MAC address assignment lookup
Why mac:vendor.
While there are a number of other MAC address lookup websites where one can lookup their MAC address most of them (at least the ones I looked at) have two major drawbacks; 1st most look only at MA-L list from IEEE for lookups, which means not all MAC addresses can be identified and 2nd lookup by vendor is not possible. Our website tries to overcome these limitations.

What is a MAC address?
A media access control address (MAC address) is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface controller (NIC) for use as a network address in communications within a network segment. This use is common in most IEEE 802 networking technologies, including Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. Within the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) network model, MAC addresses are used in the medium access control protocol sublayer of the data link layer. As typically represented, MAC addresses are recognizable as six groups of two hexadecimal digits, separated by hyphens, colons, or without a separator. MAC addresses are primarily assigned by device manufacturers, and are therefore often referred to as the burned-in address, or as an Ethernet hardware address, hardware address, or physical address. Each address can be stored in hardware, such as the card's read-only memory, or by a firmware mechanism. Many network interfaces, however, support changing their MAC address. The address typically includes a manufacturer's organizationally unique identifier (OUI). MAC addresses are formed according to the principles of two numbering spaces based on Extended Unique Identifiers (EUI) managed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): EUI-48, which replaces the obsolete term MAC-48, and EUI-64. Network nodes with multiple network interfaces, such as routers and multilayer switches, must have a unique MAC address for each NIC in the same network. However, two NICs connected to two different networks can share the same MAC address. * source: wikipedia
Notational conventions
The standard (IEEE 802) format for printing EUI-48 addresses in human-friendly form is six groups of two hexadecimal digits, separated by hyphens (-) (e.g. 01-23-45-67-89-AB). Other conventions include six groups of two hexadecimal digits separated by colons (:) (e.g. 01:23:45:67:89:AB), and three groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by dots (.) (e.g. 0123.4567.89AB). * source: wikipedia
Source lists
Source of data is IEEE registry which is responsible for MAC address assignments and upkeeping of the registry. MA-L list consists of legacy and LARGE assignments, a large assignment is a 24bit assignment where first three bytes are assigned from IEEE and the last three bytes are to be assigned by the vendor (i.e. 11:22:33:xx:xx:xx). MA-M list consists of MEDIUM assignments, a medium assignment is a 28bit assignment where first three and a half bytes are assigned from IEEE and the last two and a half bytes are to be assigned by the vendor (i.e. 11:22:33:4x:xx:xx). MA-S list constsis of SMALL assignments, a small assignment is a 36bit assignment where first four and a half bytes are assigned from IEEE and the last byte and a half are to be assgined by the vendor (i.e. 11:22:33:44:5x:xx). More information in IEEE SA - Registration Authority page.
IANA OUI Ethernet Numbers
Registries included below
IANA Unicast 48-bit MAC Addresses
Iana multicast 48-bit mac addresses, iana 64-bit mac addresses, the cfxxxx series, snap protocol numbers, iana link layer discovery protocol (lldp) tlv subtypes, iana mac address block.
| Range | Registration Procedures |
|---|---|
| Small to medium assignments of up to 65536 identifiers | Expert Review |
| Large assignments of 131072 or more identifiers | IESG Ratification, as defined in [ ], Section 5.1 |
| Assignment(s) in the 00-00-00 to 00-00-FF range | IESG Ratification, as defined in [ ], Section 5.1 |
| Addresses | Usage | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 00-00-00 to 00-00-FF | Reserved | [ ] |
| 00-01-00 to 00-01-FF | VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) | [ ] |
| 00-02-00 to 00-02-FF | VRRP IPv6 (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol IPv6) | [ ] |
| 00-03-00 to 00-51-FF | Unassigned | |
| 00-52-00 | PacketPWEthA | [ ] |
| 00-52-01 | PacketPWEthB | [ ] |
| 00-52-02 | BFD for VXLAN | [ ] |
| 00-52-03 to 00-52-12 | Unassigned (small allocations) | |
| 00-52-13 | Proxy Mobile IPv6 | [ ] |
| 00-52-14 to 00-52-FF | Unassigned (small allocations) | |
| 00-53-00 to 00-53-FF | Documentation | [ ] |
| 00-54-00 to 90-00-FF | Unassigned | |
| 90-01-00 | TRILL OAM | [ ] |
| 90-01-01 to 90-01-FF | Unassigned (small allocations requiring both unicast and multicast) | |
| 90-02-00 to FF-FF-FF | Unassigned |
| Range | Registration Procedures |
|---|---|
| Small to medium assignments of up to 65536 identifiers | Expert Review |
| Large assignments of 131072 or more identifiers | IESG Ratification, as defined in [ ], Section 5.1 |
| Addresses | Usage | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 00-00-00 to 7F-FF-FF | IPv4 Multicast | [ ] |
| 80-00-00 to 8F-FF-FF | MPLS Multicast | [ ] |
| 90-00-00 | MPLS-TP p2p | [ ] |
| 90-00-01 | Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) on Link Aggregation Group (LAG) Interfaces | [ ] |
| 90-00-02 | AllL1MI-ISs | [ ] |
| 90-00-03 | AllL2MI-ISs | [ ] |
| 90-00-04 to 90-00-FF | Unassigned (small allocations) | |
| 90-01-00 | TRILL OAM | [ ] |
| 90-01-01 to 90-01-FF | Unassigned (small allocations requiring both unicast and multicast) | |
| 90-02-00 to 90-0F-FF | Unassigned | |
| 90-10-00 to 90-10-FF | Documentation | [ ] |
| 90-11-00 to FF-FF-FF | Unassigned |
| Range | Registration Procedures |
|---|---|
| Small to medium assignments of up to 268435456 identifiers | Expert Review |
| Assignments of any size, including blocks of 536870912 or more | IESG Ratification, as defined in [ ], Section 5.1 |
| Assignments from Reserved ranges | IESG Ratification, as defined in [ ], Section 5.1 |
| Addresses | Usage | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 00-00-00-00-00 to 0F-FF-FF-FF-FF | Reserved | [ ] |
| 10-00-00-00-00 to 10-00-00-00-FF | Documentation | [ ] |
| 10-00-00-01-00 to EF-FF-FF-FF-FF | Unassigned | |
| FD-00-00-00-00 to FD-FF-FF-FF-FF | Reserved | [ ] |
| FE-00-00-00-00 to FE-FF-FF-FF-FF | IPv4 Addr Holders | [ ] |
| FF-00-00-00-00 to FF-FD-FF-FF-FF | Reserved | [ ] |
| FF-FE-00-00-00 to FF-FE-FF-FF-FF | IANA EUI-48 Holders | [ ] |
| FF-FF-00-00-00 to FF-FF-FF-FF-FF | Reserved | [ ] |
| Value | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| No registrations at this time. | ||
| Protocol Number (decimal) | Protocol Number (hex) | Description | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0000 | 0000 | reserved | [ ] |
| 0001 | 0001 | MARS Data Messages (short form) | [ ] |
| 0002 | 0002 | reserved for future NHRP use | [ ] |
| 0003 | 0003 | MARS/NHRP Control Messages | [ ][ ] |
| 0004 | 0004 | MARS Data Messages (long form) | [ ] |
| 0005 | 0005 | SCSP - Server Cache Sync Protocol | [ ] |
| 0006 | 0006 | VRID - Virtual Router MAC Address | [ ] |
| 0007 | 0007 | L2TP | [ ] |
| 0008 | 0008 | Virtual Private Network ID | [ ] |
| 0009-0065 | 0009-0041 | Unassigned | |
| 0066 | 0042 | Documentation Use | [ ] |
| 0067-65534 | 0043-FFFE | Unassigned | |
| 65535 | FFFF | Reserved | [ ] |
| Value | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Reserved | [ ] |
| 1 | the Manufacturer Usage Description (MUD) Uniform Resource Locator (URL) | [ ] |
| 2-41 | Unassigned | |
| 42 | Example for use in documentation | [ ] |
| 43-254 | Unassigned | |
| 255 | Reserved | [ ] |
Contact Information
| ID | Name | Contact URI | Last Updated |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. Knight | 1997-11 |
MAC Address Lookup
Find the vendor name of a device by entering an OUI or a MAC address
Search for manufacturer by MAC address
Just input the MAC address or the OUI and you will be shown the name, address, and country of its vendor.
In addition, we provide information on the history of MAC prefixes, including any changes to vendor names or addresses.
| Last update: | 18 September 2024 |
|---|---|
| MAC address: | 52652 |
| Download |
| MA-L | 36166 |
|---|---|
| MA-M | 5511 |
| MA-S | 6175 |
| CID | 187 |
| IAB | 4578 |
An MA-L (MAC Address Block Large) assignment includes an OUI and large blocks of EUI-48 and EUI-64 values which can be used as MAC Addresses, Bluetooth Device Addresses, Ethernet Addresses or object identifiers.
An MA-M (MAC Address Block Medium) assignment includes medium blocks of EUI-48 and EUI-64 values which can be used as MAC Addresses, Bluetooth Device Addresses, Ethernet Addresses or object identifiers.
An MA-S (MAC Address Block Small) assignment includes an OUI-36 and small blocks of EUI-48 and EUI-64 values which can be used as MAC Addresses, Bluetooth Device Addresses, Ethernet Addresses or object identifiers.
A unique 24-bit identifier that cannot be used to generate EUI-48 or EUI-64 values. Therefore, the CID (Company ID) is especially applicable in applications where unique MAC addresses are not required.
IAB, Individual Address Block, is an inactive registry activity, which has been replaced by the MA-S registry product as of January 1,2014. The owner of an already assigned IAB may continue to use the assignment until its exhaustion.
IEEE Registration Authority: Assignments

