- English Grammar
- Reported Speech

Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how far you have understood the topic.

Table of Contents
Definition of reported speech, rules to be followed when using reported speech, table 1 – change of pronouns, table 2 – change of adverbs of place and adverbs of time, table 3 – change of tense, table 4 – change of modal verbs, tips to practise reported speech, examples of reported speech, check your understanding of reported speech, frequently asked questions on reported speech in english, what is reported speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message.
Now, take a look at the following dictionary definitions for a clearer idea of what it is.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
Reported speech is a little different from direct speech . As it has been discussed already, reported speech is used to tell what someone said and does not use the exact words of the speaker. Take a look at the following rules so that you can make use of reported speech effectively.
- The first thing you have to keep in mind is that you need not use any quotation marks as you are not using the exact words of the speaker.
- You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech.
| Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said) |
- You can use verbs like said, asked, requested, ordered, complained, exclaimed, screamed, told, etc. If you are just reporting a declarative sentence , you can use verbs like told, said, etc. followed by ‘that’ and end the sentence with a full stop . When you are reporting interrogative sentences, you can use the verbs – enquired, inquired, asked, etc. and remove the question mark . In case you are reporting imperative sentences , you can use verbs like requested, commanded, pleaded, ordered, etc. If you are reporting exclamatory sentences , you can use the verb exclaimed and remove the exclamation mark . Remember that the structure of the sentences also changes accordingly.
- Furthermore, keep in mind that the sentence structure , tense , pronouns , modal verbs , some specific adverbs of place and adverbs of time change when a sentence is transformed into indirect/reported speech.
Transforming Direct Speech into Reported Speech
As discussed earlier, when transforming a sentence from direct speech into reported speech, you will have to change the pronouns, tense and adverbs of time and place used by the speaker. Let us look at the following tables to see how they work.
| I | He, she |
| Me | Him, her |
| We | They |
| Us | Them |
| You | He, she, they |
| You | Him, her, them |
| My | His, her |
| Mine | His, hers |
| Our | Their |
| Ours | Theirs |
| Your | His, her, their |
| Yours | His, hers, theirs |
| This | That |
| These | Those |
| Here | There |
| Now | Then |
| Today | That day |
| Tomorrow | The next day / The following day |
| Yesterday | The previous day |
| Tonight | That night |
| Last week | The week before |
| Next week | The week after |
| Last month | The previous month |
| Next month | The following month |
| Last year | The previous year |
| Next year | The following year |
| Ago | Before |
| Thus | So |
| Simple Present Example: Preethi said, “I cook pasta.” | Simple Past Example: Preethi said that she cooked pasta. |
| Present Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I am cooking pasta.” | Past Continuous Example: Preethi said that she was cooking pasta. |
| Present Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I have cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Present Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I have been cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Simple Past Example: Preethi said, “I cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Past Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I was cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Past Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I had cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect (No change) Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I had been cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous (No change) Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Will | Would |
| May | Might |
| Can | Could |
| Shall | Should |
| Has/Have | Had |
Here are some tips you can follow to become a pro in using reported speech.
- Select a play, a drama or a short story with dialogues and try transforming the sentences in direct speech into reported speech.
- Write about an incident or speak about a day in your life using reported speech.
- Develop a story by following prompts or on your own using reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written. Check them out.
- Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl.
- Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations.
- Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were.
- The judges announced that the Warblers were the winners of the annual acapella competition.
- Binsha assured that she would reach Bangalore by 8 p.m.
- Kumar said that he had gone to the doctor the previous day.
- Lakshmi asked Teena if she would accompany her to the railway station.
- Jibin told me that he would help me out after lunch.
- The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
- Rahul said that he was drawing a caricature.
Transform the following sentences into reported speech by making the necessary changes.
1. Rachel said, “I have an interview tomorrow.”
2. Mahesh said, “What is he doing?”
3. Sherly said, “My daughter is playing the lead role in the skit.”
4. Dinesh said, “It is a wonderful movie!”
5. Suresh said, “My son is getting married next month.”
6. Preetha said, “Can you please help me with the invitations?”
7. Anna said, “I look forward to meeting you.”
8. The teacher said, “Make sure you complete the homework before tomorrow.”
9. Sylvester said, “I am not going to cry anymore.”
10. Jade said, “My sister is moving to Los Angeles.”
Now, find out if you have answered all of them correctly.
1. Rachel said that she had an interview the next day.
2. Mahesh asked what he was doing.
3. Sherly said that her daughter was playing the lead role in the skit.
4. Dinesh exclaimed that it was a wonderful movie.
5. Suresh said that his son was getting married the following month.
6. Preetha asked if I could help her with the invitations.
7. Anna said that she looked forward to meeting me.
8. The teacher told us to make sure we completed the homework before the next day.
9. Sylvester said that he was not going to cry anymore.
10. Jade said that his sister was moving to Los Angeles.
What is reported speech?
What is the definition of reported speech.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
What is the formula of reported speech?
You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech. Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said)
Give some examples of reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written.
| ENGLISH Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Learn Insta
RD Sharma Solutions , RS Aggarwal Solutions and NCERT Solutions
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 9 CBSE With Answers
January 25, 2023 by Prasanna

This grammar section explains English Grammar in a clear and simple way. There are example sentences to show how the language is used. You can also visit the most accurate and elaborate NCERT Solutions for Class 9 English . Every question of the textbook has been answered here.
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 9 CBSE With Answers Pdf
Type 1. Statements Steps to be kept in mind for changing direct speech into indirect (statements).
Step 1. The reporting verb is changed as under. (a) We ‘say’ something but we ‘tell’ somebody. Says to …………………………… tells. (b) Says …………………………… says. (c) Said to …………………………… told/asserted/stated/informed. (d) Said …………………………… said.
Step 2. Inverted commas are dropped and the conjunction ‘that’ is used.

Note. These words refer to the speaker. So they change according to who the speaker is.
Step 4. If the reporting verb is in the present or future tense, the tense of the reported speech does not change. Meera says to Mini, “Your teacher has praised you.” Meera tells mini that her teacher has praised her.
Step 5. Words denoting nearness of time and place are generally changed into words denoting distance.
| Now | → | then |
| This | → | that |
| These | → | those |
| Here | → | those |
| jo | → | before |
| Yesterday | → | the previous day |
| Tomorrow | → | the next day, the following day |
| Today | → | that day |
| Tonight | → | that night |
Note. There are two situations where even if the reporting verb is in the past tense, the verb of the reported speech remains unchanged.
1. If the reported speech expresses a universal truth or a habitual fact.
- The teacher said, “Two and two make four.” The teacher said that two and two make four.
- Ramesh said to the tourist, “Summers in India are usually very hot.” Ramesh informed the tourist that summers in India are usually very hot.
2. The reported speech describes a situation which still exists when the speech is reported.
- The stationmaster said, “Due to heavy rains, the trains are running late”.
- The stationmaster said that due to heavy rains, the trains are running late.
Type 2. Questions
A. If the reported speech is a question, the following changes are made. The reporting verb is changed into ‘asked/required’.
| Says | asks A |
| Says to | asks |
| Said | asked |
| Said to | asked |
B. The inverted commas are removed and If/whether is used. The question mark is removed and a full stop is placed. No conjunction is used while reporting wh-questions. The direct form is changed to indirect question form. Place the subject before verb in the reported question.
- I said to Meera, “When are your parents coming?” I asked Meera when her parents were coming.
- Ramesh said to me, “Are you reading this book?” Ramesh asked me if/whether I was reading that book.
- He said, “Will you come with me?” He asked if/whether I would go with him.
Type 3. Commands and Requests
If reporting commands and requests, the indirect speech is introduced by some verbs expressing commands or requests and the imperative mood is changed into the infinitive.
Step 1. The reporting say (said) is changed to order(ed)/request(ed)/advise(d)/command(ed)/ encourage(ed) /shout(ed)/forbid (forbade), proposed, etc.
Step 2. The verb of the reported speech is changed into an infinitive and inverted commas are removed.
Step 3. Do not is changed to ‘not to’.
- He said to his sister, “Please speak slowly.” He requested his sister to speak slowly.
- The teacher said, “Keep quiet.” The teacher ordered to keep quiet.
- He said to me, “Don’t tease the animal.” He advised me not to tease the animal.
- She said to me, “Let us go for a picnic”. She proposed (or suggested) to me that we should go for a picnic.
Type 4. Exclamations and wishes Step 1. The reporting verb said is changed to exclaimed, wished, prayed, etc. Step 2. The exclamatory form is changed into the statement form and the mark of exclamation is replaced by a full stop. Step 3. The reporting verb is joined with reported speech with ‘that’. Step 4. All interjections are omitted and suitable adverbs or other expressive words are used.
| What! Oh! | surprised |
| Alas! Ah! | sadness, grief, pity |
| Hurrah! | joy, happiness |
| Bravo! | approval, cheered |
- They said, “Hurrah! We have won the match.” They exclaimed with joy that they had won the match.
- She said, “Alas! He is no more.” A She exclaimed with sorrow that he was no more.
- He said, “Good-bye friends.” He bade good-bye to his friends.
Reported Speech Solved Examples Exercises for Class 9 CBSE
Change the following from direct to indirect speech.
Question 1. The doctor said to me, “The climate of this city won’t suit you.” Answer: The doctor told me that the climate of that city wouldn’t suit me.
Question 2. Priya says, “The Earth is round.” Answer: Priya says that the Earth is round.
Question 3. My brother said to his friend, “I am very sleepy.” Answer: My brother told his friend that he was very sleepy.
Question 4. She said, “I have passed the exams.” ‘ Answer: She said that she had passed the exams.
Question 5. My friend said, “Have you ever been to London?” Answer: My friend asked me if I had ever been to London.
Question 6. The policeman said to us, “Where are you going?” Answer: The policeman enquired where we were going.
Question 7. My friend said to me, “Can you solve the problem?” Answer: My friend asked me if/whether I could solve the problem.
Question 8. My mother said to the stranger, “What is the purpose of your coming?” Answer: My mother asked the stranger what was the purpose of his coming.
Question 9. The teacher said to the students, “Complete your work.” [ Answer: The teacher ordered the students to complete their work. ,
Question 10. The Principal said to the parents, “Please sit inside the hall.” | Answer: The Principal requested the parents to sit inside the hall. j
Question 11. Sunil said to his friend, “Don’t forget to recharge your mobile.” i Answer: Sunil reminded his friend not to forget to recharge his mobile.
Question 12. My sister said to me, “Consult a doctor regarding your eyesight.” Answer: My sister advised me to consult a doctor regarding my eyesight. |
Question 13. She said, “May God bless her with a child!” Answer: She said that God might bless her with a child!
Question 14. He said, “What a terrible night it is!” Answer: He exclaimed that it was a terrible night.
Question 15. He said, “Alas! I perish by the people I made. Answer: He confessed with regret that he was perished by the people he had made.
Question 16. He said, “Alas! what a fool I am. Answer: He exclaimed with grief/regret that he was a great fool.
Change the narration of the following sentences from direct to indirect.
Question 17. The saint said, “Go to the Himalayas for meditation.” Answer: The saint ordered to go to the Himalayas for meditation.
Question 18. Sita said to Praveen, “I will return your money tomorrow.” Answer: Sita told Praveen that she would return his money the next day.
Question 19. The news said, “A strong earthquake has hit Japan.” Answer: The news said that a strong earthquake has hit Japan. . ”
Question 20. My uncle said to Sheela, “I have a surprise for you.” Answer: My uncle told Sheela that he had a surprise for her.
Question 21. She said, “Do you want to stay abroad?” Answer: She asked if he wanted to stay abroad.
Question 22. The Met Department announced, “It may rain tomorrow.” Answer: The Met. Department announced that it might rain the next day.
Question 23. I/He said, “How I wish they would come”. Answer: He exclaimed that he wished they would come.
Question 24. Ashu said to his friend, “Are you willing to share your books with me?” Answer: Ashu asked his friend if he was willing to share his books with him.
Question 25. The Major said to the jawans, “Start marching left.” Answer: The major ordered the Jawans to start marching left.
Question 26. Sheetal said to her mother, “Have you ever thought about yourself in life?” Answer: Sheetal asked her mother if she had ever thought about herself in life.
Read the following dialogues and report in indirect narration.
Question 27. Mother : Where were you? Daughter ‘ : I was on the terrace playing. Mother : Please do not go without prior permission. Daughter : This was the first time ever that I went on the terrace. Mother : Remember, do not go there alone. Answer: Mother asked her daughter where she had been. The daughter replied that she had been on the terrace playing. The mother then requested her not to go without prior permission. The daughter apologised saying that that had been the first time ever that she had gone on the terrace. The mother warned her saying not to go there alone.
Question 28. Master : How are you feeling now? Worker : I am feeling batter but I am not completely fine. Master : Do you need more rest? Worker : It is okey. I will report tomorrow. Answer: Master asked his worker how was he feeling then. The worker replied that he was feeling better but was not completely fine. The master further asked him if he needed more rest. The worker replied that that was okey and that he would report the next day.
Question 29. Rajesh : Where are you going, Rohan? Rohan : I am going to the temple to offer flowers. Rajesh : Do you worship everyday and go to the temple? Rohan : Yes, I go to the temple everyday to worship Lord Shiva. Answer: Rajesh asked Rohan where was he going. Rohan replied that he was going to the temple to offer flowers. Rajesh then asked him if he worshipped every day and went to the temple. Rohan replied in the affirmative and said that he went to the temple every day to worship Lord Shivai
Question 30. Teacher : I want all students to quietly do the work. Students : Will you allow us to go for games after this? Teacher : First, all of you have to finish your work. Students : We promise that we will finish our work first. Answer: Teacher instructed the students that she wanted them to quietly do the work. The students asked if she would allow them to go for games after that. The teacher insisted that first, all of them had to finish their work. The students then promised her that they would finish their work first.
Question 31. Father : Why did you go to the market today? Son : I had to buy some material to do my project. Father : Who gave you the project? Son : My science teacher gave the project. Father : Do you need any money for it? Ans. Father asked his son why had he gone to the market that day. Son replied that he had to buy some material to do his project. Father then asked him who had given the project. Son replied that his science teacher had given the project. Father then asked his son if he needed any money for that.
Question 32. Customer : You have a variety of frozen stuff. Shopkeeper : You can buy as much as you like. Customer : Why don’t you keep fresh vegetables? Shopkeeper : Things have become very expensive these days. Customer : You should start keeping good stuff otherwise I shall stop buying from you. Answer: Customer told the shopkeeper that he had a variety of frozen stuff. Shopkeeper replied that he could buy as much as he liked. The customer then asked the shopkeeper why he didn’t keep fresh vegetables. The shopkeeper replied that things had become very expensive those days. The customer warned him that he should start keeping good stuff otherwise, he (customer) would stop buying from him.
Question 33. Doctor : What did you eat yesterday? Patient : I could hardly eat anything as I was having stomachache. Doctor : Are you still having it? Patient : At this moment, I am having fever and feeling weak. Doctor : You most take rest. Answer: Doctor asked the patient what had he eaten the previous day. The patient repled that he could hardly eat anything as he had been having stomachache. Doctor then asked him if he was still having that. The patient replied that at that moment, he was having fever and was feeling weak. The doctor advised him to take rest.
Question 34. Employee : Please grant me two weeks’ leave. Boss : Why do you need it for such a long time? Employee : I have to visit my ailing mother. Boss : Okey, I shall grant you leave but do not overstay your leave. Answer: The employee requested his boss to grant him two weeks’ leave. The boss asked him why he needed leave for such a long time. The employee replied that he had to visit his ailing mother. The boss agreed to grant him leave but instructed him not to overstay his leave.
Question 35. Kanika : Have you seen the animation film released recently? Keshav : I am not allowed to watch films. Kanika : How is this possible in present times? Keshav : My parents are very strict. Answer: Kanika asked Keshav if he had seen the animation film released recently. Keshav replied that he was not allowed to watch films. Kanika further asked how that was possible in present times. Keshav informed that his parents were/are very strict.
Question 36. Hameed : Did you visit the national museum? Shano : How can I as there is nobody to accompany me? Hameed : Do not worry. Shano : I am not worrying but I am the only one who has not seen it. Answer: Hameed asked Shano if she had visited the national museum. Shano replied how she could as there was nobody to accompany her. Hameed told her not to worry. Shano replied taht she was not worrying but she was the only one who had not seen that.
Read the following dialogues and complete the report appropriately.
Question 37. Preeti : Where did you spend your holidays? Naman : I went to many hills stations. ‘ Preeti : Which one did you like the most? Naman : Honestly speaking. I liked all as I am very fond of hills. Preeti asked Naman (a) ………………………….. his holidays. Naman replied, (b) ………………………….. to many hill stations. Preeti then asked him (c) the most. Naman said that honestly speaking (d) ………………………….. of hills. Answer: (a) where he had spent his holidays. (b) that he had gone to many hill stations. (c) which one he had liked. „ (d) he liked all as he was very fond.
Question 38. Archna : Do you know swimming? Rudra : Yes, I do. Archna : Can you teacher me how to swim? Rudra : Yes, I will. Come to my swimming club tomorrow. Archna asked Rudra (a) ………………………….. swimming. Rudra replied in the affirmative. Then, Archna further asked him (b) ………………………….. how to swim. Rudra replied that he (c) ………………………….. he also asked Archna (d) ………………………….. club (e) …………………………. . Answer: (a) if he knew (b) if he could teach her (c) would (d) to go to his swimming (e) the next day.
Question 39. Father : How was the paper? Son : It was easy. I could solve all the problems. Father : Start preparing for the economics paper. You do not have much time left Son : Yes father, I shall immediately start. The father asked his son (a) ………………………….. Son replied that (b) ………………………….. He (c) ………………………….. all the problems. Father further advised him (d) ………………………….. economics paper. He (e) ………………………….. much time left. Son agreed with his father and said that he (f) ………………………….. start. Answer: (a) how the paper had been (b) that had been easy (c) could solve (d) to start preparing for the (e) did not have (f) would immediately
Question 40. Inspector : Were you sleeping when the robbers entered the bank? Guard : No, Sir. The bank had closed and I had just gone to relieve myself. Inspector : What did you see when you came back? Guard : The iron grill lock was broken and the bank looked ransacked but the robbers could not take away anything as I had returned quickly. Inspector : Yes, I can see that not much damage has been done but you have to be more careful in future. Inspector asked the guard (a) ………………………….. entered the bank. Guard replied in the negative and said that the bank had been closed and (b) ………………………….. Inspector further asked him (c) ………………………….. The guard replied that (d) ………………………….. and the bank had looked ransacked, but the robbers (e) ………………………….. as he (f) ………………………….. Inspector said that he (g) ………………………….. but also warned him (h) …………………………. . Answer: (a) if he had been sleeping when the robbers had (b) he had just gone to relieve himself (c) what he had seen when he had come back (d) the iron grill lock had been broken (e) could not take away anything (f) had returned quickly (g) could see that not much damage had been done (h) that he had to be more careful in future.
Question 41. You have learnt how to report questions from direct to indirect speech. Here is a paragraph with direct speech questions. Read them carefully and report into indirect speech. Rewrite the paragraph in the space given below. [NCERT Workbook]
Once an old man asked a young boy, “Who do you think are the most intelligent people?” The young man said in return, “Who do you think so?” The old man said, “How can sons and daughters be intelligent without learning from their parents?” The young man said, “How did you as a parent learn?”
The old man said, “Why are you hijacking my question by asking me back?” The young man said, “Didn’t you know that you as a parent, now have learnt all the things an your own?” The old man said, “How do you say that we all learnt from others?” The young man said, “Why do you ask me about how to operate electronic gadget all the time?” The old man said, “Why can’t I ask you because I have paid for the gadget you use?” Answer: Once an old man asked a young boy who he thought were the most intelligent people. The young man asked why he thought so. The old man further asked how sons and daughters could be intelligent without learning from their parents. The young man asked how he had learnt as a parent. The old man asked why he was hijacking his questions by asking him back.
The young man said if he hadn’t known that he as a parent, then had learnt all the things on his own. The old man said how he learnt that they all learnt from others. The young man said why he asked him how to operate electronic gadget all the time. The old man replied why he couldn’t ask him because he had paid for the gadgets he used.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
CBSE Class 9 English Grammar – Direct And Indirect Speech
September 26, 2017 by Bhagya
Formulae Handbook for Class 9 Maths and Science Educational Loans in India
1. Direct and Indirect Speech: The words spoken by a person can be reported in two ways— Direct and Indirect. When we quote the exact words spoken by a person, we call it Direct Speech.
- Sohan said to Mohan, “I am going to school.”
The exact words spoken by Sohan are put within inverted commas. But when we give the substance of what Sohan said, it is called the Indirect Speech.
You can master in English Grammar of various classes by our articles like Tenses, Clauses, Prepositions, Story writing, Unseen Passage, Notice Writing etc.
2. Reporting Clause and Reported Speech: Sohan told Mohan that he was going to school. The words which generally come before the inverted commas are called the reporting clause, i.e. Sohan said to Mohan and the verb ‘said’, is called the reporting verb. The words spoken by Sohan and put within inverted commas are called the reported speech, i.e. “I am going to school.”
More Resources for CBSE Class 9
NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Sanskrit
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 IT
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions
3. Rules for Changing Direct Speech into Indirect Speech:
- In the Indirect speech, no inverted commas are used.
- The conjunctions that, if, whether , are generally used after the reporting verb.
- The first word of the reported speech begins with a capital letter.
- The tense of the reporting verb is never changed.
- The reporting verb changes according to sense: it may be told, asked, inquired ,etc.
4. Rules for the Change of Pronouns:
- The first person pronouns (I, me, my, we, us, our) in the reported speech change according to the subject of the reporting verb.
- The pronouns of the second person (you, your, yourself) in the reported speech change according to the object of the reporting verb.
- The pronouns of the third person do not change.
For example :
- He said, “I like the book.” He said that he liked the book.
- He said to me, “Do you like the book?” He asked me if I liked the book.
- He said, “He likes the book.” He said that he liked the book.

