ENGLISH WITH ALEX
Language you can use
- Feb 17, 2023

Present Perfect Conversation Questions (100+ questions)
Updated: Nov 28, 2023

Watch the video related to this resource , and do the quiz to test your understanding.
This page is intended to be a resource for English learners and teachers . You can practice answering these present perfect discussion questions by yourself or with a partner. You can also write the answers in a notebook, in a digital document, or in the comments section below. To help learners feel more confident and to develop grammatical accuracy, the warm-up questions have some suggested answer beginnings, which make them ideal for beginners. For more challenging questions, move on to the "Let's go!" section.
Recommended levels: intermediate for "Warm-up" questions; mix of intermediate and advanced levels for majority of "Let's go!" questions.
Use a variety of tenses in your answers in addition to the present perfect. It is quite common to expand present perfect answers with the past simple. For example, "Have you ever swum in the ocean?" "Yes, I have. I swam in the Atlantic when I visited my brother last year."
How long have you studied English?
I've studied English for/since...
Have you ever met a famous person?
Yes, I have. / Yes, I have met a famous person. I met _____.
No, I haven't. / No, I've never met a famous person.
How many countries have you visited in your life? Which ones?
I've visited _____ countries in my life. / I haven't traveled outside of [the name of your country].
How much water have you drunk today?
Today, I've drunk _____ bottles/glasses/cups/liters/gallons of water.
Who is the nicest person you have ever met?
_____ is/was the nicest person I've ever met.
How have you been lately?
Lately, I've been...[great. / really good. / well. / tired. / busy. / unmotivated. / etc.]
Whom have you talked to today?
Today, I've talked to...
Have you ever swum in the ocean?
Yes, I have. / Yes, I've swum in the ocean.
No, I haven't. / No, I've never swum in the ocean.
Who has helped you a lot in your life?
_____ has/have helped me a lot in my life.
What have you done this week?
This week, I've...
What is one of the most important things you have learned in your life?
One of the most important things I have learned in my life is to/(that)...
Let's go!
How many times have you checked your phone today?
How many questions have you answered so far?
Has this week been good or bad for you?
Has anything or anyone made you laugh or smile today?
What's the strangest food you've ever eaten?
What's the farthest you've ever been from your home?
Which countries have been in the news lately?
Have you called anyone this week?
What's the biggest wedding you've ever been to?
How long have you known your closest/best friend?
How much exercise have you gotten today?
Has anything (or anyone) inspired or motivated you this week?
Have you tried anything new lately?
Which instruments have you tried playing in your life?
How much time have you spent on social media this week?
How much money have you spent this week?
Have you ever...?
You can ask about people's life experiences by asking them questions with "Have you ever...?" You can also just use "Have you...?", but adding "ever" puts emphasis on your entire life experience. You can answer with "Yes, I have" or "No, I haven't." You can also give a specific past example. For instance: "Have you ever ridden a horse?" "Yes, I have. I rode one when I was a teenager."
Have you ever ridden a horse?
Have you ever jumped out of an airplane?
Have you ever had a pet?
Have you ever been on a rollercoaster?
Have you ever traveled by train?
Have you ever seen a Marvel movie?
Have you ever written a story?
Have you ever tried to help someone but it didn't go the way you planned?
Have you ever bought a new car or a new house?
Have you ever broken up with someone?
Have you ever lived with a roommate?
Have you ever taken private English classes?
Have you ever thought about moving to another country?
Have you ever wondered if humans are truly alone in the universe?
Have you ever had to go to a hospital emergency room?
Have you ever asked for help but no one helped you?
Have you ever been mad at yourself for doing something wrong?
Have you ever been to a concert?
Have you ever been to a live sporting event (a soccer game, a basketball game, etc.)?
Have you ever been in a fight?
Have you ever been to the casino?
Have you ever returned something you bought because it was defective in some way?
Have you ever kissed an animal?
Have you ever been stopped by the police for speeding?
Have you ever been in a play? (A play is a live theatre performance.)
Have you ever gone camping?
Have you ever wished you were someone (or somewhere) else?
Have you heard of...?
One of the most common "Have you ever...?" or "Have you...?" questions is "Have you (ever) heard of...?" This question is asking if you are familiar with someone or something. Sometimes, we give more information after the question is asked, as in the examples below. You can answer the questions with "Yes, I have," or "No, I haven't." Expand on your answer if you have heard of the subjects below.
Have you heard of the artist named Banksy? He does a lot of stuff with graffiti.
Have you heard of Margaret Atwood? She's a Canadian writer.
Have you heard of Metallica? They're a heavy metal band.
Have you heard of BLACKPINK? They're a Korean pop group.
Have you heard of Tina Fey? She's an American actress.
Have you heard of Angel Falls? It's a waterfall in Venezuela.
Have you heard of Dennis Bergkamp? He's a retired Dutch football player.
Have you heard of The Little Prince ? It's a famous children's book written by a French author.
Using the present perfect with unfinished time
You can use the present perfect to talk about unfinished time. For example, someone can say, "What have you done today?" if "today" still isn't finished. You can answer by saying, "Today, I've answered a bunch of emails, I've had breakfast, lunch, and dinner, and I've gone to the gym."