MAC address vendor/manufacturer lookup tool
Mac address, general info.
A media access control address is a unique 48-bit identifier assigned to a network interface controller. It is used on data link layer (layer 2 of OSI model) of computer networking as a network address. MAC addresses are assigned by device manufacturers and usually includes manufacturer's 24-bit OUI (Organizationally Unique Identifier). Now they refers as EUI-48 identifiers.
Address details
48-bit address MAC address starts with 24-bit OUI, 28-bit OUI-28/MA-M or 36-bit OUI-36/MA-S identification numbers. IEEE 802 standard format for printing Extended Unique Identifiers (EUI-48) is six groups of two hexadecimal digits separated by hyphens.
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
Location: piscataway, new jersey, united states of america.
IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. IEEE Registration Authority deals with assigning unique identifiers to manufacturers. Obtaining registered identifiers is payable and cost depends on below block size:
- MAC Address Block Large (MA-L)
- MAC Address Block Medium (MA-M)
- MAC Address Block Small (MA-S)
Trivia Facts
Here are some interesting trivia facts about mac address lookup, vendor identification.
MAC address lookup can reveal the manufacturer or vendor of a network interface card (NIC) based on its MAC address. The first six characters of a MAC address, known as the OUI (Organizationally Unique Identifier), are assigned to specific manufacturers by the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers).
MAC addresses are intended to be globally unique identifiers for network interfaces. However, in practice, there have been instances of MAC address collisions, where two network interfaces have the same MAC address. Such occurrences are rare but can potentially cause network connectivity issues.
Permanent vs. Changeable
MAC addresses are typically hardcoded into network interface hardware and are considered permanent. However, some network interfaces, particularly in consumer devices like smartphones and laptops, allow users to change their MAC addresses through software settings. This process is known as MAC address spoofing.
Layer 2 Addressing
MAC addresses are used at the Data Link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model for addressing devices within the same local network segment. They are crucial for facilitating communication between devices on the same network, such as Ethernet LANs.
ARP Protocol
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is used in IPv4 networks to map IP addresses to MAC addresses. When a device needs to communicate with another device on the same network, it uses ARP to determine the MAC address corresponding to the destination IP address.
MAC Address Filtering
MAC address lookup is often used in network security for MAC address filtering. Network administrators can configure routers and switches to only allow specific MAC addresses to access the network, thereby enhancing security by restricting access to authorized devices.
MAC Address Privacy Concerns
While MAC addresses are essential for network communication, they can also raise privacy concerns. Persistent tracking of MAC addresses in public Wi-Fi networks or other contexts can be used for surveillance or targeted advertising purposes, leading to debates around user privacy and data protection.
These trivia bits provide insights into the role, characteristics, and implications of MAC address lookup in networking and security contexts. Fascinating, isn’t it?

OUI Lookup Tool
The Wireshark OUI lookup tool provides an easy way to look up OUIs and other MAC address prefixes. It uses the Wireshark manufacturer database , which is a list of OUIs and MAC addresses compiled from a number of sources.
Directions : Type or paste in a list of OUIs, MAC addresses, or descriptions below. OUIs and MAC addresses may be colon-, hyphen-, or period-separated.
Examples : 0000.0c 08:00:20 00-00-0C-CC-CC-CC 00d9.d110.21f9 missouri
Support open source packet analysis.
The non-profit Wireshark Foundation supports the development of Wireshark, a free, open-source tool used by millions around the world.
- Save Early: Amazon Prime Big Deal Days!
- Use This Hack for Big Deal Days
MAC Addresses With Formatting Examples
MAC addresses identify networks, not a device's location
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- University of Illinois
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/headshot-00415ba557444a8a9b6bb139498b97c5.jpg)
- MAC Address Formats
64-Bit MAC Addresses
- MAC vs. IP Addresses
MAC Address Cloning
The Media Access Control (MAC) address is a binary number used to identify computer network adapters . These numbers (sometimes called hardware addresses or physical addresses) are embedded in the network hardware during the manufacturing process or stored in firmware and designed not to be modified.
MAC addresses are also referred to as Ethernet addresses for historical reasons, but multiple types of networks use MAC addressing, including Ethernet , Wi-Fi , and Bluetooth .
The Format of a MAC Address
Traditional MAC addresses are 12-digit (6 bytes or 48 bits ) hexadecimal numbers . By convention, these addresses are usually written in one of the following three formats, although there are variations:
- MM:MM:MM:SS:SS:SS
- MM-MM-MM-SS-SS-SS
- MMM.MMM.SSS.SSS
The leftmost six digits (24 bits), called a prefix, are associated with the adapter manufacturer (M). Each vendor registers and obtains MAC prefixes as assigned by the IEEE . Vendors often possess many prefix numbers associated with their products. For example, the prefixes 00:13:10, 00:25:9C, and 68:7F:74 (plus others) belong to Linksys (Cisco Systems).
The rightmost digits of a MAC address represent an identification number for the specific device (S). Among all devices manufactured with the same vendor prefix, each is given a unique 24-bit number. Hardware from different vendors may share the same device portion of the address.
While traditional MAC addresses are 48 bits in length, a few types of networks require 64-bit addresses instead. Zigbee wireless home automation and other similar networks based on IEEE 802.15.4, for example, require 64-bit MAC addresses to be configured on their hardware devices.
TCP/IP networks based on IPv6 also implement a different approach to communicating MAC addresses compared to mainstream IPv4. Instead of 64-bit hardware addresses, IPv6 automatically translates a 48-bit MAC address to a 64-bit address by inserting a fixed (hardcoded) 16-bit value FFFE between the vendor prefix and the device identifier. IPv6 calls these numbers identifiers to distinguish them from true 64-bit hardware addresses.
For example, a 48-bit MAC address of 00:25:96:12:34:56 appears on an IPv6 network in either of these two forms:
- 00:25:96:FF:FE:12:34:56
- 0025:96FF:FE12:3456
MAC vs. IP Address Relationship
TCP/IP networks use both MAC addresses and IP addresses but for different purposes. A MAC address remains fixed to the device's hardware, while the IP address for that same device can be changed depending on its TCP/IP network configuration. Media Access Control operates at Layer 2 of the OSI model , while Internet Protocol operates at Layer 3 . This allows MAC addressing to support other kinds of networks besides TCP/IP.
IP networks manage the conversion between IP and MAC addresses using Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) relies on ARP to manage the unique assignment of IP addresses to devices.
Some internet service providers link each of their residential customer accounts to the MAC addresses of the home network router or another gateway device. The address seen by the provider doesn't change until the customer replaces their gateway, such as by installing a new router. When a residential gateway is changed, the internet provider sees a different MAC address being reported and blocks that network from going online.
A cloning process solves this problem by enabling the router (gateway) to keep reporting the old MAC address to the provider even though its hardware address is different. Administrators can configure their router (assuming it supports this feature, as many do) to use the cloning option and enter the MAC address of the old gateway in the configuration screen. When cloning isn't available, the customer must contact the service provider to register their new gateway device.
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
- What Is a SIP Address?
- Is It Possible to Trace a MAC Address?
- The Layers of the OSI Model Illustrated
- What Is a Static IP Address?
- IPv4 vs. IPv6: What's the Difference?
- MAC Address Filtering: What It Is and How It Works
- How to Use an IP Address to Find a MAC Address
- DNS Servers: What Are They and Why Are They Used?
- How to Block any IP Address
- The Best Router Settings for Home Networks
- How to Look up an IP Address Owner
- OSI Model Reference Guide
- Computer Networking Tutorial - Internet Protocol
- How to Disable DHCP
- How to Connect a Mac to a Router
- How Do Bits, Bytes, Megabytes, Megabits, and Gigabits Differ?
10 Best MAC Address Lookup Tools for Every Need

