- Starting Your Business How To Create a Full-Fledged Ecommerce Website: 7 Steps October 25, 2022
- Starting Your Business Omnichannel E-commerce: What You Need to Succeed October 28, 2022
- Starting Your Business The Guide To Opening An Online Retail Store [With 8 Steps To Follow] October 28, 2022

Digital transformation in banking: A complete guide

August 02, 2023
Digital transformation is a challenge for the banking industry, but it is necessary to adapt to the modern world where customers expect fast, efficient, and convenient services. Traditional approaches no longer meet the needs of the modern consumer. So, banks that want to remain competitive must abandon conservative methods and fully immerse themselves in the process of digital transformation.
This article discusses what is digital transformation in banking, key factors driving digital transformation , and successful examples of digital transformation in the banking industry.
What is digital transformation in banking?
5 key factors driving digital transformation in banking, technologies that drive digital transformation in banking, successful examples of digital transformation in the banking industry, how can soloway tech help you digitally transform your business.

Digital transformation in banking refers to applying new digital technologies and strategies to change and improve banking operations. This includes various changes to increase efficiency, meet customer needs, improve operational effectiveness, and develop new digital products and services.
Mobile applications and personal cabinets on the website are vivid examples of banks’ digital transformation. It is enough to press the buttons on a smartphone or computer to open an account, take out a loan, or order a new plastic card. The services are available not only to individuals but also to legal entities. The accounting departments use client-bank programs to transfer salaries to employees, pay taxes, and receive money from customers.
When you call the hotline of your financial organization, you are answered not by a specialist but by a robot. Virtual assistants have replaced some employees. Moreover, some US banks operate without branches at all. There are employees only in the head office, and customer transactions are conducted exclusively through the Internet.
It is more convenient for people to work with banks remotely, so credit institutions invest a lot of money in digital transformation. It is important that the interface of applications is user-friendly and understandable and transactions are fast. This will attract more customers and, accordingly, increase the profits of the financial company.
Pros and cons of digital transformation in banking
Digital transformation in banking is developing at a rapid pace. It has objective advantages:
- Services of financial organizations are available from anywhere in the world
- The cost of remote operations is cheaper
- There are no queues
- Improved customer service
- Improved operational efficiency
- Big Data and analytics
- Innovation and new opportunities
But there are disadvantages too:
- Dependence on the Internet
- Vulnerability of security systems and regular hacker attacks
- Inaccessibility for some customers
- Threat of job losses
- Dependence on technology
Technology should become a tool that will give banks more flexibility in decision-making and reduce risks.
Fintech companies, which have recently created large-scale services with significantly more interaction points with the client than the classic banking business, are taking the lead. Given that over the last 10 years, the banking industry has experienced a serious tightening of regulatory requirements, fintech is becoming a severe competitor for banks. The solution that banks have found is to change their business model with a focus on digitalization, create their own ecosystems, and develop non-financial services.
Ecosystems are a new global standard for business development and a major stage in the development of the economy. They aggregate data on producers and consumers and help optimize the resources of both. There is no turning back. Creating ecosystems seems to be a common vertical integration strategy for banks when related businesses are pulled up to the core business.
We highlight 5 key factors driving digital transformation in banking:
- Customer experience. Providing convenience and personalization for customers is a crucial factor in digital transformation. Banks should develop and implement innovative digital channels, such as mobile apps, online banking, chatbots, and others, to facilitate access to financial services and improve customer satisfaction.
- Automation and process optimization. The use of automation technologies, such as robo-advisors, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, helps reduce routine operations, lower costs, and improve efficiency. This can include automating lending, foreign exchange, internal audit, and more.
- Evolving regulatory landscape. Regulatory changes and initiatives have pushed banks to adopt digital transformation. Open banking regulations, data protection regulations (such as GDPR), and initiatives promoting competition and innovation have compelled banks to invest in technology to comply with regulations, foster innovation, and enhance transparency.
- Competitive pressure. Fintech startups and tech giants have disrupted the traditional banking landscape. These non-traditional players offer innovative and agile financial services, posing a competitive threat to traditional banks. To remain competitive, banks invest in digital technologies to improve their offerings, provide unique value propositions, and stay ahead of the competition.
- Enhanced customer insights. Digital transformation enables banks to gain deeper insights into customer behavior, preferences, and needs. By analyzing customer data, banks can offer personalized services, targeted marketing campaigns, and customized product recommendations, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
These factors interact with each other and require a comprehensive approach for successful digital transformation in the banking industry.
An important point is cybercrime. The emergence of new technologies has left hackers with many loopholes for hacking into networks and devices. At the current growth rate, cyberattack damage will amount to about $10.5 trillion annually by 2025 —a 300% increase from 2015.
However, cyber threats are not slowing down digital transformation. On the contrary, they drive it (this applies to banks and other organizations). The search for vulnerabilities is a never-ending process that contributes to developing security systems.
The main principle of the fight against cybercrime in many banks is that the fight should be at all levels. It means from the protection of external perimeters to specific systems at specific addresses and ports. This includes protection against DoS attacks, firewalls, full control of the bank’s systems, control of viruses to avoid data leakage, etc.
Technologies are evolving at an incredible pace. Artificial Intelligence (AI), Big Data, Blockchain, and other innovations transform how we live, work, and do business.
For example, artificial intelligence allows banks to automate processes and make customer interaction more personalized and efficient. Machine learning can analyze large amounts of data, identify patterns and trends that help make better decisions and predict risks. Machine learning and neural networks also greatly help in document recognition and remote customer verification.
Big Data analysis is becoming a valuable tool in the banking sector, allowing banks to identify patterns, trends, and useful insights hidden in huge amounts of data. It can be used to develop personalized products and services, improve decision-making, detect fraud , and understand and predict customer behavior.
Blockchain is another innovative technology that can tremendously change the banking industry. Most of the current problems in the banking sector are related to the human factor. In particular, they include high commission costs and time spent on money transfers and transactions, internal and external fraud, human error, leakage of personal data, and much more. There are several main areas where blockchain technology can be used in the banking industry:
- Smart contracts
- International payments, settlements for foreign trade transactions, and internal payments
- Transactions with securities
- National digital currency
Other technologies that drive digital transformation in banking include Cloud Computing, Internet of Things (IoT), Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Biometrics, and Open Banking APIs.
Many success stories of digital transformation in banking demonstrate how digitalization improves customer banking experience and operational efficiency. For example:
- DBS Bank (Singapore). DBS Bank is considered one of the leaders in digital transformation. They have developed a digital platform, DBS Digibank, which provides customers with a wide range of banking services through mobile apps and online banking. They actively use artificial intelligence and analytics to provide personalized recommendations and improve customer experience.
- JPMorgan Chase (USA). JPMorgan Chase has embraced digital transformation to improve operational efficiency and customer service. They have developed their proprietary digital platform, Chase Mobile Banking, which allows customers to perform various banking transactions through mobile devices. They also actively apply machine learning and analytics to better analyze data and deliver services.
- ING Bank (Netherlands). ING Bank has moved from a traditional bank to a digital organization. They provide customers convenient online services and mobile apps and actively use data analytics to provide personalized offers and improve customer experience. They have also implemented digital tools within the bank to streamline processes and improve efficiency.
- BBVA (Spain). BBVA focused on digital transformation and innovation to improve customer experience and banking processes. They developed the BBVA Digital Banking platform, which provides customers with a wide range of services through mobile apps and online banking. They have also implemented blockchain technology to improve the security and efficiency of financial transactions.
- Ally Bank (USA). Ally Bank is an example of a successful digital transformation. They provide a full range of banking services through an online platform, including account opening, lending, investments, and mortgages. Ally Bank actively utilizes digital channels and tools to provide convenience and accessibility to customers.
These examples demonstrate how banks use digital technologies to increase the availability of services, improve customer experience, and optimize their operations.

At SoloWay Tech, we specialize in providing comprehensive digital transformation and consulting services to help businesses thrive in the digital age. With our expertise and industry knowledge, we can guide your organization through the complex digital transformation process, enabling you to unlock new opportunities and achieve sustainable growth. We can:
- Consult regarding the digital transformation of your business
- Develop a digital transformation strategy
- Design digital customer experience
- Optimize business processes
- Automate business processes
- Re-engineer legacy apps
- Develop innovative products and services
- Implement end-to-end ML and AI engines
- Engineer IoT
- Build Big Data infrastructure
- Consult regarding the best implementation of IT infrastructure in your business.
At SoloWay Tech, we understand that each business has unique challenges and requirements. Our collaborative approach, deep industry expertise, and proven methodologies empower us to tailor our services to your specific needs, enabling you to achieve sustainable growth and competitive advantage through digital transformation.
Embark on your digital transformation journey with SoloWay Tech and unlock the full potential of your business in the digital era. Contact us today to learn more about our services and how we can help you drive innovation, efficiency, and success.
Digital transformation has become imperative for the banking industry to adapt to the evolving needs and expectations of customers in the modern world. The shift towards digitalization offers numerous advantages, such as enhanced customer experiences, improved operational efficiency, access to Big Data analytics, and new opportunities for innovation. However, there are also challenges to consider, including cybersecurity risks, potential job losses, and dependence on technology.
To embark on a successful digital transformation journey, businesses may seek the expertise of companies like SoloWay Tech that specialize in assisting organizations in their digitalization efforts. With the right guidance and implementation strategies, banks can harness the power of digital technologies to stay competitive, meet customer expectations, and drive innovation in the ever-evolving banking landscape.
Similar articles

Finance 2025: Digital Transformation in Finance

How To Develop A Blockchain Mobile App: Examples And Development Process

Blockchain Game Development: How to Use Blockchain Technology in Gaming Industry

Digitizing Customer Experience: Step-by-Step Guide for Business Success
We use cookies to provide you with a better on website experience, privacy setting.
This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website.
View the Cookie Policy

Fill the form below and Do your Solo
Company name, how can we help you.
About Stanford GSB
- The Leadership
- Dean’s Updates
- School News & History
- Commencement
- Business, Government & Society
- Centers & Institutes
- Center for Entrepreneurial Studies
- Center for Social Innovation
- Stanford Seed
About the Experience
- Learning at Stanford GSB
- Experiential Learning
- Guest Speakers
- Entrepreneurship
- Social Innovation
- Communication
- Life at Stanford GSB
- Collaborative Environment
- Activities & Organizations
- Student Services
- Housing Options
- International Students
Full-Time Degree Programs
- Why Stanford MBA
- Academic Experience
- Financial Aid
- Why Stanford MSx
- Research Fellows Program
- See All Programs
Non-Degree & Certificate Programs
- Executive Education
- Stanford Executive Program
- Programs for Organizations
- The Difference
- Online Programs
- Stanford LEAD
- Seed Transformation Program
- Aspire Program
- Seed Spark Program
- Faculty Profiles
- Academic Areas
- Awards & Honors
- Conferences
Faculty Research
- Publications
- Working Papers
- Case Studies
Research Hub
- Research Labs & Initiatives
- Business Library
- Data, Analytics & Research Computing
- Behavioral Lab
Research Labs
- Cities, Housing & Society Lab
- Golub Capital Social Impact Lab
Research Initiatives
- Corporate Governance Research Initiative
- Corporations and Society Initiative
- Policy and Innovation Initiative
- Rapid Decarbonization Initiative
- Stanford Latino Entrepreneurship Initiative
- Value Chain Innovation Initiative
- Venture Capital Initiative
- Career & Success
- Climate & Sustainability
- Corporate Governance
- Culture & Society
- Finance & Investing
- Government & Politics
- Leadership & Management
- Markets and Trade
- Operations & Logistics
- Opportunity & Access
- Technology & AI
- Opinion & Analysis
- Email Newsletter
Welcome, Alumni
- Communities
- Digital Communities & Tools
- Regional Chapters
- Women’s Programs
- Identity Chapters
- Find Your Reunion
- Career Resources
- Job Search Resources
- Career & Life Transitions
- Programs & Webinars
- Career Video Library
- Alumni Education
- Research Resources
- Volunteering
- Alumni News
- Class Notes
- Alumni Voices
- Contact Alumni Relations
- Upcoming Events
Admission Events & Information Sessions
- MBA Program
- MSx Program
- PhD Program
- Alumni Events
- All Other Events
- Operations, Information & Technology
- Organizational Behavior
- Political Economy
- Classical Liberalism
- The Eddie Lunch
- Accounting Summer Camp
- California Econometrics Conference
- California Quantitative Marketing PhD Conference
- California School Conference
- China India Insights Conference
- Homo economicus, Evolving
- Political Economics (2023–24)
- Scaling Geologic Storage of CO2 (2023–24)
- A Resilient Pacific: Building Connections, Envisioning Solutions
- Adaptation and Innovation
- Changing Climate
- Civil Society
- Climate Impact Summit
- Climate Science
- Corporate Carbon Disclosures
- Earth’s Seafloor
- Environmental Justice
- Operations and Information Technology
- Organizations
- Sustainability Reporting and Control
- Taking the Pulse of the Planet
- Urban Infrastructure
- Watershed Restoration
- Junior Faculty Workshop on Financial Regulation and Banking
- Ken Singleton Celebration
- Marketing Camp
- Quantitative Marketing PhD Alumni Conference
- Presentations
- Theory and Inference in Accounting Research
- Stanford Closer Look Series
- Quick Guides
- Core Concepts
- Journal Articles
- Glossary of Terms
- Faculty & Staff
- Researchers & Students
- Research Approach
- Charitable Giving
- Financial Health
- Government Services
- Workers & Careers
- Short Course
- Adaptive & Iterative Experimentation
- Incentive Design
- Social Sciences & Behavioral Nudges
- Bandit Experiment Application
- Conferences & Events
- Get Involved
- Reading Materials
- Teaching & Curriculum
- Energy Entrepreneurship
- Faculty & Affiliates
- SOLE Report
- Responsible Supply Chains
- Current Study Usage
- Pre-Registration Information
- Participate in a Study
Lloyds Banking Group: Digital Transformation
Learning objective.

- See the Current DEI Report
- Supporting Data
- Research & Insights
- Share Your Thoughts
- Search Fund Primer
- Affiliated Faculty
- Faculty Advisors
- Louis W. Foster Resource Center
- Defining Social Innovation
- Impact Compass
- Global Health Innovation Insights
- Faculty Affiliates
- Student Awards & Certificates
- Changemakers
- Dean Jonathan Levin
- Dean Garth Saloner
- Dean Robert Joss
- Dean Michael Spence
- Dean Robert Jaedicke
- Dean Rene McPherson
- Dean Arjay Miller
- Dean Ernest Arbuckle
- Dean Jacob Hugh Jackson
- Dean Willard Hotchkiss
- Faculty in Memoriam
- Stanford GSB Firsts
- Class of 2024 Candidates
- Certificate & Award Recipients
- Dean’s Remarks
- Keynote Address
- Teaching Approach
- Analysis and Measurement of Impact
- The Corporate Entrepreneur: Startup in a Grown-Up Enterprise
- Data-Driven Impact
- Designing Experiments for Impact
- Digital Marketing
- The Founder’s Right Hand
- Marketing for Measurable Change
- Product Management
- Public Policy Lab: Financial Challenges Facing US Cities
- Public Policy Lab: Homelessness in California
- Lab Features
- Curricular Integration
- View From The Top
- Formation of New Ventures
- Managing Growing Enterprises
- Startup Garage
- Explore Beyond the Classroom
- Stanford Venture Studio
- Summer Program
- Workshops & Events
- The Five Lenses of Entrepreneurship
- Leadership Labs
- Executive Challenge
- Arbuckle Leadership Fellows Program
- Selection Process
- Training Schedule
- Time Commitment
- Learning Expectations
- Post-Training Opportunities
- Who Should Apply
- Introductory T-Groups
- Leadership for Society Program
- Certificate
- 2024 Awardees
- 2023 Awardees
- 2022 Awardees
- 2021 Awardees
- 2020 Awardees
- 2019 Awardees
- 2018 Awardees
- Social Management Immersion Fund
- Stanford Impact Founder Fellowships
- Stanford Impact Leader Prizes
- Social Entrepreneurship
- Stanford GSB Impact Fund
- Economic Development
- Energy & Environment
- Stanford GSB Residences
- Environmental Leadership
- Stanford GSB Artwork
- A Closer Look
- California & the Bay Area
- Voices of Stanford GSB
- Business & Beneficial Technology
- Business & Sustainability
- Business & Free Markets
- Business, Government, and Society Forum
- Second Year
- Global Experiences
- JD/MBA Joint Degree
- MA Education/MBA Joint Degree
- MD/MBA Dual Degree
- MPP/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Computer Science/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Electrical Engineering/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Environment and Resources (E-IPER)/MBA Joint Degree
- Academic Calendar
- Clubs & Activities
- LGBTQ+ Students
- Military Veterans
- Minorities & People of Color
- Partners & Families
- Students with Disabilities
- Student Support
- Residential Life
- Student Voices
- MBA Alumni Voices
- A Week in the Life
- Career Support
- Employment Outcomes
- Cost of Attendance
- Knight-Hennessy Scholars Program
- Yellow Ribbon Program
- BOLD Fellows Fund
- Application Process
- Loan Forgiveness
- Contact the Financial Aid Office
- Evaluation Criteria
- GMAT & GRE
- English Language Proficiency
- Personal Information, Activities & Awards
- Professional Experience
- Letters of Recommendation
- Optional Short Answer Questions
- Application Fee
- Reapplication
- Deferred Enrollment
- Joint & Dual Degrees
- Entering Class Profile
- Event Schedule
- Ambassadors
- New & Noteworthy
- Ask a Question
- See Why Stanford MSx
- Is MSx Right for You?
- MSx Stories
- Leadership Development
- How You Will Learn
- Admission Events
- Personal Information
- GMAT, GRE & EA
- English Proficiency Tests
- Career Change
- Career Advancement
- Daycare, Schools & Camps
- U.S. Citizens and Permanent Residents
- Requirements
- Requirements: Behavioral
- Requirements: Quantitative
- Requirements: Macro
- Requirements: Micro
- Annual Evaluations
- Field Examination
- Research Activities
- Research Papers
- Dissertation
- Oral Examination
- Current Students
- Education & CV
- International Applicants
- Statement of Purpose
- Reapplicants
- Application Fee Waiver
- Deadline & Decisions
- Job Market Candidates
- Academic Placements
- Stay in Touch
- Faculty Mentors
- Current Fellows
- Standard Track
- Fellowship & Benefits
- Group Enrollment
- Program Formats
- Developing a Program
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Strategic Transformation
- Program Experience
- Contact Client Services
- Campus Experience
- Live Online Experience
- Silicon Valley & Bay Area
- Digital Credentials
- Faculty Spotlights
- Participant Spotlights
- Eligibility
- International Participants
- Stanford Ignite
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Founding Donors
- Location Information
- Participant Profile
- Network Membership
- Program Impact
- Collaborators
- Entrepreneur Profiles
- Company Spotlights
- Seed Transformation Network
- Responsibilities
- Current Coaches
- How to Apply
- Meet the Consultants
- Meet the Interns
- Intern Profiles
- Collaborate
- Research Library
- News & Insights
- Program Contacts
- Databases & Datasets
- Research Guides
- Consultations
- Research Workshops
- Career Research
- Research Data Services
- Course Reserves
- Course Research Guides
- Material Loan Periods
- Fines & Other Charges
- Document Delivery
- Interlibrary Loan
- Equipment Checkout
- Print & Scan
- MBA & MSx Students
- PhD Students
- Other Stanford Students
- Faculty Assistants
- Research Assistants
- Stanford GSB Alumni
- Telling Our Story
- Staff Directory
- Site Registration
- Alumni Directory
- Alumni Email
- Privacy Settings & My Profile
- Success Stories
- The Story of Circles
- Support Women’s Circles
- Stanford Women on Boards Initiative
- Alumnae Spotlights
- Insights & Research
- Industry & Professional
- Entrepreneurial Commitment Group
- Recent Alumni
- Half-Century Club
- Fall Reunions
- Spring Reunions
- MBA 25th Reunion
- Half-Century Club Reunion
- Faculty Lectures
- Ernest C. Arbuckle Award
- Alison Elliott Exceptional Achievement Award
- ENCORE Award
- Excellence in Leadership Award
- John W. Gardner Volunteer Leadership Award
- Robert K. Jaedicke Faculty Award
- Jack McDonald Military Service Appreciation Award
- Jerry I. Porras Latino Leadership Award
- Tapestry Award
- Student & Alumni Events
- Executive Recruiters
- Interviewing
- Land the Perfect Job with LinkedIn
- Negotiating
- Elevator Pitch
- Email Best Practices
- Resumes & Cover Letters
- Self-Assessment
- Whitney Birdwell Ball
- Margaret Brooks
- Bryn Panee Burkhart
- Margaret Chan
- Ricki Frankel
- Peter Gandolfo
- Cindy W. Greig
- Natalie Guillen
- Carly Janson
- Sloan Klein
- Sherri Appel Lassila
- Stuart Meyer
- Tanisha Parrish
- Virginia Roberson
- Philippe Taieb
- Michael Takagawa
- Terra Winston
- Johanna Wise
- Debbie Wolter
- Rebecca Zucker
- Complimentary Coaching
- Changing Careers
- Work-Life Integration
- Career Breaks
- Flexible Work
- Encore Careers
- Join a Board
- D&B Hoovers
- Data Axle (ReferenceUSA)
- EBSCO Business Source
- Global Newsstream
- Market Share Reporter
- ProQuest One Business
- RKMA Market Research Handbook Series
- Student Clubs
- Entrepreneurial Students
- Stanford GSB Trust
- Alumni Community
- How to Volunteer
- Springboard Sessions
- Consulting Projects
- 2020 – 2029
- 2010 – 2019
- 2000 – 2009
- 1990 – 1999
- 1980 – 1989
- 1970 – 1979
- 1960 – 1969
- 1950 – 1959
- 1940 – 1949
- Service Areas
- ACT History
- ACT Awards Celebration
- ACT Governance Structure
- Building Leadership for ACT
- Individual Leadership Positions
- Leadership Role Overview
- Purpose of the ACT Management Board
- Contact ACT
- Business & Nonprofit Communities
- Reunion Volunteers
- Ways to Give
- Fiscal Year Report
- Business School Fund Leadership Council
- Planned Giving Options
- Planned Giving Benefits
- Planned Gifts and Reunions
- Legacy Partners
- Giving News & Stories
- Giving Deadlines
- Development Staff
- Submit Class Notes
- Class Secretaries
- Board of Directors
- Health Care
- Sustainability
- Class Takeaways
- All Else Equal: Making Better Decisions
- If/Then: Business, Leadership, Society
- Grit & Growth
- Think Fast, Talk Smart
- Spring 2022
- Spring 2021
- Autumn 2020
- Summer 2020
- Winter 2020
- In the Media
- For Journalists
- DCI Fellows
- Other Auditors
- Academic Calendar & Deadlines
- Course Materials
- Entrepreneurial Resources
- Campus Drive Grove
- Campus Drive Lawn
- CEMEX Auditorium
- King Community Court
- Seawell Family Boardroom
- Stanford GSB Bowl
- Stanford Investors Common
- Town Square
- Vidalakis Courtyard
- Vidalakis Dining Hall
- Catering Services
- Policies & Guidelines
- Reservations
- Contact Faculty Recruiting
- Lecturer Positions
- Postdoctoral Positions
- Accommodations
- CMC-Managed Interviews
- Recruiter-Managed Interviews
- Virtual Interviews
- Campus & Virtual
- Search for Candidates
- Think Globally
- Recruiting Calendar
- Recruiting Policies
- Full-Time Employment
- Summer Employment
- Entrepreneurial Summer Program
- Global Management Immersion Experience
- Social-Purpose Summer Internships
- Process Overview
- Project Types
- Client Eligibility Criteria
- Client Screening
- ACT Leadership
- Social Innovation & Nonprofit Management Resources
- Develop Your Organization’s Talent
- Centers & Initiatives
- Student Fellowships
Banking on data
How Siam Commercial Bank reimagined data to drive value.
Call for change
Every day, banks generate terabytes of data—information from transactions, loan applications and more. Even a simple customer action, such as making a deposit at their local branch, creates a data point that banks can use to better understand customer needs and identify marketplace trends.
Siam Commercial Bank (SCB), the third-largest bank in Thailand by asset size, wanted to unlock the value of its data to enhance experiences for consumers, optimize operations and fuel future growth. The bank’s main repository of data—its data warehouse—was hosted on premises and outdated technology, making it costly to manage, and was limited in its ability to scale. The lake also wasn’t equipped to handle new types of unstructured data. These lake limitations prevented the bank from using more advanced data analytics to derive key insights and drive decisions.
SCB wanted to be a pioneer amongst its peers and set out on an ongoing, multi-year transformation journey to jumpstart the business. At the heart of the project was the desire to use a constant stream of data-derived insights to reinvent its approach and customer experience.

