

ISO 9001: The Ultimate QMS Guide (Basics, Implementation, ISO Templates)
Consumer Reports publishes an annual reliability survey , which includes data on over 470,000 cars.
In this report, owners of Tesla’s Model 3 experienced a number of problems, including chassis hardware, paint and trim related faults, indicative of a build quality that fell far shorter than expected standards set across the automotive industry. The Model 3 represents Tesla’s first real attempt at a mass-market electric vehicle, and the issues surrounding its launch created much frustration and controversy among electric vehicle enthusiasts.
This lack of quality assurance has lost at least one major $5 million order of Model 3 vehicles from a rental company, in relation to problems with the service and performance of previously purchased vehicles.
In an email, NextMove wrote:
“Tesla Model 3 vehicles, which NextMove was supposed to take over after payment and only a short examination, sometimes had serious defects: defective tires, paint and body damages, defective charge controllers, wrong wiring harnesses or missing emergency call buttons. Such quality defects would have endangered the safety of the customers and the profitability of NextMove.”
Stefan Moeller, Managing Director of NextMove, went on to say:
“We had to insist on compliance with general quality standards and processes in order to protect our renters and our business model.”
Why did Tesla have so many problems? Crucially, Tesla made the decision to deliver the product to market and sort out the issues later.
Basically, they didn’t have a strong enough system for managing quality.
We call these Quality Management Systems (QMS) – and they work.
The rest of the auto-industry follows a specific quality management system structure. It’s called ISO/TS 16949:2009 and it’s a variant of ISO 9001.
People follow quality management systems for various reasons; they improve quality first and foremost. But they also have a positive impact on the bottom line.
The return on investment (ROI) of a quality management system is typically impressive:
As a guide, a recent study undertaken through the American Society for Quality (ASQ) showed that for every $1 spent on your QMS, you could expect to see an additional $6 in revenue, a $16 reduction in costs, and a $3 increase in profits. On average, they saw that quality management reduced costs by 4.8% – ASQ
In this Process Street article, we’ll be looking at how ISO 9001 can be used to assure quality control across all types of organizations, with benefits like improved company performance, higher demand for products, and a competitive advantage towards increasing market share.
What we’ll cover:
ISO 9001: Free templates!
- What is ISO 9001? A simple introduction
- Anatomy of ISO 9001: 2015 for Quality Management
Quality management: What is it & why does it matter?
Iso 9001 for continuous improvement, what does it mean to be iso 9001 certified.
- ISO 9001 audit
Implement ISO 9001 with Process Street
Related iso standards.
For the uninitiated, what is ISO 9001, as simply as possible?
ISO 9001: A simple explanation for normal people
ISO deals in “standards”. That means sets of requirements, decided by experts, for doing things. ISO 9001 happens to be a standard for how to set up and maintain a QMS (quality management system) in your business.
It helps give you direction in how to write your company processes, how to structure them, organize them, check them, and improve them.
It’s about systemizing your approach to your processes across your whole company. That’s it. Don’t be intimidated.
In this article, we’re going to go through step by step and explain the technical stuff. Let’s jump right in with some of our free ISO 9001 templates which cover the basics. You can click through to navigate any of the templates embedded in this article if you want to know more.
The best way to get started with ISO 9001 is to take a look at some of our custom ISO 9001 templates, so you know what implementing ISO 9001 looks like right off the bat.
This first couple of templates offers a great jumping-off point to start understanding how successful quality management systems look in practice.
If you want to try any of the templates mentioned in this article, all you have to do is sign up for free at Process Street (it only takes two minutes!) and simply add the templates to your account.
ISO 9001 Structure Template
This ISO 9001 structure template offers a concise and easy-to-follow framework for creating a quality management system (QMS) mini-manual that complies with ISO 9001 requirements.
Despite being named “ISO 9000”, this template is in fact built with the ISO 9000 family for quality management systems in mind, and as such can be used for ISO 9001.
The purpose of this mini-manual is to provide you with an organized overview of your company’s policies and procedures that can be distributed amongst your team.
ISO 9001 Marketing Procedures
This ISO 9001 Marketing Procedures template was built following the structure of the ISO 9001 structure template mentioned above, but from the perspective of a marketing company.
It can be used as a guide to follow when creating your own mini-manual; it’s basically the structure template above, but fleshed out with example data, so you can understand what the structure template might look like in practice.
Other relevant ISO 9001 templates
Iso 9001 internal audit checklist for quality management systems.
- ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 14001:2015 Integrated Management System (IMS) Checklist
- ISO 9001 QMS Mini-Manual Structure Template
- ISO 9001 Marketing Procedures (Mini-Manual Example)
ISO 9004:2018 Self-Audit Checklist
For templates related to other ISO standards, simply scroll to the bottom of the article.
What is ISO 9001? The leading QMS standard
ISO 9001 is an international standard developed to help organizations build and optimize their quality management systems (QMS) to run more efficiently and better meet their customer needs.
The standard is used by organizations as a kind of badge of honor to show that their products and services are consistently meeting industry quality standards. This is achieved by following the standard requirements and obtaining an ISO 9001 certification.
ISO: International Organization for Standardization
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) is the largest and most well-known standards network in the world.
The organization began in Geneva, Switzerland and has, at this point, been adopted by companies throughout 164 countries around the world.
ISO doesn’t actually certify organizations themselves, but rather it offers quality standard guidelines that certification agencies can reference when performing audits and in turn certifying a company’s QMS.
ISO 9000: The Quality Management Family
ISO 9000 can be defined as a family of quality management standards created to help organizations build and maintain an effective QMS. The ISO standards are not restricted to any specific industry and can actually be used by any kind of organization of any size.
Some goals of the ISO 9000 standards include: boosting a company’s customer satisfaction, helping meet regulatory specifications, and encouraging continuous improvement. These standards are meant to act as the foundation for an organization’s QMS.
While ISO 9000 is a family of standards, ISO 9001 is an individual standard within the ISO 9000 family. It’s important to note that there also exists a single ISO 9000 standard that covers the basics and glossary for QMSs, but in this article, the term “ISO 9000” is used in reference to the family of standards, not the individual standard.
The ISO 9000 family is made up of the following standards:
- ISO 9001:2015 : Quality Management Systems – Requirements
- ISO 9000:2015 : Quality Management Systems – Fundamentals and Vocabulary
- ISO 9004:2018 : Quality Management – Quality of an Organization – Guidance to Achieve Sustained Success
- ISO 19011:2018 : Guidelines for Auditing Management Systems
Management System Standards (MSS): A quick look
ISO’s Management System Standards (MSS) are a bunch of standards that share a similar structure, designed to work together to make managing complex systems simpler, and more easy to integrate.
They set out specific requirements that companies of any size can use to build various different management systems, like quality management systems, or environmental management systems.
MSS were developed by international experts in knowledge fields like leadership strategies, international business management, and efficient business practices.
The three main ISO Management System Standards are:
- ISO 9001:2015 (Quality management systems)
- ISO/IEC 27001:2013 (Information security management systems)
- ISO 14001:2015 (Environmental management systems)
There are also ISO MSS that offer requirements and guidelines for management standards within specific sectors, such as:
- ISO 13485:2016 (Medical devices)
- ISO/TS 22163:2017 (Railway applications)
- ISO/TS 29001:2010 (Petroleum industries)
Some MSS also serve as guides on highly specific sections of a company’s management system, in order to help strengthen the understanding and implementation of the ISO standards.
These standards include:
- ISO/TS 22003:2013 (Food safety management systems)
- ISO/TR 10013:2001 (QMS documentation guidelines)
- ISO 19011:2018 (Auditing management system guidelines)
- ISO 26000:2010 (Social responsibility guide)
- ISO 31000:2018 (Risk management guide)
Annex L Annex L (formerly Annex SL) is the 10-part structure that specifies how ISO management system standards should be written.
The goal of Annex L is to encourage unity and consistency within the MSS. ISO is currently updating its standards with this structure, and eventually all standards will share this core structure to make integration and interoperability more streamlined.
The Annex L MSS structure is as follows:
- Normative references
- Terms and definitions
- Context of the organisation
Performance evaluation
Improvement, anatomy of iso 9001:2015 for quality management.
In 2015, ISO 9001 was revised to be more agile and have the ability to adapt to any organizational environment.
As the most famous standard, ISO 9001 is always under revision, but currently, ISO 9001:2015 is the most recent version.
The review cycle is typically every four years, at which point ISO will assess whether or not any given standard needs to be updated. If no updates are deemed necessary, the current standard will be renewed.
What is ISO 9001:2015 (Current Version)?
ISO 9001:2015 is the most recent version of the ISO 9001 standard which specifies requirements for companies to follow in order to build and maintain their QMSs and attain ISO 9001 certification.
Some changes between the current (2015) and previous (2008) included:
- Integration of the Annex L structure for more consistency with other ISO standards (ISO 45001, ISO 14001, etc.)
- Strengthening the connection between companies and their QMSs
- Less binding requirements compared to the previous version to promote more agility
- Greater emphasis on customer satisfaction
- More simplified terminology throughout the text for better accessibility
- Promotion of a process approach for achieving better quality results
- Newly established requirements for quality performance for use during company planning stages
- An emphasis on top managers to take the reins on their QMS
So what does ISO 9001 look like, exactly?
In the newest version of the ISO 9001 standard, it was structured following the Annex L MSS and broken up into 10 sections. The first three sections serve as introductions and the following seven sections offer the main core principles of ISO 9001.
The main seven sections include:
Context of the organization

The context of the organization section established the requirement that the organization should take time to evaluate itself and its place in the industry.
The means the organization must take note of information, such as: organization influences, how the influences manifest in their QMS, the company culture, its goals, the organization’s size, its market and customer base, etc. It’s also important to record any potential business risks.
The leadership section requires that top-level management take the lead in implementing their QMS.
Top managers must show a commitment to the success of the QMS by performing tasks, such as: developing and applying a quality policy, assigning employee responsibilities at all levels of the organization, and emphasizing the importance of customer satisfaction .
The top-level management is also required to develop plans for the ongoing maintenance of the QMS.
They should assess any risks and possibilities regarding the QMS and identify quality goals and later create the strategy plans needed to reach these goals.
The support section includes various requirements centered around resource management for the company’s QMS.
It encompasses things like employee awareness, human resources, company-wide communication, the monitoring of assets and resources, infrastructure, employee competence, and the handling of all records needed for company processes.
The operation section’s requirements focus on the development and production of the company’s product or service.
It includes requirements on: initial planning stages, product design, manufacturing , supplying the product/service, managing nonconforming products.
The performance section covers the requirements necessary to ensure that there is an effective monitoring system in place for the company’s QMS.
This system should allow for top management to easily monitor and assess company processes, measure customer satisfaction, perform internal audits , and provide regular QMS reviews to make sure everything is running smoothly and efficiently .
The improvement section is the last section and it includes the requirements necessary to improve the company’s QMS as time goes on. Top management should review and evaluate any process nonconformity and develop solutions for these processes.
Quality management can be summarized as the process necessary to ensure that a company’s products and services are consistently up to quality standards.
Quality management is composed of four components:
1. Quality planning The planning component covers the process of defining your product/service’s quality standards and determining how to meet these standards.
2. Quality improvement The improvement component involves the optimization of your company processes to better help achieve quality standards.
3. Quality control The control component emphasizes the importance of regular maintenance of your company’s quality standards to ensure ongoing quality consistency.
4. Quality assurance And the final assurance component includes any actions necessary to determine whether the system you have in place is providing consistent product/service quality.
What is a quality management system (QMS)?

A quality management system (QMS) is a set of standards and procedures that define the rules that determine how your organization will produce and provide your product or service to the customers.
While every organization’s QMS should be written specifically to meet their own needs, following the ISO 9001 standard provides a strong foundation for the QMS, making sure that nothing important is overlooked.
Benefits of a quality management system
A strong and reliable quality management system can offer organizations many benefits, such as:
- Boosting product efficiency
- Minimizing excessive waste (materials, profit, time, etc.)
- Greater customer satisfaction
- More effective marketing
- Faster and more reliable employee onboarding
- More efficient growth management
- Continuous improvement of products, services, and processes
- Better product/service quality consistency
Key principles of a QMS