For IT professionals and network admins, MAC address lookup tools are a powerful resource that can provide crucial information about connected devices to a network.
Using these tools, professionals can identify the device manufacturers and types and the other details of MAC addresses. As a result, their management efficiency and troubleshooting capability improve to a great extent.
Here, we will discuss the MAC address tools that will help you streamline network performance and improve security measures. And if you aren’t sure what MAC address is, just scroll down where I’ve given a gist with a bonus on the importance of MAC address lookup and how these tools can assist with network performance optimization.
MAC Address Lookup Tools
Mac address lookup.
Finding out the device manufacturer or device name is super-easy with the MAC Address Lookup tool. It can display vendor name, location, and MAC details from your entered OUI or a MAC address.

This comprehensive tool provides information like OUI, vendor name, address, assignment type, and initial registration date. The Details tab contains the address range, block size, UAA, transmission type, and Wireshark information.
Its database, with 48K+ MAC address prefixes, gets updated as soon as there is an update on the IEEE directory and Wireshark manufacturer database. Therefore, each search result offers you the most accurate manufacturer data with a guarantee.
This tool also has a free and public Rest API. It can handle a large volume of requests and address them at low latency.
AllDataFeeds.com
AllDataFeeds.com has a MAC address vendor lookup tool that you can use for free. Enter your MAC address in any of the standard formats, and it will fetch vendor, block, and MAC address details.

Some of the crucial parameters displayed by this tool are OUI number, company name, company address, private vendor, MAC address validity, transmission type, administration type, block size, block range, block registration status, and assignment block size.
MACVendorLookup.com
Network admins looking for a platform to know vendors, locations, and other information from a MAC address should use MACVendorLookup.com. This online tool helps you get data about the company name, address, address range for the vendor, and type.

Even if you do not know how to find your MAC address, you can use its Windows, Mac, and Linux guide. It also has a REST API that you can implement in any application you are developing.
DNSCHECKER provides you with the necessary information about the MAC address of your PC or any other device. You can use this for two different purposes. First, you can enter a MAC Address or OUI to know about its manufacturer. Or, you may enter a vendor name to find out the ranges and details of its MAC address.

The vendor data generated by this tool are address prefix, company name, company address, start address range, and end address range. Each of the information can be separately copied in one click.
It also fetches your IP address and displays it automatically in the top right corner. This platform also comes with a guide on how to locate the MAC address of your device.
WhatsMyIP.org
WhatsMyIP.org facilitates MAC address or OUI lookup solutions through this online platform. It lets you access the MAC address vendor database using a complete MAC Address, an OUI vendor prefix, or a vendor/manufacturer name.

When you enter the MAC address, the site will immediately show you the vendor name and the address prefix. By entering the vendor name, you can get the list of address prefixes along with the associated full vendor name.
Miniwebtool
You can also use Miniwebtool as the platform to find out about the vendor or manufacturer. All you have to do is enter the full MAC address or the first 6 digits of the hexadecimal address.

For the vendor lookup, it supports the common formats such as 34-C9-3D-4F-03-7B, 34:C9:3D:4F:03:7B, 34 C9 3D 4F 03 7B, or 34C93D4F037B. This tool uses the MAC address database from IEEE, so you can stay rest assured of the authenticity and accuracy of the results you get.
Miniwebtool also offers a list of MAC address prefixes depending on the vendors. For that, you need to enter the full or partial manufacturer, for example, apple or Apple Computer, Inc. Also, the results generated on this platform can be downloaded in PDF or JPG file formats.
MACVendors.com
Do you want to find MAC address vendor name instantly? MACVendors.com is here to serve you. It fetches the vendor list of 16,500 registered vendors directly from the IEEE Standards Association, which is updated multiple times a day.

This platform is devoid of any unnecessary overhead and returns you with the vendor name after you send it an HTTP GET/POST request along with the MAC address. It also comes with an API that you can use in your system.
Currently, the API gets 3.6 billion requests every year. The optimized and high-performance servers of this platform can seamlessly handle even 100,000 requests made by your application. However, If you are going to make less than 1,000 requests/day, you do not need to get the API key necessary or register on this platform.
Dan’s Tools
Another simplistic online tool for MAC address lookup is Dan’s Tools.

Here, users can either check MAC address vendor name or enter the vendor name to find out about the MAC address OUIs.
Udger is a useful resource that lets you find out about MAC address vendor information. The list of MAC address vendors used by this platform is provided by the IEEE Standards Association. The data is updated daily, so you can be assured of getting the latest and most accurate data.

Udger allows you to enter the MAC address and hit the Search button. Within a few seconds, it will generate all the vital information related to the vendor, such as vendor name, vendor code, addresses, country, and country code.
HWaddress is a minimal website for the MAC address lookup. This clutter-free platform does not distract you with loads of information or links. Instead, it only contains an empty field where you need to enter or paste the MAC address or the manufacturer name. After clicking the Search button, it displays the company name, OUI, and the MAC range.

This website also tells you how to write this MAC address in different styles like Unix, Unix zero-padded, no delimiters, etc. Moreover, after you access the interface, it will automatically show your public IP address.
If you are uncertain about the importance of MAC address lookup tools or how you can use them to solve network related issues, that’s what we will be looking at next. But first, for newbies, let’s explore what a MAC address is!
What is MAC Address?

The acronym of the MAC address is the Media Access Control address. It is a unique identifier usually embedded in the network adapter of a device during manufacturing. A MAC address contains 12 digits and is a 48-bit number. It consists of six groups of two hexadecimal digits. The groups are separated by colons or hyphens.
Computers, smartphones, routers, network switches, and every other network-enabled device have a unique MAC address. It plays a crucial role in various network operations, like device identification, security, troubleshooting, and monitoring.
Importance of MAC Address Lookup in Network Management
MAC address lookup is essential in the entire process of network management. It facilitates network monitoring, asset management, device identification, and network segmentation. Here is what network admins can do utilizing the MAC lookup feature:

#1. Device Identification
MAC address is the unique identifier attached to network interface controllers (NICs). By looking up the address, network admins can identify and distinguish devices on their network, which is important for tracking devices and managing inventory.
#2. Enhanced Network Security

It also helps to maintain a list of permitted devices and block unauthorized ones. It is also necessary for tasks like MAC address filtering, a security practice that allows devices with specific MAC addresses to connect to a network. Thus, admins can add an extra security layer to the network.
#3. Network Monitoring
MAC address lookup feature is also essential to monitor network traffic and analyze how the data flow works. Using MAC addresses, admins can identify the source and destination of network packets, get an idea about traffic patterns, and gain insights into network usage.
#4. Troubleshooting
To resolve any network issue, instant identification of the source is the key. When you have the MAC address details, it becomes easier to find the device associated with a particular MAC address for troubleshooting.
#5. Asset Management