Have you eaten today?
What have you done today?
How many messages have you received today?
Where have you gone to this week?
What is something you've done this week that you're proud of?
"I'm proud that I've..."
Who(m) have you talked to today?
How many times have you gone to the bathroom today?
Present perfect with superlative adjectives
Present perfect questions with superlative adjectives are another common way to ask about people's life experiences.
What's the biggest city you have ever been to?
Who's the nicest person you have ever met?
What's the most expensive restaurant you've ever eaten at?
What's the coldest temperature you've ever experienced?
What's the hottest temperature you've ever experienced?
What's the most beautiful place you've ever been to?
What's the longest you've ever been sick?
What's the best book you've ever read?
What's the longest book you've ever read?
Who's the most creative person you know?
What's the longest you have ever slept?
The present perfect at work or school
Here are some common questions you might hear at work or at school. Imagine yourself in these situations and answer the questions as naturally as you can.
Have you seen [someone's name] today?
Have you had time to look at the attachment I sent you?
What have you been up to today? (This means "What have you been doing today?", which is a present perfect continuous question. The present perfect question "What have you been up to?" is typically answered with the present perfect continuous: "I've been + verb+ing")
I haven't seen you all day! Where have you been?
Have you sent that email we talked about?
Have you started your homework?
Have you finished your assignment? / Have you finished your work?
Have you prepared for your presentation? / Have you prepared for the meeting?
Have you had lunch yet?
Have you checked your email yet?
Oh no! What have you done?!
Why haven't you responded to my messages?
Why have you decided to quit? / Why have you decided to drop out of school?
How has your week been so far? Have things been busy?
Why have you ignored me this week? (This question is more commonly asked in the present perfect continuous: "Why have you been ignoring me?")
Finish the sentences
I've always wanted to...
I have decided to...
I've never seen...
I've never been to...
Have you had time to...?
They haven't talked to each other since...
We haven't seen each other in...(6 months / 1 year, etc.)
Have you finished...?
She has prepared for...
Have you told anyone about...?
I've never met...
Want to learn and practice 21 of the most common present perfect questions? Watch this video lesson and do the practice quiz when you're done !
That's it! That wasn't so bad, was it? If you enjoyed this resource and you want to support my work--and if you want to continue improving your English vocabulary and speaking skills--pick up a copy of my book, 300 Practical English Words and Phrases . Thank you and good luck with your studies!
Recent Posts
Affect vs. Effect: What's the Difference? (Audio Lesson Included)
Third Conditional Discussion Questions (100+ Questions for English Conversation Practice)
"Because" vs. "Because of": The Difference in Usage (Includes Common Sentences and Audio Lesson)
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Present Perfect Tense | Examples & Use
Present Perfect Tense | Examples & Use
Published on April 4, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on September 25, 2023.
The present perfect tense is a verb form used to refer to a past action or situation that has a present consequence. It’s typically used to indicate experience up to the present, recent actions, or a change that occurred over a period of time.
The present perfect is formed using the auxiliary verb “have” and the past participle of the main verb (e.g., “I have eaten”). However, the third person singular (e.g., “he,” “she,” and “it”) uses “has” instead of “have.”