All of the ISO standards related to quality management are based on these seven quality management principles:
- Practicing a truly customer-driven approach when manufacturing and selling your product
- Top level management must commit to providing quality
- All company employees should be involved in the achievement of quality
- Quality standards should be met using a process driven approach
- Company decisions should be made based on evidence
- An ongoing commitment to continuous improvement of quality
- Open communication and good relationships between suppliers and customers
Utilizing all of these QMS principles is central to developing a reliable system for your company that meets general ISO objectives.
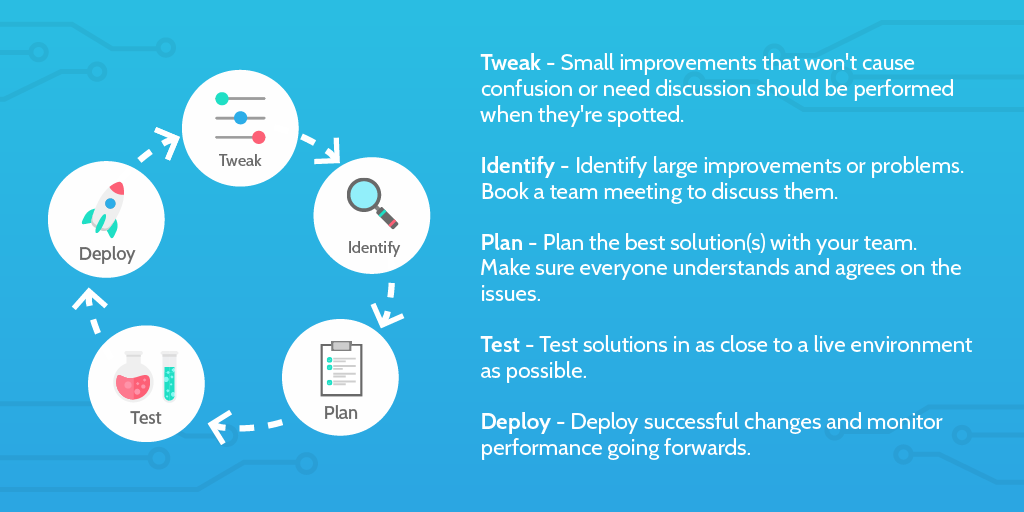
Continuous improvement can be defined as a perpetual effort to make improvements to your company’s products/services and processes.
There are generally two types of continuous improvement efforts:
- Gradual, also known as “incremental”, improvement over a period of time
- “Breakthrough” improvement, that takes place all at once.
When a company practices continuous improvement, they are constantly self-evaluating their ability to satisfy their customers and looking for ways to improve and perform more efficiently overall.
Continuous improvement is one of the key components of the ISO 9001 QMS. The ISO 9001 standard requires that all feedback is regularly reviewed and weighed against the company goals.
Understanding continuous improvement
As mentioned above, continuous improvement is typically categorized into two types: incremental and breakthrough improvements. The best way to implement continuous improvement would be to utilize both types of improvements so that you’re able to deal with more trivial problems and also tackle the larger issues your company may be dealing with.
Incremental improvement Incremental improvements involve continuously tweaking your company’s processes in order to make small improvements along the way.
These improvements are typically lower in cost and faster than breakthrough improvements, but there are some risks involved when making incremental improvements. This is because incremental improvements don’t call for reviewing entire operations, and it’s possible that some small changes could result in bigger consequences afterward.
Breakthrough improvement Breakthrough improvements refer to making larger changes to your company’s processes. This is typically done by assessing the company issue with your team and together deciding on the solution.
These improvements usually involve more time and money spent than its incremental counterpart, but result in more significant and worthwhile improvements at the end of the day. Breakthrough improvements can sometimes be necessary to make, for example, in companies where their systems in place are outdated or slow and may need a total revamp.
Though it may take longer than simply making the necessary changes yourself, involving your team in the process ensures that everyone is on the same page and the transition is seamless.
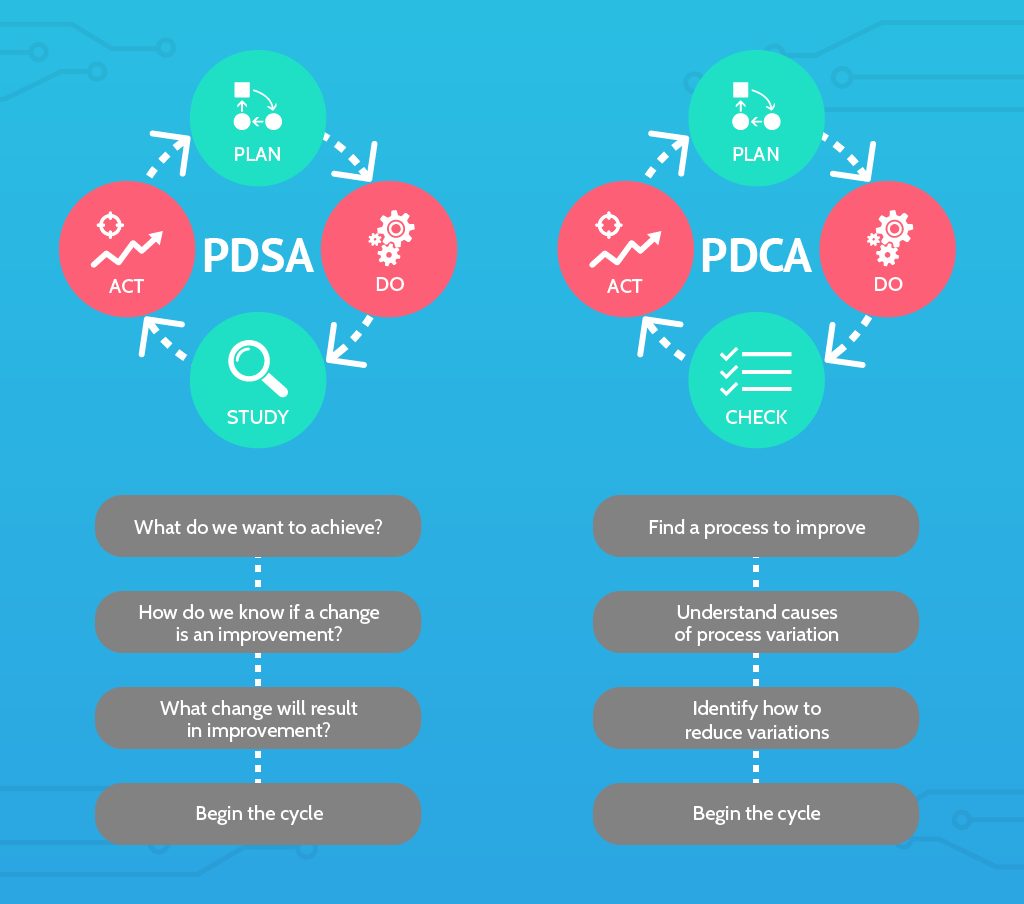
ISO 9001 was developed based on the plan-do-check-act (PDCA) methodology, AKA plan-do-study-act (PDSA). This methodology encourages a more process-oriented approach when recording and assessing company processes to achieve a reliable QMS.
Some topics covered in this methodology include:
- Specific QMS requirements
- Management responsibilities
- Resource management
- The process of developing, manufacturing, and releasing products
- Methods of QMS improvement, such as, performing internal audits and practicing corrective actions
Plan The first step of the PDSA methodology entails figuring out what your goals are and deciding what needs to be done to achieve those goals.
This step could involve tasks like:
- Figuring out what “quality” means for you and your company
- Assessing how your company is structured and how that influences quality
- Defining a concise quality policy
- Developing your QMS goals
- Understanding what processes need to be involved and how they will work
- Assessing any potential risks within your QMS
- Outlining a plan for continuous improvement
Do The second step for this methodology involves putting all the plans you made in the last step into action.
It’s important to make sure that you’ve documented and planned through any new processes before moving forward. This is so that it’s easiest for you and your team to follow and can help figure out what exactly went wrong if something does go wrong.
Study/Check This next step can only take place once all of your new processes have been set into motion. It involves closely monitoring them and determining what is and isn’t working well.
You’ll need to record all of your findings and organize them in a manner that can easily show others how your new processes are performing. It’s important to keep in mind the importance of practicing open communicating and transparency when building your QMS.
Act For the final step of the PDSA methodology, you’ll need to assess all of the recorded information from the previous step and apply corrective changes.
The goal is to perfect your company processes until they’re running effectively and efficiently. This step also involves adopting the philosophy of continuous improvement to monitor and assess all your company processes to determine whether they can be improved and how, even if they seem fine.

Other frameworks for continuous improvement
There have been many tools and systems developed over the years to help companies improve their processes. These frameworks are built so that management doesn’t have to spend unnecessary time and effort developing their own from scratch and can instead, just get started. These tools also allow them to take what has been already proven effective by others and apply it to their own company for the best chances of positive outcomes.
Some of the most famous frameworks for continuous improvement, apart from the PDSA methodology, include:
- Gemba walks
- 5 why’s
Gemba walks Gemba walks is unique in that it focuses on the value of a company’s employees.
It’s rooted in the idea that some of the most original ideas for improvement come from front line employees who are working with the flawed processes on a daily basis. This first-hand experience with their processes means that the employees gain a deeper understanding of their effectiveness and are able to offer real solutions.
Gemba walks encourage more open communication and informal interactions between management and staff at the location where they work, rather than a designated meeting room. This allows for management to observe company processes first-hand and in turn, gain a better understanding of how things are working.
This method was specifically developed to effectively gather feedback and allow management to access their employees’ experience on the floor. Gemba walks don’t provide a framework for how to utilize this feedback though, so it’s best used in combination with other methods.
5 why’s The 5 why’s framework was designed to pinpoint the root cause of issues companies may be struggling with. It allows managers to be able to see past the symptoms and actually recognizes the deeper source of the issue, simply by asking ‘why’ multiple times in a row.
This technique makes it simpler to actually address issues and helps minimize superficial conflict, such as employees passing blame around. It enables management to identify cause and effect relationships and is an easy tool to implement because there’s no real need for in-depth data analysis.
But, the 5 why’s method is also not an all-encompassing solution. It can help identify the root issues, but doesn’t offer much beyond that. So as with gemba walks, this method is best used when in combination with other frameworks.
3Ms (Muri, Mura, and Muda) The 3Ms framework refers to three different categories of underlying issues that typically are the cause of problems for businesses.
The 3Ms stand for three Japanese words that can be translated to mean:
- Muri – an overwhelmed feeling caused by insufficient resources, an excessive removal of waste, and lack of planning.
- Mura – misconduct or instability that can be the root cause of ‘muda’ waste problems.
- Muda – general waste, such as: defected products, overproduction of products, excessive fuel use, or even wasted employee time.
This framework is one of the most effective tools for tackling the deeply rooted issues that cause excessive waste. It encourages the implementation of lean manufacturing, which means identifying what truly provides value for the customer and getting rid of anything that doesn’t.
Working through the 3M’s sequentially is one of the most effective ways to apply this method. For example, beginning by identifying any instances of Muri in your company, sourcing Mura in your products to then reduce your company’s overall Muda.
Standard operating procedures (SOPs) can often be inefficient and clunky to follow, especially when using traditional paper SOPs. Because of this, ISO standards have recently made efforts to streamline these procedures by encouraging the implementation of digital SOPs.
The use of digital tools for SOPs allows for these processes to be much faster to follow and convenient to update if needed. It also makes it much easier for businesses to make sure their processes align with their goals and values because their QMS is merged into the business, rather than being just a side note.
And the most obvious of the benefits of a digital SOP tool is the convenience of storing company procedures and policies digitally, which inherently improves organization and overall communication.
Basic principles of agile ISO
The 12 basic principles presented in the Agile Manifesto are as follows:
- Regularly providing timely and quality work to achieve customer satisfaction
- Taking large work and breaking it down into manageable tasks
- Self-organization in teams is key to achieving high quality work
- Trusting and supporting driven employees to get the work done.
- Promoting sustainable outcomes within company processes.
- Working at a consistent pace in order to reliably complete work.
- Always accepting and anticipating changes in requirements.
- Holding daily meetings with top level management and the project team to maintain open communication.
- Allowing the team to provide feedback regularly and making adjustments to the processes accordingly.
- Monitoring the team’s progress by their finished work.
- Practicing continuous improvement
- Embracing change and utilizing it to gain a competitive advantage.
Agile is more of a school of thought than it is a methodology, so there isn’t an exact science to measuring whether or not a company is “true” agile.
Being agile can take many forms, as long as the agile principles are at the core. Upholding these principles is generally all that it means to be truly agile, so any framework that follows these values is fine to adopt and just as agile as the other.
Fake agile , however, is not truly abiding by the agile principles. It is a form of rebranding of the traditional, hierarchical structure in efforts to be more appealing, but it isn’t actually a well-performing process.
An example of this could be a team spending a significant amount of time and effort developing a number of working builds to later show to the customer and receive feedback, but as a result, this means much of their work will need to be either reworked or trashed to then start from scratch. This is because the customer wasn’t made much a part of their working progress as a truly agile company would have made them.
At the root, fake agile is a wasteful, inefficient process.
How Process Street fits in

A flexible team is key to achieving agility. They need to be self-reliant and organized, without the need for a strict and unwavering company structure. One way to improve your team’s agility is to implement a BPM tool like Process Street to give your team more independence and control over their own processes.
Process Street is all about streamlining your company’s processes by using super-powered checklists to effectively and simply communicate your processes to any of your team members . This means that, for example, you’d simply create a single checklist with all the necessary information and instructions and be able to easily share it with everyone on your team to ensure open and clear communication.
It’s also very easy to quickly edit your checklists whenever necessary, with our template editor tool. Using a BPM software makes following processes more efficient and consistent, and allows for your team to take control of their own processes.
Here’s a great introduction video to Process Street’s capabilities:
And if you’d like to read more about the agile methodology, here are some more resources on the subject:
- What is Task Management? 3 Proven Methods Explained
- Agile ISO: How to Combine Compliance with Rapid Process Improvement
- What Continuous Improvement Is (and How to Use It)
- The Complete Guide to Business Process Management
- Agile ISO: A Holistic Business Process Management Framework
- The 11 Agile Processes We Use to Run an Efficient Software Team
- Get More Done: The Complete Introduction to Task Management
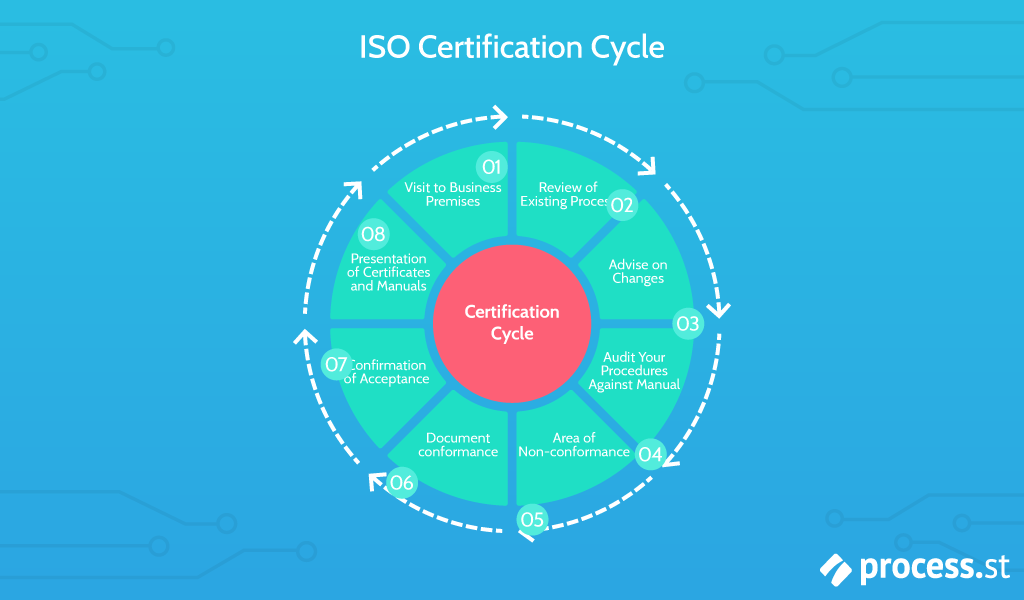
When an organization is “ISO 9001 certified”, it means they have met the ISO 9001 QMS requirements.
It’s fairly common to hear the term “ISO certified” being thrown around, but it’s not exactly accurate. This is because ISO 9001 is the only standard within the ISO 9000 family of standards that actually requires certification, so the correct terminology would be “ISO 9001 certified”.
An ISO 9001 certification is usually attained by entire companies, but could also be adjusted for specific departments within companies. It’s also open to companies of any size and industry sector and is internationally recognized as a valuable QMS standard.
Do I need to be ISO 9001 certified?
The short answer is no, you don’t need to be officially certified.
But it doesn’t hurt.
As mentioned earlier, the ISO 9001 standard is internationally recognized for developing, applying, and enhancing the QMS for organizations and companies of any industry or size.
The standard is honored as the foundation for any organization to build a QMS that guarantees customer satisfaction and overall quality improvement, and because of this, many companies require an ISO certification from their potential suppliers to ensure they’ll meet quality standards.
An ISO 9001 certification has become almost a necessity for companies and organizations to succeed in a competitive market, because obtaining that certification means your organization has gone through several auditing processes, and your customers wouldn’t need to audit your organization themselves. They can rest assured that your QMS is strong and dependable because it follows the seven quality management principles of ISO 9001.
Let’s talk about ISO 9001 certification
When achieving ISO 9001 certification, you should make clear what your goals are and what benefits your company will gain by achieving this certification, and be ready to implement your improved QMS into all aspects of your business.
You should also make efforts to communicate with your team what their new expectations and responsibilities will be, when implementing the changes necessary to achieve ISO 9001 certification.
In order to attain certification, ISO 9001 requires you to document your QMS.
The documentation should include:
- General company structure
- Name of the individual tasked with recording information and what kind of information will be recorded
- Employee responsibilities
- Company’s framework for internal communication
- Required actions
- System in place for maintaining workflow in the event that valuable staff leave the company
Defining your QMS
In order to define your company’s QMS, you’ll need to compile feedback from every department.
You should:
- Identify the customer base for each department.
- List the tasks involved in each department.
- Look over the ISO 9001 standard and assess whether the requirements have been met.
- Take note of any issues and address them.
Management of documents and records
A reliable and strict system for managing your documents is an important part of ISO 9001. It will be necessary to communicate with your team the significance of practicing proper record-keeping and following this new system.
Your record-keeping system should make sure that any old versions of procedures and policies are replaced with their updated versions and sent to all of the appropriate departments.
When establishing this new system, you should figure out what records should be kept to meet ISO 9001 requirements and which your company needs to achieve success.
Preventive and corrective actions
There are no perfect processes, but you can take measures to mitigate any damage from potential mistakes.
You should take time to carefully review your processes and identify any potential problem areas and then, develop preventive and corrective systems for each potential issue to minimize consequence or hopefully, just nip them in the bud.
Regular staff training
Though it may seem obvious, your staff needs to be properly trained in order to perform well at their job. You should also keep a record for each of your employees, including information such as, previous education, experience, and on-the-job training. This makes it easy to refer back to when deciding what tasks are appropriate to assign to your team members.
This documented information also makes it easier to spot any gaps in experience within your team and allows for better consistency of work overall.
Recurring internal quality audits
Performing regular internal quality audits of your QMS is a requirement for the ISO 9001 certification. These audits can be performed by anyone within your company, as long as they’re not directly involved with the department being audited.
You should develop a specific procedure for how internal audits are performed, including the planning stage, how it should be carried out, and documented. The auditor should then refer to this procedure when performing the audit to ensure accuracy and consistency of results.
ISO 9001 audit: Quick rundown
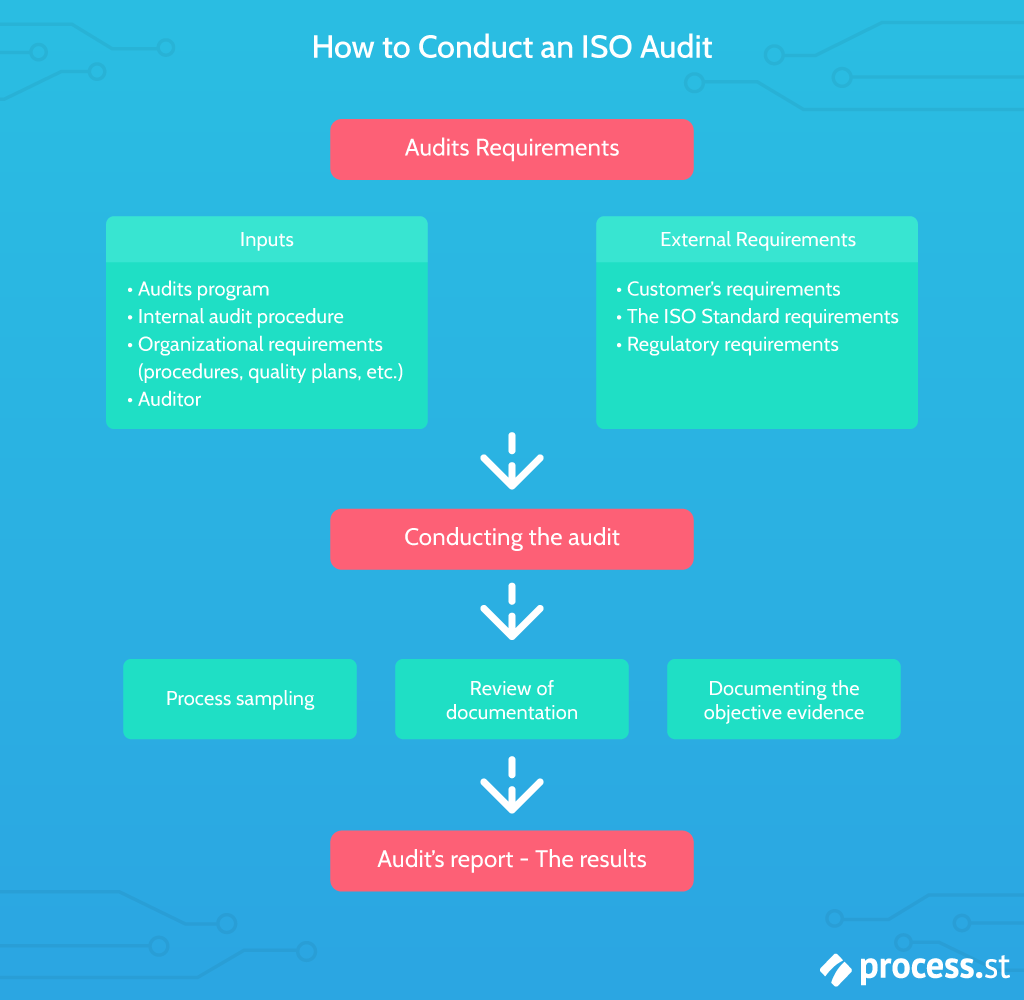
Apart from the internal quality audit, ISO 9001 also requires regular external audits in order to achieve certification.
ISO 9001 audits should help you:
- Make sure your QMS is in line with the ISO 9001 standard
- Pinpoint any problems with your QMS and solve them
- Offer new ideas for improvements to your QMS
- Make sure your company is continuing meeting quality standards
What is an ISO audit?
Simply put, an ISO audit is a systematic and objective procedure designed to gather and record feedback. These audits are performed to help bring to light any problem areas within your QMS and make sure you have the data necessary to make improvements.
As you know, one of the key requirements of ISO 9001 is the practice of continuous improvement, so it’s important to perform these internal and external audits regularly.
Different types of ISO 9001 audit