Through MAC address lookup, organizations can record MAC addresses associated with devices and track the physical location, ownership, and configuration details of network devices. When itHow to Use MAC Address Lookup Tools to Identify Network Performance Issuescomes to warranty and network infrastructure management, it plays a significant role.
#6. Network Segmentation
Network segmentation means dividing a network into smaller and isolated subnetworks. This helps to improve network performance, security, and management. With MAC address data in hand, administrators can categorize the devices based on department, function, security requirements, etc.
How to Use MAC Address Lookup Tools to Identify Network Performance Issues
While you may fetch the basic MAC address from your computer or network device, you need additional data for network performance management. That information can be easily fetched using MAC address lookup tools available on the internet. Most of these are online tools and can be used for free.
The primary purpose of these tools is to share information about the vendor or manufacturer and the type of device associated with a MAC address. None of these tools are capable of directly identifying the network performance issues you or your organization might have.
However, the information generated by these online tools or resources can be used as part of the whole troubleshooting process. Here is how you can use the tools to locate and resolve network issues:
- First of all, you need to get the MAC address of your device or the device you think might be causing the issue.
- Here comes the use of MAC address lookup tools. Enter the MAC address on that tool to get crucial information, like the vendor name, the device model, and many more.
- With those data in hand, you can search for the common network performance issues that the particular device or manufacturer is known to have. You can even visit the official website of the vendor and check its support documentation to look out for any reported issues, firmware updates, or troubleshooting guides for that device.
- That’s not all; you can also use the tool-generated data to review and analyze the network configuration of the device. Check if the device uses accurate network settings for IP configuration, subnet mask, DNS servers, etc., since misconfigured settings can cause performance issues.
- If network admins want to evaluate the network infrastructure of the organization, they can utilize these tools to get details on all the MAC addresses of the network. Thus, they can identify network congestion or misconfigurations affecting network performance.
Thus, once you are familiar with them, you can use these tools to help in resolving network related issues.
Final Words
So far, we have discussed some of the best MAC address lookup tools that are available for free use. Moreover, it is quite easy to use these platforms, and these spare you from the hassle of installing any software on the local system. Some of these even offer the API feature necessary for bulk lookup.
Go through these online platforms, and you should be able to find the one most suitable for your needs.
You can trust Geekflare
Imagine the satisfaction of finding just what you needed. We understand that feeling, too, so we go to great lengths to evaluate freemium, subscribe to the premium plan if required, have a cup of coffee, and test the products to provide unbiased reviews! While we may earn affiliate commissions, our primary focus remains steadfast: delivering unbiased editorial insights, and in-depth reviews. See how we test .
More on Mac & Address Lookup
- MAC Address Filtering: What It Is and Should You Enable It?
- Useful Online DNS and Reverse IP Address Lookup Tools
- How to Find IP Address of Windows, Linux, Mac and Website?
- How to Check and Clear the ARP Cache in Windows, Linux and Mac?
MAC Addresses Explained with Examples
This tutorial explains the MAC (Media Access Control) address in detail. Learn what the MAC address is, how it is formed, and the types of MAC addresses (unicast, multicast, and broadcast).
In network, an address provides a unique identity to an end device. Unless an end device has a unique address, it can’t communicate with other devices in the network. A unique address enables an end device to send and receive data in the network.
In the LAN network, a unique address is the combination of two addresses; software address and hardware address.
Addressing in Networking Reference models
A networking reference model defines the standards, characteristics, definitions, and functionalities of the network. There are two popular networking models; the OSI Seven Layers model and the TCP/IP model.
In both models, the software address and hardware address are defined in the network layer and data link layer, respectively. In both models, the network layer and data link layer stand on the third and second positions, respectively. Because of this, both layers are also known as layer 3 and layer 2, respectively.
Software address
The software address is also known as the network layer address or layer 3 address. This address is manageable and configurable. Based on network requirements and layout, this address can be configured and assigned to an end device. Almost all modern LAN implementations use the IP protocol in the network layer. The IP protocol uses the term IP address to define the software address.
I have already explained IP addresses in the following tutorial.
IP Address Classes and Definition Explained
In this tutorial, I will explain the hardware addresses in detail.
Hardware address
The hardware address is also known as the data link layer address or layer 2 address or MAC (Media Access Control) address. From these terms, the term MAC address is commonly used to refer to the hardware address. Unlike the IP address or software address, this address can’t be configured or managed. When you purchase a new NIC (Network Interface Card), or any device which has onboard NICs, it comes with a pre-configured MAC address.
A MAC address is 6 bytes (48 bits) long address in the binary numbers. MAC addresses are written in the hexadecimal format. The hexadecimal format uses the base-16 to refer to numbers. If we divide the total available length (48 bits) in binary numbers by the base (base-16) that is used to write a number in hexadecimal format, we get the total digits (12 = 48 ÷ 16) of that number in the hexadecimal format. Thus, if we write a 6 bytes (48bits) long binary MAC address in hexadecimal format, we get a 12 digits long hexadecimal number.
For convenience and easier readability, when writing a MAC address in hexadecimal format, extra space or periods or colons are added after every two or four digits. For example, you can write a MAC address in the following ways.
- Without any separator: - 00000ABB28FC
- Extra space after every two digits: - 00 00 0A BB 28 FC
- Extra space after every four digits: - 0000 0ABB 28FC
- Colon after every two digits: - 00:00:0A:BB:28:FC
- Colon after every four digits: - 0000:0ABB:28FC
- Period after every two digits: - 00.00.0A.BB.28.FC
- Period after every four digits: - 0000.0ABB.28FC
No matter which style you use to write the MAC address, or an application or networking software uses to display the MAC address, a MAC address is always processed in binary numbers only. NIC converts hexadecimal numbers of the MAC address in binary numbers before processing and using it.
Structure or format of the MAC address
As mentioned above, you can’t assign MAC address to a NIC or onboard NICs. When you purchase a new NIC or a device with onboard NICs, it arrives with a pre-configured MAC address or MAC addresses, respectively. Before we understand how manufacturers select MAC addresses for NICs, let’s briefly understand why a MAC should be unique in the LAN network.
If a LAN network has two or more NICs configured with the same MAC address then that network will not work. Let’s understand this with an example.
Suppose in a network three PCs; PC-A (11000ABB28FC), PC-B (00000ABB28FC) and PC-C (00000ABB28FC) are connected through a switch. NICs of PC-B and PC-C have the same MAC address 00000ABB28FC.
If PC-A sends a frame to the destination MAC address 00000ABB28FC , the switch fails to deliver this frame as it has two recipients of this frame.
The following image shows this example.

A LAN network does not work unless each device in the LAN network has a unique MAC address.
Now let's be back to our main question. How do manufacturers assign a unique MAC address to each NIC?
Before manufacturing NICs, every manufacturer obtains a universally unique 3-byte code, known as the organizationally unique identifier (OUI), from the IEEE. The IEEE is an international organization that regulates and maintains the namespace of MAC addresses.
After obtaining the OUI bytes, the manufacturer uses these OUI bytes at the beginning of the MAC address of all its NICs or on-board NIC devices. The manufacturer also assigns a unique hexadecimal value in the remaining bytes.
6 bytes MAC address = 3 bytes OUI number obtained from the IEEE + 3 bytes unique number assigned by the manufacturer

MAC addresses of all NICs or onboard NIC devices manufactured by the same manufacturer always start with the same 3-bytes OUI numbers. For example, suppose the IEEE assigns an OUI “0000AA” to the xyz company. Now the xyz company will use the OUI number 0000AA as the first 24 bits to build MAC addresses for its NICs or onboard NICs devices.
To keep each product separately from others, the manufacturer uses the remaining 3-bytes. Manufacturers are free to use any sequence or method on the remaining three bytes. For example, the xyz company can assign the MAC addresses to its NICs in the incremental order.
The following table extends this example and adds two more demo companies (ABC and JKL) in the example. It also shows MAC addresses of 5 NICs from each company.

Thus, this procedure ensures that no two NICs use the same MAC address in the universe.
Types of MAC address
There are three types of MAC address; unicast, multicast, and broadcast.