When tech meets human ingenuity
SCB partnered with Accenture to develop and deliver an award-winning digital transformation strategy. The approach combined advanced data and analytics capabilities with people-focused processes and tools.
The first step was shoring up the data lake—migrating the bank's foundational data repository to Microsoft Azure Cloud, making SCB the first bank in the region to achieve this milestone.
The team also made data and analytics easier to access and use by deploying Microsoft Power BI to create interactive dashboards for several business areas. To improve ATM cash management, the team used artificial intelligence and a combination of advanced machine learning techniques to analyze more than 12 million transactional data points and more than 200 variables—such as locations, pay days, seasons and holidays—to determine optimal cash levels for each ATM.
Creating a data-driven culture takes more than just new technologies and analytics. It requires data governance and change management to help employees adapt to new ways of working. Creating a Data Governance Office, an Analytics Center of Excellence and a bank-wide data stewardship program helped implement clear guidelines for effective and secure use of data and analytics.
Now, marketers can access insights from this data on interactive Power BI dashboards to identify and craft personalized marketing messages for prospects based on their lifestyles, interests and financial needs. Also, automated underwriting risk tools reduce time to process loan applications.
A valuable difference
Having achieved impressive results with their digital transformation efforts, the International Data Corporation (IDC) recognized the team with its Information Visionary in Thailand award in 2019.
Replacing the old data lake and migrating the new lake to the cloud reduced the bank’s data storage costs, while enabling specific functions for retail banking to apply customer insights to serve their customized needs.
Automating daily forecasts for ATM cash management began producing savings within eight weeks from idea to execution and achieved 98.8% ATM service levels with 50% less cash balance. Reducing both the amount of cash in ATM circulation and delivery costs for ATM replenishment. Centralizing institutional knowledge also ensured that insights are retained within the bank to support knowledge retention and continuous improvement.
In addition, SCB’s innovative approach to increasing unsecured lending business is getting results. Data-driven digital marketing generated 10% more campaign responses and a 3x improvement on the model. Automation reduced manual processes by 40%, improved accuracy and accelerated loan approvals and processing, securing higher customer satisfaction while effectively managing risks.
Reduction in data storage due to compression techniques
Improvement to ATM service levels
We are very grateful for the opportunity to work with SCB on this award winning, strategic transformation journey over the years.
Joon Seong Lee / ASIAM, SEA & Innovation Lead, Strategy & Consulting
ITTI UX Case Study: Next-Gen Core Banking Digital Transformation in the Cloud

The banking software vendor company, ITTI Digital, has undergone a massive transformation. They partnered with UXDA to move a 15-year-old core banking solution into the cloud. This core banking digital transformation has ensured a dramatic increase in banking's service speed, employee productivity and customer satisfaction. The learning curve of banking employees has been reduced from several weeks to a few hours. Also, the potential for costly human errors has been significantly decreased. The new cloud-based core banking system design has provided ITTI Digital with the opportunity to expand in the global market. With ITTI Digital’s permission, we are sharing an exclusive core banking case study on designing a next-gen banking back office that aimed to become a game-changer in the industry.
Core Banking Digital Transformation Wins the World-Famous IF Design Award
A few months after this case study was released, it was announced that this core banking system designed by UXDA has received one of the world's most famous design prizes - the IF Design Award.

It was awarded in the Service Design category alongside Apple that was recognized for its digital finance service design of the well-known Apple card.
The international jurors of 78 leading design experts from all over the world recognized UXDA's core banking solution UX/UI design for its exceptional transformation embodying a mission to inspire and lead the financial industry to a better future.
Problem: Outdated Core Banking System Ruins User Experience
It's a well-known yet well-hidden fact that core banking back-office solutions are causing a lot of problems. The banks themselves are often embarrassed about the outdated solutions that go against their modern-looking appearance.
The impact of an outdated banking back office system is much stronger than it seems at the outset. It drastically reduces the speed, quality and value customer service could provide. But, most importantly, such design of banking system demonstrate to banking employees that a modern digital approach is not valued. Thus, despite fancy looking customer solutions, the inner culture is often negatively impacted by a lack of human-centered solutions.
So, the ugly truth is that today the majority of current banking back-office solutions are slow, complex, clumsy and leading the employees to mistakes instead of helping to avoid them.
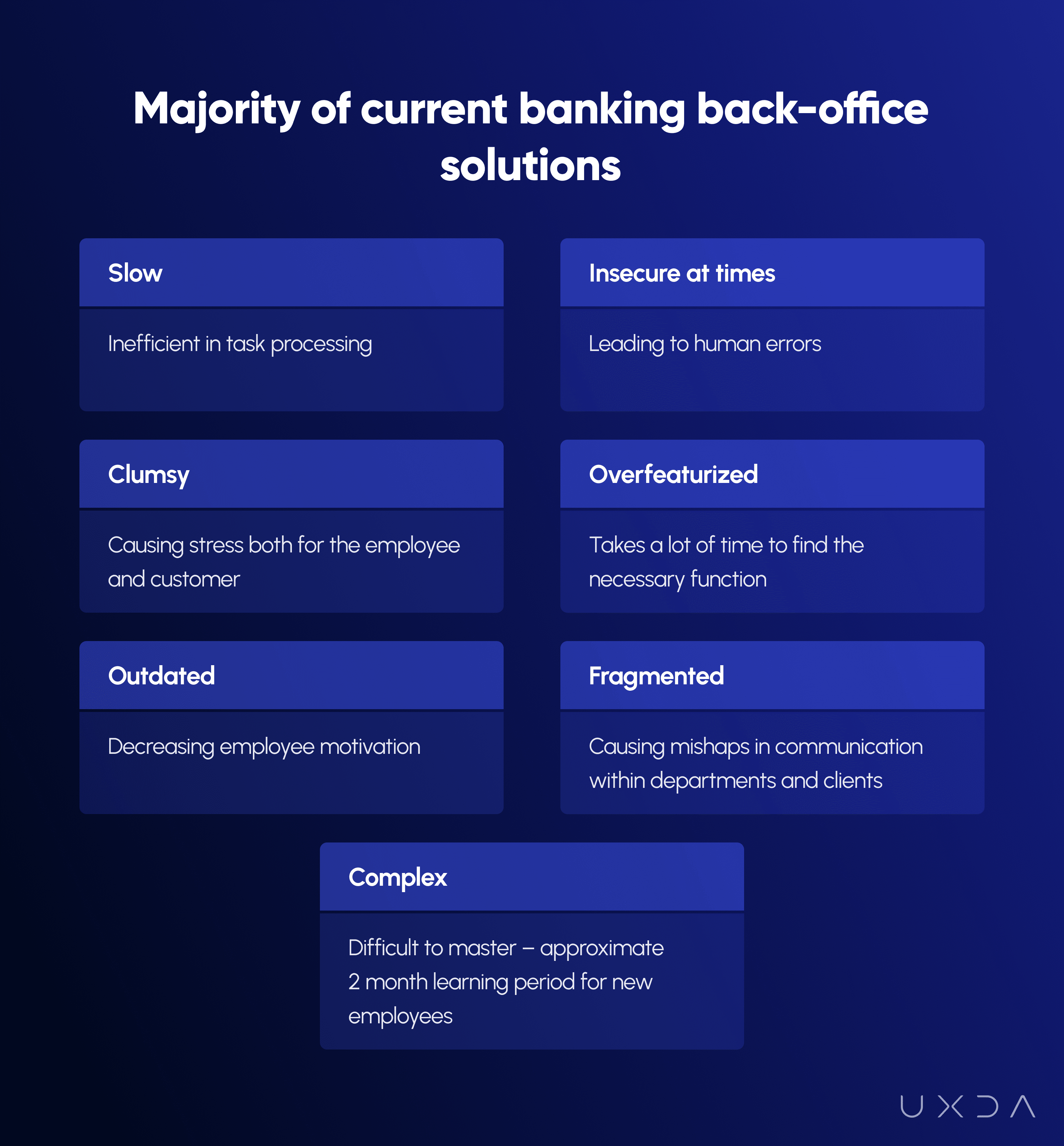
Core Banking Digital Transformation: Paraguay's Top Solution Moves to the Cloud
ITTI Digital provide the most recognized core banking solution in Paraguay with more than 20 years of evolution. It has the following modules: Clients and Signatures, Loans, Savings, Cash and Treasury, Changes, Accounting, Regulatory Reports, Cards of Credits, Collections, Fixed Assets, Suppliers, Supplies, Py Payment Systems, Money Desk, CRM, SIG (Business Intelligence), SGR (Risk Management System), SIR, Homebanking, TAS, Quotes, Superintendency, Module Accounting, Human Resources, Comex, Guarantee Management, Credit Limits, Engine, PDCA. 30% of the financial transactions carried out in Paraguay are through the Financial Core developed by ITTI Digital.
Companies around the world are moving to the cloud to increase IT agility, achieve limitless scalability, increase reliability and reduce costs. By integrating cloud banking, banks can innovate faster by focusing their IT resources on improving digital products and customer experiences rather than managing infrastructure and data processing.
Cloud-based core banking is becoming increasingly essential for banks in the future due to several key factors:
Digital Transformation
The banking industry is undergoing a significant digital transformation. Customers are demanding more convenient and personalized digital banking services. Cloud-based core banking solutions offer the agility and flexibility required to deliver innovative digital products and services quickly. Banks need to embrace cloud technology to stay relevant and meet the evolving expectations of their tech-savvy customers.
Cost Efficiency
Traditional on-premises core banking systems require significant upfront investments in hardware, infrastructure, and maintenance. Cloud-based solutions provide a cost-effective alternative by shifting the infrastructure and maintenance burden to cloud service providers. Banks can reduce capital expenditures, optimize operational costs, and allocate resources more efficiently by adopting cloud-based core banking solutions.
Scalability and Elasticity
The scalability and elasticity offered by cloud-based solutions are vital for banks to accommodate changing customer demands. Banks need to scale their resources up or down quickly to handle fluctuating transaction volumes, seasonal peaks, or sudden spikes in demand. Cloud infrastructure allows banks to dynamically adjust resources, ensuring optimal performance, and avoiding overprovisioning or underutilization.
Data Analytics and Insights
Cloud-based core banking solutions facilitate efficient data collection, storage, and processing. Banks can leverage the cloud's computing power and advanced analytics tools to gain valuable insights from their vast amounts of data. These insights enable banks to better understand customer behavior, make data-driven decisions, improve risk management, and offer personalized products and services.
Regulatory Compliance
Banks operate in a highly regulated environment. Cloud-based core banking solutions can help banks meet regulatory compliance requirements more effectively. Cloud service providers often have robust security controls and compliance frameworks in place, such as encryption, access management, and audit trails. Banks can leverage these capabilities to ensure data privacy, maintain regulatory compliance, and adhere to industry standards.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Ensuring uninterrupted banking operations and disaster recovery is crucial for banks. Cloud-based solutions offer built-in redundancy, automated backups, and disaster recovery mechanisms. In case of a disruption or disaster, banks can quickly recover data and applications from off-site cloud backups, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
Innovation and Collaboration
Cloud-based solutions provide banks with the opportunity to collaborate with fintech partners and leverage emerging technologies. Banks can easily integrate with third-party applications, open banking platforms, and other financial service providers through APIs. This integration capability enables banks to offer innovative services, expand their product offerings, and create a more connected ecosystem that benefits both the bank and its customers.
The main challenge of ITTI Digital when they started working with UXDA was to create cloud-based core banking by designing a SaaS solution 100% focused on the employees. User-centered core banking next-gen design that would take into account all bank employees’ pain points, needs and daily tasks, making their job easier, enjoyable and more meaningful from a banking end-customer perspective.
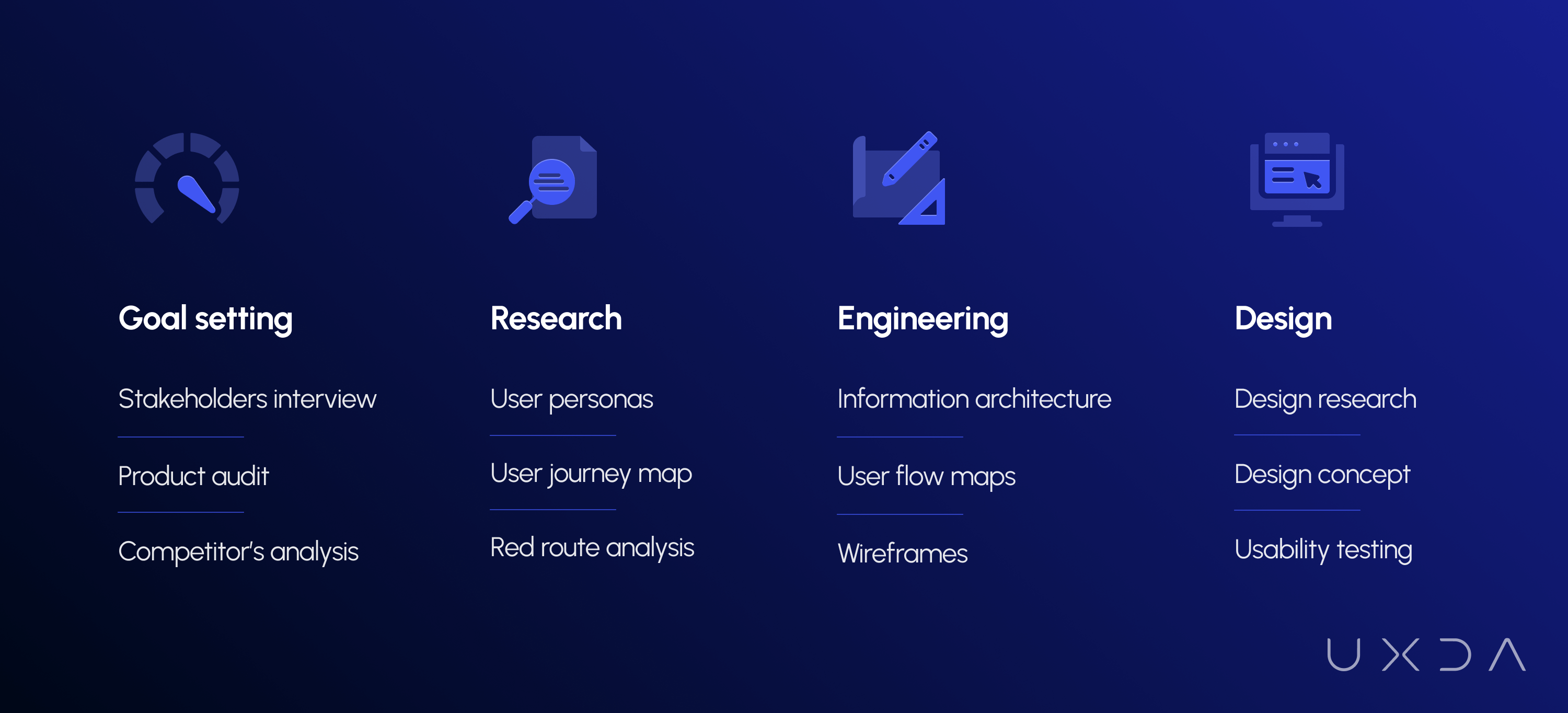
To achieve this, UXDA unique Financial UX Design Methodology was used. It was developed over a period of 10 years and has already proven itself by ensuring success for more than 100 financial digital products in 36 countries. The full ITTI Digital banking transformation can be divided into four main stages realized through UXDA Financial UX Design approach :
1. Empathize: Ultimate Power of Joined Vision
Every success is defined by a clear target statement. In this phase, together with ITTI Digital, we crystallized and developed an understanding of where the company is going with the new product. From a project success perspective, it is vitally important to ensure that all stakeholders are on the same page.
The Stakeholders’ Interview: Is That a Triangle or a Square?
One of the biggest challenges is that often large teams find it hard to reach a common understanding; everyone has their own vision about the company strategy and the new product goals.
In the worst case scenario, all of the team members are certain that they think the same until faced with problems that arise because of misunderstandings.
We started the research stage by conducting an interview with ITTI Digital stakeholders. Through this, we found the overall specifics of our client's business and motivation for redesigning their existing product.
ITTI Digital turned to UXDA after trying to make their company user-centered on their own. They had heard a lot about user experience and Design thinking, but the efforts to make it work weren't successful. There was something missing that they couldn't figure out. ITTI Digital realized that it’s not only about interface design or product features, which is why they decided to trust the financial design approach developed by UXDA.
ITTI Digital aimed for something more significant than just creating an appealing product design; they were willing to generate the next-level market opportunity.
At this point, they weren't yet aware of the huge journey this decision would take them on. In the following months, ITTI Digital underwent a courageous shift of implementing user-centered design throughout the whole core of the business, including strategy, processes, culture and customer service.

Some of the ITTI Digital team members felt nostalgic about putting the old solution to rest, as it had operated for more than 10 years, but, at the same time, they were certain that it was the right thing to do. The company was ready for in-house revolution.
Key Insight
ITTI Digital developed a strong belief that the current product was outdated and provided a terrible user experience. They agreed; in order to succeed, the product required serious and thorough changes.
The Product Audit: What do we Have Here?
After gaining a clear picture of the ITTI Digital business philosophy, strategy and goals, we investigated their current solution and its flaws. At this stage, it is important not to miss the primary product value and advantages, and explore it from a user perspective. Hundreds of functions and user scenarios can easily distract from it and hide its core value.
From the first sight, the ITTI Digital initial product was fragmented and overloaded with functionality. The appearance reminded us of Windows 98, just like most currently available core banking solutions. Instead of helping banking employees, it just confused them. That’s why weeks of learning are needed.
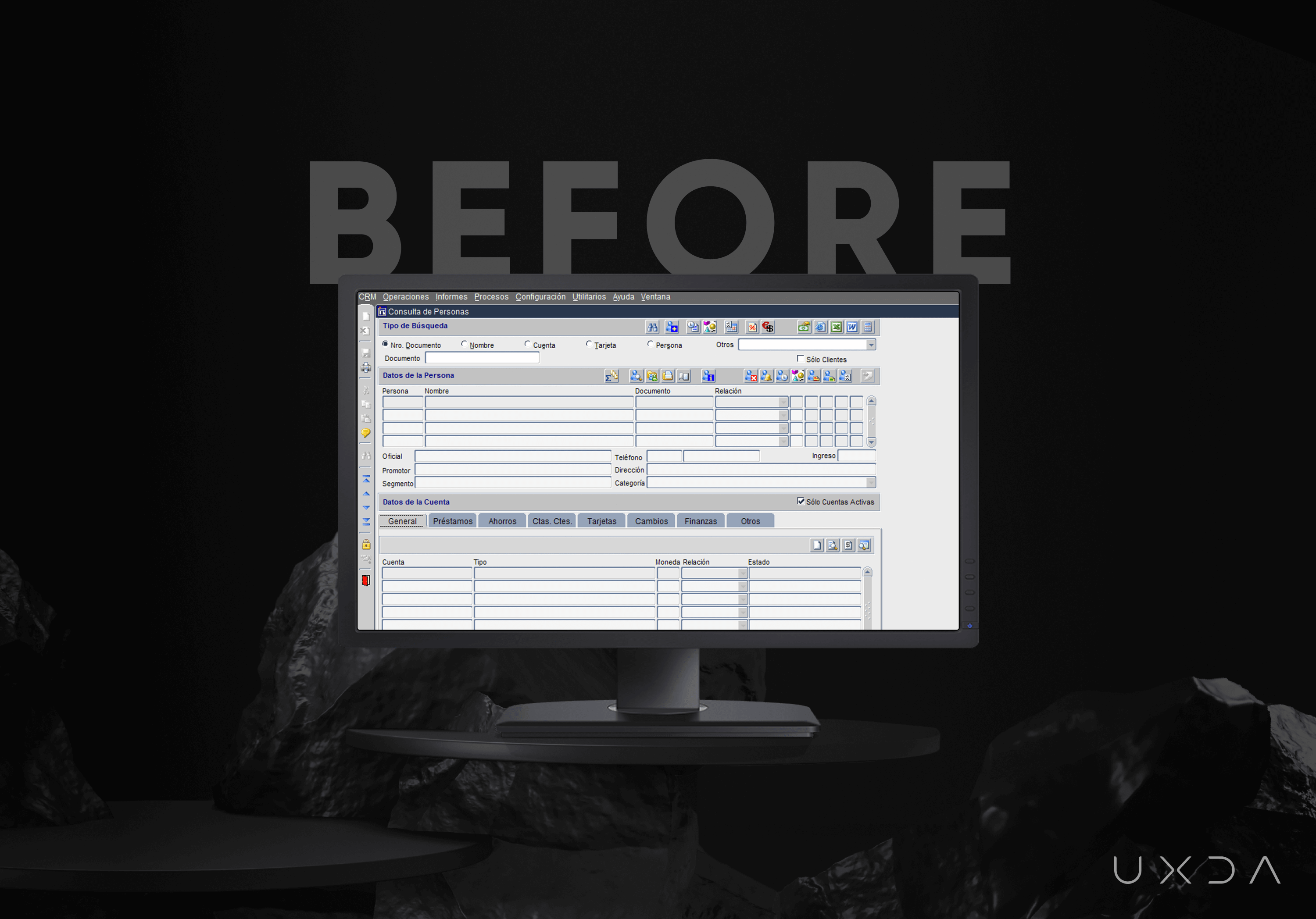
ITTI Digital Innovation manager, Hector, guided the UXDA team through the current solution. Usually, vendors know their product really well and do not notice its complexity. While guiding us through the solution, the ITTI Digital team got a chance to look at their product from aside. During this, we asked questions from a user perspective, and Hector noted himself that the solution seemed heavy, and some of the extra functionality did not make sense.
Competitors’ Analysis: Learning from Our Rivals
During this stage, we profiled the competitor companies, their core-banking solutions and how they position themselves in the market. We observed the ITTI Digital competitor successes and failures and analyzed their advantages and weak points in the customer experience. This provided a clear view of the industry background to the team.

