

You're signed out
Sign in to ask questions, follow content, and engage with the Community
- Canvas Instructor
- Instructor Guide
- What is the difference between assignment due date...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
What is the difference between assignment due dates and availability dates?
in Instructor Guide
Note: You can only embed guides in Canvas courses. Embedding on other sites is not supported.
Community Help
View our top guides and resources:.
To participate in the Instructure Community, you need to sign up or log in:
- Professional
- International
Select a product below:
- Connect Math Hosted by ALEKS
- My Bookshelf (eBook Access)
Sign in to Shop:
My Account Details
- My Information
- Security & Login
- Order History
- My Digital Products
Log In to My PreK-12 Platform
- AP/Honors & Electives
- my.mheducation.com
- Open Learning Platform
Log In to My Higher Ed Platform
- Connect Math Hosted by Aleks
Business and Economics
Accounting Business Communication Business Law Business Mathematics Business Statistics & Analytics Computer & Information Technology Decision Sciences & Operations Management Economics Finance Keyboarding Introduction to Business Insurance & Real Estate Management Information Systems Management Marketing
Humanities, Social Science and Language
American Government Anthropology Art Career Development Communication Criminal Justice Developmental English Education Film Composition Health and Human Performance
History Humanities Music Philosophy and Religion Psychology Sociology Student Success Theater World Languages
Science, Engineering and Math
Agriculture & Forestry Anatomy & Physiology Astronomy & Physical Science Biology - Majors Biology - Non-Majors Chemistry Cell/Molecular Biology & Genetics Earth & Environmental Science Ecology Engineering/Computer Science Engineering Technologies - Trade & Tech Health Professions Mathematics Microbiology Nutrition Physics Plants & Animals
Digital Products
Connect® Course management , reporting , and student learning tools backed by great support .
McGraw Hill GO Greenlight learning with the new eBook+
ALEKS® Personalize learning and assessment
ALEKS® Placement, Preparation, and Learning Achieve accurate math placement
SIMnet Ignite mastery of MS Office and IT skills
McGraw Hill eBook & ReadAnywhere App Get learning that fits anytime, anywhere
Sharpen: Study App A reliable study app for students
Virtual Labs Flexible, realistic science simulations
Inclusive Access Reduce costs and increase success
LMS Integration Log in and sync up
Math Placement Achieve accurate math placement
Content Collections powered by Create® Curate and deliver your ideal content
Custom Courseware Solutions Teach your course your way
Professional Services Collaborate to optimize outcomes
Remote Proctoring Validate online exams even offsite
Institutional Solutions Increase engagement, lower costs, and improve access for your students
General Help & Support Info Customer Service & Tech Support contact information
Online Technical Support Center FAQs, articles, chat, email or phone support
Support At Every Step Instructor tools, training and resources for ALEKS , Connect & SIMnet
Instructor Sample Requests Get step by step instructions for requesting an evaluation, exam, or desk copy
Platform System Check System status in real time
How strict should you be? A guide to assignment due dates.
Be consistent in your approach to deadline flexibility, whether you never accept late work or are always willing to make an exception..

Colleges typically require instructors to include a calendar of assignment due dates in every course syllabus. But most syllabi also include a disclaimer that assignment deadlines are subject to change.
So, how flexible should deadlines really be in a college course?
Be Flexible, or be Rigid, but Always be Consistent
Be consistent in your approach to deadline flexibility, whether you never accept late work or are always willing to make an exception. Nothing irritates strong students more than their instructor announcing, “Since so many of you asked for more time on the assignment that was due today, I’m extending its deadline to next week.”
Syllabi should always include a clearly stated policy about the circumstances under which late work might be accepted, if at all.
But should this policy be applied equally to low-stakes and high-stakes assignments?
Low-Stakes Assessments
If a course has many low-stakes assessments, like quizzes or homework problems, those assignments are usually due on the same day each week.
For example, if class meets on Tuesdays and Thursdays, there might a reading quiz due every Monday, to ensure that students are prepared for the week’s in-class discussions, and a homework problem due every Friday, to verify understanding of the week’s concepts.
Here are three solid approaches to deadline flexibility for low-stakes assessments:
1. Not flexible: Late work is never accepted
If a student misses a deadline, they receive zero points on that assignment.
This approach works best in courses that have many low-stakes assignments, such as reading quizzes on every textbook chapter, where missing one or two deadlines will not jeopardize a student’s understanding of the core concepts nor greatly impact their final letter grade.
2. Somewhat flexible: Late work is accepted, at a penalty
If a student misses a deadline, they can submit the assignment late, but their score will be penalized a specified amount (e.g. -5 points).
This approach works best in courses where content acquisition is scaffolded such that missing one assignment will negatively impact a student’s understanding of core concepts and successful completion of future assignments. In this case, students who miss deadlines should be permitted to complete the missed assignments, but with a small scoring penalty to encourage on-time submissions in future weeks.
3. Very flexible: Late work is made up, with instructor permission
If a student misses a deadline, they must contact the instructor and arrange an alternate way to complete the assignment (e.g. by taking a make-up quiz during the instructor’s office hours).
This approach works best in courses where low-stakes assessments are considered part of a student’s participation grade. In this case, missing a deadline is like missing a class meeting. Students should be encouraged to initiate contact with the instructor to arrange a way to verify their understanding of the missed assignment’s concepts.
High-Stakes Assessments
Every course has one or more high-stakes assessments, such as exams or research papers. These assessments are weighted more heavily (worth more of the overall course grade) than lower-stakes assessments because these are higher-level demonstrations of students’ proficiency in the course outcomes. Failure to successfully complete high-stakes assessments generally leads to failure of the entire course.
What kind of flexibility is appropriate then for key, high-stakes course assessments?
1. Not flexible: Deadlines do not change, under any circumstances
If a student misses a deadline, they receive zero points on that assessment.
This is the most common approach to deadlines for high-stakes assessments. It is rare for a college instructor to permit students to make up a missed midterm or final exam because students making up an exam would receive the unfair advantage of more time to prepare for the exam. Also, many final exams are scheduled for the very end of term, when there is no time remaining for make-up testing before instructors must report course grades to the college.
2. Somewhat flexible: Deadlines are extended, at a penalty
If a student misses a deadline, they can submit the assessment late, but their score will be penalized a specified amount (e.g. one letter grade per day).
This approach is more common for midterm assessments, or for courses with single high-stakes assessments, such as a research paper that students work on throughout the term. If students who miss the deadline for a high-stakes assessment can still submit their work, but their score is heavily penalized, the course grades will accurately reflect the students’ term-long proficiency in the course outcomes. For example, a student who earned “A” scores all term but submitted their final paper one day late could still finish the course with a “B” grade.
Remember, flexibility around assignments should be geared towards what makes sense in your course and for your students. While there are a lot of possible variations in regards to policy, the most critical element is to be clear and upfront with your students early in the term. This will help avoid confusion and complaints – and help you keep your sanity at the end of the term when students come looking for extra chances to make up missed work!

Anna Johnson is an award-winning instructor at Mt Hood Community College in Oregon where she has worn many hats since 2005. Joining the faculty as an instruction librarian, Anna then spent 10 years as a career-technical instructor, preparing students for living-wage jobs as administrative assistants and front-end web developers, and now leads the college’s Business transfer degree program. Anna enjoys using problem-based learning and flipped classroom methodologies to prepare students for future workplace challenges. When she's not teaching, Anna is an avid cook, formidable fantasy football player, National Park enthusiast, and volunteer usher and tour guide for Portland's performing arts center. Anna has supported other instructors in their use of SIMnet as an MHE Digital Faculty Consultant since 2015.
- Help Center
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Submit feedback
- Announcements

Due On, Due By, Or Due For? Difference Explained (+18 Examples)
Prepositions come after many words in English, and it’s important to understand how the meaning of words changes based on which preposition follows it. Let’s look at whether we use due on, due by, or due for, and what each one means.
What Is The Difference Between Due On, Due By, And Due For?
Due on should be used when something must be submitted on a given date and no other time. Due by should be used when something can be submitted on a given date or before. Due for should be used when something is submitted to a person, rather than a time.

