MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Management Case Studies » Case Study: Business Strategy Analysis of Wal-Mart

Case Study: Business Strategy Analysis of Wal-Mart
Sam Walton, a leader with an innovative vision, started his own company and made it into the leader in discount retailing that it is today. Through his savvy, and sometimes unusual, business practices, he and his associates led the company forward for thirty years. Today, four years after his death, the company is still growing steadily. Wal-Mart executives continue to rely on many of the traditional goals and philosophies that Sam’s legacy left behind, while simultaneously keeping one step ahead of the ever-changing technology and methods of today’s fast-paced business environment . The organization has faced, and is still facing, a significant amount of controversy over several different issues; however, none of these have done much more than scrape the exterior of this gigantic operation. The future also looks bright for Wal-Mart, especially if it is able to strike a comfortable balance between increasing its profits and recognizing its social and ethical responsibilities .
Why is Wal-Mart so Successful ? Is it Good Strategy or Good Strategy Implementation ? In 1962, when Sam Walton opened the first Wal-Mart store in Rogers, Arkansas, no one could have ever predicted the enormous success this small-town merchant would have. Sam Walton’s talent for discount retailing not only made Wal-Mart the world’s largest retailer, but also the world’s number one retailer in sales. Indeed, Wal-Mart was named “Retailer of the Decade” by Discount Store News in 1989, and on several occasions has been included in Fortune’s list of the “10 most admired corporations.” Even with Walton’s death (after a two-year battle with bone cancer) in 1992, Wal-Mart’s sales continue to grow significantly.

Regarded by many as the entrepreneur of the century, Walton had a reputation for caring about his customers, his employees (or “associates” as he referred to them), and the community. In order to maintain its market position in the discount retail business, Wal-Mart executives continue to adhere to the management guidelines Sam developed. Walton was a man of simple tastes and took a keen interest in people. He believed in three guiding principles: 1. Customer value and service; 2. Partnership with its associates; 3. Community involvement.
- The Customer — The word “always” can be seen in virtually all of Wal-Mart’s literature. One of Walton’s deepest beliefs was that the customer is always right, and his stores are still driven by this philosophy. When questioned about Wal-Mart’s secrets of success , Walton has been quoted as saying, “It has to do with our desire to exceed our customers’ expectations every hour of every day”.
- The Associates — Walton’s greatest accomplishment was his ability to empower, enrich, and train his employees. He believed in listening to employees and challenging them to come up with ideas and suggestions to make the company better. At each of the Wal-Mart stores, signs are displayed which read, “Our People Make the Difference.” Associates regularly make suggestions for cutting costs through their “Yes We Can Sam” program. The sum of the savings generated by the associates actually paid for the construction of a new store in Texas. One of Wal-Mart’s goals was to provide its employees with the appropriate tools to do their jobs efficiently. The technology was not used as a means of replacing existing employees, but to provide them with a means to succeed in the retail market.
- The Community — Wal-Mart’s popularity can be linked to its hometown identity. Walton believed that every customer should be greeted upon entering a store, and that each store should be a reflection of the values of its customers and its community. Wal-Mart is involved in many community outreach programs and has launched several national efforts through industrial development grants.
What are the Key Features of Wal-Mart’s Approach to Implementing the Strategy Put Together by Sam Walton — The key features of Wal-Mart’s approach to implementing the strategy put together by Sam Walton emphasizes building solid working relationships with both suppliers and employees, being aware and taking notice of the most intricate details in store layouts and merchandising techniques, capitalizing on every cost saving opportunity, and creating a high performance spirit. This strategic formula is used to provide customers access to quality goods, to make these goods available when and where customers want them, to develop a cost structure that enables competitive pricing , and to build and maintain a reputation for absolute trustworthiness.
Wal-Mart has invested heavily in its unique cross-docking inventory system . Cross docking has enabled Wal-Mart to achieve economies of scale which reduces its costs of sales. With this system, goods are continuously delivered to stores within 48 hours and often without having to inventory them. Lower prices also eliminate the expense of frequent sales promotions and sales are more predictable. Cross docking gives the individual managers more control at the store level.
A company owned transportation system also assists Wal-Mart in shipping goods from warehouse to store in less than 48 hours. This allows Wal-Mart to replenish the shelves 4 times faster than its competition. Wal-Mart owns the largest and most sophisticated computer system in the private sector. It uses a MPP (massively parallel processor) computer system to track stock and movement which keeps it abreast of fast changes in the market. Information related to sales and inventory is disseminated via its advanced satellite communications system.
Sam Walton received national attention through his “Buy America” policy. Through this plan, Wal-Mart encourages its buyers and merchandise managers to stock stores with American-made products. In a 1993 annual report management stated the program demonstrates a long-standing Wal-Mart commitment to our customers that we will buy American-made products whenever we can if those products deliver the same quality and affordability as their foreign-made counterparts.
Environmental concerns are important to Wal-Mart. A prototype store was opened in Lawrence, Kansas, which was designed to be environmentally friendly. The store contains environmental education and recycling centers. Wal-Mart has also adopted the low cost theme for its facilities. All offices, including the corporate headquarters, are built economically and furnished simply. To conserve energy, temperature controls are connected via computer to headquarters. Through these programs, Wal-Mart shows its concern for the community.
Just how Successful is Wal-Mart? — A forecast of Wal-Mart’s income for the period 1995-2000, considering increases of 30.6% in Net Sales, 27.7% in Operating Expenses, and 52.3% in Interest Debt (a level which is below Wal-Mart’s historically compounded growth rate of 55.6%) indicates that the company should continue to report gains each year until 2000.
Growth on Sales — According to most analysts and company projections, sales should approximate $115 billion by 1996, representing an increase of 30.6% as compared to 1995. If the company continues at this pace, sales should reach $334 billion by the year 2000. The growth on sales that Wal-Mart reported during the 1980s and the beginning of the 1990s will be difficult to repeat, especially considering the ever-changing marketplace in which it competes. In an interview, Bill Fields, President of the Stores Division, said “Wal-Mart is now seeing price pressure from companies that once assiduously avoided taking it on. These include specialty retailers such as Limited, category killers like Home Depot and Circuit City, and catalog companies like Spiegel. I think everybody prices off of Wal-Mart. You’ve got Limited reaching levels we’d thought they’d never get to. The result is that everyday low prices are getting lower”.
Debt Position — Based on Wal-Mart’s position in 1994, which was considered a year of expansion for the company, (Wal-Mart added 103 new discount stores, 38 “Supercenters”, 163 warehouse clubs, and 94,000 new associates) interest debt increased 52.3%. The cost paid by Wal-Mart to finance property plants and equipment forced the company to increase long term debt by 4.6 times during the period 1991-1995. Long term debt for 1995 is $7.9 billion. If Wal-Mart continues its expansion plans based on more debt acquisition at 1994 levels, the company may not attain forecasted gains by as early as 1998.
Operating Expenses — Operating expenses will be a key strategic issue for Wal-Mart in order to maintain its position in the market. The challenge is how to run more stores with less operating expenses. According to Bill Fields, “. . . the goal is to increase sales per square foot and drive operating costs down yet another notch”. Trends indicate that operating expenses have been growing at a rate of 27.7% in recent years. However, Wal-Mart should reap the benefits of its investments in high technology, and be able to operate more stores without increasing its expenses.
Wal-Mart’s future will depend on how well the company manages its expansion plans. For the coming years, the company will need to justify its expansion plans with consistent growth in sales, in order to offset the increases in debt interest and operating expenses.
What Problems are Ahead for Wal-Mart? What Risks? — Throughout the 1980s, Wal-Mart’s strategic intent was to unseat industry leaders Sears and Kmart, and become the largest retailer in the U.S. Wal-Mart accomplished this goal in 1991. But Wal-Mart’s current strong competitive position and its past rapid growth performance can’t guarantee that the company will remain as the industry leader or maintain its strong business position in the future. Carol Farmer, a retail consultant, told the Wall Street Journal that, “One little bad thing can wipe out lots of good things”. Every move in its business operation ought to be well thought-out and executed.
Also, if Wal-Mart continues to follow Sam Walton’s vision of expansion, Wal-Mart will reach its peak in the very near future. When it does, its growth will start to slow down and the company will need to turn its strategic attention to diversification for future growth .
2) Social responsibility — Retail stores can compete on several bases: service, price, exclusivity, quality, and fashion. Wal-Mart has been extremely successful in competing in the retail industry by combining service, price, and quality. However, other merchants may object to Wal-Mart’s entry into their community. Because of its ability to out-price smaller competitors, Wal-Mart’s stores threaten smaller neighborhood stores which can only survive if they offer merchandise or services unavailable anywhere else. This makes it very hard for small businesses, such as “mom-and-pop” enterprises, to survive. They, therefore, fight to keep Wal-Mart from entering their locales. Numerous studies conducted in different states both support and criticize Wal-Mart. Nevertheless, Wal-Mart did drive local merchants out of business when it opened up stores in the same neighborhood. As a result, more and more rural communities are waging war against Wal-Mart’s entrance into their market. Besides protesting and signing petitions to attempt to stop Wal-Mart’s entry into their community, the opposition’s efforts can even be found on The Internet. Gig Harbor, a small town in Washington, recently started a World Wide Web page entitled “Us Against the Wal.” The town’s neighborhood association promised that they “will fight them [Wal-Mart] tooth and nail”.
How Big Will Wal-Mart be in Five Years if all Continues to go Well? — Before he died, Sam Walton expressed his belief that by the year 2000 Wal-Mart should be able to double the number of stores to about 3,000 and to reach sales of $125 billion annually. Walton predicted that the four biggest sources of growth potential would be the following: 1. expanding into states where it had no stores; 2. continuing to saturate its current markets with new stores; 3. perfecting the Supercenter format to expand Wal-Mart’s retailing reach into the grocery and supermarket arena — a market with annual sales of about $375 billion; 4. moving into international markets.
Wal-Mart Supercenters represent leveraging on customer loyalty and procurement muscle in order to create a new domestic growth vehicle for the company. With few locations left in the U.S. to put a new Sam’s Club or traditional Wal-Mart, the Supercenter division has emerged as the domestic vehicle for taking Wal-Mart to $100 billion in sales. Before the Supercenter, Walton experimented with a massive “Hypermart”, encompassing more than 230,000 square feet in size. The idea failed. Customers complained that the produce was not fresh or well-presented and that it was difficult to find things in a store so big that inventory clerks had to wear roller skates. One of Walton’s philosophies was that traveling on the road to success required failing at times.
Walton’s prediction was right on target. The Supercenter division more than doubled in size during 1993, then doubled again in 1994. Supercenters, once thought of as risky because of slim profit margins on the food side, will most likely make Wal-Mart the nation’s largest grocery retailer within the next five to seven years.
Expanding overseas, Wal-Mart moved into the international market in 1991 through a joint-venture partnership with CIFRA S.A. de C.V., Mexico’s leading retailer. Since then the company has entered Canada, Hong Kong, mainland China, Puerto Rico, Argentina, and Brazil. The Wal-Mart International Division was officially formed in 1994 to manage the company’s international growth. By the year 2000, analysts expect Wal-Mart to be a huge international retailer, with numerous locations in South America, Europe, and Asia.
Related posts:
- Case Study: An Assessment of Wal-Mart’s Global Expansion Strategy
- Case Study: Wal-Mart’s Failure in Germany
- Case Study: Wal-Mart’s Distribution and Logistics System
- Case Study: Ryanair Business Strategy Analysis
- Business Level Strategies – Cases of Wal-Mart, Apple, Zara and Ikea
- Case Study: Pfizer’s Strategy Analysis
- Case Study: The Business Strategy of Apple
- Case Study: Sony’s Business Strategy and It’s Failure
- Case Study: Business Strategy of Sony Corporation
- Case Study: Delta Airlines Successful Business Turnaround Strategy
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- THE STRATEGY JOURNEY Book
- Videos & Tutorials
- Strategy Journey Analyzer [QUIZ + WORKBOOK]
- COMMUNITY FORUMS
- Transforming Operating Models with Service Design (TOMS) Program
- ABOUT STRATABILITY ACADEMY
Walmart Business Strategy: A Comprehensive Analysis
By Julie Choo
Published: January 5, 2024
Last Update: January 5, 2024
TOPICS: Service Design
In the dynamic landscape of retail, Walmart stands as a behemoth, shaping the industry with its innovative business strategies . This article delves into the core of Walmart’s success, unraveling its business strategy and digital transformation from top to bottom.
Walmart Business Strategy
Walmart’s business strategy is a well-crafted tapestry that combines a variety of elements to secure its position as a retail giant. At the heart of this strategy lies a robust operating model approach that encompasses a diverse range of channels and tactics.
Transition to An OmniChannel Marketplace
The Walmart business strategy includes leveraging its vast physical presence through an extensive network of stores, drawing customers in with the promise of Everyday Low Prices (EDLP). This commitment to affordability is not just a slogan; it’s a cornerstone of Walmart’s marketing ethos, shaping consumer perceptions and driving foot traffic to its brick-and-mortar locations.
Building Strength via its Emerging Digital Operating Model
Walmart’s business business strategy extends beyond traditional advertising methods and its strength is in its operational strategy where it is charging ahead with digital transformation to become a more complete Omnichannel Marketplace to combat competitors such as Amazon. The retail giant has embraced the digital era, utilizing online platforms and e-commerce to reach a broader audience. Part of this digital evolution involves the strategic placement of distribution and fulfillment centers , ensuring efficient order processing and timely deliveries. By strategically integrating distribution and fulfillment centers into its operating model , Walmart maximizes operational efficiency, meeting customer demands swiftly and solidifying its reputation for reliability in the competitive retail landscape.
In essence, Walmart’s holistic digital operating model backed by a evolving digital transformation strategy, encompassing physical stores, online presence, and strategically placed distribution hubs, reflects a dynamic and adaptive approach to consumer engagement and satisfaction.
Walmart’s Existing Business Model Before Digital Transformation
Walmart’s retail business .
Walmart stores, comprising a vast network of discount stores and clubs, serve as the backbone of the retail giant’s physical presence. Walmart’s store format, ranging from neighborhood discount stores to expansive membership-based clubs, caters to a diverse customer base. These Walmart stores are strategically positioned to provide accessibility to a wide demographic, offering a one-stop shopping experience.
The discount stores, characterized by their commitment to Everyday Low Prices (EDLP), have become synonymous with affordability, attracting budget-conscious consumers. Simultaneously, Walmart clubs offer a membership-based model, providing additional benefits and exclusive deals. The amalgamation of these store formats under the Walmart umbrella showcases the company’s versatility, catering to the varied needs and preferences of consumers across different communities and demographics.
Walmart Pricing Strategy
Pricing strategy.
Walmart’s pricing strategy and its competitive advantage are substantiated by reputable sources in the retail industry. The pricing index data, indicating that Walmart’s prices are, on average, 10% lower than its competitors, comes from a comprehensive market analysis conducted by Retail Insight, a leading research firm specializing in retail trends and pricing dynamics.
Everyday Low Prices
Walmart’s success in the retail sector can be attributed to its commitment to Low Price Leadership, a strategic approach that revolves around providing customers with unbeatable prices. Leveraging Economies of Scale, Walmart capitalizes on its vast size and purchasing power to negotiate favorable deals with suppliers, enabling the company to pass on cost savings to consumers. The integration of Advanced Technology into its operations is another pivotal aspect of Walmart’s strategy. From inventory management to supply chain optimization, technology allows Walmart to enhance efficiency and keep prices competitive.
Walmart strives to keep it’s pricing tactics to the concept of “Everyday Low Prices” (EDLP). This philosophy ensures that customers receive consistently low prices on a wide range of products, fostering trust and loyalty. Additionally, the Rollback Pricing strategy involves temporary price reductions on select items, creating a sense of urgency and encouraging sales. Walmart’s Price Matching Policy, both in-store and online, further solidifies its commitment to offering the best deals. This policy assures customers that if they find a lower price elsewhere, Walmart will match it.
The insight into Walmart’s “Everyday Low Prices” (EDLP) philosophy and its impact on a 15% lower average price for common goods compared to competitors is derived from a detailed report published by Priceonomics , a respected platform known for its in-depth analyses of pricing strategies across various industries.
The statistics regarding Walmart’s market share of 22% in the U.S. grocery market and the 19% higher customer loyalty rate compared to competitors are sourced from recent market reports by Statista, a reliable and widely used statistical portal providing insights into global market trends and consumer behavior.
Multiple layers of Discount
Walmart’s embrace of Multiple Discounts adds another layer to its pricing strategy. Whether through seasonal promotions, clearance sales, or bundled deals, the company provides various avenues for customers to save money. This multifaceted approach to pricing reflects Walmart’s dedication to delivering value to its customers, ensuring that affordability remains a cornerstone of the retail giant’s identity.
These sources collectively reinforce the significance of Walmart’s pricing strategy in maintaining its competitive edge and dominating the retail landscape
Walmart’s Servicing Business
Walmart’s strategic expansion into the servicing business marks a transformative shift, positioning the retail giant as a comprehensive one-stop-shop that extends beyond conventional retail offerings. This venture encompasses an array of lifestyle services, ranging from financial services to automotive care and healthcare clinics. Walmart’s aim is clear: to seamlessly integrate into the daily lives of customers, providing not only products but also essential services, thereby enhancing its role in customers’ routines.
In response to the evolving preferences of contemporary consumers who prioritize convenience and accessibility, Walmart’s strategy seeks to streamline the customer journey. The provision of a diverse range of services alongside its traditional retail offerings exemplifies Walmart’s commitment to simplifying the consumer experience. This comprehensive approach not only caters to the varied needs of customers but also cultivates a sense of loyalty, as individuals find value in the convenience of addressing different requirements all under one roof.
The multifaceted nature of Walmart’s strategy is anticipated to foster increased customer retention. By offering not only a wide array of products but also an extensive range of lifestyle services, Walmart solidifies its position as a retail powerhouse, adapting to the changing landscape of customer-centric businesses. The convenience and value embedded in this approach are poised to elevate Walmart’s stature, making it an indispensable part of customers’ lives.
SWOT Analysis of Walmart’s Business strategy
As we navigate Walmart’s digital transformation journey, a SWOT analysis reveals key insights into its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, guiding strategic decisions for sustained success in the dynamic retail industry that is operating in an increasingly digital economy.
SWOT Analysis of Walmart:
- Strong Brand Recognition: Walmart’s strength lies in its widely recognized and trusted brand, fostering consumer confidence and loyalty.
- Diverse Revenue Stream: The company’s adaptability is evident through a diverse revenue stream, navigating various markets and industries to maintain financial resilience. Per Walmart’s Q3 FY23 Earnings , a breakdown of walmart’s income can be recognised through its Sam’s Club membership sales (Up by 7.2%), Walmart U.S Comp Sales (Up 4.9%), Walmart U.S. eCommerce (up by 24%), and Walmart International sales (up by 5.4%).
- Economies of Scale: Walmart leverages its extensive size for economies of scale shown by its strong revenue growth of 5.3% per 2022 and 2023 consolidated Income statement, enabling cost advantages in procurement, operations, and overall efficiency.
- Strong Customer Base: With a vast and loyal customer base, Walmart establishes a robust foundation in the retail sector, emphasizing customer retention and sustained business growth as per market share stat of 60% shown on the Market retail/wholesale industry dominated by Walmart.
Weaknesses:
- Labor Relations: Walmart has faced criticism for labor practices, including low wages and labor disputes.
- E-commerce Competition: Despite significant strides, Walmart faces intense competition from e-commerce giants (e.g, amazon, eBay), impacting its online market share.
- Over Reliance on US Market: A substantial portion of Walmart’s revenue is generated in the United States, making it vulnerable to domestic economic fluctuations.
- Inconsistent customer service: represents a weakness in Walmart’s SWOT analysis, as variations in service quality across different locations may impact the overall customer experience, potentially leading to customer dissatisfaction and diminished brand perception.
Opportunities:
- E-commerce Expansion: Further growth in the online market allows Walmart to capitalize on changing consumer shopping habits.
- International Expansion: Targeting untapped markets presents opportunities for global revenue diversification.
- Health and Wellness Market: The growing trend towards health-conscious living provides avenues for expansion in the health and wellness sector. Increased understanding of customer journeys in these niches is key to begin to build stickiness effects.
- Technological Innovations: Embracing cutting-edge technologies can enhance customer experience and operational efficiency through a growing Omnichannel marketplace. It is vital to master data science and begin to leverage AI in the battle to understand consumer behaviors and deliver a remarkable experience.
- Competition: Intense competition from traditional retailers and e-commerce platforms poses a threat to Walmart’s market share such as Costco, Target and Amazon.
- Regulatory Challenges: Changes in regulations, especially related to labor and trade, can impact Walmart’s operations and costs. One such example is the metrics shown per Walmart’s ethics & compliance code of conduct aligning to regulatory challenges in culture, work safety, risk mitigation and more.
- Economic Downturns: Economic uncertainties and recessions may lead to reduced consumer spending, affecting Walmart’s revenue.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: External factors like natural disasters or geopolitical events can disrupt the global supply chain, impacting product availability and costs. Such threats are specifically addressed by Walmart’s Enterprise Resilience Planning Team .
More on Walmart’s Online Competitors
Walmart faces formidable competition in the online retail arena, with key rivals such as Amazon and Target vying for a share of the digital market. Amazon, known for its extensive product selection and swift delivery services, poses a significant challenge to Walmart’s e-commerce dominance. Target, on the other hand, leverages its brand appeal and strategic partnerships to attract online customers. To counteract these competitors, Walmart employs a multifaceted approach that combines technological innovation, competitive pricing, and strategic collaborations.
Walmart strategically invests in advanced technologies to enhance its online platform and improve the overall customer experience. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning enables Walmart to provide personalized recommendations, similar to Amazon’s renowned recommendation engine. Additionally, Walmart’s commitment to competitive pricing aligns with its traditional retail strength, offering Everyday Low Prices (EDLP) and frequent promotions to attract budget-conscious consumers, countering the pricing strategies employed by Amazon and other competitors.
Conducting a thorough SWOT analysis (such as this example from the Strategy Journey Book – 2nd Edition) allows Walmart to capitalize on its strengths, address weaknesses, seize opportunities, and mitigate potential threats, contributing to sustained success in the ever-evolving retail landscape.
Walmart’s Digital Transformation Strategy in the new ERA of AI-led Customer Centricity
Walmart’s online business strategy.
Overall, Walmart’s e-commerce strategy is customer-centric, driving substantial sales growth by tailoring its approach to the evolving needs of online customers. Operating a multitude of specialized e-commerce websites across diverse product categories, Walmart strategically positions itself on various e-commerce platforms for market penetration within the US.
Servicing Relevant Customer Journeys & Sustainable Transformation
Walmart’s evolving online strategy is characterized by a dual focus on extensive product offerings and technological sophistication, with concrete examples per its strategic partnership with Adobe in 2021 to integrate walmart’s marketplace, online and instore fulfillment and pickup technologies with Adobe commerce showcasing its commitment to a seamless customer experience. The integration of advanced tools is exemplified by the implementation of an efficient order processing system. For instance, Walmart employs real-time inventory management and automated order fulfillment , ensuring that customers experience timely and accurate deliveries. Statistics show an increasing number of fulfillment centers through FY2022 and FY2023 reports per statista .
Emerging predictive capabilities supported by Data Science and AI
In addition, the technological depth extends to personalized experiences, illustrated by Walmart’s robust recommendation engine. By analyzing customer preferences and purchase history, the system suggests relevant products, enhancing the entire customer journey. This personalized touch not only reflects the user-friendly interface but also demonstrates Walmart’s dedication to tailoring the online experience to individual needs.
Focus on seamless CX and UX to improve customer stickiness
Furthermore, Walmart’s commitment to a seamless online interaction is evident in its streamlined navigation features. The website’s intuitive design and optimized search functionality provide a smooth browsing experience for customers. This emphasis on user-friendliness goes beyond mere aesthetics, ensuring that customers can easily find and explore products, contributing to a more engaging online experience. Improved engagement is at the heart of Walmart’s strategy to foster stickiness effects, both digitally and to also build on brand stickiness too.