ITTI Digital uncovered a huge opportunity to differentiate their product because of the fact that the majority of currently available back-office products offer inconvenient and outdated solutions. This inspired the whole team to double their power in moving forward to offer the industry a brand new approach with a completely reinvented and revolutionary product.
2. Research: Pain and Gain Defines Everything
The very core of the whole ITTI Digital back-office rebirth was user research. Skipping this stage could have resulted in going in the absolutely wrong direction and could even potentially led to the launch of a completely useless product.
At the beginning, ITTI Digital might have thought that they knew their users well. However, during the research, they discovered that their assumptions about the user needs and wants didn’t always match up with reality. It is necessary to meet and try to empathize with real people.
The research phase connected ITTI Digital to its users - the banking employees. It defined what features we had to include in the new core banking solution so that users' needs and expectations would be fulfilled.
User Personas: Putting a Face to a Name
Research of ITTI Digital user personas was the foundation for a solution that would be not only aesthetically pleasing but, most importantly, highly practical and usable. Here, it was crucial for us and ITTI Digital to get in touch with the people who were using the solution every day.
ITTI Digital became aware of banking employees’ needs, emotions and pains. It was also hugely important to understand in great detail the everyday routines and duties of different employee positions in a bank.
Creation of ITTI Digital user personas required a huge amount of research. We collected data from:
- ITTI Digital inner database;
- Public databases;
- UXDA inner database;
- End-user interviews.
The most valuable insights and information were gained from conducting user interviews. This provides an emotional connection with potential users and helps you to feel their pain points and empathize with their current experience. Thanks to ITTI Digital, we got the chance to interview 21 real end users─people who were dealing with the old back-office solution daily.
I wasn't sure about the responsiveness of the employees willing to share their insights about the old solution, but it turned out to be a surprise when more and more people were willing to share their thoughts. This turned out to be a truly emotional phase of the whole process as the employees were so keen to speak out, and for the first time we really got to discover their needs that the current service wasn't satisfying. Hector Ojeda, ITTI Digital Innovation Manager
It seemed like the employees had been waiting an eternity for this moment. They were eager to share their thoughts and emotions on the current relationship with the back-office solution.
The employees felt that the current solution was overloaded and complex. Even after 15 years of working in a bank, a user still didn't understand all the functionality. Unfortunately, instead of helping, the banking software created friction.
Creation of the user personas completely changed the way ITTI Digital perceived their own product. For the first time, they viewed it through the eyes of the users. During the interviews, we found out what was missing in the service and what was causing the biggest struggles from the employee's point of view.
The banks have many departments and divisions with various employee positions, but, based on the data collected, it was enough to create four user personas in different positions within the bank:
- customer service specialist,
- branch manager,
- back office operative,
- risk manager.
The creation of these four user personas allowed us to get a detailed look at the employees’ Jobs-To-Be-Done (JTBD) or so called user scenarios by putting digital interactions into real-person experience and context. Nevertheless, the final core banking solution should be usable by every department and position in the bank because of matching architecture to a full set of jobs that customers hire product for.
We walked a day in the customers’ shoes to experience the daily lives of banking employees, and we discovered a lot of struggle and negative emotions caused by their existing solutions. This allowed us to create empathy maps, collecting what users think and feel about executing their duties. This defines very valuable context of previously detected Jobs-To-Be-Done.
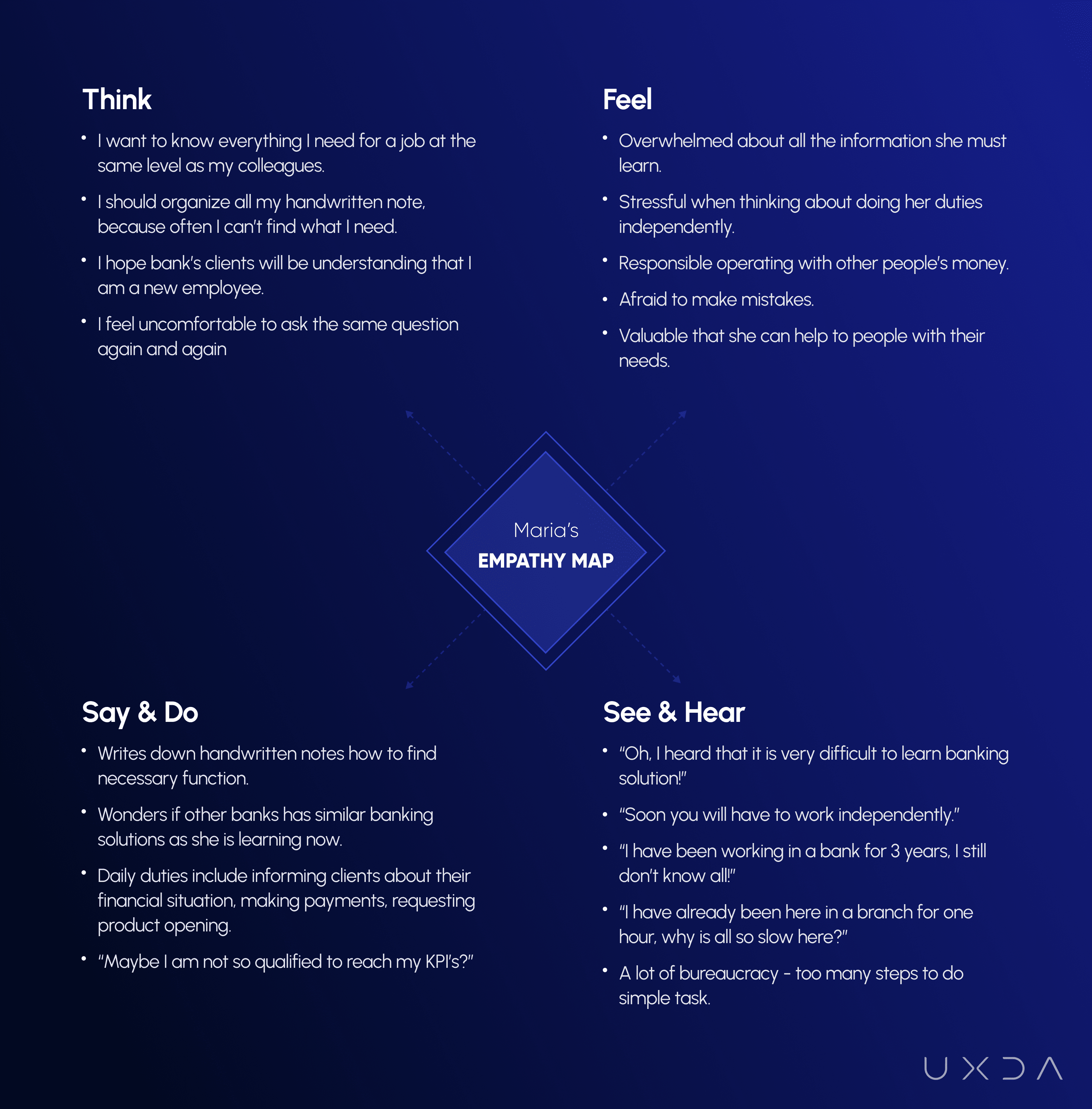
An empathy map allowed us to define more employee pain points that we had imagined there would be. This is a key milestone in extracting potential product value. Sometimes, those insights are hard to accept for product owners because they prefer to believe that everything is fine. The ITTI Digital team was happy to see those findings and were ready to use it for improvement.

3. Define: Find a Solution That Saves the World
Now it was time to gather all the insights we gleaned about business, users and product and put them all on one timeline. This timeline would show us how users will interact with the product on a step-by-step basis. As a result, we could match hundreds of previously gained findings together and, at the end, find a product idea that would provide needed solutions.
User Journey Map: Designing an Ideal User Experience
The User Journey Map was a huge turning point for the ITTI Digital business and culture. It divided everything in terms of “before” and “after” by causing a complete mindset shift in how the company viewed its product, users and even the business processes as a whole.

User Journey Map was one of the most voluminous and important deliverables of the ITTI Digital project. It was created during a two-week workshop with intense daily calls with the ITTI Digital team. Their active participation was crucial as this was another important step to ensure that all team members shared the same understanding of what Jobs-To-Be-Done customers expect from the product and how users would interact to achieve it.
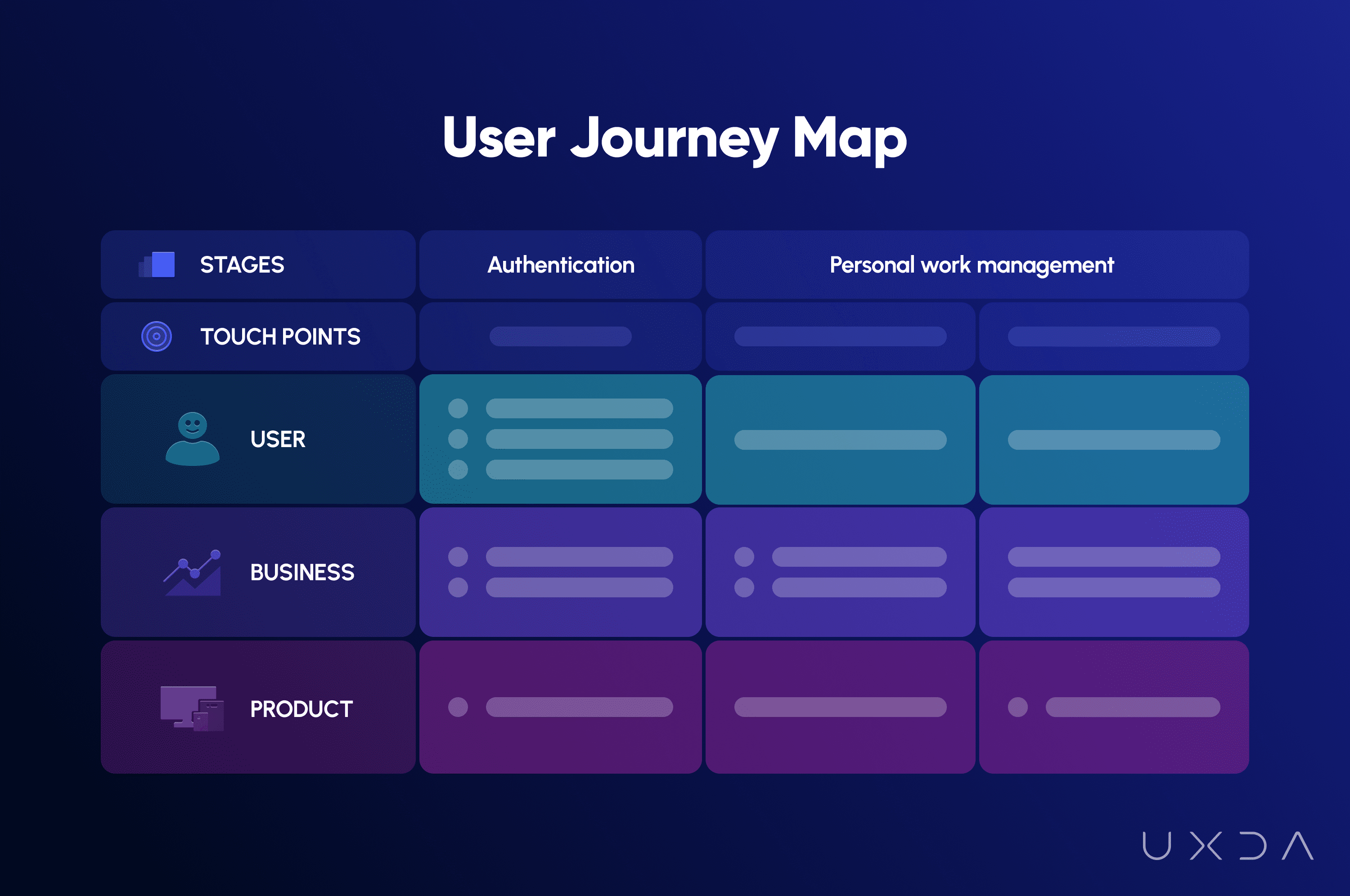
The creation of ITTI Digital User Journey Map was challenging because we had many different users with access to different functionalities. During the workshop, we changed the UJM framework five to six times until we found the best way to show one holistic user journey through it. In total, 745 inputs were added in the ITTI Digital User Journey Map.
First, we compiled all of the possible ITTI Digital user scenarios in each interaction with the banking back-office solution and defined what feelings and emotions each step could cause. In this way, we would be able to detect the main pain points, turning those into pleasant experiences.
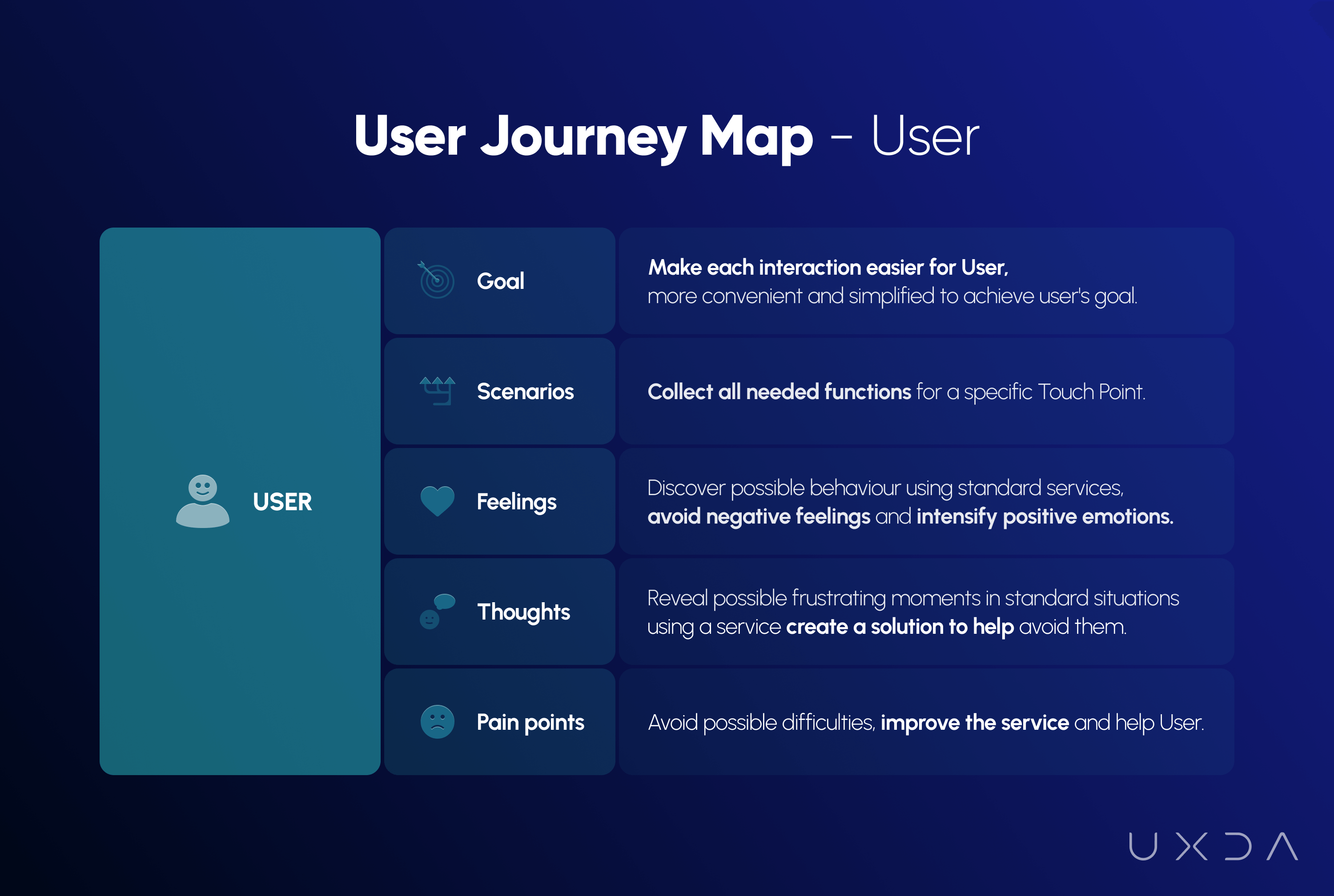
Next, we looked at the new product from a business perspective. Here, we defined the ITTI Digital business goals in every user's interaction with the back-office solution and also the key performance indicators (KPIs) to be clear how they can measure success.
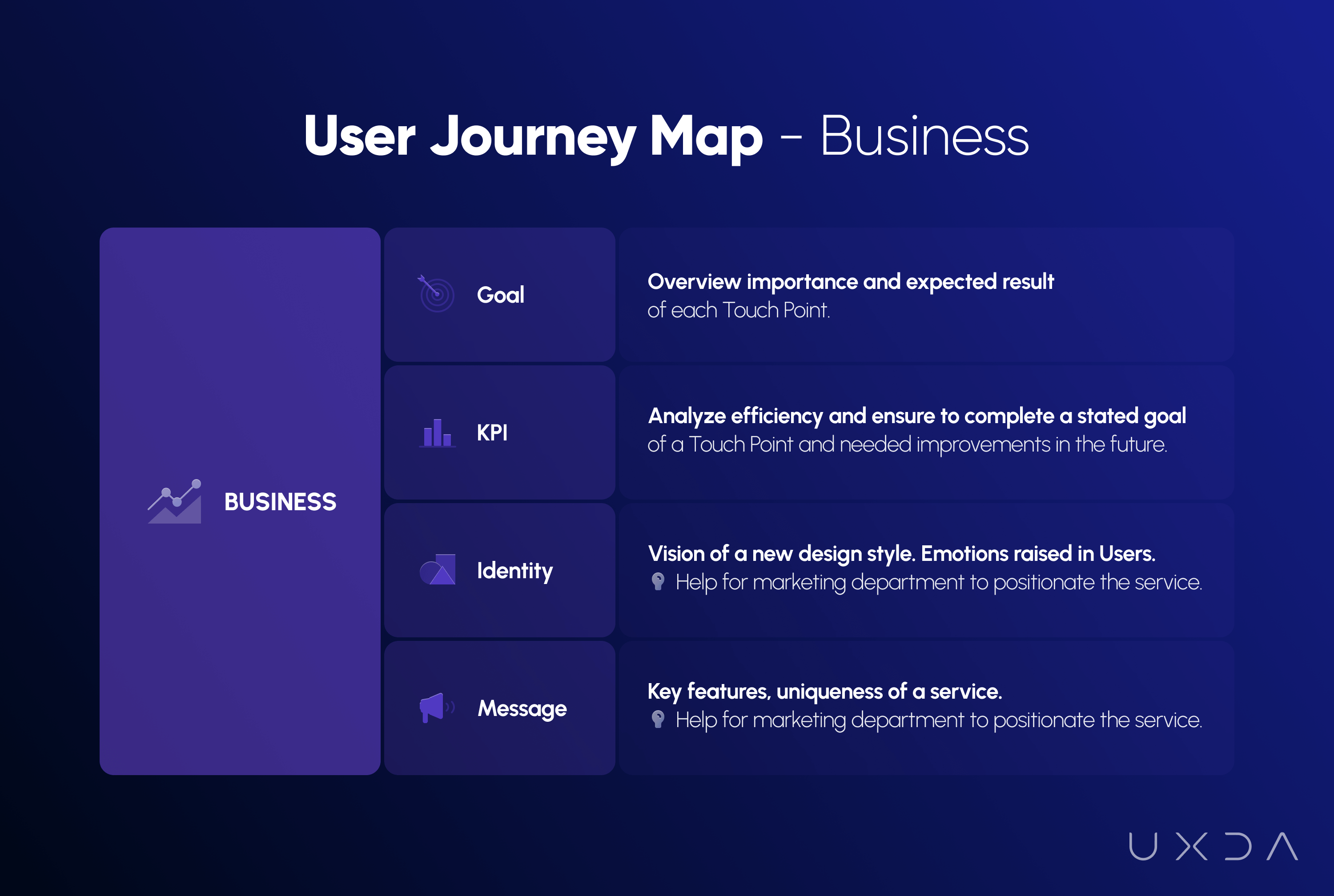
After exploring the business perspective, we moved to the product section. Based on all the detailed insights collected from user scenarios, feelings and pains, as well as business goals and KPIs, we were able to identify the exact functionality and features that ITTI Digital’s new back-office solution should have. During this phase, we had to keep in mind that this was a bank's internal solution, so every functionality and flow had to strictly meet the security requirements.
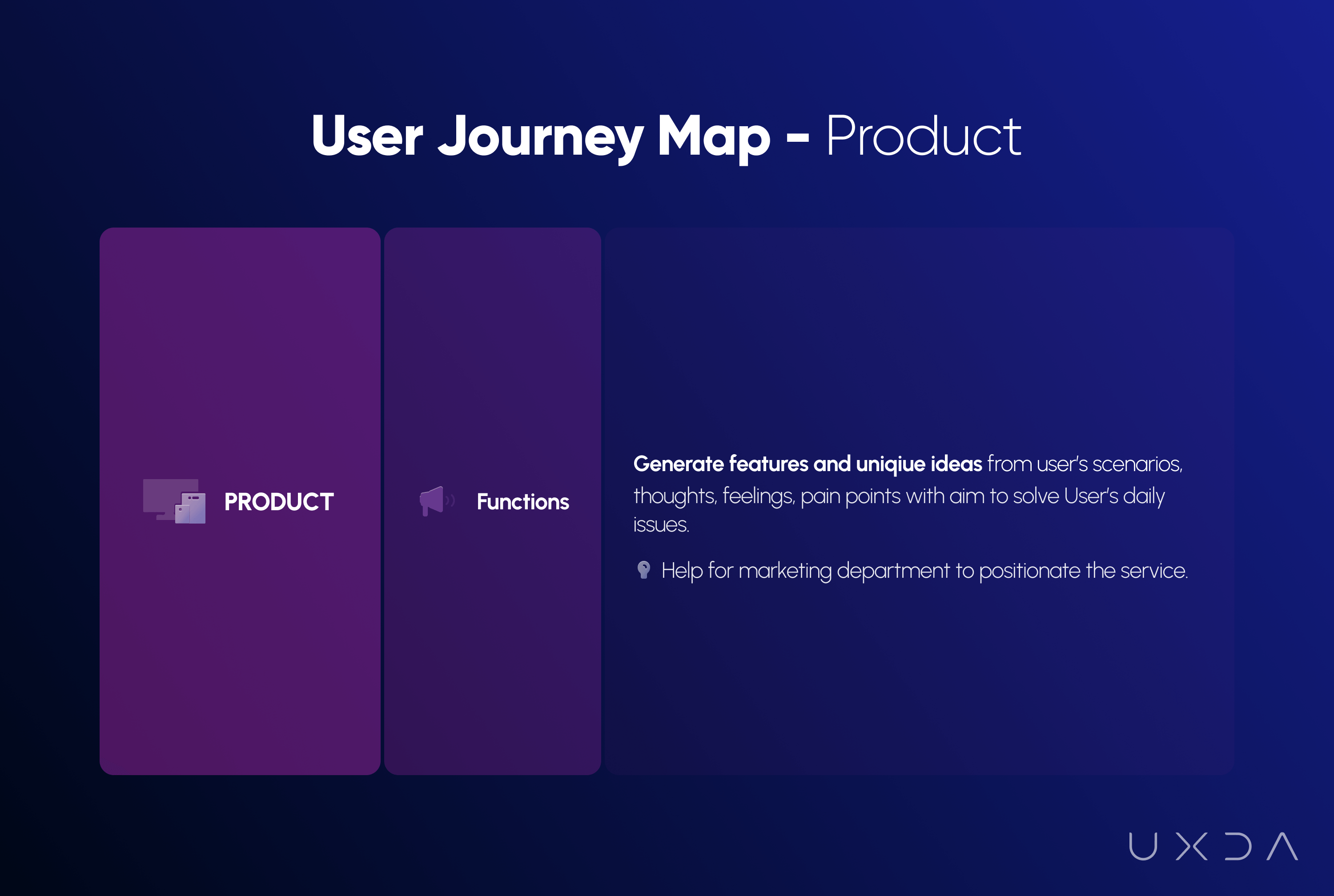
Finally, based on the synthesis of all the insights at each touchpoint, we were able to define the best possible product solution through functionality we had to include in the new ITTI Digital back office.
When we discussed the results of the User Journey Map with the ITTI Digital team, Hector voiced excitement about the functionality we had included that would ease the employees’ lives, noting:
I think our new solution will make all the dreams of banking employees come true!
The User Journey Map let us grasp the whole functionality of the new service. It provided a satisfying sense of how the employee's daily duties would be made much more convenient, increasing the speed of the service and avoiding stress, mess and mistakes, which were some of the most common pain points employees faced in the previous solution.
Until this project phase, ITTI Digital had a very fragmented vision of their banking back-office solution; they viewed it as “separate modules.” It is common in the banking industry to think this way, but, from the user's perspective, the banking employees don't care how many and what kind of modules the solution has; they see it as one continuous flow. Realizing this can bring significant power to a product team driving customer experience digital transformation in financial services because now they are able to match business goals and user needs in an appropriate way through digital technology.
During the user journey map workshop, ITTI Digital finally views their product as a single, complete and united solution - there were no modules anymore. This was the breaking point that revolutionized ITTI Digital as a company creating a shift toward an experience mindset.
At the end of the user journey mapping process, Hector admitted:
We see the value User Journey Map provides not only for this project but for the future of the company. We have gone from a complex, difficult and fragmented view to a holistic and transparent vision of the whole huge flow that's suited for the user needs.
4. Ideate: Project's Bullet-Proof Backbone
This stage allowed us to ideate solutions based on the ideas we created with ITTI Digital regarding their User Journey Map. At this crucially important digital banking transformation stage, we turned our vision of an ideal user experience into the architecture and operation of the data-rich product.
This solution is filled with tons of data, and it’s a challenge to structure and display it in an intuitive manner that’s insightful and easy to understand for the user. We believe that many financial services are actually in the data-displaying business because this is a job that users require them to do perfectly.
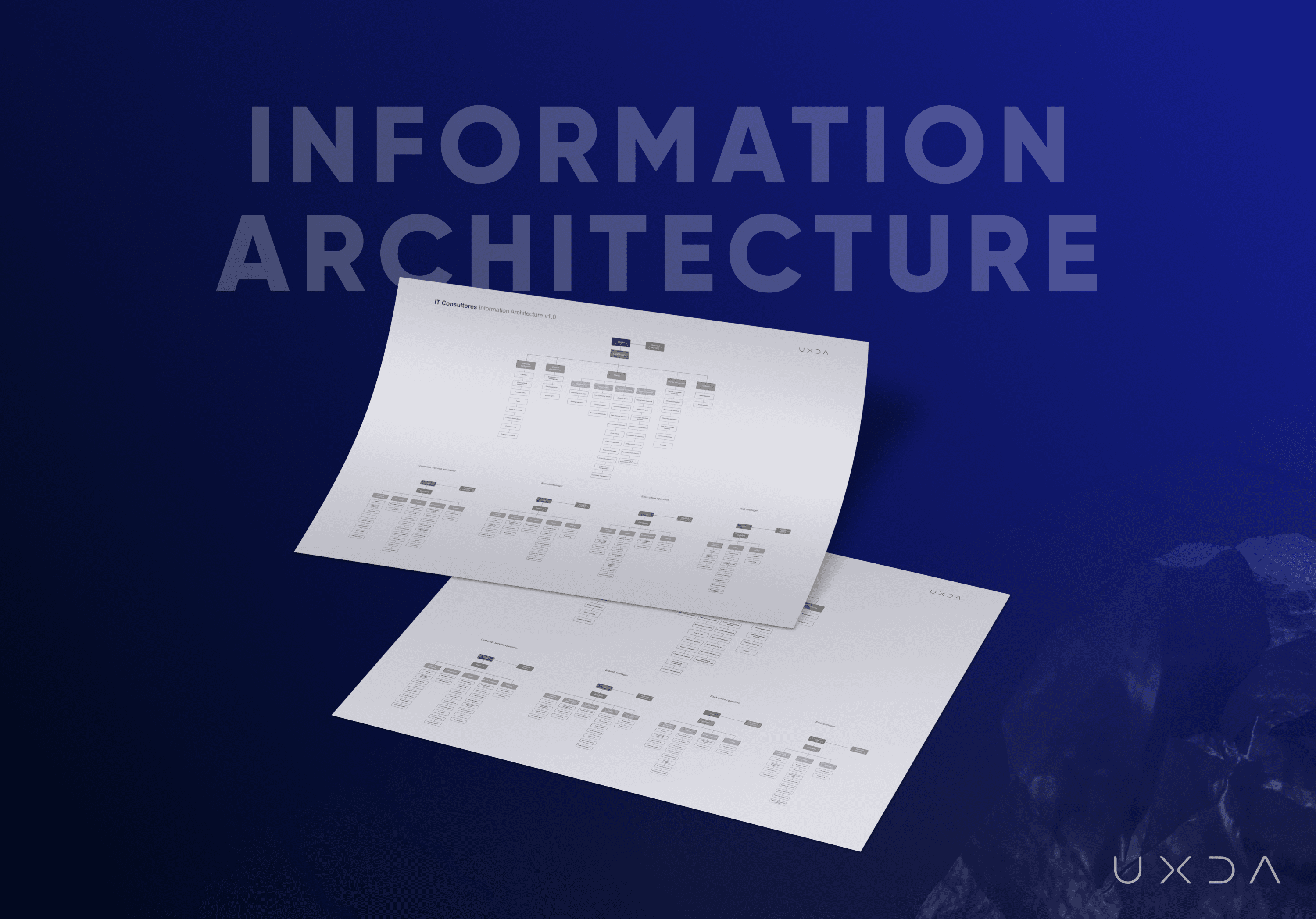
Information Architecture: Everything in Order
We tried to make the new ITTI Digital back-office solution as simple and easy to understand as possible, keeping in mind that all of the service information is divided into two main parts:
- one is individual for the banking employee;
- the other one is functions connected to client affairs.
The old ITTI Digital solution didn't include any kind of information architecture for the work management of a banking employee. As user interviews revealed, this made it messy and troubling to accomplish everyday tasks and do them effectively.
The complex part of the ITTI Digital product specifics was the requirement of customized data for each employee. This was due to different daily routines, tasks and, most importantly, internal security accesses that change according to the department and position.
To solve this, we created one overall architecture for the entire solution and also four smaller ones for each of the user personas. This allowed us to understand the differences of information we should include to keep the core banking back office product intuitive and holistic.
Wireframes: Creating the Product's Silhouette
Key dashboards of the new ITTI Digital product required a huge time investment. While architecting the key screens, we had to keep in mind all the scenarios of the solution that affect its hierarchy and usability.
The first wireframe we started with was a dashboard for a Customer Service Specialist. To reach the optimal solution, we modified it multiple times. There were several versions of the final dashboard, and we discussed how the banking employee would interact with a huge amount of data. We tested the solutions to check their usability and clarity during the main scenarios.
During the wireframe reviews with the ITTI Digital team, Hector asked if there was a possibility of including some more features. Often, it could result in over-featuring that would confuse the user. Here, it was important to clarify the purpose of these functions for the employee. In what case scenario would they be using them? This provided a mindful break for Hector as he paused for a moment and realized:
Oh, we don't need those features after all! I am still trying to switch my mindset to a user-oriented one!
This concluded the entire research stage that was basically the very core of the new product. We understood who our users were and what they needed and wanted and also explored the business goals and how the product can help to satisfy both the users and the company. Based on that evaluation, the complete service architecture and wireframes were created.
Only now, after coming a long way, did we arrive at the most exciting stage of the project: user interface design.
5. Design: Data-Rich Functionality Filled With Love
When it came to the design of the new ITTI Digital core banking system, the biggest challenge was to step outside of the boring, gray tableview design into something more appealing. A colorful and fresh solution could provide a clear difference by becoming emotionally engaging.
This was one of the most creative and excitement-charged stages of the whole ITTI Digital project. The entire UXDA team was involved during the in-house design challenge.
It took a week of intense creative work to get to the key design concept─the best possible for the ITTI Digital project.
The design concept presentation was a hugely anticipated and emotional step─both for us and for ITTI Digital. We had been working very hard on the research and engineering phases while creating the core of the solution. Now, it was finally time for ITTI Digital to meet their new world-class banking system that had already changed their business through the design process.
The Key Design Concept presentation turned out to be a truly remarkable moment. ITTI Digital team members couldn't hide their emotions of joy and delight as they admitted that they feel thrilled and the ITTI Digital design concept exceeded their expectations!
We've guided you through the whole process, and now it's time to review the results. This is the ready-made design and architecture based on the research that, as of today, is being developed by the ITTI Digital IT team and soon will be available worldwide for any bank to purchase!
Login: Start the Day off Right
We wanted to provide users with a service that would make their tasks quick and easy to implement, but their motivation and inspiration were also very important to us.
We focused carefully on the login screen, as that's the first thing greeting an employee in the morning. We wanted to provide an inspiring, calming and focused tone for the day ahead.
We did that by displaying a remarkable view of nature in the background of the screen, as well as a quote by a successful, well-known person. Every time the employee assesses the login screen, he/she is greeted by a different picture and quote to instill a peaceful mood. The login is quick, as the solution remembers the employee's user name, and only the password needs to be entered.
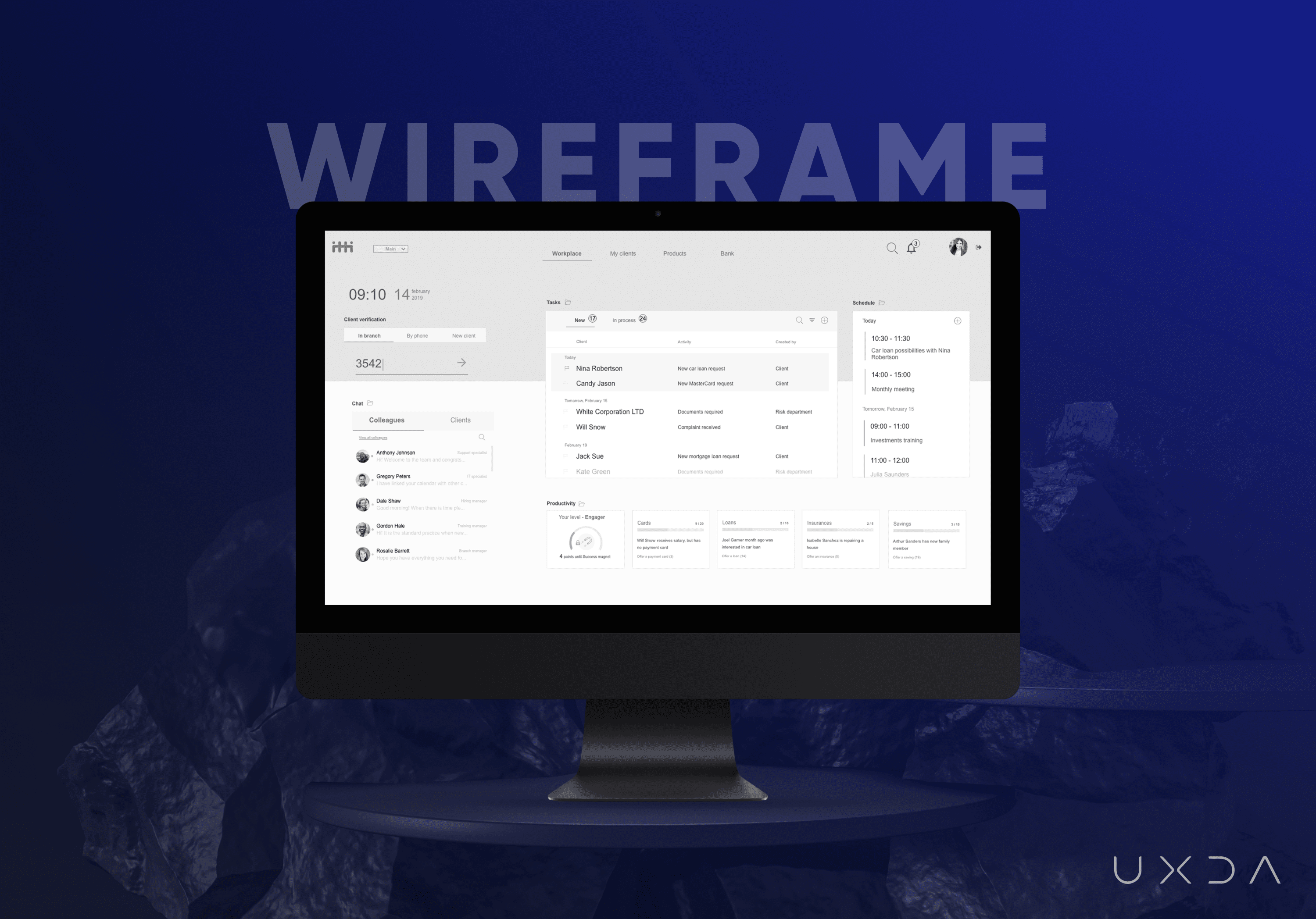
The Main Workspace: Wise Assistant for Daily Tasks
We made a flat, clean and light core banking dashboard design for bank employees so it would stand out from the boring gray screens most employees are accustomed to. We wanted to refresh the common formality in banks, replacing it with an emotionally uplifting environment.
In the example below, our user is a Customer Service Specialist, who works at a branch with clients daily. As noted before, there are different kinds of financial dashboard architectures according to the employee’s position and information required to accomplish their daily tasks.
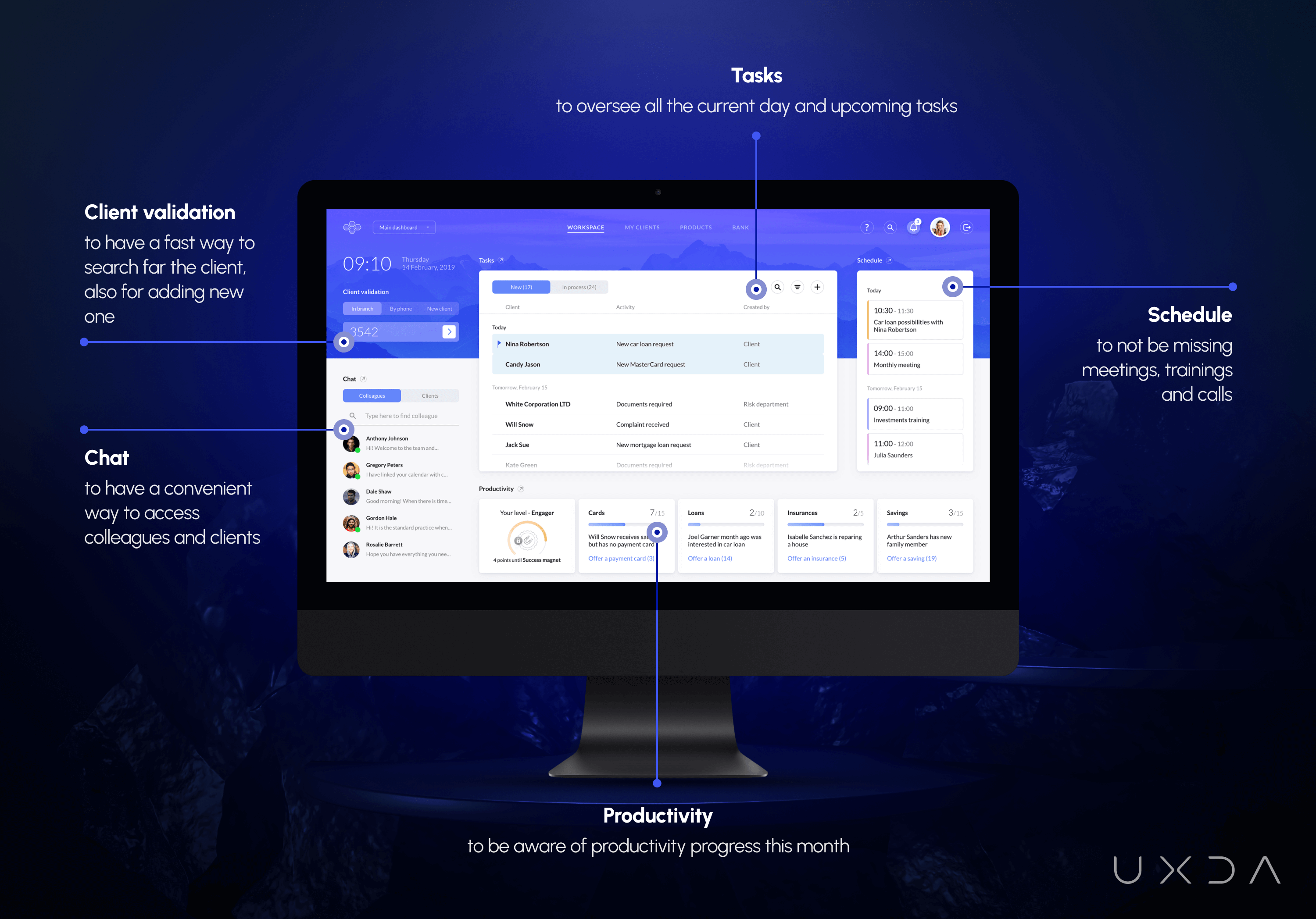
Features of the Main Banking Back Office Dashboard:
- On the left side, there is a client validation function and chat; these two blocks are accessible constantly, even when the user is navigating to a different page;
- In the middle part, there is a block of all user tasks;
- On the right side is the schedule;
- At the bottom, the productivity summary is displayed.
To see a more detailed view, the user can expand the three blocks of tasks, schedule and productivity.
The main financial dashboard design addresses a huge part of all the needs that employees indicated throughout the interviews. Here's a short overview of the solutions we created to reduce employees’ pain points and stress and make their everyday lives much simpler and more enjoyable.

It was crucial to make the solution intuitive and understandable, so the users would not need to spend two months learning it. We concentrated only on those functions─ the ITTI Digital user personas really needed for their duties.
Goals Made Fun: Gamification for Motivation
ITTI Digital had the courage to admit that their old banking back office solution was frustrating employees and stressing them out. In six months, we turned that around and designed something pleasant and enjoyable. We wanted to engage and motivate employees to reach their goals in the most effective way by addressing the users’ needs for fun, entertainment and reward.
Gamification is something completely new to banking, but ITTI Digital was eager to integrate it. When we presented the gamification in the productivity section, they were thrilled by the way we had integrated it.
We used gaming elements to inspire employees to reach their sales goals while, at the same time, keeping them informed about the progress they were making. Thus, we are using digital technologies to help employees reach their business goals in the most affordable way.
Every month, the employee embarks a journey toward his/her sales goal. To attain the superior “Sales Guru” badge, the user must unlock four previous badges by selling the bank’s products. To help them with that, we included small hints in each product group.
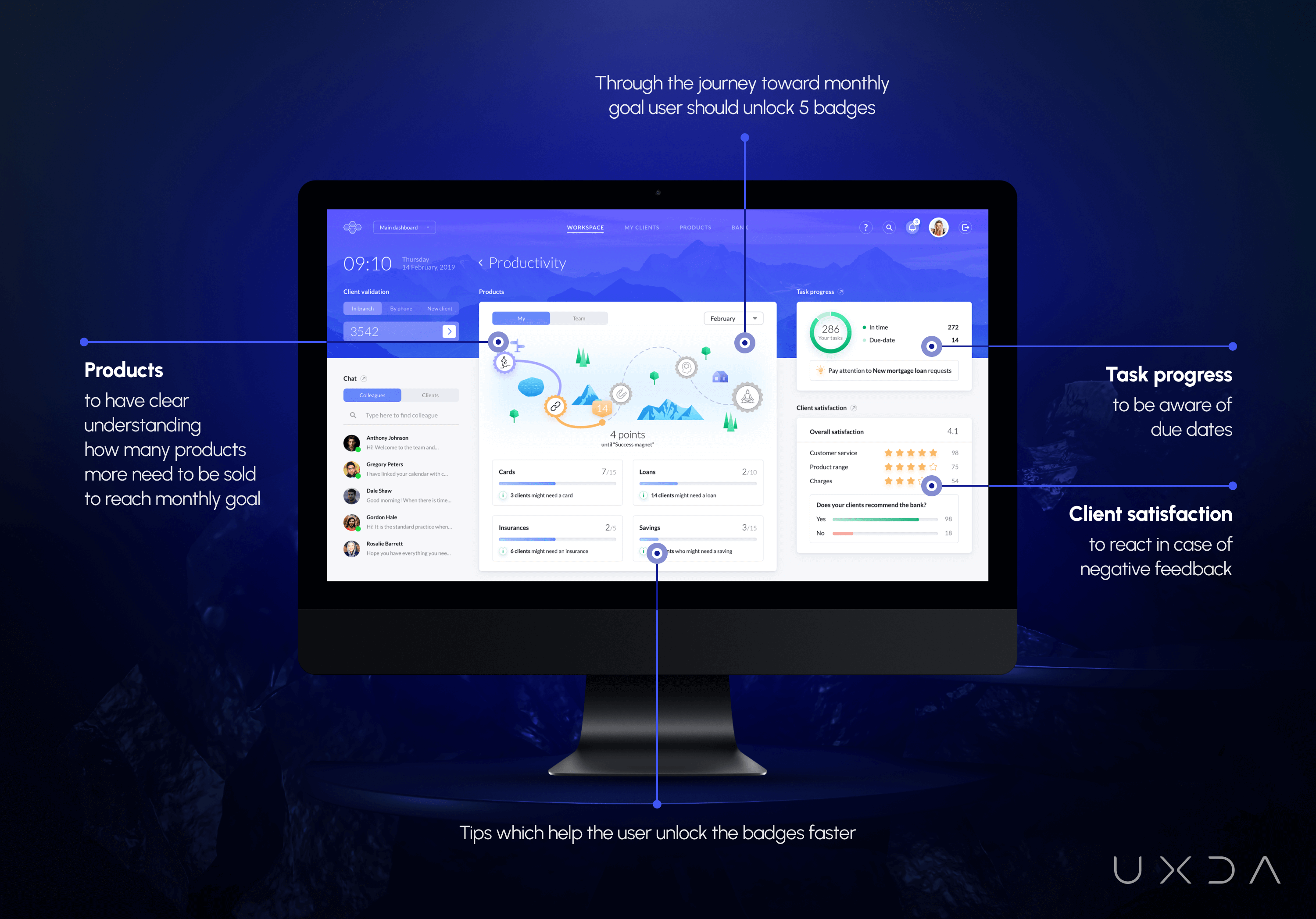
During the productivity section, the user also reviews his personal task progress: how many of them are finished on time. Here, statistical information is combined with useful insights about the tasks that the employee is most often delaying.
We have integrated a block that displays the overall client satisfaction. Unfortunately, this information that is crucial for employee self-evaluation and service quality is almost always hidden from them.
We also wanted that employees would feel appreciated by their workplace. That's why we complemented the solution with inspiring illustrations that would celebrate their successes and motivate them towards reaching higher goals. This was one of the many little details we included in the solution to ensure positive emotions for the employees, adding a sense of meaning and significance to their everyday duties.
Designed for Focus and Joy
When it comes to the design, a blue color dominates. It cultivates a feeling of calmness and serenity, which is critical for employees of a bank who have a huge responsibility on their shoulders.
It is important to note that, since ITTI Digital is a vendor that would provide this solution to different kinds of banks utilizing their own colors and brand identity, the appearance of the solution can be customized.
In the background, we have displayed a picture of mountains, which provides a relaxing appearance while keeping employees attentive. Mountains bring a feeling of open space and freedom, which is often sorely missing in the tall glass buildings of many banks. We wanted to bring joy to users’ daily lives, so we made personalization available, providing an option to change the background picture.
The Fight for a Better Future: Cloud-Based Digital Transformation in Banking
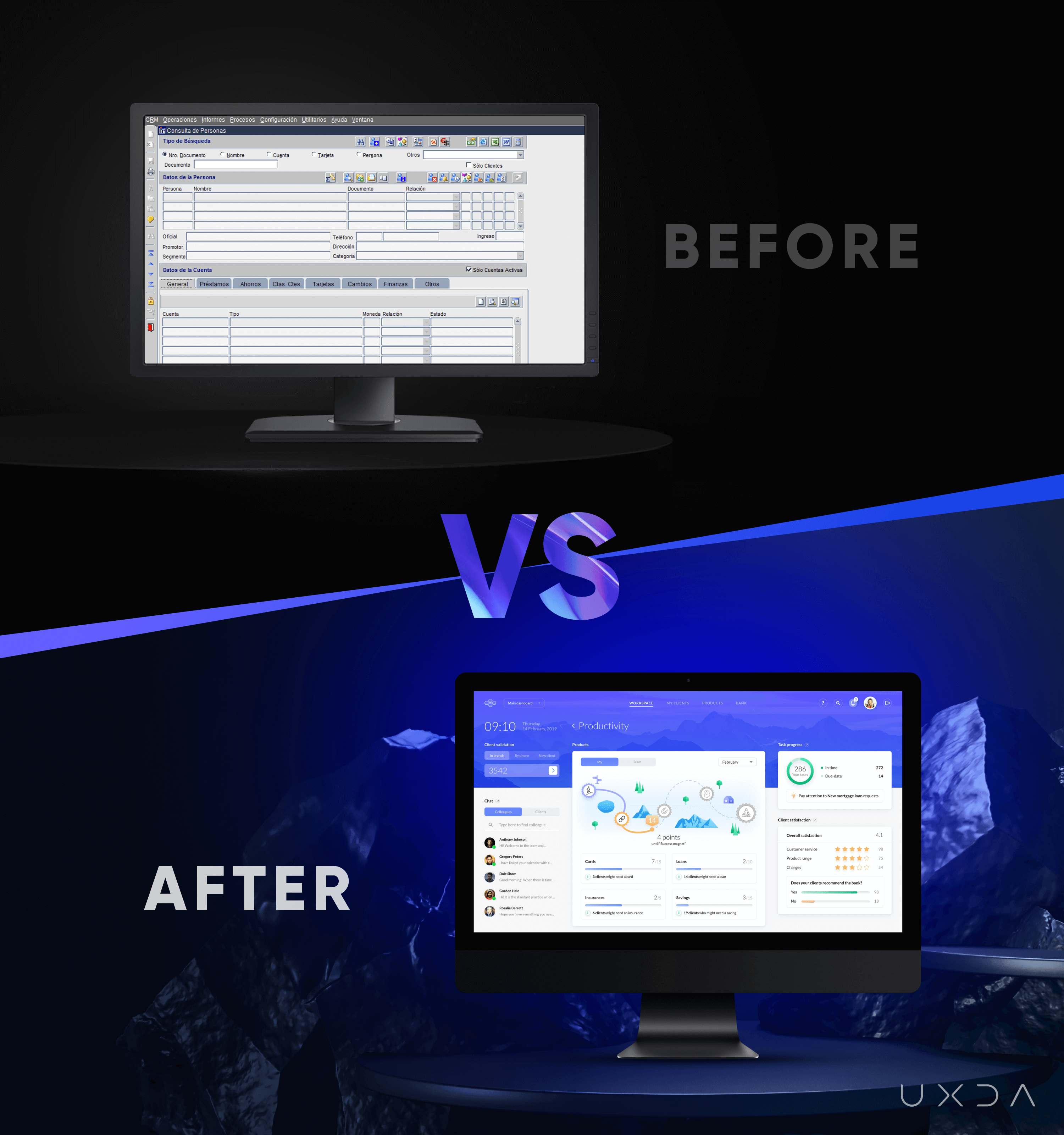
Halfway through the project, the ITTI Digital team admitted:
We understand that we should change not only our product but the whole mindset as a company, how we act like a business. Everybody in the team has started to think from the users’ perspective. It's not about the functionality. The value is not the technical features but the way a product makes people feel. Cultural change is happening.
This has been one of the most rewarding moments the UXDA team has experienced. You see, many believe that the design is about packaging─a beautiful picture and color─but, in fact, the ITTI Digital case is living proof that user-centered Design thinking is able to provide exceptional value for the whole business.
UXDA has always stated that our mission is to humanize the complex financial world, making it closer to the real end users─the people, and the way to achieve that is not by creating a pretty design. It's about shifting the mindset from profits and features toward a perspective focused on creating valuable experiences. That's exactly what ITTI Digital experienced and acknowledged during this digital banking transformation with UXDA. This led them to integrate an experience-oriented philosophy into their inner business culture.
ITTI mission is to provide cloud-based core banking for banks in the future to enable successful digital transformation, reduce costs, offer scalability, provide data insights, ensure regulatory compliance, support business continuity, and foster innovation and collaboration. Because embracing cloud technology is becoming a necessity for banks to stay competitive, meet customer expectations, and drive future growth.
The past six months have completely changed the way ITTI Digital perceives their product, users and one another on the team.
They admitted that, at the beginning of the project, the team felt skeptical of the possibility of combining back-office functionality and security measures with user centricity and delightful design.
During the project, ITTI Digital learned to make users their main priority, and their perception changed dramatically. It felt like they had finally opened their eyes to what has always been right in front of them─their users. They learned to listen to the users and focus on understanding their needs, expectations and, most importantly, their pains and struggles that the current solution was constantly causing.
Throughout this digital banking transformation process, their skepticism was overridden by inspiration, insights and revelations they had never even expected to encounter. Observing the behavior of the team, they changed and became more and more involved in the process and oriented on the best possible result they could provide for the users. It was gratifying to guide them through every stage, constantly uncovering new ideas and insights on how to improve the solution even more.
ITTI Digital admitted:
The end result over-delivered on our expectations, not only because it proved the possibility to combine the complex functionality with user centricity in an enjoyable, beautiful and delightful design, but also because we became live witnesses of the huge mindset shift a user-centered thinking creates in our organization.
Of course, it took great courage to embark on this challenging journey. Most banks reveal they are very afraid of making such a huge and revolutionary shift, changing a structure that has been working for decades, but ITTI Digital is living proof that it's 100% worth it. And we are really proud of them!
Together with ITTI Digital, we have developed a never-before-seen core banking back-office solution that will surely become a global game changer in the financial industry.
Most importantly, however, we have helped a huge financial company shift their inner mindset toward users and their needs, taking a revolutionary step toward humanizing the financial industry.
If we changed the mindset of our company while developing this core solution, then I believe the banking employee who will use this product will change his/her mindset too, and as a result this shift will change how the clients perceive their bank. I think this is a great start to do a real digital transformation in financial services. Hector Ojeda, ITTI Digital Innovation Manager
MORE UXDA CASE-STUDIES
Get UXDA Research-Based White Paper "How to Win the Hearts of Digital Customers":

- E-mail us at [email protected]
- Chat with us in Whatsapp
- Send a direct message to UXDA's CEO Alex Kreger on Linkedin
Listen to our podcast:
More from our blog

Financial UX Design Agency | UXDA is Working on The Future of Banking
It was announced that UX Design Agency, a small agency from Latvia, has been nominated for European’s Best FinTech Award. How did they achieve it?

TOP10 Misconceptions About The Financial UX Design
Thousands of digital financial services do not achieve their goals. This is partly due to the design or, specifically, to the financial UX design misconceptions.

Digital Banking UX Design: Challenges & Opportunities
20 straightforward banking UX design trends, challenges and opportunities to create amazing financial services.

Boosting The UXDA Team's Power
We truly believe that great results are made when you love your job and work side by side with likeminded people. I'm really proud that we can call UXDA team our second family.

UXDA Celebrates 8th-year Achievements Gatsby Style
Happy 8th birthday, UXDA! Every year our team reaches more and more exciting peaks and passes through different challenges. And this year we celebrated it Gatsby style!

With ITTI Digital’s permission, we are sharing an exclusive step-by-step case study on designing a next-generation banking back office that will definitely become a game changer in the industry.

Solve Pain Points through Information Architecture in Banking Product
Finance Digitalisation causes many banks to adjust their approach to the development of their products and services. Today, more and more financial companies evolve by creating user-centered services and simpler and more convenient solutions...

UXDA Is One Of The Leading FinTech Companies In German-Baltic Business Awards
UXDA has been recognized as one of the leading FinTech companies in the German-Baltic Chamber of Commerce (AHK) Awards 2019!

Banks Are Losing Customers Because of These UX Mistakes
Capgemini and Efma released their annual Retail Banking Report and there are 3 key findings about banking user experience.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Inese, lead ux architect & consultant.
Inese embodies a powerful fusion of two passions: finance and UX design. Her experience in trade finance, AML and wealth management provides her with exceptional expertise to always find the best solutions for the users. Her unique talent to find value in every product has resulted in countless success stories for our clients.
Alex, Founder/ CEO/ UX Strategist
Alex has dedicated half of his life to studying human psychology, as well as business success, developing 100+ digital projects and 30+ startups. He spent 10 years researching UX and finance to create UXDA's methodology. Alex is a passionate visionary who's capable of solving any challenge to improve the financial industry.
We use cookies
By using our website, you agree to our Cookie Policy .
- DBS transformation (C): The world’s best digital bank
This case series examines the two stage transformation of DBS 2009- 2017. In both stages the bank places the customer as the centre of its thinking about how to structure, resource and play in the market. In 2009 DBS was an underperforming national bank with overseas branches, losing traction and lacking a compelling strategy. Under new leadership the A case describes the initial implementation of its turnaround strategy with the objective of creating a competitive world class multi national bank. DBS must decide which overseas market to focus on and how to enter. It raises the issue of the role of the fintechs in shaping the future of banking and its likely impact on the bank’s strategy. The B case describes DBS’s digital pure-play entry into the Indian market, its strategic reset now with an ambition to be like a 22,000 person start up prompted by its assessment of what the fintech landscape populated by the likes of Alibaba/ant financial. The case describes significant progress but asks whether this is sufficient given how the industry is evolving. The C case describes the company’s progress up to 2017 and highlights why Euromoney named DBS as the World’s Best Digital bank. It asks whether this progress is sufficient in given the amount of sectoral change.
- This case series allows students to examine the implementation of a customer-led strategy in an industry undergoing disruption.
- More specifically students learn how to implement a customer-led strategy, how to enhance an organisation’s agility, how to embed an innovative culture.
The Case Centre
Cranfield University
Wharley End Beds MK43 0JR, UK Tel +44 (0)1234 750903 Email [email protected]
Harvard Business School Publishing
60 Harvard Way, Boston MA 02163, USA Tel (800) 545-7685 Tel (617)-783-7600 Fax (617) 783-7666 Email [email protected]
Asia Pacific Case Center
NUCB Business School
1-3-1 Nishiki Naka Nagoya Aichi, Japan 460-0003 Tel +81 52 20 38 111 Email [email protected]
IMD retains all proprietary interests in its case studies and notes. Without prior written permission, IMD cases and notes may not be reproduced, used, translated, included in books or other publications, distributed in any form or by any means, stored in a database or in other retrieval systems. For additional copyright information related to case studies, please contact Case Services .
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
- DBS transformation (A): Becoming a world-class multinational bank
- DBS transformation (B): Going digital and creating a 22,000 person start-up

Europe has enlisted Mario Draghi to boost economic dynamism. His upcoming report will address lagging growth, digital transformation, and AI invest...

Singapore-based DBS bank was being shaken by nimble competitors and needed to change fast. CEO Piyush Gupta knew spending big on technology wasn't ...

Companies that excel in both digital and sustainable transformation attract a stock market premium, according to research. So, how do you tap into ...
The increasing datafication of the workplace is often cast as a means of imposing organisational and managerial control on workers. This reflection...

Too many organizations assume late-career workers can't keep up with new technology. In doing so, they are ignoring a hugely important labor pool.

Since the dawn of video games, there have been gaming competitions. But for decades, such contests were regarded as beneath the hallowed realm of '...

Understanding your organizational capacity for agility and responding to events accordingly is the key to success in the new business environment, ...

Companies that excel in both digital and sustainable transformation attract a stock market premium, according to research by Michael Wade, Lazaros ...

- Shared Services
- Nearshore Outsourcing
- Digital Transformation
- Finance Operations
- Business Operations
- IT Operations
- M&A and Private Equity
- GBS & Shared Services
- Implementation
- Optimization
- Business Process Outsourcing
- IT Outsourcing
- Intelligent Automation
- Digital Strategy Consulting
- RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
- Intelligent Document Processing
- Test Automation
- BI & Analytics
- Key Partnerships
- Cloud Transformation
- Cloud Strategy
- Cloud Implementation
- Cloud Managed Services
- Modern Finance
- Finance Transformation Services
- Business Intelligence
- Finance & Accounting Outsourcing
- Accounts Payable (P2P)
- Accounts Receivable (O2C)
- General Accounting (R2R)
- Customer Service
- Customer Service Support
- Human Resources
- HR Outsourcing
- Revenue Cycle Management
- Banking & Financial Services
- Loan Processing
- Restaurants
- Restaurant Audit & Brand Protection Services
- Restaurant IT Support Services
- Infrastructure Management
- Hybrid Infrastructure Management
- End-User Support
- Service Desk
- IT Staffing
- Nearshore Software Development
- Cloud Partners
- Azure Services
- AWS Services
- Integrations and Carve Outs
- Private Equity
- Private Equity Services
- Delivery Centers
- Support Hubs
Industry expertise matters. We provide specialized IT and business services across all the major industries.
- Financial Services
- Other Industries
- Webinars on Demand
- Upcoming Events
- Success Stories
Learn how Auxis’ nearshore solutions strengthen processes and increase efficiency.
- Case Studies
- Our Clients & Testimonials
- About Auxis
Experience matters. We help clients overcome challenges, embrace change, and adapt their businesses for future success.
- Leadership Team
- Our Partnerships
- IRIS Payment Platform
- IRIS Bill Payment
- IRIS POS & Merchant
- IRIS Payment Gateway
- IRIS Digital Banking
- API Management
- Bill Payments
- Prepaid Cards
- Remittance Processing
- ATM Acquiring
- Internet Banking
- Mobile Banking
- Merchant & POS Acquiring
- Social Payments
- Mobile Wallets
- Virtual Cards
- Central Issuance
- Instant Issuance
- Ecommerce Payment Gateway
- Biometric Identity
- Fraud Prevention
- High Availability
- Oracle Services & Support
- Case Studies

Ooredoo Qatar enables self-service SIM dispensing with IRIS Payment Platform
Download Case Study
Partner with TPS
- Channel Partners
- Solution Partners

To find out how we can possibly partner together, please send us a message.
- Recognition

Ocean Financial Middle East selects TPS Payment Platform to drive Prepaid Cards Service in the Middle East
Our History

Chronological history of TPS from inception to present day

Ooredoo Qatar enables SIM dispensing with IRIS Payment Platform
Ooredoo Qatar attains new height in customer self-service by enabling SIM dispensing using IRIS omnichannel payment platform.

Liberia marches towards interoperable payment ecosystem
Liberia, the ‘land of free’, Africa’s first and oldest modern republic and one of the most promising countries in West Africa has..

1LINK offers Inter Bank Funds Transfer to its member banks with TPS Technology
1LINK started its journey bank in 1997 when two banks took the initiative to form a shared ATM switch. It is a consortium of major banks..

TPS helps BRAC Bank offer innovative products to its customers
BRAC Bank Limited, one of the latest generation of commercial banks which started its journey on the 4th of July 2001 with a..

IRIS Payment Platform Benchmarks with IBM Power 8
This case-study describes TPS IRIS Payment Platform’s benchmark performance test carried out in IBM Customer Center in Montpellier..
1LINK goes live with Utility Bill Payment Service
1LINK started its journey bank in 1997 when two banks took the initiative to form a shared ATM switch. It is a consortium of major..

HBL Oman deploys TPS’ EFT Switch to transform its payment infrastructure
One of HBL’s initiatives in the Middle East is HBL Oman that serves Pakistani and international customers. Over the years..
TPS enables Habib Bank Limited to migrate from MOBS to MISYS Core Banking System
Habib Bank Limited is the largest bank in Pakistan and a thoroughly established banking chain throughout the world. It has an extensive..

SCB smoothly migrates to Phoenix as a unified ATM Controller
Standard Chartered Pakistan Limited (SCBPL) had acquired Union Bank in 2006 and went through the process of integrating the software..
HBL goes online with PRISM – the complete Internet Banking Solution
Habib Bank Limited (HBL), the largest bank in Pakistan, was looking to offer a unique blend of consumer and corporate banking..
Latest Blog Posts

SOC Analyst to Combat Cyberattacks (New Approach Based on AI & ML)
April 10, 2020

Fraud Management Best Practices to Secure Digital Banking Channels
November 8, 2018
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

The Value of Digital Transformation
- Eric Lamarre,
- Shital Chheda,
- Marti Riba,
- Vincent Genest,
- Ahmed Nizam

A team at McKinsey tracked the performance of 80 banks over four years to identify exactly how their transformation efforts paid off — and how others can follow suit.
While 89% of large companies globally have a digital and AI transformation underway, they have only captured 31% of the expected revenue lift and 25% of expected cost savings from the effort. Until business leaders are convinced of the value and confident in how to get it, they are unlikely to do the difficult, hands-in-the-dirt changes needed to improve their success rate. To see where digital transformation creates value, the authors used McKinsey’s Finalta benchmark, which tracked the performance of 80 global banks every year from 2018 to 2022 against a set of 50 normalized metrics, such as digital/mobile adoption, digital sales by banking product, number of people in contact centers, and number of branches. They found that digital leaders are creating much more shareholder value than laggards, often by creating value that’s hard to copy.
“Show me the money!” Cuba Gooding Jr., playing Rod Tidwell, made those words a cultural touchstone in the movie Jerry McGuire . He was not just voicing his concerns about committing to a sports agent, played by Tom Cruise in this case; he was also questioning Cruise’s commitment.
- EL Eric Lamarre is a senior partner in McKinsey’s Boston office, leader of the Digital Practice in North America, and coauthor of REWIRED .
- SC Shital Chheda is a partner in McKinsey’s Chicago office, and co-leads the Digital Retail Banking practice and leads the Client Experience in Banking practice in North America.
- MR Marti Riba is a Partner in McKinsey’s Boston office, and co-leads the Digital Retail Banking practice in North America.
- VG Vincent Genest is an Associate Partner in McKinsey’s Boston office, and co-leads the Digital Retail Banking practice in North America.
- AN Ahmed Nizam is a senior insights manager in McKinsey’s Chicago office, and leads Finalta’s Impact partnership practice.
Partner Center
- Digital Marketing
- Facebook Marketing
- Instagram Marketing
- Ecommerce Marketing
- Content Marketing
- Data Science Certification
- Machine Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Data Analytics
- Graphic Design
- Adobe Illustrator
- Web Designing
- UX UI Design
- Interior Design
- Front End Development
- Back End Development Courses
- Business Analytics
- Entrepreneurship
- Supply Chain
- Financial Modeling
- Corporate Finance
- Project Finance
- Harvard University
- Stanford University
- Yale University
- Princeton University
- Duke University
- UC Berkeley
- Harvard University Executive Programs
- MIT Executive Programs
- Stanford University Executive Programs
- Oxford University Executive Programs
- Cambridge University Executive Programs
- Yale University Executive Programs
- Kellog Executive Programs
- CMU Executive Programs
- 45000+ Free Courses
- Free Certification Courses
- Free DigitalDefynd Certificate
- Free Harvard University Courses
- Free MIT Courses
- Free Excel Courses
- Free Google Courses
- Free Finance Courses
- Free Coding Courses
- Free Digital Marketing Courses
15 Digital Transformation Case Studies [2024]
In a world where technology relentlessly reshapes our world, businesses that fail to adapt are destined for obsolescence. These 15 digital transformation case studies present a thrilling narrative of change, charting the journeys of companies that dared to embrace the digital frontier. Each story unfolds as a high-stakes gamble where traditional practices are disrupted, often under the threat of imminent collapse. These businesses, spanning diverse industries from retail to agriculture, engaged in transformative practices not just to survive but to radically reinvent themselves. As we explore these narratives, consider them as a playbook for disruption, illustrating the necessity of digital evolution and its perils and promises.
15 Digital Transformation Case Studies
1. nordstrom: reinventing retail through digital customer experiences.
Nordstrom, an upscale American chain of department stores, has long been known for its commitment to customer service. As digital technologies evolved, Nordstrom embraced a digital transformation strategy to enhance its customer experience and seamlessly integrate online and in-store shopping.
Transformation
a. Omni-channel Integration: Nordstrom invested heavily in creating a seamless omni-channel experience. They enhanced their capabilities to monitor inventory in real-time both in stores and online, enabling customers to verify product availability and reserve items for in-store pickup.
b. Mobile App Enhancements: The Nordstrom mobile app was enhanced with features like “Style Boards,” a digital tool allowing salespeople to create and share personalized fashion recommendations virtually.
c. Data Analytics: Using advanced data analytics, Nordstrom acquired deep insights into customer preferences and shopping behaviors. This enabled them to tailor their marketing efforts and enhance customer engagement effectively.
The digital initiatives paid off by enhancing customer engagement and satisfaction. The ability to shop seamlessly between online and physical stores improved the overall shopping experience, increasing sales and customer loyalty.
Related: Evolution of Digital Transformation
2. Mayo Clinic: Digital Innovation in Healthcare
The Mayo Clinic is recognized worldwide for its specialized medical care. Faced with the growing need for healthcare modernization and improved patient outcomes, Mayo Clinic initiated a comprehensive digital transformation.
a. Telemedicine: Adopting telemedicine technologies was accelerated, allowing patients to consult with Mayo Clinic specialists remotely. This was specifically crucial during pandemic scenarios
b. Electronic Health Records (EHR): Mayo Clinic implemented a state-of-the-art EHR system to streamline patient information management across all points of care, improving coordination and treatment outcomes.
c. AI and Machine Learning: They embraced AI technologies for diagnostic imaging, predictive analytics, and personalized medicine, aiming to enhance diagnosis accuracy and patient care planning.
The digital transformation at Mayo Clinic has significantly enhanced patient accessibility, care coordination, and efficiency. Telemedicine has expanded its reach, particularly to those unable to travel for medical care, and AI integration has improved diagnostic and treatment precision.
3. Ford Motor Company: Embracing Digital Manufacturing and Connected Cars
Ford, a century-old automotive manufacturer, faced increasing competition from traditional car manufacturers and new tech-driven entrants like Tesla. In response, Ford launched an aggressive digital transformation strategy to revamp its manufacturing processes and product offerings.
a. Smart Factories: Ford introduced advanced manufacturing techniques in its factories, employing robotics, AI, and IoT to enhance production efficiency and flexibility. Using connected sensors and predictive analytics helped minimize downtime and optimize maintenance.
b. Connected Cars: Ford increased its investment in developing connected car technologies, which enable vehicles to communicate with one another and with infrastructure, enhancing safety and driving experiences. Features include remote services, real-time traffic updates, and emergency response systems.
c. Electric Vehicles (EV) Innovation: To align with global sustainability trends, Ford accelerated its development of electric vehicles, supported by a digital ecosystem that offers an integrated network of charging stations and a smart, user-friendly interface for managing vehicle charging.
Ford’s digital transformation has improved its manufacturing efficiency and positioned it as a leader in the future mobility space, with advancements in connected cars and a strong focus on electric vehicles. These efforts have helped Ford stay competitive in a rapidly evolving automotive landscape.
4. Singapore’s Public Utilities Board (PUB): Digital Water Management
Singapore’s Public Utilities Board (PUB) is responsible for the collection, development, distribution, and reclamation of water in Singapore, a nation with limited natural resources. The Public Utilities Board (PUB) initiated a digital transformation project aimed at boosting sustainability and efficiency in water management.
a. Smart Water Metering: Implementing smart meters across the city-state enabled real-time water usage monitoring, helping to detect leaks early and educate consumers about their water consumption patterns.
b. Automated Water Quality Monitoring: PUB deployed sensors throughout the water supply network to continuously monitor water quality and operational parameters, utilizing AI to predict and address potential issues before they impact consumers.
c. Virtual Singapore: PUB participated in the ‘Virtual Singapore’ project, which features a dynamic three-dimensional city model and a collaborative data platform incorporating hydrological models to simulate water movements and accumulation. This contribution enhances flood management and urban planning.
These technological advancements have made Singapore’s water management system one of the most efficient and sustainable in the world. The integration of digital tools has enabled PUB to ensure a continuous, safe water supply and effective management of the nation’s water resources, even as demand grows and climate challenges intensify.
Related: Impact of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing Sector
5. Netflix: Pioneering the Streaming Revolution
Netflix started as a DVD rental service by mail but transformed into a global streaming giant. As consumer preferences shifted from physical rentals to digital streaming, Netflix pivoted its business model to focus on online content delivery and original programming.
a. Streaming Technology: Netflix invested heavily in developing robust streaming technology, capable of delivering high-quality video content over the internet. This technology adjusts to the user’s bandwidth, ensuring an uninterrupted viewing experience.
b. Data Analytics and Machine Learning: Utilizing big data analytics and machine learning, Netflix analyzes vast amounts of data on viewer preferences to recommend personalized content and to decide which new series and films to produce.
c. Original Content: Transitioning from licensing to producing original content, Netflix created a wide array of popular shows and movies, becoming a major player in the entertainment industry, with its productions receiving critical acclaim and awards.
Netflix’s focus on technology and data-driven content creation has changed how people consume entertainment and how it’s produced. It has grown into one of the most significant entertainment platforms globally, with a vast subscriber base that enjoys content across many genres and languages.
6. DBS Bank: Leading Digital Banking in Asia
DBS Bank, the biggest bank in Southeast Asia, faced intense competition from traditional banks and new fintech startups. In response, DBS embarked on a comprehensive digital transformation journey to redefine banking in a digital world.
a. Digital-Only Banking: DBS launched Digibank, a mobile-only bank in India and Indonesia, which offers a paperless, signatureless, and branchless banking experience. This initiative aimed to tap into the mobile-savvy population in these countries.
b. API Platform: DBS was one of the first banks in Asia to create a comprehensive banking API platform, allowing businesses to integrate banking services into their applications seamlessly, enhancing customer experiences, and creating new revenue streams.
c. Data-Driven Insights: Leveraging big data, DBS provides personalized financial advice to customers. They use AI to offer tailored investment and savings solutions based on individual spending habits and financial goals.
DBS’s digital initiatives have set a new standard in the banking industry, significantly improving customer satisfaction and operational efficiencies. Their digital-first approach has attracted millions of new customers, particularly among the tech-savvy younger demographic, and has solidified their position as a leader in the digital banking space.
7. Domino’s Pizza: From Pizza Company to Tech Company
Domino’s Pizza recognized the importance of technology in the fast-food industry early and embarked on an ambitious digital transformation to become more than just a pizza company. They aimed to enhance customer experience, streamline operations, and increase sales through digital channels.
a. Online Ordering System: Domino’s developed an innovative digital ordering system with a website, mobile app, and voice-recognition system. This system made ordering pizzas quick and easy for customers.
b. Pizza Tracker: Domino’s introduced the “Pizza Tracker,” a feature that enables customers to follow their orders in real-time from preparation through delivery, thereby increasing transparency and boosting customer engagement.
c. AI and Automation: To reduce delivery times and costs, Domino’s has experimented with artificial intelligence and automation technologies, including chatbots for ordering and robotic units for pizza delivery.
These digital initiatives have transformed Domino’s into a tech-forward company, significantly boosting online sales. They have also improved operational efficiencies and customer satisfaction, keeping Domino’s competitive in a fiercely contested market.
Related: Pros and Cons of Digital Transformation
8. Delta Airlines: Enhancing Travel Experience with Digital Solutions
Delta Airlines, one of the largest airlines worldwide, has consistently sought to leverage technology to better its operational efficacy and customer service. Recognizing the evolving needs of modern travelers, Delta has invested in digital technologies to enhance the passenger experience.
a. Mobile App Innovations: Delta’s mobile app includes features like check-in, boarding pass access, flight tracking, and notifications about gate changes or delays, making travel more manageable and less stressful for passengers.
b. RFID Baggage Tracking: Delta implemented Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology for baggage handling. This tech upgrade provides customers with real-time updates on their checked luggage and significantly reduces the rate of lost or misdirected bags.
c. Biometrics for Seamless Travel: Delta has introduced biometric boarding at several airports, using facial recognition technology to speed up the boarding process while enhancing security.
Delta’s digital transformation efforts have improved customer satisfaction by making flying more pleasant less stressful and enhancing operational efficiencies. The use of advanced technology has solidified Delta’s reputation as an innovator in the airline industry.
9. Nike: Revolutionizing Retail with Digital Engagement
Nike, a leading sports apparel and equipment manufacturer, faced the challenge of staying relevant in a rapidly changing retail landscape dominated by digital engagement and e-commerce. Nike embarked on an aggressive digital transformation strategy to maintain its market leadership and connect with a global audience.
a. Nike+ Ecosystem: Nike developed the Nike+ ecosystem, which includes apps for fitness tracking, coaching, and community engagement. These apps collect data that Nike uses to improve customer engagement, tailor marketing efforts, and enhance product development.
b. Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Sales: Nike boosted its direct-to-consumer channel through its website and mobile app, enhancing the customer shopping experience with personalized recommendations based on user activity and preferences.
c. Augmented Reality: Nike introduced augmented reality features in its app, allowing customers to try on shoes virtually, ensuring a better fit and reducing return rates.
Nike’s focus on digital has dramatically shifted its sales strategy, significantly increasing its direct-to-consumer revenue. The personalized and connected experiences have fostered brand loyalty and enabled Nike to gather valuable customer data to drive future product and marketing strategies.
10. Southern California Edison: Powering Up Grid Modernization
Southern California Edison (SCE), one of the biggest electric utilities in the U.S., needed to address aging infrastructure, regulatory pressures, and increasing demand for renewable energy sources. SCE launched a digital transformation initiative to modernize its electrical grid to improve reliability, efficiency, and sustainability.
a. Smart Grid Technology: SCE implemented a smart grid with advanced metering infrastructure, digital sensors, and automated controls throughout the network. This technology provides SCE with real-time data to manage energy flow and respond to issues efficiently.
b. Renewable Integration: The utility company enhanced its grid to handle more renewable energy sources. Digital tools help manage the variability and intermittency of renewables like solar and wind.
c. Customer Engagement Platforms: SCE developed online tools and mobile applications that give customers detailed insights into their energy usage, helping them manage consumption and reduce costs.
SCE’s digital initiatives have enhanced grid reliability and efficiency, which is crucial for incorporating renewable energy. These initiatives have enabled consumers to take a more active role in managing their energy consumption, supporting broader sustainability objectives and compliance with regulatory standards.
Related: Use of Digital Transformation in Real Estate
11. L’Oréal: Digital Beauty Transformation
L’Oréal, the world’s largest cosmetics company, recognized the need to digitally transform to maintain its leadership and respond to changing consumer behaviors, particularly the rise of e-commerce and digital-first beauty brands.
a. Virtual Try-On Technology: L’Oréal acquired the augmented reality and artificial intelligence company ModiFace, which offered customers virtual try-on features for makeup and hair color, enhancing the online shopping experience.
b. Personalized Marketing: Using AI-driven analytics, L’Oréal was able to offer personalized product recommendations and targeted marketing campaigns, improving customer engagement and satisfaction.
c. E-commerce and Social Selling: L’Oréal expanded its e-commerce presence and integrated social media selling platforms, enabling customers to purchase products directly through social media ads and influencers, tapping into the social commerce trend.
These digital initiatives have improved L’Oréal’s engagement with tech-savvy consumers and boosted online sales significantly. The company has stayed competitive in a rapidly evolving beauty market, ensuring that digital and physical retail strategies complement each other.
12. The New York Times: Navigating the Shift to Digital Journalism
As the media landscape shifted from print to digital, The New York Times faced the challenge of adapting to changing reader habits and the decline of traditional newspaper revenue from ads and subscriptions.
a. Digital Subscription Model: The NYT introduced a digital subscription model, which has become a significant revenue stream. It allows them to cater to global readers online, surpassing the limitations of print distribution.
b. Enhanced Digital Content: The publication expanded its digital offerings, including podcasts, video content, and interactive journalism, providing a more comprehensive media experience that appeals to a broader audience.
c. Data Analytics: Using data analytics, The NYT can understand reader preferences and engagement, tailoring content and marketing strategies to increase subscriber retention and attract new readers.
The shift to a digital-first approach has rejuvenated The New York Times, turning it into a model for successful and effective digital transformation in the media industry. It has stabilized its revenue and expanded its audience globally, showcasing its adaptability and innovation in journalism.
13. DHL: Logistics and Supply Chain Innovation
DHL, a global leader in logistics, faced the challenge of adapting to the rapidly evolving demands of e-commerce and global trade. DHL embarked on a digital transformation journey to streamline operations and improve customer service to maintain its competitive edge.
a. Internet of Things (IoT) and Robotics: DHL invested in IoT technologies to enhance tracking and monitoring of shipments. Robotics solutions were integrated into warehouses to automate sorting and packaging processes, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
b. Predictive Analytics: By implementing predictive analytics, DHL improved its logistics planning capabilities. This technology helps anticipate delays and optimize routes in real-time, significantly reducing delivery times.
c. Customer Interaction Platforms: DHL upgraded its customer service platforms, introducing chatbots and AI-driven support systems to provide quick and reliable customer service around the clock.
These innovations have improved operational efficiencies and enhanced client satisfaction by providing more accurate and timely delivery services. DHL’s adoption of advanced technologies has solidified its position as a leader in the logistics sector, capable of handling the complexities of modern supply chains.
Related: Predictions About the Future of Digital Transformation
14. U.S. Social Security Administration (SSA): Enhancing Public Services Through Digital Outreach
The U.S. Social Security Administration, which provides financial support to millions of Americans, faced challenges in service accessibility and administrative efficiency. The SSA initiated a digital transformation strategy to address these issues and better serve the public.
a. Online Services Expansion: The SSA expanded its online platform to allow users to apply for benefits, manage their accounts, and access services without visiting a physical office. This was particularly vital during the COVID-19 pandemic.
b. Digital Documentation: The transition to digital documentation systems helped reduce paperwork, streamline processes, and increase the speed and accuracy of processing claims and applications.
c. Data Security Enhancements: With increased digital interactions, the SSA invested heavily in cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive personal information and prevent fraud.
The SSA’s digital transformation has significantly improved accessibility to services, allowing beneficiaries to manage their benefits easily and securely from home. These changes have also improved the agency’s efficiency and reduced operational costs, ensuring sustainability and responsiveness to public needs.
15. John Deere: Digital Agriculture and Smart Farming Solutions
John Deere, a leading agricultural machinery manufacturer, identified the potential of digital technologies to revolutionize farming. John Deere embarked on a digital transformation journey to maintain its leadership in the industry and help farmers increase productivity and sustainability.
a. Precision Agriculture: John Deere developed advanced precision agriculture technologies, integrating GPS and IoT sensors into their equipment. These technologies empower farmers to continuously monitor crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns in real-time, enhancing the efficiency of planting, watering, and harvesting activities.
b. Data Analytics Platforms: The company introduced platforms that analyze data collected from farm equipment to provide actionable insights, aiding farmers make informed decisions about crop management and resource allocation.
c. Autonomous Machines: John Deere invested in developing autonomous tractors and combined harvesters. These machines can operate with minimal human oversight, increasing efficiency and reducing the labor needed for various farming operations.
John Deere’s digital innovations have profoundly impacted the agricultural sector. Farmers using these advanced tools can achieve higher crop yields, reduce waste, and minimize environmental impact. The company’s commitment to integrating digital technologies into its products has solidified its position as a leader in the agricultural machinery industry, ensuring that it continues to match the evolving requirements of modern agriculture.
Related: Digital Transformation Statistics
The stories of these 15 companies culminate in a powerful testament to the transformative impact of digital technology. Each case study highlights the pivotal role of innovation in securing market leadership and underscores the broader implications for industries at large. Through their transformative journeys, these firms reveal that achieving digital excellence is a challenging endeavor, yet it is abundant with opportunities for growth and reinvention. This collection serves as both a beacon and a warning: embracing change isn’t optional to thrive in the digital era; it’s imperative.
- 10 Free Carpentry Courses [2024]
- Chief Technical Officer vs. Chief Technology Officer [Key Differences] [2024]
Team DigitalDefynd
We help you find the best courses, certifications, and tutorials online. Hundreds of experts come together to handpick these recommendations based on decades of collective experience. So far we have served 4 Million+ satisfied learners and counting.
How can a CMO enable Digital Transformation [2024]