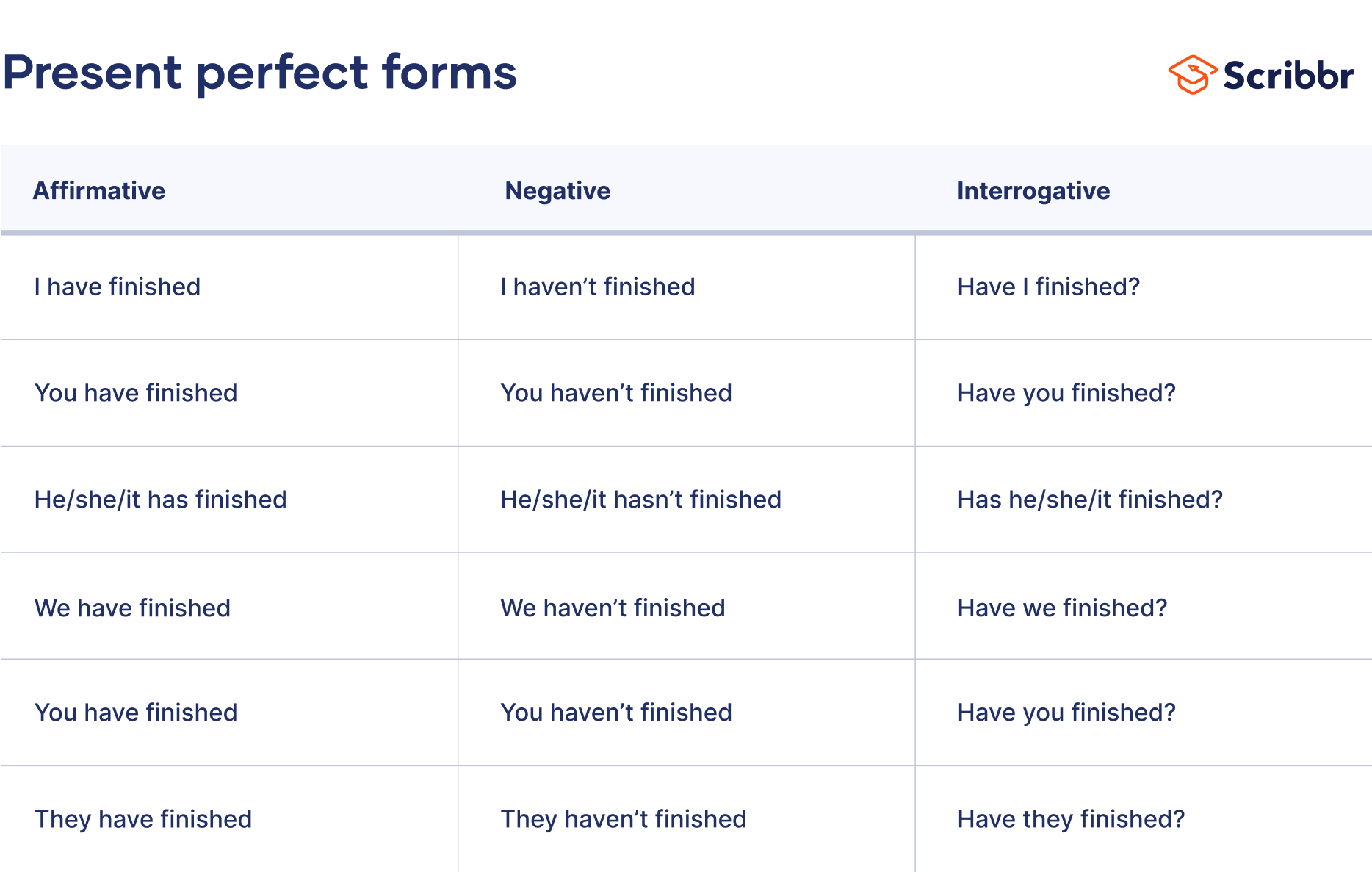
Table of contents
How to use the present perfect, past simple vs. present perfect, present perfect vs. present perfect continuous, how to form negatives, how to form questions, how to form the passive voice, other interesting language articles, frequently asked questions about the present perfect tense.
The present perfect is used to refer to a completed past action that’s relevant to the present or to an action that began in the past and may continue in the present.
It’s used to talk about experience up to now , a change that occurred over time , recent actions (often used with “just”), and unfinished action that is expected to be completed (in the negative, often with “yet”).
The present perfect is formed using the auxiliary verb “have” along with the past participle of the main verb. The only exception is the third person singular form (“he,” “she,” “it,” and singular nouns), which uses “has” instead of “have.”
In affirmative present perfect statements, the subject and auxiliary verb are often contracted (e.g., “ I’ve dreamed”).
The theater group has improved .
Sashi has just brushed his teeth.
The present perfect can also be used along with future simple tense constructions to describe a future action. In these instances, the present perfect clause is usually preceded by a subordinating conjunction (e.g., “when,” “until”).
After Anna has presented the report, we’ll take a short break . Note When the present perfect occurs more than once in a sentence and refers to the same subject, the second verb can be written without the auxiliary verb “have.” If the second instance refers to a different subject, a conjugated form of the auxiliary verb should be included.
- I’ve cleaned the kitchen and cooked dinner.
- Jennifer has left , and Henry has arrived .
Indicating time
As the present perfect refers to an action that occurred at an unspecified time in the past, sentences in the present perfect commonly use adverbs that refer to non-specific time (e.g., “ever,” “never,” “once,” and “so far”).
Expressions that refer to a specific time (e.g., “last week,” “yesterday”) are typically used along with a preposition (e.g., “for,” “since”).
- I’ve worked on this project yesterday .
- I’ve worked on this project since yesterday .
- Sophie has felt ill last week .
- Sophie has felt ill for the last week .
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
Both the present perfect and past simple refer to past action. However, they have different functions:
- The past simple is typically used to refer to an action that occurred at a definite time in the past and will not continue.
- The present perfect is used to refer to an action that occurred in the past and has present consequences or to an action that began in the past and may continue.
I have seen that film before. [I may see it again.]
I went to Toronto last year.
Both the present perfect and the present perfect continuous can be used to refer to the present consequences of a past action or situation (e.g., “I have lived here for two years” and “I have been living here for two years”).
However, they cannot always be used interchangeably:
- The present perfect can be used to refer to a past action or situation that may continue in the present.
- The present perfect continuous refers to actions or situations that began in the past and are definitely continuing in the present.
Aria has been traveling the world. [She is still traveling.] Note Stative verbs (e.g., “know,” “feel,” “want”) can be used in the present perfect to describe states of being that began in the past.
These verbs are typically not used in the present perfect continuous .
- I have been knowing him for years.
- I have known him for years.
Negatives are formed by adding the adverb “not” between the subject and the main verb . This is the case for all subjects.