- If the reporting verb is in the present or the future tense, the tense of the reported speech is not changed:
- Satish says, “I am flying a kite.”
- Satish says that he is flying a kite.
- Satish will say, “I want a glass of milk.”
- Satish will say that he wants a glass of milk.

- If the direct speech expresses a historical fact, a universal truth or a habitual fact. tense of the direct speech will not change: Direct : He said, “Honesty is the best policy.” Indirect : He said that honesty is the best policy. Direct : He said, “The sun rises in the east.” Indirect : He said that the sun rises in the east. Direct : Rakesh said, “I am an early riser.” Indirect : Rakesh said that he is an early riser. Direct : She said, “God is omnipresent.” Indirect : She said that God is omnipresent. Direct : The teacher said, “The First World War started in 1914.” Indirect : The teacher said that the First World War started in 1914.
7. Changing Statements into Indirect Speech:
- The reporting verb “said to’ is changed to ‘told, ‘replied’, ‘‘remarked’,
- The reporting verb is not followed by an object, it is not changed.
- The inverted commas are removed. The conjunction that is used to connect the reporting clause with the reported speech.
- The rules for the change of pronouns, tenses, etc. are followed. Direct : Ramu said, “I saw a lion in the forest.” Indirect : Ramu said that he had seen a lion in the forest. Direct : Satish said to me, “I am very happy here.” Indirect : Satish told me that he was very happy there. Direct : He said, “I can do this work.” Indirect : He said that he could do that work. Direct : Renu said to me, “I was washing the clothes.” Indirect : Renu told me that she had been washing the clothes. Direct : She said, “I am not well.” Indirect : She said that she was not well. Direct : He said to Sita, “I have passed the test.” Indirect : He told Sita that he had passed the test Direct : I said to my friend, “He has been working very hard.” Indirect : I told my friend that he had been working very hard. Direct : My friend said to me, “I shall go to Delhi tomorrow.” Indirect : My friend told me that he would go to Delhi the next day. Direct : I said, “I agree to what he said.” Indirect : I said that I agreed to what he had said. Direct : The student said to the teacher, “I am sorry that I am late.” Indirect : The student told the teacher that he was sorry that he was late.
8. Rules for the Change of Interrogative (Questions) sentences:
- The reporting verb ‘say’ is changed into ask, inquire,
- The interrogative sentence is changed into a statement by placing the subject before the verb and the full stop is put at the end of the sentence.
- If the interrogative sentence has a wh-word (who, when, where, how, why, etc) the wh- word is repeated in the sentence. It serves as a conjunction.
- If the interrogative sentence is a yes-no answer type sentence (with auxiliary verbs aw, are, was, were, do, did, have, shall, etc), then if or ‘ whether’ is used as a conjunction.
- The auxiliaries do, does, did in a positive question in the reported speech are dropped.
- The conjunction that is not used after the reporting clause. Direct : I said to him, “Where are you going?” Indirect : Tasked him where he was going. Direct : He said to me, “Will you go there?” Indirect : He asked me if I would go there. Direct : My friend said to Deepak, “Have you ever been to Agra?” Indirect : My friend asked Deepak if he had ever been to Agra. Direct : I said to him, “Did you enjoy the movie?” Indirect : I asked him if he had enjoyed the movie. Direct : I said to her, “Do you know him?” Indirect : I asked her if she knew him. Direct : He said to me, “Will you listen to me?” Indirect : He asked me if I would listen to him. Direct : I said to him, “When will you go there?” Indirect : I asked him when he would go there. Direct : He said to me, “How is your father?” Indirect : He asked me how my father was. Direct : I said to him, “Are you happy?” Indirect : I asked him if he was happy. Direct : He said to her, “Do you like apples?” Indirect : He asked her if she liked apples.
9. Changing Commands and Requests into Indirect Speech:
- In imperative sentences having commands, the reporting verb is changed into command, order, tell, allow, request, etc.
- The imperative mood is changed into the infinitive mood by putting to, before the verb. In case of negative sentences, the auxiliary ‘do’ is dropped and ‘to’ is placed after ‘not: Direct : She said to me, “Open the window.” Indirect : She ordered me to open the window. Direct : The captain said to the soldiers, “Attack the enemy.” Indirect : The captain commanded the soldiers to attack the enemy. Direct : I said to him, “Leave this place at once.” Indirect : I told him to leave that place at once. Direct : The teacher said to the students, “Listen to me attentively.” Indirect : The teacher asked the students to listen to him attentively. Direct : The Principal said to the peon, “Ring the bell.” Indirect : The Principal ordered the peon to ring the bell. Direct : The master said to the servant, “Fetch me a glass of water.” Indirect : The master ordered the servant to fetch him a glass of water. Direct : I said to him, “Please bring me a glass of water.” Indirect : I requested him to bring me a glass of water. Direct : I said to my friend, “Please lend me your book.” Indirect : I requested my friend to lend me his book.
Exercise (Solved)
Change the following sentences into Indirect Speech: (i) He said, “I will do it now.” Answer: He said that he would do it then.
(ii) He says, “Honesty is the best policy.” Answer: He says that honesty is the best policy.
(iii) Ramesh says, “I have written a letter.” Answer: Ramesh says that he has written a letter.
(iv) She said, “Mahesh will be reading a book.” Answer: She said that Mahesh would be reading a book.
(v) She said, “Where is your father?” Answer: She inquired where his father was.
(vi) He said to me, “Please take your book.” Answer: He requested me to take my book.
(vii) The Principal said to the peon, “Let this boy go out.” Answer: The Principal ordered the peon to let that boy go out.
(viii) He said to me, “May you live long!” Answer: He prayed that I might live long.
(ix) She said, “Goodbye friends!” Answer: She bade goodbye to her friends.
(x) The students said, “Alas! I wasted my time last year.” Answer: The students regretted that he had wasted his time the previous year.
Free Resources
Quick Resources
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students

Reported Speech Exercises for Class 9 CBSE With Answers
Reported speech is when we express or say things that have already been said by somebody else.
Basic English Grammar rules can be tricky. In this article, we’ll get you started with the basics of sentence structure, punctuation, parts of speech, and more.
We also providing Extra Questions for Class 9 English Chapter wise.
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 9 CBSE With Answers Pdf
When we say things that have been said, we use two ways of expressing it. The first is direct speech when we express what the speaker said as it is and the second is indirect speech where we express what was said in our words.
Examples: If you ask your friend Pradeep, ‘Did you take my book?’, the reply could be ‘Your book is with Jai.’ Now, we can report this statement in two ways:
- Pradeep told me, ‘Your book is with Jai’.
- Pradeep told me that my book is with Jai.

Rules For Reported Speech While changing direct speech into reported speech or vice versa, the following change:
- the reporting verb
- the pronouns
- the situations
- report using present and future tenses
- modal verbs
- word order with who, which, and what

Changes in reporting verb:
- Affirmative sentences: said, told (object), asserted, replied, assured, informed, responded, whispered, alleged, believed, assumed, though.
- Interrogative sentences: asked, inquired, wanted to know, enquired When we report.
- Imperative sentences: ordered, begged, pleaded, implored, advised, demanded.
Change of pronouns:
- Direct speech: Surabhi said, “I am reading.”
- Indirect speech: Surabhi said that she was reading.
- A first-person and second-person generally change to a third person (depending upon the object to reporting verb).
Change of tenses:
| Surabhi said, “I like to read.” Surabhi said, “I am reading.” Surabhi said, “I have read this book.” Surabhi said, “I have been reading this book.” Surabhi said, “I read this book last week.” Surabhi said, “I was reading this book when Mohan snatched it away.” Surabhi said, “I had read this book before I gave it to you.” Surabhi said, “I will read this book.” | Surabhi said that she liked to read. Surabhi said that she was reading. Surabhi said that she had read that book. Surabhi said that she had been reading that book. Surabhi said that she had read that book the previous week. Surabhi said that she had been/was reading that book when Mohan snatched it away. Surabhi said that she had read that book before she gave it to me. Surabhi said that she would read that book. |
In general, the present tense becomes past tense; past and perfect tenses become the past perfect tense.
Change Of Situations: Examples:
- Surabhi said, “I read this book last week.” (direct speech)
- Surabhi said that she had read that book the previous week, (indirect speech)
| “this” | becomes | “that” |
| “last week” | becomes | “the previous week” |
| “here” | becomes | “there” |
| “now” | becomes | “then” |
| “today” | becomes | “that day” |
| “yesterday” | becomes | “the day before/the previous day” |
| “tomorrow” | becomes | “the next day/the coming day” |
| “last week” | becomes | “the week before/the previous week” |
| “next month” | becomes | “the next month/the coming month” |
| John said, “The sun rises from the east.” Surabhi said, “I will read this book.” | John said that the sun rises from the east. Surabhi said that she would read that book. |
If the speaker talks about a universal truth, the tense is unchanged.
In case of questions and answers: Examples:
- Surabhi asked, “Have you read this book?” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi asked if/whether I had read that book. (Indirect Speech)
- Surabhi asked, “Where is the book?” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi asked where the book was. (Indirect Speech)
(a) yes/no questions – use if/whether (b) wh-questions – use the wh-word
Word Order:
- Surabhi asked, “What’s the matter?”
- Surabhi asked what the matter was. (what + the matter + was)
- Surabhi asked what was the matter, (what + was + the matter)
Can Be Either:
- who/which/what + complement + be or
- who/which/what + be + complement
Reported speech using present and future tenses: Examples:
- Surabhi said, “The sun rises in the east.” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi said that the sun rises in the east. (Indirect Speech)
- Surabhi said, “I will read this book.” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi said that she will read that book. (Indirect Speech)
If the original speaker’s present and future are still present and future, the tense remains unchanged. In case of modal verbs:
| can | becomes | could |
| will | becomes | would |
| shall | becomes | should |
| may | becomes | might |
would, should, could, might, ought to, and must remain unchanged. Example:
- Surabhi said, “I can solve this sum.” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi said that she could solve that sum. (Indirect Speech)
In our daily lives, we use reported speech in many forms. We use reported speech to report statements, questions, requests or even commands. There are certain things we need to keep in mind when we report each of them.
- When we report statements, we have to make sure what changes need to be made in the pronoun, tense or temporal-spatial expression.
- When we transform questions into reported speech, we have to check whether or not to change the tense, pronoun as well as place and time expression.
- Upon changing, we have to ensure that the question is an indirect question.
- We also have to make use of words such as where, when, how, if, whether etc.
- In transforming requests and commands into reported speech, tenses are not relevant.
- We only have to ensure that there are changes in the pronoun and the place and time expression.
Reported Speech Exercises Solved Example for Class 9 CBSE
Diagnostic Test 18

The child called out to his mother to (a) ……………………… . The mother replied that (b) ……………………… . She asked her son if (c) ……………………… . Her son replied in the affirmative. He added that (d) ……………………… . The mother then wanted to know what (e) ……………………… . The child informed her (f) ……………………… . Answer: (a) come and look as the house across the road was on fire. (b) she couldn’t go then as she was cooking. (c) the Fire Brigade was there. (d) they had just arrived and the men were jumping down from the engine. (e) the people of the house were doing. (f) that some of them were standing in the street holding an umbrella and others were throwing valuables down from the window into it.
| 5-6 – good 4 or less – You need to develop your grammar skills through adequate practice. |
Reported Speech in English Grammar for Class 9
by Meenu Saini | Apr 20, 2024 | General | 0 comments

Class 9 English Grammar Reported Speech (Direct and Indirect) Exercise with Answer
Reported Speech – Reported speech refers to recording the speaker’s speech, whether it is done directly by recording the speaker’s words or indirectly by recording the speaker’s words but changing them.