Unicast MAC address
Unicast MAC address represents a specific NIC or onboard NIC ports in the network. The inbuilt MAC address of a NIC is the unicast MAC address of that NIC.
Multicast MAC address
Multicast MAC address represents a group of devices (or NICs in Layer 2). The IEEE has reserved the OUI 01-00-5E (first 3-bytes or 24 bits) for the multicast MAC addresses. The remaining 24 bits are set by the network application or device that wants to send data in the group. A multicast MAC address always starts with the prefix 01-00-5E.
Broadcast MAC address
Broadcast MAC address represents all devices in the network. The IEEE has reserved the address FFFF.FFFF.FFFF as the broadcast MAC address. Any device that wants to send the data to all devices of the network, can use this address as the destination MAC address.
That’s all for this tutorial. If you like this tutorial, please don’t forget to share it with friends through your favorite social channel.
By ComputerNetworkingNotes Updated on 2024-09-14
ComputerNetworkingNotes CCNA Study Guide MAC Addresses Explained with Examples
- EtherChannel Load Distribution Explained
- Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) Explained
- Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP) Explained
- EtherChannel Manual Configuration
- EtherChannel Basic Concepts Explained
- STP, RSTP, PVST, RPVST, and MSTP
- Similarities and Differences between STP and RSTP
- RSTP / RPVST Explained with Examples
- PVST/RPVST and EtherChannel Explained
- STP/RSTP Timers Explained
We do not accept any kind of Guest Post. Except Guest post submission, for any other query (such as adverting opportunity, product advertisement, feedback, suggestion, error reporting and technical issue) or simply just say to hello mail us [email protected]
How-To Geek
What is a mac address, and how does it work.

