leslie A., et al. Penne and the Jets: A Love Story . Partridge, 2003.
Note that only the first author is fully named, followed by et al.
Related: Learn more about How to Use Et Al. here.
How to Cite No Author
An MLA in-text citation with no author begins with the title . If your in-text citation has no author in MLA, you can also use the title in addition to the page number.
( Encyclopedia of Football 54)
How to Cite a Journal Article
Correct MLA article citation starts with finding good, credible articles. Try looking for peer-reviewed scholarly journal articles in free research databases such as CORE and ScienceOpen.
When searching for the best journals for your topic, try to steer clear of regular search engines like Google or Yahoo. Academic databases like JSTOR and Google Scholar are the best sources for scholarly, peer-reviewed articles .
MLA journal citation elements include the title of the work, author(s), and publication date. While this information is usually found on the first page of an article, its placement can vary. It may be at the top or bottom of the first page or, in the case of database articles, on the results page or the description page.
Related: Check out our list of 17 Research Databases for Free Articles .
MLA Citation for an Article


MLA Article Citation Examples
Lau, Frank. "Vitamin D Insufficiency is Prevalent in Severe COVID-19." Journal of Health , vol. 2, no. 5, Aug. 2020, pp. 34–27.
https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.24.20075838.
Kuehn, Bridget. "Hospitals Turn to Housing to Help Homeless Patients." JAMA , Feb. 2019, pp. 5–9.
https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2018.21476.
MLA Website Article Citation Examples
Tomky, Naomi. "Explore the Oregon Coast—but don't touch the 'dragon toes.'" National Geographic , 23 Mar. 2022,
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/travel/article/explore-oregon-coast-but-dont-touch-dragon-toe-barnacles.
Gateley, Cheyne. "Netflix's Password Crackdown Will Be Tougher Than It Seems." Variety , 21 Mar. 2022,
https://variety.com/vip/netflixs-password-crackdown-will-be-tougher-than-it-seems-1235208619/.
Book Citation in MLA
If you're citing passages from a book using MLA, look at the title page of the book to find the information you need to cite the source. The title page can usually be found a couple of pages into the book. This is where you'll find the author(s), date, edition, title, editors (if any), place of publication, and publisher.
MLA Book Citation Examples
Schucman, Helen. A Course in Miracles. Edited by Robert Perry, The Circle of Atonement, Inc., 2017.
MLA Textbook Citation Examples

How to Cite an Image
Image citation in MLA requires you to first define what type of image you're sourcing. Is it an image you saw in person or an image from a website?
Asking yourself this question first will help you decide which format to use to cite your image. Let's look at a few examples below.
MLA Image Citation Examples

How to Cite an Image from a Website
To cite an image from a website in MLA, start with the image creator's last and first name, then add the image title, the website name , day, month, and year published, and the URL.
In the example below, there is no image title, so we're using a description of the image:
Yam, Marcus. Photograph of a man hurrying away from a building hit by Russian bombs. Los Angeles Times , 25 Mar. 2022,
www.latimes.com/world-nation/story/2022-03-25/ukraine-russia-war-biden-heads-to-poland .
Here is an example with an image title:
Clancy, Pat. "Foggy Sunrise." Flickr , 10 Mar. 2022,
https://www.flickr.com/photos/128721907@N02/51958337614/in/explore-2022-03-24/.
MLA Citation: Interview
When citing an interview in MLA, the information you need can vary depending on the type of interview.
For example, if you're citing an interview printed in a magazine, you can find relevant citation information in the title or subtitle of the interview page.
For online interviews, the relevant information can be found on the site where the interview was published. Typically, in the title or near the name of the person who published the interview, you'll find the names of the interviewer and interviewee, as well as the date the interview was published.
Here are a few elements you'll need if you're citing an interview in MLA:
Interviewee's first and last name
Interviewer's first and last name
Interview title
Periodical or journal title (if any)
Type of interview
Date the interview was conducted/published
URL of the interview (if online)
Page numbers of the interview (if in print)
In MLA, if you can't find the author of an interview you're trying to source, this information can be skipped. Instead, you can start your citation with the title of the interview in quotation marks. You can also skip the date of the interview if it is missing, but you should still include the access date if the interview is online.
If, for any reason, you also can't access the title of the interview, MLA allows you to replace the title with a short description. Let's look at a couple of examples below.
MLA Interview Citation Examples

How to Cite a Lecture
When citing a lecture in MLA, start with the speaker's last and first names, followed by the lecture title in quotes, then the course or event name, the day, month, and year, the institution, the location, and the word "Lecture." Below is an example of how to cite a lecture in MLA.
MLA Lecture Citation Example

How to Cite a Movie in MLA
If you need to cite a movie in MLA style, you'll need the title of the film, the director, any relevant contributors, the company that produced/distributed the film, and the release year. Be sure to add the words "Directed by" before the director's name, as you'll see in the examples below.
MLA Movie Citation Examples

How to Cite a Poem
To cite a poem in MLA, begin with listing the author's last name and first, then the poem's title in quotes, followed by the title of the book the poem was found in, and the publisher, year, and page number(s).
MLA Poem Citation Examples

Quotes in MLA Format
When you're using a quote, you're taking the exact words from an original source, so you need to make sure you're citing that source correctly.
In MLA format, quotes should be cited in the main text and on the Works Cited page. Your in-text citation will need the author's last name and the page number where you found the quote , while the Works Cited page will include the full citation. We've included examples of both MLA quote citation formats below.
MLA Short Quote Citation Examples
In-text citation example:
It appears that creating "businesses that diminish the quality of life and well-being of our citizens" (Williamson 109) will only make things worse.
Works Cited example:
Williamson, Marianne. A Politics of Love . Harper One, 2019.
MLA Format for Long Quotes
If you have to cite quotes longer than four lines in your paper, you'll want to use a block quote. The MLA format is the same on the Works Cited page for long and short quotes, but block quotes look different in the main text.
Block quotes are placed in a separate paragraph, indented 1 inch from the left margin. When using a block quote in text, include the last name of the author and page number(s) in parentheses after the closing punctuation at the end of the quote.
Note that block quotes are not enclosed in quotation marks.
How to Cite a Song in MLA
When citing a song in MLA, pay close attention to the medium you used to access it. If you heard the song on a CD or on a streaming service like Spotify, you'll want to include this in your reference.
For in-text citations of songs, you'll include your citation at the end of your paraphrased portion with the last name of the performer and the specific time stamp of the song. Other elements needed for the citation on the Works Cited page include the album name, label, and release date.
MLA Song Citation Examples

How to Cite a Video
An MLA citation for a YouTube video requires a few pieces of information, including the video creator's name, the title of the video, the website hosting the video, the name of the channel or uploader, the day, month , and year the video was published, and its URL.
Regardless of the platform from which you cite a video, MLA requires the same standard information, including the creator of the video, the title, where it was found, who uploaded it, the day, month, and year it was uploaded, and the URL.