For example Direct speech – Priya said, “I’d like to have an apple.”
Priya said is the reporting verb. “I’d like to have an apple.” is the reported speech.

| The part of the sentence which is not in the inverted commas is called the reported verb. | The part of the sentence which is under inverted commas is called reporting speech. The second part of the sentence refers to some other person, universal facts, imaginary parts, historical facts, happening events, etc. |
Direct Speech
It refers to reporting the exact words spoken by the speaker. There is no change in the verb or the sentence.
Rules of Direct Speech
- Speech should be opened with quotations or inverted commas.
- The word said is used to connect two sentences.
- Reporting clause should be used at the end of the sentence.
- At the end of the sentence full stop should be placed.
Let us look at some examples
- Rahul said, “Saina Nehwal has won the match against PV Sindhu.”
- Krish says, “I am having my dinner.”
Indirect Speech
It is the speech that tells what someone has said but it does not explain the actual words spoken by the person. It just conveys the basic narration of what is being said to the third person.
Rules of Indirect Speech
- Past tense is used when the situation is uncertain.
- The present tense of the sentence is changed to the past tense in indirect speech.
- Universal facts tense remains the same.
- The use of the word “that” connects the reported verb and reported speech.
- Shivani said that she enjoyed watching the movie Titanic.
- My mother says that she is eating watermelon.
Changing direct speech into reported speech
- Change in tenses
- When the reporting verb is in the simple present tense or simple future tense, the verb in reported speech does not change.
- When the reporting verb is in the past tense, the verb and reported speech is changed into the corresponding past tense.
- There are three situations in which, even if the reporting verb is in the past tense, we do not change the tenses in the reported speech.
- The reported speech expresses a universal truth or a habitual fact.
- The reported speech has two clauses, both in the past.
- The reported speech describes a situation which still exists when the speech is reported.
- Change in personal pronouns and possessive adjectives.
- Pronouns in the third person and their possessive adjectives do not change in reported speech.
- Pronoun of the second person and its corresponding possessive adjective change into the same person as the object of the reporting verb.
- First person pronouns and the possessive adjectives in direct speech change into the same person as the subject of the reporting verb in indirect speech.
Change of Pronouns
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
| I | He, she |
| Me | Him, her |
| We | They |
| Us | Them |
| You | He, she, they |
| You | Him, her, them |
| My | His, her |
| Mine | His, hers |
| Our | Their |
| Ours | Theirs |
| Your | His, her, their |
| Yours | His, hers, theirs |
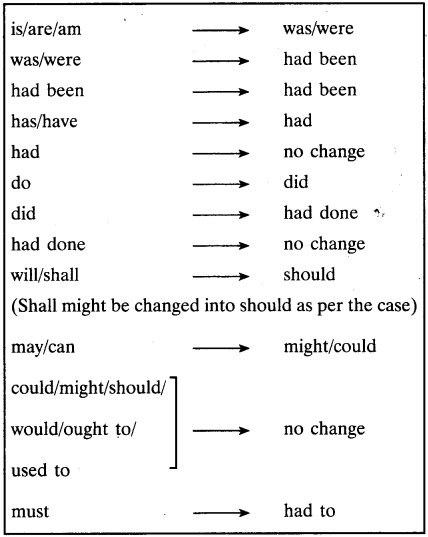
Change in Tenses
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
| is/am/are | Was/were |
| Was/were | Had been |
| Had been | (No change) |
| Has/have | Had |
| Had | (No change) |
| Do | Did |
| Did | Had done |
| Had done | (No change) |
| Will/shall | Would/Should |
| Must | Had to |
| Would/Should/Might/could/Ought to | (No change) |
Change of Adverbs of Place and Adverbs of Time
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
| Here | There |
| Now | Then |
| Today | That day |
| Tomorrow | The next day / The following day |
| Yesterday | The previous day |
| Tonight | That night |
| Last week | The week before |
| Next week | The week after |
| Last month | The previous month |
| Next month | The following month |
| Last year | The previous year |
| Next year | The following year |
| Ago | Before |
| Thus | So |
Change of Modal Verbs
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
| Will | Would |
| May | Might |
| Can | Could |
| Shall | Should |
| Has/Have | Had |
Exercise on Reported Speech (Practice Questions)
A Convert the following sentences into reported speech.
- Sana said, “Mother, where have you kept my new pair of jeans?”
- Mother said to her friend, “My daughter sang well, didn’t she?”
- Sita said to him, “Will you play today?”
- He said, “May you succeed in your venture, my daughter.”
- She said, “Oh! What a lovely dress.”
- Mridula asked Manisha, “Did you buy the magic show tickets?”
- He said, ”Let’s go to the market.”
- They said, “Alas! We have lost our way in the forest.”
- Akbar said to HImesh, “A very happy birthday.”
- The chemistry teacher said to her students, “You have understood the experiment, haven’t you?”
- Reena said, “I think the book is too expensive.”
- He said, “Oh! I have met you after a long time.”
- The compere announced, “The chief guest will reach here any moment.”
- The fisherman said to the customer, “The fish is fresh and will taste good.”
- Rahul said, “Are you exhausted today?”
- Sana asked her mother where she had kept her new pair of jeans.
- Mother asked her friend if her daughter had sung well.
- Sita asked him whether he would play that day.
- He wished that his daughter might succeed in her venture.
- She exclaimed with admiration that it was a lovely dress.
- Mridula asked Manisha if she had bought the magic show tickets.
- He suggested that they should go to the market.
- They exclaimed with regret that they had lost their way in the forest.”
- Akbar wished HImesh a very happy birthday.
- The chemistry teacher asked the students if they had understood the experiment.
- Reena thought that the book was too expensive.
- He exclaimed with surprise that he had met her after a long time.
- The compere announced that the chief guest would reach there any moment.
- The fisherman said to the customer that the fish was fresh and would taste good.
- Rahul asked if I was exhausted that day.
B Convert the following paragraph into reported speech.
He said, “Are you tired today? Let us take the children to the zoo. Tomorrow is a holiday, so we will be relaxed.” Ans He asked if I was tired that day. He suggested that we take the children to the zoo as the next day was a holiday so we would be relaxed.
C Convert the following paragraph into reported speech.
She said, “It’s very hot today, isn’t it? Summer is here to stay and it is the right time to go for a swim. Let’s also buy mangoes, ice-cream and juice cans to beat the heat.” Ans She said that it was very hot that day and summer was there to stay. It was the right time to go for a swim she added. She also suggested that we should buy mangoes, ice-cream and juice cans to beat the heat.
D Convert the following paragraph into reported speech.
My friend said, “Oh! What a pleasant surprise to have you in my house. I will prepare pasta and risotto for you. Let’s watch a movie in my home theater.” Ans My friend exclaimed with joy that it was a pleasant surprise to have me in her house. She said that she would prepare pasta and risotto for me and suggested that we should watch a movie in her home theater.
E Convert the following paragraph into reported speech.
Mother Teresa said, “Let us touch the dying, the poor, the lonely and the unwanted, according to the graces we have received and let us not be ashamed or slow to do the humble work.” Ans Mother Teresa said that we should touch the dying, the poor, the lonely and the unwanted, according to the graces we had received and we should not be ashamed or slow to do the humble work.
F Convert the following paragraph into reported speech.
Daughter: Papa, please buy a mobile phone for me. Father : What is the need of a mobile when you can use the landline? Daughter: All my friends have mobiles, I want one for myself. Father : I will buy it for you after your final exams.
Ans The daughter requested her father to buy a mobile phone for her. Father asked her what was the need of a mobile when she could use the landline. The daughter replied that all her friends had mobiles. She wanted one for herself. Father agreed and said that he would buy it for her after her final exams.
- Tenses for class 9 | Types of Tenses with Examples
- Determiners for Class 9, types, exercises
- Modals for Class 9 Definition, Examples, Exercises
- Subject Verb Agreement for Class 9, rules, Exercise
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Teacher’s Day Wishes in Hindi
- Ganesh Chaturthi Wishes in Hindi
- Janmashtami Messages in Hindi
- Raksha Bandhan Wishes in Hindi
- Birthday Wishes in Hindi
- Anniversary Wishes in Hindi
- Father’s Day Quotes and Messages
- Father’s Day quotes in Hindi
- International Yoga Day Slogans, Quotes and Sayings
- अंतर्राष्ट्रीय योग दिवस Slogans, Quotes and Sayings
- Good Morning Messages in Hindi
- Good Night Messages in Hindi | शुभ रात्रि संदेश
- Wedding Wishes in Hindi
Important Days
- National Space Day Quiz| National Space Day MCQs
- World Soil Day – Date, History, Significance
- International Yoga Day Slogans, Quotes and Sayings by Famous people 2024
- Calendar MCQ Quiz for Various Competitive Exams
- CUET 2024 MCQ Quiz on Important Dates
English Writing Skills
English Grammar Examples
All English Grammar Topics, Exercises, examples, MCQ Tests
Analytical Paragraph Writing | Format, Examples, Samples
Report Writing Format | How to Report Writing Examples, Topics, Samples and Types
Letter to Editor Class 10 to 12, Topics, Sample and Example
Informal Letter Format, Topics, Examples
Article Writing Format, Topics and Examples
Classified advertisement writing examples
Letter to the Principal, Format, Samples
Story Writing , Format, Topics, Examples
Job Application with Biodata, Format, Topics, Examples
Leave Application Format for Office, School and Sample
Leave Application for Marriage, Format, Sample, and Examples
Speech Writing format, examples for Class 11, 12
Invitation writing tips for class 12
Report writing tips for class 12
10 Important Things to DO to score more in Debate writing question
Let us revise Reported Speech in 9 Quick Steps
Job Application Writing Tips for Class 12 English
Tips to ace the question on Analytical Paragraph writing in Class 10
English Grammar
Active and Passive Voice Definition, Rules, Exercise, and Example Sentences
Countable and Uncountable Nouns Meaning, Definition, Difference and Examples
Direct and Indirect Speech, Format, Rules, Exercise, and Examples
Determiners Definition, Types, Exercise and Examples
All About Tenses | Tenses Examples, Types of Tenses in English Grammar
English Vocabulary for Bank PO Exams – Synonyms MCQ Videos
Noun Definition, Types, Exercise with Examples in Hindi and English
What is a Verb? Definition, Types of Verbs, Exercise and Verbs Examples in Hindi and English
What is a Preposition? Definition, Types, Exercise, and Examples in Hindi and English
Subject Verb Agreement Rules and Examples
Modals Definition | Modals Exercise, List of Modals with Examples
Master Tenses in English Grammar – The Easy Way
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Reported Speech

What is Reported Speech?

Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of conveying what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. Instead of using quotation marks , the speaker paraphrases or summarises the original statement. This transformation often involves changes in pronouns, tenses, and time expressions to fit the context of the reporting. Understanding reported speech is crucial for effective communication , as it allows you to relay information accurately and fluently in both spoken and written English.
| , reported speech does not use quotation marks, since it's not quoting the speaker's exact words. |
Reported Speech - How Does it Work?
Indirect speech or Reported speech is just a way of expressing your intent in questions, statements or other phrases, without essentially quoting them outrightly as the way it is done in indirect speech.
Reported Speech Rules
To understand Reported Speech Grammar and Reported Verbs, you need to first understand reported speech rules and how it works. Here are some types of reported speech:
Reported Statements
Reported speech is used when someone says a sentence, like, "I'm going to the movie tonight". Later, we want to tell a 3rd person what the first person is doing.
It works like this:
We use a reporting verb i.e 'say' or 'tell'. In the present tense, just put in 'he says.
Direct Speech: I like burgers.
Reported Speech: He says (that) he likes burgers.
You don't need to change the tense, but you do need to switch the 'person' from 'I' to 'he’. You also need to change words like 'my' and 'your'.
But, in case the reporting verb is in the past tense, then change the tenses in the reported speech itself.
Reported Questions
Reported questions to go like
Direct Speech: Where do you reside?
We make the change to reported speech by-
It is similar to reported statements. The tense changes are exact, and we keep the question’s word. But we need to change the grammar of that normal sentence into positive. For eg:
Reported Speech: He asked me where I resided.
The direct speech question is in the present simple tense. We make a present simple question with 'do' or 'does'. For that, I need to take that away. Then change the verb to the past simple.
Direct Speech: Where is Jolly?
Reported Speech: He asked me where Jolly was.
The direct question is the present simple of 'be'. We change the question form of the present simple of being by changing the position of the subject and the verb. So, change them back before putting the verb into the past simple.
Reported Speech Examples with Answers
Reported Requests
The reported speech goes a long way. What if a person asks you to do something politely or make a request? It’s called a reported request. For example
Direct Speech: Close the door, please / Could you close the door please? / Would you mind closing the door, please?
All these requests mean the same, so we don't need to report every word there when we tell a 3rd person about it.
We can simply use 'ask me + to + infinitive':
Reported Speech: They asked me to close the door.
Direct Speech: Please be punctual.
Reported Speech: They asked us to be punctual.
Reported Orders
And lastly, how about when someone doesn't ask that politely? This is known as an 'order' in English, which is when someone tells you to do something pretty much directly. This is called a reported order. For example
Direct Speech: Stand up right now!
We make this into a reported speech in the same way as that for a request. Just use 'tell' rather than 'ask':
Reported Speech: She told me to stand up right now.
Direct Order | Reported Order |
Go to sleep! | He told the child to go to sleep |
Stop worrying! | He told her to stop worrying |
Be punctual! | He told me to be punctual. |
Don't move! | He told us not to move. |
Time Expressions within the Ambit of Reported Speech
Sometimes when we want to change the direct speech into reported speech, we will have to change the time expressions too. We don't necessarily always have to do that. However, It depends on when we heard the speech in indirect form and when we said the speech in reported form.
For Example,
It's Sunday. Kiran Ma’am says "I'm leaving today".
If You tell someone on Sunday, You will say "Kiran Ma’am said she was leaving today".
If you tell someone on Tuesday, You will say "Kiran Ma’am said she was leaving yesterday".
If you tell someone on Friday, you will say "Kiran Ma’am said she was leaving on Sunday ".
If you tell someone a month later, you will say "Kiran Ma’am said she was leaving that day".
So, technically there's no easy way to convert. You need to put in real effort and have to think about it when the direct speech is said.
Conversions of Direct Speech to Reported Speech
Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
now can be converted to | then / at that time |
today can be converted to | yesterday / that day / Tuesday / the 27th of June |
yesterday can be converted to | the day before yesterday / the day before / Wednesday / the 5th of December |
last night can be converted to | the night before, Thursday night |
last week can be converted to | the week before / the previous week |
tomorrow can be converted to | today / the next day / the following day / Friday |
Now Let us Check our Understanding Through this Table
Tense | Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
present simple | I like Burger | She said (that) she liked Burger |
present continuous | I am living in Australia | She said (that) she was living in Australia |
past simple | I bought a new house | She said (that) she had bought a new house OR She said (that) she bought a new house |
past continuous | My mom was watching a movie | She said (that) her mom had been watching a movie |
present perfect | I haven't seen Ram | She said (that) she hadn't seen Ram. |
will | I will travel to Delhi | She said (that) she would travel to Delhi. |
would* | I would suggest, but..” | She said (that) she would suggest but... |
can | I can play cricket. | She said (that) she could play cricket |
could* | I could go to the wedding | She said (that) she could go to the wedding |
shall | I shall come later | She said (that) she would come later. |
should* | I should talk to her | She said (that) she should talk to her |
might* | I might be coming late | She said (that) she might be coming late |
must | I must attend the party | She said (that) she must attend the party She said she had to attend the party |
This is all about reported speech. English grammar is a tricky thing given both the rules and practice. Reading these rules solely will not help you to get a strong grasp of them. You also have to practice reported speech sentences in practical life to know how and when they can be used.
Change of Pronouns
Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
I am happy. | He/She said he/she was happy. |
You will succeed. | He/She said I would succeed. |
We are going out. | They said they were going out. |
He is my friend. | He/She said he was his/her friend. |
She loves music. | He/She said she loved music. |
They will join us. | He/She said they would join them. |
My book is here. | He/She said his/her book was there. |
Your project is good. | He/She said my project was good. |
Our team won. | They said their team won. |
Their house is beautiful. | He/She said their house was beautiful. |
Change of Adverbs Time and Place
Direct Speech (Adverbs of Place & Time) | Reported Speech (Adverbs of Place & Time) |
Here | There |
Now | Then |
Today | That day |
Tomorrow | The next day / The following day |
Yesterday | The previous day / The day before |
This week | That week |
Last week | The previous week / The week before |
Next week | The following week |
Ago | Before |
Here | There |
Tonight | That night |
Change of Modal Verbs
Direct Speech (Modal Verbs) | Reported Speech (Modal Verbs) |
Will | Would |
Can | Could |
Shall | Should |
May | Might |
Must | Had to |
Would | Would (No Change) |
Could | Could (No Change) |
Should | Should (No Change) |
Might | Might (No Change) |
Ought to | Ought to (No Change) |
Test your Knowledge of Reported Speech with Reported Speech Exercises
Exercise 1: Convert the following sentences from direct speech to reported speech.
Direct: "I am going to the market now," said John.
Reported: __________________________
Direct: "We will finish the project tomorrow," the team leader said.
Direct: "Can you help me with my homework?" Sarah asked Tom.
Direct: "She is studying French," said her teacher.
Direct: "I must complete this assignment by tonight," the student mentioned.
Exercise 2: Correct the error in the following reported speech sentences.
He said that he will go to the party the next day.
Correction: __________________________
She told me that she can come to the meeting.
They said that they are going to visit their grandparents.
The teacher told us that we must complete the homework by tomorrow.
He said that he might will arrive late.
Exercise 3: Convert the following sentences from reported speech to direct speech.
Reported: She said that she had finished her work.
Direct: __________________________
Reported: He told me that he would help me later.
Reported: They mentioned that they were planning a trip.
Reported: The doctor said that the patient needed rest.
Reported: She said that she could not attend the party.
Find out if you got them right from the answers below.
John said that he was going to the market then.
The team leader said that they would finish the project the next day.
Sarah asked Tom if he could help her with her homework.
Her teacher said that she was studying French.
The student mentioned that he/she had to complete the assignment by that night.
He said that he would go to the party the next day.
She told me that she could come to the meeting.
They said that they were going to visit their grandparents.
The teacher told us that we had to complete the homework by the next day.
He said that he might arrive late.
"I have finished my work," she said.
"I will help you later," he told me.
"We are planning a trip," they mentioned.
"The patient needs rest," the doctor said.
"I cannot attend the party," she said.
Takeaways from this Page
Understanding the reported speech requires understanding how pronouns shift based on the speaker and context.
Recognising the necessary tense changes when converting from direct to reported speech is crucial for accurate communication.
Knowing how adverbs of time and place change in reported speech ensures clarity in conveying when and where something occurred.
Familiarity with how modal verbs like "will" change to "would" helps maintain the intended meaning when reporting statements.