When Is The Deadline Day Included?
When you want to announce the deadline day, it always comes after the preposition. That means you can say “due on Friday” or “due by Tuesday next week.”
You can only put the deadline day after the preposition to indicate the urgency of the submission to the people you’re talking to. “Due on Friday” shows the urgency of getting it completed by Friday, while “due by Friday” shows that you can do it by Friday or before.
Does Due By Friday Mean On Friday Or Before Friday?
“Due by Friday” means both on and before Friday. It’s up to you how you want to interpret the message. Usually, you will start to work on the submission early and see how long it takes you to complete.
When something is “due by Friday,” it means you have until Friday to complete it. If you work on it earlier than that and complete it before Friday, you can hand it in whenever it’s ready.
Usually, tasks that are “due by” aren’t as urgent as ones that are “due on,” and there’s no given time frame for how long that task might take somebody to complete. Some people like to leave “due by” tasks until the last minute and hand it in on the last day, but this isn’t always a wise decision.
Is Completing A Task On The Due Date Considered Overdue?
Depending on what was asked of you, completing a task on the due date may be considered overdue. Typically, you want to finish the task before the due date to make sure that you can hand it in on time, ready for the due date.
Due dates usually include a day and a time. If you decide to complete your task on the expected day, you may often be overdue, as many people choose to finish their tasks earlier in the week to make sure they have something to hand in.
Of course, the time you hand something in and the time you complete it depends on the task in question. Some school assignments might take less time than a data-entry assignment would at your workplace. It’s dependent on what someone asked you to do, just as much as it’s dependent on your own work ethic.
Generally, make sure you get your task completed before the due date. That way, you’ll never hand in work that’s overdue.
6 Examples Of How To Use “Due On” In A Sentence
Let’s look through some examples now of when “due on” is used. We use this when we’re setting a specific time to hand in work. There’s no leeway or wiggle room with this time either. We typically tell them that the day is final, meaning no submissions before or after.
- This essay is due on Friday the 14th; otherwise, you will fail.
- This assignment is due on Monday next week.
- It’s due on Thursday, and I haven’t even started working on it yet!
- We’re due on Wednesday to hand this in.
- What day is the work assignment due on, sir?
- This is due on Saturday, no earlier, no later.
6 Examples Of How To Use “Due By” In A Sentence
Let’s see how “due by” is used next. There’s a lot more wiggle room and leniency when someone uses “due by.” They don’t want you to hand in the assignment later than mentioned, but they’re more than happy to accept it earlier than that if you complete it. Often, they’ll reward you for completing it quicker.
- The homework is due by Friday, okay?
- I’ve set you an assignment that’s due by Sunday.
- This piece is due by next weekend, right?
- I’ve got to finish my essay that’s due by tomorrow morning.
- The article is due by tomorrow evening.
- You have to complete the document for me. It’s due by noon!
6 Examples Of How To Use “Due For” In A Sentence
Finally, “due for” is used when the intended thing is a person or place rather than a time frame. Also, if you use the word “when” to start a question, you will finish it with “due for.”
- When is this due for again?
- Is that due for Mr. Robinson’s class?
- That’s due for Tom, isn’t it?
- That’s due for the class at six, right?
- When is our homework due for?
- When is this due for?
Is It Ever Correct To Use “Due At”?
When we want to be even more specific with our due date, we can include “due at.”
If we’re already on the day that the work was due and want to specify a time, that’s when we use “due at.” It keeps things even more specific than previously mentioned.
- This is due at six o’clock.
- This is due at two.
Quiz: Have You Mastered The Due On Vs Due By Vs Due For Grammar?
Now we’ll run you through a quick quiz to see what you’ve learned from this article! We’ll include the answers at the end for you to compare with as well.
- The homework is (A. due on / B. due by / C. due for) Friday and no earlier.
- The sooner you get it done, the better. It’s (A. due on / B. due by / C. due for) Tuesday.
- When is our essay (A. due on / B. due by / C. due for)?
- Is that (A. due on / B. due by / C. due for) Tuesday or Wednesday?
- This assignment is (A. due on / B. due by / C. due for) next week.
Quiz Answers
You might also like: “By Tomorrow” – Learn What It Actually Means! (Examples & Facts)

Martin holds a Master’s degree in Finance and International Business. He has six years of experience in professional communication with clients, executives, and colleagues. Furthermore, he has teaching experience from Aarhus University. Martin has been featured as an expert in communication and teaching on Forbes and Shopify. Read more about Martin here .
- “Next Friday” vs. “This Friday”: 8 Helpful Examples (Complete Guide)
- 15 Best Replies to “Happy Friday”
- What Does “By Friday” Mean? (Does It Include “Friday”?)
- 10 Better Ways To Write “In This Essay, I Will…”
Due On, Due By, or Due For? Understanding the Distinctions with Examples
Marcus Froland
March 28, 2024
Have you ever found yourself scratching your head over an email, trying to figure out if your project is due on , due by , or due for ? You’re not alone. These tiny prepositions can turn a simple task into a linguistic puzzle. They seem small, but boy, do they pack a punch in meaning and nuance.
The English language loves to keep us on our toes. Just when you think you’ve got the hang of it, bam, a new curveball. And today’s curveball involves deadlines. It’s not just about when something needs to be done but also about the precision of communication. Because let’s face it, timing can make or break a project.
So here we stand at the crossroads of clarification. But don’t worry; we’re about to demystify these perplexing prepositions once and for all. Ready to clear up the confusion?
Understanding the difference between due on , due by , and due for can improve your English communication. Due on refers to something that is expected exactly on a specific date. For example, “The project is due on Friday.” This means the project must be completed and submitted on Friday, not before or after.
Due by indicates a deadline before which something must be done. It gives a bit more flexibility. For instance, “The payment is due by the 5th” implies that the payment can be made any time before or on the 5th.
Last, due for suggests an action or event that is expected or scheduled. It often relates to regular occurrences or expectations, like “She is due for her annual check-up.” This means it’s time for her yearly doctor’s visit.
In brief, knowing these differences helps in precise communication about deadlines and expectations.
Introduction to Due Dates and Deadline Expressions
Due dates and deadline expressions play a pivotal role in both personal and professional settings , ensuring the timely fulfillment of obligations . They serve to communicate the expected time frame for completing payments, projects, or duties. A clear understanding and expression of due dates , such as “due on,” “due by,” and “due for,” can prevent misunderstandings and guarantee that responsibilities and commitments are met within their specified time frames. Setting accurate due dates facilitates financial planning , project management , and contractual compliance. An understanding of these terms helps individuals in managing deadlines for rental payments, loan installments, insurance premiums, and work-related projects.
- Due on is used when referring to a precise date by which a payment or task must be completed.
- Due by indicates a deadline specifying the latest time or date of completion.
- Due for anticipates events or actions expected or scheduled to occur, often referring to routine obligations .
Let’s examine how each of these terms can impact various aspects of our lives.
Understanding the nuances between “due on,” “due by,” and “due for” can aid in effectively communicating and managing deadlines in both financial and professional contexts.
Here are some examples of how these deadline expressions can be used:
- Rental payment: due on the first of the month.
- Car loan installment: due by the 15th of every month.
- Annual insurance premium: due for renewal in January.
| Expression | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Refers to a specific date for completion. | Electricity bill June 30 | |
| Specifies the latest possible time or date for completion. | Submit report 5 PM on Friday | |
| Anticipates scheduled or recurring events. | Car maintenance service in two months |
By becoming familiar with these terms and their respective meanings, you can prevent confusions and ensure your payments and tasks are efficiently managed, thereby minimizing the risk of missed financial deadlines and payment schedules .
The Meaning of “Due On” and Its Usage
The term “due on” is used to refer to a specific date when a payment, project, or task is expected to be completed or submitted. This expression is typically employed in situations where there is no room for delay, with the obligation needing to be fulfilled on a precise date. A common example of “due on” usage is rental payments, where landlords often require payment at the month’s beginning, aligning with the beginning of a new tenancy period. In professional settings , project deliverables with a “due on” date require the work to be submitted without delay on the mentioned date, emphasizing punctuality and time sensitivity.
Understanding the importance of “due on” deadlines can help you manage your financial obligations and ensure the timely completion of professional tasks. To further illustrate the implications of “due on” in different contexts, let’s explore some real-life examples:
- Mortgage Payment: A homeowner is required to make monthly mortgage payments on the 15th of each month. In such a case, the statement would read: “ Payment due on the 15th of every month .”
- Project Deadlines: A manager assigns a project with a deadline that falls on the 10th of the following month. The manager would communicate: “ Project delivery due on the 10th of next month .”
- Utility Bills: A utility company sends a bill for electricity, specifying a ‘ Payment due on the 5th of the following month ‘. Customers must submit payments by that date to avoid late fees or penalties.
It’s crucial to remember that “due on” requires action on a specific date, leaving no room for flexibility. Failure to fulfill the commitment within the defined timeframe may result in complications, such as penalties, loss of opportunities, or damage to professional relationships. To better prepare for deadlines categorized as “due on,” consider setting reminders or automated alerts several days before the precise due date to avoid last-minute stress or confusion.
How “Due By” Specifies Deadline Constraints
The expression “due by” sets a clear boundary that specifies the latest possible time or date by which a payment or task should be completed. This term is particularly crucial in professional settings and time-sensitive projects , where adhering to deadlines is of the utmost importance. Understanding how “due by” is applied in various situations can help individuals and businesses effectively plan and prioritize tasks, ensuring they meet payment deadlines and project management requirements.
Application in Professional Scenarios
In professional scenarios , “due by” is commonly used to define project deadlines , allowing professionals to understand the timeframe within which they can organize and prioritize tasks to ensure timely completion. This term provides some degree of planning flexibility within the limit, making it essential for effective time management in environments with multiple deadlines .
“Due by” deadlines allow room for professionals to organize their workflow and deliver projects on time, ensuring client satisfaction and avoiding potential penalties.
Importance in Time-sensitive Projects
For time-sensitive projects , “due by” deadlines are vital, serving as the tipping point for the delivery of work or payment. These deadlines impose constraints that categorize the priorities and urgencies of different tasks, requiring meticulous planning and project management to meet the critical cut-off date.
- Implement a task prioritization system to manage “due by” deadlines effectively.
- Utilize project management tools to track progress and enhance collaboration.
- Communicate regularly with team members to ensure alignment and address potential issues promptly.
In instances where penalties or losses can occur for late submission, a “due by” date marks the final opportunity to avoid adverse outcomes, highlighting its significance in time-sensitive environments. For example, missing a payment deadline for a loan or credit card bill can result in late fees, increased interest rates, and a negative impact on one’s credit score.
| Example | Due By Deadline | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Loan Payment | Payment the 15th of each month | Late fees, increased interest rates |
| Credit Card Bill | Payment due by the last day of the month | Late fees, increased interest rates, negative credit score impact |
| Project Submission | Report due by the end of the business day | Missed client deadlines, potential penalties, damaged professional reputation |
By understanding the importance of “due by” deadlines and effectively managing them in professional and time-sensitive projects , individuals and businesses can meet their obligations on time, maintain strong relationships with clients, and avoid costly penalties.
“Due For” and Anticipating Events or Obligations
The phrase due for is often employed when anticipating events or obligations that are scheduled to occur. It denotes an upcoming action or payment, indicating that one is entering into a period when an obligation will soon need to be met. This anticipatory term is essential for financial planning and preparing for forthcoming events or expenses. In the context of annuities or insurance premiums, “due for” signals the impending start of a new payment cycle, suggesting readiness to meet the approaching financial commitment.
Recognizing when you are due for something can significantly enhance your ability to manage scheduled obligations and navigate upcoming deadlines . By keeping track of your anticipated responsibilities and adjusting your planning accordingly, you can avoid late fees, missed opportunities, and other potential issues.
Some common examples of events or obligations you may need to anticipate include:
- Annuity payments
- Insurance premiums
- Mortgage payments
- Upcoming business or personal deadlines
Proactively planning for these events enables you to maintain financial stability and ensure timely fulfillment of your responsibilities.
“If you fail to plan, you are planning to fail!” – Benjamin Franklin
Due for deadlines provide the necessary foresight needed for effective financial and task planning. By staying aware of upcoming events or obligations and integrating them into your planning strategies, you will be better prepared to meet your scheduled responsibilities and remain in control of your personal and professional life.
Comparing “Due On,” “Due By,” and “Due For” in Context
In real-life situations, the use of “due on,” “due by,” and “due for” varies according to the context. Each term carries unique implications that correspond to different deadline requirements. To efficiently communicate and plan actions in both personal finance and professional work, it is essential to understand when to use each appropriate terminology . The following subsection breaks down the application of these terms in a variety of financial contexts and professional scenarios .
Real-life Situations Where Each Term is Appropriate
To highlight the differences between “due on,” “due by,” and “due for,” let’s examine their application in real-life situations:
| Term | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| A specific deadline that requires fulfillment on a precise date. | Filing taxes are April 15th. | |
| A final deadline by which an action must occur. | Submitting a report is 5 PM on Friday. | |
| An anticipatory term used for routine or scheduled events. | A car is a maintenance checkup based on the last service date. |
Recognizing the appropriate contexts in which to apply “due on,” “due by,” and “due for” can significantly impact the effectiveness of your communication and planning skills, ultimately preventing misunderstandings and optimizing task organization.
Due dates and deadline expressions are essential in both personal and professional settings, ensuring the timely fulfillment of obligations.
As showcased in the table above, “due on” is used when a clear, specific deadline is in place, without room for delay. Conversely, “due by” defines a deadline indicating the latest possible time or date for a task or payment completion. Finally, “due for” anticipates upcoming events or obligations and is commonly used in financial planning .
By understanding the distinctions between these terms, you can effectively navigate the diverse range of due dates found in real-life applications , such as adhering to specific deadlines in financial contexts or prioritizing tasks and projects in professional scenarios .
Examples and Tips for Remembering Each Term
Recalling the difference between “due on,” “due by,” and “due for” can be challenging. However, associating each term with a specific context or example can help you remember when to use them accurately. To provide further clarity, here are some easy-to-remember examples of each term, tips for remembering their application, and how clear communication can improve deadline management :
| Term | Association Tip | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Calendar Date | Rent due on the 1st of the month, credit card payment due on the 15th of the month | |
| Due By | Countdown | Project due by the last day of the quarter, report due by 5 PM on Friday |
| Upcoming Event | Car due for an oil change after 3,000 miles, dental checkup due for the next month |
In addition to these examples, consider these pointers to help keep these terms straight:
- Practice using all three terms when discussing deadlines or events with friends, coworkers, or business associates. This will help reinforce their meaning in your mind.
- Create mnemonic devices that relate to your personal experiences or interests. For example, if you love cooking, remember “due on” as a recipe with a specific cooking time or “due by” as the time it takes to marinate a dish.
- Visualize each term’s usage in various real-life scenarios, such as organizing a party or planning a special event.
“The key is to make a concerted effort to remember the details and nuances of these terms. Ultimately, applying the right term in the right context will aid in clear communication and effective deadline management .”
By understanding the differences between “due on,” “due by,” and “due for,” you can effectively communicate due dates, enhancing your personal and professional relationships. Proper usage of these terms eliminates misunderstandings, ensuring obligations are fulfilled and deadlines met, ultimately aiding you in overall deadline management .
Conclusion: Enhancing Communication Clarity
Clear communication is essential in successfully navigating work and financial obligations. By mastering the distinct uses of “due on,” “due by,” and “due for,” you can drastically improve your planning accuracy, meeting deadlines effectively, and avoiding any misunderstandings with clients, colleagues, or service providers.
These terms play a vital role in task prioritization and financial forecasting, all while reinforcing the importance of communication clarity in every aspect of your life. Additionally, understanding when to use each term helps emphasize the importance of meeting financial deadlines , ultimately ensuring responsible management of obligations.
Incorporate these expressions in your professional and personal tasks to enhance your effective planning and communication skills. By doing so, you will be better equipped to maintain punctuality and honor your commitments in various contexts, positively impacting your overall productivity and success.
You May Also Like:
What Does Wiseacre Mean? Definition & Examples
Timber or timbre – which is correct, what is a glitch – usage & meaning, giving or given when to use each (with examples), “yours and his” or “your and his” – which is correct, ‘heard’ vs ‘herd’ vs ‘hurd’: what’s the difference, two minute english.
English Made Simple: Two-Minute Lessons for Busy Learners
Copyright © 2024 • TwoMinEnglish.com