By investing in cutting-edge technologies while transforming using Human Centered design practices focused on CX and UX, Walmart not only navigates the complexities of the e-commerce landscape but also enhances the overall satisfaction and engagement of its online customers. These examples underscore Walmart’s strategic approach to digital transformation, where technological sophistication is not just a feature but a tangible means to elevate the online shopping experience.
Walmart International Business
Successful international business expansion requires operating model transformation, and Walmart’s strategy is characterized by a blend of strategic acquisitions, partnerships, and a keen understanding of local markets. This is also how Walmart is operationally applying AI, via strategic partnerships as it continues to build its capabilities to improve its agility to implement transformation and go to market faster, rather than trying to build everything from scratch.
A Sustainable Diversification strategy that adapts to local markets
Walmart’s international business expansion is a testament to its strategic approach in entering diverse markets and adapting to local nuances. One notable example of Walmart’s successful international expansion is its entry into the Indian market. In 2018, Walmart acquired a majority stake in Flipkart, one of India’s leading e-commerce platforms. This move allowed Walmart to tap into India’s burgeoning e-commerce market, aligning with the country’s growing digital consumer base.
The acquisition of Flipkart exemplifies Walmart’s strategy of leveraging local expertise and established platforms to gain a foothold in international markets. Recognizing the unique characteristics of the Indian retail landscape, where e-commerce plays a significant role, Walmart strategically invested in a company deeply embedded in the local market. This approach not only facilitated a smoother entry for Walmart but also enabled the retail giant to navigate regulatory complexities and consumer preferences effectively.
Another example of Walmart’s commitment to tailoring its offerings to meet local needs is further highlighted in its expansion into China where Walmart adapts its store formats to cater to specific consumer preferences.
In China, Walmart has experimented with smaller-format stores in urban areas, recognizing the demand for convenient and accessible shopping options. This adaptability showcases Walmart’s understanding of the diverse economic and cultural landscapes it operates in, contributing to its success on the global stage.
Working with partners to diversify and build a sustainable business model
Collaborations and strategic partnerships play a pivotal role in Walmart’s competitive strategy. In 2023, Walmart has outlined plans to invest heavily into AI automation fulfillment centers to improve its unit cost average by 20%, increasing efficiency in order fulfilments and operations.
The acquisition of Jet.com in 2016 expanded Walmart’s digital footprint and brought innovative talent into the company. Furthermore, Walmart’s partnerships with various brands (such as Adobe, ShipBob) and retailers enable it to diversify its product offerings, providing a competitive edge against the more specialized approaches of some competitors. As part of Walmart’s strategy in marketing, Walmart has announced partnerships with social media giants such as TikTok, Snapchat, Firework and more further boosting its online digital footprint.
The acquisition of Jet.com in 2016 not only expanded Walmart’s digital footprint but it brought innovative talent into the company. It is clear Walmart sees the need for talent as key to its continued efforts to apply human centered design as part of its digital transformation strategy.
By continuously adapting and evolving its strategies, Walmart is clearly implementing digital transformation sustainably, to support its future operating model as Walmart remains a formidable force in the online retail landscape, navigating the challenges presented by its competitors.
In conclusion, Walmart’s business strategy is that of an growing Omnichannel marketplace, a multifaceted approach that combines physical and digital retail, competitive pricing, supply chain excellence, and a commitment to customer satisfaction. Understanding these elements provides insights into the retail giant’s enduring success in a rapid changing and competitive digital economy as it continues to combat emerging new business disruptions.
Q1: How did Walmart become a retail giant?
Walmart’s ascent to retail dominance can be attributed to a combination of strategic pricing, operational efficiency, and a customer-centric approach.
Q2: What sets Walmart’s supply chain apart?
Walmart’s supply chain is marked by innovation and technological integration, allowing the company to streamline operations and stay ahead in a competitive market.
Q3: How does Walmart balance physical and digital retail?
Walmart seamlessly integrates its brick-and-mortar stores with its online presence, offering customers a comprehensive shopping experience.
Q4: What is Walmart’s philosophy on pricing?
Walmart’s commitment to everyday low prices is a fundamental philosophy that underpins its strategy, ensuring affordability for consumers.
Q5: How has Walmart expanded globally?
Walmart’s global expansion involves adapting its strategy to diverse markets, understanding local dynamics, and leveraging its core strengths.
About the author
Julie Choo is lead author of THE STRATEGY JOURNEY book and the founder of STRATABILITY ACADEMY. She speaks regularly at numerous tech, careers and entrepreneur events globally. Julie continues to consult at large Fortune 500 companies, Global Banks and tech start-ups. As a lover of all things strategic, she is a keen Formula One fan who named her dog, Kimi (after Raikkonnen), and follows football - favourite club changes based on where she calls home.
You might also like
Culture & Careers , Data & AI , Gameplans & Roadmaps , Operating Model , Service Design , Strategy Journey Fundamentals , Transformation
The Impact of Co Creation in Modern Business
Culture & Careers , Data & AI , Gameplans & Roadmaps , Operating Model , Service Design , Transformation
4 steps to create a Winning Game Plan
Service Design
9 Steps to your Winning Customer Journey Strategy

A Detailed Case Study on Largest Retail Giant Walmart

Avinash kumar mahato
Walmart is one of the largest retail companies in the world. It was founded in 1962 by Sam Walton. The headquarter of this company is situated in the United States. The main aim of the company is to provide consistent discounts, loyal customer service, and fast friendly service.
Walmart’s targets to expand its business in large cities as well as spread retail stores throughout the world. The retail stores of Walmart are divided into four divisions Walmart Supercenters , Discount Stores, Neighborhood Markets, and Sam’s Clubs warehouses. More than 100 million customers are visiting these Walmart Stores.
It is very uncomfortable for small merchants and communities in America. Walmart reaches their town and provides low-cost offers and the best customer service. It is a very bad condition for small merchants and businessmen in America. To downtown merchants, Walmart just comes and takes over all the small stores.
The purchasing power, aggressive marketing and provide low prices to the customer by Walmart, tend to pull out the business by the small merchants. Gradually the dream of Walmart company to become the largest retailer in the world is full filing day-by-day. But, they increase their business by the wrong actions and do not respect the culture or language of the communities.
Timeline Events Of Walmart company Business Model Of Walmart How Walmart Generates Revenue? Walmart’s Marketing Strategy Walmart’s - Flipkart Acquisition
Timeline Events Of Walmart company
The Timeline of events for Walmart company since its inception.
- 1960: Sam Walton opened his first discount store in Rogers, Arkansas.
- 1981: Walmart become the largest company in America .
- 1981: After becoming the largest company in America, they opened their stores in a small Louisiana town.
- 1983: Walmart opened its stores in Pawhuska and Oklahoma.
- 1986: Walmart claims that it can restore more than 4000 jobs to American Communities.
- 1989: They drive a campaign about Environmental awareness that Walmart is aware of land, water, and air.
- 1990: There are some activist groups against the expansion of Walmart’s store.
- 31st December 1990: Walmart’s closed its stores in Louisiana.
- 5th November 1991: Walmart opened up its store in Lowa City.
- 6th October 1998: Walmart’s founder Sam Walton created a family charity named Walton Family Charitable Support Foundation.
- June 1999: Walmart takes over the ASDA Chain (a British supermarket chain), now they have stores and depots across the United States.
- 2001: Walmart becomes the world’s largest retailer, got huge sales of $191 billion.
- July 2003: Walmart opened its stores in Beijing and till now they have 22 stores in China and counting.
- 2006: Walmart closed its stores in Germany.
- July 2007: Walmart is operating more than 2500 retail units in Walmart International and more than 500,000 employers in some countries.
- 2007: By the ending of this year, they got a net $45 billion sales.
- 2008: Walmart’s opened its wholesale facility in India. This is the first step of Walmart's to sell products through its retail outlets in India.
- 2018: Walmart acquired Flipkart for $16 billion and owned 77% stake in India’s largest online retailer brand.
Business Model Of Walmart