FAQs on Reported Speech
1. How do you convert present tenses to reported speech?
To convert present tenses to reported speech, follow these rules:
Present Simple changes to Past Simple.
Present Continuous changes to Past Continuous.
Present Perfect changes to Past Perfect.
Present Perfect Continuous changes to Past Perfect Continuous.
"I do yoga every morning." → She said that she did yoga every morning.
"My friend is watching a movie." → She said that her friend was watching a movie.
"I have been to the USA." → She told me that she had been to the USA.
2. How do you convert past tenses to reported speech?
To convert past tenses to reported speech, follow these rules:
Past Simple changes to Past Perfect.
Past Continuous changes to Past Perfect Continuous.
Past Perfect and Past Perfect Continuous remain unchanged.
"He arrived on Friday." → He said that he had arrived on Friday.
"I was playing cricket." → He said that he had been playing cricket.
"She had worked hard." → She said that she had worked hard.
3. What are the rules for converting future tenses to reported speech?
When converting future tenses to reported speech:
Future Simple (will) changes to would.
Future Continuous (will be) changes to would be.
Future Perfect (will have) changes to would have.
Future Perfect Continuous (will have been) changes to would have been.
"I will be attending the wedding." → She said that she would be attending the wedding.
4. How do you convert sentences with 'can' and 'can't' to reported speech?
'Can' changes to 'could'.
'Can't' changes to 'couldn't'.
"I can help you." → She said that she could help me.
"I can't come to the party." → He said that he couldn't come to the party.
5. How do you convert sentences with 'will' and 'won't' to reported speech?
'Will' changes to 'would'.
'Won't' changes to 'wouldn't'.
"I will call you tomorrow." → She said that she would call me the next day.
"I won't attend the meeting." → He said that he wouldn't attend the meeting.
6. What are some examples of reported requests?
Reported requests typically use the verb "ask" followed by an infinitive.
Direct: "Please open the window."
Reported: She asked me to open the window.
Direct: "Could you help me with this?"
Reported: He asked me to help him with that.
7. What are some examples of reported orders?
Reported orders often use the verb "tell" followed by an infinitive.
Direct: "Sit down."
Reported: The teacher told the student to sit down.
Direct: "Don't touch that."
Reported: He told me not to touch that.
8. How do time expressions change in reported speech?
Time expressions change as follows:
Today → That day
Tomorrow → The next day
Yesterday → The day before
Next week → The following week
Last week → The previous week
9. Does the past perfect tense change in reported speech?
No, the past perfect tense remains the same in reported speech.
"She had left early." → He said that she had left early.
10. What happens to pronouns in reported speech?
Pronouns in reported speech usually change based on the speaker and listener.
"I am going to the store." → He said that he was going to the store.
"You should see this." → She told me that I should see that.
- Reported Speech
Reported Speech: Whenever you are quoting someone else’s words , you use two kinds of speeches – Direct or Indirect speech . In this chapter, we will learn all about Direct and Indirect speech and how to convert one into another.
Suggested Videos
Reported speech- how does it work.

Whenever you report a speech there’s a reporting verb used like “say” or “tell”. For example:
Direct speech: I love to play football .
Reported speech: She said that she loves to play football. (Note 1 : Assume a gender if not mentioned already. Note 2: Using “that” is optional. This sentence could also have been written as “She said she loves to play football.”)
The tense doesn’t have to be changed in this case of reported speech. But of the reporting verb is in the past tense , we do change the tense of the sentence.
Browse more Topics under Transformation Sentences
- Active and Passive Voice
- Parts of Speech
- Types of Sentences
Reported speech- Play of the tenses:
| Simple present | simple past |
| present continous | past continuous |
| simple past | past perfect |
| past continuous | past perfect continuous |
| present perfect tense | past perfect tense |
| past perfect tense | past perfect tense |
Learn more about Parts of Speech here in detail
This is a summary table that will be crystal clear to you as you read further. Just come back to this table after this section and use this as a summary table:
| Simple present | I like to swim in the ocean | She said she liked to swim in the ocean | Simpe past |
| Simple present | I live in New Orleans | He said he lived in New Orleans | Simpe past |
| Past simple | I went to school in the morning | She said she had gone to school that morning | Past perfect |
| Present continuous | I was going to the Himalayas | He said he was going to the Himalayas | Past continuous |
| Past continuous | I was walking near the beach | She said that she had been walking near the beach | past perfect continuous |
| Present perfect | I have caught a few fishes | She said she had caught a few fishes | past perfect |
| Past perfect | I had trekked the Himalayas this time last year | He said he had trekked the Himalayas this time last year | Past perfect |
Some word transitions from direct to reported speech that will come in handy:
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- would stays would
- should stays should
- must stays must or had to(matter of choice)
- shall becomes should
Exception : A present tense in direct speech may not become a past tense in the reported speech if it’s a fact or something generic we are talking about in the sentence. For example-
Direct speech: The sun rises from the East.
Reported speech: She said that the sun rises/rose from the East.
Reported speech- Handling questions:
What happens when the sentence we are trying to report was actually a question? That’s something we are going to deal with in this section. Reported questions- It’s quite interesting. let’s get into it:
Well the good news is that the tense change you learnt above stays the same in reported speech for questions. The only difference is that when you report a question, you no more report it in the form of a question but in the form of a statement. For example:
Direct speech: Where do you want to eat?
Reported speech: She asked me where I wanted to eat.
Notice how the question mark is gone from the reported speech. The reported speech is a statement now. Keep that in mind as you read further.
Remember the tense change? Let’s apply that to a few questions now.
| Are you going to my house? | She asked me if I was going to her house. |
| Where were you going? | He asked me where I was going. |
| Where have you been? | She asked me where had i been. |
Now these are questions that have wordy answers to them. What about the questions that has yes/no answers to them? In these type of questions just add “if” before asking the question. For example:
- Direct speech: Would you like to eat some cupcakes?
- Reported speech: He asked me if i would like to eat some cupcakes.
- Direct speech: Have you ever seen the Van Gogh paintings?
- Reported speech: She asked me if I had ever seen the Van Gogh paintings.
- Direct speech: Are you eating your vegetables?
- Reported speech: She asked if I was eating my vegetables.
Reported speech- Reported requests:
Well not all questions require answers. Some questions are polite requests. Remember? Could you please try to remember? And then there are request statements. Let’s see how do we convert these into reported speech.
Reported request = ask me + to + verb or requested me + to +verb
Just add this rule to your reported speech and you have what is called a reported request.
| Could you please shut the door? | She asked me to shut the door. |
| Can you please help me? | She requested me to help her. |
Reported speech- Reported orders:
Well, not everyone is going to be polite. Sometimes, we get orders. Now how will you report them? Unlike the request, the reporting verb isn’t ask but told or tell. Also, when in orders, sometimes subjects are omitted but while reporting we have to revive the subjects. Let’s see a few examples:
- Direct speech: Sit down!
- Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
- Direct speech: don’t worry!
- Reported speech: She told me not to worry.
Reported speech- Time transitions:
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
| now | then / at that time |
| today | yesterday / that day / Tuesday / the 27th of June |
| yesterday | the day before yesterday / the day before / Wednesday / the 5th of December |
| last night | the night before, Thursday night |
| last week | the week before / the previous week |
| tomorrow | today / the next day / the following day / Friday |
With that, you have everything it takes to understand reported speech. you are all se to change the direct to reported speech. Go ahead and try a few examples. All the best!
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.