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that they will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply —use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove their point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, they still have to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and they already know everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality they expect.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. 24/7
- Contact us:
- +1 (213) 221-0069
- [email protected]

What Assignment Due 11:59 PM Means: What Comes After

Assignment Due 1159 PM
Assignment due dates are part of the assignment itself. The instructor/teacher/professor wants to determine whether their students can adhere to simple instructions.
This is the reason why assignments that are delivered late attract fines in terms of deduction in marks or even rejection.

Yes, some of the instructors are very strict when it comes to assignment due dates and they can reject your assignment even when it is a few minutes late!
Now, instructors can give students various due dates that determine the date, hour, and minute in which they are required to submit their completed work.
They may decide to set those due dates or let the plagiarism-checking platforms such as Turnitin or Blackboard set default deadlines.
Note that some institutions only allow their students to submit their work through such platforms so that the assignments can be automatically checked for plagiarism.
That being said, let us explore what the most common due dates and times mean for students and the submission of assignments.
Also Read: How to Write a PEEL Paragraph Essay: with Examples
What does Due 11:59 PM Mean
11:59 PM is one of the most common assignments’ due time (deadline) given to students. I know you may be wondering why this is the case. Why not any other time of the day?
Well, the reason is that in the contemporary world, institutions of learning may have students from different time zones who may be attending online classes or are required to submit their homework at the same time.
In assignment submission, 11:59 PM means that the paper or essay is due at the very last minute of that day and not even a second or a minute late. If as a student you upload a file one minute after 11:59 PM, will have submitted on the next day 00:00 AM, and not the previous day, which is a minute earlier.
For example, if the instructor states that the assignment is due, let’s say, on Friday the 16th, students should deliver their work by 11:59 PM on Friday the 16th. If you upload it on Saturday the 17th then you are late because the time will be 00:00 hours, a new day.

To coordinate the due time, a specific due date has to be set in which the final day to submit the assignments is set.
A complete day is made up of 24 hours with the start of the day being at midnight.
Midnight is written in 24hrs clock as 00:00 hours.
What this means is that when the clock reads 00:00 hours, we have entered another day.
Therefore, if students were required to submit on the previous day, it means that they are late.
Also Read: Types of Paragraphs in Essay or Academic Writing: With Examples
Is 11:59 Pm Morning or Night?
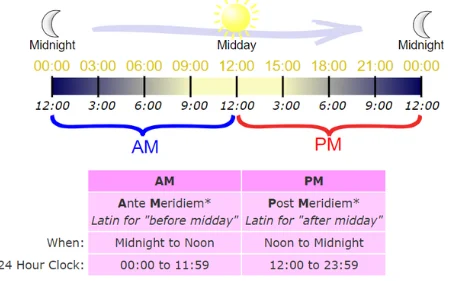
To some of us, determining whether 11:59 PM is morning or night can be confusing.
Some of the genuine reasons for this confusion are that the “PM” initials signify nighttime and most of the time zones in the world are within the dark side of the earth; meaning that they are experiencing night.
However, 00:00 hours or midnight is considered to be part of the morning because it is the start of a new day.
The problem is that 11:59 PM and 00:00 hours are separated by less than 1 minute (59 seconds) and the former is considered night while the latter is considered morning. Well, all the factors held constant, 11:59 PM should be considered night.
Don’t be confused by the aforementioned technicalities. What matters is the time of day. If it is 11:59 PM, the day has ended and a new day will begin at 00:00 hours midnight.
What Comes After 11:59 PM?
As aforementioned, 11:59 PM signifies the end of a complete day. A complete day is made up of 24 hours and 11:59 PM in 24 hours style clock is written as 23:59 hours.
This indicates that only less than a minute is left for the 24 hour-day to end. Therefore, when 11:59 PM passes, a new day comes when the clock indicates 00:00 hours or midnight.
What Does “Due Tomorrow At 11:59 PM” Mean?
As we have noted, a complete day is made up of 24 hours. What this means is that for us to experience a complete “today”, we must experience it from midnight (00:00 hours/midnight) to 23:59 hours/11:59 PM.