Your changes have been saved
Email is sent
Email has already been sent
Please verify your email address.
You’ve reached your account maximum for followed topics.
Quick Links
What is a mac address, how does a mac address work, how are mac addresses used, how do i find my mac address.
If you've ever tried to identify devices on a network or search for a nearby Bluetooth device , chances are you've dealt with MAC addresses. But what are they exactly, and how are they different from IP addresses?
Multiple hardware and software elements work together every day to connect us to the internet and get data to our devices. Hardware devices like routers and cables transmit the data we need, while software like border gateway protocol (BGP) and internet protocol (IP) addresses direct those data packets to and from those devices. Without both working together, we couldn't get online.
One of those critical elements is the media access control (MAC) address. MAC addresses are associated with specific devices and assigned to them by the manufacturer.
Other names used for MAC addresses include:
- Networking hardware address
- Burned-in address (BIA)
- Physical address
- Ethernet hardware address (EHA)
Wi-Fi, Bluetooth , and Ethernet connections all use MAC addresses.
MAC addresses work with the card in your device that lets it connect wirelessly to the internet, called a Network Interface Controller (NIC). MAC addresses are used to identify which device is which on your local network so that data gets sent to your computer and not your roommate's smartphone.
MAC addresses are always a 12 digit hexadecimal number, with the numbers separated every two digits by a colon or hyphen. So a MAC address of 2c549188c9e3, for example, would be displayed 2C:54:91:88:C9:E3 or 2c-54-91-88-c9-e3.
Large network adapter manufacturers like Dell and Cisco will often code their identifiers, called their Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI), into the MAC addresses of devices they make. They're always the first six digits. Dell's, for example, is 00-14-22.
Related: What Is a Network Adapter?
When data packets from the internet hit your router, that router needs to be able to send them to the right device on its network. It does this using MAC addresses, assigning a private IP address to each network-connected device based on that device's MAC address. This is different from the IP address your internet service provider (ISP) assigns you---that's your public IP address.
Your router tracks outbound data requests so that when the data comes back, it can attach the correct private IP to the data packets, then send them along to whichever device's MAC address matches that private IP.
Devices can have more than one MAC address because they get one for every place they can connect to the internet. If your laptop has an ethernet port and Wi-Fi , for example, it would have different MAC addresses for the Wi-Fi connection and the Ethernet connection. Bluetooth also uses its own MAC address.
Related: Wi-Fi vs. Ethernet: How Much Better Is a Wired Connection?
In addition to sending your data to the right place, your wireless router also uses MAC addresses to secure your connection by only accepting traffic from devices with MAC addresses that it recognizes. This is called MAC filtering.
Related: Internet Connection Not Working? 10 Troubleshooting Tips
MAC addresses can also be used by technicians to troubleshoot connection problems on a network . Because they're unique to each hardware device, it's easier to pinpoint which piece of hardware connected to the network is sending and receiving data by looking at the MAC address. From there, they can see which device is having trouble connecting.
If you need to find the MAC address for your device, you can usually do it by going into the settings menu. You can follow our guide to finding the MAC addresses on your Windows device , whether by the Settings app or by the command prompt.
It's also easy to find the MAC address on a Mac computer . In System Preferences, click the Network icon, select the interface you want to use, then click Advanced. You'll see the MAC address listed under the Hardware tab.
Many more devices, including smart TVs, game consoles, and smartphones have their own MAC addresses that you can find .
If you want to, it's also possible to change or "spoof" your MAC address .
Related: How to Permanently Change Your MAC Address on Linux
- Cloud & Internet
- Engineering Mathematics
- Discrete Mathematics
- Operating System
- Computer Networks
- Digital Logic and Design
- C Programming
- Data Structures
- Theory of Computation
- Compiler Design
- Computer Org and Architecture
What is MAC Address?
To communicate or transfer data from one computer to another, we need an address. In computer networks, various types of addresses are introduced; each works at a different layer. A MAC address , which stands for Media Access Control Address, is a physical address that works at the Data Link Layer. In this article, we will discuss addressing a DLL, which is the MAC Address.
So, go through the article if you are eager to learn what is MAC address and its components.
Table of Content
What is MAC (Media Access Control) Address?
Format of mac address, types of mac address.
- Reason to have both IP and MAC addresses.
- Why should the MAC address be unique in the LAN network?
- How do I find the MAC Address?
What is MAC Cloning?
Characteristics of mac address, advantages of mac address, disadvantages of mac address.
MAC Addresses are unique 48-bit hardware numbers of a computer that are embedded into a network card (known as a Network Interface Card ) during manufacturing. The MAC Address is also known as the Physical Address of a network device. In the IEEE 802 standard, the data link layer is divided into two sublayers:
- Logical Link Control (LLC) Sublayer
- Media Access Control (MAC) Sublayer
The MAC address is used by the Media Access Control (MAC) sublayer of the Data-Link Layer . MAC Address is worldwide unique since millions of network devices exist and we need to uniquely identify each.