Transformation of Sentences
- Active and Passive voice
37 responses to “Active and Passive voice”
Simple but very nice explanation and helpfull too.
What is the voice change of ” I have endeavoured to understand the fundamental truths.”
ENDEAVOUR HAS BEEN MADE BY ME TO UNDERSTAND THE FUNDAMENTAL TRUTH.
The fundamental truths have been endeavoured to be understood by me
The fundamental truths to understand had been endeavoured by him
The fundamental truths have endeavoured to be understood by me
The fundamental truths has been understood endeavoured to by me
How to change the voice for the following sentence – the books will be received by tomorrow
By whom? We need a subject. If the subject was for example “The library”, then the sentence in active voice would read “The library will receive the books by tomorrow”.
You will receive the books by tomorrow.
Tomorrow you will receive the book
You will receive the books (by) tomorrow.
Someone will receive the books by tomorrow
Tomorrow will be receive the books
HE WILL RECEIVE THE BOOKS BY TOMORROW.
By tomorrow the books will be received.
By tomorrow, you will receive the books
Tomorrow received the book
Change this “take right and turn left” into passive voice
Let the right be taken amd left be turned
‘amd’ is “and” 😅
You are advised to take right and turn left
Very helpful information thanks
Very well explained all basics that can lead to gain further knowledge very easily
What is in this box change into passive
what is the voice change of,” some people think nuclear is the best, because it doesnt add to global warming “….
Brilliant stuff!! – Rishabh
A kite was made by Ravi . What is the active form of this statement???
how to change into passive this sentence “when they were shifting the patient to the I.C.U.,he died
change into passive voice this sentence “when they were shifting the patient to I.C.U.,he died .
May you tell us tense conversion in voice.
Sentences without action like…. Jim is a doctor . Is it active or passive and if any how would you decide without having a main verb ?
It is named after the name of its principal tree ‘sundari'(passive)
how can ocean be object 🙄???
They made a bag
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Perfectyourenglish.com
English Grammar Lessons And Worksheets
- Class 9 worksheets
Reported Speech Worksheet for Class 9 CBSE
by Manjusha Nambiar · Published February 1, 2024 · Updated April 6, 2024
When we report questions, the question word (who, what, which etc.) is retained in the reported speech.
Note that a reported question has the same word order as a statement. That means the subject goes before the auxiliary verb.
- The teacher said, ‘What are you doing?’
- The teacher asked what I was doing. (NOT The Teacher asked that what I was doing.) (NOT The teacher asked what was I doing.)
In order to report Yes/No questions , we use the conjunction if or whether.
- ‘Would you like a cup of coffee?’ she asked.
- She asked if / whether I would like a cup of coffee.
Reporting commands
In order to report a command, we use a reporting verb like asked, told, requested, warned, advised, begged, urged, commanded, ordered etc.
- Direct speech: ‘Help me, please,’ she cried.
- Indirect speech: She begged them to help her.
Reported speech worksheet
Sentences are given in the direct speech. Change them into the indirect / reported speech.
1. ‘Leave me alone,’ she said.
2. ‘I don’t know what I am supposed to do,’ he said.
3. ‘How are we going to overcome this difficulty?’ they said.
4. Mother said, ‘Have you applied for that job?’
5. ‘Please wait for me,’ said the girl.
6. ‘It doesn’t work,’ she said.
7. ‘I can drive any car,’ she said.
8. Sam said, ‘I haven’t heard anything from them yet.’
9. ‘Close the doors and windows before you leave,’ said the woman.
10. ‘Should I wait any longer?’ he asked.
11. ‘Whose bag is this?’ he asked.
12. ‘I will wait outside,’ he said.
13. ‘Have you brought your lunch?’ she asked.
14. ‘Take this file with you when you go to work,’ she said to me.
15. ‘Be careful when you cross the road,’ said the mother to the children.
16. ‘Please wait a minute,’ the receptionist said to me.
17. ‘I don’t want to go,’ Maya said to me.
18. ‘Why are you crying?’ mother said to me.
19. ‘Do you know Rahul’s address?’ Rohit asked me.
20. ‘Submit your work before Monday,’ the teacher said to the students.
1. She requested / told me / us to leave her alone.
2. He said that he didn’t know what he was supposed to do.
3. They wondered how they were going to overcome that difficulty.
4. Mother asked if / whether I had applied for that job.
5. The girl requested me to wait for her.
6. She said that it didn’t work.
7. She said that she could drive any car.
8. Sam said that he hadn’t heard anything from them yet.
9. The woman told us to close the doors and windows before we left.
10. He asked if / whether he should / had to wait any longer.
11. He asked whose bag that was.
12. He said that he would wait outside.
13. She asked me if / whether I had brought my lunch.
14. She told me to take that file with me when I went to work.
15. The mother warned / advised the children to be careful when they cross the road.
16. The receptionist asked / requested me to wait a minute.
17. Maya told me that she didn’t want to go.
18. Mother asked me why I was crying.
19. Rohit asked me if / whether I knew Rahul’s address.
20. The teacher told / instructed the students to submit their work before Monday.
Related posts:
- Reported Speech Worksheet For Class 10 | Reporting Questions
- Reported Speech Worksheet for Class 10 KSEEB SSLC
- Direct And Indirect Speech Worksheet For Class 10
- Reported Speech Worksheet for Class 9
- Reported Speech Worksheet for Class 10 CBSE
- Direct And Indirect Speech Worksheet For Class 8 CBSE
- Reported Speech Worksheet For Classes 9 And 10
- Reported Speech Worksheet For Class 10
Tags: reported speech worksheet for class 9
Manjusha Nambiar
Hi, I am Manjusha. This is my blog where I give English grammar lessons and worksheets.
- Next story In The Modern World, A University Education Is Essential In Order To Get A Rewarding Job
- Previous story Gerund or Infinitive Worksheet for Class 8
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Explore perfectyourenglish.com
Useful links
- English Grammar
Learn English with me
If you need one-on-one private tuition, please send an email to [email protected]
- A word a day
- B2 First (Cambridge English)
- Bank PO English
- CBSE Grammar Worksheets
- Class 10 worksheets
- Class 11 Worksheets
- Class 2 Worksheets
- Class 3 worksheets
- Class 4 worksheets
- Class 5 worksheets
- Class 6 worksheets
- Class 7 worksheets
- Class 8 worksheets
- Class 9 and 10 worksheets
- Grammar exercises
- Karnataka Board English
- Kerala Syllabus English
- Maharashtra Syllabus English
- Phrasal verbs
- PSC Coaching
- Reading comprehension
- Sample Letters
- Tamil Nadu Board English
- Test Preparation
- Uncategorized
- Vocabulary exercises
Never Miss an Update!
Enter your email address to receive our lessons in your inbox:
Delivered by FeedBurner
Sites in our network
NCERT Guides
Learn Maths Online | Free NCERT Maths Solutions
Recent Posts
- Cars That Burn Fossil Fuels Should Be Banned
- Wealthy Nations Should Give Humanitarian Assistance to Poor Nations | IELTS Essay Sample
- People in all Modern Societies Use Drugs | IELTS Essay Sample
- The World Is Experiencing a Dramatic Increase in Population | IELTS Essay Sample
- We Are Becoming Increasingly Dependent on Computers | IELTS Essay Sample
Class 9 English Grammar: Direct And Indirect Speech
- Study Again
1. Direct and Indirect Speech: The words spoken by a person can be reported in two ways—Direct and Indirect. When we quote the exact words spoken by a person, we call it Direct Speech. Sohan said to Mohan, “I am going to school.” The exact words spoken by Sohan are put within inverted commas. But when we give the substance of what Sohan said, it is called the Indirect Speech. You can master in English Grammar of various classes by our articles like Tenses, Clauses, Prepositions, Story writing, Unseen Passage, Notice Writing etc.
2. Reporting Clause and Reported Speech: Sohan told Mohan that he was going to school. The words which generally come before the inverted commas are called the reporting clause, i.e. Sohan said to Mohan and the verb ‘said’, is called the reporting verb. The words spoken by Sohan and put within inverted commas are called the reported speech, i.e. “I am going to school.”
3. Rules for Changing Direct Speech into Indirect Speech: In the Indirect speech, no inverted commas are used. The conjunctions that, if, whether, are generally used after the reporting verb. The first word of the reported speech begins with a capital letter. The tense of the reporting verb is never changed. The reporting verb changes according to sense: it may be told, asked, inquired,etc.
4. Rules for the Change of Pronouns: The first person pronouns (I, me, my, we, us, our) in the reported speech change according to the subject of the reporting verb. The pronouns of the second person (you, your, yourself) in the reported speech change according to the object of the reporting verb. The pronouns of the third person do not change.
For example: He said, “I like the book.” He said that he liked the book. He said to me, “Do you like the book?” He asked me if I liked the book. He said, “He likes the book.” He said that he liked the book.
5. Changes in words expressing nearness, time, auxiliaries, etc.
6. Change in Tenses: If the reporting verb is in the present or the future tense, the tense of the reported speech is not changed: Satish says, “I am flying a kite.” Satish says that he is flying a kite. Satish will say, “I want a glass of milk.” Satish will say that he wants a glass of milk.
If the reporting verb is in the past tense, then the tense of the reported speech will change as follows: If the direct speech expresses a historical fact, a universal truth or a habitual fact. tense of the direct speech will not change:
Direct : He said, “Honesty is the best policy.” Indirect : He said that honesty is the best policy. Direct : He said, “The sun rises in the east.” Indirect : He said that the sun rises in the east. Direct : Rakesh said, “I am an early riser.” Indirect : Rakesh said that he is an early riser. Direct : She said, “God is omnipresent.” Indirect : She said that God is omnipresent. Direct : The teacher said, “The First World War started in 1914.” Indirect : The teacher said that the First World War started in 1914.
7. Changing Statements into Indirect Speech: The reporting verb “said to’ is changed to ‘told, ‘replied’, ‘‘remarked’, The reporting verb is not followed by an object, it is not changed. The inverted commas are removed. The conjunction that is used to connect the reporting clause with the reported speech. The rules for the change of pronouns, tenses, etc. are followed.
Direct : Ramu said, “I saw a lion in the forest.” Indirect : Ramu said that he had seen a lion in the forest. Direct : Satish said to me, “I am very happy here.” Indirect : Satish told me that he was very happy there. Direct : He said, “I can do this work.” Indirect : He said that he could do that work. Direct : Renu said to me, “I was washing the clothes.” Indirect : Renu told me that she had been washing the clothes. Direct : She said, “I am not well.” Indirect : She said that she was not well. Direct : He said to Sita, “I have passed the test.” Indirect : He told Sita that he had passed the test Direct : I said to my friend, “He has been working very hard.” Indirect : I told my friend that he had been working very hard. Direct : My friend said to me, “I shall go to Delhi tomorrow.” Indirect : My friend told me that he would go to Delhi the next day. Direct : I said, “I agree to what he said.” Indirect : I said that I agreed to what he had said. Direct : The student said to the teacher, “I am sorry that I am late.” Indirect : The student told the teacher that he was sorry that he was late.
8. Rules for the Change of Interrogative (Questions) sentences: The reporting verb ‘say’ is changed into ask, inquire, The interrogative sentence is changed into a statement by placing the subject before the verb and the full stop is put at the end of the sentence. If the interrogative sentence has a wh-word (who, when, where, how, why, etc) the wh- word is repeated in the sentence. It serves as a conjunction. If the interrogative sentence is a yes-no answer type sentence (with auxiliary verbs aw, are, was, were, do, did, have, shall, etc), then if or ‘ whether’ is used as a conjunction. The auxiliaries do, does, did in a positive question in the reported speech are dropped. The conjunction that is not used after the reporting clause.
Direct : I said to him, “Where are you going?” Indirect : Tasked him where he was going. Direct : He said to me, “Will you go there?” Indirect : He asked me if I would go there. Direct : My friend said to Deepak, “Have you ever been to Agra?” Indirect : My friend asked Deepak if he had ever been to Agra. Direct : I said to him, “Did you enjoy the movie?” Indirect : I asked him if he had enjoyed the movie. Direct : I said to her, “Do you know him?” Indirect : I asked her if she knew him. Direct : He said to me, “Will you listen to me?” Indirect : He asked me if I would listen to him. Direct : I said to him, “When will you go there?” Indirect : I asked him when he would go there. Direct : He said to me, “How is your father?” Indirect : He asked me how my father was. Direct : I said to him, “Are you happy?” Indirect : I asked him if he was happy. Direct : He said to her, “Do you like apples?” Indirect : He asked her if she liked apples.
9. Changing Commands and Requests into Indirect Speech: In imperative sentences having commands, the reporting verb is changed into command, order, tell, allow, request,etc. The imperative mood is changed into the infinitive mood by putting to, before the verb. In case of negative sentences, the auxiliary ‘do’ is dropped and ‘to’ is placed after ‘not:
Direct : She said to me, “Open the window.” Indirect : She ordered me to open the window. Direct : The captain said to the soldiers, “Attack the enemy.” Indirect : The captain commanded the soldiers to attack the enemy. Direct : I said to him, “Leave this place at once.” Indirect : I told him to leave that place at once. Direct : The teacher said to the students, “Listen to me attentively.” Indirect : The teacher asked the students to listen to him attentively. Direct : The Principal said to the peon, “Ring the bell.” Indirect : The Principal ordered the peon to ring the bell. Direct : The master said to the servant, “Fetch me a glass of water.” Indirect : The master ordered the servant to fetch him a glass of water. Direct : I said to him, “Please bring me a glass of water.” Indirect : I requested him to bring me a glass of water. Direct : I said to my friend, “Please lend me your book.” Indirect : I requested my friend to lend me his book.
Exercise (Solved) Change the following sentences into Indirect Speech: (a) He said, “I will do it now.” Answer: He said that he would do it then. (b) He says, “Honesty is the best policy.” Answer: He says that honesty is the best policy. (c) Ramesh says, “I have written a letter.” Answer: Ramesh says that he has written a letter. (d) She said, “Mahesh will be reading a book.” Answer: She said that Mahesh would be reading a book. (v) She said, “Where is your father?” Answer: She inquired where his father was. (vi) He said to me, “Please take your book.” Answer: He requested me to take my book. (vii) The Principal said to the peon, “Let this boy go out.” Answer: The Principal ordered the peon to let that boy go out. (viii) He said to me, “May you live long!” Answer: He prayed that I might live long. (ix) She said, “Goodbye friends!” Answer: She bade goodbye to her friends. (x) The students said, “Alas! I wasted my time last year.” Answer: The students regretted that he had wasted his time the previous year.
The Lake Isle of Innisfree (Poem) (21 Item/s)
Rain on the roof (poem) (12 item/s), packing (30 item/s), the fun they had (30 item/s), wind (poem) (18 item/s), course after 12th: visual illustration (design / graphic designing), ncert solutions for class 10 - the shady plot, general science: 600+ most important science facts - part 1, teacher interview questions (sample), questions & answers: u. s. government - elections in the united states.

250+ Top Skills To Find & Keep A Job

500+ Pages of Distilled Wisdom
250+ easy-to-follow guides 5000+ proven tips 13 types of essential skills the world's first & only encyclopedia of self help, self improvement & career advice, welcome to fatskills, join 4 million+ people from around the world who have taken our online quizzes to test & improve their basic knowledge of what they are studying..
❤ If you liked Fatskills , you can support us by checking out Tiny Skills - 250+ Top Work & Persoal Skills Made Easy Our mission is to help improve your scores in any subject and exam using 28500+ online quizzes, practice tests & study guides.
21.5k practice tests / practice exams and online quizzes. 1.85 million+ multiple choice test questions / practice questions 700+ subjects covering all test prep, competitive exams, certification exams, entrance exams, & school / college exams., about | explore | user guide | topics | subjects | career aptitude tests | community | resources | what should we know privacy | terms |, without work one finishes nothing. - ralph waldo emerson © the simple project 2024, all trademarks, logos and brand names are the property of their respective owners. all company, product and service names used in this website are for identification purposes only. use of these names, trademarks and brands does not imply endorsement..
©2024 The Simple Project .
Reported Speech – Rules, Examples
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
They say gossip is a natural part of human life. That’s why language has evolved to develop grammatical rules about the “he said” and “she said” statements. We call them reported speech.
Every time we use reported speech in English, we are talking about something said by someone else in the past. Thinking about it brings me back to high school, when reported speech was the main form of language!
Learn all about the definition, rules, and examples of reported speech as I go over everything. I also included a worksheet at the end of the article so you can test your knowledge of the topic.
What Does Reported Speech Mean?
Reported speech is a term we use when telling someone what another person said. You can do this while speaking or writing.
There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I’ll break each down for you.
A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example:
- Kryz said, “These are all my necklaces.”
Indirect speech changes the original speaker’s words. For example:
- Kryz said those were all her necklaces.
When we tell someone what another individual said, we use reporting verbs like told, asked, convinced, persuaded, and said. We also change the first-person figure in the quotation into the third-person speaker.
Reported Speech Examples
We usually talk about the past every time we use reported speech. That’s because the time of speaking is already done. For example:
- Direct speech: The employer asked me, “Do you have experience with people in the corporate setting?”
Indirect speech: The employer asked me if I had experience with people in the corporate setting.
- Direct speech: “I’m working on my thesis,” I told James.
Indirect speech: I told James that I was working on my thesis.
Reported Speech Structure
A speech report has two parts: the reporting clause and the reported clause. Read the example below:
- Harry said, “You need to help me.”
The reporting clause here is William said. Meanwhile, the reported clause is the 2nd clause, which is I need your help.
What are the 4 Types of Reported Speech?
Aside from direct and indirect, reported speech can also be divided into four. The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative.
Reported Speech Rules
The rules for reported speech can be complex. But with enough practice, you’ll be able to master them all.
Choose Whether to Use That or If
The most common conjunction in reported speech is that. You can say, “My aunt says she’s outside,” or “My aunt says that she’s outside.”
Use if when you’re reporting a yes-no question. For example:
- Direct speech: “Are you coming with us?”
Indirect speech: She asked if she was coming with them.
Verb Tense Changes
Change the reporting verb into its past form if the statement is irrelevant now. Remember that some of these words are irregular verbs, meaning they don’t follow the typical -d or -ed pattern. For example:
- Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken.
Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken.
Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form.
Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting. This verb tense also works if the report is something someone would repeat. For example:
- Slater says they’re opening a restaurant soon.
- Maya says she likes dogs.
This rule proves that the choice of verb tense is not a black-and-white question. The reporter needs to analyze the context of the action.
Move the tense backward when the reporting verb is in the past tense. That means:
- Present simple becomes past simple.
- Present perfect becomes past perfect.
- Present continuous becomes past continuous.
- Past simple becomes past perfect.
- Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous.
Here are some examples:
- The singer has left the building. (present perfect)
He said that the singers had left the building. (past perfect)
- Her sister gave her new shows. (past simple)
- She said that her sister had given her new shoes. (past perfect)
If the original speaker is discussing the future, change the tense of the reporting verb into the past form. There’ll also be a change in the auxiliary verbs.
- Will or shall becomes would.
- Will be becomes would be.
- Will have been becomes would have been.
- Will have becomes would have.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I will be there in a moment.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would be there in a moment.
Do not change the verb tenses in indirect speech when the sentence has a time clause. This rule applies when the introductory verb is in the future, present, and present perfect. Here are other conditions where you must not change the tense:
- If the sentence is a fact or generally true.
- If the sentence’s verb is in the unreal past (using second or third conditional).
- If the original speaker reports something right away.
- Do not change had better, would, used to, could, might, etc.
Changes in Place and Time Reference
Changing the place and time adverb when using indirect speech is essential. For example, now becomes then and today becomes that day. Here are more transformations in adverbs of time and places.
- This – that.
- These – those.
- Now – then.
- Here – there.
- Tomorrow – the next/following day.
- Two weeks ago – two weeks before.
- Yesterday – the day before.
Here are some examples.
- Direct speech: “I am baking cookies now.”
Indirect speech: He said he was baking cookies then.
- Direct speech: “Myra went here yesterday.”
Indirect speech: She said Myra went there the day before.
- Direct speech: “I will go to the market tomorrow.”
Indirect speech: She said she would go to the market the next day.
Using Modals

If the direct speech contains a modal verb, make sure to change them accordingly.
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- Shall becomes should or would.
- Direct speech: “Will you come to the ball with me?”
Indirect speech: He asked if he would come to the ball with me.
- Direct speech: “Gina can inspect the room tomorrow because she’s free.”
Indirect speech: He said Gina could inspect the room the next day because she’s free.
However, sometimes, the modal verb should does not change grammatically. For example:
- Direct speech: “He should go to the park.”
Indirect speech: She said that he should go to the park.
Imperative Sentences
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please . Instead, say request or say. For example:
- “Please don’t interrupt the event,” said the host.
The host requested them not to interrupt the event.
- Jonah told her, “Be careful.”
- Jonah ordered her to be careful.
Reported Questions
When reporting a direct question, I would use verbs like inquire, wonder, ask, etc. Remember that we don’t use a question mark or exclamation mark for reports of questions. Below is an example I made of how to change question forms.
- Incorrect: He asked me where I live?
Correct: He asked me where I live.
Here’s another example. The first sentence uses direct speech in a present simple question form, while the second is the reported speech.
- Where do you live?
She asked me where I live.
Wrapping Up Reported Speech
My guide has shown you an explanation of reported statements in English. Do you have a better grasp on how to use it now?
Reported speech refers to something that someone else said. It contains a subject, reporting verb, and a reported cause.
Don’t forget my rules for using reported speech. Practice the correct verb tense, modal verbs, time expressions, and place references.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
Mathematics
Social Science
Reported Speech - Class 9 English - Chapter 6 - Notes, NCERT Solutions & Extra Questions
Renews every month. Cancel anytime
On this page:
- Questions & Answers
- Line-by-line explanation in Hindi
Reported Speech - Questions and Answers | Grammar | English | Class 9
Reported speech - line by line explanation in hindi | class 9 grammar | english, we've got so much more in store, just for you 🤩.
Sign up to unlock Line-by-line explanation in Hindi and everything else
Quiz - Reported Speech | Class 9 Grammar | English
Your mission, should you choose to accept it.
is to attempt this quiz!
Online Education Reported Speech Exercises for Class 9 CBSE With Answers

This grammar section explains Online Education English Grammar in a clear and simple way. There are example sentences to show how the language is used. You can also visit the most accurate and elaborate NCERT Solutions for Class 9 English . Every question of the textbook has been answered here. https://ncertmcq.com/reported-speech-exercises-for-class-9/
Online Education Reported Speech Exercises for Class 9 CBSE With Answers Pdf
Reported Speech Class 9
Type 1. Statements Steps to be kept in mind for changing direct speech into indirect (statements).
Step 1. The reporting verb is changed as under. (a) We ‘say’ something but we ‘tell’ somebody. Says to …………………………… tells. (b) Says …………………………… says. (c) Said to …………………………… told/asserted/stated/informed. (d) Said …………………………… said.
Step 2. Inverted commas are dropped and the conjunction ‘that’ is used.