ISO 9001 internal audits Internal audits, or first-party audits, are performed by an internal team member to establish whether or not a company’s QMS complies with the ISO 9001 standard requirements, as well as other company policies.
These audits should be objective, unbiased, and conducted following your company’s pre-established internal audit procedures. The auditor should review your company’s processes and policies and determine whether they comply with what’s been recorded within your company’s QMS.
Usually, checklists are used by auditors to help ensure consistency from audit to audit and allow for them to quickly and easily assess how well the company processes align with their QMS standards.
The audit results should be recorded and reviewed as a team regularly throughout the year, so that everyone can be kept on the same page and solutions to any issues found can be brainstormed together as a team.
ISO 9001 external audits Rather than using a company employee, external audits are conducted by a third-party auditor (or team of auditors) who are sent by your organisation’s ISO 9001 registrar.
As with internal audits, these audits are used to ensure that your QMS complies with the ISO 9001 standard and is running smoothly, but guarantees a level of objectivity based on the fact that the auditor is from a third-party source. This then allows your registrar to provide you with your ISO 9001 certification.
Process Street makes following processes easy. With an intuitive, no-code editor, your employees will have no trouble building and managing their recurring processes.
All it takes is creating a template, and then simply running a checklist from those templates. You can think of templates as the process sketch, and the checklist as the finished, working process.
In order to use Process Street for ISO 9001 compliance, you’ll need to:
1. Build your Process Street processes Decide on which processes you and your team use, and simply have each employee build their own processes themselves within the software. This way, they’ll gain a sense of ownership over their processes and customize them to their own particular needs. Start simple, and work your way up to more complex processes as time goes on.
2. Organize your folder library Make use of folders , subfolders, and tags to keep track of all of your processes and keep it easy to access. We have a great post on process libraries that might help inspire some ideas for your own setup. You can also use our Permissions feature to protect any sensitive information and easily move your employee processes into their corresponding folders.
3. Design your meta-processes Meta-processes involve creating processes to help manage other processes. This can be for things like how to build new processes, processes for optimizing other processes, or processes for assessing risk.
Some examples of meta-processes are:
- FMEA Template: Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
- The Process for Optimizing a Process
4. Record your company policies The quickest and most effective way to do this is by jotting down a straightforward structure with information such as, Context of the Company, Support, Operations, etc. and then ask your team for feedback on it.
5. Create your official document Your Process Street process library will have a folder in which you can keep track of your policy templates. These templates probably won’t be run as checklists, but it’s good practice to keep everything organized in a single system. You’re able to easily export templates and checklists to PDF, if you also would like to keep a physical copy of these processes.
And that’s all it takes to get started using Process Street for ISO!
There’s no need to have to make physical updates to your procedure and policy documents every time you make a small change. You can make these changes quickly by editing your processes and creating improved versions that are easy to use and distribute.

ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 Integrated Management System (IMS) Checklist
This ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 Integrated Management System (IMS) Checklist was built to streamline the process of merging your existing EMS and QMS procedures into a single document.
It will keep you from having to do more work than necessary and allow you to ensure that your policies are in line with your environmental objectives while maintaining a synergistic relationship between the two systems.
This template provides you with a strong foundation to get started integrating your systems, as well as clear steps to follow in order to complete your IMS.
As ISO’s most recognized standard, ISO 9001 offers the framework for building, maintaining, and optimizing quality management systems.
This ISO 9001 Internal Audit Checklist for Quality Management Systems template was built to use as a supplement when conducting internal ISO 9001 audits, to make sure all of the basic requirements are being met and all necessary information is being recorded.
Conducting a self-audit can help to pinpoint any potential problem areas in your management systems and offer objective perspective, while also maintaining sights on company goals and standards.
This ISO 9004:2018 Self-Audit Checklist was built to strengthen the self-auditing process and ensure it complies with ISO 9004:2018 standards. It provides a jumping off point for making improvements to your QMS based on ISO 9004 principles.
More ISO 9001 resources
Here are some more ISO and standard operating procedure related resources if you’re interested in reading more:
- ISO 26000 for Corporate Social Responsibility: How to Get Started
- 20 Free SOP Templates to Make Recording Processes Quick and Painless
- What is an ISO Audit? Free ISO 9000 Self-Audit Checklist (ISO 9004:2018)
- How to Write an Actionable Policy and Procedure Template (ISO Compliant!)
- What is Quality Management? The Definitive QMS Guide (Free ISO 9001 Template)
- What is ISO 9001 Certification? How to Get Certified (For Beginners)
- Processes, Policies and Procedures: Important Distinctions to Systemize Your Business
And here are some our other ISO checklists we’ve built:
- ISO 27001 Information Security Management System (ISO 27K ISMS) Audit Checklist
- ISO 14001 Environmental Management Self Audit Checklist
- SWOT Analysis Template
- ISO 19011 Management Systems Audit Checklist
- ISO 14001 EMS Structure Template
- ISO 14001 EMS Mini-Manual Procedures
- ISO 45001 Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) Audit Checklist
- ISO 26000 Social Responsibility Performance Assessment Checklist
ISO 14001 for Environmental Management
Out of the 14000 family of standards, ISO 14001 is the most well known and establishes the requirements and principles for an efficient and effective environmental management system (EMS).
So, in a way, it’s comparable to the ISO 9001 standard, but instead of focusing on quality management, it focuses on requirements for environmental management.
This ISO 14001 EMS Structure Template was specifically designed to help you build and utilize SOPs for EMS that comply with ISO 14001 standard.
It offers concise, step-by-step instructions for working through each ISO 14001 section and when finished, you’ll have the ability to export your document as a PDF to keep everything organized.
Here are a few other articles we’ve written regarding ISO 14001:
- 5 Free ISO 14001 Checklist Templates for Environmental Management
- What is Environmental Management? How You Can Implement it Today
ISO 19011 for Management System Audits
Unlike ISO 9001, you can’t get an ISO 19011 certification because it isn’t a set of requirements.
ISO 19011 offers guidelines designed to help organizations build audit programs to then use to audit management systems such as, QMS, EMS, etc.
This ISO 19011:2018 Checklist for Auditing Management Systems template was created to help guide auditors through the internal audit process for ISO management systems, including:
- ISO 9001:2015 (quality management systems)
- ISO 14001:2015 ( environmental management systems )
- ISO 27001:2013 (information security management systems)
- ISO 45001:2018 (occupational health and safety management systems)
How are you implementing ISO 9001 in your company? Do you consider yourself agile? Let us know in the comments below! We’d love to feature you in an upcoming article.
Get our posts & product updates earlier by simply subscribing
Oliver Peterson
Oliver Peterson is a content writer for Process Street with an interest in systems and processes, attempting to use them as tools for taking apart problems and gaining insight into building robust, lasting solutions.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Take control of your workflows today
For those planning training sessions or candidates intending to take an online exam during this period, we will be offering online exam sessions on December 27 and 29, as well as January 5, 2024. You can check the link to online exam events here .
An online learning platform offering expert-led video capsules and certificate programs to unlock a world of knowledge.
A gathering of professionals and experts who discuss on the latest trends and topics
An authentic source of information and inspiration
Online store for ISO and IEC standards, Toolkits, eBooks, etc.
- / Resources
ISO 9001 Implementation: A Step-by-Step Guide

ISO 9001 is a globally recognized standard that specifies the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving a Quality Management System (QMS) in any organization.
ISO 9001 helps organizations consistently provide products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements. It is based on seven quality management principles , and it aims to help organizations be more efficient, monitor and improve processes, reduce costs, and increase customer satisfaction.
The seven quality management principles are:
- Customer focus
- Engagement of people
- Process approach
- Improvement
- Evidence-based decision-making
- Relationship management

This standard’s operating principle is the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle which is a quality management methodology that aims to continuously improve processes.
An Overview of ISO 9001:2015
ISO 9001:2015 is the final edition of ISO 9001. This version was last reviewed and confirmed in 2021 and remains current.
ISO 9001’s first three clauses are introductory:
- Clause 1: Scope
- Clause 2: Normative references
- Clause 3: Terms and definitions
The remaining are as follows:
Clause 4: Context of the Organization
Organizations should analyze and determine relevant internal and external factors which affect their strategies, objectives, and results.
This clause involves:
- Defining the scope of the QMS
- Considering the organizations’ strategic objectives
- Main products and services, risk tolerance, and any regulatory
- Contractual or stakeholder obligations.
Clause 5: Leadership
Leadership and commitment are two important traits that should be demonstrated by the top management, who are mainly responsible to:
- Taking accountability for the effectiveness of the QMS
- Ensuring the compatibility of the QMS within the context of the organization
- Communicating the process within the organization and making sure it is understood and applied
- Integrating the QMS requirements into the organization’s processes
- Assigning roles and responsibilities and also directing and supporting staff to contribute to the QMS
Clause 6: Planning for the Quality Management System
Organizations should establish strategic objectives and guiding principles for the overall QMS process. Clause 6 of ISO 9001 outlines the requirements for planning the QMS of organizations. It covers more on the actions to address risks and opportunities, quality objectives and how to achieve them, and the needed changes.
Clause 7: Support
In order to function, organizations need various resources such as people, equipment, infrastructure, etc. In this clause, requirements specifically cover the resources, competence, awareness, communication, and documented information.
Clause 8: Operation
This clause is concerned with the phase when organizations put into operation the planned QMS. It includes:
- Operational planning and control
- Determination of requirements for products and services
- Design and development of products and services
- Control of externally provided products and services
- Production and service provision
- Release of products and services
- Control of nonconforming process outputs, products, and services
Clause 9: Performance Evaluation
The primary purpose of this clause is to establish a system of monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation of the QMS's performance. It requires permanent monitoring of the system.
Clause 10: Improvement
This clause includes identifying and implementing changes needed to improve the process and meet customer requirements. Management systems can be continually improved by using quality policies, objectives, and audit results, monitoring of events, indicators, risk analysis, corrective actions, and management reviews.

How to Implement ISO 9001
The key implementation steps of ISO 9001 are:

Step 1 – Seek Senior Management Support
The implementation of ISO 9001 requires the support and commitment of senior management and their active involvement in the process. They need to understand the benefits of ISO 9001 and then allocate the necessary resources for its implementation.
Step 2 – Understand the Requirements of ISO 9001
Before implementing the ISO 9001 standard, it is important to get familiar with the standard, understand its requirements, and learn its basic structure, principles, and concepts. Implementers need to read the standard, review the requirements of the ten sections, which cover different aspects of a quality management system, and identify the requirements that apply to your organization. Understanding the requirements of the standard is crucial for a successful implementation.
Step 3 – Conduct a Gap Analysis
Once there is an understanding of the requirements of ISO 9001, the next step is to identify the gaps between your organization's current practices and ISO 9001 requirements. Organizations should develop an action plan to address the gaps, and they should define roles and responsibilities for implementing the action plan. The gap analysis will help to identify the areas where your organization needs to improve to meet the standard.
Step 4 – Establish a Quality Management System
Establishing a QMS requires a structured and systematic approach and involves several actions. To establish a QMS, organizations need to identify the key responsibilities within the organization and determine roles among the staff.
The next step is to develop policies, procedures, and strategies, which will guide the implementation and creation of documents such as the quality manual. Furthermore, organizations should also establish measurable specific objectives, which should be communicated to all employees and should regularly be tracked.
Step 5 – Implement the Quality Management System
Organizations should implement a QMS based on the policies, plans, and objectives established previously. They should carefully follow all the requirements and implement all the necessary activities.
Step 6 – Monitor and Measure Performance
To ensure that your quality management system is effective, organizations need to monitor and measure its performance, which can be done through established metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs). They should monitor and measure the performance of the processes, products, and services and conduct internal audits to identify areas where your organization can improve.
Step 7 – Seek for Certification
The ISO 9001 certification process can be initiated once the QMS has been operational for three or six months. The organization's QMS should first be evaluated by an accredited auditor. If everything has been successfully implemented in accordance with all ISO 9001 requirements and effective thus far, the organization will be granted the ISO 9001 certification.
Step 8 – Continuously Improve the Quality Management System
Continually analyze the results of monitoring and measurement activities to identify opportunities for improvement. Implement corrective and preventive actions to address issues and prevent them from occurring in the future. Continuously improve your quality management system to ensure that it remains effective.
Challenges of ISO 9001 Implementation
Implementing ISO 9001 can be a challenging process, especially if organizations face difficulties such as:
- Resistance to change
- Lack of management commitment
- Limited resources
- Lack of awareness and understanding
- Lack of competency
- Poor design and development process
- Insufficient documentation
- Inadequate team support
Training and Certification of Professionals
PECB training courses are tailored to increase the skills and expertise of professionals and help overcome challenges that may come up when implementing ISO 9001.
PECB offers four ISO 9001 Quality Management training courses:
- ISO 9001 Introduction
- ISO 9001 Foundation
- ISO 9001 Lead Implementer
- ISO 9001 Lead Auditor
About the Author
Vlerë Hyseni is the Digital Content Officer at PECB. She is in charge of doing research, creating, and developing digital content for a variety of industries. If you have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact her at: [email protected] .
- Quality Management System
- Health, Safety, and Environment
- Continuity, Resilience, and Service Management
- Information Security Management
- Risk and Management
- IT Security
- Governance, Risk, and Compliance
- Transportation, Telecom, and Energy
- Cybersecurity
- Sustainability
- Privacy and Data Protection
- Digital Transformation
Latest Articles
Applying iso/iec 27001 in the telecommunications industry.

AI Under Watch: The EU AI Act

What is Risk Mitigation and Why is it Important?

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER
Training & Certification
- Ethical Hacking
- Training Course Catalog
- Territory Management
Examination
- Exam Rules and Policies
- Online Exam Manual
- Invigilator Guide
- Candidate Handbooks
Certification
- Certification Rules and Policies
- Certification Maintenance
- Certificate Verification
- Master Credentials
- Leadership, Committees and Advisory Boards
- PECB Code of Ethics
- Affiliations
Terms, Conditions, and Policies | Privacy Statement | Cookie Preferences
© 2024 Professional Evaluation and Certification Board. All rights reserved.

ISO 9001 Explained: A Comprehensive Guide to Quality Management Systems
Table Of Contents:
- 1) What is ISO 9001?
- 2) What is a Quality Management System (QMS)?
- 3) Core Principles of ISO 9001
- 4) The Structure of ISO 9001
- 5) The Certification Process
- 6) Who Uses ISO 9001?
- 7) Benefits of ISO 9001 Certification
- 8) Common Misconceptions about ISO 9001
- 9) Best Practices for Implementing ISO 9001
- 10) Conclusion: The Power of ISO 9001
- 11) Additional Resources:
ISO 9001 has become the quintessential international standard for quality management systems. Adopted by over 1 million global organisations, certification helps companies streamline operations, boost customer satisfaction, and align processes with strategic objectives, laying down a framework that ensures a brand’s products or services meet and often exceed customer and regulatory benchmarks.
However, ISO 9001 is complex, particularly for first-time adopters. This blog provides an executive overview of the critical things decision-makers need to know before starting the certification path. We delve deeper into the intricacies of the ISO 9001 certification, highlighting its relevance, importance, and approach to attaining it.
What is ISO 9001?
Let’s start with what ISO 9001 is. At its heart, it is an international standard published by the International Organization for Standardization that outlines requirements for a comprehensive quality management system (QMS). It helps organisations establish policies and objectives that meet customer needs and improve overall performance.
The current iteration is ISO 9001:2015, which emphasises risk-based thinking to enhance results. Fundamental principles include customer focus, process approach, improvement, evidence-based decision-making, and relationship management.
What is a Quality Management System (QMS)?
But let’s take a step back. What exactly is a Quality Management System (QMS)? Well, it’s a formalised set of policies, processes, procedures, and responsibilities that an organisation establishes to ensure its products or services meet the required quality standards. It acts as a framework that guides and directs an organisation to achieve and maintain consistent product quality, resulting in enhanced customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
Core Components of a QMS
- Policy and Objective Setting: The organisation defines its quality policy—a statement of intent regarding its commitment to quality—and sets measurable objectives based on this policy.
- Processes and Procedures: The organisation establishes standardised processes and procedures to ensure tasks and activities are carried out consistently, leading to predictable outcomes.
- Document Control: Documentation, whether in manuals, records, or electronic files, is controlled to ensure accuracy, relevance, and accessibility.
- Resource Management: Resources, including human resources, infrastructure, and the work environment, are managed to ensure they can support the delivery of quality products or services.
- Product Realisation: All steps from design and development to product or service delivery are managed to ensure they meet quality criteria and customer requirements.
- Measurement, Analysis, and Improvement: The organisation sets up mechanisms to measure and analyse various metrics (like customer satisfaction or product conformity) and implements corrective actions if deviations are detected.
- Continuous Improvement: Based on data, feedback, and analysis, the QMS promotes a culture of continuous improvement, refining processes and methodologies over time.
Core Principles of ISO 9001
The ISO 9001 standard is underpinned by seven Quality Management Principles (QMPs). These principles provide a foundational framework that guides organisations in pursuing improved performance and enhanced customer satisfaction. They are universally applicable regardless of the organisation’s size, type, or nature of its products or services. Here’s an overview of the seven QMPs:
Customer Focus:
- Essence: Understand and meet customer requirements and strive to exceed their expectations.
- Benefits: Increased customer value, loyalty, and repeat business.
Leadership:
- Essence: Establish a clear vision, direction, and an environment encouraging employee engagement.
- Benefits: Direction and purpose are more clearly set, resulting in improved alignment and better coordination of the organisation’s objectives.
Engagement of People:
- Essence: Ensure that people at all levels are competent, empowered, and engaged in delivering value.
- Benefits: Improved understanding of responsibilities and roles, increased motivation, and greater involvement in improving the processes.
Process Approach:
- Essence: Consistent and predictable results are achieved more efficiently when activities are understood and managed as interrelated processes that function as a coherent system.
- Benefits: Improved performance through optimised capabilities of processes, efficient use of resources, and reduced cross-functional barriers.
Improvement:
- Essence: Organisations should consistently focus on improvement to maintain current performance and react to changes in the internal and external environment.
- Benefits: Improved performance, organisational agility, and enhanced ability to identify opportunities for change and innovation.
Evidence-Based Decision Making:
- Essence: Decisions are more reliable when based on data and analysis rather than gut feelings or intuition.
- Benefits: Improved decision-making, better assessment of process performance, and greater ability to demonstrate the effectiveness of past decisions.
Relationship Management:
- Essence: Manage relationships with relevant stakeholders, such as suppliers, to create sustained success.
- Benefits: Enhanced performance of the organisation and its stakeholders, better management of shared value across the supply chain.
These principles are interrelated and should be considered comprehensively rather than in isolation. Adopting the mindset and methodologies they represent helps organisations consistently deliver value to their customers and other stakeholders, promoting a culture of continuous improvement and operational excellence.
The Structure of ISO 9001
ISO 9001 has been designed to integrate seamlessly with other management system standards, thanks to its ‘High-Level Structure’ (HLS). Let’s break down its structure and delve into its key components.
The High-Level Structure (HLS)
The introduction of the HLS, or Annex SL as it’s otherwise known, was a game-changer for the ISO suite of standards. This common structure, introduced in recent iterations of ISO 9001, facilitates integration with other ISO management system standards like ISO 27001 (Information Security Management Systems) and ISO 22301 (Business Continuity Management Systems).
Features of HLS:
- Unified Structure: The HLS provides a standardised 10-clause structure, making integration more streamlined.
- Common Text: The HLS has standardised core definitions and texts.
- Common Terms & Definitions: Shared vocabulary across the standards ensures clarity and consistency.
The primary motivation behind HLS is to provide a harmonised and integrated approach, especially for organisations seeking multi-standard certifications.
Key Clauses and Their Purpose
ISO 9001’s structure, aligned with the HLS, is segmented into ten clauses:
- Scope: Outlines the purpose and applicability of the QMS.
- Normative References: Any reference documents essential for the application of the standard.
- Terms and Definitions: Explains the specific terminology used within the standard.
- Context of the Organization: Requires the organisation to identify internal and external issues, interested parties, and the scope of the QMS.
- Leadership: Addresses top management’s roles and responsibilities, including establishing a quality policy and ensuring alignment with business strategy.
- Planning: Emphasises addressing risks and opportunities and planning for changes.
- Support: Deals with resources, competence, awareness, communication, and documented information.
- Operation: This clause encompasses operational planning and control, requirements for products and services, design, management of external providers, production, and service provisions.
- Performance Evaluation: Requires organisations to monitor, measure, analyse, and evaluate the QMS’s performance. It also covers management reviews.
- Improvement: Emphasises the importance of continuous improvement and guides organisations on handling non-conformities and taking corrective actions.
For an organisation to be ISO 9001 certified, it must meet the requisites laid out in several of the clauses:
- Quality Management System Requirements: This section underscores the need for a structured QMS, including documented information, processes, and their interactions.
- Management Responsibility: Top management must demonstrate its commitment to the QMS, setting and reviewing quality objectives and ensuring integration into the organisation’s processes.
- Resource Management: This part pertains to the personnel, infrastructure, and environment for the operation of processes, highlighting the importance of adequate resourcing.
- Product/Service Development: Emphasises the controlled conditions for creating and delivering products/services, ensuring they meet specification requirements.
- Production and Service Provisions: This section ensures that organisations consistently meet the criteria set for their products or services.
- Measurement, Analysis, and Improvement: Organisations must measure and analyse their performance, ensuring customer and regulatory requirements adherence. When discrepancies occur, corrective actions must be instituted.
ISO 9001’s structure, underscored by its High-Level Structure, ensures both comprehensive coverage of quality management principles and compatibility with other management system standards. Its systematic approach, requiring organisations to meet all its sections, emphasises quality throughout the organisation.
The Certification Process
Obtaining ISO 9001 certification requires careful planning and execution. The main steps are:
Pre-Audit to Identify Any Major Gaps:
Also known as a gap analysis, this initial step involves a preliminary review of the organisation’s existing Quality Management System (QMS) to identify areas that do not meet the requirements of the ISO 9001 standard.
- Pinpoint weaknesses or omissions in the QMS.
- Provide a clear roadmap for what must be addressed before the formal audit.
- Save time and resources in the long run by addressing significant issues early on.
Formal Audit by a Certification Body:
The formal audit is a detailed, structured assessment conducted by an accredited certification body. It usually unfolds in two stages:
Stage 1 – Readiness Review:
- Evaluate if the organisation’s documentation aligns with ISO 9001 requirements.
- Verifies if the organisation is ready for the Stage 2 audit.
- Typically reviews quality manuals, documented procedures, and company policies.
Stage 2 – Certification Audit:
- A thorough examination of the QMS’s effectiveness in practice.
- Assesses compliance with specified requirements and the successful deployment of the management system.
- Includes interviews, observations, and reviews of records to ensure the system does what the organisation says it does.
Any Necessary Corrective Actions:
Corrective actions must be taken if non-conformities or areas of concern are identified during the formal audit.
- Address and rectify the root causes of the identified issues.
- Demonstrate the organisation’s commitment to achieving and maintaining the standards set by ISO 9001.
- Ensure the efficacy and reliability of the QMS.
Final Review and Certification Decision:
Post the corrective actions, the certification body reviews the changes made and assesses their adequacy. If the organisation has successfully addressed all concerns:
- The certification body will grant the ISO 9001 certification.
- The organisation receives an official certificate, signalling its adherence to international quality standards.
Maintenance:
Certificates are valid for three years. However, it’s essential to note that holding an ISO 9001 certification isn’t a one-time achievement but a continuous commitment.
- Annual Surveillance Audits: These are periodic reviews conducted by the certification body to ensure that the organisation continues to comply with the standard. It is less extensive than the initial certification audit but still crucial to maintaining the certification.
In summary, obtaining an ISO 9001 certification is a systematic journey that underscores an organisation’s dedication to quality. By understanding and meticulously following the process, organisations can enhance their credibility, optimise their operations, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Who Uses ISO 9001?
ISO 9001 adoption spans industries and organisations of all types and sizes. Top adopters include manufacturing, construction, wholesale/retail, and professional services. Highly regulated sectors like aerospace, automotive , medical devices , and government also leverage ISO 9001 heavily.
ISO 9001 is designed to work for any organisation, regardless of size, industry, or sector. Over 1 million companies in over 170 countries have achieved certification.
Benefits of ISO 9001 Certification
ISO 9001 delivers a range of tangible and intangible benefits that can significantly impact an organisation’s bottom line, customer loyalty, and long-term success. According to ISO, ISO 9001 certification can lead to a 20% increase in productivity and a 50% reduction in errors. Other benefits include:
Improved Efficiency and Streamlined Operations:
- Holistic Approach: The ISO 9001 standards necessitate a process approach, which integrates multiple business activities, reducing silos and ensuring smoother operations.
- Elimination of Waste: Organisations can reduce waste by identifying redundancies and streamlining processes, thereby saving time and resources.
- Continual Improvement: A foundational tenet of ISO 9001, the focus on continuous improvement ensures that the organisation continually strives to refine its processes and methodologies.
Increased Customer Satisfaction and Retention:
- Consistency in Delivery: Adherence to standardised processes means that customers receive consistent quality, enhancing their overall experience.
- Feedback Mechanism: ISO 9001 requires processes for capturing customer feedback, leading to better responsiveness to customer needs and concerns.
- Trustworthiness: An ISO 9001-certified company is considered reliable, instilling customer confidence in the organisation’s commitment to quality.
Demonstrated Commitment to Quality Management:
- Internal Morale: Certification can boost morale, showing employees that their efforts align with internationally recognised standards.
- Stakeholder Confidence: Investors, partners, and other stakeholders gain assurance knowing that the organisation values and implements a systematic approach to quality.
Ability to Bid on Tenders Requiring Certification:
- Access to New Markets: Many public sector and large corporate contracts mandate ISO 9001 certification in their tendering processes. Thus, certification unlocks a broader spectrum of opportunities.
- Competitive Edge: In competitive tender situations, being ISO 9001 certified can offer an edge over organisations that lack this credential.
Enhanced Reputation and Brand Image:
- Recognition: Achieving ISO 9001 certification offers a recognised mark of quality, which can be pivotal in attracting new customers and clients.
- Credibility Boost: An ISO 9001 badge reflects commitment, consistency, and credibility, fostering trust among both existing and prospective clients.
- Positive Public Perception: The proactive stance towards quality and continuous improvement can elevate an organisation’s image in the public eye, cultivating a reputation for excellence.
ISO 9001 certification is not just a testament to an organisation’s commitment to quality; it’s a strategic tool. It drives operational excellence, fosters stakeholder trust, and paves the way for sustained business growth. As businesses navigate an increasingly competitive and dynamic marketplace, such certifications can serve as anchors, providing direction and assurance of a commitment to excellence.
Common Misconceptions about ISO 9001
The ISO 9001 certification is a hallmark of quality management but is often misunderstood. Several myths surround this certification, some of which may discourage organisations from pursuing it. Let’s demystify some of these misconceptions and uncover the truth beneath them.
Myth: ISO 9001 is only for big corporations
Reality: Companies of any size and sector can benefit from ISO 9001. It provides value for small businesses, non-profits, government agencies, and more. Over 1 million organisations in over 170 countries have achieved certification.
Myth: ISO 9001 creates paperwork
Reality: The paperwork is a tool to capture quality processes, not the end goal. Effective implementation improves day-to-day operations and management.
Myth: ISO 9001 ensures perfection
Reality: ISO 9001 supports consistency, not perfection. The goal is to minimise errors and defects through sound quality principles.
Myth: ISO 9001 is too complex for our business
Reality: ISO 9001 is flexible and can be tailored to organisations of varying complexity. With training and guidance, certification is achievable.
Myth: ISO 9001 is expensive and time-consuming
Reality: The investment pays dividends through efficiency gains, risk reduction, and improved customer satisfaction. Many find the time and cost are recouped quickly.
Myth: It Stifles Innovation
Reality: ISO 9001 provides structure, not restriction. It paves the way for innovation within a quality framework.
While ISO 9001 has some persistent misconceptions, the reality is that it’s an invaluable framework for managing quality that delivers real business benefits. With commitment and a sound implementation approach, certification is within reach for organisations of all types.
Best Practices for Implementing ISO 9001
Implementing ISO 9001 is not just about achieving certification—it’s about embracing a culture of quality management that permeates every level of an organisation. Here’s a guide to best practices that can ensure a smooth, effective ISO 9001 implementation:
Employee engagement and training
Thoroughly train employees on ISO 9001 principles, documentation, and implementation across all levels. Engaged and knowledgeable staff will help drive a successful certification journey.

Executive-level commitment
Obtain buy-in and participation from senior leadership. Visible support from upper management provides critical motivation.
Close collaboration with stakeholders
Work hand-in-hand with parties like suppliers and contractors to integrate ISO 9001 into supply chains and shared processes.
Regular reviews and updates
Conduct internal audits and reviews frequently. This allows you to detect issues and opportunities to improve the QMS quickly.
Data-driven management
Leverage performance metrics and trend analysis to make evidence-based decisions for enhancing the QMS.
Customer feedback loops
Actively solicit customer feedback to understand their evolving needs and perceptions of quality over time.
Continuous monitoring and improvement
Regularly evaluate the QMS post-certification. Continual improvement is vital to maximising ISO 9001 benefits long-term.
In essence, ISO 9001 implementation is a journey, not a destination. The practices above are not one-time activities but ongoing processes that, when adopted and nurtured, can ensure that an organisation achieves certification and thrives within the quality management framework.
Conclusion: The Power of ISO 9001
ISO 9001 provides an internationally recognised framework for managing quality across any organisation’s processes, products, and services. Certified companies can increase efficiency, reduce risks, and consistently meet customer requirements.
While attaining ISO 9001 certification requires commitment and diligent implementation, the investment pays dividends through streamlined operations, defect reduction, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced business performance.
- Universal Applicability: ISO 9001 is designed for entities of all sizes and sectors, debunking the myth that it’s reserved solely for large corporations.
- Beyond Paperwork: While it encompasses documentation, its core lies in fostering efficient processes and championing continuous improvement.
- Investment, Not Expense: The initial costs of ISO 9001 are often outweighed by the many benefits, from operational efficiency to enhanced market reputation.
- A Living Commitment: Achieving certification is just the beginning. Maintaining the ISO 9001 standard means embedding a quality and continuous improvement culture.
- Operational Excellence: ISO 9001 ensures streamlined processes, reduced waste, and heightened customer satisfaction, offering organisations a competitive edge in the market.
Adopting ISO 9001 isn’t just about adhering to a set of standards. It’s about embracing a quality-centric ethos that promises sustainable growth, innovation, and an unwavering focus on stakeholder satisfaction.
Do not hesitate to reach out if you have questions or need clarity on any aspect of ISO 9001. Our team is always available to provide insights, guide you through the process, and ensure that your journey towards quality management is both rewarding and transformative.
Additional Resources:
Diving deeper into ISO 9001 and its intricacies can be tremendously beneficial. Here are some resources that will aid your understanding and provide valuable information on quality management:
Official ISO Sites:
- ISO 9001:2015 : Official page for the latest version of ISO 9001, offering detailed insights into the standard.
Further Reading:
- ISO 9001 Implementation Guide : A practical guide on implementing ISO 9001:2015.
- Quality Management Made Easy : Find out how ISMS.online can offer a simple, sustainable route to ISO 9001 success

Rebecca Harper
Rebecca is the ISMS.online Head of Content Marketing. With over 12 years in the information and cybersecurity industry, Rebecca is dedicated to educating, building awareness and empowering businesses to achieve compliance, information and cybersecurity management goals.
View all posts by Rebecca Harper
Related Posts

Global Change Your Password Day: A Call to Action
- The CrowdStrike Outage: A Case for Reinforcing Incident Response with ISO 27001
- Is Negotiation Your Best Strategy When It Comes To Ransomware?
- How Much Does Cybercrime Really Cost UK Businesses?
- What Are Infostealers and Why Should My Business Be Concerned?
- From RSA to SolarWinds: Lessons Learned from a Decade of Supply Chain Breaches
- Certification
- Cyber security
- Data Privacy
- Data Protection
- General Data Protection Regulation GDPR
- Information Security
- Information Security Management System ISMS
The State of Information Security Report 2024 Now Live - Read Now
Choose your region and currency
Get Certified
ISO 9001 Certification Process
Learn how to quickly implement a business-friendly ISO 9001 system.
Guided DIY Toolkit
Full-Service Consulting
Hybrid ISO 9001 Certification
Maintain & Improve
How to Improve Your QMS
Turn your underperforming ISO 9001 system around.
Documentation Templates
ISO Consulting Service
ISO Internal Audit Service
Document Review
Training Recommendations
Find the ISO 9001 training course you really need.
Online Training
Custom Training
Video Courses
Learning Center
A wealth of information on everything ISO 9001.
Case Studies
Free Downloads
Registrar Finder
What are you looking for?
HOME / learning center / iso 9001 implementation and certification checklist
ISO 9001 Implementation and Certification Checklist
Your ISO 9001 implementation can become more manageable by breaking it down into distinct tasks. This handy checklist reflects our proven simplified approach to ISO 9001 that focuses not only on easy, stress-free implementation but also on efficient, non-bureaucratic processes that truly benefit your business.
Also available: PDF download of this practical checklist
More about each implementation task: 5-step guide to ISO 9001 certification
Preparation
Define your goals.
Your organization can gain numerous internal and marketing benefits from ISO 9001 – if it first defines and then actively pursues them. Focus on operations and current shortcomings. Convert into SMART objectives.
Find out what benefits are possible
Use our guide to identifying internal benefits
Define the Scope
You aren't required to apply ISO 9001 to your entire organization. Decide if any departments should be excluded. Decide on a gradual roll-out.
Choose Your Implementation Approach
Do-It-Yourself kit, consultant, or a hybrid approach? Each could be done remotely.
Practical guidance on ISO 9001 implementation
Assign Responsibilities
No matter which implementation approach you choose and which ISO tasks you outsource, somebody needs to be the ISO 9001 point person. If you do it all in-house, you might even appoint an implementation team.
Learn the ISO 9001 Requirements
The ISO 9001 point person and the implementation team should have a solid understanding of the standard and its requirements. Some of this knowledge can also be acquired by working alongside a consultant.
Read up on the basics
Buy the ISO 9001 standard
Take online implementation training
Get custom training for an implementation team
Gain Management Support
Don't take this lightly. It's crucial that top management not only support the ISO project but also "walk the talk". The first step in achieving active support is providing management with the needed knowledge.
Concise online training for executives
Custom on-site or remote course for leadership teams
Generate Employee Buy-In
Inform your staff early and before rumors start. Show how employees will benefit from ISO 9001 and explain how everyone can contribute positively to the project.
Provide online training
Show a short video course
Get custom on-site or remote employee training
Conduct a Gap Analysis
A gap analysis prior to project planning is particularly useful for larger companies or if a consultant is involved. Small and mid-size companies could conduct several small gap analyses during the documentation or implementation phases.
Buy a gap analysis checklist
Have a consultant conduct the gap analysis
Develop a Project Plan
Plan the ISO 9001 implementation as a project. Focus on implementation steps, milestones, and target dates. Assign responsibilities. And keep it simple!
Have a consultant develop a custom plan for you
Documentation
Start with the document control procedure.
The ISO 9001:2015 standard includes explicit and implicit requirements for documents and records, as well as stringent document control guidelines. Since all (ISO 9001) documents must be controlled, it is wise to develop your document control procedure first.
Read up on document control
ISO 9001 Quality Management Manual
Create the High-Level Documents
These documents form the basis of your QMS: scope statement, quality policy, quality objectives, and process map.
Develop Your Procedures
Take one clause at a time and determine the organizational functions that are impacted. Establish the current level of compliance and – together with affected management – work out how to fill the gaps.
List of recommended procedures
Create Forms and Checklists
Forms and checklists save time. They can support work processes and record keeping. Develop forms and checklists that simplify compliance with your procedures.
ISO 9001 Forms Collection
Implementation
Provide manager training.
Teach department managers and team leaders how to use ISO to achieve tangible benefits. Then let this key group adopt an active role during implementation.
Targeted manager training
Introduce the Procedures
Introduce staff to your new procedures, one at a time. Use employee meetings or teach managers to inform their staff. Start with document control.
Achieve Process Improvement
Empower staff to redesign their work processes along the new ISO 9001 requirements. Processes are best analyzed and fine-tuned through flowcharts on a white board. Redesigned process should be documented.
Buy Flowcharting Software
Get help from a consultant
Have Staff Write Their Own Work Instructions
Work instructions are step-by-step directions on how to perform an activity. Work instructions are best written by staff who actually perform the work. You may need to verify compliance with your new procedures.
Keep Records
As you are implementing new processes, be sure to generate and keep records. Certification auditors will use them to verify compliance.
List of required records
Market Your Upcoming Certification
Gain early marketing benefits through advertising your pending accreditation. Add substance by describing your QMS, summarizing your procedures, and announcing your certification date.
Use our Quality Manual Template for marketing
Internal Audit
Set up the audit program.
The audit program includes an audit schedule, methods for audit planning, auditing forms and checklists, and a team of auditors. A procedure is useful.
ISO 9001 Audit Toolkit
Provide Auditor Training
Auditors need to be familiar with the ISO 9001:2015 standard, be able to verify if its requirements are effectively implemented, and ideally have the skills to promote best practices and add operational value.
Online internal auditor training
Online lead auditor training
Custom on-site or remote course for audit teams
Support Your Implementation Through Audits
Start your audits early to support your implementation efforts. Leverage your audits as a training tool. Initially, focus on particular requirements or procedures.
Conduct a Complete Audit
Conclude one complete internal audit and ensure that any identified nonconformities are addressed prior to certification. Keep records.
Outsource your audit and get our certification guarantee
Certification
Select your registrar.
Choose an accredited registrar that meets your company's specific needs.
Learn about registrars
Get custom quotations through our free registrar finder service
Prepare Company and Staff
Tidy up work areas, and remove uncontrolled and obsolete documents. Prepare staff and rehearse typical auditor questions.
Read our audit preparation tips
Prepare staff through a short video
Pass the Certification Audit
Undergo the stage 1 and stage 2 audits. Address any nonconformities and inform your registrar.
Market Your Certification
Publicize your certification through press releases, your website and company stationary. Inform current and prospective customers.
Maintain Registration
Make sure your QMS remains implemented and used in daily operations. Continue your internal audits. Have your registrar perform surveillance audits. Address any nonconformities.
Keep staff motivation up with a short video

Consultant and Product Manager
Naomi holds dual responsibility as an ISO 9001 consultant and product manager, and is an enthusiastic contributor to our online and print resources.
If you enjoyed this article, subscribe for updates.
Stay in touch with our free resources on ISO 9001.
We won't send you spam. Unsubscribe at any time.
Think your associates and colleagues might enjoy this article too? Share it!
Copyright (©) 2004-2024. 9001Simplified.com. All Rights Reserved.
How can we help?
Please enter your full name
Please enter a valid email
Please enter a valid phone number
Please enter a message
Send Inquiry
Thanks. Your message has been sent. We'll get back to you as soon as possible.
Looking for information or advice? Ask us anything
We'll reply ASAP
ISO 9001 checklist
| | |
- Gap Analysis
- Internal Audit
- Quality Manuals
- Integrated Management Systems
- Free Downloads
How To Implement ISO 9001 (In 8 Steps)
How to Implement A Quality Management System in 8 Steps Familiarize Yourself with ISO 9001 Plan Identify Responsibilities, Policies, and Objectives Develop Your Documentation Launch Your Quality Management System Review Your Performance Register for Certification Continual Improvement ISO Project Plans [Template downloads]
The secret to implementing ISO 9001 and new business systems is:
- Good planning , and
- Buy-in + Approval of a detailed project plan by top-management
ISO 9001 is a wonderful way to show your customers that you are committed to giving them the best quality products available. While it's not a necessity, having an ISO 9001 certification is evidence that your business keeps to a certain standard and requirements when it comes to managing quality.
Don't Try To Manage It All Alone!
Our ISO 9001 Project Plan Template is proven to work.

Step One: Familiarize Yourself with ISO 9001
You should absolutely purchase a copy of the ISO 9001 standard and review the key concepts. Everyone should have a firm grasp on the requirements of the standard, the documented procedure requirements, and the sort of documents and records required of you.
ISO 9001 provides a structure for the core requirements of a quality management system but is flexible so that it can suit all types of businesses. It's important for you to understand how the standard applies to your business specifically. This flexibility will allow you to meet the requirements set out in a way that makes sense for your organization.
Get Top Management on Board
It is essential when making any large changes to any business that you and everyone involved in your Top Management understand what it is you're trying to do.
Making sure that the people at the top of your management understand what ISO 9001 means for your business and why it's being implemented is absolutely key to everything running smoothly. Without everyone completely committed it becomes much more difficult to affect change throughout the business.
Find out Where You Stand
Once you have everyone on board you should analyze your current system and compare it to the ISO 9001 standard. You should have a good working knowledge of how close or far you are from meeting the standard requirements as it is. With this data, you can easily create to-do lists on how to modify your existing system to meet the standard.
Do a Gap Analysis
The purpose of this gap analysis is to identify the areas in your company that require change in order to be compliant.
Our Quality Manual Template includes a 18-page gap analysis template which:
- presents an overview of the requirements of each section
- allows space for findings and noting implementation actions
- questions are phrased to allow one word answers (yes/no)
In doing this, you ensure that everyone involved in implementing the new system is on the same page. Make sure to check with all of your Top Management before beginning the next step just to be certain they understand the need for a new Quality Management System and that they are 100% committed to helping implement it.
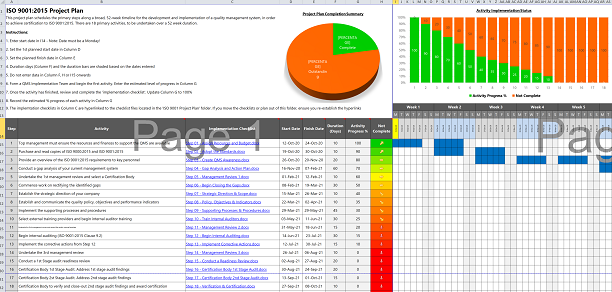
Step Two: Plan
Having a solid plan in place is essential to making the transition to a new system. When you have the right people on the job the process will be much easier to get through. Your team will create a workable plan that will set your business up for success.
Start with Expert Templates, then Make Them Yours
Decide on an implementation team.
To begin implementation, your Top Management should decide on and create an implementation team to head the effort. This team should be made up of managers from different areas of your business. An implementation team will ensure the success of your transition to the new Quality Management System.
The implementation team should be headed by the Management Representative that will oversee all parts of the implementation process. This person should hold a perfect understanding of the ISO 9001 standard. They will be the line of communication between the implementation team and the ISO 9001 registrar that will eventually certify your business.
The Management Representative should be a member of management that is respected and has a passion for managing and maintaining the Quality Management System far into the future.
Identify Core and Support Processes
It will be much easier to map out a plan for meeting the standards when you are aware of which processes within your organization coordinate with which requirements. It's extremely helpful to use flow charts and turtle diagrams to figure out exactly how your business gets from Point A to Point B when it comes to creating new products for customers.
You can do something as sophisticated as using computer software to define each step of the process, or simply use post-it notes on a wall. Once you can see the entire process in front of you, it's time to decide which of the items is a core process and which is a support process.
Examples of core processes are things such as design and delivery. These are the processes which contribute directly to getting the customer what they want. Support processes are not directly responsible for it but do help the core processes to do their job. These processes are things like training and facility maintenance.
- view sample process map
Create a Plan
In order to keep the transition to ISO 9001 running smoothly, there should be a structured plan set into place. Using the to-do list created from your analyses in step one, the implementation team should create milestones and deadlines to get things done.
Having a plan in place is key in implementing any system in a timely and effective manner. Without ensuring things are done at specific times under controlled conditions, they may get pushed aside and take much longer.
Why Reinvent the Wheel?
Get everyone involved.
With a plan set out before you, it's time to let everyone in on the change. Every single person that works within your organization should be aware that change is coming. Hold seminars to let them in on the way things are going to change and why.
Make sure when you introduce the concept of such a large change that you tell your employees how it will affect them. Include research that supports why implementing ISO 9001 is a good thing for the business and for them. Let them know how their work might be changed in the process so that they are prepared.
Communication is key in implementing change. Keep everyone in the loop so that they don't feel they are being jilted in any way. Set up displays on notice boards that show the progress being made. Listen to any concerns or complaints. Make everything feel included.

Step Three: Identify Responsibilities, Policies, and Objectives
The Quality Policy within your company is an integral part of keeping your business committed to meeting objectives and focusing on customer satisfaction. Your Quality Policy is one of the key things that will be used to measure your organization when determining the success of your Quality Management System.
Define Your Quality Policy and Objectives
There is no set definition of quality that applies to all businesses. Your definition of quality is one that is agreed upon by your Top Management team. It should build on your current values and identify objectives that are able to be measured to determine quality.
Quality Objectives are the way that the quality of your products will be measured. There isn't a specific way that ISO 9001 asks for objectives to be documented. Your quality objectives can be related to budget, business plans, or management review. It's important that these objectives suit both your business and your customers.
Once you have your Quality Policy in place you need to communicate it effectively to all members of your organization. You don't have to force the entire thing down their throat verbatim, but make sure they know where they can find a copy of the document if they should need it.
Try to shorten the key concepts of your Quality Policy into a few short sentences or a handful of keywords that make sense to employees at all levels. Do this for each department depending on what part of the Quality Policy directly correlates to the work they are doing. Put this shortened version up on notice boards so that they are always aware of it.
Establish New Roles and Responsibilities
Every area of your organization should have managers and staff who are directly responsible for quality-related tasks and upkeep. You can create entirely new roles for these people or change already existing job descriptions to include the needed responsibilities.
You should have staff in each department that is capable of performing audits, maintaining documentation, conduct management reviews, and implement any needed changes. Make sure the people you choose to undertake these responsibilities are fully aware of what the job entails and how it relates to the Quality Management System.

Step Four: Develop Your Documentation
Keeping records of your Quality Management System is required to be ISO 9001 certified. There are certain documents you are required to keep and others which may just be helpful in keeping everything running as it should.
Organizing and preparing your documentation is usually done according to the importance of the documents.
At the top, you have your Quality Manual. This includes your companies quality policy and objectives as well as how your quality system functions. It will have descriptions of all of the processes within your system and how they interact. You should always go back and refer to your Quality Manual as you implement changes to ensure all process descriptions are up to date.
Second, there are procedure documents. These documents detail all of the individual business processes and how they operate. They will show how each process is designed and controlled, including what checks are carried out to keep them in line.
Third, there are work instructions. These are very specific documents that detail the necessary instructions required to perform every task within the business.
Last, you have your forms and records. These are exactly what they sound like. Forms are used to collect information for record-keeping purposes. Records are required to show how your Quality Management System is operating and if it is up to standard.
To help you with 90% of the documentation, We recommend using a Quality Manual Template .
The Template includes everything you need for ISO 9001 documentation - quality policy, scope, what procedures you're planning to implement, flow charts, objectives and forms that ISO 9001 certification may require.
Jump start your ISO documentation
Our Quality Manual Template is proven to work.
Make a List of Already Existing Documents
Your business probably already has extensive documentation going over processes and procedures, as well as forms and records.
It would benefit you to make a list of all of the documents that already exist and note their current status. Many of these documents may not be completed or up to date or might be lacking specific details required by the ISO 9001 standard. This list will give you a good idea of where to start in moving forward.
Create Templates for All Document Types
All of the documentation within your Quality Management System should be uniform in style and format so they are easy to navigate and read. Be sure to check what each type of document is required to have in it so that you can include these things in your template.
Having ready-made templates will make the daunting task of documenting your Quality Management System a lot easier to handle for everyone involved.
Implement a Document Control System
It is required that all documentation associated with your Quality Management System is well controlled and up to date. This ensures that your employees only have access to the most recent version of all documents.
Your Documents & Records Should Include:
- A letter code that identifies each type of document and a sequential number
- Revision control where each revision results in an increase in the revision number
- A change history summarizing all changes made to each document
- Signatures of who prepared and who approved the document
- The date of the version or revision
Step Five: Launch Your Quality Management System
Now it's time for the biggest step. You've done all of the work required to set up your business for success in transitioning to ISO 9001, all you have to do is launch your plan. You will start to see changes come into action and you will have to be mindful to ensure they go as planned.
Provide Employee Training
Every employee is crucial to keeping your Quality Management System running as it should. It's time to train all of them on the parts of the system that are specific to their area of work. When they understand how their work affects the system they will be helping to move your business in the right direction.
Training Should Teach Your Employees:
- The procedures that apply to their work
- Which forms they should be using and how to complete and process them
- How to find the Quality Policy and how it relates to their position
- How to report issues so that they can be fixed
- Where to find all relevant documents
Always go into training with a plan to equip each and every member of your team with the tools they require to be an effective part of your new Quality Management System.
Implement the System
Use your structured plan to begin putting your Quality Management System into action. Keep a close eye on every part of the plan as it begins to make sure things are moving forward. Monitor process performance and start internal audits to check that all standard requirements are being met.
It's essential to keep your implementation team on task. The Management Representative should have a checklist on hand at team meetings to review with everyone. Any problems that arise during the implementation process should be handled as promptly as possible.
This is also a good time to make sure documentation is being developed properly. Work instructions and forms should all be written and available to employees.
Audit the System
Two to three months after the documentation has been prepared and things have started being implemented, you should conduct internal audits to identify any problems within the scope of your Quality Management System. Any corrective measures that need to be taken should be taken without any delays. If needed, documentation should be revised.
Auditors will ensure that all procedures are well implemented, documented, and understood by the staff carrying them out. They will check that the system meets standard requirements, is effective, and is showing improvement.
Never spring an audit on your employees. They should not feel surprised or like they aren't being involved in the entire transition process. Always plan the audits well in advance. Let everyone know when the audit will take place and what departments will be audited.

Step Six: Review Your Performance
After you have done your internal audit and your Quality Management System has been up and running for six months or so, you should review the progress your business is making. This review will help your team identify any underlying issues and the corrective actions that need to be taken to get everything in line with requirements.
Conduct a Management Review
Management Review is a useful tool that will give you a precise look at the performance of your Quality Management System and any problems that have come about. You may find through your review that changes need to made to your quality policy or objectives.
Your Management Review Should Include:
- Audit Results
- Customer Feedback
- Process Performance
- Product Conformity
- Status of Corrective Actions
- Follow-Up Actions From Previous Reviews
- Changes That Could Affect the System
- Recommendations for System Improvement
With all of this information on hand, your team can successfully correct the direction in which your system is headed so that it's forward once more.
Implement System Changes
This is as straightforward as it gets. Once you have identified the places where your Quality Management System needs fixing, it's time to fix them. Take prompt action and get everything corrected. Don't forget to revise the necessary documentation related to anything you change.
If you neglect needed changes you will not be able to register your system. Certification bodies prefer at least three months of records related to refining your Quality Management System.
Integrate reviews into your regular management system and keep clear records of everything you review and change. It's vital that you have all of your documents up to date. Continue to ensure the result of your management reviews is functioning as it should.

Step Seven: Register for Certification
Your Quality Management System has been up and running for three to six months and everything seems stable and ready to be registered. Now is the time for you to carry on with the certification process to officially become ISO 9001 certified.
Registration Audit
Your registrar will perform a two-step audit to confirm your business meets the requirements set out by the ISO 9001 standard.
They will first audit your documentation. This can take place either at their personal office or within your organization. The registrar will ensure that your documentation is all in place and controlled in compliance with the standard. If you don't have your documentation in order there's no real reason to continue on with the rest of the audit.
If all of your documents meet the standard requirements, the registrar will come to your business to audit your processes.
There is always the option of carrying out a pre-assessment audit, which is basically like a practice audit. Your registrar will assess your Quality Management System around six weeks before registration takes place and give you advice on any corrective actions that should be taken before your audit. Some people find this advice invaluable to the registration process.
Take Corrective Action
After your audit you will be given the opportunity to fix any non-conformances that the registrar found. It is paramount that you take any issues that do not comply with the ISO 9001 standard seriously and fix them without hesitation.
Common non-conformances found in audits are a lack of proper training for internal auditors, reports of audits were not completed or managed, or personnel were found to be auditing their own work.
Receive Your Certification
Your registrar will perform a second audit to ensure that all of the non-conformances that were found have been properly taken care of. They will systematically evaluate your entire Quality Management System against the standard to ensure it meets all requirements.
There must be objective evidence that your system conforms to the ISO 9001 standard and that all procedures are being followed. The registrar will document all of this before you become certified.
Certification generally lasts for three years. Receiving your ISO 9001 certificate isn't the end, though. Your registrar will perform surveillance audits one or two times a year to ensure your Quality Management System continues to meet the standard.

Step Eight: Continual Improvement
It is required by the ISO 9001 standard that certified companies continue to show improvement in the effectiveness of their Quality Management System. You should always aim to satisfy customers by identifying processes in your system which can be improved.
Implement a system that makes continual improvement easy for your team to carry out. It's as simple as following a repeating four-step process for checking up on your Quality Management System.
1. Plan out a time-line for internal audits and management reviews. Make sure all objectives and processes are well established and understood to deliver results in compliance with your quality policy. Use feedback from employees and customers to identify where things are going wrong and put a plan into place to see that they are fixed.
2. Create a small sample of changes you wish to implement. Before you interrupt the flow of work by taking an action, it would benefit you and your system to ensure the change will actually work beforehand on a smaller scale.
3. Regularly check all products and processes against policies and customer requirements. Report the results of these checks. Check up on all key activities to ensure the output is conforming.
4. Put successful changes into action. If a change did well in testing then it's time to put it into the full system to improve it. Involve everyone that will be affected by the changes in making them. Ensure that all changes are documented and that everything is up to date and meets requirements.

Implementing ISO 9001 Is Doable for You
Making such a large change can seem like moving mountains in the beginning. It's difficult to know where to start or what order to do everything in. But it doesn't have to be a hassle to implement a new Quality Management System in your business.
To make sure you start out on the right track, we recommend you start out with a tried and tested ISO 9001 Project Plan .
ISO 9001 Implementation What are the steps for ISO certification? (Overview) How Hard is it to Get ISO 9001 Certification? How to Implement ISO 9001 (In 8 Steps) ISO 9001 Project Plan ISO 9001 Implementation Guide (detailed, 27 Steps) How To Gain ISO 9001 Certification
Updated: 3rd Feb 2024 Author: Richard Keen

Richard Keen
Richard is our Compliance Director, responsible for content & product development. But most importantly he is ISO's biggest fanboy and a true evangelist of the standards. Learn more about Richard
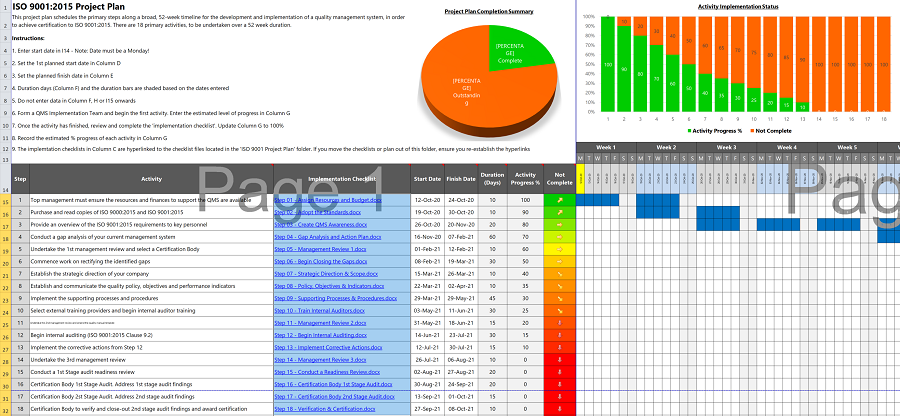
Don’t Try to Manage It All Alone!
Our ISO Auditors and Quality Manager Trainers have been in this industry for years, and since 2002 we’ve been providing thousands of small businesses and large corporations with the tools they need to get certified.
Instead of trying to create a project plan and checklist from scratch, use ours.
Before you invest all the hours reinventing the wheel, before you spend countless dollars outsourcing the task — try our templates.
| A complete 18-step project plan for ISO 9001 using MS Excel.
-
Implementation checklists for each of the 18 steps, MS Word.
- | $39 USD
| |||
| A complete 18-step project plan for ISO 14001 using MS Excel.
-
Implementation checklists for each of the 18 steps, MS Word.
- |
| $39 USD
| ||
| A complete 18-step project plan for ISO 45001 using MS Excel.
-
Implementation checklists for each of the 18 steps, MS Word.
- |
| $39 USD
| ||
| A complete 18-step project plan for ISO 9001 and ISO 14001.
-
Implementation checklists for each of the 18 steps, MS Word.
- | $39 USD
| |||
| A complete 18-step project plan for ISO 9001 and ISO 45001 using MS Excel.
-
Implementation checklists for each of the 18 steps, MS Word.
- | $39 USD
| $39 USD
| ||
| An integrated 18-step project plan for
-
Implementation checklists for each of the 18 steps, MS Word.
- | $39 USD
| |||
- Written in International English
- Fully-editable MS Word or Excel files, compatible with Google Docs and Apple Pages
- All the templates use styles – making reformatting and rebranding a breeze
- Immediate download

|
Please . |
Are The Templates Suitable For You?
Bought by Small Businesses and Large Corporations our templates have been sold online and CD since 2002.
- Small Businesses – dentists, accountants, engineers
- Large organizations – hospitals, power plants, aircraft manufacturers
The Templates are used by first-timers following our step-by-step, clause-by-clause guidance documents; and experienced Quality Managers wishing to streamline and improve their existing documentation.
The application of our templates is scalable and generic ; regardless of the size and type of organization. The elements that form the quality management system are the same.
Five Reasons To Choose Our Templates
1. Our customizable templates save you time and money by offering a streamlined process to create your quality documentation
2. They’ve got everything you need in one simple template
3. Proven to work our templates have helped thousands of businesses big and small achieve certification
4. Documents use styles to make reformatting and rebranding a breeze
5. Our templates are generalizable for any industry or sector . The application of our templates is scalable and generic ; regardless of the size and type of organization.
FAQs About Our Templates
- Top 10 FAQs
- Payment and Billing
- Downloading and Delivery
- Systems Requirements
- License and Updates
Ask Us a Question
- Enquiries [email protected]
- Support [email protected]
- Call 0845 054 2886 (UK only)
More Information
- Client list

| | | |
| Endeavour Technical Limited © 2002 - 2023 | |
| 71–75 Shelton Street, Covent Garden, London WC2H 9JQ, United Kingdom | |
| Registered in England No. 07175526 | |
| Telephone: (UK only) | |
| | | |
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Learn More Got it!
Get a 50% discount on ISO 22301 when you buy ISO 27001 ! Click here to download
- Project Management
- ITSM Templates
- Compliance Automation
- ISO 27001 Automation
- NIST Automation
- SOC 2 Automation
- GDPR Automation
- HIPAA Automation
- ISO 27001 ISMS
- ISO 9001 QMS
- ISO 22301 BCMS
- ISO 45001 OHSMS
- ISO 20000 IT Service Management
- ISO 14001 Environmental Management System
- ISO Concepts
- ISO 27001 FAQs
- Free Templates

Sign up today and we'll send you a 10% discount code towards your first purchase.
ISO 9001 Implementation Plan
Implementing ISO 9001, the international standard for quality management systems, can be a daunting task for organizations. However, with proper planning and execution, it can bring numerous benefits to the organization, such as improved customer satisfaction, increased operational efficiency, and enhanced reputation.
This blog post will provide a step-by-step implementation plan for ISO 9001, outlining the key activities and considerations at each stage of the process. Whether you are new to ISO 9001 or looking to improve your existing system, this guide will help you navigate the implementation process and achieve certification successfully.
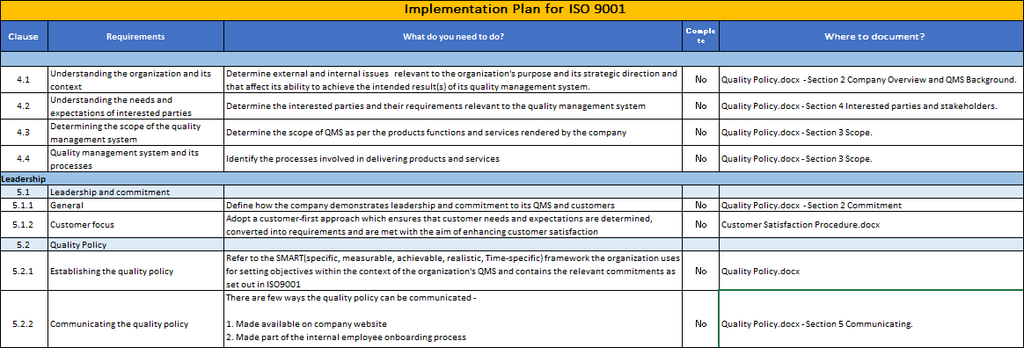
Purpose of the implementation plan
The purpose of the implementation plan for ISO 9001 is to provide organizations with a structured approach to effectively implement the requirements of the standard within their operations. The plan serves as a roadmap, guiding organizations through the various stages of implementation and ensuring that all necessary steps are taken to achieve compliance with ISO 9001.
By following the implementation plan, organizations can streamline their processes, identify areas for improvement, and enhance overall quality performance. Additionally, the plan helps organizations develop a systematic and consistent approach to managing quality, ensuring that all employees are aligned with the organization's quality objectives and working towards achieving them.
key features of implementation plan
Now that we have examined the benefits of using an implementation plan for ISO 9001, let's delve into the key features that make up an effective plan. Having a clear understanding of these features will help organizations develop a comprehensive and successful implementation strategy. Leadership First and foremost, leadership must demonstrate a commitment to quality by setting clear expectations and goals for the implementation process. They should communicate the importance of ISO 9001 and why it is beneficial for the organization and its stakeholders. This commitment should be evident through their actions, as they lead by example and actively participate in the implementation efforts. Furthermore, leadership is responsible for creating a supportive and empowering work environment. They should foster open communication channels, where employees feel comfortable sharing their ideas, concerns, and suggestions related to the implementation process. This will encourage engagement and ownership from all levels of the organization, leading to a more successful implementation.

Planning One of the first steps in the planning phase is to form a dedicated team responsible for overseeing the implementation process. This team should consist of individuals from different departments and levels within the organization to ensure a comprehensive approach. Their primary responsibility is to develop a detailed implementation plan, outlining key activities, timelines, and responsible individuals. Identifying organizational needs and establishing measurable objectives is another critical aspect of the planning process. The implementation team should conduct a thorough review of existing processes and identify areas that need improvement. These areas should align with the goals of ISO 9001, such as enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing errors. Additionally, clear objectives serve as benchmarks to measure progress throughout the implementation journey. Support Support starts with leadership commitment and involvement. It is essential for top management to actively demonstrate their support for the ISO 9001 implementation. This can be done by allocating necessary resources, providing clear directives, and regularly monitoring progress. When employees see that their leaders are fully committed to the process, they are more likely to embrace the changes and contribute to its success. support plays a critical role in the successful implementation of ISO 9001. Leadership commitment, a support structure, training and education, feedback mechanisms, and recognition all contribute to creating a supportive environment for employees. In the next section, we will delve into the importance of effective monitoring and evaluation throughout the implementation process.
To ensure effective operation management, organizations need to define their key processes and determine how they interact with each other. This involves identifying inputs, outputs, resources, and controls for each process. Defining process interactions helps organizations understand the flow of activities, dependencies, and potential areas for improvement. successful ISO 9001 implementation requires organizations to effectively manage their operations. This includes defining key processes, establishing clear procedures, monitoring performance, implementing controls, and managing risks and opportunities. In the next section, we will explore the importance of continual improvement and how it contributes to the long-term success of ISO 9001 implementation. Performance Evaluation
Organizations should establish a systematic approach to evaluate performance based on defined metrics and set objectives. This can involve conducting internal audits, customer satisfaction surveys, and other performance measurement methods. By collecting and analyzing data, organizations can assess whether their processes are meeting the desired outcomes and identify any areas where improvement is needed. By implementing consistent performance evaluations, organizations demonstrate their commitment to continuous improvement and ensure that the ISO 9001 implementation remains effective over time. In the next section, we will delve into the concept of continual improvement and how it drives the long-term success of ISO 9001. Improvement Continual improvement is a fundamental principle of ISO 9001. It involves constantly seeking ways to enhance processes, products, and services in order to meet customer requirements and exceed expectations. This iterative approach to improvement ensures that organizations stay competitive and adapt to evolving market demands. By embracing a culture of continual improvement and utilizing effective improvement strategies, organizations can sustain the momentum of ISO 9001 implementation and ensure long-term success.
Benefits of the Implementation Plan
The implementation plan for ISO 9001 offers several benefits to organizations that choose to adopt it. By following a structured plan, organizations can streamline their processes and improve overall efficiency. Here are some key benefits of using an implementation plan:
- Clear roadmap: The implementation plan provides organizations with a clear roadmap of the steps and actions needed to achieve ISO 9001 compliance. This helps organizations stay organized and focused throughout the implementation process.
- Risk mitigation: By conducting an initial assessment and identifying gaps in current processes, the implementation plan allows organizations to proactively address potential risks and prevent future issues. This minimizes disruptions to operations and helps ensure continuous improvement.
- Enhanced communication: The implementation plan facilitates effective communication among employees and stakeholders. By clearly defining roles and responsibilities, everyone involved in the implementation process can work together towards the common goal of achieving ISO 9001 compliance.
- Continuous improvement: The implementation plan emphasizes the importance of regular monitoring and evaluation. This fosters a culture of continuous improvement within the organization, leading to increased customer satisfaction and business growth.
In conclusion, strong leadership is essential in driving a culture of continual improvement within organizations during ISO 9001 implementation. Effective leaders prioritize improvement, communicate its importance, and provide the necessary resources and support. They lead by example, setting clear improvement goals and aligning them with the organization's strategic objectives.
By measuring progress and fostering collaboration, leaders create an environment where innovative ideas and improvement opportunities thrive. In the next section, we will explore practical strategies that leaders can employ to drive continual improvement within their organizations. Stay tuned to discover actionable tips for successfully implementing ISO 9001 and cultivating a culture of excellence.

- Advisera Home
- ISO in General
Partner Panel
Company Training Account
Products by framework:
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) according to the ISO 27001 standard.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an ISMS according to ISO 27001.
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful ISMS.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Compliance and training products for critical infrastructure organizations for the European Union’s Network and Information Systems cybersecurity directive.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the NIS 2 cybersecurity directive.
Company-wide training program for employees and senior management to comply with Article 20 of the NIS 2 cybersecurity directive.
Compliance and training products for personal data protection according to the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the EU GDPR privacy regulation.
Accredited courses for individuals and privacy professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the ISO 9001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a QMS according to ISO 9001.
Accredited courses for individuals and quality professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 and the QMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for Environmental Management Systems (EMS) according to the ISO 14001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an EMS according to ISO 14001.
Accredited courses for individuals and environmental professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 14001 and the EMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation and training products for Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems (OHSMS) according to the ISO 45001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an OHSMS according to ISO 45001.
Accredited courses for individuals and health & safety professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Implementation and training products for medical device Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the ISO 13485 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a medical device QMS according to ISO 13485.
Accredited courses for individuals and medical device professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Compliance products for the European Union’s Medical Device Regulation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the EU MDR.
Implementation products for Information Technology Service Management Systems (ITSMS) according to the ISO 20000 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an ITSMS according to ISO 20000.
Implementation products for Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS) according to the ISO 22301 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a BCMS according to ISO 22301.
Implementation products for testing and calibration laboratories according to the ISO 17025 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement ISO 17025 in a laboratory.
Implementation products for automotive Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the IATF 16949 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an automotive QMS according to IATF 16949.
Implementation products for aerospace Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the AS9100 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an aerospace QMS according to AS9100.
Solutions for industries:
- Consultants
- IT & SaaS companies
- Critical infrastructure
- Manufacturing
- Transportation & distribution
- Telecommunications
- Banking & finance
- Health organizations
- Medical device
- Laboratories
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for consultancies.
Handle multiple ISO 27001 projects by automating repetitive tasks during ISMS implementation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement various standards and regulations for your clients.
Organize company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for your client’s employees and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited ISO 27001, 9001, 14001, 45001, and 13485 courses for professionals who want the highest-quality training and recognized certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS), ISO 9001 (QMS), and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Find new clients, potential partners, and collaborators and meet a community of like-minded professionals locally and globally.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for the IT industry.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 22301 (business continuity), ISO 20000 (IT service management), GDPR (privacy), and NIS 2 (cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Compliance, training, and knowledge products for essential and important organizations.
Documentation to comply with NIS 2 (cybersecurity), GDPR (privacy), ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), and ISO 22301 (business continuity).
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for manufacturing companies.
Documentation to comply with ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety).
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for transportation & distribution companies.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for schools, universities, and other educational organizations.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), and GDPR (privacy).
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS) and ISO 9001 (QMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for telecoms.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for banks, insurance companies, and other financial organizations.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 22301 (business continuity), GDPR (privacy), and NIS 2 (cybersecurity).
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for local, regional, and national government entities.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), GDPR (privacy), and NIS 2 (cybersecurity).
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for hospitals and other health organizations.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), ISO 45001 (health & safety), and GDPR (privacy).
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the medical device industry.
Documentation to comply with MDR and ISO 13485 (medical device), ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), ISO 45001 (health & safety), and GDPR (privacy).
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the aerospace industry.
Documentation to comply with AS9100 (aerospace), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety).
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the automotive industry.
Documentation to comply with IATF 16949 (automotive), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety).
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for laboratories.
Documentation to comply with ISO 17025 (testing and calibration laboratories) and ISO 9001 (quality).
- White Papers
- Templates & Tools
By Standard
- Live Consultations
- Consultant Directory

Carlos Pereira da Cruz
- Get Started
ISO 9001 requirements

Updated: December 22, 2023.
If you’re planning to comply with ISO 9001, you probably do not know how the standard is structured and what it requires to implement a QMS. Read further to learn more.
- Clauses 0 to 3: Introduction, Scope, References, Terms and Definitions
Clause 4: Context of the organization
Clause 5: leadership and commitment, clause 6: planning for the qms, clause 7: support & resource management, clause 8: operational planning and control, clause 9: performance evaluation, clause 10: improvement actions.
The ISO 9001 requirements provide a set of standard elements that will guide you in the implementation, maintenance, and improvement of a Quality Management System (QMS). The requirements are designed to be applicable to any kind of organization, for profit or nonprofit, manufacturing or service-based, large or small, regardless of the economic sector. ISO 9001 requirements describe which elements are mandatory in a QMS, but not how to implement those necessary elements. Organizations with a QMS according to ISO 9001 can be certified in what is called ISO 9001 certification – such ISO certification is often required by the main customers.
For more information on ISO 9001 mandatory and non-mandatory documents, you can see the article: ISO 9001 Documentation Requirements – The complete list .
The structure of the ISO 9001 clauses
The ISO 9001:2015 requirements are broadly separated into 11 ISO 9001 sections (called ISO 9001 clauses ).
Clauses 0 to 3 are not mandatory for implementation, while clauses 4 to 10 are mandatory; the exception to this mandatory rule in ISO 9001:2015 is clause 8, from which requirements can be excluded during implementation if the company finds those processes to not be applicable.
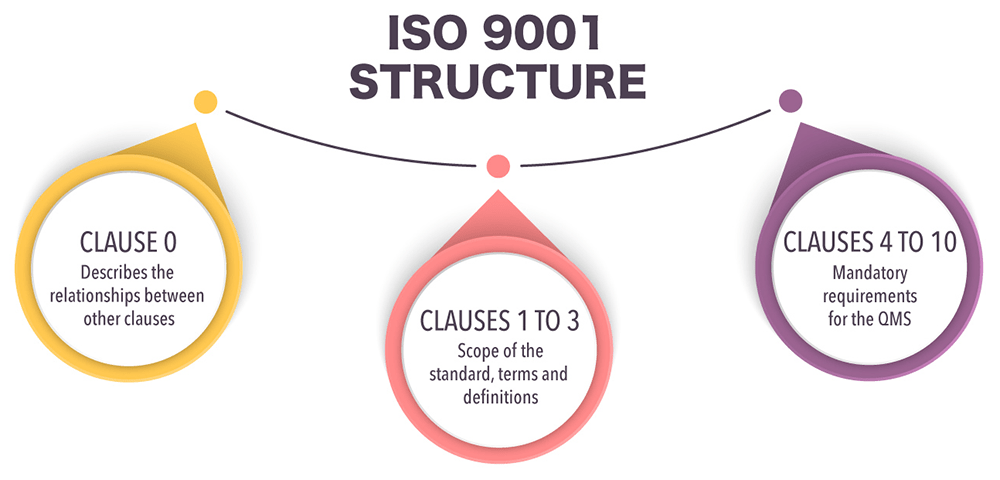
ISO 9001 clauses 0 to 3: Introduction, Scope, References, Terms and Definitions
Clause 0 mentions the benefits of implementing a QMS and the quality management principles, and presents the process approach, the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle, and risk-based thinking. These ISO 9001 elements are important for understanding the ISO 9001 sections that follow. People often overlook this clause, but they shouldn’t, as it frames much of the information that comes next, especially about how the various clauses relate to each other.
Clauses 1 through 3 include no requirements, but instead deal with the scope of the standard, references to better understand the standard, and terms and definitions. The remaining clauses include the ISO 9001:2015 requirements for a QMS.
Clause 4 is the first clause of ISO 9001 that contains the requirements for an ISO 9001 Quality Management System. An organization is not a closed system, isolated from the outside; it is inserted in a particular context and cannot be independent of what customers are looking for, or what regulators define. So, this section deals with the internal and external issues that can influence an organization in setting and meeting its objectives, as well as the interested parties that interact with the QMS. It also includes the requirements about the scope of the QMS and the process mapping and characterization.
The section on leadership outlines the requirements concerning top management, which are:
- promoting a customer focus all over the organization,
- developing and standing by a Quality Policy that sets direction and alignment, and
- determining responsibilities and authorities all over the QMS, to make clear who has the power to make decisions, and what is expected from every function working in the system.
This section presents the requirements for determining and working with risks and opportunities, as well as those for setting quality objectives, aligned with the Quality Policy, and plans to meet them.
Clause 7 is a very diverse section that includes requirements for management to provide resources, i.e., human resources, infrastructure (including equipment, hardware and software, and building facilities), work environment (including temperature control, humidity control, dust control, and sterilization control), the control of any equipment used to monitor or measure the product or service, and the organizational knowledge required to operate the QMS. The importance of competence, awareness, and communication for human resources is emphasized.
This section is the only part of the standard where a company can choose to exclude sections of the requirements (such as excluding the design requirements if your company does not do design work). The requirements deal with planning for product (or service) and include determining and reviewing the product requirements, design and development, and purchasing, followed by manufacturing of a product or provision of a service and its supply. The final requirements deal with quality control and product or service nonconformities.
The performance evaluation section outlines requirements for assessing customer satisfaction, internal audit, monitoring, analysis, and evaluation of process performance. Also included are the requirements of the management review, including the mandatory inputs and outputs for the review.
The last section deals with improving your QMS through corrective actions and continual improvement. This is the final clause of the standard and the completion of the ISO 9001:2015 requirements.
There is also an appendix that clarifies and explains the ISO 9001 requirements in the preceding ISO 9001 sections, but it does not include further ISO 9001 Quality Management System requirements.
An important note about the implementation
The greatest difficulty when implementing the ISO 9001:2015 requirements is to ensure that the resulting collection of policies, procedures, processes, and records meets the needs of the company and its customers, while still allowing for improvement of the system. Improvement of the system is one of the main reasons for implementing a QMS, as it benefits the company in the long run. A QMS is a system, and a system is more than just the simple sum of answers to requirements.
To implement ISO 9001 requirements yourself, easily and efficiently, get this: ISO 9001 Documentation Toolkit .

ISO 9001 Documentation Toolkit
Step-by-step implementation for smaller companies

Related Products

ISO 9001 Foundations Course
Experta: AI-Powered Knowledge Base
Suggested reading.
You may unsubscribe at any time. For more information, please see our privacy notice .

- Search forums
- National and International Business System Standards
- ISO 9000, ISO 9001, and ISO 9004 Quality Management Systems Standards
Business Continuity Planning in ISO 9001?
- Thread starter qualprod
- Start date Feb 6, 2021
- Feb 6, 2021
Hello to all. I share this need of one of our customers. Is asking us a contingency plan. We are a small manufacturing company 90 people, producing labels of several material for the industry. Under 8.2.21 e) establishing specific requirements for contingency actions, when relevant. At what level we have to comply with this under ISO 9001? Could it be enough to have a risk detected with action plans regarding in how to comply the customer in case o f internal or external problems? For example, to have more suppliers of raw material, to have spare equipment in case of failures, more people trained in case of absences of someone? also is considered the Covid issue. Or should we comply with a special requirement of a BCP addressing specifics, issues? Could you share contingency plans which comply with this requirement of the standard? Thanks in advance.
- Feb 7, 2021
qualprod said: Hello to all. I share this need of one of our customers. Is asking us a contingency plan. We are a small manufacturing company 90 people, producing labels of several material for the industry. Under 8.2.21 e) establishing specific requirements for contingency actions, when relevant. At what level we have to comply with this under ISO 9001? Could it be enough to have a risk detected with action plans regarding in how to comply the customer in case o f internal or external problems? For example, to have more suppliers of raw material, to have spare equipment in case of failures, more people trained in case of absences of someone? also is considered the Covid issue. Or should we comply with a special requirement of a BCP addressing specifics, issues? Could you share contingency plans which comply with this requirement of the standard? Thanks in advance. Click to expand...
qualprod said: Under 8.2.21 e) establishing specific requirements for contingency actions, when relevant. Click to expand...
the organization should...ensure that it is proactive in communicating with the customer about possible contingency actions that can be taken, if the need occurs, to avoid having a detrimental effect on meeting customer requirements; this could include situations such as natural disasters, weather, labour disputes, shortfall of raw materials or of backup external providers Click to expand...
qualprod said: I share this need of one of our customers. Is asking us a contingency plan . Click to expand...
Tagin said: That requirement, 8.2.1e , is specific to 8.2.1 Customer communication , and according to TS9002 it means: So, that is really about how are you going to inform the customer when the unexpected occurs that might affect customer requirements, such as delivery schedules. A typhoon in the Pacific may not affect your plant, but it might affect your supply chain, which might interrupt or delay deliveries to your customer. So, a business continuity plan is not central to 'contingency' as used in this clause element (unless you extend your BCP to include your supply chain). So, by 'contingency plan' do they mean some form of disaster recovery plan or business continuity plan? Probably. Some customers have that as a 'checkbox' item for their suppliers and just want to see some disaster recovery or business continuity document, whether it is realistic or not. But if you are going to create one, you might as well have one that actually is useful for your organization. Beyond that, the customer may specify some criteria for the contingency plan, but usually do not. To me, DR/BCP arises from: 4.1 (determine external and internal issues) affecting 4.2 (needs and expectation of interested parties) addressed via 6.1 (actions to address risk and opportunities). So, combined into a sentence, it is a plan that addresses: What are the external and internal issues that potentially could impact our ability to meet the needs of interested parties, such as customers (and maybe the banks and employee payroll too!), and how can we plan ahead to address those risks if they occur? Click to expand...
qualprod said: On the other hand, you are right, it could be a good Idea to ask the customer, what is the specific need. Contingency plan or BCP? Altough in some way, is basically the same, dont´you think? Click to expand...
Ok, I understand what you mean. Based on the customer ´s requirements to define the BCP. On the other hand, what is the difference between BCP and contingency plan? I think is ths same but different names or is it a different scope? I didnt explain it, FODA is the SWOT.
- Feb 8, 2021
qualprod said: On the other hand, what is the difference between BCP and contingency plan? I think is ths same but different names Click to expand...
- Contingency plan - general term for any kind of plan to deal with major risks that will interrupt or cause to fail a project, business, etc.
- Business Continuity Plan - a contingency plan focused on making sure the business keeps operating even if major risk events occur.
- Disaster Recovery - a contingency plan that is a subset of a BCP, focused on restoring infrastructure and equipment to operation; often is assumed to refer specifically to recovery of IT systems.
- Feb 9, 2021
Tagin said: I look at it as: Contingency plan - general term for any kind of plan to deal with major risks that will interrupt or cause to fail a project, business, etc. Business Continuity Plan - a contingency plan focused on making sure the business keeps operating even if major risk events occur. Disaster Recovery - a contingency plan that is a subset of a BCP, focused on restoring infrastructure and equipment to operation; often is assumed to refer specifically to recovery of IT systems. Click to expand...
- Feb 10, 2021
I view 8.2.1e as dealing with contingencies as they arise and determining how to best handle it. Since a customer asked about contingency plans, before trying to develop far more work than necessary, talk to your customer and find out what his concerns are.
Jim I ´d add the next. As you said, it depends of customer, for example: if requirements of this customer are very strictive (contingencies plan against fire, flood, loss of power and facilities, terrorism, etc. but this customer buys only 500 USD a month. Well, I can say this customer , is not possible to have a plan for you in this way, I can´t afford it. So, under this case, I think, I comply by just having a short agreement mentioning few and simple contingencies, , e.g. Raw material shortage, having spare parts for machines, having personnel in stand-by waiting in case of absences and that´s all. If it were a customer who has high consumption of products, and this allow me to have high profits, well, In this is possible to have a robust BCP well documented where is included all what is necessary, all kind of contingencies, how to recover the plant in case is destroyed, how to have an agreement with another supplier to produce, while plant is down, to ensure the payments to employees while, plant is under rebuilding, the testing of the plans, etc. Is it ok, my assumption? Thanks
Lead Auditor Practitioner Qualification - ISO 9001
View the qualifications guide (PDF) for more information.
This first step on your auditor qualification journey will give you the foundational knowledge of the ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management System (QMS) standard and the understanding of the key principles. You’ll understand how to build relationships with stakeholders, and how to lead and manage an audit team in your organization. Led by expert BSI trainers, this qualification is designed for anyone who needs to audit an organization’s ISO 9001:2015 QMS.
Unlock the understanding you need for managing quality and driving improvements across an organization.
How will you benefit?
- Gain the skills you need to plan, conduct, report and follow up on a QMS audit
- Understand the key benefits and requirements of an ISO 9001:2015 QMS
- Achieve formal recognition of your knowledge and the ability to apply your skills within your organization
- Advance your career progression and continue your learning journey to unlock further qualifications to allow development within your role
- Access a global community of like-minded and qualified professionals to share experiences and practical advice to use in your everyday life
Which qualification will I achieve?

On successful completion of your qualification, you’ll receive a BSI Mark of Trust that can be shared across within your organization and across your network of contacts.
ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Practitioner qualification includes:
ISO 9001:2015 Requirements
- Learn the importance and benefits of an ISO 9001:2015 QMS
- Understand the key requirements and terms and definitions of ISO 9001:2015
- Recognize the structure of ISO 9001:2015, which incorporates the Annex SL common framework for management system standards
- Understand main concepts such as risk-based thinking, process approach, Plan-Do-Check-Act, and 7 management principles.
ISO 9001:2015 Lead Auditor (5 days classroom – in-person or virtual)
- On completion, successful delegates will have the knowledge and skills to perform first, second and third-party audits of quality management systems against ISO 9001, in accordance with ISO 19011 and ISO/IEC 17021, as applicable.
- Explain the purpose of a QMS and QMS standards and its business benefits
- Learn management system audit
- Gain third-party certification
- Explain the role and responsibilities of an auditor to plan, conduct, report and follow-up a QMS audit in accordance with ISO 19011, and ISO/IEC 17021, as applicable
- Gain the stills to plan, conduct, and report an audit
- Understand how to follow-up an audit of a QMS to establish conformity (or otherwise) with ISO 9001 and in accordance with ISO 19011, and ISO/IEC 17021, as applicable
Each module is followed by a mandatory online multiple-choice examination. Delegates must pass the examination to be awarded the qualification .
Anyone with the need to audit an organization's ISO 9001:2015 QMS.

After completing your Practitioner level qualification, why not undertake the next step and become an ISO 9001 Internal Auditor Professional qualification holder. Professional level takes you beyond conformity audits and develops your ability to audit improvement initiatives.
The focus of this advanced qualification is to expand upon process improvement approaches that can help strengthen and improve your organization’s quality management system.

The final step on the Auditor qualification pathway provides the opportunity to get your Professional Auditor qualification certified. Demonstrating that you have applied everything that you have learned in practice and in your work.
Let's shape your organization's future together
Reach out and see how we can help guide you on your path to sustainable operational success.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
An ISO 9001 Quality Management Plan is a crucial document that outlines the quality management processes and procedures to be followed in an organization. This plan serves as a guide for implementing and maintaining a quality management system that meets the requirements of the ISO 9001 international standard. By using this template, organizations can ensure that they have a comprehensive and ...
An ISO 9001 Project Plan will give you an overview of the steps required for achieving certification as well as a better understanding of the scope of the project. ... be coherent, and align with the overall business objectives, including customer expectations. 7. Start your Quality Manual. Use our Quality Manual Template to help document your ...
An ISO 9001 certification can open up a lot of business opportunities for you and your company. For instance, when bidding for contracts, an ISO 9001 certification is commonly a requirement. It was shown in a recent study by the American Society for Quality, that every $1 invested into your QMS results in an average increase of $6 in revenue ...
ISO 9001 was developed based on the plan-do-check-act (PDCA) methodology, AKA plan-do-study-act (PDSA). This methodology encourages a more process-oriented approach when recording and assessing company processes to achieve a reliable QMS. ... Agile ISO: A Holistic Business Process Management Framework; The 11 Agile Processes We Use to Run an ...
In order to effectively transform business ideas into actions, you need a plan. A quality plan. Guidance on how to create one has just been updated, providing a powerful tool to complement any quality management system, including ISO 9001.
Step 3 - Conduct a Gap Analysis. Once there is an understanding of the requirements of ISO 9001, the next step is to identify the gaps between your organization's current practices and ISO 9001 requirements. Organizations should develop an action plan to address the gaps, and they should define roles and responsibilities for implementing the ...
ISO 9001:2015 is the new business improvement tool that helps drive continual improvement and deliver results in your organization. It helps your business stand out, gain a competitive edge, and grow. ... Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) is the operating principle of ISO 9001. It's applied to all processes and the QMS as a whole. This diagram shows how
1 Scope. This International Standard specifies requirements for a quality management system when an organization: a) needs to demonstrate its ability to consistently provide products and services that meet customer and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements, and. b) aims to enhance customer satisfaction through the effective ...
ISO 9001 has become the quintessential international standard for quality management systems. Adopted by over 1 million global organisations, certification helps companies streamline operations, boost customer satisfaction, and align processes with strategic objectives, laying down a framework that ensures a brand's products or services meet and often exceed customer and regulatory benchmarks ...
an ISO 9001 QMS. It can be sensible to work your way through each clause one a time, using the structure of ISO 9001 itself as a guiding step-by-step 'checklist'. Clauses 2 and 3 are reference and guidance clauses and require no action from you. Clause 1, 'Scope', and Clause 4, 'Context', can form a useful interacting first step as ...
ISO 9001 is a globally recognized standard for quality management. It helps organizations of all sizes and sectors to improve their performance, meet customer expectations and demonstrate their commitment to quality. Its requirements define how to establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve a quality management system (QMS).
ISO 9001 is defined as the international standard that specifies requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Organizations use the standard to demonstrate the ability to consistently provide products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements. It is the most popular standard in the ISO 9000 series and the only standard ...
Learn how to quickly implement a business-friendly ISO 9001 system. Guided DIY Toolkit. Full-Service Consulting. Hybrid ISO 9001 Certification. Maintain & Improve. ... Develop a Project Plan. Plan the ISO 9001 implementation as a project. Focus on implementation steps, milestones, and target dates. Assign responsibilities.
Here is a detailed, 27-step ISO 9001 implementation guide. Implementing ISO 9001 can appear daunting — that's why we've written this ISO 9001 implementation guide and produced a Project Plan with 18-Step Implementation Checklist.. We aim to give you a thorough understanding of the scope of the project and a detailed, actionable framework for the different stages of implementation.
How to Implement A Quality Management System in 8 Steps. Familiarize Yourself with ISO 9001. Plan. Identify Responsibilities, Policies, and Objectives. Develop Your Documentation. Launch Your Quality Management System. Review Your Performance. Register for Certification. Continual Improvement.
The globally acclaimed ISO 9001 - Quality Management Systems standard serves as a potent tool for business enhancement, helping you achieve precisely this objective. Rooted in principles like process optimization, customer-centricity, and ongoing improvement, ISO 9001 offers comprehensive guidance for elevating your business performance.
The new version of ISO 9001 has a new approach to documents and records (see also New approach to document and record control in ISO 9001:2015) and this opportunity should definitely be seized.Without so many mandatory procedures as the previous version of the standard, requirements for documenting processes to ensure they deliver intended results can be approached differently.
Implementing ISO 9001, the international standard for quality management systems, can be a daunting task for organizations. However, with proper planning and execution, it can bring numerous benefits to the organization, such as improved customer satisfaction, increased operational efficiency, and enhanced reputation. This blog post will provide a step-by-step implementation plan for ISO 9001 ...
ISO 9001 builds on seven quality management principles. Following these principles will ensure your organization or business is set up to consistently create value for its customers. With these seven pillars firmly in place, implementing a quality management system will be much easier. The seven quality management principles are : Customer ...
Here are some ISO 9001 quality objectives examples: If the Quality Policy of a widget manufacturer had identified a customer need for just-in-time delivery with no defects as the most important requirement, the goal from the Quality Policy might read: "To deliver widgets to our customers when they need them, with no defects, every time.".
ISO 9001 clauses 0 to 3: Introduction, Scope, References, Terms and Definitions. Clause 0 mentions the benefits of implementing a QMS and the quality management principles, and presents the process approach, the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle, and risk-based thinking. These ISO 9001 elements are important for understanding the ISO 9001 sections that ...
I don't find any reference to a business plan in ISO 9001:2008. I suppose a business plan could be used to help fulfill the requirements of element 5.4.2, but I have never seen that approach used. Business plan is recalled and cited in ISO TS 16949 in clause 5.4.1.1. However you can include how the management deals with quality objectives and ...
Find expert ISO 9001 consulting services to ensure your business meets quality management standards with our helpful guide on what to look for in a reliable partner. ... 6 Plan for Future.
Tagin said: I look at it as: Contingency plan - general term for any kind of plan to deal with major risks that will interrupt or cause to fail a project, business, etc. Business Continuity Plan - a contingency plan focused on making sure the business keeps operating even if major risk events occur.
Understand the key requirements and terms and definitions of ISO 9001:2015 ; Recognize the structure of ISO 9001:2015, which incorporates the Annex SL common framework for management system standards ; Understand main concepts such as risk-based thinking, process approach, Plan-Do-Check-Act, and 7 management principles. ISO 9001:2015 Lead ...