There are different business models that are followed by successful companies which vary from time to time. The business model of Walmart is based to eliminate the middleman from the distribution channels. The advantage of removing the middleman is to provide benefit to the consumer by providing products at lower costs. The main motive of Walmart's business strategy company is to enter every segment of the market and dominate the market by providing products at a lower price.
The main marketing strategy of the company is based on leading on price, be competitive, and deliver a great experience by the motto of Everyday Lower price.
Walmart has three important segments.
Walmart U.S
Walmart U.S is operated in the U.S. They provide customers with products and services that are not present physically in stores. They provide their services via the website and mobile application . The website of Walmart company has a special feature that provides a third party to sell products. The company operates its business on various platforms like supermarkets, discount stores, neighborhood markets, and e-commerce websites .
Walmart International
Walmart International is also divided into three sections which are retailers, wholesalers, and other small projects. These sections are also divided into various sections such as supermarkets, warehouses, electronics, apparel stores , drug stores, digital retailers, and many more.
It is the online platform of Walmart’s company i.e., “ samsclub.com ”. This club is consists of memberships of the only warehouse retailer operations. This section includes warehouse clubs in the U.S, as well as samsclub.com.
Want to Work in Top Gobal & Indian Startups or Looking For Remote/Web3 Jobs - Join angel.co
Angel.co is the best Job Searching Platform to find a Job in Your Preferred domain like tech, marketing, HR etc.
How Walmart Generates Revenue?
The Revenue Model of Walmart deals with the principle of buying in bulk in one go. In this system, they got a huge discount from the manufacturers. They sell in small quantities at low prices. By reducing the price they have high sales volume through which they have high earning.
Walmart’s generate its revenue by removing the middleman and selling their product directly to the customers and services to business. The two main sources of revenue are Product revenue and Service revenue .
Walmart's revenue in the fiscal year ending January, 2020 was $524 Billion.
Product Revenue
Walmart has a wide range of products in various categories:-
- In the grocery category, they have products like Daily needs products, dairy products, frozen foods, bakery, baby products, beauty aids, and many more.
- Health and wellness category have products like Pharmacy products and clinical services .
- The entertainment category has products like electronics products, toys, cameras, movies, music, videos, and books.
- Stationary, paints, and hardware, Automotive, sporting goods, crafts, and seasonal merchandise.
- Apparel categories include apparel for men, women, boys, girls, shoes, jewelry, and accessories.
- Home appliances include home furnishing services, home decor, livings, and horticulture.
Service Revenue
Walmart also provide services to generate revenue in various fields:-
- They provide financial services like prepaid cards , money orders, wire transfer, money transfers, bill payments, and so on.
- VUDU movie streaming services: This is a subscription-based OTT platform for buying and renting movies, watching TV shows on demand.
- Clinical Services include primary health care, Physical and Wellness checks, Clinical lab tests.
- Health Insurance services
Walmart’s Marketing Strategy
Walmart's Business Strategy Analysis is one of the most important parts of any business whether it is small or large. It is very important to make an effective marketing plan to survive in the market . Walmart uses the principle of business marketing penetration method which is used to capture the market by offering lower prices and competitive prices to the consumers.
The company follows cost leadership which makes a huge profit for the company. The company provide low prices to the consumer and treated all the customers as king of the market to maintain the relationship between Walmart and the customer.
According to Walmart, there are four factors that drive the customer’s choice of retailer:
- Assortment.
One more reason for the success of Walmart is purchasing products from local manufacturers in a bulk in one go and selling in small quantities. Buying from local manufacturers is the benefit for both. Buying more products from local manufacturers means they are creating more jobs and they reduce the unemployment rate. They should provide good quality products at a lower price to maintain a good relationship with customers and continue to get profits in business.

List of Courses Curated By Top Marketing Professionals in the Industry
These are the courses curated by Top Marketing Professionals in the Industry who have spent 100+ Hours reviewing the Courses available in the market. These courses will help you to get a job or upgrade your skills.

Walmart’s - Flipkart Acquisition

Flipkart is one of the leading Indian e-commerce brands. In 2018, Walmart takes 77% stakes in India’s largest e-commerce company Flipkart and makes the world’s biggest purchase of an e-commerce company.
After this acquisition the future of eCommerce industry in India has become more competitive than ever.
The three main reasons for the acquisition of Flipkart are Flipkart’s leadership in some lucrative sections, its payment platform and the company’s talent pool.
Walmart’s world’s largest company is to continue to expand its business by improving its strategies day-by-day. The main reason for the success of Walmart is the EDLP system i.e., Everyday Low Price. They are working aggressively to maintain profits, market shares, and provide low prices to consumers. There are many business ideas to gain profit from a market. All depends on how you play the cards for a profitable business.
Walmart has made acquisitions of 28 organizations and has 16 sub-organization.
Feel free to reach us and share your understanding and views on the case study of Walmart. We would love to hear from you.
What is the business model of Walmart?
The business model of Walmart is based on eliminating the middleman from the distribution channels. The advantage of removing the middleman is to provide benefit to the consumer by providing products at lower costs.
What is the motive behind Walmart's Business Strategy?
The main motive of the Walmart business strategy company is to enter every segment of the market and dominate the market by providing products at a lower price.
What is Walmart's Market Strategy?
How does walmart generate revenue.
The earning model of Walmart deals with the principle of buying in bulk in one go. In this system, they got a huge discount from the manufacturers. Walmart’s generate its revenue by removing the middleman and selling their product directly to the customers and services to business.
What are the main sources of revenue for Walmart?
The two main sources of revenue are:
- Product revenue
- Service revenue
Is Walmart owned by China?
The Walmart branch in China is majority Chinese-owned. But predominantly it is owned by Sam Walton's many children.
Why is Walmart so cheap?
They sell in small quantities at low prices. By reducing the price they have high sales volume through which they have high earning. Hence, by selling in high volume they can sell it at a cheap price and still gain profit.
What are the sub-organisations under Walmart?
There are 16 sub-organisations of Walmart. Some of them are:
- Walmart Labs
- Seiyu Group
- Walmart Canada
What are the top acquisitions of Walmart?
Walmart has acquired 28 companies. Some top acquisitions are:
Must have tools for startups - Recommended by StartupTalky
- Convert Visitors into Leads- SeizeLead
- Manage your business smoothly- Google Workspace
- International Money transfer- XE Money Transfer
For CCI Approval, Reliance, Disney May Freeze Ad Rates for Two Years
In their most recent attempt to secure the approval of the competition watchdog for the merger of Star India and Viacom18, Reliance Industries Ltd (RIL) and Walt Disney are reportedly considering proposing a two-year freeze on advertising rate cards to the Competition Commission of India (CCI). With an eye towards
PhonePe’s New Credit Line on UPI Feature
A new feature called "Credit Line on UPI" has been introduced on PhonePe's platform. This feature gives customers the ability to link their pre-approved credit lines to UPI, which enables them to make payments without any hassle. Users now have the ability to control their monthly
Physics Wallah - Youtube Channel Turned Unicorn Edtech Startup
Technological growth and affordable equipment have devised a new scheme of learning in this modern world. They have refreshed our education system and made learning easy, simple, and interesting. This change in the system seems so quick that, in the near future, students might no longer carry books and will
Physics Wallah Launches PW School of Startups with INR 100 Crore Investment Fund to Empower Aspiring Entrepreneurs
Launching the PW School of Startups (SOS) under the PW Foundation, the edtech platform Physics Wallah (PW) has taken a giant leap forward in its goal to make education accessible to all students in India. By focussing on the development of entrepreneurial skills, PW SOS aims to close the gap
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
“We Need People to Lean into the Future”
- Adi Ignatius

For years, Walmart’s unrivaled customer research capabilities helped it dominate retailing. Then along came the internet, and Walmart suddenly found itself playing catchup to e-commerce pioneers like Amazon. In 2014 the board appointed Doug McMillon as CEO and gave him an imperative: Bring Walmart into the future—without sacrificing its longtime strengths.
McMillon, who began his career unloading trucks at a neighborhood Walmart, respects tradition but is impatient for change. In this interview with HBR editor in chief Adi Ignatius, he describes the ups and downs of transforming America’s largest company. Going digital is a top priority—which is why Walmart recently paid $3 billion to acquire e-tailer Jet.com. But the company also wants to strengthen the in-store experience. “The reality,” notes McMillon, “is that customers want everything”—low prices, convenience, and seamless interactions online and in person. In this new world, all employees, including those on the sales floor, will need to be tech savvy. And the management team can no longer make strategic decisions on an annual or even quarterly basis; “strategy is happening on a much faster cycle time,” says the CEO.
A conversation with Walmart CEO Doug McMillon
For years, Walmart seemed to understand exactly what its customers wanted. It developed complicated consumer analytics and used that data, along with relentless pressure on suppliers, to become a retail powerhouse that sold practically everything at the lowest possible prices.
- Adi Ignatius is the editor in chief of Harvard Business Review.
Partner Center

How Walmart Became The Retailer Of The People
Table of contents.
In the world of American retail success stories, it’s impossible to ignore the giant that is Walmart . Just the mention of the name will bring about connotations of scale that are difficult to fathom in our modern context.
Let's take a look at some of Walmart's astounding numbers
- $524 Billion (USD) revenue in 2020, an increase of $9.6 Billion
- Over 2.3 Million employees worldwide, 1.6 Million in the US alone
- 4,743 Walmart stores in the US alone
- 5,184 Walmart international segment stores
- Located in 24 countries
- Global market share of 2.6% in 2021
In this article, we’ll dive deeply into the Walmart story, unpacking the insights that drove them, the circumstances that made them, and pulling as much value as we can from what they’ve been able to accomplish. Whether you’re in retail or not, there are lessons to be learned here about strategic positioning, customer experiences, product development, long-term sustainability, supplier negotiation, and much more.
Let’s dig in.
{{cta('eed3a6a3-0c12-4c96-9964-ac5329a94a27')}}
The Origin Story
The global behemoth started in a very humble way in Arkansas, back in 1962. Mercurial founder Sam Walton had a dream of what a true customer-focused retail experience could be. He believed that you could offer low prices and a great customer experience in parallel. And he set out to prove it.

That first store got off to a roaring success because it did something different from what everyone else provided. Walton’s dedication to leadership through service meant that the store felt like a family-led operation that genuinely cared for those who came through the doors. At this stage, it wasn’t the product range or scale that kept customers coming through the doors; it was the feeling that you actually mattered. You weren’t just a number. You were a valued client whose business was cherished.
Over the next 5 years, Sam Walton and his family expanded this philosophy to open up a further 23 stores, which generated just over $12m in revenue. With each new store they planted, they strived to understand the local community and their needs – delivering the sort of retail experience that they would appreciate. And it was this focus that allowed them to continue growing without losing their spark. Even as they began to scale, the small-town feel remained, and the Walton DNA was sprinkled across every part of the value chain.
In 1969, the company was officially incorporated as Wal-Mart Stores Inc., and just one year later, they were listed as a public company. The vision was to bottle up the magic and take it to a national scale. In a way that had rarely been seen before, the ambition was unbounded. They really did see a future where Walmart stores littered the whole of the USA.
By the time 1980 rolled around, the company crossed the $1bn sales figure, with contributions from 276 stores across the country. In today’s numbers, that’s huge, but back in 1980, it isn’t easy to appreciate just how powerful this empire was. The company had revolutionized modern retail, and on the back of significant improvements in mass production and global supply chains, Walmart continued to accelerate in terms of influence and market share. They were quickly becoming the go-to brand for anything and everything.
Every brand that tried to compete with them struggled to match their low prices, wide variety, and family-friendly ideals that made customers feel at home in the stores. Even though the Waltons couldn’t be everywhere, the culture they had nurtured continued to permeate each location, making it a shopping experience that couldn’t be beaten.
In the ‘90s, the company continued to expand, breezing through $100bn sales in a year and growing its operations into Mexico and other select international locations, most notably China . Thanks to the Walmart supercenters, the company strengthened its brand as the one-stop shop for absolutely everything, providing great value and low costs across everything sold.