To ask a yes–no question in the present perfect, put the auxiliary verb first, followed by the subject and the past participle of the main verb.
To ask a question using a wh-word (an interrogative pronoun like “what” or an interrogative adverb like “when”), place the pronoun or adverb before “have” (or “has” for the third person singular).
What have we done?
In a passive sentence, the subject is acted upon (rather than performing the action). In the present perfect, the passive voice is formed by adding the past participle of the verb “be” (i.e., “been”) between the auxiliary verb and the past participle of the main verb .
The thieves have been followed by the police.
If you want to know more about nouns , pronouns , verbs , and other parts of speech , make sure to check out some of our other language articles with explanations and examples.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Possessive nouns
- Indefinite pronouns
- Relative pronouns
- Interrogative pronouns
- Simple present
- Modal verbs
- Conditional sentences
- Subjunctive mood
- Imperative mood
- Interjections
- Determiners
- Prepositions
The present perfect tense and the present perfect continuous can both be used to refer to the present consequences of a past action or situation:
- The present perfect can be used to refer to a past action that may continue in the present (e.g., “I have lived here for six months”).
- The present perfect continuous refers to actions or situations that began in the past and are definitely continuing in the present (e.g., “I have been arguing with him constantly”).
- The past simple is typically used to refer to an action that was completed at a definite time in the past (e.g., “I slept in this morning”).
- The present perfect is used to refer to a past action that has present consequences or to an action that began in the past and may continue (e.g., “I have written a book”).
Sources in this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
Ryan, E. (2023, September 25). Present Perfect Tense | Examples & Use. Scribbr. Retrieved September 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/verbs/present-perfect/
Aarts, B. (2011). Oxford modern English grammar . Oxford University Press.
Butterfield, J. (Ed.). (2015). Fowler’s dictionary of modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Garner, B. A. (2022). Garner’s modern English usage (5th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, simple present tense | examples, use & worksheet, the subjunctive mood | definition & examples, verb tenses in academic writing | rules, differences & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

- Start Learning
- Free Resources
- Manage Subscriptions
- Classroom Login
Present Perfect: Learn How to Use Correctly
- LLS English
- September 4, 2024
- One Comment
Present Perfect: Usually Simple, But Can Be Tricky
The English language has a variety of different grammar rules, and one that is often confusing for non-native speakers is the use of the Present Perfect. What does it mean? Why do people use it? And when should you use it? To help you get a better grasp, here are some helpful guidelines that will make things much simpler.
What is the Present Perfect?
The present perfect is a verb tense which is used to show that an action has been completed at the present time. The present perfect is made up of two parts: the present tense of the verb “to have” (I have, you have, he/she/it has) and the past participle of the main verb (written as -ed for regular verbs or irregular verbs with regular past participles, and -en for irregular verbs with irregular past participles).

The present perfect can be used in two ways: to describe an action which has just been completed, or to describe an action which began in the past and is still continuing.
Here are some examples of the present perfect being used to describe an action which has just been completed:
- I have finished my essay.
- You have cleaned your room.
- He has taken out the trash.
- We have made dinner.
Notice that in each of these examples, the present perfect verb tense is made up of the present tense form of “to have” plus the past participle form of the main verb. This tense is used to describe actions which have just been completed.
Now let’s look at some examples of the present perfect being used to describe an action which began in the past and is still continuing:
- I have lived in New York for five years.
- You have worked at that company for six months.
- The has known him since they were children.
Basic Uses of the Present Perfect
The present perfect is a verb tense which is used to show that an action has been completed at the present time. The present perfect is made up of two parts: the present tense of the verb “to have” (I have, you have, we have, they have) and the past participle of the main verb (run, written, spoken). The present perfect can be used in a number of different ways, but some of the most common uses are outlined below.
1. To describe an experience: I’ve climbed Mount Everest. 2. To describe a change that has taken place: She’s grown so much! 3. To talk about something that happened in the past but is relevant to the present: We’ve moved house. 4. To describe an action which started in the past and continues in the present: I’ve worked here for five years. 5. To talk about repeated actions: I’ve been to France three times this year.

Simple Past vs. Present Perfect
The present perfect tense is used to describe an event that happened at some point in the past, but its effects are still relevant in the present. For example, you might say “I have read that book” to describe a past event with current consequences. The simple past tense, on the other hand, is used to describe a past event without any connection to the present. So, you would use the simple past tense to say “I read that book yesterday.”
When choosing between the two tenses, it’s important to consider whether or not the event is still affecting your life in some way. If it is, then you should use the present perfect tense. If not, then the simple past tense will suffice.
When to Use the Present Perfect
The present perfect tense is used to talk about actions or states that began in the past and continue into the present.
It can also be used to describe past actions that are connected to the present in some way.
Here are some examples of when to use the present perfect:
I’ve read two books this week.
This sentence describes an action that began in the past (reading) and continues into the present (I have two books left to read).
I’ve known her for years.
This sentence describes a state that began in the past (knowing) and continues into the present (we’re still friends). The state could also be described as “being friends for years.”
We’ve been trying to sell our house for months.