How to Cite a Website in MLA
The MLA format for websites requires a few core elements, including the author, title of the source and container, relevant contributors, version, publisher, publication date in day-month-year format, and DOI or URL .
Some of this information can be omitted if it isn't available. See the examples below.
MLA Format for Websites

More about MLA Style and Format
Mla heading format.
When you're writing a paper in MLA format, headings go on the first page . Your heading should include the following information:
Instructor's name
Course name or number
Submission date
Your MLA heading goes in the upper left corner of your paper, double-spaced. Try not to confuse an MLA heading with an MLA header, which is in the upper right corner of every page of your paper and includes your last name and the page number.
MLA Format Heading Examples
Here are two example headings in MLA format for reference. Keep in mind that these should be double-spaced in your paper.
Cody Anderson
Professor Lockhart
Astronomy 103
23 March 2022
Raquel Smith
Professor Snape
Humanities 605
25 February 2021
MLA In-Text Citation
In the next few sections, we'll look at MLA formatting for sources cited within the main text of your paper, also called in-text citations. In-text citations give your reader a clue about where to find the source you referenced in the Works Cited section at the end of your paper.
MLA format for books requires that you briefly acknowledge your sources in the main body of the text by using the author's name and the page number in parentheses.
Note the following example:
(Clinton 440).
The reader knows to consult page 440 of Clinton's book.
Larger Works
If you refer to the title of a large published work in your paper, such as a novel or movie, it should appear as follows:
John Clinton's A Study of Life.
Please note the use of capital letters and italics.
Smaller Works
Titles of smaller works, such as poems, short stories, chapters, and articles, should be written in the text as follows:
Raymond Carver's "Cathedral."
Please note that smaller works are put in quotation marks and are not italicized.
MLA Works Cited
To obtain further information, the reader can refer to the alphabetical references section, called the Works Cited page, at the end of the paper. There, the reader can find the full details of each cited publication.
Note the following MLA Works Cited example:
Clinton, John. A Study of Life . London: Hodder, 1998. Print.
Our John Clinton example is MLA style referencing in its simplest form: one author and one book. MLA citation for multiple authors of a single book and MLA citation for multiple books by a single author tend to complicate matters. However, if you have the basics right and have made good notes for all your source material, these problems are manageable.
Multiple Books by One Author
When citing two or more books by one author in your Works Cited section, MLA requires the author's name in the first entry only. In the next entry, replace the author's name with an em dash (—), a period, and the second book title. The em dash takes the place of the author's name. In terms of the order of the books by one author on your Works Cited page, alphabetize the list by title.
Brunson, Russell. DotCom Secrets . Morgan James Publishing, 2015.
—. Traffic Secrets . Hay House, Inc., 2020.
MLA Format with Multiple Authors
When citing three or more authors in MLA, you'll want to use "et al.," which means "and others."
Levine, Robert S., et al. The Norton Anthology of American Literature . 9th ed., W.W. Norton & Company, 2022.
Missing Items
If you're trying to cite a source in MLA with missing information, you have a few options available to you depending on what information is missing.
If you're missing the author of a source, use the title of the work in its place for both in-text citations and citations in the Works Cited in MLA format. If your title is also missing, use the source instead.
If your source has no page numbers, you can omit these in your citations and use paragraph or line numbers if they are available.
If the date of the publication is missing, you don't have to include it. But if it's a resource you accessed online, include the access date at the end of the citation—for example, "Accessed 14 Sep. 2021."
You can also omit the publisher if this information is missing.
MLA Format Works Cited Page Tips
When formatting your Works Cited page in MLA format, be sure to pay close attention to all the guidelines. MLA requires all lines to be double-spaced with a hanging indent. A hanging indent is when the first line of your reference starts at the beginning of the line while the next lines are indented by an inch and a half from the left.
Free Download
To keep all of these MLA examples in one sheet for easy reference, we've compiled a free download. This way, you can review MLA citation examples anytime you need them, either for your Works Cited page or in-text citations, for multiple types of work.
Once downloaded, you'll have all of the MLA citation examples you need in your back pocket. This guide will give you examples of MLA citations for the following types of sources:
Books (with one author, multiple authors, or no author)
Download our free MLA downloadable here.
Download Now
Writing a paper in mla format.
When writing a paper in MLA format, you'll need to cover your bases when it comes to citing your sources. Not only do your sources need to be correct to account for wherever you're pulling information from, but they also need to follow MLA paper formatting basics .
So far, we've covered how to cite sources in your Works Cited list and in-text citations. Now, let's talk about how to use footnotes in an MLA paper with a couple of examples.
As a general rule, footnotes should be used sparingly in MLA. However, when they are used, there are two types: bibliographical footnotes and content footnotes.
Bibliographical footnotes allow you to add more relevant sources. Content footnotes allow you to add commentary or explanations about your topic. We'll look at examples of both of these below.
MLA Footnote Examples
Bibliographical footnote:
1 See Clinton, John. A Study of Life . Hodder, 1998. Additional references are for this edition and appear within the text.
Content footnote:
1 In a lecture from 2013, Peters mentions his love of science and how science will shape our future.
MLA Title Page Format
The MLA format cover page is not an entirely separate page. It begins with a 1-inch margin, flush left with your name, your instructor's name, the course name or number, and the date typed on separate, double-spaced lines.
The title of your research paper should then be centered on the MLA format title page. There is no need for it to be presented in bold, italics, or capital letters.
MLA Parenthetical Citation
When citing a source in your text in MLA, use a parenthetical citation.
Parenthetical citations in MLA should include the author's last name and the page number where you found the information.
For example: (Lars 86).
MLA Page Number Format
In MLA format, page numbers appear in the top right-hand corner with a 0.5-inch margin from the top and a flush right margin. It is good practice to include your last name before the page number in case pages go astray. Do not use the abbreviation p. before the page number or add any other mark or symbol. You may not need to include a page number on the front page—check with your instructor.
Sometimes, it is appropriate to draw attention to particular words in your paper, but using italics for emphasis ("He really ate a lot ") is inappropriate in research writing and inconsistent with MLA style. Generally, in MLA format, italics should be reserved for titles of longer works (e.g., books, films), non-English words, and words and letters referred to as words and letters.
MLA Format Essay Tips
Your instructor may issue particular instructions if you are to use MLA citation in an essay—if so, follow them. Otherwise, the following MLA essay formatting tips will help you set out your research paper in MLA style.
The MLA Style Guide recommends using a clear typeface (Arial or Times New Roman) in a readable size (at least 11 point).
Justification
Justify the text to the left margin, leaving the right margin ragged. Leave 1-inch margins on the top, bottom, left, and right of the page.
Indent the first word in each paragraph by 0.5 inches. Indent set-off block quotations by 1 inch.
Use double-spacing throughout. In accordance with the MLA guide, use single spaces after periods, commas , exclamation marks, etc.
Good grammar, punctuation , and spelling are essential parts of your research paper—not just when using MLA style citation. There is no room for typos at this level.