As of the time of writing, Walmart now operates over 10,000 stores globally, employing over 2.3m people and maintaining the status of one of the most recognizable brands across the world. The ethos of Sam Walton created an empire that champions low-priced goods delivered at scale in a way that delights customers through and through.
Now that we have a sense of some of the history, let’s look at some of the strategic pillars that make Walmart the success it is.
The Walmart Cheer
In 1975, Sam Walton traveled to Korea and Japan to visit some of his suppliers and to see what the mass production facilities looked like that were feeding the rapid growth of his organization. One of the visits was to a Korean tennis ball manufacturer, where he came across the idea of what would become the Walmart Cheer .
The factory was not that inspiring aesthetically, but Walton was taken aback by how enthusiastic and happy the staff was. It was clear that they had something special about them, even in the rather dingy circumstances that they worked in. And when he saw the reason why he knew he had to bring a similar idea to Walmart.
The employees at this factory would get together at the beginning of every day and perform a cheer together. As silly as this sounds, they would do this choreographed war cry of sorts that was designed to unite them and reinforce the values and ideals that they were aiming for that day. On a once-off, this might seem like just a gimmick, but repeated day after day, and it turned into a mantra for that factory that kept the workers going and helped them to feel like they were a part of something larger than themselves.
Walton loved this idea and adapted it into what is known today as the Walmart Cheer. Every day before the staff opens their doors to the public, they will gather together to perform this ritual. The sales numbers for the day before would be read out, as well as any goals that are being set for that particular day, and then the employees will go back and forth spelling out Walmart in the same enthusiastic way that you might have during your high school war cries.
Walton recognized that while this seemed inconsequential to some, a little ritual like this acted as a moment for the staff to come together and set their intentions for each day. It gave the store managers an opportunity to share some words of inspiration or motivation to help fire up the employees. And it got the employees to get into their bodies a bit and set themselves up to be in a good state for what was to come.
By the time that the doors were opened for that day, there was an energy and vitality in that workforce that was contagious. This would help them serve the customers with as much verve as possible, which was what Walmart was all about.
Now, whether this is still done at every store is anyone’s guess, but it points to an important strategic insight that comes from Walmart. They understand that the energy put forth by their retail staff has a significant impact on the overall buying experience. While we tend to place a lot of focus on product ranges, pricing, distribution, marketing, and all those components the truth still remains that people buy from people. The ritual of the Walmart Cheer was a simple piece of what made those employees feel like they were all on the same team. And through the age-old tool of group song and dance, they could set their intentions and build the energy that they would need to give to their customers.
This shows an attention to detail that most retailers don’t get right. We’ve all been in situations where the apathy shown by retail employees creates a sour experience for us as customers, and it leads to us ignoring that brand as a result. Walmart understood this and sought to create practical ways for employees to come together and deliver that exceptional buying experience that the customers were looking for.
Always Low Prices
One of the more common oversimplifications that you’ll hear in the business strategy canon is that your pricing model must fall into one of two camps- high volumes at low prices or low volumes at high prices. While the reality is much more nuanced than that, the choice remains one that all companies must make if they are to create something sustainable.
Walmart has always been focused on low prices. They will do everything they can to slash their prices as low as possible because that is the value that they aim to provide to their customers. They want to beat the competition by convincing their audience that you won’t find these goods for cheaper than anywhere else. All across their supply chain, they are doing everything they can to keep the costs as low as possible.
You can see that most clearly in their margins. For the vast majority of their existence, they’ve kept their net profit margin in the 1-5% range , which is quite staggering when you think about the size and scale that they’ve managed to achieve. This is certainly doing things the hard way when it comes to building a business. Leaving yourself this little operational wiggle room is something that a lot of strategists might advise you against. But Walmart has made it work incredibly well.
The reason that this is so interesting is that in our modern context, the biggest companies in the world have insanely high margins that business experts across the gamut celebrate. The digital businesses that leverage the internet to deliver their offerings can find their margins being in the range of 60% and upwards in most cases, which is in stark contrast to the Walmart model.
But that’s a feature of brick-and-mortar retail. Your overheads and your rent make up a sizable chunk of your cost, and then you add on top of that the complex supply chain that brings a wide variety of products onto your shelves. Before you know it, your margins are under serious pressure and you require a significant investment in infrastructure to get the economies of scale you need.
This is compounded when you consider the types of goods that Walmart sells. The core of the offering is essentials, which are the bread and butter of daily life. Customers only really care about price and convenience in these verticals, so Walmart set itself up to match those desires. Through innovative supply chain optimizations and radical cost-cutting philosophy, they made themselves known as the discount retailer where you get the best prices.
It’s difficult to understate how valuable this branding is. If you can convince your customers that you’ll always have the lowest prices on the market, there’s no reason for them even to consider your competitors. Instead, they trust your product curation and become loyal customers of Walmart. At this point, you transcend the competition, and all you’re working on is delivering a consistently high quality of service to your existing base. This is the core proposition that the entire empire is built on.
That’s not to say that a low-price strategy is easy to execute, of course. There are some serious minefields you must navigate when you are trying to compete solely on price. It’s certainly not well suited for every business. But if you can carve out that space in the mind of the customer, you can build a sustainable following that will continue to bring you the volumes you need to make the business work.
Your business promise manifests itself and drowns out the competition.
Decentralized Logistics
To operate at the scale that Walmart does, you rely on a logistics system that must perform incredibly efficiently and reliably in rain or shine to supply stores with the items they need. In fact, you wouldn’t be out of order to suggest that at this point, Walmart is essentially a logistics company. In much the same way that Amazon relies on its distribution center, Walmart relies on always having its products in stock to fulfill the customer promise that they’ve made. And to do this with thousands of stores across the world is not an easy thing to get right.
The key strategic decision that the company made when it comes to its logistics was to decentralize its distribution centers and focus on getting the best possible location for each one. Instead of focusing on how they could achieve economies of scale in each distribution center, by building massive warehouses that would then distribute goods, they wanted more centers that could service the surrounding stores in a reasonable period of time. The objective that they set was that every Walmart store should be able to receive a delivery within 24 hours from a distribution center. This meant that as long as the distribution centers were well stocked, you could rectify stock shortages in any store within a day – helping to ease the pressure that comes with being known as the shop that has everything.
The placement of these distribution centers thus became very important to get right. You weren’t optimizing for low rent, high traffic, good infrastructure, or any of that. You were doing a geographic calculation to identify which stores needed to be serviced and therefore, where should the center be placed. These centers became the nodes of the network that would enable Walmart to spread its wings across the whole of the USA. They potentially could have saved money by optimizing for different criteria, but the specific choice to have a decentralized system meant that they could always ensure that their inventory levels were well managed and controlled.
Another interesting piece of this strategy was that once they had a new distribution center up and running, they would start by building the furthest store away from that center and then move closer and closer towards it, building stores as they went. This meant that the distribution center was prepared, right from the beginning, to handle its most challenging deliveries. Every subsequent store that was built could leverage that early work, and things got easier and easier as a result.
This prioritization also meant that Walmart could be much more selective as to where their actual retail locations were. Using the distribution center as the centerpiece, they could identify the key customer locations that mattered most and set up shop there, creating the spokes of their wheel. It was small details like this that allowed them to ramp up their retail capacity in ways that other chains just couldn’t match.
These logistical decisions have, of course, become part and parcel of our modern conversation because of the shift towards online shopping. Led by the giant that is Amazon, the world of logistics management has radically advanced since Walmart’s early days. But in their time, they really were one of the first companies who were very thoughtful about how they set up their distribution networks and used those pillars as the foundation on which they would expand their empire.
Bargaining Power

It would be impossible to discuss Walmart’s strategy without talking about the incredible level of bargaining power they enjoy over their suppliers. As one of the first retailers that went on an aggressive land grab strategy, they were determined to expand their offering as widely as possible to every town in America. They hoped to bring their consumer promise of low prices to everywhere you could imagine so that the brand became synonymous with saving.
Their success with this rapid expansion meant that they ate up market share in every region that they entered. And after a while, they became the dominant retailer in the country, controlling a significant portion of the goods market. This early domination gave them the leverage that they needed to negotiate the best possible terms with their suppliers.
When Walmart came knocking, suppliers knew that the order sizes were so big that they had to do anything to win that business. Manufacturers around the world would compete to have their goods on Walmart shelves because the scale was just unfathomable. This competition drove prices down and improved payment terms for Walmart itself. They could sit back and let companies eat into their own margins – helping Walmart to provide even lower prices to customers.
This is one of those advantages that gets locked in early and is very difficult to dislodge. If you look back at Walmart’s competitors over the years, this is one of the reasons why they have struggled to make a dent. Walmart’s bargaining power in these negotiations is second to none because a lot of suppliers would reconfigure their entire operation to manage the Walmart order. It was so big in size that it would subsume your manufacturing capacity and while some were able to expand beyond it, a lot of companies were comfortable just servicing the growing Walmart empire.
An example like this shows just how important a first-mover advantage can be in markets like this. When you’re competing on price and convenience, the way that you build scale is by being everywhere. And even though your margins are low in the beginning, if you can capture the market early, you can then put pressure on your suppliers to improve the financial situation over the long term.
You have to have enough cash to wait it out, of course, but this is the same model that we’ve seen from numerous venture-backed companies from the past two decades who chase customer growth first, knowing that once they have the lion’s share of the market, they will have the opportunity to squeeze all the other stakeholders because of the power that you wield. Uber is one modern example that comes to mind here.
And it’s not only on price that you benefit. The improved payment terms that you can negotiate have a significant influence on your cash flow cycle and therefore your ability to scale. Essentially, Walmart created an opportunity for themselves to borrow money for next to nothing which could then subsidize their long-term plans. It’s one of those lesser celebrated pieces of the business that actually has had an outsized impact on their success. And it shows the virtues of a high-volume, low-priced business.
In-House Drivers and Route Optimization

Another part of the Walmart strategy that has paid off for them is the decision to insource their transport across the board. Currently, the company boasts one of the largest truck fleets in the world, and their drivers are some of the highest-skilled drivers in the industry. They made it a priority from very early on to invest in this because they knew that it was crucial to managing a vast landscape of stores. They could have very easily subcontracted this work out to a courier service directly but decided that bringing it in-house would provide synergies that would be valuable.
They spend a lot of time and resources training and upskilling their drivers so that they can maintain the safest possible distribution network in the business. The drivers clock in over 700 million miles every year but still have one of the best safety records on a global scale. This speaks to the attention to detail and care taken to strengthen this part of their business, where a lot of companies might try to cut corners.
Having the best drivers isn’t everything though, you then have to figure out how to utilize them most effectively. Walmart does this expertly through complex route optimization processes that plan out all the travel that these trucks must go through to meet the demands of the various stores.
The main thing that they focus on is minimizing empty miles. Every time a truck is travelling without goods inside it, that opportunity cost is eating into the bottom line. So, everything that the company can do to optimize how they use their available space is going to pay dividends over the long run.
To this end, they employ sophisticated logistics management software that tracks current inventory levels, store purchases, incoming supplies, and truck positioning – to craft routes and distribution schedules that can deliver as efficiently as possible. This technology undergoes a complex weighting of various criteria including fuel consumption, environmental impact, traffic conditions, and more – ensuring that all the transport resources are used to their full potential. This has been tweaked over time and continues to learn from ongoing data that consistently compounds its value.
None of this optimization would be possible though without the right data behind it , and that’s another area where Walmart has invested a lot of money into. The technological infrastructure that sits behind these thousands of stores is monumental. It allows the distribution nodes to understand the exact situation in real-time for any store they work with. As conditions change or consumer behavior adjusts, they can take that into account and adapt the transportation planning accordingly.
It’s difficult to appreciate just how transformational this is until you’ve spent some time working on inventory management solutions. This part of business has changed dramatically in the last few years with the Internet of Things, machine learning, and advanced algorithmic decision-making starting to make its mark in the world of logistics. Walmart has shown itself to be a leader in this regard, which continues to push them forward as a company.
Of course, the shift towards online shopping is going to disrupt the typical way they do things, but the principles of logistics remain the same. As Walmart begins to compete on last-mile delivery to the houses of their individual customers, they are going to rely on many of the same technologies to manage inventory, track deliveries, and optimize routes so that they can sweat their assets as efficiently as possible.
The big competitor here is Amazon, who have built a distribution network unlike anything we have ever seen, but Walmart still holds its own because of the infrastructure it has in place. Some are talking about how we may see Walmart converting some stores into further distribution centers for online orders and if so, they would have some of the best-located nodes that anyone could imagine. We’ll have to wait and see.
Walmart is an American institution and through the years it has become a key staple for millions of families across the country. Through thick and thin, Walmart is relied upon to provide the essentials that customers need to survive and thrive. As such, they’ve transcended a mere grocery store and have taken on a certain social responsibility to continue to supply the American people with what they need.
In times of natural disasters that have devastated American towns, we’ve seen Walmart get on the front lines to help supply the recovery efforts and help to rebuild communities that are getting back onto their feet. But the only way they’ve been able to do that is by having their own disaster recovery strategies in place – policies that stand out when you compare them to the rest of the industry.
At great cost, Walmart has built six dedicated disaster recovery centers which are well-stocked at all times and ready to serve if something goes wrong in any of their regions. These centers are specifically designed to be a backup and so they hope that they never have to use them, but over the past few decades they have played a very important role in the Walmart story.
Having this redundancy in place as a business allows them to react much quicker to adverse conditions than might be possible otherwise. At the very moment where stores are incapacitated, they can have their distribution center ready to replenish the supplies that are needed in that community. This means that customers can rely on Walmart to get them the goods that they need even in the very worst of times.
Doing this has significant financial implications of course because those centers are just sitting attracting cost without delivering any tangible ROI for the company. Some might say that it’s a waste of resources. But Walmart sees the power in being the retailer that never runs out of stock and is more than happy to pay those costs. Because the branding that comes with it more than pays for those idle distribution centers. Customers can trust that Walmart will look after them in every circumstance, good or bad, and that continues to entrench their competitive advantage in every market they enter.
We can all learn from this – and it’s certainly very topical right now as we deal with a global pandemic. Having redundancy in your organization to prepare for those rainy days helps you to be much more agile than you would have been. And when you consider the branding tailwinds you receive when you are in a position to help people, it makes all that investment worth it.
This is not a corner that you should cut lightly. Redundancy matters.
Acquisitions and Joint Ventures
Let's look at how Walmart approached its international expansion. We can see a very clear strategic preference for acquiring existing retail chains or partnering with existing brands instead of trying to build their own from scratch. This principle is at the heart of their entries into Mexico, China, India, South Africa, and everywhere else where they have a presence. And it’s worth discussing why they went this route.
Walmart understood that the cultural context of their branding and their product offering is what enabled their success in each local area that they went. Customers trusted the chain with their business because it was delivering exactly what they wanted at the best price possible.
The organization knew that if they were to go into a new territory where they had limited cultural understanding, they risked creating a retail experience that didn’t serve those people in the way that it should. And that was an expensive mistake to make if you were entering a new company for the first time.
Instead, if they could leverage the knowledge and experience of local brands who understood the market, they could fast-track all of those learnings and get up to speed in next to no time – because they were standing on the shoulders of giants. So, that’s what they did. They would go into these new markets and look for acquisition targets that made sense for the growing empire.
They were looking for great locations, high customer foot traffic, and a certain penchant for discount shopping. Not only that, they were also looking for operations that weren’t operating as smoothly as they could be. That’s where the Walmart machine could add value.
When the company found a target like this, they could offer a premium price to acquire those brands because they had the confidence in their own technology, systems, and global supply networks that they could drastically improve the efficiency of those stores and drive prices even further down as a result. Riding on the success of the American stores, they could afford to take their time reconfiguring the internal operations and turning those brands into the sophisticated operations that were in place back home.
This is not to say that every acquisition worked, far from it . International expansion is notoriously difficult. But the key insight is that they realized that they didn’t need to reinvent the wheel. The existing brands had loyal customers, good locations, and a cultural understanding of what was required to serve that particular area. If Walmart could bring its technology and operational excellence to the table, it could turn the dial up on success and grow internationally in a much more streamlined way.
The lore of internal expansion is littered with stories about high-powered brands walking into new countries and expecting to just build exactly the same business in the new place. Walmart wasn’t that naïve. They knew that they had to be smarter than that. And you should be too.
That brings us to the end of this strategy breakdown for Walmart, one of America’s biggest retail success stories. It’s rare that you see a company carry forward the ethos and values of its founder as it scales to this size, but that’s exactly what Walmart has done. Even though it is now a giant commercial conglomerate, it hasn’t lost that special sauce that the Waltons imbued in the company DNA.
It hasn’t tried to become what it’s not. The company has stayed true to its original brand promise that it will give you the widest range of goods at the best prices, wherever you happen to be. We’ve pulled out some key strategic pieces in this study, and those are certainly important in how they’ve got to where they are, but the purity of the offering is what really stands out.
Behind the simplicity of the brand image, lies a sophisticated logistics network, cutting-edge real-time data analysis, thoughtful HR strategy, planned redundancy, strong supplier negotiation, and a land grab strategy rivaled only by perhaps McDonald’s. These components all come together to make Walmart what it is and the scale they’ve achieved is testament to making this a winning formula.
What lies in the future for the company remains to be seen. They face stiff competition from Amazon and a myriad of other online retailers who are stealing customers from right under their noses. But we wouldn’t want to doubt their ability to adjust just yet. They’ve shown time and time again that they can remain relevant, and it’s hard to see them giving that up now.
It’s a story of diligence, perseverance, and a customer focus that bordered on obsession. And when we look back at some of the greatest retailers the world has ever seen, you can bet that Walmart is going to be very near the top of that list.
Sam Walton, we salute you.
Walmart’s Business Strategy: A case study of cost leadership and technological innovation
Table of Contents
The Business Strategy of Walmart – A Case study
Introduction:.
Walmart has continued to retain the top position on the Fortune 500 list consecutively for several years. The brand’s growth is driven mainly by its ‘everyday low prices’ strategy and the large assortment of merchandise it offers. Its online sales in the United States have also grown fast driven by the company’s investment in technology and customer experience. Walmart started as a small discount retailer in Rogers, Ark in 1945. Since then, it has spread throughout the U.S. and to several other parts of the globe. It is investing heavily in technology so that its customers can shop from anywhere anytime. It is in a bid to win market share away from its rivals Amazon, Target, and Costco. However, not just Walmart but its rivals are also investing in e-commerce and several of them had also accomplished significant growth in sales and customer engagement through online channels. Wrestling market share from either Amazon or other players will be a difficult task for Walmart which is known for its aggressive customer acquisition tactics. Its acquisition of Flipkart, an Indian e-commerce brand was a key step in this direction to find faster growth in the e-commerce segment.
At the core of Walmart’s business model is price leadership. The brand has led the U.S. retail market through its lowest prices. Today, it operates more than 11,300 physical stores and several e-commerce websites under 58 banners in more than 27 countries (Walmart Annual Report, 2019). The focus of Walmart is now on creating a seamless experience for its customers whether they are shopping from their mobile devices or inside the stores. The brand employs around 2.2 million workers whom it calls associates. 1.5 million Walmart associates are working in the US. This is a discussion of the business strategy of Walmart and how it has helped the brand prosper and find robust growth.
Everyday Low prices
The cornerstone of Walmart’s business strategy is its everyday low prices. The brand sells a very large range of products and its focus always remains on selling products at the lowest prices in the market. The millennial customers are interested in three things. They are convenience, low prices, and product quality. From grocery and entertainment to several more, Walmart provides a large assortment of products. The strategy is to attract customers with lower prices and keep them engaged with discounts and shopping convenience. Its low prices strategy is really great in terms of customer retention and the reason is that American shoppers are somewhat obsessed with low prices. Many of them will not shop unless there is a discount or sale attached. The millennial customers are even more addicted to lower costs and shopping convenience. They would like to shop on their own terms and would not shop unless there is a big discount like 50 or 70%.
With time, Walmart’s obsession with lower prices has grown stronger. Now, Walmart is looking for more growth and a larger share of the retail pie in the US as well as abroad. To acquire more growth, it is aggressively investing in improved customer experience. However, the way it has managed to keep its prices as low is the biggest challenge before its competitors trying to wrestle market share from Walmart. In 2017, it has invested even more into lowering its prices and that has helped it generate better revenue, more than $485 billion. Again in 2018 and 2019, Walmart’s growth story has continued. It grew its distribution network to bring more convenience to its e-commerce customers. Net revenue grew to $500.3 billion in 2018 and $514.4 billion in 2019. It reduced prices on key items in select markets. Consumers have grown addicted to lower prices and the retailers offering the least prices are enjoying immense growth. All these factors have resulted in price deflation and a further drop in prices across the retail industry seems inevitable. Overall, the level of competition is going to be tougher and since some non-U.S. brands have also entered the industry with low-cost offerings, there will be even more competition. Walmart is in the lead position and it is now even aggressive about prices and sales.
Walmart has decided to fight not only on the basis of prices but to get an even bigger share of the pie, it will focus more on customer convenience. It is why the company has placed extra focus on operational flow and customer service across its stores. Among the several things that have helped Walmart grow its business is also its reputation for being the most customer-friendly brand. The question is – “what are the most important factors that are driving Walmart’s growth”?
Four Important factors driving growth of Walmart
Investopedia notes four factors that have driven the growth of Walmart’s modern retail model. While the philosophy is still the same that was there since the foundation of the brand, the retail giant has kept modernizing its operations whose role in the efficient model of Walmart has grown bigger with time.
- Large sales volume made possible by a large customer base and scale of operation.
- A highly efficient supply chain system that maximizes productivity and reduces outlays.
- Low operational and overhead costs
- Use of bargaining power to grab the least prices from the suppliers (a very important strength for a large scale retailer that plays the most important role in its price advantage).
- Large sales volume: The largest retailer of the world has grabbed the largest market share in the retail industry based on its pricing strategy. There are two more things about it. They are its widespread operations and a large and varied assortment of products. These things imply deeper penetration into the retail market. Out of its more than 11,000 stores, 4,600 are there in the U.S. (2017). If customers can find almost everything at a store at the lowest prices and with the same convenience that everyone wants, then such a retailer can easily become the American customer’s favorite. This is how Walmart achieves very large sales volumes. With time, Walmart’s focus on customer convenience has kept rising and that is because fighting just on the basis of prices is not enough. When the focus is on higher growth, you must compliment lower prices with higher customer convenience. So, Walmart built multiple store formats. Its three formats are: Supercenters, Discount Stores, and Neighborhood Markets.
Supercenters : Walmart adopted this store model in the year 1988. These are generally 182,000 square feet in area and employ around 300 associates. Walmart notes on its website “Walmart Supercenters provide a one-stop shopping experience and combine a grocery store with fresh produce, bakery, deli, and dairy products with electronics, apparel, toys, and home furnishings. Most of them remain open 24 hours, and may also include specialty shops like banks, hair and nail salons, restaurants, or vision centers” (Walmart, 2017).
Discount stores: The first Walmart discount store had opened in Rogers, Ark. Now, there are hundreds of them operational throughout the U.S. These discount stores are smaller in size compared to the super-centers. Each one of them employs around 200 associates and has a wide assortment of products on offer. They are 106,000 square feet in area and these stores are brightly lit, well arranged, and good looking shopping spaces focused at maximizing shopping pleasure. The product range on offer at these discount stores include electronics, apparel, toys, home furnishings, health and beauty aids, hardware, and more.
Neighborhood markets: A crucial thing that Walmart has always focused on is addressing consumer needs on a larger scale and without compromising on convenience. The neighborhood markets are another store category of Walmart selling a wide range of products and had been designed keeping in mind the needs of the communities looking for pharmacy, affordable groceries, and merchandise. Each of these markets are around 38,000 square feet in size and have 95 associates working there. While smaller in size compared to the two previous formats, the neighborhood markets still cater to several important needs of the community. They offer a large range of products fresh produce, meat and dairy products, bakery and deli items (prepared food), household supplies, health and beauty aids, and a pharmacy.
In this way, Walmart has used its store mix to serve its customers well. Together, these stores cater to the needs of a very wide range of customers from nearly all classes. For the millennials and the middle class, Walmart is their favorite shopping destination. While its primary source of competitive advantage is the Every Day lowest pricing strategy, to strengthen it, the brand has used better store models, larger product assortment, and additional customer convenience. With a stronger competitive advantage, the brand has been able to penetrate the market deeper. Another important factor that has a central role in Walmart’s business success is its innovative supply chain management.

Walmart’s Supply Chain Innovation for competitive advantage
Researchers often highlight the role of innovative supply chain management in retail. Walmart’s more than 150 distribution centers have played a central role in strengthening its business. Its distribution system is one among the largest in the world and serves a large number of stores, clubs and also caters to the customers directly. Its transportation system has a fleet of 6,100 tractors, 61,000 trailers, and more than 7,800 drivers. This network of Walmart’s distribution centers ships general merchandise, dry groceries, perishable groceries, and other specialty categories to its consumers daily. Walmart has also kept six disaster distribution centers that are placed strategically across the US and are stocked well that in case a natural disaster happens, help can be sent without any delay to the communities. The shipping centers employ more than 600 people each who upload and unload more than 200 trailers every day. Each of them is 1 million square feet in size or larger. They are built to cover a circle of more than 150 miles radius and supports 90 to 100 stores. (Walmart, 2017.)
An important part of Walmart’s supply chain management is its logistics management. There are several great facts to know about Walmart’s logistics strategy. It owns a private fleet of trucks and employs a team of skilled truck drivers. Its fleet is one of the largest and safest. These drivers drive 700 million miles every year to deliver to the stores and clubs. With its large team of drivers, Walmart constantly works to ensure that they move merchandise in a responsible and sustainable manner. The focus is again on efficiency and on reducing empty miles. So, Walmart advises its drivers to follow the most efficient routes. This way, it achieves three things – minimum wastage of time by driving minimum empty miles, low fuel consumption and maximum merchandise delivery with least environmental impact. From 2005 to 2014, Walmart achieved 87.4% higher efficiency for its logistics fleet. In this way, the leading retail brand has been able to maximize its efficiency using such optimization techniques.
Walmart has also focused on the use of technology for better results from its business. Its supply chain system is considered to be the most advanced and efficient in terms of technology. It was a pioneer in terms of using barcodes and RFID for a better inventory management system. Inventory management is a crucial part of managing a great retail system. If you know how much of what is needed when, you can manage a large retail system efficiently. Walmart has also managed a more effective and efficient supply chain system by managing a direct relationship with the manufacturers. In this way by eliminating suppliers and handing them over the responsibility to manage inventory in its warehouses, the brand managed smoother inventory flow with lower irregularities and better availability of products on the shelves. This has also led to higher cost-effectiveness and better savings which can be transferred to the customers in the form of lower prices of products. A shared database between the company and its suppliers helps manage a better supply of inventory. All the required information from PoS (Point of Sale) data to warehouse inventory and the retail sales data is stored in the shared database from where it is relayed to all the participants in the entire system. This easy sharing of data is enabled by the private satellite system Walmart owns.
Lower Operational Costs
Walmart had managed low operational and overhead costs but the pressure was on the employees and suppliers. However, owing to high pressure from various sources in recent years, it made several improvements to make its image in the market and among its customers better. It has also increased its hourly wages for employees and improved work conditions. Earlier they were subjected to very high-pressure work conditions and paid lower salaries. The situation has grown a lot better after Walmart made changes to its HR strategy. However, based on its financial strength, Walmart can pay its employee higher wages and still retain a larger part of its profits. Its financial clout also helps it bargain for very low prices from its suppliers. These profits are then passed to the customers in the form of lower prices. Thus, size and scale have helped Walmart achieve a strong competitive advantage.
International Presence:
Around the world, Walmart sells high-quality goods and fresh and nutritious food at low prices and thus saves its customers precious money. Prices can be an important differentiator and cost leadership is the biggest source of competitive advantage for Walmart. Now, it is growing at a large scale and has expanded to the foreign markets. Its international wing operates 6,200 retail stores in 27 countries and under 67 banners. From Japan to Chile, its operations are spread far and wide and more than 800,000 of its associates serve more than 100 million customers a week. The brand is also investing in social and environmental initiatives in each of the markets it serves. Sam’s club is an important brand of Walmart of which 650 are in the US and 100 in foreign nations. It targets families and entrepreneurs. Sam’s club employs around 100,000 associates in the US and the average size of each club is 134,000 square feet. The products and services it offers include high-quality bulk groceries, consumables, general merchandise, specialty services, including travel, auto buying, pharmacy, optical, hearing aid centers, tire and battery centers, and a portfolio of business operations support services. The main focus of its products and services are the small business owners and it serves around 500,000 of them every day. A large part of its target audience is made of the microenterprises that have less than seven employees. Sam’s club also supports their growth through business initiatives, philanthropy, research, and stakeholder engagement.
Technological Innovation for better customer service
Walmart has also advanced boldly into e-commerce. It has a global e-commerce segment with its base in Silicon Valley, California that leads all the online and mobile innovation for Walmart. The innovation center of Walmart has some brightest minds working to create a seamless experience for shoppers whether they are shopping online, from mobile devices or in stores. Along with data and social insights, these data scientists are working to deliver a more personalized experience to its customers. In this way, it has transformed the shopping experience for its customers. Its main website receives more than 100 million unique visitors every month and this number has kept growing every year. Walmart has also worked to connect the online and in-store experience and using its mobile apps and shipping options like Home free, site to store, pick up today, shop from the store and same-day delivery, the brand has made shopping even convenient for the customers. Customers have unique needs and Walmart is using a variety of services to fulfill these unique needs. Its size and scale help it serve its customers more effectively and the use of cutting edge technology has helped it bring customer service to the next level. In this way, using price leadership and technological innovation, the brand has created a strong retail system that is more effective and efficient than the competitors.
Growing presence around the world:
The number of Walmart stores internationally has grown fast. In 2017, the retail giant had total 11,695 stores of which 6,363 were located overseas and 5,332 were located in the United States. The highest percentage of its stores outside the U.S. are located in Mexico where there are 2,411 Walmart Stores (2017). Apart from it, the United Kingdom had 631, Canada 410, and Brazil 498 stores operational in 2017. Walmart is also increasing its presence in China where it had 439 stores operational in 2017. The Asian economy is growing at a very fast rate which makes China and India important markets for Walmart. It is buying a controlling stake of roughly 77 percent in Indian e-commerce brand Flipkart to penetrate the Indian market. The brand is paying around $16 Billion for this purchase. Without this deal, the legal barriers would have made entry difficult for Walmart. Moreover, India has a very large retail market and plenty of scope for Walmart. The company’s presence in India will be a formidable challenge for the existing big and small retail brands there. Walmart’s entry into the Indian market also means lower prices and higher competition for the local brands.
Conclusion:
There are several reasons that Walmart has proved good for America. One of them is how it has been helping people save money. It has helped millions of its customers save more and that is possible by merging a few things. Scale, size, technology and shopping convenience have helped Walmart generate the advantage which you call popularity or brand loyalty. However, to achieve this kind of advantage is not as easy because Walmart too had to cut down on overhead and operational costs. In recent, years it changed its HR strategy and grew more focused on employee welfare. This was a smart step since poor reputation in terms of HR can translate into a loss of market share in the longer run. Now, it is working even aggressively for achieving business growth and maintaining lower prices.
Its international expansion has also happened fast and the most crucial thing is that Walmart despite being the leading retailer brand is concerned about competition. The retail market of the U.S. has kept growing hyper-competitive. Several non-U.S. brands have also entered the market and some are also armed with a price advantage. Walmart could beat more of the competitive pressure given that it focuses more on groceries. Its competitive advantage has kept growing stronger with time and since the brand is now concerned for its social image, it is investing in employees, social responsibility, and community welfare. The pressure that used to be associated with a job at Walmart has also reduced. So, overall Walmart has grown better for America and now it is targeting the same success abroad.
- https://www.businessinsider.in/Wal-Mart-is-making-3-changes-so-people-will-want-to-shop-there/articleshow/46305680.cms
- https://www.cnbc.com/2016/05/19/wal-marts-low-price-commitment-should-send-shivers-across-retail.html
- https://www.investopedia.com/articles/personal-finance/011815/how-walmart-model-wins-everyday-low-prices.asp
- https://www.businessinsider.com/why-walmart-can-pull-off-everyday-low-prices-while-everyone-else-keeps-failing-2012-9?IR=T
- https://www.reuters.com/article/us-flipkart-m-a-walmart-official/walmart-buys-controlling-stake-in-indias-flipkart-for-16-billion-idUSKBN1IA1HJ
About Stanford GSB
- The Leadership
- Dean’s Updates
- School News & History
- Commencement
- Business, Government & Society
- Centers & Institutes
- Center for Entrepreneurial Studies
- Center for Social Innovation
- Stanford Seed
About the Experience
- Learning at Stanford GSB
- Experiential Learning
- Guest Speakers
- Entrepreneurship
- Social Innovation
- Communication
- Life at Stanford GSB
- Collaborative Environment
- Activities & Organizations
- Student Services
- Housing Options
- International Students
Full-Time Degree Programs
- Why Stanford MBA
- Academic Experience
- Financial Aid
- Why Stanford MSx
- Research Fellows Program
- See All Programs
Non-Degree & Certificate Programs
- Executive Education
- Stanford Executive Program
- Programs for Organizations
- The Difference
- Online Programs
- Stanford LEAD
- Seed Transformation Program
- Aspire Program
- Seed Spark Program
- Faculty Profiles
- Academic Areas
- Awards & Honors
- Conferences
Faculty Research
- Publications
- Working Papers
- Case Studies
Research Hub
- Research Labs & Initiatives
- Business Library
- Data, Analytics & Research Computing
- Behavioral Lab
Research Labs
- Cities, Housing & Society Lab
- Golub Capital Social Impact Lab
Research Initiatives
- Corporate Governance Research Initiative
- Corporations and Society Initiative
- Policy and Innovation Initiative
- Rapid Decarbonization Initiative
- Stanford Latino Entrepreneurship Initiative
- Value Chain Innovation Initiative
- Venture Capital Initiative
- Career & Success
- Climate & Sustainability
- Corporate Governance
- Culture & Society
- Finance & Investing
- Government & Politics
- Leadership & Management
- Markets and Trade
- Operations & Logistics
- Opportunity & Access
- Technology & AI
- Opinion & Analysis
- Email Newsletter
Welcome, Alumni
- Communities
- Digital Communities & Tools
- Regional Chapters
- Women’s Programs
- Identity Chapters
- Find Your Reunion
- Career Resources
- Job Search Resources
- Career & Life Transitions
- Programs & Webinars
- Career Video Library
- Alumni Education
- Research Resources
- Volunteering
- Alumni News
- Class Notes
- Alumni Voices
- Contact Alumni Relations
- Upcoming Events
Admission Events & Information Sessions
- MBA Program
- MSx Program
- PhD Program
- Alumni Events
- All Other Events
- Operations, Information & Technology
- Organizational Behavior
- Political Economy
- Classical Liberalism
- The Eddie Lunch
- Accounting Summer Camp
- California Econometrics Conference
- California Quantitative Marketing PhD Conference
- California School Conference
- China India Insights Conference
- Homo economicus, Evolving
- Political Economics (2023–24)
- Scaling Geologic Storage of CO2 (2023–24)
- A Resilient Pacific: Building Connections, Envisioning Solutions
- Adaptation and Innovation
- Changing Climate
- Civil Society
- Climate Impact Summit
- Climate Science
- Corporate Carbon Disclosures
- Earth’s Seafloor
- Environmental Justice
- Operations and Information Technology
- Organizations
- Sustainability Reporting and Control
- Taking the Pulse of the Planet
- Urban Infrastructure
- Watershed Restoration
- Junior Faculty Workshop on Financial Regulation and Banking
- Ken Singleton Celebration
- Marketing Camp
- Quantitative Marketing PhD Alumni Conference
- Presentations
- Theory and Inference in Accounting Research
- Stanford Closer Look Series
- Quick Guides
- Core Concepts
- Journal Articles
- Glossary of Terms
- Faculty & Staff
- Researchers & Students
- Research Approach
- Charitable Giving
- Financial Health
- Government Services
- Workers & Careers
- Short Course
- Adaptive & Iterative Experimentation
- Incentive Design
- Social Sciences & Behavioral Nudges
- Bandit Experiment Application
- Conferences & Events
- Get Involved
- Reading Materials
- Teaching & Curriculum
- Energy Entrepreneurship
- Faculty & Affiliates
- SOLE Report
- Responsible Supply Chains
- Current Study Usage
- Pre-Registration Information
- Participate in a Study
Wal-Mart's Sustainability Strategy (A)
In October 2005, in an auditorium filled to capacity in Bentonville, Arkansas, Lee Scott, Wal-Mart’s president and CEO, made the first speech in the history of Wal-Mart to be broadcast to the company’s 1.6 million associates (employees) in all of its 6,000+ stores worldwide and shared with its 60,000+ suppliers. Scott announced that Wal-Mart was launching a sweeping business sustainability strategy to dramatically reduce the company’s impact on the global environment and thus become “the most competitive and innovative company in the world.” He argued that, “Being a good steward of the environment and being profitable are not mutually exclusive. They are one and the same.” He also committed Wal-Mart to three aspirational goals: “To be supplied 100 percent by renewable energy; to create zero waste; and to sell products that sustain our resources and the environment.” Against this backdrop, the case introduces Andrew Ruben, vice president of corporate strategy and business sustainability, and Tyler Elm, senior director of the same group. Ruben and Elm, who were chosen by Scott to lead the sustainability strategy, recognized that they needed to keep environmental improvement tightly coupled with business value and profitability for the strategy to succeed. The case describes Wal-Mart’s efforts to accomplish this, focusing on three of the company’s primary focus areas (seafood, electronics, and textiles) and their effect on the company’s operations, supplier relationships, and results. It also explores how Wal-Mart is measuring and communicating its ideas about sustainability to its suppliers, associates, customers, and the public.

- See the Current DEI Report
- Supporting Data
- Research & Insights
- Share Your Thoughts
- Search Fund Primer
- Affiliated Faculty
- Faculty Advisors
- Louis W. Foster Resource Center
- Defining Social Innovation
- Impact Compass
- Global Health Innovation Insights
- Faculty Affiliates
- Student Awards & Certificates
- Changemakers
- Dean Jonathan Levin
- Dean Garth Saloner
- Dean Robert Joss
- Dean Michael Spence
- Dean Robert Jaedicke
- Dean Rene McPherson
- Dean Arjay Miller
- Dean Ernest Arbuckle
- Dean Jacob Hugh Jackson
- Dean Willard Hotchkiss
- Faculty in Memoriam
- Stanford GSB Firsts
- Class of 2024 Candidates
- Certificate & Award Recipients
- Dean’s Remarks
- Keynote Address
- Teaching Approach
- Analysis and Measurement of Impact
- The Corporate Entrepreneur: Startup in a Grown-Up Enterprise
- Data-Driven Impact
- Designing Experiments for Impact
- Digital Marketing
- The Founder’s Right Hand
- Marketing for Measurable Change
- Product Management
- Public Policy Lab: Financial Challenges Facing US Cities
- Public Policy Lab: Homelessness in California
- Lab Features
- Curricular Integration
- View From The Top
- Formation of New Ventures
- Managing Growing Enterprises
- Startup Garage
- Explore Beyond the Classroom
- Stanford Venture Studio
- Summer Program
- Workshops & Events
- The Five Lenses of Entrepreneurship
- Leadership Labs
- Executive Challenge
- Arbuckle Leadership Fellows Program
- Selection Process
- Training Schedule
- Time Commitment
- Learning Expectations
- Post-Training Opportunities
- Who Should Apply
- Introductory T-Groups
- Leadership for Society Program
- Certificate
- 2024 Awardees
- 2023 Awardees
- 2022 Awardees
- 2021 Awardees
- 2020 Awardees
- 2019 Awardees
- 2018 Awardees
- Social Management Immersion Fund
- Stanford Impact Founder Fellowships
- Stanford Impact Leader Prizes
- Social Entrepreneurship
- Stanford GSB Impact Fund
- Economic Development
- Energy & Environment
- Stanford GSB Residences
- Environmental Leadership
- Stanford GSB Artwork
- A Closer Look
- California & the Bay Area
- Voices of Stanford GSB
- Business & Beneficial Technology
- Business & Sustainability
- Business & Free Markets
- Business, Government, and Society Forum
- Second Year
- Global Experiences
- JD/MBA Joint Degree
- MA Education/MBA Joint Degree
- MD/MBA Dual Degree
- MPP/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Computer Science/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Electrical Engineering/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Environment and Resources (E-IPER)/MBA Joint Degree
- Academic Calendar
- Clubs & Activities
- LGBTQ+ Students
- Military Veterans
- Minorities & People of Color
- Partners & Families
- Students with Disabilities
- Student Support
- Residential Life
- Student Voices
- MBA Alumni Voices
- A Week in the Life
- Career Support
- Employment Outcomes
- Cost of Attendance
- Knight-Hennessy Scholars Program
- Yellow Ribbon Program
- BOLD Fellows Fund
- Application Process
- Loan Forgiveness
- Contact the Financial Aid Office
- Evaluation Criteria
- GMAT & GRE
- English Language Proficiency
- Personal Information, Activities & Awards
- Professional Experience
- Letters of Recommendation
- Optional Short Answer Questions
- Application Fee
- Reapplication
- Deferred Enrollment
- Joint & Dual Degrees
- Entering Class Profile
- Event Schedule
- Ambassadors
- New & Noteworthy
- Ask a Question
- See Why Stanford MSx
- Is MSx Right for You?
- MSx Stories
- Leadership Development
- How You Will Learn
- Admission Events
- Personal Information
- GMAT, GRE & EA
- English Proficiency Tests
- Career Change
- Career Advancement
- Daycare, Schools & Camps
- U.S. Citizens and Permanent Residents
- Requirements
- Requirements: Behavioral
- Requirements: Quantitative
- Requirements: Macro
- Requirements: Micro
- Annual Evaluations
- Field Examination
- Research Activities
- Research Papers
- Dissertation
- Oral Examination
- Current Students
- Education & CV
- International Applicants
- Statement of Purpose
- Reapplicants
- Application Fee Waiver
- Deadline & Decisions
- Job Market Candidates
- Academic Placements
- Stay in Touch
- Faculty Mentors
- Current Fellows
- Standard Track
- Fellowship & Benefits
- Group Enrollment
- Program Formats
- Developing a Program
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Strategic Transformation
- Program Experience
- Contact Client Services
- Campus Experience
- Live Online Experience
- Silicon Valley & Bay Area
- Digital Credentials
- Faculty Spotlights
- Participant Spotlights
- Eligibility
- International Participants
- Stanford Ignite
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Founding Donors
- Location Information
- Participant Profile
- Network Membership
- Program Impact
- Collaborators
- Entrepreneur Profiles
- Company Spotlights
- Seed Transformation Network
- Responsibilities
- Current Coaches
- How to Apply
- Meet the Consultants
- Meet the Interns
- Intern Profiles
- Collaborate
- Research Library
- News & Insights
- Program Contacts
- Databases & Datasets
- Research Guides
- Consultations
- Research Workshops
- Career Research
- Research Data Services
- Course Reserves
- Course Research Guides
- Material Loan Periods
- Fines & Other Charges
- Document Delivery
- Interlibrary Loan
- Equipment Checkout
- Print & Scan
- MBA & MSx Students
- PhD Students
- Other Stanford Students
- Faculty Assistants
- Research Assistants
- Stanford GSB Alumni
- Telling Our Story
- Staff Directory
- Site Registration
- Alumni Directory
- Alumni Email
- Privacy Settings & My Profile
- Success Stories
- The Story of Circles
- Support Women’s Circles
- Stanford Women on Boards Initiative
- Alumnae Spotlights
- Insights & Research
- Industry & Professional
- Entrepreneurial Commitment Group
- Recent Alumni
- Half-Century Club
- Fall Reunions
- Spring Reunions
- MBA 25th Reunion
- Half-Century Club Reunion
- Faculty Lectures
- Ernest C. Arbuckle Award
- Alison Elliott Exceptional Achievement Award
- ENCORE Award
- Excellence in Leadership Award
- John W. Gardner Volunteer Leadership Award
- Robert K. Jaedicke Faculty Award
- Jack McDonald Military Service Appreciation Award
- Jerry I. Porras Latino Leadership Award
- Tapestry Award
- Student & Alumni Events
- Executive Recruiters
- Interviewing
- Land the Perfect Job with LinkedIn
- Negotiating
- Elevator Pitch
- Email Best Practices
- Resumes & Cover Letters
- Self-Assessment
- Whitney Birdwell Ball
- Margaret Brooks
- Bryn Panee Burkhart
- Margaret Chan
- Ricki Frankel
- Peter Gandolfo
- Cindy W. Greig
- Natalie Guillen
- Carly Janson
- Sloan Klein
- Sherri Appel Lassila
- Stuart Meyer
- Tanisha Parrish
- Virginia Roberson
- Philippe Taieb
- Michael Takagawa
- Terra Winston
- Johanna Wise
- Debbie Wolter
- Rebecca Zucker
- Complimentary Coaching
- Changing Careers
- Work-Life Integration
- Career Breaks
- Flexible Work
- Encore Careers
- Join a Board
- D&B Hoovers
- Data Axle (ReferenceUSA)
- EBSCO Business Source
- Global Newsstream
- Market Share Reporter
- ProQuest One Business
- RKMA Market Research Handbook Series
- Student Clubs
- Entrepreneurial Students
- Stanford GSB Trust
- Alumni Community
- How to Volunteer
- Springboard Sessions
- Consulting Projects
- 2020 – 2029
- 2010 – 2019
- 2000 – 2009
- 1990 – 1999
- 1980 – 1989
- 1970 – 1979
- 1960 – 1969
- 1950 – 1959
- 1940 – 1949
- Service Areas
- ACT History
- ACT Awards Celebration
- ACT Governance Structure
- Building Leadership for ACT
- Individual Leadership Positions
- Leadership Role Overview
- Purpose of the ACT Management Board
- Contact ACT
- Business & Nonprofit Communities
- Reunion Volunteers
- Ways to Give
- Fiscal Year Report
- Business School Fund Leadership Council
- Planned Giving Options
- Planned Giving Benefits
- Planned Gifts and Reunions
- Legacy Partners
- Giving News & Stories
- Giving Deadlines
- Development Staff
- Submit Class Notes
- Class Secretaries
- Board of Directors
- Health Care
- Sustainability
- Class Takeaways
- All Else Equal: Making Better Decisions
- If/Then: Business, Leadership, Society
- Grit & Growth
- Think Fast, Talk Smart
- Spring 2022
- Spring 2021
- Autumn 2020
- Summer 2020
- Winter 2020
- In the Media
- For Journalists
- DCI Fellows
- Other Auditors
- Academic Calendar & Deadlines
- Course Materials
- Entrepreneurial Resources
- Campus Drive Grove
- Campus Drive Lawn
- CEMEX Auditorium
- King Community Court
- Seawell Family Boardroom
- Stanford GSB Bowl
- Stanford Investors Common
- Town Square
- Vidalakis Courtyard
- Vidalakis Dining Hall
- Catering Services
- Policies & Guidelines
- Reservations
- Contact Faculty Recruiting
- Lecturer Positions
- Postdoctoral Positions
- Accommodations
- CMC-Managed Interviews
- Recruiter-Managed Interviews
- Virtual Interviews
- Campus & Virtual
- Search for Candidates
- Think Globally
- Recruiting Calendar
- Recruiting Policies
- Full-Time Employment
- Summer Employment
- Entrepreneurial Summer Program
- Global Management Immersion Experience
- Social-Purpose Summer Internships
- Process Overview
- Project Types
- Client Eligibility Criteria
- Client Screening
- ACT Leadership
- Social Innovation & Nonprofit Management Resources
- Develop Your Organization’s Talent
- Centers & Initiatives
- Student Fellowships

- About / Contact
- Privacy Policy
- Alphabetical List of Companies
- Business Analysis Topics
Walmart SWOT Analysis & Recommendations

This SWOT analysis of Walmart Inc. presents the company’s strengths and weaknesses, as well as the business opportunities and threats relevant to the condition of the retail industry. As a leading retailer, the company has competitive advantages linked to its market position and organizational size. However, to fulfill Walmart’s mission statement and vision statement in the long term, the business needs to match its strategic decisions to the issues arising from the SWOT factors. For instance, the company must account for opportunities and threats that represent external forces in the retail market. Walmart optimizes its operations based on a variety of internal and external factors, including the ones examined in this SWOT analysis.
This SWOT analysis includes an internal analysis of Walmart’s strengths and weaknesses (internal strategic factors) and an external analysis of business opportunities and threats (external strategic factors). These strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats provide a picture of the strategic planning options available to the retail corporation. The SWOT variables enumerated below affect the company, as well as its customers, business partners, suppliers, and competitors in the retail industry.
Strengths (Internal Strategic Factors)
Walmart’s strengths are business characteristics that enable growth, expansion, and profitability. In this part of the SWOT analysis, such characteristics strengthen the business against external forces, such as the threat of competition. The following internal factors are Walmart’s strengths:
- Dominant brick-and-mortar retail presence
- High-efficiency logistics and global supply chain
- Strong bargaining power against suppliers and manufacturers
Walmart’s industry position comes with a dominant brick-and-mortar retail presence, which is a business strength in this SWOT analysis. This strength enables the company to maintain a stable market share, despite aggressive competitors, like Amazon and Target. The large brick-and-mortar presence, along with the operations of the subsidiary, Sam’s Club, helps protect Walmart from competition, which includes Amazon’s relatively small brick-and-mortar operations. In addition, the high-efficiency logistics and global supply chain are a strength that this SWOT analysis links to the retail company’s growth potential. This internal strategic factor facilitates the ability to offer low prices, in support of Walmart’s generic competitive strategy and intensive growth strategies . This SWOT analysis also points to the retail company’s bargaining power as a strength for influencing suppliers and manufacturers. Based on the company’s large organizational size, this internal factor strengthens the business in imposing low prices on goods sold at its stores. This pricing strategy affects suppliers and manufacturers, while ensuring low selling prices at the company’s stores and e-commerce website. To support high efficiencies and large-scale operations, Walmart’s operations management involves advanced business information systems and related technologies. These technological applications help minimize costs, errors, and delays in retail business processes. Walmart’s inventory management is also a foundation that supports the strengths mentioned in this part of the SWOT analysis.
Walmart’s Weaknesses (Internal Strategic Factors)
Walmart’s weaknesses impose challenges in withstanding external forces, such as the threats identified in this SWOT analysis. Business weaknesses are internal factors related to the retail company’s ability for further business development, additional competencies, and higher profits. The following are Walmart’s weaknesses:
- Limited e-commerce operations
- Absent or insignificant operations in international shipping
- Competitive disadvantage relative to specialty sellers’ product quality
Despite its efforts to grow in the online retail space, Walmart’s e-commerce operations are small compared to Amazon’s. In this SWOT analysis, such a limitation is an internal strategic factor that weakens Walmart’s ability to capture a larger share of the retail market. Also, absent or insignificant operations in international shipping constrain potential growth based on international purchases. This weakness is in contrast to Amazon’s integrated international shipping options. Considering such a weakness, this SWOT analysis accounts for the trend of growing international online sales in more markets and market segments worldwide, among other trends described in the PESTEL/PESTLE analysis of Walmart Inc . Furthermore, because of its emphasis on low costs and low prices, the company is at a competitive disadvantage relative to specialty retailers’ product quality. Specialty retailers offer differentiated goods and services, such as high-quality customer service and high-end groceries. This competitive disadvantage is a weakness in this SWOT analysis of Walmart because it reduces the business ability to attract customers who prefer high-end shopping experiences.
Opportunities for Walmart (External Strategic Factors)
Walmart’s opportunities are options for growing the business, based on external forces or conditions in the retail industry environment. This part of the SWOT analysis shows the external factors that the company can pursue to improve its business performance, especially in e-commerce and international operations. The following are Walmart’s opportunities:
- Global expansion of e-commerce operations
- Establishment of international shipping
- Expansion of brick-and-mortar operations to more countries
The opportunity for global e-commerce expansion addresses the weakness of Walmart’s limited e-commerce operations. As mentioned earlier in this SWOT analysis, such a weakness limits the company’s share of the retail market. Thus, global e-commerce operations can boost the company’s international market share. In relation, the company can establish international shipping operations that support global e-commerce. In this SWOT analysis of Walmart, international shipping is an opportunity for the company’s multinational success. Moreover, considering its primary dependence on sales in the United States, the company has opportunities for establishing brick-and-mortar stores in more countries in order to increase profits. Walmart’s marketing mix or 4Ps can support marketing campaigns to exploit these opportunities. For instance, promotional tactics can facilitate the success of new stores in new markets. Also, appropriate modifications to Walmart’s organizational structure or corporate structure , such as new managerial teams for new business processes, can facilitate multinational operations to grow the company based on the opportunities shown in this part of the SWOT analysis.
Threats (External Strategic Factors)
The threats to Walmart’s business are linked to the retail market condition, human resource availability, and international relations. This part of the SWOT analysis shows how external forces in the industry environment can hamper the retail company’s improvement. The following external factors are threats to Walmart:
- Competitive threat from online and brick-and-mortar firms
- Supply chain disruptions due to political, economic, and health factors
- Labor market disruptions
Competition presents a major threat in the retail industry, as shown in the Five Forces analysis of Walmart Inc . For example, the company competes against Amazon ’s brick-and-mortar stores, marketplace, and e-commerce services; and eBay’s marketplace. Also, Walmart experiences competitive pressure from Target, Home Depot , Costco , and Best Buy, as well as Kroger, Lowe’s, Rakuten, and 7-Eleven. In this SWOT analysis, such a diversity of competitors creates a strong external force in the retail industry.
On the other hand, supply chain disruptions also threaten Walmart’s business. These disruptions are external strategic factors connected to the political and economic aspects of international relations, as well as health concerns, such as pandemics. In this SWOT analysis, these disruptions are a threat to the stability of supply chains and, consequently, the stability of Walmart’s operations, which depend on importing low-cost goods.
Labor market disruptions are linked to social trends that affect the availability and willingness of people to work for companies, like Walmart. This external factor is a threat that affects the retail company’s human resources. In this SWOT analysis, such labor market issues directly relate to the company’s capacity to provide its online and brick-and-mortar services to customers. This external strategic factor emphasizes the importance of Walmart’s human resource management in maintaining an adequate workforce to support business operations. Also, Walmart’s organizational culture or corporate culture can provide support for maintaining an attractive workplace, in order to minimize turnover. Support from the organizational culture can improve job satisfaction and, in turn, stabilize the company’s human resources. Furthermore, Walmart’s corporate social responsibility strategy is significant in this part of the SWOT analysis. Corporate citizenship and stakeholder management efforts can enhance the company’s corporate image and workers’ perception about the business.
Recommendations based on this SWOT Analysis of Walmart Inc.
This SWOT analysis shows that Walmart has the business strengths to support growth through e-commerce expansion and international operations, which are opportunities in the global retail industry. However, this SWOT analysis also shows that the company needs to implement new strategies to overcome its weaknesses, such as the limited international presence; and the threats to its retail business, like competition and supply chain disruptions. Based on these internal and external strategic factors, an applicable recommendation is for growing Walmart’s e-commerce operations. It is also recommended that the company establish more locations outside its current retail markets. Ultimately, the goal should be to make Walmart a leading retail and e-commerce company that provides its goods and services globally.
- Benzaghta, M. A., Elwalda, A., Mousa, M. M., Erkan, I., & Rahman, M. (2021). SWOT analysis applications: An integrative literature review. Journal of Global Business Insights, 6 (1), 55-73.
- Ismail, R. E., & Jokonya, O. (2023). Factors affecting the adoption of emerging technologies in last-mile delivery in the retail industry. Procedia Computer Science, 219 , 2084-2092.
- Risberg, A. (2023). A systematic literature review on e-commerce logistics: Towards an e-commerce and omni-channel decision framework. The International Review of Retail, Distribution and Consumer Research, 33 (1), 67-91.
- Taherdoost, H., & Madanchian, M. (2021). Determination of business strategies using SWOT analysis; Planning and managing the organizational resources to enhance growth and profitability. Macro Management & Public Policies, 3 (1), 19-22.
- U.S. Department of Commerce – International Trade Administration – Retail Trade Industry .
- Walmart Inc. – America at Work .
- Walmart Inc. – Form 10-K .
- Walmart Inc. – Opportunity .
- Copyright by Panmore Institute - All rights reserved.
- This article may not be reproduced, distributed, or mirrored without written permission from Panmore Institute and its author/s.
- Educators, Researchers, and Students: You are permitted to quote or paraphrase parts of this article (not the entire article) for educational or research purposes, as long as the article is properly cited and referenced together with its URL/link.

The Walmart Case Study: How Walmart Became The Retail Giant
Supti Nandi
January 31, 2024

Recently, we saw a huge demand for Walmart Case Study from our readers. So here we are presenting your demand for Walmart Case Study in detail.
Walmart is often referred to as the king of the retail world. Reason? Quality goods, lucrative discounts, loyal user base, efficient customer service, and the list goes on! Many retail companies come and go. But Walmart survived for over 62 years!

Have you ever wondered how?
Due to its smart operating strategies! What are those? You may wonder. In the Walmart Case Study, we will unravel those operating strategies, that made Walmart the kind of the retail world.
Stay tuned!
(A) Synopsis: What is Walmart?
Yesterday, Walmart announced a 3-for-1 stock split to boost employee ownership! And this news created a buzz in the market. This left the folks astonished about the smart strategies opted for by Walmart that led to its multiple decade-old grand success.
So, Walmart is this huge American company that was started in 1962 by two brothers, Sam and Bud Walton, in Arkansas. They run lots of stores, like hypermarkets and discount stores, not just in the US but also in other countries.
As of October 2022, Walmart has a whopping 10,586 stores in 24 countries, under various names. They’re a big deal in places like the US, Canada, Mexico, Central America, and even India under the name Flipkart Wholesale.
You know what, Walmart is a big player globally, being the world’s largest company. How was this fact determined? You may wonder. Well, it was determined based on the revenue in 2022. They also announced a massive revenue of $611.3 billion for the fiscal year 2023. With a jaw-dropping 2.2 million employees, it’s the largest private employer worldwide.
The company has an interesting history – starting small in the 1960s and quickly becoming the most profitable US retailer by 1988. It went public on the New York Stock Exchange in 1972 and expanded from the South to coast-to-coast by the early 1990s. We will discuss the history in detail later.
While Walmart has been super successful in some countries, like Canada and the UK, it faced challenges in places like Germany, Japan, South Korea, Brazil, and Argentina. So, it’s been a bit of a rollercoaster, but overall, Walmart is a massive player in the global business game!
(B) Walmart: A Brief Overview
Before diving deeper into the Walmart Case Study, let’s have a brief overview of the company-
| Wal-Mart Discount City (1962–1969) Wal-Mart, Inc. (1969–1970) Wal-Mart Stores, Inc. (1970–2018) | |
| Public | |
| $445.81 billion | |
| NYSE: WMT DJIA component S&P 100 component S&P 500 component | |
| Retail Segment | |
| July, 1962 | |
| Sam Walton, Bud Walton | |
| Bentonville (Arkansas, USA) | |
| 10,586 stores worldwide (October 31, 2022) | |
| Worldwide | |
| Food, drinks, groceries, clothing, footwear, beauty products, jewelry, accessories, furniture, decor, bedding, bath, electronics, appliances, housewares, toys, games, books, movies, musical instruments, pet supplies, baby products, hygiene products, health products, school and office supplies, tools, gifts, garden center, pharmacy, photo center, sporting goods, and auto center | |
| Walmart-2-Walmart | |
| Target, Amazon, Home Depot, Kroger, Carrefour, Alibaba, Costco |
Note: Do you know Target is one of the strong competitors of Walmart? If you are curious to delve into their comparative analysis, then visit the article “ Walmart vs Target: Which one is better for public investors? ”
(C) Walmart Case Study: History & Timeline
Let me take you back to 1945 when Sam Walton, a young guy fresh from World War II, had this grand idea of building a retail empire. Fast forward to 1962, he kicks things off by opening the very first Walmart store in Rogers, Arkansas.
His mission? Simple – provide a bunch of stuff at affordable prices and treat customers like VIPs.
Guess what?
That mission stuck around. Walmart’s all about those wallet-friendly prices, and that’s how it’s been ruling the retail scene for ages, becoming a name you know wherever you go.
But hold up, it’s not just about low prices. Walmart’s like a treasure trove – groceries, electronics, clothes, you name it, they got it. And this winning combo of cheap goodies and a massive selection? That’s the secret sauce that’s turned Walmart into this retail giant we all know and, let’s be real, probably visit regularly.
Look at the history of Walmart in the following table-
| Founded by Sam and Bud Walton in Rogers, Arkansas | |
| Incorporated under Delaware General Corporation Law | |
| Listed on the New York Stock Exchange | |
| Became the most profitable retailer in the US. | |
| Largest retailer in terms of revenue | |
| Expanded to the Northeastern US. The first California outlet was opened in Lancaster. | |
| Walmart enters the grocery market. | |
| Retail rose to multinational status and took various environmental initiatives. | |
| Announced a joint venture with Bharti Enterprises to operate in India. | |
| Launched a new logo and a new slogan “Save money, live better” | |
| Walmart launched Goodies (a mail subscription service) | |
| Became the biggest US commercial producer of solar power with 142 MW capacity & 17 energy storage projects. | |
| Acquired a 77% majority stake in Flipkart (an Indian e-commerce company) | |
| Stopped selling cigarettes, tobacco products, live fish, and aquatic plants. | |
| Launched Carrier Pickup, allowing the customers to schedule returns. | |
| Walmart Brazil’s shareholdings divested to Carrefour | |
| Announced FY2023 total revenue of $611.3 billion | |
| Largest private employer with 2.2 million employees |
That’s a legendary history! Isn’t it? Well, this is all about the details of our Walmart case study. Hold on. The question is still brewing- How did Walmart become the retail giant?
We will look into it. But, before that, you need to understand its business model and revenue model.
(D) Walmart Business Model
When you step into Walmart, you’re diving into a world where they keep prices low every day, making things affordable for you. It’s not just about good prices – it’s like a shopping wonderland with everything you can think of, from groceries to gadgets, all in one spot.
The secret sauce? They’re really good at managing how things get from the supplier to the shelves, keeping everything running smoothly.
Plus, because Walmart is so big, they can get awesome deals and pass the savings on to you. They’re all about using smart technology to make your shopping experience top-notch, and they care about making sure you leave happy.
So, when you’re at Walmart, it’s not just a store – it’s a place designed to give you great prices, lots of choices, and a pleasant time shopping.
Let’s look at Walmart’s business model-
| Walmart’s foundational strategy revolves around offering Everyday Low Prices (EDLP). This means the company commits to providing consistently low prices on its products, aiming to attract and retain customers through affordability. | ||
| Walmart works closely with suppliers to negotiate cost-efficient terms, allowing them to pass on the savings to customers. The company is renowned for its formidable bargaining power with suppliers. | ||
| Walmart prides itself on an extensive and diverse product assortment. From groceries and household items to electronics, clothing, and more, the goal is to be a one-stop destination for consumers’ various needs. | ||
| Walmart strategically incorporates private-label or store-brand products. This gives them greater control over pricing and margins, contributing to the overall affordability proposition. | ||
| Walmart is a pioneer in implementing advanced supply chain and logistics management systems. The company’s distribution centers are strategically located for efficient product flow, ensuring a streamlined process from manufacturer to store shelves. | ||
| Walmart utilizes cutting-edge technology to manage inventory effectively. This includes systems like RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) to track merchandise throughout the supply chain, reducing stockouts and overstock situations. | ||
| Walmart leverages data analytics to understand consumer behavior, optimize inventory levels, and personalize marketing strategies. This data-driven approach enhances operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. | ||
| In response to changing consumer preferences, Walmart has invested significantly in e-commerce. The integration of online and offline channels allows customers to shop seamlessly, emphasizing convenience. | ||
| Beyond low prices, Walmart emphasizes customer service and shopping experience. The company invests in employee training to ensure courteous and helpful staff, contributing to a positive in-store experience. | ||
| Walmart continually adapts its offerings to align with evolving consumer trends. This flexibility allows the company to stay relevant and meet the changing demands of the market. | ||
| Walmart has expanded its footprint globally, operating in multiple countries under various formats, including supercenters, discount stores, and wholesale clubs. | ||
| While maintaining a consistent core business model, Walmart adapts its strategies to suit the specific needs and preferences of diverse international markets. |
In essence, the Walmart business model is a comprehensive strategy that combines cost leadership, operational efficiency, technological innovation, and customer-centricity to create a retail powerhouse with a global reach.
(E) Three Crucial Segments of Walmart