This sentence describes an action that began in the past (trying to sell) and continues into the present (we haven’t sold it yet).
The Difference Between
The present perfect tense is formed by using the present tense of the verb “have” plus the past participle of the main verb. The past participle is usually formed by adding “-ed” to the base form of regular verbs, as in “walked,” “talked,” or “decided.” For irregular verbs, the past participle is often a different word from the base form, as in “written,” “spoken,” or “gone.”
The present perfect tense is used to describe actions that have recently been completed or that started in the past and continue into the present. It can also be used to describe experiences that happened at an unspecified time in the past.

The main difference between the present perfect and other tenses is that the present perfect always includes some connection to now. This connection can be explicit, as when we say something like “I have finished my homework,” or it can be implicit, as when we say something like “We have been friends for years.”
Why Learn Laugh Speak is the only full-digital, CEFR-aligned application.
Find the right course for you! Whether you’re an absolute beginner or an advanced student, we have a variety of different courses to help you accomplish your goals.
You can take your English proficiency to the next level in 33,000 hours of full digital learning. This includes all of the grammar you need to learn. Furthermore, it will fully prepare you for the Common European Framework of Reference level A1-C2.
Throughout the duration of your studying, there are some practices that can help you maximize your score on the exam. One of those is through practice. Using our specially curated materials, you’ll be sure to always go over questions that are similar to what you’ll find on the real exam. The more time you spend preparing with these types of questions, the more at ease you’ll feel when it comes time for the test. With 33,000 lessons designed to teach students how to ace their exams and 280,000 native audio recordings, now’s never been a better time than now to take your test prep to the next level.
Learn Laugh Speak provides a convenient and inexpensive way to learn the English language without the time commitment of individual lessons. With our help, you’ll be able to reach your goals and gain knowledge in the language.
Get started in minutes, not days. You can work at your own pace–from anywhere that has Internet. By using your mobile device or computer you can study on the go or when it’s convenient for you.
Talk to us today to help you improve your English level!
Thank you for Reading!
This was written by me. Bryce Purnell, founder of Learn Laugh Speak.
Check out more on my Medium or send me an email if you’re ever curious about anything at all
CLICK HERE

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Sign me up for the newsletter!
LEARN LAUGH LIBRARY
Username or email address *
Password *
Remember me Log in
Lost your password?
What Is the Present Perfect Tense?
The present perfect tense is an English verb tense used for past actions that are related to or continue into the present. It’s easily recognized by the auxiliary verbs (or helper verbs) have and has , as in, “I have gone fishing since I was a child.”
Of all the English verb tenses, the present perfect is one of the most complicated because there’s not always a direct translation in other languages. So in this guide, we explain everything you need to know to use it perfectly, including how and when to use it, with plenty of present perfect tense examples. Give your writing extra polish Grammarly helps you communicate confidently Write with Grammarly
What is present perfect tense?
The present perfect tense is one of the common verb tenses in English, used to show an action that happened in the past that is directly related to the present, such as actions that are still continuing or that indicate a change over time. We cover a complete list of when to use the present perfect tense below.
Don’t let the name confuse you—even though the word present is there, the present perfect tense deals with actions that happened or started in the past. In fact, the present perfect tense is often used interchangeably with the simple past tense, although there are some special situations in which you can only use one or the other, also explained below.
How do you use the present perfect tense?
In the present perfect tense, the main verbs always use the auxiliary verbs (helper verbs) has or have . The main verb takes a participle form, specifically the past participle . The past participle is often the same form as the simple past form of the verb, unless it’s an irregular verb , which each have their own unique past participle form. We explain in more detail how to form them in our guide to participles .
Only the auxiliary verbs are conjugated to fit the subject-verb agreement in the present perfect tense; the past participle of the main verb remains the same no matter what the subject is. Generally, you use have for all subjects except the singular third-person, which instead uses has .
First-person : I have come a long way.
Second person : You have come a long way.
Third-person plural : They have come a long way.
Third-person singular : He/she/it has come a long way.
The present perfect tense has specific constructions for standard statements, negatives, and questions, explained below. We also discuss how to use the present perfect tense with adverbs and with the passive voice.
The present perfect tense for statements
For general statements, the most common use of the present perfect, use have or has plus the past participle form of the main verb.
[ have / has ] + [past participle]
Charlotte has become friends with Wilbur.
We’ ve broken up before, but this time feels different.
The present perfect tense for negatives
To use the present perfect tense in the negative, simply add the negative word (like not or never ) after the auxiliary verb but before the past participle.
[ have / has ] + [negative] + [past participle]
I have not slept well since exams started.
My Midwestern friend has never seen the ocean.
This construction works for neither, nor sentences, too.
It’s 11 in the morning, and she has neither eaten breakfast nor gotten dressed.
Please note that it’s clearest to avoid subject contractions when using the present perfect tense with the negative , at least in American English.
I’ve not seen the Eiffel Tower.
I have not seen the Eiffel Tower.
The present perfect tense for questions
When asking a question in the present perfect tense, the auxiliary verb comes first, followed by the subject, and then the past participle of the main verb. This follows a similar construction as questions with the auxiliary verb do , which also comes before the subject.