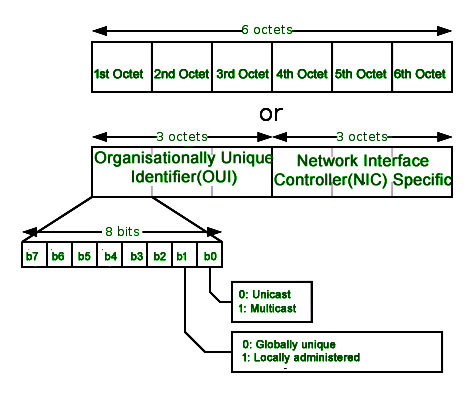
To understand what is MAC address is, it is very important that first you understand the format of the MAC Address. So a MAC Address is a 12-digit hexadecimal number (48-bit binary number), which is mostly represented by Colon-Hexadecimal notation.
The First 6 digits (say 00:40:96) of the MAC Address identify the manufacturer, called the OUI ( Organizational Unique Identifier ). IEEE Registration Authority Committee assigns these MAC prefixes to its registered vendors.
Here are some OUI of well-known manufacturers:
The rightmost six digits represent Network Interface Controller , which is assigned by the manufacturer.
As discussed above, the MAC address is represented by Colon-Hexadecimal notation. But this is just a conversion, not mandatory. MAC address can be represented using any of the following formats:
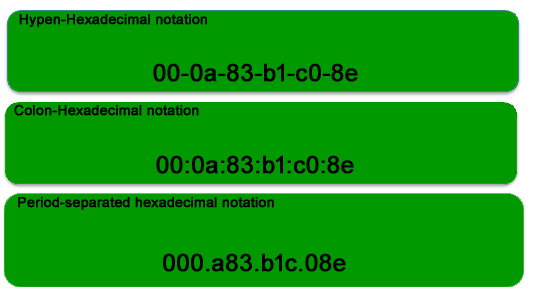
Note: Colon-Hexadecimal notation is used by Linux OS and Period-separated Hexadecimal notation is used by Cisco Systems .
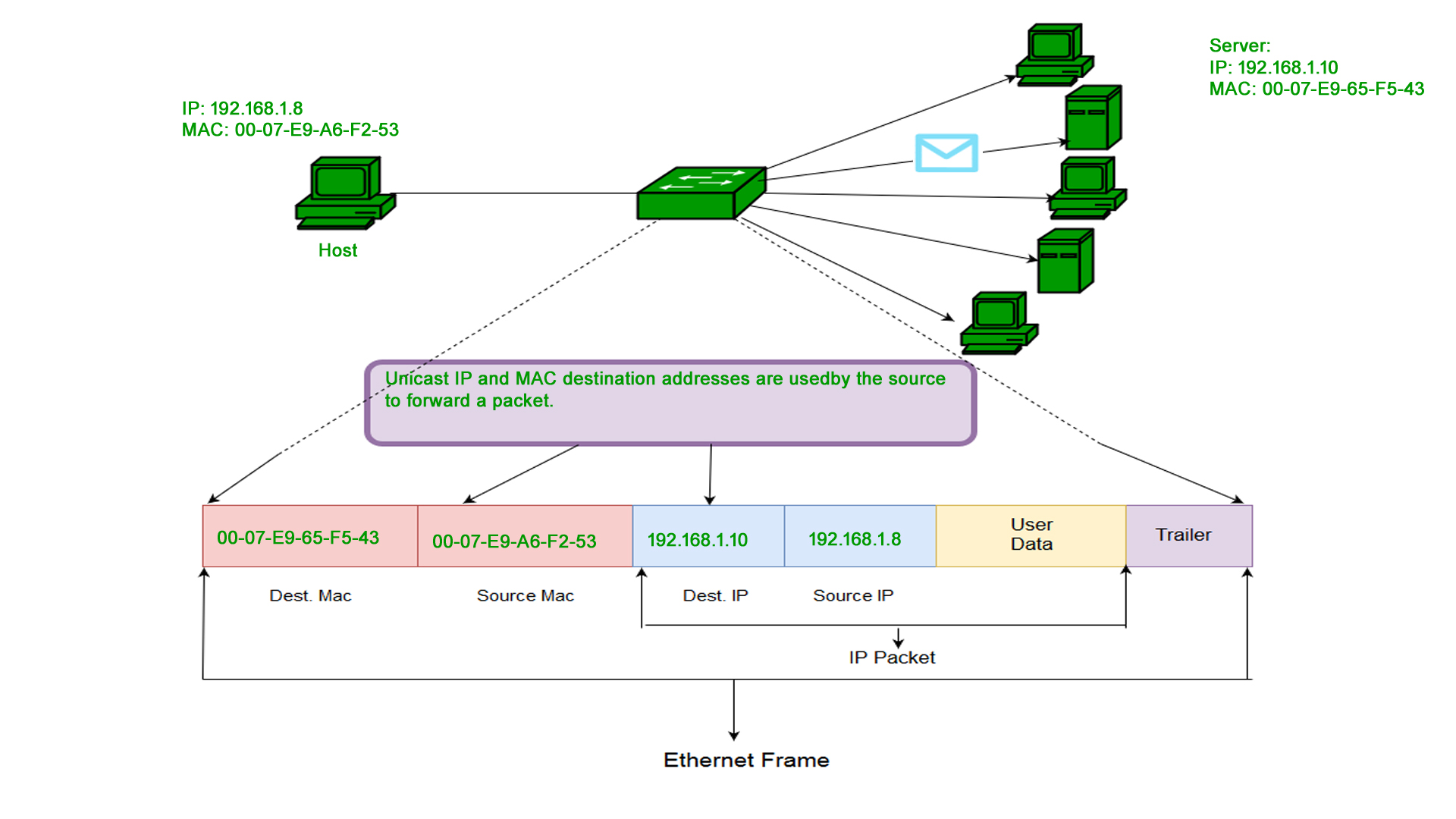
1. Unicast: A Unicast-addressed frame is only sent out to the interface leading to a specific NIC. If the LSB (least significant bit) of the first octet of an address is set to zero, the frame is meant to reach only one receiving NIC. The MAC Address of the source machine is always Unicast.
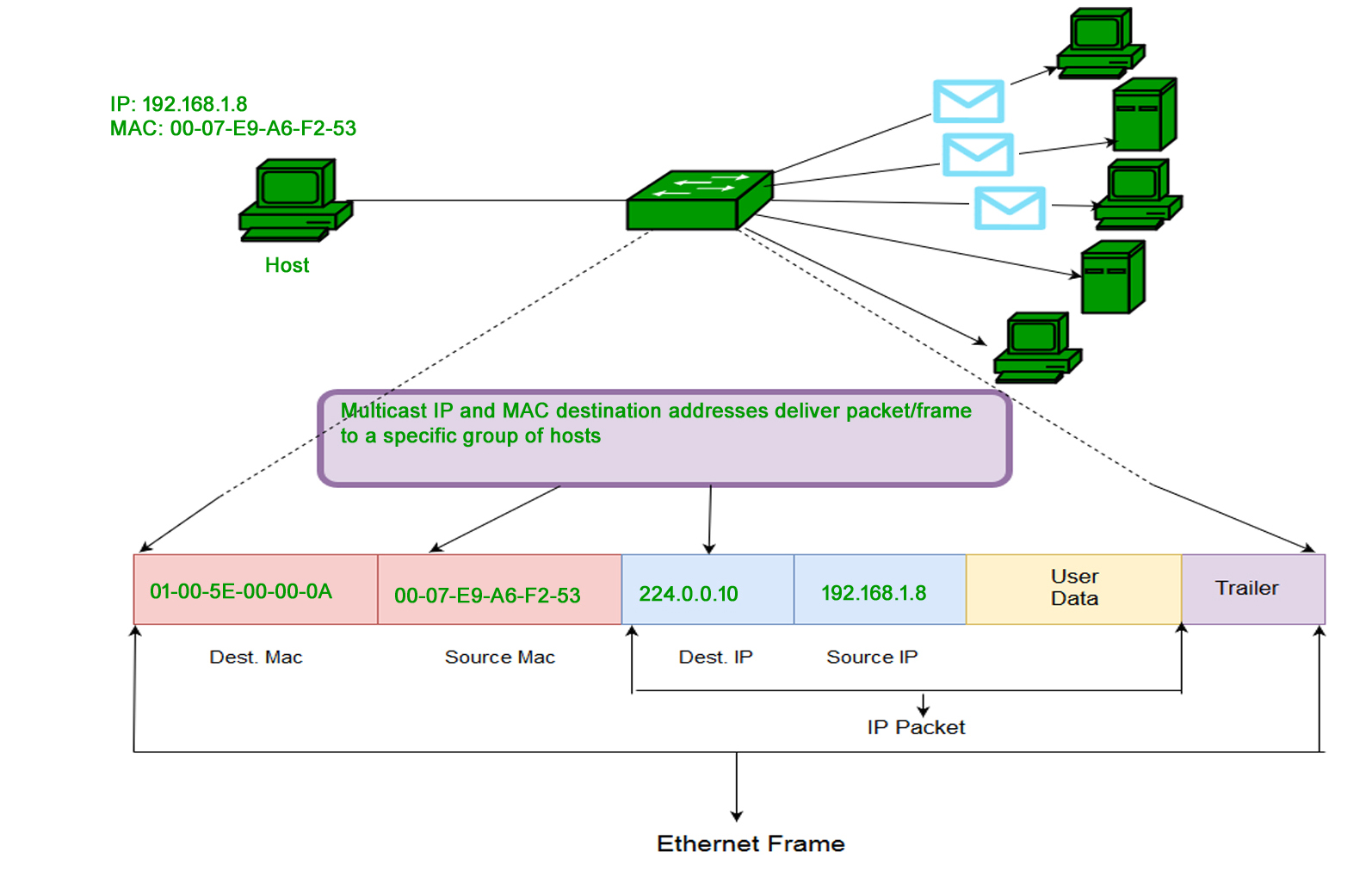
2. Multicast: The multicast address allows the source to send a frame to a group of devices. In Layer-2 (Ethernet) Multicast address, the LSB (least significant bit) of the first octet of an address is set to one. IEEE has allocated the address block 01-80-C2-xx-xx-xx (01-80-C2-00-00-00 to 01-80-C2-FF-FF-FF) for group addresses for use by standard protocols.
3. Broadcast: Similar to Network Layer, Broadcast is also possible on the underlying layer( Data Link Layer). Ethernet frames with ones in all bits of the destination address (FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF) are referred to as the broadcast addresses. Frames that are destined with MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF will reach every computer belonging to that LAN segment.
Reason to Have Both IP and MAC Addresses.
The reason for having both IP and MAC addresses lies in the way the Internet works, specifically in the structure of the OSI Model. This model is a conceptual framework that describes how data is sent and received over a network. It’s divided into seven layers, each performing specific functions.
- Layer 2 uses MAC addresses and is responsible for packet delivery from hop to hop .
- Layer 3 uses IP addresses and is responsible for packet delivery from end to end .
Layer 2 (Data Link Layer ) uses a MAC (Media Access Control) address . These are unique identifiers assigned to network interfaces for communications at the data link layer. The primary function of MAC addresses is to manage how data is transported from one network node to another on a direct, physical basis – this is also referred to as “hop to hop” delivery.
On the other hand, Layer 3 ( Network Layer ) uses an IP (Internet Protocol) address . These IP addresses are used to identify devices on a network and to route traffic between networks. The IP addresses ensure that the data gets from its original source reaches its final destination and it is also called “end-to-end” delivery of data.
When a computer sends data, it first wraps it in an IP header, which includes the source and destination IP addresses. This IP header, along with the data, is then encapsulated in a MAC header, which includes the source and destination MAC addresses for the current “hop” in the path.
As the data travels from one router to the next, the MAC address header is stripped off and a new one is generated for the next hop. However, the IP header, which was generated by the original computer, remains intact until it reaches the final destination. This process illustrates how the IP header manages the “end to end” delivery, while the MAC headers handle the “hop to hop” delivery.
So, Both IP and MAC addresses are essential for the functioning of the Internet. While MAC addresses facilitate the direct, physical transfer of data between network nodes, IP addresses ensure that the data reaches its final destination.
Why Should the MAC Address Be Unique in the LAN Network?
Consider a LAN ( Local Area Network ) as a large gathering where everyone is engaged in conversations. Now, let’s suppose that there are two individuals at this gathering who coincidentally share the same name. This scenario would inevitably create confusion, right? If someone calls out that name, both individuals would respond, making it challenging to discern the intended recipient of the message.
In a similar manner, within a network, each device possesses a distinct identifier referred to as a MAC (Media Access Control) address. Think of it as a unique name assigned to the device. When information is transmitted across the network, it is directed to a specific MAC address, much like a letter being addressed to a specific individual.
However, if multiple devices within the same network were to have identical MAC addresses, it would result in confusion and disrupt the network’s functioning. The network would struggle to ascertain which device should receive the transmitted information. To prevent this confusion and ensure the accurate delivery of information, it is vital for each device on a network to possess a unique MAC address.
How Do I Find the MAC Address?
A MAC address is mostly used to configure a router for a network device or during troubleshooting. The address of our computer device can be easily checked with any operating device. All the Apple devices connected to our home network contain a unique MAC address. Manufacturers may identify a MAC address by other names, such as the physical address, hardware ID, wireless ID, and Wi-Fi address.
Following are the steps which help to find MAC addresses for different OS
MAC address on Windows
Here is the Step-by-Step guide to finding MAC addresses on Windows.
Step 1 – Press Window Start or Click on Windows Key.