Our advice is to check and check again, and don't just rely on your word processor's spell-checker. Get a second pair of eyes to look over your paper. T ry our essay editors to ensure that the MLA formatting is consistent throughout your paper and there are no grammatical errors.
Related: Avoid These Common Mistakes in Academic and Scientific Writing
The importance of citing your references in your essay cannot be understated. Any time you include a piece of information in your essay that you didn't write yourself, MLA requires two forms of citation: one in the main text and one at the end of your paper in the Works Cited section.
MLA Format Essay Example
To see how all these formatting elements come together to make an MLA paper, see the example below.
https://p113.p2.n0.cdn.getcloudapp.com/items/v1ugxp7E/9e3b21d9-758c-4e27-b6cb-caa1059c0547.jpeg?v=559e925043cbfee9fe816e0568ab3d3b
Electronic Sources and MLA Formatting
In this computerized age, electronic publications are widely used as source materials for essays. However, electronic texts are prone to frequent and rapid change—one minute you see them online, and the next they are gone. Therefore, it is important to provide more information when references to electronic works are made.
When accessing electronic information, note the following elements:
Name of the author, editor, etc.
Title of the work
Title of the website (if distinct from the title of the work)
Version/edition used, if applicable
Publisher or sponsor of the site (if not available, use n.p.)
Date of publication (day, month, and year, if available; if no date is available, use n.d.)
Medium of publication (web)
Date of access (day, month, and year)
Note the following example of MLA citation:
Smith, George. "Trees of the Southern Hemisphere." The International Leaf. Barker University, 2008. Web. 6 Feb. 2009.
Please note that the MLA formatting and style guide no longer recommends including the URL of a document. Nevertheless, the URL can be included if it is required by your instructor or if your readers will have difficulty locating the source without it.
MLA Format Letter
Below, you'll find examples of how to apply the MLA letter format. Much of the formatting will be similar to that of MLA-style papers, including using double-spaced lines in your text.
MLA Letter Heading Format
Start your MLA-formatted letter with your two-line mailing address in the upper left-hand corner, an inch from the top of the page. Skip to the next line and add the date in day-month-year format.
On the next line, include the addressee's information, starting with the recipient's title, such as Mr., Ms., or Dr. You can also include their address and contact information.
On yet another line, include your salutation—for example, "Dear Ms. Smith"—followed by a colon. If you don't have a name for the person you're writing to, use the person's title—for example, "Dear Director of Operations."
When writing a letter in MLA format, be sure to use double-spacing throughout as you would in an MLA paper.
Chicago vs. MLA vs. APA Citation
The formatting of citations varies among style guides like Chicago, MLA, and APA. While each style guide has its own way of formatting sources and cover pages, one of the biggest differences is in how they format in-text citations. Let's look at how they differ.
MLA stands for the Modern Language Association and is a style used for papers in the humanities. In-text citations in MLA use the author's last name and page number in parentheses: (Smith 15).
APA stands for the American Psychological Association and is a style used for scientific papers. In-text citations in APA style include a bit more information than those in MLA style. For example, APA uses the author's last name, year of publication, and page number: (Smith, 2021, p. 15).
Chicago style is used mainly for manuscripts by writers, designers, and publishers. In-text citations in this style include the last name of the source, the publication year, and the page number in parentheses, with slightly different formatting than APA: (Smith 2021, 15).
Frequently Asked Questions
How do i cite a website in mla.
To cite a website in MLA, start with the author's last name and first name separated by a comma and punctuated with a period. Next, include the title of the article or page in headline case and in quotes with a period, followed by the title of the website in italics. After that, add a comma, the name of the publisher, the publication date in day-month-year format, and the URL.
Shields, Ronan. "'The Threat is Hollow': True Transparency is Some Way Off for Scaled Advertisers." Digiday , Digiday Media, 25
Mar. 2022, https://digiday.com/marketing/the-threat-is-hollow-true-transparency-is-some-way-off-for-scaled-advertisers/.
Basu, Tyler. "How to Build a Personal Brand (Complete Guide)." Thinkific , Thinkific, 7 Sep. 2021,
https://www.thinkific.com/blog/personal-branding-guide/.
For an MLA website in-text citation, simply put the last name of the author in parentheses: (Shields).
How Do I Cite a Journal Article in MLA?
The MLA citation for a journal article begins with the author's last name and first name separated by a comma. Next, include the title of the article in quotes, punctuated by a period, then the journal title in title case and italics, and then a comma before the volume or issue number. This is followed by the date of publication, the page range, and the DOI or URL (without https://). Finally, add the access date if no publication date is listed.
How Do I Write In-Text Citations in MLA?
In-text citations allow readers to identify which of the items on your Works Cited page you're referencing. MLA requires the source's last name to be set in parentheses, followed by the page number where you found the information. Below are a few examples of how to use in-text citations in MLA format.
(Smith and Jones 53)
(Smith et al. 33)
(Smith 56–58)
(Smith 56–58, 73)
How Do I Cite a YouTube Video in MLA?
For MLA YouTube citation, start with the video creator's last name and first name, separated by a comma and punctuated by a period. Next, include the title of the video in quotes, also punctuated by a period (inside the quotation marks).
Add the website hosting the video in italics (in this case, YouTube), the name of the channel or uploader, and the day, month, and year the video was published. Include the URL at the end of the MLA video citation.
Forleo, Marie. "Can You Age in Reverse? Tony Robbins Says Yes." YouTube , uploaded by Marie Forleo, 14 Feb. 2022,
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YAb5z7NbMYk.
Snipes, Doc. "15 Tips to Stop Ruminating and Get Out of Your Head." YouTube , uploaded by Doc Snipes, 23 Mar. 2022,
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yMZpMtM7TkI.
How Do I Use MLA Format for Headings?
Put your MLA heading in the upper left-hand corner of the first page of your paper , double-spaced. It should have your name, your instructor's name, the course name or number, and the date. Here are two examples of how to format your headings in MLA:
How Do I Cite a Movie in MLA Format?
To cite a movie in MLA style, start with the title of the film in italics, then the name of the director, followed by any relevant contributors. Next, include the company that produced or distributed the film and the release year.
Jaws . Directed by Steven Spielberg, performances by Roy Scheider and Robert Shaw, Universal Pictures, 1975.
To cite a movie from a streaming service such as Netflix, use the following format:
Jaws . Directed by Steven Spielberg, performances by Roy Scheider and Robert Shaw, Universal Pictures, 1975. Netflix app.
How Do I Format My Paper Using MLA?
To recap the most important MLA formatting guidelines, be sure to use 1-inch margins all around your paper, set the font to 12-point Times New Roman (or another easy-to-read font), and double-space the lines in your text. Make sure each word at the start of your paragraphs is indented half an inch from the left margin, and do the same for any block quotations.
You must cite all your sources in MLA, both in the text and on the Works Cited page found at the end of your paper. Use the examples and guidelines above to make sure you're formatting your paper and citations according to MLA guidelines.
How Do I Cite a Person in MLA?
If you're citing an interview, use the last and first name of the person interviewed at the start of your MLA Works Cited citation. Then, add the interview title, periodical title, type of interview, date, and URL of the interview (if online).
If the person you're referencing was interviewed in print, include the page numbers.
For an in-text citation of an interview, use the last name of the person being interviewed—for example: (Smith).
Download our free MLA format PDF for more examples of how to cite a person in MLA for an interview, either one you've conducted yourself or one you found elsewhere.
About the Author

Scribendi's in-house editors work with writers from all over the globe to perfect their writing. They know that no piece of writing is complete without a professional edit, and they love to see a good piece of writing transformed into a great one. Scribendi's in-house editors are unrivaled in both experience and education, having collectively edited millions of words and obtained nearly 20 degrees. They love consuming caffeinated beverages, reading books of various genres, and relaxing in quiet, dimly lit spaces.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

Examples of MLA Citations

MLA Citations: A How-To Guide

MLA Formatting and MLA Style: An Introduction
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
| File | Word Count | Include in Price? |
|---|
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

This site uses cookies to provide you with more responsive and personalized service and to collect certain information about your use of the site. You can change your cookie settings through your browser. If you continue without changing your settings, you agree to our use of cookies. See our Privacy Policy for more information.
- Student Resources
Student Financial Services
- Student Accounts
Insight Live Boxcast
Chapel audio.
- PCM Sign-In
- My PCM Information
- My PCM Team
- PCM Homepage
- PCM Attendance
- Book Appointment
- PCM Ministry List
Student Resources - Chicago
- MBI Discounts on Office Supplies & Technology Products
- Directory of Department
Student Resources - Spokane
- Spokane Flight Board
- Spokane Ministry Covenant
- Print Request Form
- Spokane Internship Form
Student Resources - MDL
- MDL Payment Plan
- FE 400 Internship Request Form
- Scholarship Applications
- FAFSA Verification Forms
- Satisfactory Academic Progress
Paying Your Bill
- How to Pay Your Bill
- International Payments
Billing Information
- Payment Policies & Deadlines
- Moody Payment Plan
- Adjustments, Refunds, Appeals
- FERPA Billing Disclosure
Miscellaneous
- Health Insurance
- Tax Information (1098-T)
- Submit ACH Form
- Strategic Resource Allocation Committee (SRAC)
- Chicago Campus Redevelopment FAQ
- myMoody FAQ
- Insight Live Archive
- Chapel Audio Spring 2017
- Chapel Audio Fall 2016
- Chapel Audio Spring 2016
- Chapel Audio Fall 2015
- Map and Library Equipment
- Policies and Guidelines
- Staff Directory
- Group Study Room
- New Library Materials
- Databases and Articles
- Searching in I-Share
- 000-999 Dewey Decimal Guide
- 200-299 (Religion) Dewey Decimal Guide
- ILL Request Form
- Placing I-Share Requests
- Collection Development Policy
- Request In Library Instruction
- Reserve Request
- Torah Usage Form
- Curriculum Lab (CurLab)
- Juvenile Collection
- Educational Links
- CurLab and Juvenile Map
- Music Scores and CDs Dewey Decimal Guide
- Alumni Access
- Recommend a Purchase
- About Aviation Resources
- Library of Congress Guide
- Research Help
- Interlibrary Loan
- Request In-Library Instruction
- Online Library Resources
- Interlibrary Loan Moody Online
- Request Embedded Librarian Service
- Materials Request Form
- Library Material Types
- New Arrivals
- Mobile Apps
- Online Research
- Library Catalog
- Other Library Catalogs
- Free Resources and Databases
- Research Help Tools
- How to Search Tips
- Users with Disabilities
- Best Internet Resources
- Database Finder Results
- Guide to Google
- Library Calendar
- News and Updates
- Computer Usage Policy
- Social Media
- Ask a Librarian
- Report a Problem
- Audio Library
- Dwight L. Moody
- William Culbertson
- James M. Gray
- William Henry Houghton
- Cyrus Hall McCormick
- Ira D. Sankey
- Reuben Archer Torrey
- Torah Scroll Gallery
- Archives Checkout Policy
- Archives Class Projects
- Archives Collection Development
- Archives Copy/Scan Requests
- Archives Visitor Policy
- Recorded Messages Policy
- Education Site Map
MLA Style Sheet
General guidelines.
Please also visit the Academic Integrity LibGuide , which provides a Citation guide for your information.
- Everything in the paper is double-spaced : works cited, indented quotes, etc.
- Pagination: student's last name and the page number are placed on each page's upper right-hand corner.
- Quotes that are more than four lines long are indented one inch from the left margin only.
- Title Page: ask the professor for his or her preference.
- Punctuation: the period always goes after the documentation parentheses except in an indented quote, where it goes before.
MLA Works Cited
A BOOK BY A SINGLE AUTHOR Sayers, Dorothy L. The Nine Tailors. San Diego: Harcourt, 1962. Print.
A BOOK BY MORE THAN ONE AUTHOR (OR EDITOR) Kerrigan, William, and Gordon Braden. The Idea of the Renaissance. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins UP, 1989.Print.
Dyal, James A.,William C. Corning, and Dale M. Willows. Readings in Psychology: The Search for Alternatives. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw, 1975. Print.
WORKS BY MORE THAN THREE AUTHORS (OR EDITORS) Nielsen, Niels C., Jr., et al. Religions of the World. 3rd ed. New York: St. Martin's, 1992. Print.
A BOOK COMPILED BY AN EDITOR(S) Arp, Thomas R. and Greg Johnson, eds. Perrine's Story and Structure. 12th ed. Boston: Wadsworth/Cengage Learning, 2009. Print.
A WORK IN AN ANTHOLOGY OR A COLLECTION Fairbairn-Dunlop, Peggy. "Women and Agriculture in Western Samoa." Different Places, Different Voices. Ed.
Janet H. Momsen and Vivian Kinnaird. London: Routledge, 211-26. Print.
AN ARTICLE WITHOUT AN AUTHOR IN A REFERENCE BOOK "Hadadrimmon." Davis Dictionary of the Bible. John D. Davis, ed. 4th ed. Nashville: Broadman Press, 1972. Print.
AN ARTICLE FROM A WEEKLY OR BIWEEKLY MAGAZINE Glastris, Paul. "The New Way to Get Rich." U.S. News & World Report 7 May 1990: 26-36. Print.
AN ARTICLE FROM A DAILY NEWSPAPER Wilford, John N. "Corn in the New World: A Relative Latecomer." New York Times 7 Mar. 1995, late ed.: C1+. Print.
AN ARTICLE IN A SCHOLARLY JOURNAL Rosen, Jonathan. "The Celestial Rolodex." The American Scholar 73 (Autumn 2004): 115-118. Print.
AN ANONYMOUS ARTICLE "Awash in Garbage." New York Times 15 Aug. 1987, sec. 1: 26. Print.
INTERNET AND OTHER SOURCES
INTERNET SOURCE (without author) "Bertha Advances toward Bahamas." CNN WORLD News. 9 July 1996. Web. 21 March 2011.
ARTICLE FROM A SCHOLARLY JOURNAL ONLINE Brittain, Clark M. "The Architecture of Redemption: Spatiality in the Short Stories of Flannery O'Connor." The Journal of Southern Religion 4 (2001). 25 July 2005. Web. 25 March 2011.
MATERIAL FROM A DATABASE ON CD-ROM Grych, John H. "Patterns of Adjustment among Children of Battered Women." Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 68 (2000): 84-94. Abstract. PsycLIT. CD-ROM. Silverplatter. 23 July 2003.
FILM, VIDEO, OR FILM CLIP ONLINE "The Glory Suffered: The Transfiguration of the Cross." The History of the Orthodox Christian Church. 2003. GoTelecom Online. 24 Oct. 2003. Web. 5 April 2011.
BIBLE Bible. Revised Standard Version. Cleveland: Word Publishing Company, 1962. Print.
LECTURE Mitten, David M. "Greek Art and Architecture in the West: Southern Italy, Sicily, and Campania." Class lecture. Harvard University. Cambridge, 15 May 1989.
MUSIC Sting, narr. Peter and the Wolf, op. 67. By Sergei Prokofiev. Chamber Orch. of Europe. Cond. Claudio Abbado. Deutsche Grammophon, 1990.
Parenthetical Documentation
BASIC FORM (last name and page number) Dr. James is described as a "not-too-skeletal Ichabod Crane" (Johnson 68).
AUTHOR'S NAME IN TEXT Johnson describes Dr. James as a "not-too-skeletal Ichabod Crane" (68).
SOURCE BY TWO OR THREE AUTHORS The Authority-Rebel "tends to see himself as superior to other students in the class" (Dyal, Corning, and Willows 4).
A MULTIVOLUME WORK In the middle of several volumes of modern literary criticism, Rene Wellek admits, "An evolutionary history of criticism must fail. I have come to this resigned conclusion" (5: xxii).
ONE OF TWO (or more) WORKS BY THE SAME AUTHOR A friend of C. S. Lewis once said that Lewis "gave me not only love, but wisdom and understanding and, when necessary, severity" (Vanauken, Severe 21).
WORK LISTED ONLY BY THE TITLE (magazine article) An international pollution treaty would prohibit plastic garbage from being dumped at sea ("Awash" 26).
SECONDARY SOURCE THAT QUOTES THE ORIGINAL E. M. Forster says, "The collapse of all civilization, so realistic for us, sounded in Matthew Arnold's ears like a distant and harmonious cataract" (qtd. in Trilling 11).
INTERNET SOURCE Often there are no page numbers for the source, so indicate in the text who the author is. For example, Hershel Winthrop interprets Hawthorne's stories as the search for holiness in a corrupt Puritan society.
May 2012, compiled and updated by Karyn Hecht at Moody Bible Institute, Chicago
Need More Help?
Our staff of expert librarians are ready to lend you a hand.
© Moody Bible Institute | Privacy Policy
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA In-Text Citations: The Basics

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Guidelines for referring to the works of others in your text using MLA style are covered throughout the MLA Handbook and in chapter 7 of the MLA Style Manual . Both books provide extensive examples, so it's a good idea to consult them if you want to become even more familiar with MLA guidelines or if you have a particular reference question.
Basic in-text citation rules
In MLA Style, referring to the works of others in your text is done using parenthetical citations . This method involves providing relevant source information in parentheses whenever a sentence uses a quotation or paraphrase. Usually, the simplest way to do this is to put all of the source information in parentheses at the end of the sentence (i.e., just before the period). However, as the examples below will illustrate, there are situations where it makes sense to put the parenthetical elsewhere in the sentence, or even to leave information out.
General Guidelines
- The source information required in a parenthetical citation depends (1) upon the source medium (e.g. print, web, DVD) and (2) upon the source’s entry on the Works Cited page.
- Any source information that you provide in-text must correspond to the source information on the Works Cited page. More specifically, whatever signal word or phrase you provide to your readers in the text must be the first thing that appears on the left-hand margin of the corresponding entry on the Works Cited page.
In-text citations: Author-page style
MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the sentence itself or in parentheses following the quotation or paraphrase, but the page number(s) should always appear in the parentheses, not in the text of your sentence. For example:
Both citations in the examples above, (263) and (Wordsworth 263), tell readers that the information in the sentence can be located on page 263 of a work by an author named Wordsworth. If readers want more information about this source, they can turn to the Works Cited page, where, under the name of Wordsworth, they would find the following information:
Wordsworth, William. Lyrical Ballads . Oxford UP, 1967.
In-text citations for print sources with known author
For print sources like books, magazines, scholarly journal articles, and newspapers, provide a signal word or phrase (usually the author’s last name) and a page number. If you provide the signal word/phrase in the sentence, you do not need to include it in the parenthetical citation.
These examples must correspond to an entry that begins with Burke, which will be the first thing that appears on the left-hand margin of an entry on the Works Cited page:
Burke, Kenneth. Language as Symbolic Action: Essays on Life, Literature, and Method . University of California Press, 1966.
In-text citations for print sources by a corporate author
When a source has a corporate author, it is acceptable to use the name of the corporation followed by the page number for the in-text citation. You should also use abbreviations (e.g., nat'l for national) where appropriate, so as to avoid interrupting the flow of reading with overly long parenthetical citations.
In-text citations for sources with non-standard labeling systems
If a source uses a labeling or numbering system other than page numbers, such as a script or poetry, precede the citation with said label. When citing a poem, for instance, the parenthetical would begin with the word “line”, and then the line number or range. For example, the examination of William Blake’s poem “The Tyger” would be cited as such:
The speaker makes an ardent call for the exploration of the connection between the violence of nature and the divinity of creation. “In what distant deeps or skies. / Burnt the fire of thine eyes," they ask in reference to the tiger as they attempt to reconcile their intimidation with their relationship to creationism (lines 5-6).
Longer labels, such as chapters (ch.) and scenes (sc.), should be abbreviated.
In-text citations for print sources with no known author
When a source has no known author, use a shortened title of the work instead of an author name, following these guidelines.
Place the title in quotation marks if it's a short work (such as an article) or italicize it if it's a longer work (e.g. plays, books, television shows, entire Web sites) and provide a page number if it is available.
Titles longer than a standard noun phrase should be shortened into a noun phrase by excluding articles. For example, To the Lighthouse would be shortened to Lighthouse .
If the title cannot be easily shortened into a noun phrase, the title should be cut after the first clause, phrase, or punctuation:
In this example, since the reader does not know the author of the article, an abbreviated title appears in the parenthetical citation, and the full title of the article appears first at the left-hand margin of its respective entry on the Works Cited page. Thus, the writer includes the title in quotation marks as the signal phrase in the parenthetical citation in order to lead the reader directly to the source on the Works Cited page. The Works Cited entry appears as follows:
"The Impact of Global Warming in North America." Global Warming: Early Signs . 1999. www.climatehotmap.org/. Accessed 23 Mar. 2009.
If the title of the work begins with a quotation mark, such as a title that refers to another work, that quote or quoted title can be used as the shortened title. The single quotation marks must be included in the parenthetical, rather than the double quotation.
Parenthetical citations and Works Cited pages, used in conjunction, allow readers to know which sources you consulted in writing your essay, so that they can either verify your interpretation of the sources or use them in their own scholarly work.
Author-page citation for classic and literary works with multiple editions
Page numbers are always required, but additional citation information can help literary scholars, who may have a different edition of a classic work, like Marx and Engels's The Communist Manifesto . In such cases, give the page number of your edition (making sure the edition is listed in your Works Cited page, of course) followed by a semicolon, and then the appropriate abbreviations for volume (vol.), book (bk.), part (pt.), chapter (ch.), section (sec.), or paragraph (par.). For example:
Author-page citation for works in an anthology, periodical, or collection
When you cite a work that appears inside a larger source (for instance, an article in a periodical or an essay in a collection), cite the author of the internal source (i.e., the article or essay). For example, to cite Albert Einstein's article "A Brief Outline of the Theory of Relativity," which was published in Nature in 1921, you might write something like this:
See also our page on documenting periodicals in the Works Cited .
Citing authors with same last names
Sometimes more information is necessary to identify the source from which a quotation is taken. For instance, if two or more authors have the same last name, provide both authors' first initials (or even the authors' full name if different authors share initials) in your citation. For example:
Citing a work by multiple authors
For a source with two authors, list the authors’ last names in the text or in the parenthetical citation:
Corresponding Works Cited entry:
Best, David, and Sharon Marcus. “Surface Reading: An Introduction.” Representations , vol. 108, no. 1, Fall 2009, pp. 1-21. JSTOR, doi:10.1525/rep.2009.108.1.1
For a source with three or more authors, list only the first author’s last name, and replace the additional names with et al.
Franck, Caroline, et al. “Agricultural Subsidies and the American Obesity Epidemic.” American Journal of Preventative Medicine , vol. 45, no. 3, Sept. 2013, pp. 327-333.
Citing multiple works by the same author
If you cite more than one work by an author, include a shortened title for the particular work from which you are quoting to distinguish it from the others. Put short titles of books in italics and short titles of articles in quotation marks.
Citing two articles by the same author :
Citing two books by the same author :
Additionally, if the author's name is not mentioned in the sentence, format your citation with the author's name followed by a comma, followed by a shortened title of the work, and, when appropriate, the page number(s):
Citing multivolume works
If you cite from different volumes of a multivolume work, always include the volume number followed by a colon. Put a space after the colon, then provide the page number(s). (If you only cite from one volume, provide only the page number in parentheses.)
Citing the Bible
In your first parenthetical citation, you want to make clear which Bible you're using (and underline or italicize the title), as each version varies in its translation, followed by book (do not italicize or underline), chapter, and verse. For example:
If future references employ the same edition of the Bible you’re using, list only the book, chapter, and verse in the parenthetical citation:
John of Patmos echoes this passage when describing his vision (Rev. 4.6-8).
Citing indirect sources
Sometimes you may have to use an indirect source. An indirect source is a source cited within another source. For such indirect quotations, use "qtd. in" to indicate the source you actually consulted. For example:
Note that, in most cases, a responsible researcher will attempt to find the original source, rather than citing an indirect source.
Citing transcripts, plays, or screenplays
Sources that take the form of a dialogue involving two or more participants have special guidelines for their quotation and citation. Each line of dialogue should begin with the speaker's name written in all capitals and indented half an inch. A period follows the name (e.g., JAMES.) . After the period, write the dialogue. Each successive line after the first should receive an additional indentation. When another person begins speaking, start a new line with that person's name indented only half an inch. Repeat this pattern each time the speaker changes. You can include stage directions in the quote if they appear in the original source.
Conclude with a parenthetical that explains where to find the excerpt in the source. Usually, the author and title of the source can be given in a signal phrase before quoting the excerpt, so the concluding parenthetical will often just contain location information like page numbers or act/scene indicators.
Here is an example from O'Neill's The Iceman Cometh.
WILLIE. (Pleadingly) Give me a drink, Rocky. Harry said it was all right. God, I need a drink.
ROCKY. Den grab it. It's right under your nose.
WILLIE. (Avidly) Thanks. (He takes the bottle with both twitching hands and tilts it to his lips and gulps down the whiskey in big swallows.) (1.1)
Citing non-print or sources from the Internet
With more and more scholarly work published on the Internet, you may have to cite sources you found in digital environments. While many sources on the Internet should not be used for scholarly work (reference the OWL's Evaluating Sources of Information resource), some Web sources are perfectly acceptable for research. When creating in-text citations for electronic, film, or Internet sources, remember that your citation must reference the source on your Works Cited page.
Sometimes writers are confused with how to craft parenthetical citations for electronic sources because of the absence of page numbers. However, these sorts of entries often do not require a page number in the parenthetical citation. For electronic and Internet sources, follow the following guidelines:
- Include in the text the first item that appears in the Work Cited entry that corresponds to the citation (e.g. author name, article name, website name, film name).
- Do not provide paragraph numbers or page numbers based on your Web browser’s print preview function.
- Unless you must list the Web site name in the signal phrase in order to get the reader to the appropriate entry, do not include URLs in-text. Only provide partial URLs such as when the name of the site includes, for example, a domain name, like CNN.com or Forbes.com, as opposed to writing out http://www.cnn.com or http://www.forbes.com.
Miscellaneous non-print sources
Two types of non-print sources you may encounter are films and lectures/presentations:
In the two examples above “Herzog” (a film’s director) and “Yates” (a presentor) lead the reader to the first item in each citation’s respective entry on the Works Cited page:
Herzog, Werner, dir. Fitzcarraldo . Perf. Klaus Kinski. Filmverlag der Autoren, 1982.
Yates, Jane. "Invention in Rhetoric and Composition." Gaps Addressed: Future Work in Rhetoric and Composition, CCCC, Palmer House Hilton, 2002. Address.
Electronic sources
Electronic sources may include web pages and online news or magazine articles:
In the first example (an online magazine article), the writer has chosen not to include the author name in-text; however, two entries from the same author appear in the Works Cited. Thus, the writer includes both the author’s last name and the article title in the parenthetical citation in order to lead the reader to the appropriate entry on the Works Cited page (see below).
In the second example (a web page), a parenthetical citation is not necessary because the page does not list an author, and the title of the article, “MLA Formatting and Style Guide,” is used as a signal phrase within the sentence. If the title of the article was not named in the sentence, an abbreviated version would appear in a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence. Both corresponding Works Cited entries are as follows:
Taylor, Rumsey. "Fitzcarraldo." Slant , 13 Jun. 2003, www.slantmagazine.com/film/review/fitzcarraldo/. Accessed 29 Sep. 2009.
"MLA Formatting and Style Guide." The Purdue OWL , 2 Aug. 2016, owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/747/01/. Accessed 2 April 2018.
Multiple citations
To cite multiple sources in the same parenthetical reference, separate the citations by a semi-colon:
Time-based media sources
When creating in-text citations for media that has a runtime, such as a movie or podcast, include the range of hours, minutes and seconds you plan to reference. For example: (00:02:15-00:02:35).
When a citation is not needed
Common sense and ethics should determine your need for documenting sources. You do not need to give sources for familiar proverbs, well-known quotations, or common knowledge (For example, it is expected that U.S. citizens know that George Washington was the first President.). Remember that citing sources is a rhetorical task, and, as such, can vary based on your audience. If you’re writing for an expert audience of a scholarly journal, for example, you may need to deal with expectations of what constitutes “common knowledge” that differ from common norms.
Other Sources
The MLA Handbook describes how to cite many different kinds of authors and content creators. However, you may occasionally encounter a source or author category that the handbook does not describe, making the best way to proceed can be unclear.
In these cases, it's typically acceptable to apply the general principles of MLA citation to the new kind of source in a way that's consistent and sensible. A good way to do this is to simply use the standard MLA directions for a type of source that resembles the source you want to cite.
You may also want to investigate whether a third-party organization has provided directions for how to cite this kind of source. For example, Norquest College provides guidelines for citing Indigenous Elders and Knowledge Keepers —an author category that does not appear in the MLA Handbook . In cases like this, however, it's a good idea to ask your instructor or supervisor whether using third-party citation guidelines might present problems.
Generate accurate MLA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- A complete guide to MLA in-text citations
MLA In-text Citations | A Complete Guide (9th Edition)
Published on July 9, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on March 5, 2024.
An MLA in-text citation provides the author’s last name and a page number in parentheses.
If a source has two authors, name both. If a source has more than two authors, name only the first author, followed by “ et al. ”
If the part you’re citing spans multiple pages, include the full page range. If you want to cite multiple non-consecutive pages at the same time, separate the page numbers with commas.
| Number of authors | Example |
|---|---|
| 1 author | (Moore 37) |
| 2 authors | (Moore and Patel 48–50) |
| 3+ authors | (Moore et al. 59, 34) |
Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text.
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Where to include an mla in-text citation, citing sources with no author, citing sources with no page numbers, citing different sources with the same author name, citing sources indirectly, frequently asked questions about mla in-text citations.
Place the parenthetical citation directly after the relevant quote or paraphrase , and before the period or other punctuation mark (except with block quotes , where the citation comes after the period).
If you have already named the author in the sentence, add only the page number in parentheses. When mentioning a source with three or more authors outside of parentheses, use “and others” or “and colleagues” in place of “et al.”
- MLA is the second most popular citation style (Smith and Morrison 17–19) .
- According to Smith and Morrison , MLA is the second most popular citation style (17–19) .
- APA is by far “the most used citation style in the US” (Moore et al. 74) , but it is less dominant in the UK (Smith 16) .
- Moore and colleagues state that APA is more popular in the US than elsewhere (74) .
Combining citations
If a sentence is supported by more than one source, you can combine the citations in a single set of parentheses. Separate the two sources with a semicolon .
Livestock farming is one of the biggest global contributors to climate change (Garcia 64; Davies 14) .
Consecutive citations of the same source
If you cite the same source repeatedly within a paragraph, you can include the full citation the first time you cite it, then just the page number for subsequent citations.
MLA is the second most popular citation style (Smith and Morrison 17–19) . It is more popular than Chicago style, but less popular than APA (21) .
You can do this as long as it remains clear what source you’re citing. If you cite something else in between or start a new paragraph, reintroduce the full citation again to avoid ambiguity.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
For sources with no named author , the in-text citation must match the first element of the Works Cited entry. This may be the name of an organization, or the title of the source.
If the source title or organization name is longer than four words, shorten it to the first word or phrase in the in-text citation, excluding any articles ( a, an, and the ). The shortened title or organization name should begin with the word the source is alphabetized by in the Works Cited.
Follow the general MLA rules for formatting titles : If the source is a self-contained work (e.g. a whole website or an entire book ), put the title in italics; if the source is contained within a larger whole (e.g. a page on a website or a chapter of a book), put the title in quotation marks.
| Full source title or organization name | In-text citation |
|---|---|
| ( 187) | |
| “Sources of Greenhouse Gas Emissions” | (“Sources”) |
| “A Quick Guide to Proofreading” | (“Quick Guide”) |
| National Academy of Sciences and the Royal Academy | (National Academy 24) |
If a source does not have page numbers but is divided into numbered parts (e.g. chapters, sections, scenes, Bible books and verses, Articles of the Constitution , or timestamps), use these numbers to locate the relevant passage.
If the source does not use any numbering system, include only the author’s name in the in-text citation. Don’t include paragraph numbers unless they are explicitly numbered in the source.
| Source type | What to do | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Source divided into numbered parts | Add a comma after the author and give a paragraph, section, or chapter number with a relevant abbreviation. | (Luxemburg, ch. 26) |
| with numbered lines | Include the act, scene, and line numbers, separated by periods, instead of a page number. | ( 1.2.95) |
| Audiovisual source | Include the time range as displayed in the media player. | (Wynn 10:23–45) |
| Source with no numbered divisions | Include only the author’s name (or, if there is no author, the shortened title). | (Rajaram) |
Note that if there are no numbered divisions and you have already named the author in your sentence, then no parenthetical citation is necessary.
If your Works Cited page includes more than one entry under the same last name, you need to distinguish between these sources in your in-text citations.
Multiple sources by the same author
If you cite more than one work by the same author, add a shortened title to signal which source you are referring to.
In this example, the first source is a whole book, so the title appears in italics; the second is an article published in a journal, so the title appears in quotation marks.
Different authors with the same last name
To distinguish between different authors with the same last name, use the authors’ initials (or, if the initials are the same, full first names) in your in-text citations:
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Sometimes you might want to cite something that you found quoted in a secondary source . If possible, always seek out the original source and cite it directly.
If you can’t access the original source, make sure to name both the original author and the author of the source that you accessed . Use the abbreviation “qtd. in” (short for “quoted in”) to indicate where you found the quotation.
In these cases, only the source you accessed directly is included in the Works Cited list.
You must include an MLA in-text citation every time you quote or paraphrase from a source (e.g. a book , movie , website , or article ).
Some source types, such as books and journal articles , may contain footnotes (or endnotes) with additional information. The following rules apply when citing information from a note in an MLA in-text citation :
- To cite information from a single numbered note, write “n” after the page number, and then write the note number, e.g. (Smith 105n2)
- To cite information from multiple numbered notes, write “nn” and include a range, e.g. (Smith 77nn1–2)
- To cite information from an unnumbered note, write “un” after the page number, with a space in between, e.g. (Jones 250 un)