Note. These words refer to the speaker. So they change according to who the speaker is.
Reported Speech Class 9 Exercise With Answers
Step 4. If the reporting verb is in the present or future tense, the tense of the reported speech does not change. Meera says to Mini, “Your teacher has praised you.” Meera tells mini that her teacher has praised her.
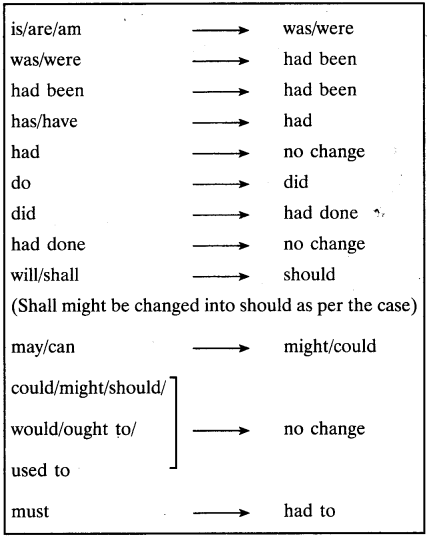
Reported Speech Exercises For Class 9
Step 5. Words denoting nearness of time and place are generally changed into words denoting distance.
| Now | → | then |
| This | → | that |
| These | → | those |
| Here | → | those |
| jo | → | before |
| Yesterday | → | the previous day |
| Tomorrow | → | the next day, the following day |
| Today | → | that day |
| Tonight | → | that night |
Note. There are two situations where even if the reporting verb is in the past tense, the verb of the reported speech remains unchanged.
1. If the reported speech expresses a universal truth or a habitual fact.
- The teacher said, “Two and two make four.” The teacher said that two and two make four.
- Ramesh said to the tourist, “Summers in India are usually very hot.” Ramesh informed the tourist that summers in India are usually very hot.
2. The reported speech describes a situation which still exists when the speech is reported.
- The stationmaster said, “Due to heavy rains, the trains are running late”.
- The stationmaster said that due to heavy rains, the trains are running late.
Reported Speech Worksheet For Class 9 Pdf
Type 2. Questions
A. If the reported speech is a question, the following changes are made. The reporting verb is changed into ‘asked/required’.
| Says | asks A |
| Says to | asks |
| Said | asked |
| Said to | asked |
B. The inverted commas are removed and If/whether is used. The question mark is removed and a full stop is placed. No conjunction is used while reporting wh-questions. The direct form is changed to indirect question form. Place the subject before verb in the reported question.
- I said to Meera, “When are your parents coming?” I asked Meera when her parents were coming.
- Ramesh said to me, “Are you reading this book?” Ramesh asked me if/whether I was reading that book.
- He said, “Will you come with me?” He asked if/whether I would go with him.
Reported Speech Class 9 Exercise
Type 3. Commands and Requests
If reporting commands and requests, the indirect speech is introduced by some verbs expressing commands or requests and the imperative mood is changed into the infinitive.
Step 1. The reporting say (said) is changed to order(ed)/request(ed)/advise(d)/command(ed)/ encourage(ed) /shout(ed)/forbid (forbade), proposed, etc.
Step 2. The verb of the reported speech is changed into an infinitive and inverted commas are removed.
Step 3. Do not is changed to ‘not to’.
- He said to his sister, “Please speak slowly.” He requested his sister to speak slowly.
- The teacher said, “Keep quiet.” The teacher ordered to keep quiet.
- He said to me, “Don’t tease the animal.” He advised me not to tease the animal.
- She said to me, “Let us go for a picnic”. She proposed (or suggested) to me that we should go for a picnic.
Class 9 Reported Speech Exercises
Type 4. Exclamations and wishes Step 1. The reporting verb said is changed to exclaimed, wished, prayed, etc. Step 2. The exclamatory form is changed into the statement form and the mark of exclamation is replaced by a full stop. Step 3. The reporting verb is joined with reported speech with ‘that’. Step 4. All interjections are omitted and suitable adverbs or other expressive words are used.
| What! Oh! | surprised |
| Alas! Ah! | sadness, grief, pity |
| Hurrah! | joy, happiness |
| Bravo! | approval, cheered |
- They said, “Hurrah! We have won the match.” They exclaimed with joy that they had won the match.
- She said, “Alas! He is no more.” A She exclaimed with sorrow that he was no more.
- He said, “Good-bye friends.” He bade good-bye to his friends.
Reported Speech Solved Examples Exercises for Class 9 CBSE
Change the following from direct to indirect speech.
Reported Speech Class 9 Worksheet
Question 1. The doctor said to me, “The climate of this city won’t suit you.” Answer: The doctor told me that the climate of that city wouldn’t suit me.
Question 2. Priya says, “The Earth is round.” Answer: Priya says that the Earth is round.
Question 3. My brother said to his friend, “I am very sleepy.” Answer: My brother told his friend that he was very sleepy.
Question 4. She said, “I have passed the exams.” ‘ Answer: She said that she had passed the exams.
Question 5. My friend said, “Have you ever been to London?” Answer: My friend asked me if I had ever been to London.
Question 6. The policeman said to us, “Where are you going?” Answer: The policeman enquired where we were going.
Question 7. My friend said to me, “Can you solve the problem?” Answer: My friend asked me if/whether I could solve the problem.
Question 8. My mother said to the stranger, “What is the purpose of your coming?” Answer: My mother asked the stranger what was the purpose of his coming.
Question 9. The teacher said to the students, “Complete your work.” [ Answer: The teacher ordered the students to complete their work. ,
Question 10. The Principal said to the parents, “Please sit inside the hall.” | Answer: The Principal requested the parents to sit inside the hall. j
Question 11. Sunil said to his friend, “Don’t forget to recharge your mobile.” i Answer: Sunil reminded his friend not to forget to recharge his mobile.
Question 12. My sister said to me, “Consult a doctor regarding your eyesight.” Answer: My sister advised me to consult a doctor regarding my eyesight. |
Question 13. She said, “May God bless her with a child!” Answer: She said that God might bless her with a child!
Question 14. He said, “What a terrible night it is!” Answer: He exclaimed that it was a terrible night.
Question 15. He said, “Alas! I perish by the people I made. Answer: He confessed with regret that he was perished by the people he had made.
Question 16. He said, “Alas! what a fool I am. Answer: He exclaimed with grief/regret that he was a great fool.
Change the narration of the following sentences from direct to indirect.
Question 17. The saint said, “Go to the Himalayas for meditation.” Answer: The saint ordered to go to the Himalayas for meditation.
Question 18. Sita said to Praveen, “I will return your money tomorrow.” Answer: Sita told Praveen that she would return his money the next day.
Question 19. The news said, “A strong earthquake has hit Japan.” Answer: The news said that a strong earthquake has hit Japan. . ”
Question 20. My uncle said to Sheela, “I have a surprise for you.” Answer: My uncle told Sheela that he had a surprise for her.
Question 21. She said, “Do you want to stay abroad?” Answer: She asked if he wanted to stay abroad.
Question 22. The Met Department announced, “It may rain tomorrow.” Answer: The Met. Department announced that it might rain the next day.
Question 23. I/He said, “How I wish they would come”. Answer: He exclaimed that he wished they would come.
Question 24. Ashu said to his friend, “Are you willing to share your books with me?” Answer: Ashu asked his friend if he was willing to share his books with him.
Question 25. The Major said to the jawans, “Start marching left.” Answer: The major ordered the Jawans to start marching left.
Question 26. Sheetal said to her mother, “Have you ever thought about yourself in life?” Answer: Sheetal asked her mother if she had ever thought about herself in life.
Read the following dialogues and report in indirect narration.
Question 27. Mother : Where were you? Daughter ‘ : I was on the terrace playing. Mother : Please do not go without prior permission. Daughter : This was the first time ever that I went on the terrace. Mother : Remember, do not go there alone. Answer: Mother asked her daughter where she had been. The daughter replied that she had been on the terrace playing. The mother then requested her not to go without prior permission. The daughter apologised saying that that had been the first time ever that she had gone on the terrace. The mother warned her saying not to go there alone.
Question 28. Master : How are you feeling now? Worker : I am feeling batter but I am not completely fine. Master : Do you need more rest? Worker : It is okey. I will report tomorrow. Answer: Master asked his worker how was he feeling then. The worker replied that he was feeling better but was not completely fine. The master further asked him if he needed more rest. The worker replied that that was okey and that he would report the next day.
Question 29. Rajesh : Where are you going, Rohan? Rohan : I am going to the temple to offer flowers. Rajesh : Do you worship everyday and go to the temple? Rohan : Yes, I go to the temple everyday to worship Lord Shiva. Answer: Rajesh asked Rohan where was he going. Rohan replied that he was going to the temple to offer flowers. Rajesh then asked him if he worshipped every day and went to the temple. Rohan replied in the affirmative and said that he went to the temple every day to worship Lord Shivai
Question 30. Teacher : I want all students to quietly do the work. Students : Will you allow us to go for games after this? Teacher : First, all of you have to finish your work. Students : We promise that we will finish our work first. Answer: Teacher instructed the students that she wanted them to quietly do the work. The students asked if she would allow them to go for games after that. The teacher insisted that first, all of them had to finish their work. The students then promised her that they would finish their work first.
Question 31. Father : Why did you go to the market today? Son : I had to buy some material to do my project. Father : Who gave you the project? Son : My science teacher gave the project. Father : Do you need any money for it? Ans. Father asked his son why had he gone to the market that day. Son replied that he had to buy some material to do his project. Father then asked him who had given the project. Son replied that his science teacher had given the project. Father then asked his son if he needed any money for that.
Question 32. Customer : You have a variety of frozen stuff. Shopkeeper : You can buy as much as you like. Customer : Why don’t you keep fresh vegetables? Shopkeeper : Things have become very expensive these days. Customer : You should start keeping good stuff otherwise I shall stop buying from you. Answer: Customer told the shopkeeper that he had a variety of frozen stuff. Shopkeeper replied that he could buy as much as he liked. The customer then asked the shopkeeper why he didn’t keep fresh vegetables. The shopkeeper replied that things had become very expensive those days. The customer warned him that he should start keeping good stuff otherwise, he (customer) would stop buying from him.
Question 33. Doctor : What did you eat yesterday? Patient : I could hardly eat anything as I was having stomachache. Doctor : Are you still having it? Patient : At this moment, I am having fever and feeling weak. Doctor : You most take rest. Answer: Doctor asked the patient what had he eaten the previous day. The patient repled that he could hardly eat anything as he had been having stomachache. Doctor then asked him if he was still having that. The patient replied that at that moment, he was having fever and was feeling weak. The doctor advised him to take rest.
Question 34. Employee : Please grant me two weeks’ leave. Boss : Why do you need it for such a long time? Employee : I have to visit my ailing mother. Boss : Okey, I shall grant you leave but do not overstay your leave. Answer: The employee requested his boss to grant him two weeks’ leave. The boss asked him why he needed leave for such a long time. The employee replied that he had to visit his ailing mother. The boss agreed to grant him leave but instructed him not to overstay his leave.
Question 35. Kanika : Have you seen the animation film released recently? Keshav : I am not allowed to watch films. Kanika : How is this possible in present times? Keshav : My parents are very strict. Answer: Kanika asked Keshav if he had seen the animation film released recently. Keshav replied that he was not allowed to watch films. Kanika further asked how that was possible in present times. Keshav informed that his parents were/are very strict.
Question 36. Hameed : Did you visit the national museum? Shano : How can I as there is nobody to accompany me? Hameed : Do not worry. Shano : I am not worrying but I am the only one who has not seen it. Answer: Hameed asked Shano if she had visited the national museum. Shano replied how she could as there was nobody to accompany her. Hameed told her not to worry. Shano replied taht she was not worrying but she was the only one who had not seen that.
Read the following dialogues and complete the report appropriately.
Question 37. Preeti : Where did you spend your holidays? Naman : I went to many hills stations. ‘ Preeti : Which one did you like the most? Naman : Honestly speaking. I liked all as I am very fond of hills. Preeti asked Naman (a) ………………………….. his holidays. Naman replied, (b) ………………………….. to many hill stations. Preeti then asked him (c) the most. Naman said that honestly speaking (d) ………………………….. of hills. Answer: (a) where he had spent his holidays. (b) that he had gone to many hill stations. (c) which one he had liked. „ (d) he liked all as he was very fond.
Question 38. Archna : Do you know swimming? Rudra : Yes, I do. Archna : Can you teacher me how to swim? Rudra : Yes, I will. Come to my swimming club tomorrow. Archna asked Rudra (a) ………………………….. swimming. Rudra replied in the affirmative. Then, Archna further asked him (b) ………………………….. how to swim. Rudra replied that he (c) ………………………….. he also asked Archna (d) ………………………….. club (e) …………………………. . Answer: (a) if he knew (b) if he could teach her (c) would (d) to go to his swimming (e) the next day.
Question 39. Father : How was the paper? Son : It was easy. I could solve all the problems. Father : Start preparing for the economics paper. You do not have much time left Son : Yes father, I shall immediately start. The father asked his son (a) ………………………….. Son replied that (b) ………………………….. He (c) ………………………….. all the problems. Father further advised him (d) ………………………….. economics paper. He (e) ………………………….. much time left. Son agreed with his father and said that he (f) ………………………….. start. Answer: (a) how the paper had been (b) that had been easy (c) could solve (d) to start preparing for the (e) did not have (f) would immediately
Question 40. Inspector : Were you sleeping when the robbers entered the bank? Guard : No, Sir. The bank had closed and I had just gone to relieve myself. Inspector : What did you see when you came back? Guard : The iron grill lock was broken and the bank looked ransacked but the robbers could not take away anything as I had returned quickly. Inspector : Yes, I can see that not much damage has been done but you have to be more careful in future. Inspector asked the guard (a) ………………………….. entered the bank. Guard replied in the negative and said that the bank had been closed and (b) ………………………….. Inspector further asked him (c) ………………………….. The guard replied that (d) ………………………….. and the bank had looked ransacked, but the robbers (e) ………………………….. as he (f) ………………………….. Inspector said that he (g) ………………………….. but also warned him (h) …………………………. . Answer: (a) if he had been sleeping when the robbers had (b) he had just gone to relieve himself (c) what he had seen when he had come back (d) the iron grill lock had been broken (e) could not take away anything (f) had returned quickly (g) could see that not much damage had been done (h) that he had to be more careful in future.
Question 41. You have learnt how to report questions from direct to indirect speech. Here is a paragraph with direct speech questions. Read them carefully and report into indirect speech. Rewrite the paragraph in the space given below. [NCERT Workbook]
Once an old man asked a young boy, “Who do you think are the most intelligent people?” The young man said in return, “Who do you think so?” The old man said, “How can sons and daughters be intelligent without learning from their parents?” The young man said, “How did you as a parent learn?”
The old man said, “Why are you hijacking my question by asking me back?” The young man said, “Didn’t you know that you as a parent, now have learnt all the things an your own?” The old man said, “How do you say that we all learnt from others?” The young man said, “Why do you ask me about how to operate electronic gadget all the time?” The old man said, “Why can’t I ask you because I have paid for the gadget you use?” Answer: Once an old man asked a young boy who he thought were the most intelligent people. The young man asked why he thought so. The old man further asked how sons and daughters could be intelligent without learning from their parents. The young man asked how he had learnt as a parent. The old man asked why he was hijacking his questions by asking him back.
The young man said if he hadn’t known that he as a parent, then had learnt all the things on his own. The old man said how he learnt that they all learnt from others. The young man said why he asked him how to operate electronic gadget all the time. The old man replied why he couldn’t ask him because he had paid for the gadgets he used.