Step 3 – Click on cmd, the command prompt window will display,

Step 4 – In the command prompt type ipconfig/all command and then press enter.

Step 5 – As you will scroll down, each physical address is the MAC address of your device.
.jpg)
MAC Address on MacOS
Here is a step-by-step guide to finding MAC addresses on a Mac operating system.
Command for MAC Address in MacOS:
Step 1 – Click on System Settings.

Step 2 – In the system settings, click on the MAC network option.

Step 3 – Then go to the advanced settings.

Step 4 – Here you find your MAC address.

MAC Address on Unix/Linux
Here is a step-by-step guide to finding MAC addresses on a Unix/Linux operating system.
Command For MAC Address in Unix/Linux:
Note: LAN technologies like Token rings and Ethernet use MAC Addresses as their Physical address but there are some networks (AppleTalk) that do not use MAC addresses. for further details .
Some ISPs use MAC addresses to assign an IP address to the gateway device. When a device connects to the ISP, the DHCP server records the MAC address and then assigns an IP address. Now the system will be identified through the MAC address. When the device gets disconnected, it loses the IP address.
If the user wants to reconnect, the DHCP server checks if the device is connected before. If so, then the server tries to assign the same IP address (in case the lease period has not expired). In case the user changed the router, the user has to inform the ISP about the new MAC address because the new MAC address is unknown to ISP , so the connection cannot be established.
Or the other option is Cloning , user can simply clone the registered MAC address with ISP. Now router keeps reporting the old MAC addresses to ISP and there will be no connection issue.
The Media Access Control address (MAC address) is a unique identifier assigned to most network adapters or network interface cards (NICs) by the manufacturer for identification and use in the Media Access Control protocol sub-layer.
An Ethernet MAC address is a 48-bit binary value expressed as 12 hexadecimal digits (4 bits per hexadecimal digit). MAC addresses are in a flat structure and thus they are not routable on the Internet. Serial interfaces do not use MAC addresses. It does NOT contain a network and host portion with the address. It is used to deliver the frame to the destination device.
- MAC addresses are used in LAN (Local Area Network) environments to identify devices and allow communication between them.
- MAC addresses are burned into the hardware of a network interface card (NIC) and cannot be changed, except in some rare cases where the manufacturer has provided a specific tool to do so.
- The first 3 bytes of a MAC address represent the manufacturer ID, while the last 3 bytes represent a unique identifier assigned by the manufacturer.
- MAC addresses are often used in conjunction with ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) to resolve IP addresses to MAC addresses for communication on a LAN.
- Some operating systems, such as Windows and Linux , allow you to view the MAC address of your network adapter through a command prompt or network settings.
- Uniqueness: Each MAC address is unique, which means that devices on the network can be easily identified and managed.
- Simplicity: MAC addresses are easy to configure and manage, and do not require any additional network infrastructure.
- Compatibility: MAC addresses are widely used and supported by a variety of networking technologies and protocols, making them compatible with many different systems.
- Security: MAC addresses can be used to restrict access to a network by only allowing devices with authorized MAC addresses to connect.
- Fault-tolerance: In case of hardware or software failure, a device can be easily replaced without affecting the network, as long as the new device has the same MAC address as the old one.
- Multicasting: MAC addresses can be used for multicasting, allowing a single packet to be sent to multiple devices at once.
- Efficiency: MAC addresses allow for efficient communication on the network, as they enable devices to quickly and easily identify and communicate with each other.
- Lower network overhead: MAC addresses reduce network overhead by allowing devices to communicate directly with each other without the need for additional routing or addressing.
- Ease of troubleshooting: MAC addresses can be used to troubleshoot network issues by identifying the source of problems and tracking network activity.
- Flexibility: MAC addresses can be used to support a variety of network configurations and topologies, including peer-to-peer, client-server, and hybrid models.
- Limited address space: MAC addresses are 48-bit numbers, which means that there is a finite number of possible MAC addresses. This can lead to address conflicts if multiple devices have the same MAC address.
- Spoofing: MAC addresses can be easily spoofed, allowing unauthorized devices to gain access to the network.
- Inefficiency: MAC addresses are not hierarchical, which can make it difficult to efficiently manage large networks.
- Static addressing: MAC addresses are typically assigned at the time of manufacture and cannot be easily changed. This can be a disadvantage in situations where devices need to be reconfigured or replaced.
- Limited scope: MAC addresses are only used for identifying devices within a local network segment, and cannot be used to identify devices outside of this segment.
- Hardware-dependent: MAC addresses are tied to the network interface card (NIC) of a device, which means that if the NIC fails or is replaced, the MAC address also changes.
- Lack of encryption: MAC addresses are sent in plain text, which can make them vulnerable to interception and eavesdropping.
- No inherent security: While MAC filtering can be used to restrict access to a network, MAC addresses themselves do not provide any inherent security features.
- MAC address collisions: In rare cases, MAC addresses can collide, which can cause network disruptions and make it difficult to identify and manage devices on the network.
FAQs on MAC Address
Q1. what is mac address used for.
MAC address is used to identify devices in the same network. On the other hand, IP Addresses also did the same thing but that is used to identify Device devices globally or through its internet address.
Q2. Can we change MAC address?
No , MAC address is a permanent address of a device which is also hardcoded in the Network Interface Card (NIC). However, many drivers allow the MAC address to be changed.
Q3. What is my MAC address number?
To find the MAC address of any device, you can follow these general steps: Open the Settings app on your device. Navigate to the Network & Internet section. Select Properties. Scroll down to the bottom of the page until you find the Physical Address (MAC). For Further Details:- Check Here
Q4. Difference between MAC Address and IP Address?
The Difference points between MAC Address and IP Address MAC Address IP Address MAC Address stands for Media Access Control Address. IP Address stands for Internet Protocol Address. MAC Address is a six byte hexadecimal address. IP Address is either a four-byte (IPv4) or a sixteen-byte (IPv6) address. A device attached with MAC Address can retrieve by ARP protocol. A device attached with IP Address can retrieve by RARP protocol. NIC Card’s Manufacturer provides the MAC Address. Internet Service Provider provides IP Address. For more Details :- Check Here
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Best External Hard Drives for Mac in 2024: Top Picks for MacBook Pro, MacBook Air & More
- How to Watch NFL Games Live Streams Free
- OpenAI o1 AI Model Launched: Explore o1-Preview, o1-Mini, Pricing & Comparison
- How to Merge Cells in Google Sheets: Step by Step Guide
- #geekstreak2024 – 21 Days POTD Challenge Powered By Deutsche Bank
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
List of MAC addresses with vendors identities Raw. mac-vendor.txt ... 0000A6 Network General (internal assignment, not for products) 0000A7 NCD: 0000A8 Stratus Computer, Inc. 0000A9 Network Systems: 0000AA Xerox Xerox machines: 0000AB LOGIC MODELING CORPORATION:
We update MAC address lookup database as soon as we have new information from the IEEE database and Wireshark manufacturer database. There are more than 52K MAC address prefixes in the database. The database was last updated on 17 September 2024 Data. For each search, you will always have the most accurate manufacturer, vendor or organization ...
Source of data is IEEE registry which is responsible for MAC address assignments and upkeeping of the registry. MA-L list consists of legacy and LARGE assignments, a large assignment is a 24bit assignment where first three bytes are assigned from IEEE and the last three bytes are to be assigned by the vendor (i.e. 11:22:33:xx:xx:xx).
For some information on IEEE 802 number assignments by the IEEE Registration Authority and how to contact that authority, see the [IANA registry ieee-802-numbers]. Available Formats XML HTML ... These values are prefixed with 00-00-5E to form unicast MAC addresses, with 01-00-5E to form multicast MAC addresses, with 02-00-5E to form unicast ...
An MA-S (MAC Address Block Small) assignment includes an OUI-36 and small blocks of EUI-48 and EUI-64 values which can be used as MAC Addresses, Bluetooth Device Addresses, Ethernet Addresses or object identifiers. CID. A unique 24-bit identifier that cannot be used to generate EUI-48 or EUI-64 values. ...
The assignee (registrant/owner of the assignment) may be identified as either an organization or company in the public listing. Please select a Product All MAC (MA-L, MA-M, MA-S) MAC Address Block Large (MA-L) MAC Address Block Medium (MA-M) MAC Address Block Small (MA-S) Company ID EtherType™ ManufacturerID IEEE 802.16 Operator ID IAB
A Universally Administered Address Block allocated for the assignment of Group MAC Addresses for use in Standards. Learn More. IEEE 1667 Silo Type Identifier (STID) IEEE 1667 specifies the interface to and behavior of several silos (e.g., Probe Silo, TCG Storage Transport Silo, Password Silo, and Smart Card Transport Silo). External silos may ...
MAC address lookup can reveal the manufacturer or vendor of a network interface card (NIC) based on its MAC address. The first six characters of a MAC address, known as the OUI (Organizationally Unique Identifier), are assigned to specific manufacturers by the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers).
Step 1 - Enter the Required Information. You can provide any of the following to get the details you are looking for: MAC Address. A unique identifier (00-1B-63-84-45-E6) is assigned to a device's network interface. OUI. Part of the MAC address (00-1B-63) identifies the manufacturer. Vendor Name.
Group MAC address assignments for standards use 1. IEEE Std 802.1D and IEEE Std 802.1Q reserved addresses Table 1 - IEEE Std 802.1D and IEEE Std 802.1Q reserved addresses Group MAC address value Organization using the value Standard using the value Notes 01-80-C2-00-00-00 IEEE 802 IEEE Std 802.1D, IEEE Std 802.1Q
Simply send us an HTTP GET/POST request with your MAC address and we'll return the vendor. No registration or api key necessary for up to 1,000 requests per day. We want you to feel comfortable building your systems around ours. Since launching in 2011, we have grown at an incredible pace. Today our API receives over 3.6 billion requests per year!
A MAC address (short for medium access control address) is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface controller (NIC) for use as a network address in communications within a network segment. This use is common in most IEEE 802 networking technologies, including Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. Within the Open Systems Interconnection ...
In other words: uniqueness of MAC addresses is guaranteed the same way that uniqueness of telephone numbers, Internet Domain Names, Internet Mail addresses, IP addresses, etc. is guaranteed: by having a single global registry (the ITU for phone numbers, IANA for IP addresses, etc.) that splits the address space into disjoint non-overlapping ...
MAC Group Addresses used in ISO 9542 . Prior to the allocation of a 48-Bit Universal Address for use by standard protocols the following two Group MAC Address values were assigned, in perpetuity to ISO, for use in ISO 9542 . MAC Group Addresses used in ISO 9542: 09-00-2B-00-00-04 and 09-00-2B-00-00-05 . Token Ring LAN Functional Addresses
OUI Lookup Tool. The Wireshark OUI lookup tool provides an easy way to look up OUIs and other MAC address prefixes. It uses the Wireshark manufacturer database, which is a list of OUIs and MAC addresses compiled from a number of sources. Directions: Type or paste in a list of OUIs, MAC addresses, or descriptions below.
The Standard Group MAC Address assignment is a universally administered address block for use in standards by standards developers. If you require MAC Addresses for your products, please refer to the information on purchasing and using an MA-L, MA-M or MA-S assignment to create MAC Addresses for your products.
Follow these steps to find the MAC address on your Mac computer: Select the Apple icon in the top left corner. Select System Preferences. Select Network. Select the button in the bottom right corner that says Advanced. Ensure Hardware is selected at the top and look for MAC Address. The characters that appear next to this are your MAC address ...
By convention, these addresses are usually written in one of the following three formats, although there are variations: MM:MM:MM:SS:SS:SS. MM-MM-MM-SS-SS-SS. MMM.MMM.SSS.SSS. The leftmost six digits (24 bits), called a prefix, are associated with the adapter manufacturer (M). Each vendor registers and obtains MAC prefixes as assigned by the IEEE.
Here, users can either check MAC address vendor name or enter the vendor name to find out about the MAC address OUIs. Try Dan's Tools Udger. Udger is a useful resource that lets you find out about MAC address vendor information. The list of MAC address vendors used by this platform is provided by the IEEE Standards Association.
6 bytes MAC address = 3 bytes OUI number obtained from the IEEE + 3 bytes unique number assigned by the manufacturer. MAC addresses of all NICs or onboard NIC devices manufactured by the same manufacturer always start with the same 3-bytes OUI numbers. For example, suppose the IEEE assigns an OUI "0000AA" to the xyz company. ...
An MA-S assignment includes an OUI-36 and small blocks of EUI-48 and EUI-64 values which can be used as MAC Addresses, Bluetooth Device Addresses, Ethernet Addresses or object identifiers. Through the IEEE SA, industry, and government support, select IEEE standards are available for download at no charge. Learn more information about the GET ...
MAC addresses work with the card in your device that lets it connect wirelessly to the internet, called a Network Interface Controller (NIC). MAC addresses are used to identify which device is which on your local network so that data gets sent to your computer and not your roommate's smartphone. MAC addresses are always a 12 digit hexadecimal ...
The MAC address is assigned by the embedded Network Interface Card (NIC) of each device and cannot be altered once set. 1 min read. Difference Between MAC Address and IP Address. Both MAC Address and IP Address are used to uniquely define a device on the internet. NIC Card's Manufacturer provides the MAC Address, on the other hand, the ...
MAC Address Table. When you use bridge groups, the ASA learns and builds a MAC address table in a similar way as a normal bridge or switch: when a device sends a packet through the bridge group, the ASA adds the MAC address to its table. The table associates the MAC address with the source interface so that the ASA knows to send any packets addressed to the device out the correct interface.