Therefore, when someone tells you that they expect something tomorrow, it means that today must pass; or rather we must pass 11:59 PM and transition to 12 AM or 00:00 hours because that would be a new day (tomorrow).
Now, if your instructor tells you that your assignment is due tomorrow at 11:59 PM, it means that they expect the assignment the next day one minute before midnight.
For example, if today is Friday the 16th and the instructor has told students that their assignment is due tomorrow at 11:59 PM, they will have to submit their work by Saturday the 17th at 11:59 PM. If students submit their work one minute after that, they will have delivered on a Sunday morning (12 AM or 00:00 hours).
What Happens when you Submit an Assignment at 11:59 Pm?
If you submit your assignment at exactly 11:59 PM, you are okay because you have not breached the deadline.
An important thing you should note as students is that when your instructors ask you to submit your assignment, they tell you to do so via plagiarism-checking tools such as Turnitin or Blackboard. Such tools set their default deadlines at 11:59 PM because it is the end of a complete day.
They do not count the seconds between 11:59 PM and 12 AM. According to such tools, you only need to submit your work before the clock in your time zone reads 00:00 hours or midnight.
Also Read: Essay Reading: Practice and Importance of Reading Essays
Tips on how to Submit an Assignment at 11:59 PM
1. upload one file.
As noted, students should make sure that they upload their assignments before midnight because the assignments will be past due.
If you are submitting your assignment at 11:59 PM, it means that you only have less than 1 minute (60 seconds) to upload your assignment files.
To ensure that your assignment is successfully uploaded within a few seconds, it is best to upload it as one file to avoid wasting time. It takes more time to upload several files, meaning that you will be late.
2. Use Fast Internet
Bearing in mind that you only have a few seconds to upload your assignment files, you should use fast internet. Fast internet will allow you to upload your files within a short time and beat the deadline.
Slow internet is not only annoying but it can make you submit your work past the deadline because by the time it uploads the complete file, the 59-second window will have passed.
3. Ensure the Computer is Plugged
This should be an obvious thing to do. Your computer should be plugged in to ensure that there are no disruptions when uploading your assignment files.
4. Upload a Small Size File
Small file sizes can be uploaded faster compared to larger files. Additionally, if your internet is slow, the process of uploading a small-size file will be faster.
Larger files will take more time even when there is moderate-speed internet.
5. Do not Close the Window/tab
It is also very important to not close the window or tab of your browser as you are uploading your assignment. This is because if you close, the window or tab will take more time to reload the content and this will make you late.
6. Wait until the Upload is Confirmed

Finally, it is important to wait until the uploaded assignment has been confirmed.
Do not be in a hurry to close the browser window/tab before confirming that the file upload has been successful.
This is because it might not be successful at times and you may be required to retry uploading the file again.
Therefore, to avoid submitting your assignments late and consequently being penalized, take note of the explanations and tips in this article.

With over 10 years in academia and academic assistance, Alicia Smart is the epitome of excellence in the writing industry. She is our chief editor and in charge of the writing department at Grade Bees.
Related posts

cheating on math homework
How to Cheat on Math Homework and the Best Websites to Use

Motivate Yourself do Homework
How to Motivate Yourself to Do Homework and Study

Doing Homework At Work
Doing Homework At Work: How to do your Assignment Fast
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Understanding Writing Assignments

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
How to Decipher the Paper Assignment
Many instructors write their assignment prompts differently. By following a few steps, you can better understand the requirements for the assignment. The best way, as always, is to ask the instructor about anything confusing.
- Read the prompt the entire way through once. This gives you an overall view of what is going on.
- Underline or circle the portions that you absolutely must know. This information may include due date, research (source) requirements, page length, and format (MLA, APA, CMS).
- Underline or circle important phrases. You should know your instructor at least a little by now - what phrases do they use in class? Does he repeatedly say a specific word? If these are in the prompt, you know the instructor wants you to use them in the assignment.
- Think about how you will address the prompt. The prompt contains clues on how to write the assignment. Your instructor will often describe the ideas they want discussed either in questions, in bullet points, or in the text of the prompt. Think about each of these sentences and number them so that you can write a paragraph or section of your essay on that portion if necessary.
- Rank ideas in descending order, from most important to least important. Instructors may include more questions or talking points than you can cover in your assignment, so rank them in the order you think is more important. One area of the prompt may be more interesting to you than another.
- Ask your instructor questions if you have any.
After you are finished with these steps, ask yourself the following:
- What is the purpose of this assignment? Is my purpose to provide information without forming an argument, to construct an argument based on research, or analyze a poem and discuss its imagery?
- Who is my audience? Is my instructor my only audience? Who else might read this? Will it be posted online? What are my readers' needs and expectations?
- What resources do I need to begin work? Do I need to conduct literature (hermeneutic or historical) research, or do I need to review important literature on the topic and then conduct empirical research, such as a survey or an observation? How many sources are required?
- Who - beyond my instructor - can I contact to help me if I have questions? Do you have a writing lab or student service center that offers tutorials in writing?
(Notes on prompts made in blue )
Poster or Song Analysis: Poster or Song? Poster!
Goals : To systematically consider the rhetorical choices made in either a poster or a song. She says that all the time.
Things to Consider: ah- talking points
- how the poster addresses its audience and is affected by context I'll do this first - 1.
- general layout, use of color, contours of light and shade, etc.
- use of contrast, alignment, repetition, and proximity C.A.R.P. They say that, too. I'll do this third - 3.
- the point of view the viewer is invited to take, poses of figures in the poster, etc. any text that may be present
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing I'll cover this second - 2.
- ethical implications
- how the poster affects us emotionally, or what mood it evokes
- the poster's implicit argument and its effectiveness said that was important in class, so I'll discuss this last - 4.
- how the song addresses its audience
- lyrics: how they rhyme, repeat, what they say
- use of music, tempo, different instruments
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing
- emotional effects
- the implicit argument and its effectiveness
These thinking points are not a step-by-step guideline on how to write your paper; instead, they are various means through which you can approach the subject. I do expect to see at least a few of them addressed, and there are other aspects that may be pertinent to your choice that have not been included in these lists. You will want to find a central idea and base your argument around that. Additionally, you must include a copy of the poster or song that you are working with. Really important!
I will be your audience. This is a formal paper, and you should use academic conventions throughout.
Length: 4 pages Format: Typed, double-spaced, 10-12 point Times New Roman, 1 inch margins I need to remember the format stuff. I messed this up last time =(
Academic Argument Essay
5-7 pages, Times New Roman 12 pt. font, 1 inch margins.
Minimum of five cited sources: 3 must be from academic journals or books
- Design Plan due: Thurs. 10/19
- Rough Draft due: Monday 10/30
- Final Draft due: Thurs. 11/9
Remember this! I missed the deadline last time
The design plan is simply a statement of purpose, as described on pages 40-41 of the book, and an outline. The outline may be formal, as we discussed in class, or a printout of an Open Mind project. It must be a minimum of 1 page typed information, plus 1 page outline.
This project is an expansion of your opinion editorial. While you should avoid repeating any of your exact phrases from Project 2, you may reuse some of the same ideas. Your topic should be similar. You must use research to support your position, and you must also demonstrate a fairly thorough knowledge of any opposing position(s). 2 things to do - my position and the opposite.
Your essay should begin with an introduction that encapsulates your topic and indicates 1 the general trajectory of your argument. You need to have a discernable thesis that appears early in your paper. Your conclusion should restate the thesis in different words, 2 and then draw some additional meaningful analysis out of the developments of your argument. Think of this as a "so what" factor. What are some implications for the future, relating to your topic? What does all this (what you have argued) mean for society, or for the section of it to which your argument pertains? A good conclusion moves outside the topic in the paper and deals with a larger issue.
You should spend at least one paragraph acknowledging and describing the opposing position in a manner that is respectful and honestly representative of the opposition’s 3 views. The counterargument does not need to occur in a certain area, but generally begins or ends your argument. Asserting and attempting to prove each aspect of your argument’s structure should comprise the majority of your paper. Ask yourself what your argument assumes and what must be proven in order to validate your claims. Then go step-by-step, paragraph-by-paragraph, addressing each facet of your position. Most important part!
Finally, pay attention to readability . Just because this is a research paper does not mean that it has to be boring. Use examples and allow your opinion to show through word choice and tone. Proofread before you turn in the paper. Your audience is generally the academic community and specifically me, as a representative of that community. Ok, They want this to be easy to read, to contain examples I find, and they want it to be grammatically correct. I can visit the tutoring center if I get stuck, or I can email the OWL Email Tutors short questions if I have any more problems.
My assignment is due tomorrow and I haven't even started it yet!

English expert at Atomi

Well, if it really is due tomorrow, let’s do this and do it quick! You could have anything due tomorrow, so instead of a step-by-step guide let’s focus on some tips and tricks to pull off this craziness. Legions of students before you have done it and legions of students after you will do it so have faith—you can do it 💪.
1. Prioritise
This probably doesn’t need to be said but if it’s due tomorrow then clear your schedule tonight—this is absolutely your top priority right now! Normally we recommend getting plenty of sleep but if you have something due tomorrow, tonight's the night to push your bedtime back a little bit (still no all-nighters though!)
2. Get your head in the game
Okay, no matter how much of a mountain it seems, this has to be done tonight. Don’t let yourself even consider the option of handing it in late—just thinking that will make it even harder to finish in time.
It’s time to get your head in the game and focus on the task ahead. You want to grab some water and make sure you’ve eaten. Then, set yourself up in a clean, bright area, find a supportive chair and grab all of the resources you'll need to do your assignment.
You can check out our video on Study Spaces for everything you need to set up the perfect workspace.
3. Work out exactly what you need to do
To work as efficiently as possible you should first understand exactly what you need to do.
That means you need to think about exactly what ideas or topics you need to cover and what your approach should be. So, read the assignment and marking criteria carefully and identify any keywords. Also highlight any important details, like the word count or page limit, the submission format and any other info that will affect how you approach this task.
This will vary massively depending on the assignment. The point is basically just that you should make sure you know exactly what you need to do before you start. Trust me, it’ll make everything quicker if you do ⏰.
4. Do a brief plan
To make sure we can get this done properly in one night, the next step is to plan your answer. This will make it a lot easier to start writing and, if you have to do any research, you will know exactly what you’re looking for.
So, sketch out a brief plan onto a page. Work out what needs to go into your answer and how it’s going to be structured. It might feel difficult or pointless to plan at this point, but if you can get some of the hard work out of the way here it’ll become much easier to write!
5. Research efficiently
Now, this one is obviously only relevant if you need research for your answer. Gathering research for an essay or report can take time. By using the keywords from the syllabus and assessment notification, you’ll be able to focus on the resources that you actually need. As far as you can, drop your research straight into the plan and you’ll be moving much more efficiently.
Don’t forget to reference as you go! This will save you time and ensure you don’t make any mistakes 😅.
6. Quality over quantity
This is a seriously important tip. When you’re really under pressure, it can be tempting to just smash out as many words as possible so you can hit that word count—don’t do this! It’s just going to give you a whole lot of waffle and even worse marks.
Instead of waffling, stick to your answer plan, use your research and fall back on the ideas in our lessons . It will get you a much better result for not that much extra work ✅.

7. Do your final read over tomorrow morning
Once you’ve finally pulled off that answer, it’s time to go to bed. You’re probably going to be too tired, too stressed and too wrapped up in your answer to be able to give it a proper check and edit.
So, just get some sleep now, set the alarm 30mins earlier tomorrow and read over it again with fresh eyes and a clear mind. You should be able to pick up any little mistakes and make the whole thing read a lot better and generally end up with a stronger answer!
Even though this isn’t ideal, you can still pull it off! The secret is to be as efficient as possible. So, keep calm, find out exactly what you need to do, plan, research properly and don’t waffle.
Oh and next time, don’t leave your assignments to the last minute 😅. Instead, watch our lesson on Planning an Assignment and use the downloadable planner so you aren’t in this sticky situation again.
For more study tips, tricks and advice, keep reading the student blog or follow Atomi on Instagram . See you there 👋.
Published on
March 15, 2022
Recommended reads

How to plan an assignment
Sitting trials or internal assessments at home read this.

5 Tips for tackling a take-home assessment
What's atomi.
Engaging, curriculum-specific videos and interactive lessons backed by research, so you can study smarter, not harder.
With tens of thousands of practice questions and revision sessions, you won’t just think you’re ready. You’ll know you are!
Study skills strategies and tips, AI-powered revision recommendations and progress insights help you stay on track.
Short, curriculum-specific videos and interactive content that’s easy to understand and backed by the latest research.
Active recall quizzes, topic-based tests and exam practice enable students to build their skills and get immediate feedback.
Our AI understands each student's progress and makes intelligent recommendations based on their strengths and weaknesses.

Quality Point(s): 2.72K
Answer: 955
- English (US)
- English (UK)
What is the difference between assignments due and assignments ?Feel free to just provide example sentences.
- Report copyright infringement

Quality Point(s): 134634
Answer: 30734
Like: 31383
@sa_ra_ “due this week” means they have to be handed in this week. If they don’t say ‘due’ it means they are doing some assignments, and we don’t know when they might be due. So this ‘due’ is like “The bus is due in half an hour.” It means that is the scheduled time. ‘Due’ has other meanings, like “There was flooding due to the rain.” That ‘due’ means ‘because of’.
Was this answer helpful?
- Why did you respond with "Hmm..."?
- Your feedback will not be shown to other users.

Quality Point(s): 92
Ask native speakers questions for free

Solve your problems more easily with the app!
- Find the answer you're looking for from 45 million answers logged!
- Enjoy the auto-translate feature when searching for answers!
- It’s FREE!!
- What is the difference ...
IntelyCare for Healthcare Facilities > Resources > Nurse Management > How to Manage an Assignment Despite Objection: 5 Tips for Facilities
How to Manage an Assignment Despite Objection: 5 Tips for Facilities
Search resource center.

Nurses are legally accountable for the quality of care they provide to patients. Under that responsibility, they must ensure that they’re competent to provide the treatment necessary for each individual assigned to their care. While most supervisors attempt to allocate patients according to each nurse’s ability, there are instances where a nurse may believe that their assignment places themselves or their patients at risk.
In these situations, it is the nurse’s duty to complete an Assignment Despite Objection (ADO) form . You may be wondering — What does ADO paperwork look like, and what are the steps required to ensure the forms are completed appropriately?
In this article, we introduce the purpose of ADO forms, review an example scenario that highlights the ADO paperwork submission process, and list five tips for facilities looking to appropriately manage ADO situations to ensure staff protection and patient safety.
What Does Assignment Despite Objection Mean?
The term “Assignment Despite Objection” is used to describe a situation in which a nurse has been made responsible for an unmanageable patient load. Despite making it clear to unit leadership that the staff member feels unsafe, unqualified, or unsupported in managing the care of that particular assignment, they have been mandated to assume care for that assignment. A nurse may complete an ADO for a number of reasons, including:
- Being assigned to care for a number of patients that falls outside of any legal nurse-to-patient ratio .
- Feeling inexperienced or untrained in a particular area or specialty.
- Experiencing a shortage of support staff that would make the assignment manageable.
- Lacking sufficient safety equipment or machinery to provide care effectively.
- Being forced to work overtime or miss meal breaks.
ADO paperwork helps provide legal protection for nurses who believe they may be put in an unsafe patient care situation. “Whistleblowing” the potential for patient harm doesn’t completely remove liability from the nurse, but it does raise concerns for facility leadership and can put them on notice of elevated patient care risks. State nursing boards and nursing unions encourage staff to complete ADO paperwork to protect themselves and their patients.
What Does ADO Paperwork Look Like?
Each state nursing board or nursing union utilizes its own version of an ADO form , which covers employees working in that state. While they all vary in terms of layout or design, each form contains similar elements, including:
- The nurse’s name, license number, and place of employment.
- The supervisor’s name and date/time of notification.
- The reason for the nurse’s objection.
- The unit’s census details, including the number of patients and staff members.
- A space to outline any actual or potential patient harm that may have been caused.
Assignment Despite Objection: Example Scenario
The ADO process can seem confusing out of clinical context. The table below lists the steps involved when a nursing professional files an ADO, along with a scenario to help highlight the process in a realistic clinical situation.
|
| |
|---|---|
| Nurse Emily has been assigned the care of three complex patients in her ICU unit. According to her state’s nurse staffing ratios, she should be responsible for a maximum of two patients at any given time. Upon receiving her assignment, Emily raises her concerns about patient safety and the inappropriateness of the assignment to her unit manager. | |
| Emily finds a copy of her state’s ADO form on her hospital’s website and completes the form, filling in details about the assignment and her attempt to find a resolution. She submits copies to her supervisor, the facility’s professional practice committee (PPC), and her labor representative. She also keeps a copy in her own personal records. | |
| Emily’s unit manager signs and dates the form once it has been received. | |
| Emily’s manager has one week to process and review the form, and respond to her submission. When she receives her response later that week, it contains a written apology from Emily’s unit manager for placing her in that challenging situation and outlines a plan forward to prevent the situation from happening again in the future. | |
Managing an ADO: 5 Tips for Facilities
As you review how the Assignment Despite Objection form submission process works, you’re probably looking for tips on how to effectively manage these situations in your unit or facility. Below, we review five key strategies for managing an ADO safely and effectively.
1. Ensure All Patient Assignments Meet Mandated State Staffing Ratios
A key step to keeping clinical operations running smoothly is to prevent ADO situations from arising in the first place. Adhering to your state’s legally mandated staffing ratios is the first step to ensuring compliance and safety .
2. Provide Staff Training on ADO Protocol
Many nurses might not be familiar with the ADO process. They may not know how to speak up if they find themselves in a situation where they aren’t able to practice safely or competently. One way to prevent this from happening is to include Assignment Despite Objection education as part of your employee onboarding training .
Be sure to show staff where to find the forms, explain how to complete them, and relay who to submit them to when necessary. This not only helps your staff feel empowered and supported, but also ensures that your patients receive the best possible care.
3. Encourage Team Cohesion
As the term “objection” implies, ADO submissions can become contentious if management and nursing staff perceive each other to be on separate teams. It’s important that both sides abandon the “them versus us” mentality and understand that the entire unit is focused on preserving staff and patient safety.
Team bonding activities can help to unite facility leadership and bedside staff and ensure that no side feels like they’re fighting against the other. Collaborative team meetings can also help clinical leaders and staff work side-by-side to discuss mutual issues and problem solve together.
4. Incorporate Per Diem and Float Pool Nurses to Cover Schedule Gaps
One of the most common reasons an ADO arises is due to short staffing . By utilizing flexible staffing solutions, you can ensure that all patient assignments can be safely distributed, even during high census.
Per diem nurses, who work only one or two shifts a week, could be added into the staffing matrix on busy shifts or during predictable nursing shortages like maternity leaves or staff vacations. Float pool nurses, alternatively, could be requested on short notice to assist with unpredictable staff shortages like sick calls.
5. Review Submitted ADO Paperwork to Plan Long-Term Solutions
The submission of an ADO form only means that the situation has been documented. It doesn’t mean that the situation was handled safely or that outcomes were improved.
Therefore, it’s essential that facility management reviews those forms and performs a root-cause analysis to prevent future improper patient assignments. Typically, this is done in unit leadership meetings or in a facility-wide shared governance committee .
Discover More Ways to Promote Patient Safety in Your Facility
Safely managing an Assignment Despite Objection situation prevents future patient harm and ensures your staff members practice safely and effectively. Follow along in our expertly-written newsletter for additional tips and strategies on encouraging employee engagement and optimizing care quality.
Legal Disclaimer: This article contains general legal information, but it is not intended to constitute professional legal advice for any particular situation and should not be relied on as professional legal advice. Any references to the law may not be current, as laws regularly change through updates in legislation, regulation, and case law at the federal and state level. Nothing in this article should be interpreted as creating an attorney-client relationship. If you have legal questions, you should seek the advice of an attorney licensed to practice in your jurisdiction.
Related Articles
Hospital discharge planning: 5 best practices, what is the crna scope of practice overview and faq, how to thank a nurse: 5 ideas for facility leaders, for-profit hospitals vs. nonprofit: key differences, what is the rn scope of practice overview and faq, related jobs, stay in the know, with the latest industry insights and trends.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
WHEN or WHAT is the due date for this assignment?
I want to know due date for my assignment which is given by teacher. In this situation, is it correct to say
When is the due date for this assignment?
What is the due date for this assignment?
or other things you recommend?
- word-choice
2 Answers 2
In casual, every day use, both would be fine, but if you want to be strict, you would either say:
"What is the due date for this assignment" or "When is this assignment due?"
The "what" is asking for a specific name / figure denoting a point in time, and the "when" is actually asking for a point in time - the answer does not have to take the form of a date. For example you could answer "tomorrow", or "in 4 weeks", whereas the first question specifically asks for a date.
Both are correct. Likewise, What is the DEADLINE? or When is the DEADLINE?
See more examples from the Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English :
The new Jan. 22 due date also applies to taxpayers in Washington, Mr Keith adds. The amount and due date will be announced in advance. It was less than satisfying; and yet as his due date neared he kept on, sometimes all night. A loan stock holder is not hampered by such restrictions if his loan stock is not paid on the due date. My first child arrived quite quickly on the due date. The covenant to pay the rent on the due date, quarterly in advance usually, is absolutely fundamental. The due date coincides with the closing ceremonies in Atlanta. Fewer than 5 percent of women deliver on their due date. Only a significantly wrong due date separates Lou Madden from a perfect Super Bowl attendance record.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged word-choice questions ..
- Featured on Meta
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
Hot Network Questions
- On a 3D Gagliardo-Nirenberg inequality
- Is the theory of ordinals in Cantor normal form with just addition decidable?
- How Can this Limit be really Evaluated?
- Why did General Leslie Groves evade Robert Oppenheimer's question here?
- Can I use "historically" to mean "for a long time" in "Historically, the Japanese were almost vegetarian"?
- Why are most big lakes in North America aligned?
- Why are AAVs not a replacement for through-roof vent pipe?
- Is every recursively axiomatizable and consistent theory interpretable in the true arithmetic (TA)?
- ST_Curvetoline creates invalid geometries
- Is it possible for a fuse to blow at extremely low temperatures?
- Can I share a Live Motion Photo as a video?
- How to allocate memory in NASM without C functions (x64)?
- How to respond to reviewers who ask for more work by saying that the paper is complete?
- How could Bangladesh protect itself from Indian dams and barrages?
- Story of man abandoning annoying wife and son but not daughter during car escape from nuclear attack
- Meaning of “ ’thwart” in a 19th century poem
- I'm trying to remember a novel about an asteroid threatening to destroy the earth. I remember seeing the phrase "SHIVA IS COMING" on the cover
- What is the significance of bringing the door to Nippur in the Epic of Gilgamesh?
- What happens when a helicopter loses the engine and autorotation is not initiated?
- What is this strengthening dent called in a sheet metal part?
- What would the appropriate cost be for a magical set of full plate with a Cast On and Cast Off property?
- How do I alter a table by using AFTER in hook update?
- Is there any video of an air-to-air missile shooting down an aircraft?
- How can I move TikZ pictures in 3D space?
Sentence examples for the assignment is due from inspiring English sources
Login and get your AI feedback from Ludwig. Login and get your AI feedback from Ludwig.
Is your sentence correct in English?
Login and get your AI feedback from Ludwig.
The assignment is due Friday, November 16 at 11AM.
The assignment is due Wednesday November 7 at 11AM.
The assignment is due Wednesday, November 28 at 11AM.
The assignment is due Friday October 19 at 11AM, but make sure to get started early!
The assignment is due Mon. 4/29 at 11 59PM PST.
The assignment is due Monday October 29 at 11AM, but make sure to get started early!
The assignment is due Friday October 12 at 11AM, but make sure to get started early!
Write in English at your best, with Ludwig
Used by millions of students, scientific researchers, professional translators and editors from all over the world.

Cristina Valenza
Be a smart writer
Most frequent sentences:, write in english at your best with ludwig.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Due by, due on, due for - what's the difference?
When someone says "I need x by Friday", I usually take it to mean they want x in their hands when Friday begins. However, when that same person says "I need x on Friday", I understand them to mean they want x no later than the end of the day Friday.
What about "I need x for Friday"? Is "for" in this context synonymous with "by" or "on"?
Do other people understand "due by" and "due on" in the same way I do? Is there a common consensus?
2 Answers 2
I think two of these are more-or-less interchangeable, but one is not. They also lend themselves to different levels of clarification and specificity in their request, and a different order to the information presented.
"Due by" implies that there is a set time of when it is due. "The sales report is due by 12pm on Friday." The day something is due follows the time, which is given more importance. The time can be stripped and the sentence will still work, one just loses the precision of the request.
"Due on" places more importance on the day something is due, and not so much the time. "Your membership fee is due on Friday." A specific time can be added but it would follow the day/date.
"Due for," however, is more about the person or event something is due for, and not so much when it is due. "Is that essay due for Mr. Green's class today?"
- While I agree that "due for" usually refers to a person and event and not the time something is due, I received an email recently where someone said "we need this for Thursday". When "for" is followed by a temporal noun, what is the precise meaning? Given your example with 'Mr. Green's Class', "due for" seems closer to "due on", putting more emphasis on the date than the precise time. Would that be your interpretation? – Delyle Commented Nov 18, 2015 at 21:32
- I feel my answer may be getting a little far into the realm of opinion, but hopefully it still works. When saying something is due for Thursday, I am inclined to believe that whatever is due is needed for Thursday. Be it a speech that will be given that day, a list of names/set of data for something, or what-have-you. Whatever is due will be used then. So, one could say that the report is due on Wednesday by 11:30 for Thursday. Where "on" gives the broad time, "by" gives the specific time, and "for" gives the reason or event. – Zach W Commented Dec 15, 2015 at 19:39
- I love it when they say something like "due by Friday and no late applications will be accepted." Please people, add a time when you say "due by". – Virgo Commented Jul 6, 2018 at 1:32
I see no substantive difference between these three. Even with "due by," I think it would be ambiguous as to whether someone wanted x by the beginning or the end of Friday. Personally, I would use "due by" to cover all three and would take it to mean something like "up to and including Friday." "Due on" Friday seems strange because it could imply that it is due only on that day and couldn't be handed in sooner, and "due for" sounds idiomatically strange, with "for" seeming like a wrong prepositional choice to me.
- Anywhere I've ever worked, when something is due on/by Friday, it means by the close of business on Friday. Otherwise it is stated: This is due 9 a.m. on Friday. "Due for" is used more in the following kind of sentence: I haven't had a raise in five years; I think I'm due for one. Or: We're due for some rain this weekend. – Steven Littman Commented Nov 18, 2015 at 2:58
- I interpret "due for Friday" to mean that there is a meeting on Friday, and that I should complete the assignment before Friday. – LexieLou Commented Nov 18, 2015 at 3:12
- @Steven Littman -- Yes, true about that use of "due for" -- though that's not the sense being discussed here ("due" has a somewhat different meaning in that context). – Languagemaven Commented Nov 18, 2015 at 14:26
- @ Lexielou -- Sounds strange to me, but interesting nevertheless. – Languagemaven Commented Nov 18, 2015 at 14:27
Your Answer
Sign up or log in, post as a guest.
Required, but never shown
By clicking “Post Your Answer”, you agree to our terms of service and acknowledge you have read our privacy policy .
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged technical or ask your own question .
- Featured on Meta
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
Hot Network Questions
- How to attach a 4x8 plywood to a air hockey table
- Why doesn't the world fill with time travelers?
- My school wants me to download an SSL certificate to connect to WiFi. Can I just avoid doing anything private while on the WiFi?
- Can a TL431 be configured to output a negative reference voltage?
- Why are most big lakes in North America aligned?
- Is every recursively axiomatizable and consistent theory interpretable in the true arithmetic (TA)?
- Change output language of internal commands like "lpstat"?
- DATEDIFF Rounding
- Are quantum states like the W, Bell, GHZ, and Dicke state actually used in quantum computing research?
- How bad would near constant dreary/gloomy/stormy weather on our or an Earthlike world be for us and the environment?
- Why does a halfing's racial trait lucky specify you must use the next roll?
- `Drop` for list of elements of different dimensions
- How long does it take to achieve buoyancy in a body of water?
- Can I share a Live Motion Photo as a video?
- Is there any video of an air-to-air missile shooting down an aircraft?
- Fill a grid with numbers so that each row/column calculation yields the same number
- ST_Curvetoline creates invalid geometries
- What issues are there with my perspective on truth?
- What happens when a helicopter loses the engine and autorotation is not initiated?
- Meaning of “ ’thwart” in a 19th century poem
- The answer is not wrong
- What is the spiritual difference between hungering and thirsting? (Matthew 5:6)
- Replacing a multi character pattern that includes a newline with some characters
- How to justify our beliefs so that it is not circular?
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of assignment
task , duty , job , chore , stint , assignment mean a piece of work to be done.
task implies work imposed by a person in authority or an employer or by circumstance.
duty implies an obligation to perform or responsibility for performance.
job applies to a piece of work voluntarily performed; it may sometimes suggest difficulty or importance.
chore implies a minor routine activity necessary for maintaining a household or farm.
stint implies a carefully allotted or measured quantity of assigned work or service.
assignment implies a definite limited task assigned by one in authority.
Examples of assignment in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'assignment.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
see assign entry 1
14th century, in the meaning defined at sense 1
Phrases Containing assignment
- self - assignment
Dictionary Entries Near assignment
Cite this entry.
“Assignment.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/assignment. Accessed 28 Aug. 2024.
Legal Definition
Legal definition of assignment, more from merriam-webster on assignment.
Nglish: Translation of assignment for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of assignment for Arabic Speakers
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Plural and possessive names: a guide, 31 useful rhetorical devices, more commonly misspelled words, why does english have so many silent letters, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, popular in wordplay, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, it's a scorcher words for the summer heat, 7 shakespearean insults to make life more interesting, birds say the darndest things, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), games & quizzes.

Buffalo: (716) 970-4007 | Toronto: (866) 697-1832

Buffalo: (716) 970-4007 | Toronto: (866) 697-1832
What does it mean for a policy to be enjoined & What does it mean for Form I-131F?

New immigration policies are often met with a sea of lawsuits attempting to stop the new rule from coming to fruition. Most recently, sixteen states joined together to sue the Biden administration’s implementation of Form I-131F, Application for Parole in Place for Certain Noncitizen Spouses and Stepchildren of U.S. Citizens. This has resulted in the policy being enjoined.
What does it mean for a policy to be “Enjoined?”
When any government agency enacts a new policy, legal challenges to the policy are often brought to the courts by a state, organization, or large group of affected individuals. Most often, the legal challenge is based on the new policy’s conflict with existing law, including the Constitution, how it was implemented, and/or the policy’s violation of basic rights.
When a challenge such as this is brought to a court, oftentimes that court issues an “injunction” on the policy while it determines the merits of the claim. In plain language, this means the policy is put on hold while the court determines if the policy is legal. We most recently saw this in action with the enjoinment of Form I-131F, Application for Parole in Place for Certain Noncitizen Spouses and Stepchildren of U.S. Citizens under the Biden administration’s “Keeping Families Together” program.
What is the argument against Form I-131F?
Sixteen states have joined together to sue the federal government, arguing the new pathway for spouses and stepchildren of U.S. Citizens to adjust status and obtain a green card contradicts existing U.S. immigration law under the Immigration and Nationality Act (“INA.”) As of August 27, 2024, the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of Texas enjoined the new Form I-131F while it hears the case brought by these sixteen states. This means, for now, USCIS is accepting Form I-131F, but will not adjudicate them until/unless the Court finds the policy is legal.
Litigation of new immigration policy is common and expected. We will continue to watch what happens in the Eastern District of Texas, but it is likely further suits will be filed against the new Keeping Families Together policies. The world of immigration law changes rapidly. If you believe you or your family members may benefit from the Keeping Families Together policy, it’s advisable to consult an immigration attorney for the most up to date information.
Schedule a Consultation with an Immigration Lawyer
- I-131F, Application for Parole in Place for Certain Noncitizen Spouses and Stepchildren of U.S. Citizens
We Can Help!
If you have questions regarding Form I-131F Parole in Place for Noncitizen Spouses, we invite you to contact our team at Richards and Jurusik for detailed guidance and assistance. We aim to provide the most accurate and up-to-date information to make your immigration process smoother and less stressful. The immigration lawyers at Richards and Jurusik have decades of experience helping people to work and live in the United States. Read some of our hundreds of 5-star client reviews ! Contact us today to assess your legal situation.
Similar Posts

Navigating Green Card Renewal: A Comprehensive Guide
Discover the essential steps for renewing or replacing your green card with precision and ease. Whether your card is expiring, lost, or needs updating, this comprehensive guide walks you through the process, ensuring a smooth renewal journey.

Diversity Visa Lottery: A Guide to Selection and Next Steps
The Diversity Immigrant Visa Program, commonly known as the Diversity Visa Lottery, is a pivotal U.S. government initiative that facilitates up to 50,000 immigrant visas annually. Originating from the Immigration Act of 1990, it’s designed to diversify the U.S. immigrant population by selecting applicants from countries with historically low immigration rates to the United States. We discuss the diversity lottery system here.

L1A Visa: Qualifications for Managers and Executives
On August 16, 2022, USCIS issued updates regarding L1A Visa eligibility, impacting US employers seeking to transfer managerial and executive-level employees from foreign offices to the United States. To qualify for L1A Visa status, it’s essential to understand the nuanced definitions of Managers and Executives under USCIS guidelines.
How to Use Nunc Pro Tunc for an Immigration Case
Nunc Pro Tunc is a legal remedy used in immigration cases to correct administrative errors. This article explains the concept, how it can be applied, and its limitations. Learn about the specific conditions under which Nunc Pro Tunc is granted and how it can impact your immigration status.
Department of Homeland Security Update: Navigating the DHS Final Rule on Public Charge: Key Changes and Effective Date
The US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) has recently released a final rule reshaping the landscape of Public Charge Inadmissibility grounds. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the key determinants and changes introduced in this rule, slated to be effective from December 23, 2022.
TN Visa Status: The J1 Visa Two-Year Home Residency
Canadian and Mexican professionals who want to take advantage of the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) opportunities encounter unique challenges in the U.S. immigration system. One key issue is the two-year home-country physical presence requirement, as outlined in the Immigration and Nationality Act (INA) 212(e), which can be confusing for many navigating this process.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Options and Derivatives
- Strategy & Education
Assignment: Definition in Finance, How It Works, and Examples
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)
What Is an Assignment?
Assignment most often refers to one of two definitions in the financial world:
- The transfer of an individual's rights or property to another person or business. This concept exists in a variety of business transactions and is often spelled out contractually.
- In trading, assignment occurs when an option contract is exercised. The owner of the contract exercises the contract and assigns the option writer to an obligation to complete the requirements of the contract.
Key Takeaways
- Assignment is a transfer of rights or property from one party to another.
- Options assignments occur when option buyers exercise their rights to a position in a security.
- Other examples of assignments can be found in wages, mortgages, and leases.
Uses For Assignments
Assignment refers to the transfer of some or all property rights and obligations associated with an asset, property, contract, or other asset of value. to another entity through a written agreement.
Assignment rights happen every day in many different situations. A payee, like a utility or a merchant, assigns the right to collect payment from a written check to a bank. A merchant can assign the funds from a line of credit to a manufacturing third party that makes a product that the merchant will eventually sell. A trademark owner can transfer, sell, or give another person interest in the trademark or logo. A homeowner who sells their house assigns the deed to the new buyer.
To be effective, an assignment must involve parties with legal capacity, consideration, consent, and legality of the object.
A wage assignment is a forced payment of an obligation by automatic withholding from an employee’s pay. Courts issue wage assignments for people late with child or spousal support, taxes, loans, or other obligations. Money is automatically subtracted from a worker's paycheck without consent if they have a history of nonpayment. For example, a person delinquent on $100 monthly loan payments has a wage assignment deducting the money from their paycheck and sent to the lender. Wage assignments are helpful in paying back long-term debts.
Another instance can be found in a mortgage assignment. This is where a mortgage deed gives a lender interest in a mortgaged property in return for payments received. Lenders often sell mortgages to third parties, such as other lenders. A mortgage assignment document clarifies the assignment of contract and instructs the borrower in making future mortgage payments, and potentially modifies the mortgage terms.
A final example involves a lease assignment. This benefits a relocating tenant wanting to end a lease early or a landlord looking for rent payments to pay creditors. Once the new tenant signs the lease, taking over responsibility for rent payments and other obligations, the previous tenant is released from those responsibilities. In a separate lease assignment, a landlord agrees to pay a creditor through an assignment of rent due under rental property leases. The agreement is used to pay a mortgage lender if the landlord defaults on the loan or files for bankruptcy . Any rental income would then be paid directly to the lender.
Options Assignment
Options can be assigned when a buyer decides to exercise their right to buy (or sell) stock at a particular strike price . The corresponding seller of the option is not determined when a buyer opens an option trade, but only at the time that an option holder decides to exercise their right to buy stock. So an option seller with open positions is matched with the exercising buyer via automated lottery. The randomly selected seller is then assigned to fulfill the buyer's rights. This is known as an option assignment.
Once assigned, the writer (seller) of the option will have the obligation to sell (if a call option ) or buy (if a put option ) the designated number of shares of stock at the agreed-upon price (the strike price). For instance, if the writer sold calls they would be obligated to sell the stock, and the process is often referred to as having the stock called away . For puts, the buyer of the option sells stock (puts stock shares) to the writer in the form of a short-sold position.
Suppose a trader owns 100 call options on company ABC's stock with a strike price of $10 per share. The stock is now trading at $30 and ABC is due to pay a dividend shortly. As a result, the trader exercises the options early and receives 10,000 shares of ABC paid at $10. At the same time, the other side of the long call (the short call) is assigned the contract and must deliver the shares to the long.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-592232681-0bedb3d0696b45df845dc5f05a1843c9.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
Get the Reddit app
A place for learning English. 英語の学びのスペースです。 Un lugar para aprender Inglés. مكان لتعلم اللغة الإنجليزية. Un lieu pour apprendre l'Anglais. Ein Ort zum Englisch lernen.
Is this sentence correct? The assignment is *due today*.
Or should I say: the assignment is due for today / due on today?
I'm just a bit confused about the prepositions used with due. Thanks.
By continuing, you agree to our User Agreement and acknowledge that you understand the Privacy Policy .
Enter the 6-digit code from your authenticator app
You’ve set up two-factor authentication for this account.
Enter a 6-digit backup code
Create your username and password.
Reddit is anonymous, so your username is what you’ll go by here. Choose wisely—because once you get a name, you can’t change it.
Reset your password
Enter your email address or username and we’ll send you a link to reset your password
Check your inbox
An email with a link to reset your password was sent to the email address associated with your account
Choose a Reddit account to continue
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of assignment in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- It was a jammy assignment - more of a holiday really.
- He took this award-winning photograph while on assignment in the Middle East .
- His two-year assignment to the Mexico office starts in September .
- She first visited Norway on assignment for the winter Olympics ten years ago.
- He fell in love with the area after being there on assignment for National Geographic in the 1950s.
- act as something
- all work and no play (makes Jack a dull boy) idiom
- be at work idiom
- be in work idiom
- housekeeping
- in the line of duty idiom
- join duty idiom
You can also find related words, phrases, and synonyms in the topics:
assignment | American Dictionary
Assignment | business english, examples of assignment, collocations with assignment.
These are words often used in combination with assignment .
Click on a collocation to see more examples of it.
Translations of assignment
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
get away from it all
to go somewhere, usually on holiday, where you can completely relax and forget your responsibilities or problems

Trial, judge, and jury: talking about what happens when a criminal is caught

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- on assignment
- American Noun
- Collocations
- Translations
- All translations
To add assignment to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add assignment to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
- Daily Crossword
- Word Puzzle
- Word Finder
- Word of the Day
- Synonym of the Day
- Word of the Year
- Language stories
- All featured
- Gender and sexuality
- All pop culture
- Writing hub
- Grammar essentials
- Commonly confused
- All writing tips
- Pop culture
- Writing tips
Advertisement
[ uh - sahyn -m uh nt ]
She completed the assignment and went on to other jobs.
Synonyms: job , obligation
He left for his assignment in the Middle East.
- an act of assigning; appointment.
- the transference of a right, interest, or title, or the instrument of transfer.
- a transference of property to assignees for the benefit of creditors.
/ əˈsaɪnmənt /
- something that has been assigned, such as a mission or task
- a position or post to which a person is assigned
- the act of assigning or state of being assigned
assignment of a lease
- the document effecting such a transfer
- the right, interest, or property transferred
- law (formerly) the transfer, esp by an insolvent debtor, of property in trust for the benefit of his creditors
- logic a function that associates specific values with each variable in a formal expression
- history a system (1789–1841) whereby a convict could become the unpaid servant of a freeman
Other Words From
- misas·signment noun
- nonas·signment noun
- reas·signment noun
Word History and Origins
Origin of assignment 1
Synonym Study
Example sentences.
Yariel Valdés González and I faced these challenges while on assignment in South Florida and the Deep South from July 21-Aug.
They’re putting time into decoration just as they would in their physical classroom, and students can interact with the space by, say, clicking on a bookshelf to get a reading assignment.
For now, if the district moves to in-person learning, instruction in Carlsbad will take place on campus five days per week and students may engage in additional independent practices and other assignments at home.
The assignments must also respect the relationships between the elements in the group.
It’s very hard, by the way, to do real random assignment studies of couples therapy.
His most recent assignment was the 84th Precinct, at the Brooklyn end of the Brooklyn Bridge.
When Lewis was shipped off to Vietnam, his son was just three months old, and the timing of the assignment worried Lewis.
When Vial got that first assignment, she was just beginning her photography career, and Cirque du Soleil was only a few years old.
“For our winter issue, we gave ourselves one assignment: Break The Internet,” wrote Paper.
By the 1950s the rapid assignment of gender to an ambiguously gendered infant had become standard.
Consent to an assignment may be given by the president of the company, without formal vote by the directors.
A transfer by the lessee of the whole or a part of his interest for a part of the time is a sublease and not an assignment.
An assignment to one who has an insurable interest as relative, creditor and the like, is always valid.
When an assignment of it is made, the assignee may sue in his own name for rent accruing after the assignment.
In some states statutes forbid the assignment of such policies for the benefit of creditors.
Related Words
- appointment

IMAGES
COMMENTS
What is the difference between assignment due dates and availability dates? In addition to setting a due date for an assignment, instructors can specify a specific date range when students can submit the assignment. These dates are called availability dates. These dates are optional and can be set depending how you want to manage the assignment.
How strict should you be? A guide to assignment due dates. Be consistent in your approach to deadline flexibility, whether you never accept late work or are always willing to make an exception. Colleges typically require instructors to include a calendar of assignment due dates in every course syllabus.
This help content & informationGeneral Help Center experience Search
Prepositions come after many words in English, and it's important to understand how the meaning of words changes based on which preposition follows it. Let's look at whether we use due on, due by, or due for, and what each one means.
Due on is used when referring to a precise date by which a payment or task must be completed. Due by indicates a deadline specifying the latest time or date of completion. Due for anticipates events or actions expected or scheduled to occur, often referring to routine obligations.
An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment. Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand.
In addition to setting a due date for an assignment, instructors can specify a specific date range when students can submit the assignment. These dates are called availability dates. These dates are optional and can be set depending how you want to manage the assignment. Note: Beneath the Due Date and Availability date fields, Perceivant will ...
What does Due 11:59 PM Mean 11:59 PM is one of the most common assignments' due time (deadline) given to students. I know you may be wondering why this is the case. Why not any other time of the day?
This resource describes some steps you can take to better understand the requirements of your writing assignments. This resource works for either in-class, teacher-led discussion or for personal use.
Assignment due date and time as you work an item. — Its due date and time always appears above the list of items it contains on the assignment summary page. This is true whether the assignment is incomplete, complete, or past due. — To look back at the assignment due date and time on most assignments, select the assignment name link (top ...
My assignment is due tomorrow and I haven't even started it yet! Uh oh…. Well, if it really is due tomorrow, let's do this and do it quick! You could have anything due tomorrow, so instead of a step-by-step guide let's focus on some tips and tricks to pull off this craziness. Legions of students before you have done it and legions of ...
The phrase "I understand the assignment" is often used by someone indicating their intentions to go above and beyond to do a good job. That's the general strategy behind the organic campaign in support of Vice President Kamala Harris being spread on social that made the catchphrase resurface in late July 2024.
What Does Flexibility Regarding Assignment Due Dates Mean? A Guide for Implementation We have learned that faculty and students would like more guidance regarding the accommodation "flexibility regarding assignment due dates." This information is designed to help faculty in assessing how to implement this accommodation in the classroom.
Synonym for assignments due @sa_ra_ "due this week" means they have to be handed in this week. If they don't say 'due' it means they are doing some assignments, and we don't know when they might be due. So this 'due' is like "The bus is due in half an hour." It means that is the scheduled time.
What Does Assignment Despite Objection Mean? The term "Assignment Despite Objection" is used to describe a situation in which a nurse has been made responsible for an unmanageable patient load. Despite making it clear to unit leadership that the staff member feels unsafe, unqualified, or unsupported in managing the care of that particular ...
"What is the due date for this assignment" or "When is this assignment due?" The "what" is asking for a specific name / figure denoting a point in time, and the "when" is actually asking for a point in time - the answer does not have to take the form of a date.
The sentence 'the assignment is due' is correct and usable in written English. You can use it when referring to a specific assignment that must be completed by a certain date. For example, "The assignment is due on Friday, so please make sure to have it finished by then." The assignment is due February 9th.
Personally, I would use "due by" to cover all three and would take it to mean something like "up to and including Friday." "Due on" Friday seems strange because it could imply that it is due only on that day and couldn't be handed in sooner, and "due for" sounds idiomatically strange, with "for" seeming like a wrong prepositional choice to me.
In many contexts there would be no difference. In some, "due by" implies that the assignment may be submitted before the due date; whereas "due on" does not make this as implicit. Normally there's no difference, but it might be this: Due on Monday - you have to give it on Monday, not after and preferably not before.
The meaning of ASSIGNMENT is the act of assigning something. How to use assignment in a sentence. Synonym Discussion of Assignment.
New immigration policies are often met with a sea of lawsuits attempting to stop the new rule from coming to fruition. Most recently, sixteen states joined together to sue the Biden administration's implementation of Form I-131F, Application for Parole in Place for Certain Noncitizen Spouses and Stepchildren of U.S. Citizens. This has resulted in the
Assignment: An assignment is the transfer of an individual's rights or property to another person or business. For example, when an option contract is assigned, an option writer has an obligation ...
The assignment is due today is correct. 6. Award. Or should I say: the assignment is due for today / due on today? I'm just a bit confused about the prepositions used with due.
ASSIGNMENT definition: 1. a piece of work given to someone, typically as part of their studies or job: 2. a job that…. Learn more.
Assignment definition: something assigned, as a particular task or duty. See examples of ASSIGNMENT used in a sentence.
Q. What does the phrase "Hit me with your best shot" mean? The phrase "Hit me with your best shot" is a powerful mantra that encourages us to embrace challenges and to take our best shot. It is a testament to our inner strength and resilience, and a reminder of our potential for greatness. Q. How should I approach challenges in life?