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Reported Speech: Definition, Rules, Usage with Examples, Tips, Exercises for Students
- Updated on
- Jan 10, 2024

Reported Speech: Reported Speech or also known as indirect speech, is typically used to convey what has been said by someone at a particular point of time. However, owing to the nuances of the systems involved, English grammar may be a complicated language to learn and understand. But once you get hold of the grammar fundamentals , you can be a pro. It’s these fundamentals that will help you create a solid base. The rest of the journey becomes much easier once you get a good grip on the english grammar for competitive exams . So, today, we’re going to talk about one of those basics that is an important part of English grammar, i.e., Reported Speech with multiple definition, usage with examples and numerous practise exercicses.
This Blog Includes:
What is reported speech, definition of reported speech, reported speech rules, rules for modal verbs, rules for pronouns, rules for change in tenses, rules for changing statements into reported speech, rules for changing interrogative sentences into reported speech, rules for changing commands and requests into indirect speech, tips to practise reported speech, fun exercises for reported speech with answers.
When we use the exact words spoken by someone, it is known as Direct Speech or Reported Speech. Reporting speech is a way to effectivley communication something that has been spoken, usually in the past, by the speaker. It is also possible to describe it from the speaker’s perspective from the third person. Since you are only communicating the message and are not repeating the speaker’s exact words, you do not need to use quotation marks while using this type of speaking.
For example: Rita said to Seema, “ I am going to bake a cake ”
Here we are using the exact words spoken by Rita, however, reported or Indirect speech is used when we are reporting something said by someone else but we do not use the exact words. So, we use this form of speech to talk about the past. For example:
Rita told Seema that she was going to bake a cake
In this case, we haven’t used the exact words of Rita but conveyed her message.
Difference Between Reporting Clause and Reported Speech
The words that come before the inverted commas are known as the reporting clause, in the example given above, the reporting clause will be – Rita said to Seema, where ‘said’ is the verb and is known as the reporting clause/verb . The words written within the inverted commas are known as the Reported speech, in the above example, the reported speech is “I am going to bake a cake” .
Also Read: 55+ Phrases with Meaning to Boost Your Vocabulary
Here are some common definitions of reported speech for your reference:
➡️ An Oxford Learner’s Dictionary definition of reported speech is “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.”
➡️ Reporter speech is described as “speech which tells you what someone said but does not use the person’s actual words” by the Collins Dictionary.
➡️ “The act of reporting something that was said, but not using the same words,” according to the Cambridge Dictionary.
➡️ Reported speech is defined as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said” by the Macmillan Dictionary.
Also Read: Adjective: Definition, Usage, Example, Forms, Types
Now let us take a look at the rules for changing direct speech to indirect or reported speech –
➡️ First and foremost, we do not use inverted commas in reported speech which must be clear from the example given above.
➡️ We use conjunctions like ‘if’, and ‘whether’ after the reporting verb in reported speech
➡️ The reporting verb’s tense is never altered.
➡️ The verb of reporting varies according to sense: it can be told, inquired, asked, etc.
For example: Direct : Mohan said to Sohan, “I am going to school” Reported : Mohan told Sohan that he is going to school
Also Read: Useful Idioms for IELTS Exams That Will Boost Your Score
Modal words are used to show a sense of possibility, intent, necessity or ability. Some common examples of verbs can include should, can and must. These words are used to express hypothetical conditions. Check the table of contents below for rules with examples of modal verbs.
| this | that |
| there | those |
| now | then |
| Here | There |
| today | That day |
| tomorrow | The next day |
| yesterday | The previous day |
| last night | The previous night |
| can | Could |
| may | Might |
| shall | Should |
| will | Would |
| ago | Before |
| just | Then |
| come | Go |
Also Read: Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises With Answers for Class 12
Listed below are some common rules followed in pronouns using reported speech:
✏️ We change the first-person pronouns (I, my, us, our, me, we) as per the subject of the reporting verb in the reported speech. ✏️ We change the second-person pronouns (you, your, yourself) as per the object of the reporting verb in the reported speech. ✏️ There is no change in the third-person pronouns.
| I | He, she |
| We | They |
| Me | Him, her |
| Us | Them |
| My | His, her |
| You | He, she, they |
| Our | Their |
| Your | His, her, their |
| Mine | His, hers |
| Ours | Theirs |
| You | Him, her, them |
| Yours | His, hers, theirs |
For example:
Direct : Rita said, “I like the book.” Reported : Rita said that she likes the book.
Direct : Arun said to me, “Do you like to eat cakes?” Reported : Arun asked me if I liked eating cakes.
Direct : Ravi said, “I enjoy fishing.” Reported : Ravi said that he enjoys fishing.
Also Read: Reported Speech Interrogative: Rules, Examples & Exercise
Here are some common ruled used for change in tenses:
✏️ The tense of the reported speech is not changed if the reporting verb is in the present or the future tense. ✏️ If a historical fact, a universal reality or a habitual fact is conveyed in a direct speech. The indirect speech tense will not change. ✏️ If the reporting verb is in the past tense, then it will change the tense of the reported speech as follows:
| Simple Present Sheela said, “I wash clothes.” | Simple Past Sheela said she washed clothes |
| Present Continuous Sheela said, “I am washing clothes.” | Past continuous Sheela said that she was washing clothes. |
| Present Perfect Sheela said, “I have washed clothes.” | Past Perfect Sheela said that she has washed clothes. |
| Simple Past Sheela said, “I washed clothes.” | Past Perfect Sheela said that she has washed clothes. |
| Past Continuous Sheela said, “I was washing clothes.” | Past Perfect Continuous Sheela said she had been washing clothes. |
Direct : Reema says, “I am going out.” Reported : Reema says that she is going out.
Direct : Ramesh said, “Honesty is the best policy.” Reported : Ramesh said that honesty is the best policy.
Direct : Vishnu said that, “India gained independence in 1947.” Reported : Vishnu said that India gained independence in 1947.
Direct : Akshat will say, “I want a slice of cake.” Reported : Akshat will say that he wants a slice of cake.
Direct : Reena said, “I am writing a novel.” Reported : Reena said that she was writing a novel.
Direct : Ayushi said, “I was working on my project.” Reported : Ayushi said that she had been working on her project.
Also Read: Exploring the Types of Reported Speech: A Complete Guide
Here are some common rules for changing statements into reported speech:
✏️ The “said to” reporting verb is changed to “told,” “replied,” “remarked,” ✏️ We do not change the object i.e., the reporting verb is not followed by an object. ✏️ We drop the inverted commas and use a conjunction to join the reporting clause and speech/ ✏️ The laws are followed for the changing of pronouns, tenses, etc.
Direct: Ramu said, “I saw a lion in the forest.” Indirect: Ramu said that he had seen a lion in the forest.
Direct : Satish said to me, “I am very happy here.” Indirect : Satish told me that he was very happy there.
Direct : He said, “I can do this work.” Indirect: He said that he could do that work.
50 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech Interrogative Sentences
Here are some common rules followed for changing interrogative sentences into reported speech:
✏️ The reporting verb “say” is transformed into “ask, inquire,” ✏️ By inserting the subject before the verb, the interrogative clause is converted into a declaration and the full stop is inserted at the end of the sentence. ✏️ The wh-word is repeated in the sentence if the interrogative sentence has a wh-word (who, where, where, how, why, etc). This works as a conjunction. ✏️ If the asking phrase is a yes-no answer style phrase (with auxiliary verbs are, were, were, do, did, have, shall, etc.), then if or whether is used as a conjunction. ✏️ In the reported speech, the auxiliaries do, did, does drop in a positive question. ✏️ The conjunction after the reporting clause is not used.
Direct: I said to him, “Where are you going?” Indirect: Tasked him where he was going.
Direct: He said to me, “Will you go there?” Indirect: He asked me if I would go there.
Direct: My friend said to Deepak, “Have you ever been to Agra?” Indirect: My friend asked Deepak if he had ever been to Agra.
How to Change Sentences into Indirect Speech
The reporting verb is changed into command, order, say, enable, submit, etc. in imperative sentences that have commands.
✏️ By positioning it before the verb, the imperative mood is converted into the infinitive mood. The auxiliary ‘do’ is dropped in the case of negative sentences, and ‘to’ is substituted after ‘not
Direct: She said to me, “Open the window.” Indirect: She ordered me to open the window.
Direct: The captain said to the soldiers, “Attack the enemy.” Indirect: The captain commanded the soldiers to attack the enemy.
Direct: I said to him, “Leave this place at once.” Indirect: I told him to leave that place at once.
Also Read: Direct And Indirect Speech Questions
Indirect speech, sometimes referred to as reported speech, is used to communicate ideas without directly quoting another person. The following advice will help you become proficient in reported speech:
👉 Understand the Basics : Ensure you have a solid understanding of direct speech (quoting exact words) before moving on to reported speech.
👉 Identify Reporting Verbs : Recognize common reporting verbs such as “say,” “tell,” “ask,” “inform,” etc. These verbs are often used to introduce reported speech.
👉 Practice with Various Tenses : Work on reported speech with different tenses (present, past, future) to become comfortable with each.
👉 Use Reporting Words Appropriately : Experiment with different reporting words to convey the speaker’s attitude or emotion accurately. For example, “complain,” “admit,” “suggest.”
👉 Write Dialogues : Create dialogues and convert them into reported speech. This will help you practice both creating and transforming speech.
👉 Use Authentic Materials : Practice reported speech by reading books, articles, or watching videos. Try to convert the direct speech in these materials into reported speech.
Here are a few exercises for reported speech along with answers:
Change the following sentences from direct speech to reported speech.
- Answer: She said that she loved watching movies.
- Answer: He told me not to forget to buy some milk on my way home.
- Answer: Peter said that he would visit his grandparents the following weekend.
- Answer: She announced that she had finished her homework.
- Answer: They exclaimed that they were going to the beach the next day.
Reported Speech Exercises For Class 9
Combine the following sentences into reported speech.
- Answer: Mary said that she was going to the store because she needed some groceries.
- Answer: He remarked that it was raining outside.
- Answer: She explained that she couldn’t attend the meeting because she had a doctor’s appointment.
- Answer: They assured us that they would finish the project by Friday.
- Answer: He admitted that he had never been to Paris.
Transform the sentences into reported speech.
- Answer: She asked why I was late.
- Answer: He requested me to help him with that heavy box.
- Answer: She inquired if I could pass her the salt.
- Answer: The guide told the visitors not to touch the paintings.
- Answer: He said that he must finish that report that day.
Direct And Indirect Speech Questions: Comprehensive Guide with Examples
Reporting speech is the way we present our own or other people’s words. Direct speech and indirect speech are the two primary categories of reported speech. Direct communication restates the speaker’s precise words or their words as we recall them: “I didn’t realize it was midnight,” Barbara remarked.
The speech that is being reported may be declarative, interrogative, exclamatory, or imperative.
Quote marks are not used when putting the speaker’s words or ideas into a sentence in reported speech. Typically, noun clauses are employed. When reading a reported speech, the reader should not assume that the words are exactly what the speaker said; frequently, they are paraphrased.
The reported speech can be Assertive/Declarative, Imperative, Interrogative, and Exclamatory.
We hope that this blog helped you learn about the basics of Reported Speech. Planning for English proficiency exams like IELTS or TOEFL ? Our Leverage Edu experts are here to guide you through your exam preparation with the best guidance, study materials and online classes! Sign up for a free demo with us now!
Vaishnavi has 2+ years of experience in SEO and Content Marketing. She is highly proficient in English, possessing exceptional language skills and a deep understanding of English grammar and communication. Currently working on Ed Tech, Finance, Lifestyle, and other niches. All her works are infused with love for writing!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
i visited this website during my exams so it was really helpful.. my dounts are cleared… Thanks alot to leverageedu.. i will also suggest this website to my frnds..
Thank you Hansini! Your comment just made our day!
I love it, it like the best to me

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2025
September 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
MCQ Questions
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 9 CBSE With Answers

This grammar section explains English Grammar in a clear and simple way. There are example sentences to show how the language is used. You can also visit the most accurate and elaborate NCERT Solutions for Class 9 English . Every question of the textbook has been answered here.
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 9 CBSE With Answers Pdf
Type 1. Statements Steps to be kept in mind for changing direct speech into indirect (statements).
Step 1. The reporting verb is changed as under. (a) We ‘say’ something but we ‘tell’ somebody. Says to …………………………… tells. (b) Says …………………………… says. (c) Said to …………………………… told/asserted/stated/informed. (d) Said …………………………… said.
Step 2. Inverted commas are dropped and the conjunction ‘that’ is used.

Note. These words refer to the speaker. So they change according to who the speaker is.
Step 4. If the reporting verb is in the present or future tense, the tense of the reported speech does not change. Meera says to Mini, “Your teacher has praised you.” Meera tells mini that her teacher has praised her.