5 Digital Transformation in Manufacturing Case Studies [2024]

Is Digital Transformation a Good Career Option for Women? [2024]

5 Ways Airline Industry Is Implementing Digital Transformation [2024]

Pros and Cons of being a Chief Digital Officer [2024]

How to Make the Perfect Digital Transformation Resume? [With Examples][2024]
More From Forbes
The rise of digital banking: a paradigm shift in fintech.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Founder and CEO of FortySeven Software Professionals , with over a decade of experience advising F500 companies and growth-stage startups.
We live in the era of digitalization. This is a well-known fact, and the banking industry specifically has recently been revolutionized by technology. The advent of digital banks—or neobanks as some refer to them—is changing the financial landscape. With the right approach, a digital bank can be more than just a platform for transactions. It can become a financial ecosystem, offering everything from banking to investment products all in one place.
This goes hand in hand with statistics that promise growth. A recent CB Insights report reveals that investment in fintech, although it saw a decline in Q1 of this year, it was the only sector to see an uptick in quarterly deal volume.
What Sets Apart Digital Banks?
Digital banks are essentially banks that operate without physical branches and are built to provide financial services remotely through digital platforms such as mobile apps and online portals. Of course, it reduces significant costs and therefore gives these banks the opportunity to invest in technologies to improve the business.
Digital banks utilize cloud computing to ensure scalability and reliability, enabling them to manage large volumes of transactions seamlessly. AI and ML can provide personalized banking experiences, fraud detection and predictive analytics. It's no surprise that the global AI in fintech market size was valued at $8.23 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach $61.30 billion by 2031.
Blockchain offers an unprecedented level of security and transparency in transactions. Digital banks incorporate multiple cybersecurity measures, including end-to-end encryption, multifactor authentication, KYC and more. These measures ensure customers' financial information remains protected, making digital banking as safe as, if not safer than, traditional banking.
The Future Of Fintech Funding—A Closer Look
Despite the investment fluctuations, the future of fintech funding remains bright. The $7.3 billion invested in Q1 2024 across 904 deals, as reported by CB Insights , is no small feat. It's a sign of the capital's continued belief in the promise of fintech and digital banking. U.S.-based fintech companies led the charge for this quarter, securing $3.3 billion across 393 deals, followed by the European fintech sector with $2.2 billion from 203 deals. Asian fintechs ranked third, with $1 billion from 210 deals. Noteworthy transactions include a $430 million funding round for the U.K.'s Monzo, led by Alphabet in March, and significant raises by U.S. firms Bilt Rewards and Kore.ai in January, totaling $200 million and $150 million, respectively.
The Rise Of Digital Banks: A Response To Consumer Preferences
The rise of digital banks is not only a technological endeavor but also a response to shifting consumer preferences. Today's customers expect services that fit within their digital lives. They want to manage their finances the same way they shop, communicate and live: digitally, seamlessly and on-demand.
The success of early disruptors like Revolut only underscores this shift. Most digital banks offer accounts that are easier to open, have lower fees and often come with features that make them more customer-centric, like included insurance or the possibility to make investments easily. In my own practice, we’ve built more than 100 digital banks, payment institutions and neobanks for new players on the market, and the one common thread is the mindset of the entrepreneurs who run these businesses: They are all eager to make people's lives easier.
And we see this with digital banks providing customers with the ability to pay or invest on the go. It’s not only about the preferences of the customers but more about the necessity of the real world. As an entrepreneur and owner of a company that has been part of this fintech transformation since its inception, as we look ahead, our vision for the future of finance is one that is inclusive, innovative and, most importantly, digital.
Investing In Innovation: The Key To Digital Banking Success
The industry is highly competitive, with new players entering the market regularly and established banking institutions quickly pivoting to offer digital solutions. To stay ahead, these banks invest heavily in technology, user experience and security. There are a lot of ways to build your own digital bank, and one of them is the implementation of the concept of "banking as a platform," where digital banks open their APIs to third-party developers, allowing them to create complementary services. This approach fosters a rich ecosystem of financial tools and benefits both the banks and their customers.
Since the implementation of cutting-edge technologies is crucial for the success of digital banks, it underscores the necessity of selecting the right technology partners. It's vital to thoroughly vet potential partners to ensure they meet all technical and business requirements. This includes assessing the scalability of their solutions, transaction capabilities, data storage practices and the costs associated with each service.
Choosing a partner that aligns with your own vision for innovation and customer service is key. Attention must be paid to where information is stored to comply with data protection regulations and understand the financial commitment required for scaling infrastructure to meet growing customer demands. This is a mistake that many startups make. In order to avoid it, check first how scalable the solution is.
This comprehensive approach ensures that digital banks can provide secure, efficient and cost-effective services to their users, paving the way for sustained growth and success in the competitive financial landscape.
Final Thoughts
The digital revolution in banking is not just a trend; it's a significant metamorphosis that is shaping how we manage our money, conduct our business and plan our futures. Digital banks are the architects of a more accessible, personalized and efficient financial world. With the right vision and investment, they can direct the way for a financial future that is dynamic and adaptable.
Forbes Technology Council is an invitation-only community for world-class CIOs, CTOs and technology executives. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Why most digital banking transformations fail—and how to flip the odds
April 11, 2023 by Akhil Babbar, Raghavan Janardhanan , Remy Paternoster, and Henning Soller
Digitalization has become an imperative for banks. As we have seen in our review of our case examples, a successful digital transformation can lead to better business outcomes, including higher balances for current account savings accounts, lower cost-to-income ratios, increased customer acquisition and retention rates, and faster time to market.
However, only 30 percent of banks that have undergone a digital transformation report successfully implementing their digital strategy, and the majority fall short of their stated objectives. 1 This low success rate holds true for most industries and has remained constant for many years despite significant technological and organizational innovations, though technology-focused companies typically fare better.
In this post, we discuss why banks often fail to execute their digital transformations—and what they can do to tilt the odds in their favor.
Common traps to avoid
Banks often argue that if they had a sufficient technology budget, their transformations would be successful. But we have seen several banks in recent years allocate significant resources to their digital transformations and still struggle to execute them.
The nature of the banking industry poses specific challenges. For one, banks have invested in technology for decades and thus typically have developed a significant amount of technical debt , along with a siloed and complex IT architecture. Separation between the business and IT makes it more challenging to implement the necessary cultural shifts. Finally, banks also face an aging workforce, particularly compared with purely digital fintechs.
We have identified a common set of execution challenges that threaten to derail banks’ digital transformations, and follow with a set of recommendations for how to overcome them.
Underestimating complexity and cost
A digital strategy begins with a business case, and every business case is calculated with a specific time to impact. Once transformation initiatives extend beyond the expected project duration, the increase in cost can often overtake the projected value of the original transformation or lead to its cancellation.
More than half of digital banking transformations exceed their initial timeline and budget—or fail. 2 Leaders often underestimate the complexities of executing a digital transformation , which typically involve complicated interfaces, data management, and interdependencies across initiatives. Common mistakes include not fully involving all stakeholders in the development of the strategy and blueprint, miscalculating the extent to which existing business processes need to change, and not sufficiently implementing the magnitude of changes required to truly reap the benefits of the transformation. These challenges are especially relevant for banks, given that the business side is often removed from technology developments, business processes are assumed to be fixed, and the IT architecture landscape is particularly complex.
Initial budgets often fail to account for these factors, which can lead to a delay in the impact and the impression that costs have spiraled “out of control” when, in reality, the program was never feasible in the way it was originally envisioned. According to our research, 70 percent of digital transformations exceed their original budgets, and 7 percent end up costing more than double the initial projection. 3
Underestimating technical debt
The need to address technical debt —by cleaning up legacy technology stacks, unused applications, and excessive infrastructure—is often missing from initial transformation budgets or perceived to be less important than other transformation initiatives. It is, however, a critical prerequisite to executing a digital transformation at pace, even if the work does not generate an immediate financial gain. Therefore, banks need to assess and prioritize the work of addressing technical debt from the beginning of a digital transformation.
In general, because banks have many legacy IT applications, they have higher technical debt compared with other industries, making it harder for them to create the platform they need for the digital future (exhibit).
Challenges in measuring impact
As the saying goes, what gets measured gets done. Yet few organizations effectively measure, and therefore deliver, top- and bottom-line value over the course of a digital transformation. Banking leaders must identify critical impact metrics, baseline the current state, and track the impact during and after the transformation. Only then can they achieve the full financial benefits of the transformation effort.
In our experience, banks struggle to accurately quantify and track the impact of their digital strategy and to establish a clear link between specific initiatives and their revenue and profit growth. Too often, leaders do not capture the full value of their digital strategy because they lack well-defined success parameters, inadequately engage the full set of end users (customers, employees, and other stakeholders), and fail to consider the potential adverse effects on customer satisfaction.
Slow pace of change
Large banks typically lag their competitors on innovation speed and productivity. A reliance on traditional operating models, coupled with limited adoption of agile ways of working, can hinder the success of their digital transformation. A McKinsey banking survey conducted in 2021 found that while fintechs and neobanks release new product features every two to four weeks on average, traditional banks have product rollout cycles of four to six months. Our research also shows that large banks are 40 percent less productive than digital natives. 4 This slow pace of change can cause banks to give up on their digital transformations rather than attempt to overcome the underlying cultural barriers that inhibit the speed of the transformation.
Missing talent
While traditional banks know how to hire banking talent, the same is not always true for tech talent . Typically, banks are not the preferred destination for tech talent—but talent is a key prerequisite for making the digital transformation work. Our research suggests that at least 50 percent of employees involved in the transformation should be in-house—and that risks increase significantly when 70 percent or more of the employees involved in the transformation are outsourced. 5 To ensure the success of their digital programs, traditional banks need to refine their employee value proposition to attract more tech talent—for example, by providing incentives and work environments that rival those of fintechs.
Organizational silos
A successful digital transformation relies on close collaboration and coordination across the organization. However, many banks continue to operate in traditional functional or business silos, which leads to conflicting or misaligned priorities, lack of clarity, and a fragmented approach to execution. In our experience, banks often have duplicate systems and solutions, such as customer-relationship-management (CRM) platforms and small and medium-size enterprises (SME) channels, across business lines. Similarly, banks with strong country-level operating models typically overlook efficiency gains that could result from reusing existing functionalities across geographies.
A better path forward
Meeting these challenges requires banking leaders to take a holistic approach across the business, technology landscape, and operating model. However, our experience shows that going all in on a digital transformation can help banks avoid some of the most common pitfalls and yield significant benefits. For example, one major European bank redesigned its operating model and reset roles and responsibilities to embed agile practices throughout the organization. At the same time, it revamped its core banking system, including a complete overhaul of its integration architecture and data architecture. These measures generated cost savings of 30 percent and enhanced the bank’s capacity to deliver value well into the future.
Imperatives for success
Banks can address these challenges by taking several actions, not all of which are intuitive:
- Reduce complexity (which may require simplifying interfaces and addressing dependencies) and avoid surprises by budgeting the necessary time and resources up front (for example, by using micro front ends and reusable APIs and by implementing DevSecOps as a standard across digital initiatives).
- Estimate the technical debt and ensure that the initial budget includes the cost to remove it; otherwise, the debt will lead to delays and cost increases.
- Overinvest in the cultural shift, even if it might not be directly related to technology.
- Attract tech talent and do not try to outsource the transformation.
- Break down organizational silos and design a holistic transformation road map (not just by business area).
To measure the change, agile practices and processes such as quarterly business reviews should be in place to allow for effective prioritization and value tracking. Traditional oversight should be replaced by cross-functional collaboration, cross-silo performance management, and a new concept of joint accountability across the business and IT. Along the way, leaders can highlight “lighthouse” projects to inspire employees and build momentum.
A large-scale digital transformation is not easy, and it is not surprising that most banks struggle to achieve their business objectives on time and within budget. However, banking leaders can take steps to avoid the most common mistakes by defining clear goals and metrics that reflect not only the business change but also the cultural and technical changes required. By doing so, banks can increase their chances for success and reap the full potential of their digital transformations.
Akhil Babbar is a knowledge expert in McKinsey’s Gurugram office, Raghavan Janardhanan is a partner in the Chennai office, Remy Paternoster is a partner in the Madrid office, and Henning Soller is a partner in the Frankfurt office.
1 McKinsey and Oxford Global Projects study on large-scale IT projects, 2001–21. 2 Ibid. 3 Ibid. 4 Average of 15 digital bank examples in comparison to five fintechs in terms of IT productivity. 5 McKinsey and Oxford Global Projects study on large-scale IT projects, 2001–21.
- Perspectives
- Best Practices
- Inside Amplitude
- Customer Stories
- Contributors
Digital Transformation Case Studies: 3 Successful Brand Examples
Learn how three companies—Walmart, Ford, and Anheuser-Busch InBev—successfully transformed their business through digital initiatives to improve the customer experience.

Originally published on March 30, 2022
3 digital transformation case studies
Overcoming common digital transformation challenges, tips for building a digital transformation strategy, always focus on your customers.
Digital transformation is a process in which a company invests in new digital products and services to position it for growth and competition. A successful digital transformation improves the customer experience and enhances the way a company operates behind the scenes.
During a digital transformation, your business deploys new products and technologies and develops new ways to connect with your customers. Once the investment in digital begins, your business can use feedback and data to identify growth opportunities.
The three case studies below—from Ford, Walmart, and Anheuser-Busch InBev (AB InBev)—show how legendary companies went beyond simply creating an app and truly re-thought how digital transformation efforts supported sustainable growth for the business.
- A digital transformation is a major business transformation that employs technology to meet business goals and fundamentally change how companies operate.
- A digital transformation drives new products and services that improve the customer experience.
- A digital transformation gives you more informative behavioral data and more touchpoints with the customer.
- AB InBev, Walmart, and Ford invested in digital technology to accelerate internal processes and develop new digital products, which gave them valuable data on the customer experience and influenced future business investments.
Here are three examples of digital transformation. These leading companies carefully considered how new technology could generate data that made internal processes more efficient and produced insights about how to grow customer value.
Brewing company AB InBev underwent a digital transformation while compiling its network of independent breweries into a unified powerhouse . One of the team’s priorities was moving all their data to the cloud . By doing so, AB InBev enabled all employees to quickly and easily pull global insights and use them to make data-backed decisions.
For example, more accurate demand forecasting means AB InBev teams can match supply with demand, which is essential for such a large company with a complex supply chain. Access to big data from all the breweries means employees can experiment faster and roll out changes that improve business processes.
Gathering more data and opening up that data to internal teams was just the first step of the process, though. AB InBev capitalized on its digital investments by launching an e-commerce marketplace called BEES for its SMB customers—the “mom-and-pop shops”—to order products from. With the BEES platform, AB InBev found that their small and medium-sized businesses browsed the store on the mobile app and added items to their cart throughout the day. However, they only made the final purchases later in the evening.
Based on this behavioral data, the BEES team started sending push notifications after 6:00 p.m. recommending relevant products, which led to increased sales and greater customer satisfaction. Through these efforts, BEES gained over 1.8 million monthly active users and captured over $7.5B in Gross Merchandise Volume.
By closely monitoring metrics such as user engagement and purchasing patterns on the BEES platform, AB InBev has made a big impact with its marketing strategies and improved customer retention.
Jason Lambert, SVP of product at BEES, credits their success with the hard data that told them how their customers behaved and what they needed: “It turned out to be a thousand times better than any of our previous strategies or assumptions.” BEES used behavioral analytics to respond quickly, changing the buying experience to match the needs and habits of their retailers.
As a traditional brick-and-mortar retailer, Walmart began a digital transformation by opening an online marketplace. However, digital transformation is an ongoing process—it doesn’t end at the first website. A digital transformation means companies refocus their operations around digital technology. This usually happens both internally and in a customer-facing way.
To drive more customer value through digital touchpoints, Walmart set up mobile apps and a website to enable customers to purchase goods online. After analyzing customer behavioral information from its app, Walmart added more services such as same-day pickup, mobile ordering, and “buy now, pay later.”
These changes were made to meet customer expectations and improve the customer experience. Walmart’s introduction of a seamless online shopping experience represents a pivotal step in digital innovation, setting new standards for retail convenience and efficiency.
In 2024, Walmart announced an AI-powered logistics product called Route Optimization. This product uses AI to find the most straightforward driving routes, pack trailers efficiently, and reduce miles traveled. In addition to using this product internally, Walmart plans to offer it to other businesses that need to employ more efficient supply chain and logistic processes.
Aside from improving customer experience and logistics, Walmart’s head of mobile marketing , Sherry Thomas-Zon, also notes the importance of data—and access to data—in digital transformations. “Our marketing and product teams are always looking at numbers,” Thomas-Zon said. “It keeps our teams agile despite our size and the increasing amount of data we collect and analyze.”
Ford has embraced several digital transformation initiatives, including using technology to transform and improve manufacturing at one of its biggest automotive factories.
Not having the correct parts available holds up workers and slows down the production process. Ford introduced a material flow wireless parts system so they could track the quantities of different parts and make sure there were enough available. Ford’s use of automation has significantly improved its inventory management process by reducing manual tasks and enhancing worker efficiency.
In 2016, Ford also introduced a digital product for its customers: the FordPass app . It enables Ford owners to control their vehicles remotely. For example, drivers can check their battery or fuel levels and lock or unlock their cars from their phones.
In 2024, Ford took its digital transformation even further when it launched the Ford and Lincoln Digital Experience . Key features include personalized vehicle settings, real-time traffic updates, and seamless integration with smart home devices. The platform also provides advanced navigation, remote control of vehicle functions via the FordPass app, and in-depth vehicle health monitoring.
To capitalize on these digital touchpoints, Ford uses data from its app to improve user experiences . With the ability to capture and analyze data in real-time, Ford’s leadership can now make quicker, more informed decisions that directly enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Ford’s success is grounded in the same process as Walmart and AB InBev. They used their digital transformation to gather detailed information about how customers interact with their products. Then, they made data-driven decisions to provide more value.
It’s not called a transformation for no reason. You’re changing the way your business operates, which is no easy feat. Planning and effective change management strategies are key to overcoming digital transformation challenges.
Create a digital transformation strategy roadmap that outlines your integration strategy and details how this will affect your teams, processes, and workflows. Once you’ve created your plan, share it with the entire company so everyone can use it as a single reference point. Use a project management tool that enables team members to get a big-picture overview and see granular details like the tasks they’re responsible for.
It takes time for teams to onboard and move away from what was successful under the previous system, for example, shifting from heavyweight to lightweight project planning. Make sure you factor some breathing space into your roadmap—giving everyone a chance to get used to the new way of operating.
As part of a digital transformation, you’ll want your team to develop new skills as well. Upskill your team by incorporating digital skills into your employee development plans . Provide people with opportunities to learn and then track their progress. Promote platforms like LinkedIn Learning to help your teams understand the nuances of digital transformation and boost their skills.
If you believe there’s an end-state to digital transformation, more challenges will arise. New technology and consumer behaviors are always emerging, meaning digital transformation is ongoing. It’s not something you’ll complete in a week. Rather, it’s a continuous state of experimentation and improvement.
At Amplitude, we refer to this process as digital optimization . If digital transformation brings new products, services, and business models to the fold, then digital optimization is about improving these outputs. Both digital transformation and digital optimization are important—digital transformation signals the start of new investments, and digital optimization compounds them.
Examine how each part of the transformation will affect your customers and your employees. Then, you can be intentional and introduce initiatives that positively impact your business.
Diagnose what you want from a digital transformation first
There are different ways of approaching a digital transformation. Some companies prefer to implement an all-inclusive digital strategy, transforming all parts of their organization at the same time. Others opt for a less risky incremental strategy. Every company is different. To choose the best approach, examine your whole organization and analyze where digital systems could help.
Consider your business goals. Investigate how a digital transformation could impact the customer experience. What new products could you provide? How could you improve your services? For example, you might use artificial intelligence to create a chatbot that reduces customer service wait times—or purchase software that does the same.
You’ll also want to review your business processes. How could a digital transformation speed up your current workflows, improve your operations, or enable more collaboration between teams? Asking these questions lets you challenge the way you operate and will help you identify problems in your organization that you might not have noticed before. For example, perhaps your deliveries are often delayed, and you could make delivery smoother by digitizing elements of your supply chain .
Get cross-team involvement
Though different teams may work separately, your customers are affected by each department. Collaboration elevates everyone’s work because it means people can make informed decisions.
Make sure you get input from all of the right stakeholders when you create your digital transformation strategy. Ask:
- What processes hold you up?
- Where are the bottlenecks?
- What data would be useful for you?
Enable everyone to access the data they need without input from anyone else. Help your employees improve their data literacy . Start by training all your employees to use your organization’s data tools and software. To help everyone in your organization access and analyze data, adopt easy-to-use self-service tools (e.g., an analytics tool and a CRM). Then, lead by example. Provide inspiration by using data storytelling in your presentations to explain the decisions you make.
Encourage collaboration between teams by creating shared resources so they have spaces to present insights and submit suggestions. This could be as simple as creating a Google Doc for brainstorming that multiple teams can access or sharing charts directly within your analytics solution, like with Amplitude Notebooks . Then, you can start to experiment and make improvements to the digital customer experience like Walmart, Ford, and AB InBev did.
Once your digital transformation is moving, a digital optimization strategy is an opportunity to generate growth. Your digital transformation initiatives will continue in parallel, and the process will become a feedback loop:
- Deploy new digital systems and products.
- Analyze the data that comes forth from these investments. Use it to draw insights about your customers or processes.
- Make decisions based on the data and make changes.
Keep customer needs at the heart of your work. Let them guide you as you undergo digital transformation. As you gather more data about how your customers interact with your new digital products, use it to make the experience even better for them. This will lead to more trust and loyalty and, ultimately, more recurring revenue.
To continue your learning about digital transformation and optimization, join an Amplitude workshop or webinar or read our Guide to Digital Optimization .
- MIT Sloan. How to build data literacy in your company
- Ernst & Young. How global supply chain strategy is changing and what comes next
- Datanami. From Big Beer to Big Data: Inside AB InBev’s Digital Transformation
- Predictable Profits. How Ford Embraced Digital Transformation
- APMG International. Heavyweight vs Lightweight Management

About the Author
More best practices.

What is a Data Warehouse?
The guide to data accessibility, what is a product roadmap a definitive guide, new amplitude + snowflake integration delivers the modern data stack, digital optimization vs. digital transformation explained, 6 essential digital optimization skills you need, what is martech full guide and how to build your stack, recurring revenue 101: mrr vs. arr.
- Schedule a Demo
Posted by MeridianLink | July 15, 2024
How Broadway Bank leveraged MeridianLink® One to Meet Customer Needs
A story of efficiency, profitability, and compliance shared on the Banking Transformed Podcast
The materials available in this article are for informational purposes only and not for the purpose of providing legal advice. You should contact your own advisors with questions regarding digital banking solutions herein. The opinions expressed in this article are of the individual authors and may not reflect the opinions of MeridianLink, Inc.
In this special eight-part series of the Banking Transformed podcast —recorded at MeridianLink ® LIVE! and featuring MeridianLink ® customers—industry leaders discuss their journeys and lessons learned along their unique paths to digital growth.
“If you’re not where your customers are, you might miss out on an opportunity,” remarked Lynn Yznaga. The Senior Vice President at Broadway Bank shares the importance on the need for digital banking solutions.
Digital growth guides Broadway Bank as it navigates growth, banking customer experience, and risk sensitivity through digital banking solutions. This episode of the Banking Transformed features Broadway Bank — on how a bank can achieve success with strategy and technology.
Learn more about how MeridianLink ® helps our customers operationalize their path to digital growth.
A Case Study in Lending Efficiency and Digital Banking Solutions
Broadway Bank’s adoption of MeridianLink ® One transformed its consumer and mortgage lending into a unified platform. It consolidated multiple applications into one cohesive system. Lynn explains, “We had six or seven different applications that we were using bank-wide, and with MeridianLink, we were able to consolidate all that information into one spot for seamless digital banking.”
This interconnectivity led to significant enhancements in their digital banking solutions. Lynn points out, “Processes have become much more efficient, and our turnaround time for the purchase of money decreased by at least six days. The system is centralized, and customers can even track their applications in real-time.”
Lynn reflects on their approach to addressing internal changes: “Our biggest challenge was modifying our internal processes. We learned not to force the system to fit our processes but rather to adapt our processes to fit the system.”
Broadway Bank’s decision to opt for an out-of-the-box solution without heavy customization proved beneficial as well. Lynn notes, “We received positive feedback on MeridianLink’s ease of use and minimal maintenance requirements. It’s been a streamlined experience in digital banking without constant customization needs.”
Knowing Your Customers Can Yield Great Returns From Great Banking Customer Service
Like many financial institutions, Broadway Bank still has customers who prefer to meet face-to-face in a branch. So, whether it’s digital or in person, they want to be able to give every customer that same experience, supported by their comprehensive digital banking solutions.
A study by Accenture reveals that more than six in 10 customers turn to branches to solve complicated problems.
Lynn explains how they combine digital and human interactions to create a smooth experience: “It’s important to have a loan officer up front who can conduct a good interview with the customer and share that information with the back office. Then, we provide the online tools and resources the customer needs.”
Accenture data also shows that banks have an opportunity to strengthen fraying customer connections with life-centric solutions and better engagement across digital and physical channels. An approach that could lead to a boost in revenue from primary customers by up to 20%.
Discover how solutions like MeridianLink ® One help banks provide customers with an integrated experience across all touchpoints without disruptions or data loss, leveraging advanced digital banking solutions.
Balancing Simplicity and Risk
Creating user-friendly processes without compromising on risk or regulatory standards is essential for any financial institution. Lynn says that one way Broadway Bank manages this balance is by maintaining open communication and a collaborative approach across all lines of business.
“Befriending your compliance partners is the key to balancing simplicity and risk effectively. This approach allows me to speak intelligently about how any mortgage transaction might impact other potential loan scenarios, ensuring a comprehensive and compliant experience with our digital banking solutions.”
Broadway Bank also conducts monthly meetings to share updates across departments and discuss what we are seeing and what’s coming up next. This holistic communication allows for a comprehensive understanding of different loan scenarios and their interconnectedness.
Listen to the full podcast episode below and stay tuned for the next installment of this Banking Transformed Podcast series!
Similar Posts

Optimize Applicant Engagement With Automated Cross-Sell: Key Takeaways
Anywhere from a quarter to half of all banking purchases go to financial institutions that are not the consumer’s primary…

Consumer Expectations Have Transformed
This digital reality has inspired a new wave of expectations for consumers, paving the way for financial institutions (FIs) to…

The Future of Collections Is in the Cloud
Debt collection has long been a major pain point for financial institutions, one made even more difficult by the limitations…

Data-Driven Insights for Better Decision-Making: How Financial Institutions Can Use Data Analytics To Drive Success
Implementing a powerful, turnkey business intelligence tool that enables your financial institution to make better business decisions faster through access…

Arc Award Winners: Celebrating Creative Innovation
Strategic thinking, innovation, and effectiveness. Three essential ingredients to financial institutions contributing to and participating in the future of banking.

2023 MeridianLink User Forum in Review
The 2023 MeridianLink® User Forum was, in a word, magical! Thank you to all the customers, partners, and colleagues who…
Navigating Digital Transformation: A Risk-Based Approach for Industry 4.0 Innovation
- Published: 21 August 2024
Cite this article

16 Accesses
Explore all metrics
This study addresses the critical gap in understanding the risks associated with digital transformation, particularly focusing on their impact on business innovation and growth within Industry 4.0. While the transformative potential of digital technologies is well-documented, the inherent challenges remain underexplored. This research introduces an innovative decision-support model designed to evaluate and prioritize risks unique to digital transformation in the industrial sector. Utilizing Pythagorean fuzzy sets (PFSs) and multicriteria decision-making (MCDM) techniques, the model systematically assesses and ranks risks to enhance informed decision-making processes. An extensive case study reveals that key risks include a lack of commitment from top management and unstable market environments, which significantly jeopardize the digital transformation journey. The study’s findings underscore the importance of a strategic approach in mitigating these risks, facilitating a smoother transition to the digital economy. The proposed model offers actionable insights for organizations to optimize their digital transformation strategies by integrating advanced analytics and machine learning. This research contributes to the knowledge economy by providing a robust framework for managing the complexities of digital transformation, promoting sustainable innovation, and enhancing overall business performance. The study’s strengths are further reinforced through sensitivity and comparison analyses, highlighting the resilience and practical applicability of the decision-support model. These insights are invaluable for policymakers, industry leaders, and scholars focused on leveraging technology to drive economic growth and societal progress in the era of Industry 4.0.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

A Framework for Continuous Assessment of IT Value in Industry 4.0
Managerial challenges of industry 4.0: an empirically backed research agenda for a nascent field.
Industry 4.0: critical investigations and synthesis of key findings
Explore related subjects.
- Artificial Intelligence
- Medical Ethics
Abbassi, R., Arzaghi, E., Yazdi, M., Aryai, V., Garaniya, V., & Rahnamayiezekavat, P. (2022). Risk-based and predictive maintenance planning of engineering infrastructure: Existing quantitative techniques and future directions. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 165 , 776–790.
Article Google Scholar
Aceto, G., Persico, V., & Pescapé, A. (2020). Industry 4.0 and health: Internet of things, big data, and cloud computing for healthcare 4.0. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 18 , 100129.
Ande, R., Adebisi, B., Hammoudeh, M., & Saleem, J. (2020). Internet of Things: Evolution and technologies from a security perspective. Sustainable Cities and Society, 54 , 101728.
Ansong, E., & Boateng, R. (2019). Surviving in the digital era–business models of digital enterprises in a developing economy. Digital Policy, Regulation and Governance, 21 (2), 164–178.
Avelar-Sosa, L., García-Alcaraz, J. L., Mejía-Muñoz, J. M., Maldonado-Macías, A. A., & Hernández, G. A. (2018). Government support and market proximity: Exploring their relationship with supply chain agility and financial performance. Sustainability, 10 (7), 2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072441
Balakrishnan, R., & Das, S. (2020). How do firms reorganize to implement digital transformation? Strategic Change, 29 (5), 531–541.
Barroso, M., & Laborda, J. (2022). Digital transformation and the emergence of the Fintech sector: Systematic literature review. Digital Business, 2 (2), 100028.
Borchardt, M., Pereira, G. M., Milan, G. S., Scavarda, A. R., Nogueira, E. O., & Poltosi, L. C. (2022). Industry 5.0 beyond technology: An analysis through the lens of business and operations management literature. Organizacija, 55 (4), 305–321.
Bresciani, S., Huarng, K. H., Malhotra, A., & Ferraris, A. (2021). Digital transformation as a springboard for product, process and business model innovation. Journal of Business Research, 128 , 204–210.
Butt, J. (2020). A conceptual framework to support digital transformation in manufacturing using an integrated business process management approach. Designs, 4 (3), 17.
Chen, Y., Fan, X., & Zhou, Q. (2020). An inverted-U impact of environmental regulations on carbon emissions in China’s iron and steel industry: Mechanisms of synergy and innovation effects. Sustainability, 12 (3), 1038.
Chen, M., Sinha, A., Hu, K., & Shah, M. I. (2021). Impact of technological innovation on energy efficiency in industry 4.0 era: Moderation of shadow economy in sustainable development. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 164 , 120521.
Choong, K. K., & Leung, P. W. (2022). A critical review of the precursors of the knowledge economy and their contemporary research: Implications for the computerized new economy. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 13 (2), 1573–1610.
Cichosz, M., Wallenburg, C. M., & Knemeyer, A. M. (2020). Digital transformation at logistics service providers: Barriers, success factors and leading practices. The International Journal of Logistics Management, 31 (2), 209–238.
Demiralay, E., & Paksoy, T. (2022). Strategy development for supplier selection process with smart and sustainable criteria in fuzzy environment. Cleaner Logistics and Supply Chain, 5 , 100076.
Ding, Y., Fan, L., & Liu, X. (2021). Analysis of feature matrix in machine learning algorithms to predict energy consumption of public buildings. Energy and Buildings, 249 , 111208.
Dutta, G., Kumar, R., Sindhwani, R., & Singh, R. K. (2020). Digital transformation priorities of India’s discrete manufacturing SMEs–A conceptual study in perspective of Industry 4.0. Competitiveness Review: An International Business Journal, 30 (3), 289–314.
Dwivedi, A., Agrawal, D., Jha, A., & Mathiyazhagan, K. (2023). Studying the interactions among Industry 5.0 and circular supply chain: Towards attaining sustainable development. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 176 , 108927.
Edirisinghe, D., Nazarian, A., Foroudi, P., & Lindridge, A. (2020). Establishing psychological relationship between female customers and retailers: A study of the small-to medium-scale clothing retail industry. Qualitative Market Research: An International Journal, 23 (3), 471–501.
Einabadi, B., Baboli, A., & Ebrahimi, M. (2019). Dynamic predictive maintenance in Industry 4.0 based on real time information: Case study in automotive industries. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 52 (13), 1069–1074.
Favoretto, C., Mendes, G. H. D. S., Filho, M. G., Gouvea de Oliveira, M., & Ganga, G. M. D. (2022). Digital transformation of business model in manufacturing companies: Challenges and research agenda. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 37 (4), 748–767.
Ghosh, S., Hughes, M., Hodgkinson, I., & Hughes, P. (2022). Digital transformation of industrial businesses: A dynamic capability approach. Technovation, 113 , 102414.
Goyal, N., Howlett, M., & Taeihagh, A. (2021). Why and how does the regulation of emerging technologies occur? Explaining the adoption of the EU General Data Protection Regulation using the multiple streams framework. Regulation & Governance, 15 (4), 1020–1034.
Graa, A., & Abdelhak, S. (2020). The determinants of electronic word of mouth’ influence in algerian consumer choice: The case of restaurant industry. Acta Oeconomica Universitatis Selye, 9 (2), 35–47.
Grandhi, B., Patwa, N., & Saleem, K. (2021). Data-driven marketing for growth and profitability. EuroMed Journal of Business, 16 (4), 381–398.
Griffith, J. A., Baur, J. E., & Buckley, M. R. (2019). Creating comprehensive leadership pipelines: Applying the real options approach to organizational leadership development. Human Resource Management Review, 29 (3), 305–315.
Haleem, A., Javaid, M., Singh, R. P., & Suman, R. (2021). Telemedicine for healthcare: Capabilities, features, barriers, and applications. Sensors International, 2 , 100117.
Haleem, A., Javaid, M., Qadri, M. A., Singh, R. P., & Suman, R. (2022). Artificial intelligence (AI) applications for marketing: A literature-based study. International Journal of Intelligent Networks, 3 , 119–132.
Hassoun, A., Aït-Kaddour, A., Abu-Mahfouz, A. M., Rathod, N. B., Bader, F., Barba, F. J.,... & Regenstein, J. (2023). The fourth industrial revolution in the food industry—Part I: Industry 4.0 technologies. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 63 (23), 6547–6563.
Helbing, D. (2019). Societal, economic, ethical and legal challenges of the digital revolution: From big data to deep learning, artificial intelligence, and manipulative technologies (pp. 47–72). Springer International Publishing.
Hermes, S., Riasanow, T., Clemons, E. K., Böhm, M., & Krcmar, H. (2020). The digital transformation of the healthcare industry: Exploring the rise of emerging platform ecosystems and their influence on the role of patients. Business Research, 13 (3), 1033–1069.
Jamwal, A., Agrawal, R., Sharma, M., & Giallanza, A. (2021). Industry 4.0 technologies for manufacturing sustainability: A systematic review and future research directions. Applied Sciences, 11 (12), 5725.
Javaid, M., Haleem, A., Singh, R. P., Suman, R., & Gonzalez, E. S. (2022). Understanding the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies in improving environmental sustainability. Sustainable Operations and Computers, 3 , 203–217.
Karachi, S., & Rehan, M. (2021). Impact of crude oil, exchange rate and gold price on kse100 index: Before & during covid-19 pandemic by using var model. Journal of Contemporary Issues in Business and Government, 27 (6), 420–439.
Google Scholar
Kaur, S. J., Ali, L., Hassan, M. K., & Al-Emran, M. (2021). Adoption of digital banking channels in an emerging economy: Exploring the role of in-branch efforts. Journal of Financial Services Marketing, 26 , 107–121.
Koh, L., Orzes, G., & Jia, F. J. (2019). The fourth industrial revolution (Industry 4.0): Technologies disruption on operations and supply chain management. International Journal of Operations & Production Management, 39 (6/7/8), 817–828.
Korherr, P., Kanbach, D. K., Kraus, S., & Mikalef, P. (2022). From intuitive to data-driven decision-making in digital transformation: A framework of prevalent managerial archetypes. Digital Business, 2 (2), 100045.
Kumar, R., Singh, R. K., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2020). Application of industry 4.0 technologies in SMEs for ethical and sustainable operations: Analysis of challenges. Journal of cleaner production, 275 , 124063.
Lai, K. H., Feng, Y., & Zhu, Q. (2023). Digital transformation for green supply chain innovation in manufacturing operations. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 175 , 103145.
Lehtinen, J., Aaltonen, K., & Rajala, R. (2019). Stakeholder management in complex product systems: Practices and rationales for engagement and disengagement. Industrial Marketing Management, 79 , 58–70.
Leso, B. H., Cortimiglia, M. N., & Ghezzi, A. (2023). The contribution of organizational culture, structure, and leadership factors in the digital transformation of SMEs: A mixed-methods approach. Cognition, Technology & Work, 25 (1), 151–179.
Li, F. (2020). Leading digital transformation: Three emerging approaches for managing the transition. International Journal of Operations & Production Management, 40 (6), 809–817.
Li, K., Kim, D. J., Lang, K. R., Kauffman, R. J., & Naldi, M. (2020). How should we understand the digital economy in Asia? Critical assessment and research agenda. Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 44 , 101004.
Loutet, M. G., Zhang, J., Varsaneux, O., Ferguson, A., Hulme, J., Stone, S.,... & Piggott, T. (2020). Using experiential simulation-based learning to increase engagement in global health education: An evaluation of self-reported participant experience. Medical Science Educator, 30 , 1245-1253.
Malodia, S., Mishra, M., Fait, M., Papa, A., & Dezi, L. (2023). To digit or to head? Designing digital transformation journey of SMEs among digital self-efficacy and professional leadership. Journal of Business Research, 157 , 113547.
Mendhurwar, S., & Mishra, R. (2023). ‘Un’-blocking the industry 4.0 value chain with cyber-physical social thinking. Enterprise Information Systems, 17 (2), 1930189.
Mohiuddin, I., Ali Jinnah University Karachi, Alvi, M., Scholar, J., Ghazanfer Inam, P., Mohammad Ali Jinnah Universityc Karachi, S., & Rehan, M. (2021). Impact of crude oil, exchange rate and gold price on kse100 index: before & during covid-19 pandemic by using var model. Journal of Contemporary Issues in Business and Government, 27 (6), 420–439.
Mohsin, M., Ullah, H., Iqbal, N., Iqbal, W., & Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. (2021). How external debt led to economic growth in South Asia: A policy perspective analysis from quantile regression. Economic Analysis and Policy, 72 , 423–437.
Mont, O., Curtis, S. K., & Voytenko Palgan, Y. (2021). Organisational response strategies to COVID-19 in the sharing economy. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 28 , 52–70.
Muganyi, T., Yan, L., & Sun, H. P. (2021). Green finance, fintech and environmental protection: Evidence from China. Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, 7 , 100107.
Naveed, R. T., Alhaidan, H., Al Halbusi, H., & Al-Swidi, A. K. (2022). Do organizations really evolve? The critical link between organizational culture and organizational innovation toward organizational effectiveness: Pivotal role of organizational resistance. Journal of Innovation & Knowledge, 7 (2), 100178.
Nwankpa, J. K., Roumani, Y., & Datta, P. (2022). Process innovation in the digital age of business: The role of digital business intensity and knowledge management. Journal of Knowledge Management, 26 (5), 1319–1341.
Nyagadza, B., Pashapa, R., Chare, A., Mazuruse, G., & Hove, P. K. (2022). Digital technologies, Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) & Global Value Chains (GVCs) nexus with emerging economies’ future industrial innovation dynamics. Cogent Economics & Finance, 10 (1), 2014654.
Owens, J., & Cribb, A. (2019). ‘My Fitbit thinks I can do better!’ Do health promoting wearable technologies support personal autonomy? Philosophy & Technology, 32 , 23–38.
Pangarkar, A., Arora, V., & Shukla, Y. (2022). Exploring phygital omnichannel luxury retailing for immersive customer experience: The role of rapport and social engagement. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 68 , 103001.
Qinqin, W., Qalati, S. A., Hussain, R. Y., Irshad, H., Tajeddini, K., Siddique, F., & Gamage, T. C. (2023). The effects of enterprises’ attention to digital economy on innovation and cost control: Evidence from A-stock market of China. Journal of Innovation & Knowledge, 8 (4), 100415.
Rainnie, A., & Dean, M. (2020). Industry 4.0 and the future of quality work in the global digital economy. Labour & Industry: A Journal of the Social and Economic Relations of Work, 30 (1), 16–33.
Ranjan, J., & Foropon, C. (2021). Big data analytics in building the competitive intelligence of organizations. International Journal of Information Management, 56 , 102231.
Regmi, R., Rai, D., & Khanal, S. (2021). Fintech and blockchain: Contemporary issues, new paradigms, and disruption. The Palgrave Handbook of FinTech and Blockchain (pp. 71–85). Springer International Publishing.
Ricci, R., Battaglia, D., & Neirotti, P. (2021). External knowledge search, opportunity recognition and industry 4.0 adoption in SMEs. International Journal of Production Economics, 240 , 108234.
Rodgers, W., Murray, J. M., Stefanidis, A., Degbey, W. Y., & Tarba, S. Y. (2023). An artificial intelligence algorithmic approach to ethical decision-making in human resource management processes. Human Resource Management Review, 33 (1), 100925.
Rosati, R., Romeo, L., Cecchini, G., Tonetto, F., Viti, P., Mancini, A., & Frontoni, E. (2023). From knowledge-based to big data analytic model: A novel IoT and machine learning based decision support system for predictive maintenance in Industry 4.0. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 34 (1), 107–121.
Rotz, S., Duncan, E., Small, M., Botschner, J., Dara, R., Mosby, I.,... & Fraser, E. D. (2019). The politics of digital agricultural technologies: A preliminary review. Sociologia Ruralis, 59 (2), 203-229.
Savastano, M., Amendola, C., Bellini, F., & D’Ascenzo, F. (2019). Contextual impacts on industrial processes brought by the digital transformation of manufacturing: A systematic review. Sustainability, 11 (3), 891.
Siagian, H., & Tarigan, Z. (2021). The central role of it capability to improve firm performance through lean production and supply chain practices in the COVID-19 era. Uncertain Supply Chain Management, 9 (4), 1005–1016.
Singh, A., Klarner, P., & Hess, T. (2020). How do chief digital officers pursue digital transformation activities? The role of organization design parameters. Long Range Planning, 53 (3), 101890.
Sousa, M. J., & Rocha, Á. (2019). Digital learning: Developing skills for digital transformation of organizations. Future Generation Computer Systems, 91 , 327–334.
Sovacool, B. K., Martiskainen, M., & Furszyfer Del Rio, D. D. (2021). Knowledge, energy sustainability, and vulnerability in the demographics of smart home technology diffusion. Energy Policy, 153 , 112196.
Ulanday, M. L., Centeno, Z. J., Bayla, M. C., & Callanta, J. (2021). Flexible learning adaptabilities in the new normal: E-learning resources, digital meeting platforms, online learning systems and learning engagement. Asian Journal of Distance Education, 16 (2). https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5762474
Van Veldhoven, Z., & Vanthienen, J. (2022). Digital transformation as an interaction-driven perspective between business, society, and technology. Electronic Markets, 32 (2), 629–644.
Wang, S., Sun, L., & Iqbal, S. (2022). Green financing role on renewable energy dependence and energy transition in E7 economies. Renewable Energy, 200 , 1561–1572.
Weber, E., Büttgen, M., & Bartsch, S. (2022). How to take employees on the digital transformation journey: An experimental study on complementary leadership behaviors in managing organizational change. Journal of Business Research, 143 , 225–238.
Wen, H., Lee, C. C., & Zhou, F. (2022). How does fiscal policy uncertainty affect corporate innovation investment? Evidence from China’s new energy industry. Energy Economics, 105 , 105767.
Wirtz, B. W., Weyerer, J. C., & Geyer, C. (2019). Artificial intelligence and the public sector—Applications and challenges. International Journal of Public Administration, 42 (7), 596–615.
Xiang, Y., Shao, W., Wang, S., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Study on regional differences and convergence of green development efficiency of the chemical industry in the Yangtze River Economic Belt based on grey water footprint. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19 (3), 1703.
Yang, H., Kumara, S., Bukkapatnam, S. T., & Tsung, F. (2019). The internet of things for smart manufacturing: A review. IISE Transactions, 51 (11), 1190–1216.
Yanguas Parra, P., Hauenstein, C., & Oei, P. Y. (2021). The death valley of coal – Modelling COVID-19 recovery scenarios for steam coal markets. Applied Energy, 288 , 116564.
Yaqub, M. Z., & Alsabban, A. (2023). Industry-4.0-enabled digital transformation: Prospects, instruments, challenges, and implications for business strategies. Sustainability, 15 (11), 8553.
Yousefian, M., Bascompta, M., Sanmiquel, L., & Vintró, C. (2023). Corporate social responsibility and economic growth in the mining industry. The Extractive Industries and Society, 13 , 101226.
Zhang, J., Liu, Y., Saqib, N., & Waqas Kamran, H. (2022). An empirical study on the impact of energy poverty on carbon intensity of the construction industry: Moderating role of technological innovation. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 10 , 929939.
Zhu, X., Ge, S., & Wang, N. (2021). Digital transformation: A systematic literature review. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 162 , 107774.
Ziadlou, D. (2021). Strategies during digital transformation to make progress in achievement of sustainable development by 2030. Leadership in Health Services, 34 (4), 375–391.
Zonta, T., Da Costa, C. A., da Rosa Righi, R., de Lima, M. J., da Trindade, E. S., & Li, G. P. (2020). Predictive maintenance in the Industry 4.0: A systematic literature review. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 150 , 106889.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Marxism, Ningxia University, Yinchuan, 750021, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Zhi Li .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Li, Z. Navigating Digital Transformation: A Risk-Based Approach for Industry 4.0 Innovation. J Knowl Econ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-024-02264-6
Download citation
Received : 30 April 2024
Accepted : 28 July 2024
Published : 21 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-024-02264-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Pythagorean fuzzy sets
- Digital economy transformation risks
- Multicriteria decision-making
- Risk prioritization
- Business innovation
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Asking the better questions that unlock new answers to the working world's most complex issues.
Trending topics
AI insights
EY podcasts
EY webcasts
Operations leaders
Technology leaders
Marketing and growth leaders
Cybersecurity and privacy leaders
Risk leaders
EY Center for Board Matters
EY helps clients create long-term value for all stakeholders. Enabled by data and technology, our services and solutions provide trust through assurance and help clients transform, grow and operate.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Strategy, transaction and transformation consulting
Technology transformation
Tax function operations
Climate change and sustainability services
EY Ecosystems
Supply chain and operations
EY Partner Ecosystem
Explore Services
We bring together extraordinary people, like you, to build a better working world.
Experienced professionals
MBA and advanced-degree students
Student and entry level programs
Contract workers
EY-Parthenon careers
Discover how EY insights and services are helping to reframe the future of your industry.
Case studies
Energy and resources
How data analytics can strengthen supply chain performance
13 Jul 2023 Ben Williams
How Takeda harnessed the power of the metaverse for positive human impact
26 Jun 2023 Edwina Fitzmaurice
Banking and Capital Markets
How cutting back infused higher quality in transaction monitoring
11 Jul 2023 Ron V. Giammarco
At EY, our purpose is building a better working world. The insights and services we provide help to create long-term value for clients, people and society, and to build trust in the capital markets.
New EY research finds AI investment is surging, with senior leaders seeing more positive ROI as hype continues to become reality
15 Jul 2024 Lizzie McWilliams
New EY Consumer Products and Retail Executive Pulse reveals perception vs. reality gap for AI maturity
09 Jul 2024 EY Americas
EY Announces Winners for the Entrepreneur Of The Year® 2024 Mid-Atlantic Award
21 Jun 2024 Victoria Kasper
No results have been found
Recent Searches

CIO Survey: will you set the GenAI agenda or follow the leaders?
Get insights on how CIOs will address the challenges and capture the full benefits of GenAI in the 2024 EY CIO Sentiment Survey.

How a flexible supply chain raised the bar for the beverage industry
The client’s goal: better accommodate future growth, predict customer demands, and add agility to inventory and production lines. Learn how we did it.

How can your business go from competitive to cutting edge?
Learn how the EY-Microsoft Alliance delivers AI driven strategies and smart business solutions using cloud technology.
Select your location

How esure’s digital transformation enhanced customer experience
esure aimed to tackle widespread dissatisfaction among UK insurance customers with a bold multi-year transformation journey.

- 1. The better the question
- 2. The better the answer
- 3. The better the world works
How EY can help
The better the question
How can we “fix insurance for good?”
Many UK consumers are dissatisfied with their insurance provider. esure wanted to correct this – and transform its business.
e sure is a well-established PE-backed player in the UK personal insurance market and has served home and motor customers since 2000. From day one, esure challenged market norms, offering some of the first online and digital insurance products and services. But in a fast-moving market, esure’s pace of innovation and change had slowed.
With a burst of new energy and commitment, esure challenged itself to transform the insurance market – with an ambition to tackle poor industry practices that have reduced the UK’s customer trust levels to one of the worst in Europe.
esure set out on an ambitious strategy to “fix insurance for good ”, transforming the business to become a leading pure-play scalable digital insurer, and to completely decommission its legacy IT systems. It developed a goal to provide market-leading customer experiences through generative AI (GenAI), other innovative technology and state-of-the-art data solutions, powered by a lean agile operating model.
This required a shift from a 20-year-old legacy system to EIS – a modern-architected, event-based, next-generation platform. This was a complex, high-profile program aimed at revolutionizing the UK personal insurance market, which would become the first technology implementation of its kind in Europe, and the first business-wide transformation of its kind to cover all elements of people, technology, data and processes together.
The ultimate goal of the program was to harness esure’s original challenger energy and transform it into a tech-enabled disruptor that offers innovative customer propositions with a best-in-class, low-cost operating model.
Together, EY teams and the esure team embarked on the journey to “fix insurance for good.”

The better the answer
A customer-centric tech-enabled revolution
EY teams developed a new end-to-end business model based on a pioneering scalable tech platform.
Related article
How do you harness the power of people to double transformation success?
Read about how EY and the University of Oxford explored the emotional cost of failed transformations and what it takes to get them right.
To truly deliver on esure’s game-changing strategy to “fix insurance for good,” the EY team helped the company design and build an entirely new business, based on a platform that is already integrated to over 30 leading cloud solutions including OpenAI, Braze, Segment, Adyen, and RightIndem. With this platform, esure is servicing over 2 million customers in the UK at present, with ambitious targets to increase market share.
The EY team and esure had a long-standing collaboration following early work to identify rapid solutions to particular pain point areas, and together they quickly established highly skilled and experienced delivery teams called “squads” across the program. The EY team’s roles and responsibilities included program management, service design, full stack developers and testers, cloud and data engineering, Insurance operations professionals, and culture and change management. The initial approach was centered on building strong, capable value streams that could embed agile practices throughout the squads and build a strong culture of success.
“This initiative was one of the most expansive and collaborative undertakings in the EY organization’s history, with more than 150 EY people from 10 different countries offering multi-functional, integrated advisory and delivery support – all working cohesively as one group to help deliver a truly differentiated platform for esure vs. their UK peers,” says Preetham Peddanagari, EY EMEIA Digital Insurance Leader.
Throughout the program the EY team put humans at the center of the design, the delivery and changes. For example, a working group centralized all communications to drive culture and community; support development, knowledge transfer and learning; and promote wellbeing and opportunity on the program.
The EY team focused on instilling consistent ways of working, helping manage information and leading practices; leveraging knowledge from across the EY organization, esure and other partner teams on the program. The EY team built a planning approach that combined a strong balance of significant releases, with smaller, iterative improvements to offer continuous benefit to the business. The teams worked together to design a state-of-the-art future-proof operating model for the digitally enabled insurer, building on esure’s digital-first strategy and vision. That model provided a tangible view of the design and capabilities of the post-transformation business and how esure would provide improved customer outcomes at a lower unit cost.
The EY team and esure built a brand-new environment powered by EIS, using best-of-breed cutting-edge technologies. This established esure as the first scaled UK player to truly enter the platform age with a full-stack, cloud-native platform, with GenAI solutions rapidly embedded and deployed throughout the business and customer-service journey.
“This platform enabled us to take a new approach to pricing, with data scientists building machine learning models to provide fairer, more accurate pricing for all our customers,” says Peter Martin-Simon, esure’s Chief Customer Officer. esure was also able to create a state-of-the art claims platform integrated into an insurance ecosystem comprising suppliers, repairers, regulators, and others, and offer customers an integrated digital claims solution.
As part of the program, the esure and EY team migrated 1.8m existing policies and 248,000 claims from the legacy platform to the new business solution, adopting the market’s first ever mid-term migration approach.
“The advanced migration capability offers substantial opportunities by helping enable seamless integration onto the new technology platform,” explains Peddanagari. This reusable solution provides a significant advantage in terms of speed and flexibility; esure were able to migrate their home insurance customer base swiftly over a seven-week period – which would usually take over a year using a conventional market approach. This helped esure to fully exit and decommission its legacy IT estate within months of completing the migration, achieving the goal of becoming the UK’s first scaled, cloud-only digital insurer.

The better the world works
Capturing insights to help deliver leading service
The new model and platform enable unprecedented analytics and speed of responding to claims.
esure has deployed a scaled use of state-of-the-art GenAI, alongside strong data science capability, automated indemnity controls and market-leading fraud and analytics capabilities to drive a real-time trading approach and help enable not only a deeper understanding of customers, but also a significant reduction in indemnity spend.
“We are capturing data on every second that the customer is in our customer journey, which helps us rapidly develop propositions that are designed around them. We are changing pricing on a near-daily basis as well,” says Martin-Simon.
The program has not only created a new business, but an entirely new paradigm in customer experience, featuring seamless and intuitive digital journeys. Today, 78% of policy updates can be fully self-served online and 90% of all claim types can be initiated online, and these numbers will continue to grow as more journeys are built and optimized.
How can the moments that threaten your transformation define its success?
Leaders that put humans at the center to navigate turning points are 12 times more likely to significantly improve transformation performance. Learn More.
esure has quickly built on the game-changing platform capabilities and is now one of the most advanced adopters of GenAI solutions in the market, with the unique ability to deploy multiple GenAI and machine learning use cases at speed. “Our innovative use of GenAI means we’ve fully integrated our customer support channels in our online portal, combining chatbot, live chat and voice in one place,” says esure CEO David McMillan. “So if a customer needs to switch channels – moving from live chat to speaking to a colleague on the phone – all of the customer’s request and history is retained in-journey, removing friction and making it simpler to quickly resolve customer requests.”
esure is now able to manage complex claims on a straight through, digital-only basis. Vehicle “write-off” claims, which traditionally take the industry between two and four weeks to process, can now be notified, assessed and paid in just four hours, end to end, meaning the customer has the certainty and cash they need to purchase a replacement car almost immediately.
The transformation has made a big impact on the business, materially reducing unit cost per policy. This lower-cost model enables esure to set fairer, more accurate prices for every customer. And by using machine learning to identify fraud, esure is saving £2m annually. The program has also transformed the working experience for employees, through automation of previously manual processes.
Overall, the program has not only provided a significant transformation within esure and in the UK insurance market, it has also set up esure’s business to drive continuous change with a highly scalable model, bringing long-term value in a highly competitive marketplace.
“By eradicating customer frustrations, fueled by smart use of data, rapid customer testing and our flexible tech platform, we’re confident we can fix today’s broken sector and deliver the insurance that customers expect and value,” says McMillan.
Evolving technology and data through cloud services
EY’s Business transformation through cloud services can help your business unlock the agility, efficiency and innovation of composable business services. Learn more.

- Connect with us
- Our locations
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Legal and privacy
- Accessibility
- Open Facebook profile
- Open X profile
- Open LinkedIn profile
- Open Youtube profile
EY refers to the global organization, and may refer to one or more, of the member firms of Ernst & Young Global Limited, each of which is a separate legal entity. Ernst & Young Global Limited, a UK company limited by guarantee, does not provide services to clients.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to search
- Skip to footer
Products and Services

Making AI work for you
Cisco AI is where the AI hype ends and meaningful help begins.
Certifications
Cisco Validated
Our latest innovations
Cisco XDR with AI Assistant
Remediate the highest-priority incidents with an AI-first XDR solution.

Cisco Networking Cloud
One platform experience. Assured, secured, and simplified.

Secure Firewall 1200 Series
Compact, all-in-one firewall for your distributed enterprise branch.
Build network assurance expertise with Cisco U.
Harness the power of end-to-end visibility and proactive monitoring with our free tutorials.
Identity is the new perimeter
Stop identity-based attacks while providing a seamless authentication experience with Cisco Duo's new Continuous Identity Security.

Engineering excellence with McLaren F1
In the race against time, McLaren Formula 1 trusts Cisco connectivity, performance, and security solutions to power its operations.
Inside Cisco
- More events
Press Release
Cisco reports fourth quarter and fiscal year 2024 earnings
Bringing our portfolio together by chuck robbins.
Industry report
Cisco unveils 2024 State of Industrial Networking Report
Analyst report
Forrester names Cisco a Leader in OT cybersecurity
2024 global networking trends report, cisco becomes official network equipment partner of la28 games.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
In this case study, we look at how Singapore-based DBS Bank, is reaching a new generation of tech-savvy customers by transforming digital banking.
As the world grows more and more digital, customers across every industry are expecting digital-first, timely assistance and support. As shown in this digital transformation in banking case study roundup, all businesses — including banks — have been forced to change and evolve with the times.
In this case study, we look at how Kiwibank, the largest New Zealand-owned bank, is using data and AI to reach new levels of digital transformation in banking.
Regions looked to reinforce their commitment to satisfying both customers and workforce as well as modernizing banking. How? With a digital transformation.
Becoming more than a bank: Digital transformation at DBS In an interview with McKinsey's Joydeep Sengupta, Chng Sok Hui, Chief Financial Officer of DBS, discusses how mindsets and culture are just as important as technology for a digital-forward bank.
Digital transformation is a challenge for the banking industry, but it is necessary to adapt to the modern world where customers expect fast, efficient, and convenient services. Traditional approaches no longer meet the needs of the modern consumer. So, banks that want to remain competitive must abandon conservative methods and fully immerse themselves in the process of digital transformation.
Banking Transformed with Jim Marous. U.S. Bank: A Case Study in Digital Banking Transformation Success. Dominic Venturo, senior executive vice president and chief digital officer at U.S. Bank, discusses how important leadership and culture are to the success of digital transformation at banks and credit unions. 00:00:00.
This case describes the transformation of the UK's oldest financial services franchise from a product-aligned and brick-and-mortar traditional banking institution to a customer-aligned and digital-first technology organization. The case parallels Lloyds' business transformation with the growth of its digital-focused Transformation division - which commenced as a small hundred-person task ...
Partly as a result of the rise of FinTechs, banking is a sector that is facing significant disruption. In this case study, we identify some of the innovations that are being made both by young start-ups and long-established banks. We explore emerging opportunities in...
SCB partnered with Accenture to develop and deliver an award-winning digital transformation strategy. The approach combined advanced data and analytics capabilities with people-focused processes and tools. The first step was shoring up the data lake—migrating the bank's foundational data repository to Microsoft Azure Cloud, making SCB the ...
From large-scale core banking or payment transformation to adoption of cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence, analytics, blockchain and robotic process automation, we partner with FIs to envision and build the digital bank of the future.
How to use UX design for customer-centered core banking digital transformation in the cloud? We reveal redesign case study that bring us the world famous IF Design Award.
As retail and commercial banks face consumer demand for increased digital experiences, bank executives consider core banking transformation.
This article will unpack the layers of digital transformation in transaction banking, highlighting how it's reshaping the landscape for banks and financial institutions. We'll explore transformative case studies, offering a guide for navigating the digital revolution in the banking sector.
The C case describes the company's progress up to 2017 and highlights why Euromoney named DBS as the World's Best Digital bank. It asks whether this progress is sufficient in given the amount of sectoral change. This case series examines the two stage transformation of DBS 2009- 2017.
The bank confronted a formidable challenge in the digital transformation of their client information management system. They needed to implement digital initiatives to update the records of over 4,000 high-risk clients in the Bank core system, which is the back-end system that processes daily banking transactions and posts updates to accounts ...
Customer case studies from TPS demonstrate how our payment solutions help banks and financial insitutions accelerate digital transformation.
While 89% of large companies globally have a digital and AI transformation underway, they have only captured 31% of the expected revenue lift and 25% of expected cost savings from the effort ...
This collection of the best UX case studies on creating and researching the customer experience in digital banking and Fintech apps. These articles are collected from Medium and arranged based on the amount of applause in 2023. This banking apps collection offers an excellent opportunity to get instant inspiration from 30 insightful UX case studies demonstrating how to design modern digital ...
These 15 digital transformation case studies present a thrilling narrative of change, charting the journeys of companies that dared to embrace the digital frontier. Each story unfolds as a high-stakes gamble where traditional practices are disrupted, often under the threat of imminent collapse. These businesses, spanning diverse industries from ...
Abstract The digital transformation of the Indian banking sector presents a paradigm shift in how financial services are delivered, accessed, and managed. This paper explores the opportunities and challenges associated with digital transformation in Indian banking, focusing on key areas such as evolution, current state, opportunities, challenges, case studies, future trends, and outlook ...
The Future Of Fintech Funding—A Closer Look. Despite the investment fluctuations, the future of fintech funding remains bright. The $7.3 billion invested in Q1 2024 across 904 deals, as reported ...
EY discussions with banking transformation leaders across the globe uncover six recommendations for overhauling organizational change. Learn more. ... Read the case study. David Deane + 4. ... EY Nexus for Banking platform was key to transforming one traditional bank into a future-ready, digital bank of tomorrow.
Why most digital banking transformations fail—and how to flip the odds Success in digital transformation calls for banks to reimagine their approach across the business, technology landscape, and operating model.
Explore digital transformation case studies through the lens of three successful brands—Walmart, Ford, and Anheuser-Busch InBev. Platform. One platform, countless insights. ... Personalize the banking experience. B2B. Maximize product adoption. Media. Identify impactful content. Healthcare.
A Case Study in Lending Efficiency and Digital Banking Solutions . Broadway Bank's adoption of MeridianLink ® One transformed its consumer and mortgage lending into a unified platform. It consolidated multiple applications into one cohesive system.
The authors wish to thank all employees from the case organizations for their willingness to spend some of their precious time answering the questions and giving feedback on the results. We also thank the anonymous reviewers for the time and effort they spent and for suggesting improvements to an earlier draft of this study.
This study addresses the critical gap in understanding the risks associated with digital transformation, particularly focusing on their impact on business innovation and growth within Industry 4.0. While the transformative potential of digital technologies is well-documented, the inherent challenges remain underexplored. This research introduces an innovative decision-support model designed to ...
e sure is a well-established PE-backed player in the UK personal insurance market and has served home and motor customers since 2000. From day one, esure challenged market norms, offering some of the first online and digital insurance products and services. But in a fast-moving market, esure's pace of innovation and change had slowed.
Cisco is a worldwide technology leader. Our purpose is to power an inclusive future for all through software, networking, security, computing, and more solutions.