[ have / has ] + [subject] + [past participle]
Have you eaten dinner yet?
Has the party started ?
How to use the present perfect tense with adverbs
Although you can still use adverbs after the verb (as you do normally), with the present perfect tense you can also place the adverb between the auxiliary verb and the past participle.
[ have / has ] + [adverb] + [past participle]
They have gradually advanced their career from cashier to senior manager.
All the guests have already arrived .
Be careful, though. Certain adverbs—especially yet and just —have special rules for where they’re placed. Moreover, because these adverbs relate to time, they’re often used together with the present perfect tense.
The adverb yet , used often with a negative or in questions, almost always comes at the end of a sentence or clause.
Sadly, he hasn’t finished the race yet .
Have you finished your homework yet ?
Conversely, the adverb just is always placed between the auxiliary verb and the past participle.
I’ ve just woken up .
Their plane has just landed .
How to use the present perfect tense in the passive voice
When discussing writing, we often talk about the active vs. passive voice . Although we recommend using the active voice as much as possible, sometimes the passive voice is unavoidable.
To use the present perfect tense in the passive voice, use been (the past participle of the verb be ) before the past participle of the main verb.
[ have / has ] + [ been ] + [past participle]
She has been given an award.
You have just been handed a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity.
How to use the present perfect continuous tense
You can also combine the present perfect tense with the present continuous tense to show an ongoing action that started in the past and continues to the present. This hybrid tense is called the present perfect continuous tense . The construction is similar to using the present perfect tense in the passive voice, except that the main verb uses the present participle instead of the past participle.
[ have / has ] + [ been ] + [present participle]
She has been seeing a physical therapist since her surgery.
It has been raining all day.
Like all continuous tenses, the present perfect continuous tense can not be used with stative verbs like want, need, love, or hate.
Here’s a tip: You don’t have to guess whether you’re using certain words correctly or breaking grammar rules in your writing. Just copy and paste your writing to check your grammar and get instant feedback on grammar, spelling, punctuation, and other mistakes you might have missed.
6 examples of when to use the present perfect tense
Knowing when to use the present perfect tense is an important part of English grammar, but it can be confusing even for primary English speakers. Below, we explain the six main uses of the present perfect tense, including examples.
1 An ongoing action that started in the past, but has not yet been completed
This is the main usage of the present perfect tense, which demonstrates the relationship between an action started in the past and its effects on the present.
The professor has taught here for two decades.
They have played piano since the age of three.
Note that you can also use the present perfect continuous tense for this situation, as long as the action has not been completed yet (and it’s not a stative verb). The difference between the present perfect tense and the present perfect continuous tense, in this case, is emphasis:
- The present perfect tense emphasizes the effects or consequences of the action.
- The present perfect continuous tense emphasizes the action itself or the length of time.
So, for example, if you want to plainly say where you live, use the normal present perfect tense.
I’ ve lived in Lagos my whole life.
If you want to emphasize how long you’ve been living in a place, use the present perfect continuous tense.
I’ ve been living in Lagos my whole life.
What about an action started in the past that has already been completed? For that, you can use the simple past.
She worked there for five years but was fired last week.
2 A series of the same action completed multiple times in the past, likely to happen again in the future
When the same action has happened a few times already, you can use the present perfect tense if the action will likely happen again in the future. If the action probably won’t happen again, you can use the simple past tense.
I’ ve seen the movie six times! [probably will see it again]
I saw the movie six times! [probably will not see it again]
3 An action that was completed very recently (often used with just or now )
If an action was only completed very recently, you can describe it with the present perfect tense. Even though the action happened in the past, it was so recent that it’s directly connected to the present. These cases usually use adverbs like just or now to show that the action happened not long ago.
I shouldn’t eat anymore because I’ ve just brushed my teeth.
We’ ve finished practice now, so let’s go home.
4 A change over time
The present perfect tense is often used to emphasize a change that happened over an extended period of time.
My cousin has grown so much since I saw her two years ago.
Thanks to the many months of playing, I have become an expert at Wordle.
5 An uncompleted action that is expected to be finished (in the negative)
If an action started in the past but was not completed, you can describe it with the present perfect tense if it’s likely to be completed in the future. This situation uses the negative form to show that the action is still unfinished and often uses the adverb yet .
The jury has not reached a verdict yet.
I haven’t finished my paper, but it’s due in an hour!
6 To add significance to a completed action
Last, you can use the present perfect tense to make any past action sound more important. The present perfect tense is often used with great achievements or accomplishments, as well as dramatic or rare events. This makes it appropriate for newsworthy events or major life experiences.
Macbeth has killed the king.
I’ ve met the love of my life!
When not to use the present perfect tense
Now that you know when to use the present perfect tense, let’s talk about when to avoid it.
A lot of times, the difference between the present perfect tense and the simple past tense is a matter of emphasis or whether or not the action is truly finished. However, there’s one rule in particular that should be mentioned: Do not use the present perfect tense with a specific time .
I have gone for a walk on Tuesday.
I went for a walk on Tuesday.
This might be confusing, however, because you can use the present perfect tense with a broad time period. The present perfect tense is only incorrect if used with one specific time. Using the present perfect tense with a general time range is perfectly acceptable.
I have gone for a walk every Tuesday this year.
Present perfect tense FAQs
What is the present perfect tense.
The present perfect tense is an English verb tense used to describe a past action that is related to the present.
How does the present perfect tense work?
The present perfect tense uses the auxiliary verb has or have and the past participle form of the main verb. For example, if you want to use go in the present perfect tense, you say, “I have gone.”
When is the present perfect used?
The present perfect tense is commonly used with events that started in the past and continue into the present. However, it has a few other uses too, including events that happened very recently in the past.














![present perfect tense essay topics #318: Collocations with Situation | Advanced Vocabulary [+ Free Worksheet]](https://www.speakconfidentenglish.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Collocations-with-Situation-400x250.webp)



































IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Present Tense Writing Prompts. The present tense, in these cases, includes the simple present ("She always forgets something") and the present continuous ("I am coming"), as well as the trickier present perfect ("We have seen The Matrix far too many times") and present perfect continuous ("She has been singing since her second glass of wine"). However, it is of course possible to split the ...
Present Perfect Conversation Questions (100+ questions) Updated: Nov 28, 2023. Watch the video related to this resource, and do the quiz to test your understanding. This page is intended to be a resource for English learners and teachers. You can practice answering these present perfect discussion questions by yourself or with a partner.
Choose past tense or present perfect tense for the verbs in parentheses. More than one answer may be correct, so be prepared to explain why you chose the form you did. The first one has been done for you. Bambang Soetomo (1) (come) to the United States last January to get a degree in mechanical engineering. Since he (2) (be) in the United ...
As the present perfect refers to an action that occurred at an unspecified time in the past, sentences in the present perfect commonly use adverbs that refer to non-specific time (e.g., "ever," "never," "once," and "so far"). Examples: Present perfect and adverbs. Joseph has never lived in South Africa. Laura has eaten at this ...
I have finished my essay. You have cleaned your room. He has taken out the trash. We have made dinner. ... The present perfect tense is formed by using the present tense of the verb "have" plus the past participle of the main verb. The past participle is usually formed by adding "-ed" to the base form of regular verbs, as in "walked ...
The present perfect tense is an English verb tense used for past actions that are related to or continue into the present. It's easily recognized by the auxiliary verbs (or helper verbs) have and has, as in, "I have gone fishing since I was a child.". Of all the English verb tenses, the present perfect is one of the most complicated ...
The present perfect can give a starting time or an amount of time only if you use the words since and for.When using these words, the sentence usually means that the action is continuing.If you do not use since or for, the sentence means the action is finished, and it may or may not continue in the future.Take a look at these examples:
Ask your students to share two or three things they have done that they are most proud of, and have them do it in front of the class. Allow the rest of the class to ask questions of each classmate after the presentation. Encourage your students to use the adverb 'already' in their presentations. 2.
The Present Perfect Tense is used to describe actions that have happened at an unspecified time before now. It connects the past with the present. Common uses include: Experiences: "She has visited Paris.". Changes over time: "He has grown taller.". Incomplete actions: "They have not finished their homework.". Keywords.
The Form of the Present Perfect Simple Tense. The structure of the Present Perfect Simple is quite straightforward. It consists of "have" (in the simple present) followed by the past participle form of the verb: Have (in the simple present) + Verb (in the past participle form) Positive. Negative. Interrogative.
Present Perfect with for/since. The present perfect is also used with for and since to talk about actions that began in the past and continue to the present. • "I've lived here since 2004.". • "I've lived here for 8 years.". Since is used with a point in time, and means "from that point in time until the present.".
The present perfect tense is an English verb tense used to describe an action that began in the past (despite being a present tense). For example: John has taken Sarah's advice. They have fixed the fence. The present perfect tense is formed liked this: [subject] +. "has" or "have". +.
Movie Worksheet: "Back To The Future" (Present Perfect) This is a great movie and I'm sure every student will enjoy it. If you have the time, have them watch the first half the movie (this activity begins at about 00:11:00 int... 1766 uses. A selection of English ESL present perfect tenses printables with creative writing prompt, writing practice.
Creative Writing: The Most Exciting Thing I've Ever Done #6 A2 Level. Let's do English ESL creative writing prompt. Another activity for the A2 My Writings booklet. This time practice with the present perfect and the past simple.….
In general, we form the present perfect with the following positive structure: Subject + have/has + past participle. In its negative form, the structure is: Subject + have/has + not + past participle. Ex. "I have been to the museum.". Ex. "Margot hasn't watched the movie.". Ex. "Nikita has worked at this bank.". Ex.
ESL Worksheets and Activities for Kids: Teach kids? We've got a resource that's going to help save you some prep time. Lot's of great worksheets and activities to keep your students engaged and learning. Available on Amazon (paperback) or Gumroad (PDF)! These discussion questions are great for practicing the present perfect or to just ask ...
How To Teach The Present Perfect Tense Step 1: The Two Main Uses. To begin the lesson, explain to students that there are two main uses of the present perfect tense; to talk about finished past actions, and to talk about an action that started in the past and continued to the present.Write these two uses as headings on the board and draw a simple timeline below each heading.
Writing Prompt: The present perfect continuous tense is used to talk about an action from the past that has recently stopped or is still continuing. As with other perfect tenses, the words for and since are often used to indicate time. Review the structure and uses of the present perfect continuous tense.Then demonstrate your understanding by writing a script for a short interview between two ...
The main objectives of this lesson with Present Perfect activities are to: differentiate the use of Present Perfect and Past Simple. This lesson contains standalone activities where students can create sentences using Present Perfect with already, just and yet. They associate descriptions with pieces of news using the tense, ask and answer ...
ESL Present Perfect Worksheet - Grammar Exercises: Gap-fill, Categorising, Writing Sentences - Speaking Activity: Asking and Answering Questions, Giving Information - Pair Work - Intermediate (B1) - 35 minutes. In this productive present perfect worksheet, students revise the various uses of the present perfect tense and related vocabulary.
The general formula of the present perfect tense is as described below: Subject + have/has + past participle + the rest of the sentence. The structure of the present perfect tense can be analysed with reference to positive, negative, interrogative and negative interrogative types of sentences. Have a look at the table given below for a closer ...
The present perfect tense is a tense used in present to indicate the action that has taken place at some specific time. It uses auxiliary verb and past participle for the main verb i.e. verb + ed. Some examples of present perfect tense are - I have watched this movie before, He has completed his homework. You will mostly use the present perfect in daily conversation while talking about some ...
Browse Topics: Grammar Topics General Topics. 217 Present perfect writing English ESL worksheets pdf & doc. SORT BY. Most popular. TIME PERIOD. All-time. meva. Present perfect simp-short grammar revie. 6146 uses. ... Present tenses exerc. Exercises with prese. 397 uses. morewk. Simple Past vs. Pres.
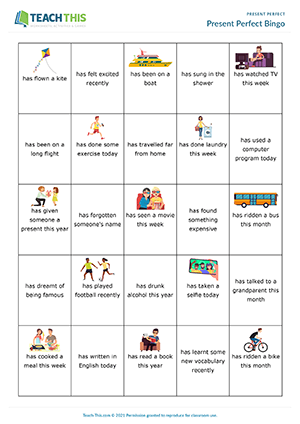
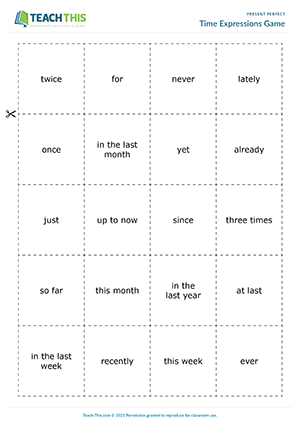
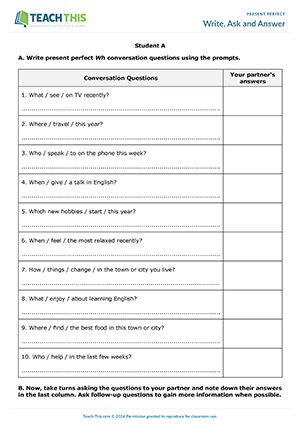
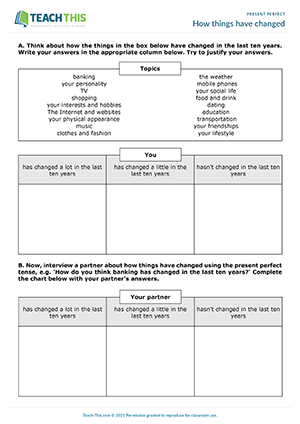
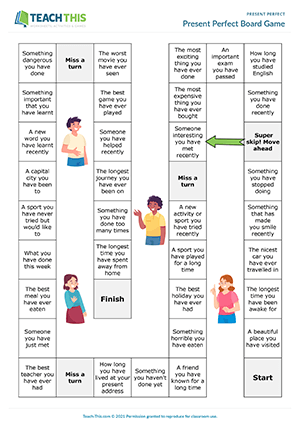
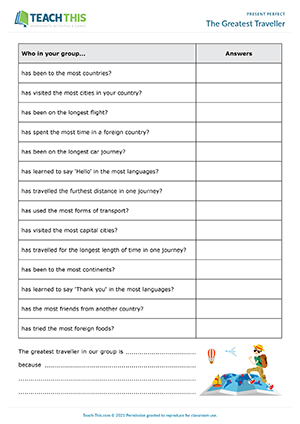
This ready to use TEFL resource includes everything from flash cards to activities as well as conversation topics and writing drills. Designed to boost language proficiency, this engaging lesson plan covers the fundamental concepts and practical exercises related to using the present perfect tense to talk about past experiences and actions with ...