Step 5. Words denoting nearness of time and place are generally changed into words denoting distance.
| Now | → | then |
| This | → | that |
| These | → | those |
| Here | → | those |
| jo | → | before |
| Yesterday | → | the previous day |
| Tomorrow | → | the next day, the following day |
| Today | → | that day |
| Tonight | → | that night |
Note. There are two situations where even if the reporting verb is in the past tense, the verb of the reported speech remains unchanged.
1. If the reported speech expresses a universal truth or a habitual fact.
- The teacher said, “Two and two make four.” The teacher said that two and two make four.
- Ramesh said to the tourist, “Summers in India are usually very hot.” Ramesh informed the tourist that summers in India are usually very hot.
2. The reported speech describes a situation which still exists when the speech is reported.
- The stationmaster said, “Due to heavy rains, the trains are running late”.
- The stationmaster said that due to heavy rains, the trains are running late.
Type 2. Questions
A. If the reported speech is a question, the following changes are made. The reporting verb is changed into ‘asked/required’.
| Says | asks A |
| Says to | asks |
| Said | asked |
| Said to | asked |
B. The inverted commas are removed and If/whether is used. The question mark is removed and a full stop is placed. No conjunction is used while reporting wh-questions. The direct form is changed to indirect question form. Place the subject before verb in the reported question.
- I said to Meera, “When are your parents coming?” I asked Meera when her parents were coming.
- Ramesh said to me, “Are you reading this book?” Ramesh asked me if/whether I was reading that book.
- He said, “Will you come with me?” He asked if/whether I would go with him.
Type 3. Commands and Requests
If reporting commands and requests, the indirect speech is introduced by some verbs expressing commands or requests and the imperative mood is changed into the infinitive.
Step 1. The reporting say (said) is changed to order(ed)/request(ed)/advise(d)/command(ed)/ encourage(ed) /shout(ed)/forbid (forbade), proposed, etc.
Step 2. The verb of the reported speech is changed into an infinitive and inverted commas are removed.
Step 3. Do not is changed to ‘not to’.
- He said to his sister, “Please speak slowly.” He requested his sister to speak slowly.
- The teacher said, “Keep quiet.” The teacher ordered to keep quiet.
- He said to me, “Don’t tease the animal.” He advised me not to tease the animal.
- She said to me, “Let us go for a picnic”. She proposed (or suggested) to me that we should go for a picnic.
Type 4. Exclamations and wishes Step 1. The reporting verb said is changed to exclaimed, wished, prayed, etc. Step 2. The exclamatory form is changed into the statement form and the mark of exclamation is replaced by a full stop. Step 3. The reporting verb is joined with reported speech with ‘that’. Step 4. All interjections are omitted and suitable adverbs or other expressive words are used.
| What! Oh! | surprised |
| Alas! Ah! | sadness, grief, pity |
| Hurrah! | joy, happiness |
| Bravo! | approval, cheered |
- They said, “Hurrah! We have won the match.” They exclaimed with joy that they had won the match.
- She said, “Alas! He is no more.” A She exclaimed with sorrow that he was no more.
- He said, “Good-bye friends.” He bade good-bye to his friends.
Reported Speech Solved Examples Exercises for Class 9 CBSE
Change the following from direct to indirect speech.
Question 1. The doctor said to me, “The climate of this city won’t suit you.” Answer: The doctor told me that the climate of that city wouldn’t suit me.
Question 2. Priya says, “The Earth is round.” Answer: Priya says that the Earth is round.
Question 3. My brother said to his friend, “I am very sleepy.” Answer: My brother told his friend that he was very sleepy.
Question 4. She said, “I have passed the exams.” ‘ Answer: She said that she had passed the exams.
Question 5. My friend said, “Have you ever been to London?” Answer: My friend asked me if I had ever been to London.
Question 6. The policeman said to us, “Where are you going?” Answer: The policeman enquired where we were going.
Question 7. My friend said to me, “Can you solve the problem?” Answer: My friend asked me if/whether I could solve the problem.
Question 8. My mother said to the stranger, “What is the purpose of your coming?” Answer: My mother asked the stranger what was the purpose of his coming.
Question 9. The teacher said to the students, “Complete your work.” [ Answer: The teacher ordered the students to complete their work. ,
Question 10. The Principal said to the parents, “Please sit inside the hall.” | Answer: The Principal requested the parents to sit inside the hall. j
Question 11. Sunil said to his friend, “Don’t forget to recharge your mobile.” i Answer: Sunil reminded his friend not to forget to recharge his mobile.
Question 12. My sister said to me, “Consult a doctor regarding your eyesight.” Answer: My sister advised me to consult a doctor regarding my eyesight. |
Question 13. She said, “May God bless her with a child!” Answer: She said that God might bless her with a child!
Question 14. He said, “What a terrible night it is!” Answer: He exclaimed that it was a terrible night.
Question 15. He said, “Alas! I perish by the people I made. Answer: He confessed with regret that he was perished by the people he had made.
Question 16. He said, “Alas! what a fool I am. Answer: He exclaimed with grief/regret that he was a great fool.
Change the narration of the following sentences from direct to indirect.
Question 17. The saint said, “Go to the Himalayas for meditation.” Answer: The saint ordered to go to the Himalayas for meditation.
Question 18. Sita said to Praveen, “I will return your money tomorrow.” Answer: Sita told Praveen that she would return his money the next day.
Question 19. The news said, “A strong earthquake has hit Japan.” Answer: The news said that a strong earthquake has hit Japan. . ”
Question 20. My uncle said to Sheela, “I have a surprise for you.” Answer: My uncle told Sheela that he had a surprise for her.
Question 21. She said, “Do you want to stay abroad?” Answer: She asked if he wanted to stay abroad.
Question 22. The Met Department announced, “It may rain tomorrow.” Answer: The Met. Department announced that it might rain the next day.
Question 23. I/He said, “How I wish they would come”. Answer: He exclaimed that he wished they would come.
Question 24. Ashu said to his friend, “Are you willing to share your books with me?” Answer: Ashu asked his friend if he was willing to share his books with him.
Question 25. The Major said to the jawans, “Start marching left.” Answer: The major ordered the Jawans to start marching left.
Question 26. Sheetal said to her mother, “Have you ever thought about yourself in life?” Answer: Sheetal asked her mother if she had ever thought about herself in life.
Read the following dialogues and report in indirect narration.
Question 27. Mother : Where were you? Daughter ‘ : I was on the terrace playing. Mother : Please do not go without prior permission. Daughter : This was the first time ever that I went on the terrace. Mother : Remember, do not go there alone. Answer: Mother asked her daughter where she had been. The daughter replied that she had been on the terrace playing. The mother then requested her not to go without prior permission. The daughter apologised saying that that had been the first time ever that she had gone on the terrace. The mother warned her saying not to go there alone.
Question 28. Master : How are you feeling now? Worker : I am feeling batter but I am not completely fine. Master : Do you need more rest? Worker : It is okey. I will report tomorrow. Answer: Master asked his worker how was he feeling then. The worker replied that he was feeling better but was not completely fine. The master further asked him if he needed more rest. The worker replied that that was okey and that he would report the next day.
Question 29. Rajesh : Where are you going, Rohan? Rohan : I am going to the temple to offer flowers. Rajesh : Do you worship everyday and go to the temple? Rohan : Yes, I go to the temple everyday to worship Lord Shiva. Answer: Rajesh asked Rohan where was he going. Rohan replied that he was going to the temple to offer flowers. Rajesh then asked him if he worshipped every day and went to the temple. Rohan replied in the affirmative and said that he went to the temple every day to worship Lord Shivai
Question 30. Teacher : I want all students to quietly do the work. Students : Will you allow us to go for games after this? Teacher : First, all of you have to finish your work. Students : We promise that we will finish our work first. Answer: Teacher instructed the students that she wanted them to quietly do the work. The students asked if she would allow them to go for games after that. The teacher insisted that first, all of them had to finish their work. The students then promised her that they would finish their work first.
Question 31. Father : Why did you go to the market today? Son : I had to buy some material to do my project. Father : Who gave you the project? Son : My science teacher gave the project. Father : Do you need any money for it? Ans. Father asked his son why had he gone to the market that day. Son replied that he had to buy some material to do his project. Father then asked him who had given the project. Son replied that his science teacher had given the project. Father then asked his son if he needed any money for that.
Question 32. Customer : You have a variety of frozen stuff. Shopkeeper : You can buy as much as you like. Customer : Why don’t you keep fresh vegetables? Shopkeeper : Things have become very expensive these days. Customer : You should start keeping good stuff otherwise I shall stop buying from you. Answer: Customer told the shopkeeper that he had a variety of frozen stuff. Shopkeeper replied that he could buy as much as he liked. The customer then asked the shopkeeper why he didn’t keep fresh vegetables. The shopkeeper replied that things had become very expensive those days. The customer warned him that he should start keeping good stuff otherwise, he (customer) would stop buying from him.
Question 33. Doctor : What did you eat yesterday? Patient : I could hardly eat anything as I was having stomachache. Doctor : Are you still having it? Patient : At this moment, I am having fever and feeling weak. Doctor : You most take rest. Answer: Doctor asked the patient what had he eaten the previous day. The patient repled that he could hardly eat anything as he had been having stomachache. Doctor then asked him if he was still having that. The patient replied that at that moment, he was having fever and was feeling weak. The doctor advised him to take rest.
Question 34. Employee : Please grant me two weeks’ leave. Boss : Why do you need it for such a long time? Employee : I have to visit my ailing mother. Boss : Okey, I shall grant you leave but do not overstay your leave. Answer: The employee requested his boss to grant him two weeks’ leave. The boss asked him why he needed leave for such a long time. The employee replied that he had to visit his ailing mother. The boss agreed to grant him leave but instructed him not to overstay his leave.
Question 35. Kanika : Have you seen the animation film released recently? Keshav : I am not allowed to watch films. Kanika : How is this possible in present times? Keshav : My parents are very strict. Answer: Kanika asked Keshav if he had seen the animation film released recently. Keshav replied that he was not allowed to watch films. Kanika further asked how that was possible in present times. Keshav informed that his parents were/are very strict.
Question 36. Hameed : Did you visit the national museum? Shano : How can I as there is nobody to accompany me? Hameed : Do not worry. Shano : I am not worrying but I am the only one who has not seen it. Answer: Hameed asked Shano if she had visited the national museum. Shano replied how she could as there was nobody to accompany her. Hameed told her not to worry. Shano replied taht she was not worrying but she was the only one who had not seen that.
Read the following dialogues and complete the report appropriately.
Question 37. Preeti : Where did you spend your holidays? Naman : I went to many hills stations. ‘ Preeti : Which one did you like the most? Naman : Honestly speaking. I liked all as I am very fond of hills. Preeti asked Naman (a) ………………………….. his holidays. Naman replied, (b) ………………………….. to many hill stations. Preeti then asked him (c) the most. Naman said that honestly speaking (d) ………………………….. of hills. Answer: (a) where he had spent his holidays. (b) that he had gone to many hill stations. (c) which one he had liked. „ (d) he liked all as he was very fond.
Question 38. Archna : Do you know swimming? Rudra : Yes, I do. Archna : Can you teacher me how to swim? Rudra : Yes, I will. Come to my swimming club tomorrow. Archna asked Rudra (a) ………………………….. swimming. Rudra replied in the affirmative. Then, Archna further asked him (b) ………………………….. how to swim. Rudra replied that he (c) ………………………….. he also asked Archna (d) ………………………….. club (e) …………………………. . Answer: (a) if he knew (b) if he could teach her (c) would (d) to go to his swimming (e) the next day.
Question 39. Father : How was the paper? Son : It was easy. I could solve all the problems. Father : Start preparing for the economics paper. You do not have much time left Son : Yes father, I shall immediately start. The father asked his son (a) ………………………….. Son replied that (b) ………………………….. He (c) ………………………….. all the problems. Father further advised him (d) ………………………….. economics paper. He (e) ………………………….. much time left. Son agreed with his father and said that he (f) ………………………….. start. Answer: (a) how the paper had been (b) that had been easy (c) could solve (d) to start preparing for the (e) did not have (f) would immediately
Question 40. Inspector : Were you sleeping when the robbers entered the bank? Guard : No, Sir. The bank had closed and I had just gone to relieve myself. Inspector : What did you see when you came back? Guard : The iron grill lock was broken and the bank looked ransacked but the robbers could not take away anything as I had returned quickly. Inspector : Yes, I can see that not much damage has been done but you have to be more careful in future. Inspector asked the guard (a) ………………………….. entered the bank. Guard replied in the negative and said that the bank had been closed and (b) ………………………….. Inspector further asked him (c) ………………………….. The guard replied that (d) ………………………….. and the bank had looked ransacked, but the robbers (e) ………………………….. as he (f) ………………………….. Inspector said that he (g) ………………………….. but also warned him (h) …………………………. . Answer: (a) if he had been sleeping when the robbers had (b) he had just gone to relieve himself (c) what he had seen when he had come back (d) the iron grill lock had been broken (e) could not take away anything (f) had returned quickly (g) could see that not much damage had been done (h) that he had to be more careful in future.
Question 41. You have learnt how to report questions from direct to indirect speech. Here is a paragraph with direct speech questions. Read them carefully and report into indirect speech. Rewrite the paragraph in the space given below. [NCERT Workbook]
Once an old man asked a young boy, “Who do you think are the most intelligent people?” The young man said in return, “Who do you think so?” The old man said, “How can sons and daughters be intelligent without learning from their parents?” The young man said, “How did you as a parent learn?”
The old man said, “Why are you hijacking my question by asking me back?” The young man said, “Didn’t you know that you as a parent, now have learnt all the things an your own?” The old man said, “How do you say that we all learnt from others?” The young man said, “Why do you ask me about how to operate electronic gadget all the time?” The old man said, “Why can’t I ask you because I have paid for the gadget you use?” Answer: Once an old man asked a young boy who he thought were the most intelligent people. The young man asked why he thought so. The old man further asked how sons and daughters could be intelligent without learning from their parents. The young man asked how he had learnt as a parent. The old man asked why he was hijacking his questions by asking him back.
The young man said if he hadn’t known that he as a parent, then had learnt all the things on his own. The old man said how he learnt that they all learnt from others. The young man said why he asked him how to operate electronic gadget all the time. The old man replied why he couldn’t ask him because he had paid for the gadgets he used.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Reported Speech Exercises For Class 9 Reported speech is a grammatical component that is used to communicate what has been said by someone to another person. Knowing for sure how to use the direct and reported speech can be achieved only with continuous practice, just like it is with every other English grammar topic.
Learn what reported speech is, how to use it and when to use it with examples. Find out the rules for changing pronouns, adverbs, tenses and modal verbs in reported speech.
Reported Speech Solved Examples Exercises for Class 9 CBSE. Change the following from direct to indirect speech. Type 1. Question 1. The doctor said to me, "The climate of this city won't suit you." Answer: The doctor told me that the climate of that city wouldn't suit me. Question 2. Priya says, "The Earth is round." Answer:
Reported Speech Rules to Know. Quiz for Reported Speech Exercises for Class 9. Exercise 1: Change Direct Speech to Reported Speech. Exercise 2: Choose the Correct Reported Speech. Exercise 3: Create Reported Speech. Exercise 4: Fill in the Blanks with the Appropriate Reported Speech. Exercise 5: Convert Sentences to Indirect Speech.
CBSE Class 9 English Grammar - Direct And Indirect Speech. Formulae Handbook for Class 9 Maths and Science Educational Loans in India. 1. Direct and Indirect Speech: The words spoken by a person can be reported in two ways—Direct and Indirect. When we quote the exact words spoken by a person, we call it Direct Speech.. Sohan said to Mohan, "I am going to school."
In transforming requests and commands into reported speech, tenses are not relevant. We only have to ensure that there are changes in the pronoun and the place and time expression. Reported Speech Exercises Solved Example for Class 9 CBSE. Diagnostic Test 18. Look at the comic strip and complete the passage given below.
Class 9 English Grammar Reported Speech (Direct and Indirect) Exercise with Answer. Reported Speech - Reported speech refers to recording the speaker's speech, whether it is done directly by recording the speaker's words or indirectly by recording the speaker's words but changing them. For example. Direct speech - Priya said, "I'd ...
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of conveying what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. Instead of using quotation marks, the speaker paraphrases or summarises the original statement.This transformation often involves changes in pronouns, tenses, and time expressions to fit the context of the reporting. . Understanding reported speech is crucial for ...
This English video for Class 9 of the Chapter- Reported Speech and will help you understand the concepts better.The Chapter is taught by Chahat, brought to y...
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called "backshift.". Here are some examples in different verb tenses: "I want to go home.". She said she wanted to go home. "I 'm reading a good book.". She said she was reading a good book. "I ate pasta for dinner last night.".
Whenever you report a speech there's a reporting verb used like "say" or "tell". For example: Direct speech: I love to play football. Reported speech: She said that she loves to play football. (Note 1 : Assume a gender if not mentioned already. Note 2: Using "that" is optional.
Direct speech: 'Help me, please,' she cried. Indirect speech: She begged them to help her. Reported speech worksheet. Sentences are given in the direct speech. Change them into the indirect / reported speech. 1. 'Leave me alone,' she said. 2. 'I don't know what I am supposed to do,' he said. 3.
1. Direct and Indirect Speech: The words spoken by a person can be reported in two ways—Direct and Indirect. When we quote the exact words spoken by a person, we call it Direct Speech. Sohan said to Mohan, "I am going to school.". The exact words spoken by Sohan are put within inverted commas. But when we give the substance of what Sohan ...
Online Test for Reported Speech - English Grammar for Class 9. After completing the Reported Speech it becomes important for students to evaluate themselves how much they have learned from the chapter. Here comes the role of chapter-wise Tests of Reported Speech. EduRev provides you with three to four tests for each chapter.
There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I'll break each down for you. A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example: Kryz said, "These are all my necklaces.". Indirect speech changes the original speaker's words. For example: Kryz said those were all ...
Direct: "I do my exercises every morning.". Reported: He explained that he did his exercises every morning. Direct: "She is going to start a new job.". Reported: He heard she was going to start a new job. Direct: "I can solve this problem.". Reported: She said she could solve that problem.
1. Read the conversation between a young boy and his mother. The boy is determined to go to camp, despite his mother's refusal to let him (from George Layfon's short story "The Holiday"). It wasn't fair. Tony and Barry were going. In fact, nearly all of them in Class Three and Four were going, except me.
Full explanatory video in Hindi and English, detailed summary, quizzes, notes, flashcards, tests, and cheat-sheets of Reported Speech. And the best part? It's free! Courses. Explore Our Courses. Designed to help you understand better, smarter, and faster. ... Reported Speech - Class 9 English - Chapter 6 - Notes, NCERT Solutions & Extra ...
Step 1. The reporting verb said is changed to exclaimed, wished, prayed, etc. Step 2. The exclamatory form is changed into the statement form and the mark of exclamation is replaced by a full stop. Step 3. The reporting verb is joined with reported speech with 'that'.
The words written within the inverted commas are known as the Reported speech, in the above example, the reported speech is "I am going to bake a cake ... Reported Speech Exercises For Class 9. Exercise 2. Combine the following sentences into reported speech. Mary said, "I am going to the store. I need some groceries."
Step into the world of reported speech with our dedicated quiz designed for Class 9 students! This quiz is expertly crafted to assess your proficiency in converting direct speech into indirect or reported speech, a crucial aspect of English grammar. Reported speech allows you to convey messages spoken by yourself or others, often in the past tense. Whether you're a passionate grammar ...
Reported Speech Solved Examples Exercises for Class 9 CBSE. Change the following from direct to indirect speech. Type 1. Question 1. The doctor said to me, "The climate of this city won't suit you." Answer: The doctor told me that the climate of that city wouldn't suit me. Question 2. Priya says, "The Earth is round." Answer: