- Fact sheets
- Facts in pictures
Publications
- Questions and answers
- Tools and toolkits
- Endometriosis
- Excessive heat
- Mental disorders
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- All countries
- Eastern Mediterranean
- South-East Asia
- Western Pacific
- Data by country
- Country presence
- Country strengthening
- Country cooperation strategies
- News releases
- Feature stories
- Press conferences
- Commentaries
- Photo library
- Afghanistan
- Cholera
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
- Greater Horn of Africa
- Israel and occupied Palestinian territory
- Disease Outbreak News
- Situation reports
- Weekly Epidemiological Record
- Surveillance
- Health emergency appeal
- International Health Regulations
- Independent Oversight and Advisory Committee
- Classifications
- Data collections
- Global Health Estimates
- Mortality Database
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Health Inequality Monitor
- Global Progress
- World Health Statistics
- Partnerships
- Committees and advisory groups
- Collaborating centres
- Technical teams
- Organizational structure
- Initiatives
- General Programme of Work
- WHO Academy
- Investment in WHO
- WHO Foundation
- External audit
- Financial statements
- Internal audit and investigations
- Programme Budget
- Results reports
- Governing bodies
- World Health Assembly
- Executive Board
- Member States Portal
- Health topics /
Research is indispensable for resolving public health challenges – whether it be tackling diseases of poverty, responding to rise of chronic diseases, or ensuring that mothers have access to safe delivery practices.
Likewise, shared vulnerability to global threats, such as severe acute respiratory syndrome, Ebola virus disease, Zika virus and avian influenza has mobilized global research efforts in support of enhancing capacity for preparedness and response. Research is strengthening surveillance, rapid diagnostics and development of vaccines and medicines.
Public-private partnerships and other innovative mechanisms for research are concentrating on neglected diseases in order to stimulate the development of vaccines, drugs and diagnostics where market forces alone are insufficient.
Research for health spans 5 generic areas of activity:
- measuring the magnitude and distribution of the health problem;
- understanding the diverse causes or the determinants of the problem, whether they are due to biological, behavioural, social or environmental factors;
- developing solutions or interventions that will help to prevent or mitigate the problem;
- implementing or delivering solutions through policies and programmes; and
- evaluating the impact of these solutions on the level and distribution of the problem.
High-quality research is essential to fulfilling WHO’s mandate for the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health. One of the Organization’s core functions is to set international norms, standards and guidelines, including setting international standards for research.
Under the “WHO strategy on research for health”, the Organization works to identify research priorities, and promote and conduct research with the following 4 goals:
- Capacity - build capacity to strengthen health research systems within Member States.
- Priorities - support the setting of research priorities that meet health needs particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
- Standards - develop an enabling environment for research through the creation of norms and standards for good research practice.
- Translation - ensure quality evidence is turned into affordable health technologies and evidence-informed policy.
- Prequalification of medicines by WHO
- Global Observatory on Health R&D
- Global Observatory on Health Research and Development
- Implementation research toolkit
- Ethics in implementation research: participant's guide
- Ethics in implementation research: facilitator's guide
- Ethics in epidemics, emergencies and disasters: Research, surveillance and patient care: WHO training manual
- WHA58.34 Ministerial Summit on Health Research
- WHA60.15 WHO's role and responsibilities in health research
- WHA63.21 WHO's role and responsibilities in health research
- EB115/30 Ministerial Summit on Health Research: report by the Secretariat
- Science division
WHO consults on action plan for sustainable clinical research infrastructure
WHO advisory group convenes its first meeting on responsible use of the life sciences in Geneva
Challenging harmful masculinities and engaging men and boys in sexual and reproductive health
Stakeholders convene in Uganda on responsible use of the life sciences


Target product profiles for animal plasma-derived antivenoms: antivenoms for treatment of snakebite envenoming...
We describe here WHO public-benefit Target Product Profiles (TPPs) for antivenoms intended to be used for treatment of snakebite envenoming in South Asia,...

WHO global research priorities for sexually transmitted infections
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are widespread globally and negatively affect sexual and reproductive health. Gaps in evidence and in available...

Report of the sixth meeting of the WHO Diagnostic Technical Advisory Group for Neglected Tropical Diseases:...
The World Health Organization’s Global Neglected Tropical Diseases Programme (WHO/NTD) manages a diverse portfolio of 21 diseases and disease groups,1 ...

Target product profile for a diagnostic test to confirm cure of visceral leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is caused by protozoan parasites which are transmitted by the bite of infected female phlebotomine sandflies. The disease is poverty-related...
Coordinating R&D on antimicrobial resistance
Ensuring responsible use of life sciences research
Prioritizing diseases for research and development in emergency contexts
Promoting research on Buruli ulcer
Research in maternal, perinatal, and adolescent health
Undertaking health law research
Feature story
One year on, Global Observatory on Health R&D identifies striking gaps and inequalities

Video: Open access to health: WHO joins cOAlition S

Video: Multisectional research on sleeping sickness in Tanzania in the context of climate change
Related health topics
Clinical trials
Global health ethics
Health Laws
Intellectual property and trade
Related links
Research and Development Blueprint
WHO Collaborating Centres
R&D Blueprint for Action to Prevent Epidemics
International Clinical Trials Registry Platform
Masks Strongly Recommended but Not Required in Maryland, Starting Immediately
Due to the downward trend in respiratory viruses in Maryland, masking is no longer required but remains strongly recommended in Johns Hopkins Medicine clinical locations in Maryland. Read more .
- Vaccines
- Masking Guidelines
- Visitor Guidelines
Understanding Clinical Trials
Clinical research: what is it.
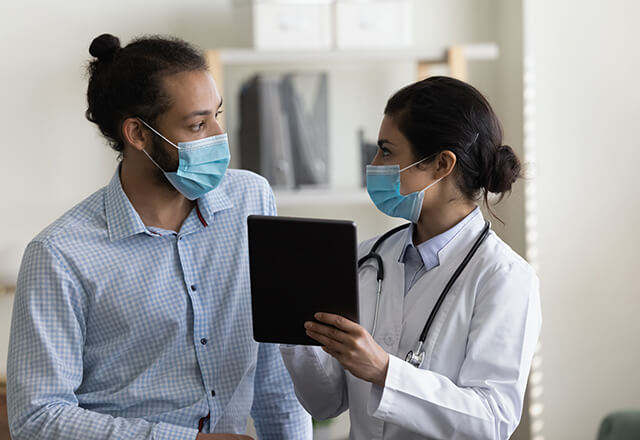

Your doctor may have said that you are eligible for a clinical trial, or you may have seen an ad for a clinical research study. What is clinical research, and is it right for you?
Clinical research is the comprehensive study of the safety and effectiveness of the most promising advances in patient care. Clinical research is different than laboratory research. It involves people who volunteer to help us better understand medicine and health. Lab research generally does not involve people — although it helps us learn which new ideas may help people.
Every drug, device, tool, diagnostic test, technique and technology used in medicine today was once tested in volunteers who took part in clinical research studies.
At Johns Hopkins Medicine, we believe that clinical research is key to improve care for people in our community and around the world. Once you understand more about clinical research, you may appreciate why it’s important to participate — for yourself and the community.
What Are the Types of Clinical Research?
There are two main kinds of clinical research:
Observational Studies
Observational studies are studies that aim to identify and analyze patterns in medical data or in biological samples, such as tissue or blood provided by study participants.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials, which are also called interventional studies, test the safety and effectiveness of medical interventions — such as medications, procedures and tools — in living people.
Clinical research studies need people of every age, health status, race, gender, ethnicity and cultural background to participate. This will increase the chances that scientists and clinicians will develop treatments and procedures that are likely to be safe and work well in all people. Potential volunteers are carefully screened to ensure that they meet all of the requirements for any study before they begin. Most of the reasons people are not included in studies is because of concerns about safety.
Both healthy people and those with diagnosed medical conditions can take part in clinical research. Participation is always completely voluntary, and participants can leave a study at any time for any reason.
“The only way medical advancements can be made is if people volunteer to participate in clinical research. The research participant is just as necessary as the researcher in this partnership to advance health care.” Liz Martinez, Johns Hopkins Medicine Research Participant Advocate
Types of Research Studies
Within the two main kinds of clinical research, there are many types of studies. They vary based on the study goals, participants and other factors.
Biospecimen studies
Healthy volunteer studies.
Clinical trials study the safety and effectiveness of interventions and procedures on people’s health. Interventions may include medications, radiation, foods or behaviors, such as exercise. Usually, the treatments in clinical trials are studied in a laboratory and sometimes in animals before they are studied in humans. The goal of clinical trials is to find new and better ways of preventing, diagnosing and treating disease. They are used to test:
Drugs or medicines

New types of surgery

Medical devices

New ways of using current treatments

New ways of changing health behaviors

New ways to improve quality of life for sick patients

Goals of Clinical Trials
Because every clinical trial is designed to answer one or more medical questions, different trials have different goals. Those goals include:
Treatment trials
Prevention trials, screening trials, phases of a clinical trial.
In general, a new drug needs to go through a series of four types of clinical trials. This helps researchers show that the medication is safe and effective. As a study moves through each phase, researchers learn more about a medication, including its risks and benefits.
Is the medication safe and what is the right dose? Phase one trials involve small numbers of participants, often normal volunteers.
Does the new medication work and what are the side effects? Phase two trials test the treatment or procedure on a larger number of participants. These participants usually have the condition or disease that the treatment is intended to remedy.
Is the new medication more effective than existing treatments? Phase three trials have even more people enrolled. Some may get a placebo (a substance that has no medical effect) or an already approved treatment, so that the new medication can be compared to that treatment.
Is the new medication effective and safe over the long term? Phase four happens after the treatment or procedure has been approved. Information about patients who are receiving the treatment is gathered and studied to see if any new information is seen when given to a large number of patients.
“Johns Hopkins has a comprehensive system overseeing research that is audited by the FDA and the Association for Accreditation of Human Research Protection Programs to make certain all research participants voluntarily agreed to join a study and their safety was maximized.” Gail Daumit, M.D., M.H.S., Vice Dean for Clinical Investigation, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
Is It Safe to Participate in Clinical Research?
There are several steps in place to protect volunteers who take part in clinical research studies. Clinical Research is regulated by the federal government. In addition, the institutional review board (IRB) and Human Subjects Research Protection Program at each study location have many safeguards built in to each study to protect the safety and privacy of participants.
Clinical researchers are required by law to follow the safety rules outlined by each study's protocol. A protocol is a detailed plan of what researchers will do in during the study.
In the U.S., every study site's IRB — which is made up of both medical experts and members of the general public — must approve all clinical research. IRB members also review plans for all clinical studies. And, they make sure that research participants are protected from as much risk as possible.
Earning Your Trust
This was not always the case. Many people of color are wary of joining clinical research because of previous poor treatment of underrepresented minorities throughout the U.S. This includes medical research performed on enslaved people without their consent, or not giving treatment to Black men who participated in the Tuskegee Study of Untreated Syphilis in the Negro Male. Since the 1970s, numerous regulations have been in place to protect the rights of study participants.
Many clinical research studies are also supervised by a data and safety monitoring committee. This is a group made up of experts in the area being studied. These biomedical professionals regularly monitor clinical studies as they progress. If they discover or suspect any problems with a study, they immediately stop the trial. In addition, Johns Hopkins Medicine’s Research Participant Advocacy Group focuses on improving the experience of people who participate in clinical research.
Clinical research participants with concerns about anything related to the study they are taking part in should contact Johns Hopkins Medicine’s IRB or our Research Participant Advocacy Group .
Learn More About Clinical Research at Johns Hopkins Medicine
For information about clinical trial opportunities at Johns Hopkins Medicine, visit our trials site.
Video Clinical Research for a Healthier Tomorrow: A Family Shares Their Story
Clinical Research for a Healthier Tomorrow: A Family Shares Their Story

Participating in Health Research Studies
What is health research.
- Is Health Research Safe?
- Is Health Research Right for Me?
- Types of Health Research
The term "health research," sometimes also called "medical research" or "clinical research," refers to research that is done to learn more about human health. Health research also aims to find better ways to prevent and treat disease. Health research is an important way to help improve the care and treatment of people worldwide.
Have you ever wondered how certain drugs can cure or help treat illness? For instance, you might have wondered how aspirin helps reduce pain. Well, health research begins with questions that have not been answered yet such as:
"Does a certain drug improve health?"
To gain more knowledge about illness and how the human body and mind work, volunteers can help researchers answer questions about health in studies of an illness. Studies might involve testing new drugs, vaccines, surgical procedures, or medical devices in clinical trials . For this reason, health research can involve known and unknown risks. To answer questions correctly, safely, and according to the best methods, researchers have detailed plans for the research and procedures that are part of any study. These procedures are called "protocols."
An example of a research protocol includes the process for determining participation in a study. A person might meet certain conditions, called "inclusion criteria," if they have the required characteristics for a study. A study on menopause may require participants to be female. On the other hand, a person might not be able to enroll in a study if they do not meet these criteria based on "exclusion criteria." A male may not be able to enroll in a study on menopause. These criteria are part of all research protocols. Study requirements are listed in the description of the study.
A Brief History
While a few studies of disease were done using a scientific approach as far back as the 14th Century, the era of modern health research started after World War II with early studies of antibiotics. Since then, health research and clinical trials have been essential for the development of more than 1,000 Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved drugs. These drugs help treat infections, manage long term or chronic illness, and prolong the life of patients with cancer and HIV.
Sound research demands a clear consent process. Public knowledge of the potential abuses of medical research arose after the severe misconduct of research in Germany during World War II. This resulted in rules to ensure that volunteers freely agree, or give "consent," to any study they are involved in. To give consent, one should have clear knowledge about the study process explained by study staff. Additional safeguards for volunteers were also written in the Nuremberg Code and the Declaration of Helsinki .
New rules and regulations to protect research volunteers and to eliminate ethical violations have also been put in to place after the Tuskegee trial . In this unfortunate study, African American patients with syphilis were denied known treatment so that researchers could study the history of the illness. With these added protections, health research has brought new drugs and treatments to patients worldwide. Thus, health research has found cures to many diseases and helped manage many others.
Why is Health Research Important?
The development of new medical treatments and cures would not happen without health research and the active role of research volunteers. Behind every discovery of a new medicine and treatment are thousands of people who were involved in health research. Thanks to the advances in medical care and public health, we now live on average 10 years longer than in the 1960's and 20 years longer than in the 1930's. Without research, many diseases that can now be treated would cripple people or result in early death. New drugs, new ways to treat old and new illnesses, and new ways to prevent diseases in people at risk of developing them, can only result from health research.
Before health research was a part of health care, doctors would choose medical treatments based on their best guesses, and they were often wrong. Now, health research takes the guesswork out. In fact, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requires that all new medicines are fully tested before doctors can prescribe them. Many things that we now take for granted are the result of medical studies that have been done in the past. For instance, blood pressure pills, vaccines to prevent infectious diseases, transplant surgery, and chemotherapy are all the result of research.
Medical research often seems much like standard medical care, but it has a distinct goal. Medical care is the way that your doctors treat your illness or injury. Its only purpose is to make you feel better and you receive direct benefits. On the other hand, medical research studies are done to learn about and to improve current treatments. We all benefit from the new knowledge that is gained in the form of new drugs, vaccines, medical devices (such as pacemakers) and surgeries. However, it is crucial to know that volunteers do not always receive any direct benefits from being in a study. It is not known if the treatment or drug being studied is better, the same, or even worse than what is now used. If this was known, there would be no need for any medical studies.
- Next: Is Health Research Safe? >>
- Last Updated: May 27, 2020 3:05 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/healthresearch
| | |
- Education Home
- Medical Education Technology Support
- Graduate Medical Education
- Medical Scientist Training Program
- Public Health Sciences Program
- Continuing Medical Education
- Clinical Performance Education Center
- Center for Excellence in Education
- Research Home
- Biochemistry & Molecular Genetics
- Biomedical Engineering
- Cell Biology
- Genome Sciences
- Microbiology, Immunology, & Cancer Biology (MIC)
- Molecular Physiology & Biological Physics
- Neuroscience
- Pharmacology
- Public Health Sciences
- Office for Research
- Clinical Research
- Clinical Trials Office
- Funding Opportunities
- Grants & Contracts
- Research Faculty Directory
- Cancer Center
- Cardiovascular Research Center
- Carter Immunology Center
- Center for Behavioral Health & Technology
- Center for Brain Immunology & Glia
- Center for Diabetes Technology
- Center for Immunity, Inflammation & Regenerative Medicine
- Center for Membrane & Cell Physiology
- Center for Research in Reproduction
- Myles H. Thaler Center for AIDS & Human Retrovirus Research
- Child Health Research Center (Pediatrics)
- Division of Perceptual Studies
- Research News: The Making of Medicine
- Core Facilities
- Virginia Research Resources Consortium
- Center for Advanced Vision Science
- Charles O. Strickler Transplant Center
- Keck Center for Cellular Imaging
- Institute of Law, Psychiatry & Public Policy
- Translational Health Research Institute of Virginia
- Clinical Home
- Anesthesiology
- Dermatology
- Emergency Medicine
- Family Medicine
- Neurosurgery
- Obstetrics & Gynecology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedic Surgery
- Otolaryngology
- Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
- Plastic Surgery, Maxillofacial, & Oral Health
- Psychiatry & Neurobehavioral Sciences
- Radiation Oncology
- Radiology & Medical Imaging
- UVA Health: Patient Care
- Diversity Home
- Diversity Overview
- Student Resources
- GME Trainee Resources
- Faculty Resources
- Community Resources
What is Clinical Research?
Clinical research is the study of health and illness in people. It is the way we learn how to prevent, diagnose and treat illness. Clinical research describes many different elements of scientific investigation. Simply put, it involves human participants and helps translate basic research (done in labs) into new treatments and information to benefit patients. Clinical trials as well as research in epidemiology, physiology and pathophysiology, health services, education, outcomes and mental health can all fall under the clinical research umbrella.
Clinical Trials
A clinical trial is a type of clinical research study. A clinical trial is an experiment designed to answer specific questions about possible new treatments or new ways of using existing (known) treatments. Clinical trials are done to determine whether new drugs or treatments are safe and effective. Clinical trials are part of a long, careful process which may take many years to complete. First, doctors study a new treatment in the lab. Then they often study the treatment in animals. If a new treatment shows promise, doctors then test the treatment in people via a clinical trial.
Clinical Research vs. Medical Care
People often confuse a clinical research or clinical trials with medical care. This topic can be especially confusing if your doctor is also the researcher. When you receive medical care from your own doctor, he or she develops a plan of care just for you. When you take part in a clinical research study, you and the researcher must follow a set plan called the “study protocol.” The researcher usually can’t adjust the plan for you – but the plan includes steps to follow if you aren’t doing well. It’s important to understand that a clinical trial is an experiment. By its nature, that means the answer to the research question is still unknown. You might or might not benefit directly by participating in a clinical research study. It is important to talk about this topic with your doctor/the researcher.
- Clinical Trials Unit
- Diversity in Clinical Research
- Research Resources
- Study Management
- Participate in a Trial
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
Medical research articles from across Nature Portfolio
Medical research involves research in a wide range of fields, such as biology, chemistry, pharmacology and toxicology with the goal of developing new medicines or medical procedures or improving the application of those already available. It can be viewed as encompassing preclinical research (for example, in cellular systems and animal models) and clinical research (for example, clinical trials).
The MARIPOSA trials — implications for the treatment of EGFR -mutant NSCLC
In the past 2 years, substantial improvements have been made in the management of advanced-stage EGFR -mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Recent studies have suggested added benefit from the combination of third-generation tyrosine-kinase inhibitors with either chemotherapy or a bispecific antibody targeting EGFR and MET. Herein, we summarize these advances and their implications for clinical practice.
- Fatemeh Ardeshir-Larijani
- Suresh S. Ramalingam
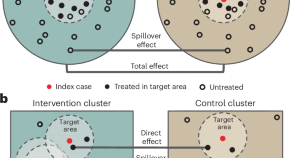
Spillover effects of targeted malaria interventions benefit neighboring areas
In a setting of low malaria transmission, preventive interventions that target human and mosquito parasite reservoirs located near malaria cases reduced malaria among non-recipients up to 3 km away. Accounting for these ‘spillover effects’ reveals a higher population-level health benefit, and increased cost-effectiveness compared with previous analyses.
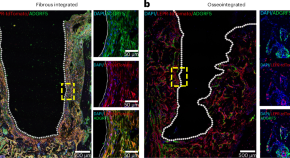
The formation and maintenance of peri-implant fibrosis requires skeletal cells expressing the leptin receptor
The cellular composition of fibrous tissue around orthopaedic implants and the genetic pathways involved in its formation are unclear. We find that leptin-receptor-expressing cells activate the adhesion G-protein-coupled receptor F5 (ADGRF5) pathway to form peri-implant fibrous tissue. Inhibition of ADGRF5 in leptin-receptor-expressing cells can prevent and reverse peri-implant fibrosis.
Related Subjects
- Drug development
- Epidemiology
- Experimental models of disease
- Genetics research
- Outcomes research
- Paediatric research
- Preclinical research
- Stem-cell research
- Clinical trial design
- Translational research
Latest Research and Reviews
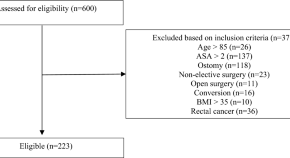
Morbidity after accelerated enhanced recovery protocol for colon cancer surgery
- Misha A. T. Sier
- Sarah L. Dekkers
- Jan H. M. B. Stoot
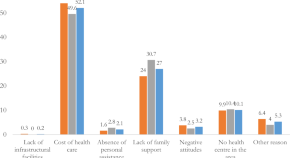
Healthcare services access challenges and determinants among persons with disabilities in Bangladesh
- Mizanur Rahman
- Md Shohel Rana
- Md Nuruzzaman Khan
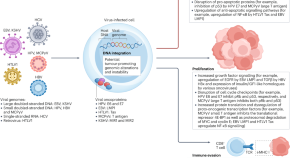
Applications of cell therapy in the treatment of virus-associated cancers
Several different viruses have a role in cancer pathogenesis, contributing to the development of various haematological malignancies and solid tumours via diverse, multifaceted mechanisms. However, this viral aetiology presents a unique opportunity for adoptive virus-specific T cell (VST) therapy. This Review summarizes the mechanisms of viral carcinogenesis and describes the current clinical experience with adoptive cellular immunotherapies for virus-related cancers, predominantly using non-genetically modified VSTs. The authors also discuss challenges and future directions for the ongoing clinical development of VST therapies.
- Chase D. McCann
- Catherine M. Bollard
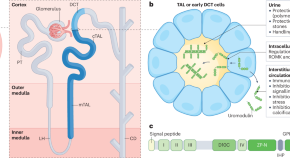
Advances in uromodulin biology and potential clinical applications
In this Review, the authors examine advances in uromodulin biology, including the existence of non-polymeric forms of the protein, its versatile functions, crosstalk with the immune system, its potential as a biomarker and its role in kidney disease, as well as considering how uromodulin might be targeted therapeutically.
- Azuma Nanamatsu
- Larissa de Araújo
- Tarek M. El-Achkar
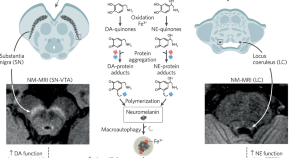
Neuromelanin-sensitive MRI for mechanistic research and biomarker development in psychiatry
- Kenneth Wengler
- Paula Trujillo
- Guillermo Horga
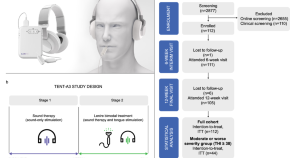
Combining sound with tongue stimulation for the treatment of tinnitus: a multi-site single-arm controlled pivotal trial
Bimodal neuromodulation combining sound therapy with electrical tongue stimulation using the Lenire device is a nonsurgical treatment for tinnitus. Here, the authors show the positive efficacy and safety results of a controlled one-arm pivotal trial that led to FDA De Novo approval of the Lenire device.
- Michael Boedts
- Andreas Buechner
- Thomas Lenarz
News and Comment
IL-23 inhibitors go head to head in Crohn’s disease
Risankizumab outperformed ustekinumab for the treatment of moderate to severe Crohn’s disease in patients refractory to anti-TNF therapy.
- Karen O’Leary
Inulin supplementation in pediatric obesity management: a critical appraisal of efficacy and limitations
- Yanggang Hong

Child with ultra-rare disease gets a treatment just for her
Therapy designed for one seems to have improved a young girl’s quality of life.
Hopes dashed for drug aimed at monkeypox virus spreading in Africa
Early results from clinical trial show that the antiviral drug tecovirimat is no better than placebo against the clade I virus type.
- Mariana Lenharo
The mysteries of inflammatory bowel disease are being cracked — offering hope for new therapies
Advances in understanding the causes of the autoimmune disorder could aid in matching people with the right treatment.
- Heidi Ledford
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Medical Research
Scientists and physicians in academic medicine conduct groundbreaking biomedical research that improves our knowledge of human health and promotes the development of treatments from bench to bedside to community.

Through policy and advocacy initiatives, data and research projects, professional learning and networking opportunities, and the development of tools and resources, the AAMC supports the entire spectrum of medical research from basic discovery and translational science to clinical and population health research, research policies and regulations that promote robust and ethical science and minimize administrative burden and a diverse biomedical research workforce and an inclusive and equitable research environment across all career stages.
On this page:
Science policy updates .
AAMC updates on federal science policy and regulatory topics impacting institutions and researchers can be found below.
The AAMC submitted a letter to FDA and HHS on draft guidance.
- May 3, 2024
AAMC submitted comments to the Department of Justice regarding access to bulk sensitive personal data by countries of concern.
- April 26, 2024
AAMC submitted comments to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) on the updated NIH Strategic Plan for Data Science, 2023-2028
- March 15, 2024
For more on the latest legislative and regulatory activities affecting academic medicine, check out Washington Highlights . For the latest news, current trends, and ongoing conversations about the most important topics in academic medicine, visit AAMCNews .
Meet our New Chief Scientific Officer

As chief scientific officer, Elena Fuentes-Afflick, MD, MPH, leads AAMC programs that support medical research and the training of physician-scientists and researchers in academic medicine. In this role, she provides leadership and vision for addressing research and science policy and other related critical issues facing academic medicine, medical schools, teaching health systems, and teaching hospitals. Learn more about Dr. Fuentes-Afflick .
Connect with Colleagues
The AAMC convenes several affinity groups focused on connecting individuals who work in biomedical research or support researchers at their institution. Affinity groups include councils, professional development groups, and other organizations that provide individuals at member institutions access to professional growth, leadership development, networking, and collaboration opportunities.
Find information about how to join each group on the pages below.
CFAS represents the collective interests of medical school faculty and academic societies on a range of cross-cutting issues.
GRAND convenes research leaders in discussion of issues critical to the research enterprise and linking research advancements with improvements to health.
GREAT provides a forum for discussion of the research training enterprise with leadership of biomedical graduate, postdoctoral, and MD-PhD programs.
FOCI provides a national forum for leadership who oversee and manage conflict of interest related to research, medical education, and clinical decision-making.
The GDI unites expertise, experience, and innovation to guide the advancement of diversity, equity, and inclusion throughout medicine and biomedical sciences.
The research subgroup of COF promotes compliance and ethical conduct in academic medicine with a specific focus on research and laboratory issues.
Attend an Event
The AAMC is committed to providing professional learning opportunities for biomedical researchers in every stage of their career. Find information about the AAMC’s webinars, meetings, and more below.
Related AAMC Initiatives
The AAMC engages in other work that may be of interest to researchers and scientists:
An optimal research environment that drives impactful biomedical discovery is supportive, diverse, equitable, and inclusive.
The Center sparks community-centered, multi-sector research, collaboration, and action to make the case for policies and practices that ensure all communities have an equal opportunity to thrive.

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction

Levels of health care
- In the developing countries
- In the developed countries
- Administration of primary health care
- United States
- Other developed countries
- Other developing countries
- Alternative or complementary medicine
- Specialties in medicine
- Periodic medical examination
- The industrial and the personal physician
- Industrial health services
- Family health care
- Former Soviet Union
- Army medical organization
- Naval and air force medicine
- Historical notes
- Clinical observation
- Drug research
- Screening procedures

Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- National Center For Biotechnological Information - PubMed Central - History of Medicine between tradition and modernity
- Official Site of the National Institutes of Health
- Merck Manual - Consumer Version - The Science of Medicine
- medicine - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
- medicine - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)
- Table Of Contents

medicine , the practice concerned with the maintenance of health and the prevention, alleviation, or cure of disease .
The World Health Organization at its 1978 international conference held in the Soviet Union produced the Alma-Ata Health Declaration, which was designed to serve governments as a basis for planning health care that would reach people at all levels of society. The declaration reaffirmed that
health, which is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being, and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity, is a fundamental human right and that the attainment of the highest possible level of health is a most important world-wide social goal whose realization requires the action of many other social and economic sectors in addition to the health sector.
In its widest form, the practice of medicine—that is to say, the promotion and care of health—is concerned with this ideal.
Organization of health services

It is generally the goal of most countries to have their health services organized in such a way to ensure that individuals, families, and communities obtain the maximum benefit from current knowledge and technology available for the promotion, maintenance, and restoration of health. In order to play their part in this process, governments and other agencies are faced with numerous tasks, including the following: (1) They must obtain as much information as is possible on the size, extent, and urgency of their needs; without accurate information, planning can be misdirected. (2) These needs must then be revised against the resources likely to be available in terms of money, manpower, and materials; developing countries may well require external aid to supplement their own resources. (3) Based on their assessments , countries then need to determine realistic objectives and draw up plans. (4) Finally, a process of evaluation needs to be built into the program; the lack of reliable information and accurate assessment can lead to confusion, waste, and inefficiency.
Health services of any nature reflect a number of interrelated characteristics, among which the most obvious, but not necessarily the most important from a national point of view, is the curative function; that is to say, caring for those already ill. Others include special services that deal with particular groups (such as children or pregnant women) and with specific needs such as nutrition or immunization; preventive services, the protection of the health both of individuals and of communities; health education; and, as mentioned above, the collection and analysis of information.
In the curative domain there are various forms of medical practice. They may be thought of generally as forming a pyramidal structure, with three tiers representing increasing degrees of specialization and technical sophistication but catering to diminishing numbers of patients as they are filtered out of the system at a lower level. Only those patients who require special attention either for diagnosis or treatment should reach the second (advisory) or third (specialized treatment) tiers where the cost per item of service becomes increasingly higher. The first level represents primary health care , or first contact care, at which patients have their initial contact with the health-care system.
Primary health care is an integral part of a country’s health maintenance system, of which it forms the largest and most important part. As described in the declaration of Alma-Ata, primary health care should be “based on practical, scientifically sound and socially acceptable methods and technology made universally accessible to individuals and families in the community through their full participation and at a cost that the community and country can afford to maintain at every stage of their development.” Primary health care in the developed countries is usually the province of a medically qualified physician; in the developing countries first contact care is often provided by nonmedically qualified personnel.
The vast majority of patients can be fully dealt with at the primary level. Those who cannot are referred to the second tier ( secondary health care , or the referral services) for the opinion of a consultant with specialized knowledge or for X-ray examinations and special tests. Secondary health care often requires the technology offered by a local or regional hospital . Increasingly, however, the radiological and laboratory services provided by hospitals are available directly to the family doctor, thus improving his service to patients and increasing its range. The third tier of health care, employing specialist services, is offered by institutions such as teaching hospitals and units devoted to the care of particular groups—women, children, patients with mental disorders, and so on. The dramatic differences in the cost of treatment at the various levels is a matter of particular importance in developing countries, where the cost of treatment for patients at the primary health-care level is usually only a small fraction of that at the third level; medical costs at any level in such countries, however, are usually borne by the government.
Ideally, provision of health care at all levels will be available to all patients; such health care may be said to be universal. The well-off, both in relatively wealthy industrialized countries and in the poorer developing world, may be able to get medical attention from sources they prefer and can pay for in the private sector. The vast majority of people in most countries, however, are dependent in various ways upon health services provided by the state, to which they may contribute comparatively little or, in the case of poor countries, nothing at all.
Office: 919.785.1304 | Fax: 919.785.1306

- Donate to SUBR
- Copyright and Privacy Statements
- Why Are Animals Needed in Research?
- What About Using Fewer Animals or No Animals?
- Product and Environmental Safety Research
- What is Biomedical Research?
- Biomedical Research Definitions
- Research Options
- How Animals Help
- Member Organizations
WHAT IS BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH?
Biomedical research is the broad area of science that looks for ways to prevent and treat diseases that cause illness and death in people and in animals. This general field of research includes many areas of both the life and physical sciences.
Utilizing biotechnology techniques, biomedical researchers study biological processes and diseases with the ultimate goal of developing effective treatments and cures. Biomedical research is an evolutionary process requiring careful experimentation by many scientists, including biologists and chemists. Discovery of new medicines and therapies requires careful scientific experimentation, development, and evaluation.
Why are Animals Used in Biomedical Research?
The use of animals in some types of research is essential to the development of new and more effective methods for diagnosing and treating diseases that affect both humans and animals. Scientists use animals to learn more about health problems, and to assure the safety of new medical treatments. Medical researchers need to understand health problems before they can develop ways to treat them. Some diseases and health problems involve processes that can only be studied in living organisms. Animals are necessary to medical research because it is impractical or unethical to use humans.
Animals make good research subjects for a variety of reasons. Animals are biologically similar to humans. They are susceptible to many of the same health problems, and they have short life-cycles so they can easily be studied throughout their whole life-span or across several generations. In addition, scientists can easily control the environment around animals (diet, temperature, lighting), which would be difficult to do with people. Finally, a primary reason why animals are used is that most people feel it would be wrong to deliberately expose human beings to health risks in order to observe the course of a disease.
Animals are used in research to develop drugs and medical procedures to treat diseases. Scientists may discover such drugs and procedures using alternative research methods that do not involve animals. If the new therapy seems promising, it is tested in animals to see whether it seems to be safe and effective. If the results of the animal studies are good, then human volunteers are asked to participate in a clinical trial. The animal studies are conducted first to give medical researchers a better idea of what benefits and complications they are likely to see in humans.
A variety of animals provide very useful models for the study of diseases afflicting both animals and humans. However, approximately 95 percent of research animals in the United States are rats, mice, and other rodents bred specifically for laboratory research. Dogs, cats, and primates account for less than one percent of all the animals used in research.
Those working in the field of biomedical research have a duty to conduct research in a manner that is humane, appropriate, and judicious. CBRA supports adherence to standards of care developed by scientific and professional organizations, and compliance with governmental regulations for the use of animals in research.
Scientists continue to look for ways to reduce the numbers of animals needed to obtain valid results, refine experimental techniques, and replace animals with other research methods whenever feasible.
© California Biomedical Research Association
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services

- Virtual Tour
- Staff Directory
- En Español
You are here
Nih clinical research trials and you, glossary of common terms, clinical research.
Clinical research is medical research that involves people to test new treatments and therapies.
Clinical Trial
A research study in which one or more human subjects are prospectively assigned to one or more interventions (which may include placebo or other control) to evaluate the effects of those interventions on health-related biomedical or behavioral outcomes.
Healthy Volunteer
A Healthy volunteer is a person with no known significant health problems who participates in clinical research to test a new drug, device, or intervention.
Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria are factors that allow someone to participate in a clinical trial are inclusion criteria . Those that exclude or not allow participation are exclusion criteria .
Informed Consent
Informed consent explains risks and potential benefits about a clinical trial before someone decides whether to participate.
Patient Volunteer
A patient volunteer has a known health problem and participates in research to better understand, diagnose, treat, or cure that disease or condition.
Phases of Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are conducted in “phases.” The trials at each phase have a different purpose and help researchers answer different questions.
- Phase I trials — An experimental drug or treatment in a small group of people (20–80) for the first time. The purpose is to evaluate its safety and identify side effects.
- Phase II trials — The experimental drug or treatment is administered to a larger group of people (100–300) to determine its effectiveness and to further evaluate its safety.
- Phase III trials — The experimental drug or treatment is administered to large groups of people (1,000–3,000) to confirm its effectiveness, monitor side effects, compare it with standard or equivalent treatments.
- Phase IV trials — After a drug is licensed and approved by the FDA researchers track its safety, seeking more information about its risks, benefits, and optimal use.
A placebo is a pill or liquid that looks like the new treatment but does not have any treatment value from active ingredients.
A Protocol is a carefully designed plan to safeguard the participants’ health and answer specific research questions.
Principal Investigator
A Principal Investigator is a doctor who leads the clinical research team and, along with the other members of the research team, regularly monitors study participants’ health to determine the study’s safety and effectiveness.
Randomization
Randomization is the process by which two or more alternative treatments are assigned to volunteers by chance rather than by choice.
Single- or Double-Blind Studies
Single- or double-blind studies (also called single- or double-masked studies) are studies in which the participants do not know which medicine is being used, so they can describe what happens without bias. In single-blind ("single-masked") studies, you are not told what is being given, but the research team knows. In a double-blind study, neither you nor the research team are told what you are given; only the pharmacist knows. Members of the research team are not told which participants are receiving which treatment, in order to reduce bias. If medically necessary, however, it is always possible to find out which treatment you are receiving.
Types of Clinical Trials
- Diagnostic trials determine better tests or procedures for diagnosing a particular disease or condition.
- Natural history studies provide valuable information about how disease and health progress.
- Prevention trials look for better ways to prevent a disease in people who have never had the disease or to prevent the disease from returning.
- Quality of life trials (or supportive care trials) explore and measure ways to improve the comfort and quality of life of people with a chronic illness.
- Screening trials test the best way to detect certain diseases or health conditions.
- Treatment trials test new treatments, new combinations of drugs, or new approaches to surgery or radiation therapy.
This page last reviewed on April 20, 2023
Connect with Us
- More Social Media from NIH
- ABBREVIATIONS
- BIOGRAPHIES
- CALCULATORS
- CONVERSIONS
- DEFINITIONS

Vocabulary
What does medical research mean?
Definitions for medical research med·ical re·search, this dictionary definitions page includes all the possible meanings, example usage and translations of the word medical research ., wikipedia rate this definition: 0.0 / 0 votes.
Medical research
Biomedical research (or experimental medicine) encompasses a wide array of research, extending from "basic research" (also called bench science or bench research), – involving fundamental scientific principles that may apply to a preclinical understanding – to clinical research, which involves studies of people who may be subjects in clinical trials. Within this spectrum is applied research, or translational research, conducted to expand knowledge in the field of medicine. Both clinical and preclinical research phases exist in the pharmaceutical industry's drug development pipelines, where the clinical phase is denoted by the term clinical trial. However, only part of the clinical or preclinical research is oriented towards a specific pharmaceutical purpose. The need for fundamental and mechanism-based understanding, diagnostics, medical devices, and non-pharmaceutical therapies means that pharmaceutical research is only a small part of medical research. The increased longevity of humans over the past century can be significantly attributed to advances resulting from medical research. Among the major benefits of medical research have been vaccines for measles and polio, insulin treatment for diabetes, classes of antibiotics for treating a host of maladies, medication for high blood pressure, improved treatments for AIDS, statins and other treatments for atherosclerosis, new surgical techniques such as microsurgery, and increasingly successful treatments for cancer. New, beneficial tests and treatments are expected as a result of the Human Genome Project. Many challenges remain, however, including the appearance of antibiotic resistance and the obesity epidemic. Most of the research in the field is pursued by biomedical scientists, but significant contributions are made by other type of biologists. Medical research on humans, has to strictly follow the medical ethics sanctioned in the Declaration of Helsinki and hospital review board where the research is conducted. In all cases, research ethics are expected.
Wikidata Rate this definition: 0.0 / 0 votes
Biomedical research, in general simply known as medical research, is the basic research, applied research, or translational research conducted to aid and support the body of knowledge in the field of medicine. Medical research can be divided into two general categories: the evaluation of new treatments for both safety and efficacy in what are termed clinical trials, and all other research that contributes to the development of new treatments. The latter is termed preclinical research if its goal is specifically to elaborate knowledge for the development of new therapeutic strategies. A new paradigm to biomedical research is being termed translational research, which focuses on iterative feedback loops between the basic and clinical research domains to accelerate knowledge translation from the bedside to the bench, and back again. Medical research may involve doing research on public health, biochemistry, clinical research, microbiology, physiology, oncology, surgery and research on many other non-communicable diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. The increased longevity of humans over the past century can be significantly attributed to advances resulting from medical research. Among the major benefits have been vaccines for measles and polio, insulin treatment for diabetes, classes of antibiotics for treating a host of maladies, medication for high blood pressure, improved treatments for AIDS, statins and other treatments for atherosclerosis, new surgical techniques such as microsurgery, and increasingly successful treatments for cancer. New, beneficial tests and treatments are expected as a result of the Human Genome Project. Many challenges remain, however, including the appearance of antibiotic resistance and the obesity epidemic.
How to pronounce medical research?
Alex US English David US English Mark US English Daniel British Libby British Mia British Karen Australian Hayley Australian Natasha Australian Veena Indian Priya Indian Neerja Indian Zira US English Oliver British Wendy British Fred US English Tessa South African
How to say medical research in sign language?
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of medical research in Chaldean Numerology is: 2
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of medical research in Pythagorean Numerology is: 7
Examples of medical research in a Sentence
Martin Sikora :
The last 40 to 50 years have been exceptionally quiet for us, because we've had such tremendous progress in medical research , the combination of vaccines and antibiotics, the eradication of smallpox gives us hope for the current situation.
Brian Schatz :
Whether inspecting our food, conducting medical research or caring for our veterans, federal workers play an important role in our everyday lives and deserve pay which reflects that, after years of pay freezes, our bill gives these dedicated public servants a much-deserved raise.
Balaram Bharghava :
Therefore Indian Council of Medical Research creates more fear, more paranoia and more hype.
Sabina Malgora :
Studying ancient diseases and wounds is important for modern medical research ... we can study the cancer or the arteriosclerosis of the past and this can be useful for modern research.
Wang Linfa :
It wasn't seen as a sexy branch of medical research .
- ^ Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Medical_Research
- ^ Wikidata https://www.wikidata.org/w/index.php?search=medical research
Translations for medical research
From our multilingual translation dictionary.
- بحث طبى Arabic
Word of the Day
Would you like us to send you a free new word definition delivered to your inbox daily.
Please enter your email address:
Citation
Use the citation below to add this definition to your bibliography:.
Style: MLA Chicago APA
"medical research." Definitions.net. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 20 Aug. 2024. < https://www.definitions.net/definition/medical+research >.
Discuss these medical research definitions with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe. If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
You need to be logged in to favorite .
Create a new account.
Your name: * Required
Your email address: * Required
Pick a user name: * Required
Username: * Required
Password: * Required
Forgot your password? Retrieve it
Are we missing a good definition for medical research ? Don't keep it to yourself...
Image credit, the web's largest resource for, definitions & translations, a member of the stands4 network, image or illustration of.
- medical research

Free, no signup required :
Add to chrome, add to firefox, browse definitions.net, are you a words master, quickly aroused to anger, Nearby & related entries:.
- medical referral source
- medical regulating
- medical reimbursements of america
- medical relation noun
- medical report noun
- medical savings account
- medical savings accounts
- medical school noun
- medical science noun
- medical scientist noun
Alternative searches for medical research :
- Search for medical research on Amazon

- Download PDF
- Share X Facebook Email LinkedIn
- Permissions
Prioritizing Nutrition Security in the US
- 1 Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy, Tufts University, Boston, Massachusetts
- 2 Georgetown University Law Center, Washington, DC
- 3 World Central Kitchen, Washington, DC
- Invited Commentary Food Is Medicine: The Promise and Challenges of Integrating Food and Nutrition Into Health Care Dariush Mozaffarian, MD, DrPH; Jerold Mande, MPH; Renata Micha, RD, PhD JAMA Internal Medicine
- Viewpoint US Dietary Guidelines and Lifting the Total Dietary Fat Ban Dariush Mozaffarian, MD, DrPH; David S. Ludwig, MD, PhD JAMA
- The JAMA Forum Food Insecurity and a Threatened Safety Net Diana J. Mason, PhD, RN JAMA
- Research Letter Risk Factors Associated With Food Insecurity in the Medicare Population Jeanne M. Madden, PhD; Prathwish S. Shetty, MSc; Fang Zhang, PhD; Becky A. Briesacher, PhD; Dennis Ross-Degnan, ScD; Stephen B. Soumerai, ScD; Alison A. Galbraith, MD, MPH JAMA Internal Medicine
- Original Investigation Receipt of Unemployment Insurance and Food Insecurity During the COVID-19 Pandemic Julia Raifman, ScD; Jacob Bor, ScD; Atheendar Venkataramani, MD, PhD JAMA Network Open
The prevalence of nutrition-sensitive conditions such as obesity and type 2 diabetes has increased substantially in the US during the past 30 years. These conditions, combined with other diet-related ones such as cardiovascular diseases and certain cancers, are associated with the majority of morbidity, mortality, and health care spending nationally. Simultaneously, income inequality has increased, with accompanying self-reported food insecurity disproportionately affecting individuals with lower incomes. Food insecurity has been defined as the state of being without reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, nutritious food, and in 2019 was estimated to affect 10.5% of US households. 1 Food insecurity and poor nutrition are closely linked: individuals who report being most food insecure also have higher risks of developing obesity, diabetes, hypertension, coronary disease, stroke, cancer, and associated conditions, even after adjusting for other risks such as age, sex, employment, marital status, race/ethnicity, smoking, insurance status, family size, education, and income. 2
- Invited Commentary Food Is Medicine: The Promise and Challenges of Integrating Food and Nutrition Into Health Care JAMA Internal Medicine
Read More About
Mozaffarian D , Fleischhacker S , Andrés JR. Prioritizing Nutrition Security in the US. JAMA. 2021;325(16):1605–1606. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1915
Manage citations:
© 2024
Artificial Intelligence Resource Center
Cardiology in JAMA : Read the Latest
Browse and subscribe to JAMA Network podcasts!
Others Also Liked
Select your interests.
Customize your JAMA Network experience by selecting one or more topics from the list below.
- Academic Medicine
- Acid Base, Electrolytes, Fluids
- Allergy and Clinical Immunology
- American Indian or Alaska Natives
- Anesthesiology
- Anticoagulation
- Art and Images in Psychiatry
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assisted Reproduction
- Bleeding and Transfusion
- Caring for the Critically Ill Patient
- Challenges in Clinical Electrocardiography
- Climate and Health
- Climate Change
- Clinical Challenge
- Clinical Decision Support
- Clinical Implications of Basic Neuroscience
- Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Consensus Statements
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Critical Care Medicine
- Cultural Competency
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Diagnostic Test Interpretation
- Drug Development
- Electronic Health Records
- Emergency Medicine
- End of Life, Hospice, Palliative Care
- Environmental Health
- Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
- Facial Plastic Surgery
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Genomics and Precision Health
- Global Health
- Guide to Statistics and Methods
- Hair Disorders
- Health Care Delivery Models
- Health Care Economics, Insurance, Payment
- Health Care Quality
- Health Care Reform
- Health Care Safety
- Health Care Workforce
- Health Disparities
- Health Inequities
- Health Policy
- Health Systems Science
- History of Medicine
- Hypertension
- Images in Neurology
- Implementation Science
- Infectious Diseases
- Innovations in Health Care Delivery
- JAMA Infographic
- Law and Medicine
- Leading Change
- Less is More
- LGBTQIA Medicine
- Lifestyle Behaviors
- Medical Coding
- Medical Devices and Equipment
- Medical Education
- Medical Education and Training
- Medical Journals and Publishing
- Mobile Health and Telemedicine
- Narrative Medicine
- Neuroscience and Psychiatry
- Notable Notes
- Nutrition, Obesity, Exercise
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Occupational Health
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Care
- Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
- Patient Care
- Patient Information
- Performance Improvement
- Performance Measures
- Perioperative Care and Consultation
- Pharmacoeconomics
- Pharmacoepidemiology
- Pharmacogenetics
- Pharmacy and Clinical Pharmacology
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapy
- Physician Leadership
- Population Health
- Primary Care
- Professional Well-being
- Professionalism
- Psychiatry and Behavioral Health
- Public Health
- Pulmonary Medicine
- Regulatory Agencies
- Reproductive Health
- Research, Methods, Statistics
- Resuscitation
- Rheumatology
- Risk Management
- Scientific Discovery and the Future of Medicine
- Shared Decision Making and Communication
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports Medicine
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Substance Use and Addiction Medicine
- Surgical Innovation
- Surgical Pearls
- Teachable Moment
- Technology and Finance
- The Art of JAMA
- The Arts and Medicine
- The Rational Clinical Examination
- Tobacco and e-Cigarettes
- Translational Medicine
- Trauma and Injury
- Treatment Adherence
- Ultrasonography
- Users' Guide to the Medical Literature
- Vaccination
- Venous Thromboembolism
- Veterans Health
- Women's Health
- Workflow and Process
- Wound Care, Infection, Healing
- Register for email alerts with links to free full-text articles
- Access PDFs of free articles
- Manage your interests
- Save searches and receive search alerts
Warning: The NCBI web site requires JavaScript to function. more...
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Institute of Medicine (US) Clinical Research Roundtable; Tunis S, Korn A, Ommaya A, editors. The Role of Purchasers and Payers in the Clinical Research Enterprise: Workshop Summary. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2002.

The Role of Purchasers and Payers in the Clinical Research Enterprise: Workshop Summary.
- Hardcopy Version at National Academies Press
Appendix V Definitions of Clinical Research and Components of the Enterprise
- DEFINITION OF CLINICAL RESEARCH
(Clinical Research: A National Call to Action, November 1999) Clinical research is a component of medical and health research intended to produce knowledge valuable for understanding human disease, preventing and treating illness, and promoting health. Clinical Research embraces a continuum of studies involving interactions with patients, diagnostic clinical materials or data, or populations in any of the following categories: (1) disease mechanisms (etiopathogenesis); (2) bi-directional integrative (translational) research; (3) clinical knowledge, detection, diagnosis and natural history of disease; (4) therapeutic interventions including development and clinical trials of drugs, biologics, devices, and instruments; (5) prevention (primary and secondary) and health promotion; (6) behavioral research; (7) health services research, including outcomes, and cost-effectiveness; (8) epidemiology; and (9) community-based and managed care-based trials.
- MAJOR COMPONENTS OF THE CLINICAL RESEARCH ENTERPRISE
Sponsors include private and public sector funding organizations such as the National Institutes of Health, pharmaceutical companies, medical device manufacturers, biotechnology firms, universities, private foundations, and national societies. Within the public sector the National Institutes of Health (NIH) is the largest clinical research sponsor, followed by the Department of Defense (DOD), the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), and the Centers for Disease Control (CDC).
Research Organizations
Research organizations include academic health centers, private research institutes, survey research organizations, federal government intramural research programs, and contract research organizations.
Investigators
Investigators are the scientists performing clinical research from varied disciplines with a range of academic qualifications (e.g., MD, Ph.D., RN, DDS, PharmD).
Participants
Participants are the human volunteers, medical information and biological materials of human origin, or data derived from volunteers. Participants may have particular health conditions or may be healthy volunteers or populations at large.
Oversight Entities
Oversight entities include Institutional Review Boards, Food and Drug Administration, Department of Health and Human Services, Veterans Affairs, National Committee for Quality Assurance, and other national regulatory agencies.
Stakeholders/Consumers
Stakeholders/Consumers include health insurers, managed care organizations, health care systems, organized medicine, voluntary health agencies, patient advocacy groups, purchasers of health care, and providers of health care, public health systems, and individual consumers.
- Cite this Page Institute of Medicine (US) Clinical Research Roundtable; Tunis S, Korn A, Ommaya A, editors. The Role of Purchasers and Payers in the Clinical Research Enterprise: Workshop Summary. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2002. Appendix V, Definitions of Clinical Research and Components of the Enterprise.
- PDF version of this title (1.0M)
In this Page
Recent activity.
- Definitions of Clinical Research and Components of the Enterprise - The Role of ... Definitions of Clinical Research and Components of the Enterprise - The Role of Purchasers and Payers in the Clinical Research Enterprise
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
Last Updated: January 02, 2023
Medically reviewed by NKF Patient Education Team
Table of Contents
About dialysis, how it works, effectiveness, side effects, additional considerations, preparing for your appointment.
Dialysis is a type of treatment that helps your body remove extra fluid and waste products from your blood when the kidneys are not able to. Dialysis was first used successfully in the 1940's and became a standard treatment for kidney failure starting in the 1970s. Since then, millions of patients have been helped by these treatments.
Dialysis can be done in a hospital, a dialysis center, or at home. You and your doctor will decide which type of dialysis and which place is best, based on your medical condition and your wishes.
Check out our online communities to connect, learn more and hear from others going through similar experiences.
Dialysis is helpful for two different situations:
- Acute kidney injury (AKI) : a sudden episode of kidney failure or kidney damage that happens within a few hours or days. AKI is usually treated in a hospital setting with intravenous fluids (given through the vein). In severe cases, dialysis may also be needed for a short time until the kidneys get better.
- Kidney failure : when 10-15% of your kidney function remains, measured by an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of less than 15 mL/min. At this stage, your kidneys are no longer able to keep you alive without some extra help. This is also known as end-stage kidney disease (ESKD). With kidney failure, dialysis is only able to do some of the work of healthy kidneys, but it is not a cure for kidney disease. With ESKD, you will need dialysis for the rest of your life or until you are able to get a kidney transplant .
Sign up for a deep dive into dialysis
Learn about the different types of dialysis, receive additional resources, and learn so much more.
Dialysis performs some of the duties that your kidney usually does to keep your body in balance, such as:
- removing waste and extra fluids in your body to prevent them from building up in the body
- keeping safe levels of minerals in your blood, such as potassium, sodium, calcium, and bicarbonate
- helping to regulate your blood pressure
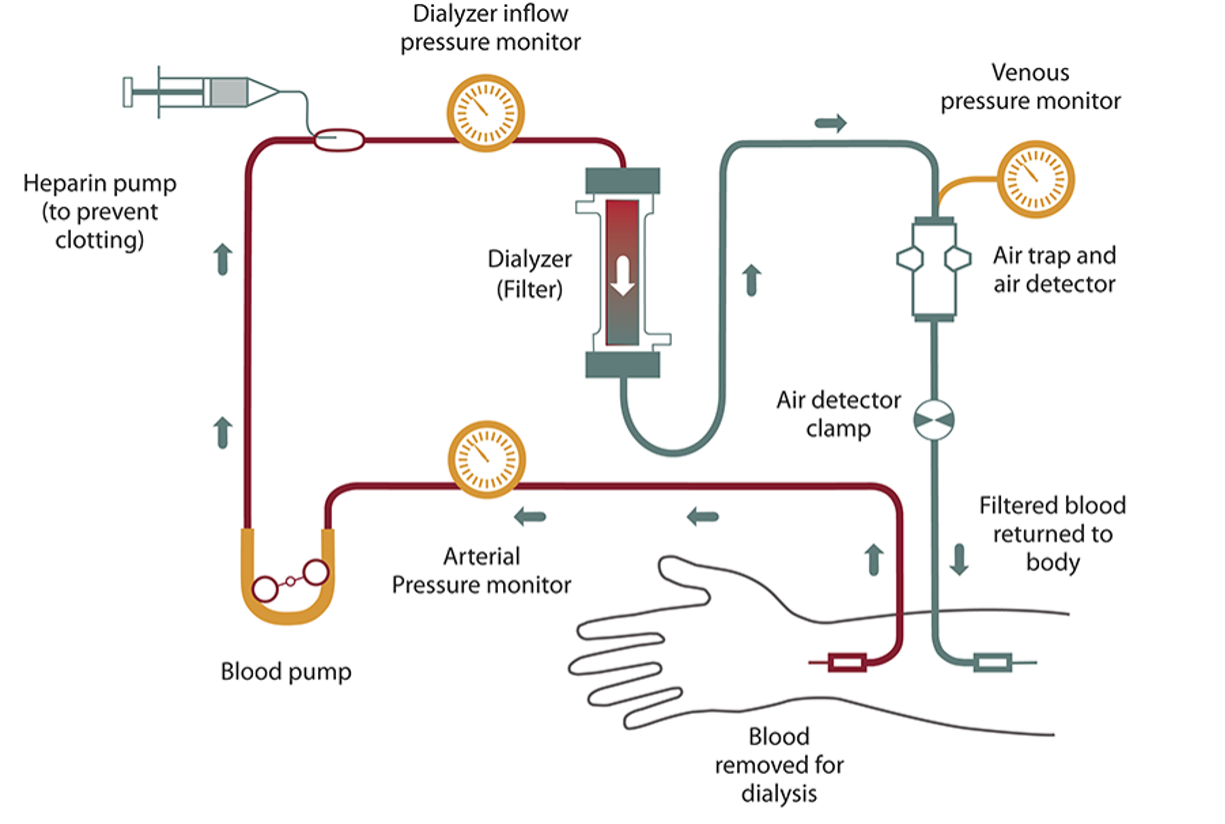
Hemodialysis (HD)
In hemodialysis , a dialyzer (filtering machine) is used to remove waste and extra fluid from your blood, and then return the filtered blood into your body. Before starting hemodialysis, a minor surgery is needed to create a vascular access site (opening into one of your blood vessels), usually in your arm. This access site is important to have an easy way to get blood from your body, through the dialyzer, and back into your body. Hemodialysis can be done at a dialysis center or at home. Treatments usually last about four hours and are done three times per week. Some people may need more time for treatments based on their specific needs.
Peritoneal Dialysis (PD)
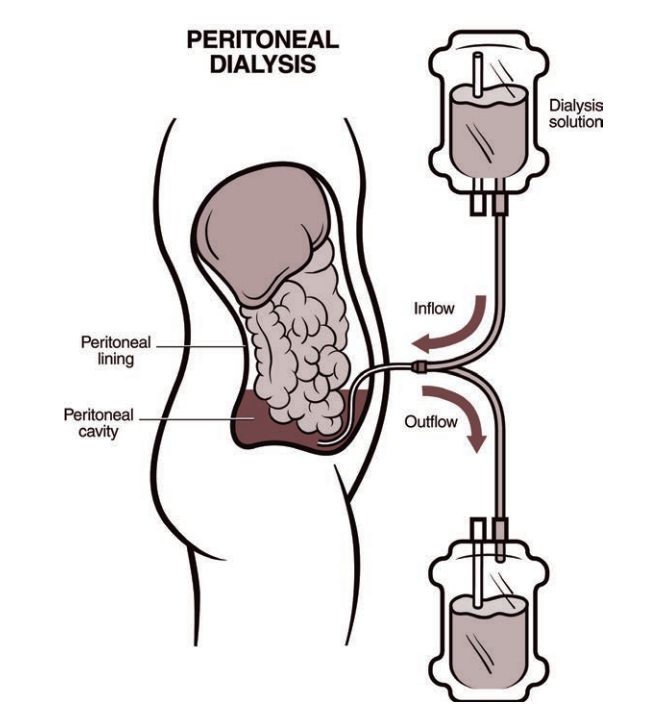
In peritoneal dialysis , your blood is filtered inside your own body instead of using a dialyzer machine. For this type of dialysis, the lining of your abdomen or belly area (also called the peritoneum) is used as a filter. Before starting peritoneal dialysis, a minor surgery is needed to place a catheter (soft tube) in your belly. During each treatment, your belly area is slowly filled with dialysate (a cleansing fluid made from a mixture of water, salt, and other additives) through the catheter. As your blood flows naturally through the area, extra fluid and waste products are pulled out of the blood vessels and into the belly area by the dialysate (almost like a magnet). After a few hours, the fluid mixture is drained from your belly using the same catheter and bag that was used at the beginning of the treatment. Peritoneal dialysis can be done almost anywhere if you have the supplies required to perform the treatment. Two of the most common types of peritoneal dialysis are:
- Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD)
- Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD)
Honor a Hero. Save a life.
Dialysis is a very effective treatment option for clearing waste products and extra fluid from your blood. However, it does not fully replace all the kidney’s functions, so it is not considered a cure for kidney disease or kidney failure.
All types of dialysis are equally effective, but your medical condition and personal preferences may match one treatment approach better than others. You and your doctor will discuss this and decide which type of dialysis and which place is best. You may also find it helpful to talk with other people who are living with dialysis to learn from their experiences.
The following steps can help increase the effectiveness of your dialysis treatments:
- complete your treatments according to your prescribed schedule
- follow your customized eating plan recommended by your kidney dietitian
- get as much physical activity as possible to boost your strength and heart health
- talk with your dialysis provider and pharmacist about any medications, supplements, or herbal products you are taking or are considering starting
- talk with your dialysis team about any concerns or side effects that you may have
Both types of dialysis come with side effects. It can also be hard to tell for sure whether a symptom is because of the dialysis or the kidney failure that is also affecting the body. Some of the most common side effects that people report include:
- Blockage in your vascular access site (entrance point)
- Muscle cramps
- Hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Weakness, dizziness, or nausea
Peritoneal dialysis (PD)
- Hernia (weakness in your abdomen muscle, often presenting as a lump or swollen area)
- Weight gain
Both HD and PD
- Infection of the skin, blood, and/or peritoneum (belly area) - if left untreated, these can cause sepsis (a life-threatening condition leading to multiple organ failure).
- Fatigue (feeling tired) - This can affect anyone but is usually more common for people who have been on dialysis for a long time. It is often hard to tell for sure if this is a side effect of the dialysis or a symptom of long-term kidney disease.
- Pruritus - itchy skin that people with kidney disease may experience, especially in more advanced stages of CKD and people on dialysis. Like fatigue, it is often hard to tell for sure if this is a side effect of the dialysis or a symptom of long-term kidney disease.
Every person responds differently to dialysis, and your level of risk for each side effect will differ from others. If you have concerns about any of these risks, talk to your doctor and dialysis team about ways you can lower your risk. Although these side effects may sound scary, they should be compared to the risks that come from continuing to live with untreated kidney failure.
Impact on regular routine
Most people on dialysis are able to keep a regular routine except for the time needed for treatments. Dialysis often makes people feel better because it helps clear the waste products that have built up in the blood between treatments. However, some people report feeling tired after dialysis, especially if they have been getting dialysis treatments for a long time.
People receiving dialysis treatments also need to be mindful of what they eat. The specific meal plan recommended for you may vary depending on which type of dialysis you receive. Work with your kidney dietitian to create a meal plan that fits your routine and lifestyle.
Traveling is also a possibility for people on dialysis. Dialysis centers are in every part of the United States and many other countries. The treatment is standardized. You must make an appointment for dialysis treatments at another dialysis center before you go. The staff at your current center may help you make the appointment. Visit the NKF Travel Tips AtoZ page for more information.
Many people on dialysis can go back to work after they have gotten used to dialysis. However, if your job has a lot of physical labor (heavy lifting, digging, etc.), you may need to look for a different type of work. Visit the NKF Working with Kidney Disease AtoZ page for more information.
It will likely take you and your family some time to get used to including dialysis treatments into a new routine.
Dialysis treatments are very expensive. However, most people with kidney failure are eligible for Medicare when they start dialysis. This means the federal government pays 80 percent of all dialysis costs. Private health insurance or state Medicaid programs may also help with the costs. Visit the NKF resource on insurance options for people on dialysis or with a kidney transplant to learn more.
You may have some discomfort as the needles are put into your access site. Over time, people usually get used to being around these needles and equipment. The dialysis treatment itself is painless.
Life Expectancy
Life expectancy on dialysis varies depending on your other medical conditions, how well you follow your treatment plan, and various other factors. The average life expectancy on dialysis is 5-10 years. However, many patients have lived well on dialysis for 20 or even 30 years. Talk to your healthcare team about how to take care of yourself and stay healthy on dialysis.
Questions to Ask
- Which type of dialysis might work best for my situation?
- Would I be a candidate for completing my dialysis treatments at home?
- How do I determine which dialysis center I should go to?
- How can I lower my risk of infection and other side effects while on dialysis?
- Do I need to adjust any of my medications because of these dialysis treatments?
- What type of meal plan should I be following while I’m on dialysis?
- How can I get added to the kidney transplant waitlist?
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- NKF Council on Renal Nutrition CKD Kidney Dietitian Directory
What’s your story?
We want to hear about your unique experience with a kidney transplant, living donation, or kidney disease. Your story may be the one that gives someone hope.
How helpful was this content?
Related kidney topics, missing dialysis treatment is dangerous for your health, foods to avoid after transplantation, what is dry weight, kidney stone treatment: shock wave lithotripsy, five drugs you may need to avoid or adjust if you have kidney disease, taking care of your peritoneal dialysis (pd) catheter, related news and stories.

July 25, 2024
The Future of Artificial Kidneys

December 12, 2018
Modern Family Star Opens Up About Her Kidney Disease and Transplants

June 18, 2024
A Son’s Gift. A Wife’s Promise: Fighting for Living Kidney Donors

June 04, 2024
Unfiltered Story: Losing a Transplant
May 31, 2024
Breaking Ground in Transplantation: A New Era with Xenotransplantation

April 24, 2024
Unfiltered Story: Anthony Tuggle

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The University of Florida Cancer and Genetics Research Complex is an integrated medical research facility. Medical research (or biomedical research ), also known as health research, refers to the process of using scientific methods with the aim to produce knowledge about human diseases, the prevention and treatment of illness, and the promotion ...
Health research entails systematic collection or analysis of data with the intent to develop generalizable knowledge to understand health challenges and mount an improved response to them. The full spectrum of health research spans five generic areas of activity: measuring the health problem; understanding its cause(s); elaborating solutions; translating the solutions or evidence into policy ...
Clinical research is the comprehensive study of the safety and effectiveness of the most promising advances in patient care. Clinical research is different than laboratory research. It involves people who volunteer to help us better understand medicine and health. Lab research generally does not involve people — although it helps us learn ...
Medical research often seems much like standard medical care, but it has a distinct goal. Medical care is the way that your doctors treat your illness or injury. Its only purpose is to make you feel better and you receive direct benefits. On the other hand, medical research studies are done to learn about and to improve current treatments.
The chapter also explains how the definition of research has become quite complex under the various federal regulations, which make a distinction between research and some closely related health practice activities that also use health data, such as quality improvement initiatives. ... Advances in information-based medical research could also ...
Medical research can have an enormous positive impact on human health. Health research improves the quality of human lives and society which plays a vital role in social and economic development of the nation. Financial support is crucial for research. However, winning a research grant is a difficult task.
Basic medical research (otherwise known as experimental research) includes animal experiments, cell studies, biochemical, genetic and physiological investigations, and studies on the properties of drugs and materials. In almost all experiments, at least one independent variable is varied and the effects on the dependent variable are ...
Clinical research is the study of health and illness in people. It is the way we learn how to prevent, diagnose and treat illness. Clinical research describes many different elements of scientific investigation. Simply put, it involves human participants and helps translate basic research (done in labs) into new treatments and information to ...
Office of Inspector General. USA.gov. NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health ®. National Institutes of Health, 9000 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, Maryland 20892. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Clinical research occurs in many formats and can involve anyone. Learn how you can participate and contribute to medical advances.
Definition. Medical research involves research in a wide range of fields, such as biology, chemistry, pharmacology and toxicology with the goal of developing new medicines or medical procedures or ...
Research conducted for the purpose of contributing towards science by the systematic collection, interpretation and evaluation of data and that, too, in a planned manner is called scientific research: a researcher is the one who conducts this research. The results obtained from a small group through scientific studies are socialised, and new ...
Medical Research. Scientists and physicians in academic medicine conduct groundbreaking biomedical research that improves our knowledge of human health and promotes the development of treatments from bench to bedside to community. Through policy and advocacy initiatives, data and research projects, professional learning and networking ...
1. The organized quest for new knowledge and better understanding (e.g., of the natural world or determinants of health and disease). Five types of research are recognized: observational (empiric), analytic, experimental, theoretic, applied. 2. To conduct such scientific inquiry.
Medicine, the practice concerned with the maintenance of health and the prevention, alleviation, or cure of disease. Learn about the organization of health services, medical practices around the world, fields of medicine, alternative medicine, and clinical research.
When asked about the purpose of medical research most people would hopefully reply: to advance knowledge for the good of society; to improve the health of people worldwide; or to find better ways to treat and prevent disease. The reality is different. The research environment, with its different players, is now much less conducive to thinking ...
Clinical research includes all research that involves people. Types of clinical research include: Epidemiology, which improves the understanding of a disease by studying patterns, causes, and effects of health and disease in specific groups. Behavioral, which improves the understanding of human behavior and how it relates to health and disease.
Research This means (among others): • IRB review according to regulatory requirements & criteria • Informed consent according to regulatory requirements (unless waived) Requirements Typically Do NOT Apply • When project is not Research, or • When project is not Human Subjects Research, or • When project is Exempt Human Subjects Research
Biomedical scientists bridge the gap between the basic sciences and medicine. The Ph.D. degree is the gateway to a career in biomedical research. Biomedical scientists: Think outside the box and are innovators. Are critical and analytical thinkers. Get excited by discovering new things. Look at biology and see previously unrecognized patterns.
Clinical research is an alternative terminology used to describe medical research. Clinical research involves people, and it is generally carried out to evaluate the efficacy of a therapeutic drug, a medical/surgical procedure, or a device as a part of treatment and patient management.
Biomedical research is the broad area of science that looks for ways to prevent and treat diseases that cause illness and death in people and in animals. This general field of research includes many areas of both the life and physical sciences. Utilizing biotechnology techniques, biomedical researchers study biological processes and diseases ...
Clinical Research. Clinical research is medical research that involves people to test new treatments and therapies. Clinical Trial. A research study in which one or more human subjects are prospectively assigned to one or more interventions (which may include placebo or other control) to evaluate the effects of those interventions on health-related biomedical or behavioral outcomes.
Definition of medical research in the Definitions.net dictionary. Meaning of medical research. Information and translations of medical research in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the web.
WASHINGTON — A new National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine report says the federal government, state and local authorities, clinicians, medical societies and organizations, public health practitioners, employers, educators, and others should adopt a new definition for "Long COVID" — that it is an infection-associated chronic condition that occurs after COVID-19 ...
This Viewpoint addresses nutrition security—defined as having consistent access, availability, and affordability of foods and beverages that promote well-being and prevent or even treat disease—and its importance to clinical care and public policy in the US.
(Clinical Research: A National Call to Action, November 1999) Clinical research is a component of medical and health research intended to produce knowledge valuable for understanding human disease, preventing and treating illness, and promoting health. Clinical Research embraces a continuum of studies involving interactions with patients, diagnostic clinical materials or data, or populations ...
Hemodialysis (HD) In hemodialysis, a dialyzer (filtering machine) is used to remove waste and extra fluid from your blood, and then return the filtered blood into your body.Before starting hemodialysis, a minor surgery is needed to create a vascular access site (opening into one of your blood vessels), usually in your arm. This access site is important to have an easy way to get blood from ...