If a source has two authors, name both authors in your MLA in-text citation and Works Cited entry. If there are three or more authors, name only the first author, followed by et al.
| Number of authors | In-text citation | Works Cited entry |
|---|---|---|
| 1 author | (Moore 37) | Moore, Jason W. |
| 2 authors | (Moore and Patel 37) | Moore, Jason W., and Raj Patel. |
| 3+ authors | (Moore et al. 37) | Moore, Jason W., et al. |
If a source has no author, start the MLA Works Cited entry with the source title . Use a shortened version of the title in your MLA in-text citation .
If a source has no page numbers, you can use an alternative locator (e.g. a chapter number, or a timestamp for a video or audio source) to identify the relevant passage in your in-text citation. If the source has no numbered divisions, cite only the author’s name (or the title).
If you already named the author or title in your sentence, and there is no locator available, you don’t need a parenthetical citation:
- Rajaram argues that representations of migration are shaped by “cultural, political, and ideological interests.”
- The homepage of The Correspondent describes it as “a movement for radically different news.”
Yes. MLA style uses title case, which means that all principal words (nouns, pronouns , verbs, adjectives , adverbs , and some conjunctions ) are capitalized.
This applies to titles of sources as well as the title of, and subheadings in, your paper. Use MLA capitalization style even when the original source title uses different capitalization .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2024, March 05). MLA In-text Citations | A Complete Guide (9th Edition). Scribbr. Retrieved August 30, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/mla/in-text-citations/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to format your mla works cited page, block quoting in mla style, how to cite a book in mla, what is your plagiarism score.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
MLA General Format MLA Style specifies guidelines for formatting manuscripts and citing research in writing. MLA Style also provides writers with a system for referencing their sources through parenthetical citation in their essays and Works Cited pages.
The MLA Handbook provides guidelines for creating MLA citations and formatting academic papers. This includes advice on structuring parenthetical citations, the Works Cited page, and tables and figures. This quick guide will help you set up your MLA format paper in no time.
This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use. This resource contains a sample MLA paper that adheres to the 2016 updates. To download the MLA sample paper, click this link.
MLA title page format. To create an MLA format title page, list the following on separate lines, left-aligned at the top of the page: Then leave a few blank lines and list the title of the paper, centered and in title case, halfway down the page. All text should be double-spaced and in the same font as the rest of the paper.
How to Format Your MLA Cover Page: This page is double spaced and the letters are centered. The first letter of each word should be capitalized with the exception of very short words such as: the, and, of, or, a, an, in, to, for. Note: the first letter of the first word should be capitalized, regardless of what kind of word it is.
MLA format recommends adding an MLA heading to the first page of your paper. This contains the same information as a title page, but the information is formatted differently and is on the same page on which your actual research paper begins.
MLA Style Guide, 8th & 9th Editions: Formatting Your MLA Paper MLA recommends using 12-point Times New Roman font or another readable typeface (e.g. serif ).
Learn how to create an impeccable MLA title page for your academic paper. Find steps to format your cover page and get some MLA title page examples.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Learn how to format your student paper using MLA 9th edition. Step-by-step explainer with examples and a free MLA template.
Learn how to format your MLA paper according to the 9th edition of the MLA Handbook, with examples and tips from Taft College librarians.
The MLA heading appears at the top of the first page of an MLA formatted paper and contains similar information to a title page: your name, instructor's name, class or course name, and date.
While MLA format calls for the header to appear on the first page, some instructors may ask that there be no header on the first page since your name is already there. To remove the header from the first page, check Different first page in the Header tool. These instructions may work for higher versions of Works.
Formatting the Header in MLA. To create a header for your first page, follow these steps: Begin one inch from the top of the first page and flush with the left margin. Type your name, your instructor's name, the course name and number, and the date on separate lines, using double spaces between each.
This page contains guidelines on how to properly format the headings of your research paper using the MLA format. 1. The Opening Page: On the opening page or the first page, you would include the whole heading and your paper's title. The whole heading would include the following information: Your Name Your Instructor's Name Your.
Learn how to create an MLA header for your paper, including what to include and how to format it. Scribbr provides clear examples and tips.
A cover page is the first page of a paper or report that lists basic information, such as the title, author (s), course name, instructor, date, and sometimes the name of the institution. Also known as a title page, a cover page is a requirement of some formatting styles. But certain instructors or assignments may request them regardless of the style requirements.
The first page of a paper written in MLA format includes the following components: Page header in the upper right-hand corner. Half an inch from the top of the page and flush with the right margin, type your last name, a space, and then insert the page number. Name and course information in left corner.
MLA format is a set of formatting and citation guidelines for how an academic paper should look, similar to other styles such as Chicago or APA format. We use MLA format for topics in the humanities, including languages, philosophy, and the arts, but not history (which uses Chicago) or the social sciences, like psychology or education (which use APA format).
This article will explain MLA style citation, give examples of MLA formatting for specific aspects of references, provide an MLA format example for each category of source material, and share essay formatting tips that our editors have learned over the years.
Make sure your paper also adheres to MLA format: one-inch margins, double spacing, and indented paragraphs, with an MLA style heading on the first page. You can create citations automatically with our free MLA Citation Generator. Enter a URL, DOI, or ISBN, and the generator will retrieve the necessary information.
MLA Style Sheet General Guidelines. Please also visit the Academic Integrity LibGuide, which provides a Citation guide for your information.. Everything in the paper is double-spaced: works cited, indented quotes, etc.; Pagination: student's last name and the page number are placed on each page's upper right-hand corner. Quotes that are more than four lines long are indented one inch from the ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
An MLA in-text citation provides the author's last name and a page number in parentheses.