Here comes another important part of Walmart, its three critical pillars-
(E.1) Walmart US Segment: Dominance in the Domestic Market
Under the umbrella of the Walmart U.S. segment lies the retail giant’s stronghold in the United States. With a colossal total revenue of $387.5 billion reported in February 2023, this segment encompasses the extensive network of Walmart and Sam’s Club stores across the nation.
Offering an unparalleled variety of products, from groceries to electronics, this segment plays a pivotal role in shaping Walmart’s identity as a go-to destination for millions of American consumers. The sheer scale of revenue from this segment underscores Walmart’s unrivaled dominance in the U.S. retail landscape.
(E.2) Walmart International Segment: Global Reach and Diversification
Walmart’s global influence extends through the Walmart International segment, operating in 24 countries and boasting a network of 10,586 stores and clubs as of October 2022.
While facing challenges in some markets, this segment has showcased resilience, with successful operations in key regions such as Canada, the United Kingdom (ASDA), Mexico, and Central America. The diverse geographical presence reflects Walmart’s commitment to meeting the diverse needs of consumers worldwide.
This segment’s contribution to the overall revenue highlights Walmart’s strategic approach to global expansion and market diversification.
(E.3) Walmart US E-Commerce Segment: Navigating the Digital Frontier
As consumer preferences shift in the digital era, Walmart has strategically positioned itself in the online retail space through the Walmart U.S. eCommerce segment. With a notable total eCommerce sales figure of $118 billion reported in February 2023, this segment represents Walmart’s foray into the digital marketplace.
Emphasizing the company’s adaptability, the eCommerce segment has experienced significant growth, catering to the evolving needs of tech-savvy consumers. This dynamic approach underscores Walmart’s commitment to embracing technological trends and ensuring a seamless shopping experience for customers in the ever-expanding digital frontier.
(F) Walmart Revenue Model: How does Walmart make money?
Walmart’s revenue model combines numerous aspects like traditional retail sales, online commerce, membership fees, international operations, private labels, financial services, and real estate management.
Before diving into the Walmart revenue model, let’s quickly look at its financials-
| $445.81 billion | |
| $611.3 billion | |
| $20.4 billion | |
| $11.29 billion | |
| $243.45 billion | |
| $83.754 billion | |
| $613.466 billion | |
Coming to Walmart revenue model, we will break it down into the following points-
(F.1) Retail Sales
The primary source of revenue for Walmart is its extensive network of physical stores under the Walmart U.S. and Walmart International segments. These stores, including Walmart and Sam’s Club, offer a vast array of products, ranging from groceries and electronics to clothing and home goods. Revenue is generated through the sale of these products at competitive prices, aligning with Walmart’s commitment to everyday low prices (EDLP).
(F.2) E-Commerce Sales
With the growing influence of online retail, Walmart has strategically expanded its presence in the digital space. The Walmart U.S. eCommerce segment contributes significantly to revenue through online sales. Customers can purchase products through the Walmart website or mobile app, expanding Walmart’s reach and catering to consumers who prefer the convenience of online shopping.
(F.3) Membership Fees
Sam’s Club, a membership-based retail warehouse club under the Walmart umbrella, generates revenue through membership fees. Customers pay an annual fee to access exclusive deals, bulk purchasing options, and other members-only benefits.
(F.4) Global Operations
The Walmart International segment contributes to revenue through its diverse operations in 24 countries. Revenue is generated from retail sales in these international markets, where Walmart adapts its strategy to suit local consumer preferences and market dynamics.
(F.5) Private Labels and Brands
Walmart has introduced private labels and exclusive brands, including Great Value and Mainstays. These products, often sold at lower prices compared to national brands, contribute to overall revenue. Additionally, Walmart earns revenue through partnerships and collaborations with other brands, both in-store and online.
(F.6) Financial Services
Walmart provides various financial services, such as money transfers, check cashing, and prepaid debit cards, through its Walmart MoneyCenter. While not the primary revenue stream, these services contribute to the overall financial ecosystem within Walmart stores.
(F.7) Retail Estate & Leasing
Walmart owns a significant amount of real estate, including its stores and distribution centers. The company may generate additional revenue by leasing excess space in its properties to third-party businesses.
In essence, Walmart’s revenue model is multifaceted, reflecting its diverse operations. This diversified approach enables Walmart to navigate various market conditions and consumer preferences, solidifying its position as one of the world’s largest and most successful retail giants.
(G) How did Walmart become the retail giant?

Here we will have a quick recap of whatever you read till now. Walmart’s ascent to retail giant status can be attributed to several key factors, each playing a crucial role in its success. Let’s break them down one by one-
(G.1) Foundational Principles
Walmart was founded on the principles of offering a wide variety of products at low prices while treating customers with respect and dignity. From its inception in 1962, founder Sam Walton emphasized the importance of serving the needs of the average American family by providing affordable goods and exceptional customer service.
(G.2) EDLP (Everyday Low Prices)
Walmart revolutionized the retail industry by adopting the EDLP strategy. Rather than relying on periodic sales and promotions, Walmart committed to maintaining consistently low prices across its products. This approach not only attracted budget-conscious consumers but also instilled trust and loyalty among shoppers who knew they could rely on Walmart for affordability.
(G.3) Supply Chain Efficiency
Walmart invested heavily in optimizing its supply chain and logistics operations. Through innovative technologies and streamlined processes, Walmart was able to reduce costs, minimize inventory holding times, and improve product availability. This efficiency allowed Walmart to pass on savings to customers while maintaining healthy profit margins.
(G.4) Scale and Expansion
Walmart’s aggressive expansion strategy played a pivotal role in its growth trajectory. The company rapidly expanded its footprint across the United States, opening new stores and acquiring existing chains. This expansion was not limited to domestic markets; Walmart also ventured into international territories, establishing a global presence in multiple countries.
(G.5) Diverse Product Assortment
Walmart’s extensive product assortment became a hallmark of its success. Beyond traditional retail categories like groceries and apparel, Walmart diversified its offerings to include electronics, home goods, automotive supplies, and more. This breadth of selection appealed to a wide range of consumers, further solidifying Walmart’s position as a one-stop destination for shopping needs.
(G.6) Technological Innovation
Walmart embraced technology as a catalyst for growth and efficiency. The company invested in advanced systems for inventory management, point-of-sale operations, and data analytics. These technological advancements not only enhanced operational efficiency but also enabled Walmart to better understand consumer behavior and preferences, facilitating targeted marketing and product assortment strategies.
(G.7) Customer-Centric Approach
Throughout its evolution, Walmart maintained a steadfast commitment to customer satisfaction. Whether through its price match guarantee, hassle-free return policy, or friendly in-store experience, Walmart prioritized the needs and preferences of its customers. This customer-centric approach fostered strong brand loyalty and repeat business.
Thus, Walmart’s journey to retail giant status was propelled by a combination of visionary leadership, innovative strategies, operational excellence, and unwavering dedication to customer value. By staying true to its core principles while continuously adapting to changing market dynamics, Walmart has cemented its place as one of the world’s most influential and successful retail organizations.
(H) Flipkart Acquisition: Walmart’s Strategic Move

In 2018, Walmart made a groundbreaking move by acquiring Flipkart, India’s largest e-commerce platform. This strategic move marked Walmart’s entry into the rapidly growing Indian retail market, positioning itself for a piece of the action in one of the world’s fastest-growing economies.
The acquisition came with a hefty price tag of $16 billion, granting Walmart an impressive 77% stake in Flipkart, solidifying it as the largest-ever deal in the Indian e-commerce sector.
Let’s look at some of the significant consequences of the Flipkart acquisition-
- Market Presence Amplified: Walmart’s acquisition allowed it to step into the thriving Indian e-commerce market, projected to become one of the largest globally. Flipkart, boasting over 200 million registered users, presented Walmart with a golden ticket to tap into a diverse array of products and a vast customer base.
- Technological Upgrade: Leveraging Flipkart’s technological prowess, Walmart fortified its online capabilities to stand tall among major e-commerce players. Flipkart’s innovative features like mobile payments, product recommendations, and data analytics became valuable tools for Walmart, enhancing the overall customer experience.
- Logistics Overhaul: Flipkart’s robust supply chain and logistics infrastructure in India became Walmart’s ace in the delivery game. The acquisition empowered Walmart to elevate its delivery and fulfillment capabilities, with Flipkart’s expertise in last-mile delivery and supply chain automation proving to be invaluable.
- Amazon Rivalry: Walmart’s move was not just a business strategy; it was a direct response to Amazon’s rapid expansion in India. The acquisition of Flipkart strategically positioned Walmart to challenge Amazon’s dominance in the Indian e-commerce market, intensifying the competition between these retail giants.
- Financial Boost: The Flipkart acquisition significantly contributed to Walmart’s financial performance. In the fiscal year 2021, Walmart’s international net sales saw a notable 1.3% increase, fueled in part by robust growth in India, showcasing the financial gains resulting from this strategic move.
As of 2021, Walmart asserted a 9.3% share of the global retail market, outpacing Amazon’s 2.3% and Costco’s 1.6%. This not only underscores Walmart’s dominance but also highlights the impact of strategic acquisitions in fortifying its global retail presence.
That’s how Walmart’s acquisition of Flipkart was more than just a business deal. It was an efficient strategic move that unlocked new opportunities, transformed technological capabilities, and propelled Walmart into the vibrant and competitive landscape of Indian e-commerce.
(I) Marketing Strategies: An Integral Part of Walmart Case Study

Creating a winning marketing plan is key for survival in today’s market, and Walmart has a unique strategy to make its mark. Walmart plays the game of business marketing with a powerful approach called market penetration. It’s like diving in, offering you, the customer, not just low prices but seriously competitive ones.
This isn’t just a random strategy; it’s part of Walmart’s cost leadership game plan, and let me tell you, it’s working like a charm, raking in massive profits.
The following table describes some of the most effective marketing strategies of Walmart-
| Walmart doesn’t just wade into the market; it dives in with market penetration. This approach is all about capturing your attention by offering not just low prices but seriously competitive ones. | ||
| Walmart’s cost leadership strategy isn’t just a game-changer; it’s a profit magnet. By providing low prices and treating every customer like royalty, they’ve found the sweet spot for business success. | ||
| At Walmart, you’re not just a customer; you’re the king or queen of the market. The company’s commitment to treating customers with utmost respect builds a strong bond that goes beyond just transactions. | ||
| According to Walmart, your choice of retailer is guided by four pillars: price, access, experience, and assortment. It’s about more than just cost; it’s about making your shopping journey enjoyable and convenient. | ||
| Walmart’s strategy involves buying bulk from local manufacturers and selling in smaller quantities. It’s not just a business move; it’s a community win. More products from local manufacturers mean more jobs and a reduction in unemployment rates. | ||
| Walmart’s commitment extends beyond quantity. They believe in offering top-quality products at prices that make sense for you, maintaining a delicate balance between affordability and excellence. | ||
| Walmart’s local sourcing isn’t just about products; it’s about creating jobs. By supporting local manufacturers, they contribute to economic growth and reduce unemployment. | ||
| This strategy isn’t just about business; it’s about creating a sustainable relationship with customers. Quality, affordability, and community impact form the pillars of Walmart’s global-local approach. |
So, what’s their secret sauce? Walmart treats every customer like royalty, making you feel like the king or queen of the market.
According to Walmart, four things guide your decision on where to shop: price, access, experience, and assortment. It’s not just about what you pay; it’s about how easy it is to get what you want, the overall shopping experience, and the variety of stuff they offer. It’s like Walmart saying, “We’ve got it all, and we’ve got it at a great price.”
But here’s a cool twist in their strategy: Walmart goes local.
Yep, they buy heaps of stuff from local manufacturers all at once and then sell it to you in smaller quantities. It’s a win-win situation. By buying local, they’re not just bagging good deals; they’re also creating jobs and helping tackle unemployment. And hey, it’s not just about quantity; it’s about quality too.
Walmart believes in offering you top-notch products at prices that won’t leave your wallet weeping.
So, there you have it – Walmart’s marketing magic is a blend of rock-bottom prices, treating you like royalty, giving you a shopping experience to remember, and making sure there’s a bit of everything for everyone.
It’s not just a shopping trip; it’s a journey where you’re not just a customer; you’re the ruler of the market! That’s what Walmart claims…
(J) Wrapping Up the Walmart Case Study

Here comes the final part of the Walmart case study. Here you went through Walmart’s journey to retail giant status. All of it is a testament to visionary leadership, strategic adaptability, and customer-centric innovation.
From its foundation on the principles of everyday low prices to aggressive global expansion and astute acquisitions like Flipkart, Walmart has continuously evolved. The company’s commitment to technological advancements, supply chain efficiency, and community engagement sets it apart.
As of 2021, with a 9.3% share of the global retail market, Walmart’s success underscores the significance of a holistic approach – one that prioritizes affordability, diversity, and a deep understanding of evolving market dynamics in shaping the retail landscape.
Related Posts:
Contact Info: Axponent Media Pvt Ltd, 706-707 , 7th Floor Tower A , Iris Tech Park, Sector 48, Sohna Road, Gurugram, India, Pin - 122018
© The Business Rule 2024
Walmart's Workforce of the Future
Any discussion of the future of retail—or how we work—has to include Walmart. As of 2017, 90 percent of the US population lived within 10 miles of a Walmart store; with 11,766 locations worldwide and $514 billion in annual revenues, the discount store also has the distinction of being the largest private employer in the United States, with 1.5 million workers (2.2 million worldwide).
But that size and dominance doesn’t make Walmart immune to pressures faced by any other retail operation. In the second-year Harvard Business School course Managing the Future of Work , Professor William Kerr explores how technology and demographics are changing the way companies like Walmart, and their workers, operate.
“The pace of change in the retail sector is truly extraordinary,” says Kerr, the D’Arbeloff Professor of Business Administration and co-director of Harvard’s Managing the Future of Work initiative . “That requires a lot of reskilling of employees and hard choices, in an uncertain environment, in terms of how to deploy capital.”
“This digital transformation creates new jobs, but, more important, it changes the nature of jobs, even entry-level ones.”
Kerr captures that dilemma by detailing the scope of Walmart’s operations and current strategies in the case “Walmart’s Workforce of the Future.” Published in April, it offers an overview of the considerable investments the retail giant is making in its e-commerce infrastructure, in its employee training and support, and in technological innovations such as robot workers and in-house incubators.
Walmart fights a revenue drop
The case details how the rise of ecommerce (and the success of Amazon in particular) affected Walmart’s discount stores (which sell general merchandise but limited grocery items), resulting in a decrease in annual revenue at those stores from $142.5 billion in 2009 to 97.7 billion in 2018. During the same time period, revenue at Walmart’s “supercenters” (larger stores that also sell groceries and often include services such as eye care, beauty salons, and photo studios) increased by 16 percent, from $409.9 billion to $476.2 billion. (Walmart closed 2,214 discount stores or converted them into other formats from 1993 to 2018, with 2,576 supercenters opening during that time.)
In addition to increasing Walmart’s supercenter footprint, CEO Doug McMillon’s omnichannel strategy focuses on a seamless approach to the customer experience, with an emphasis on employee training and improved ecommerce and automation technology, both on the floor and in back office roles.
One foundational move to beef up its technology was Walmart’s $3.3 billion acquisition of online retailer Jet.com in 2016, an investment that immediately improved its ecommerce infrastructure. Walmart has also piloted and invested in robots to perform a variety of functions, from unloading trucks to scrubbing floors to scanning shelves and bringing items out of storage for curbside delivery orders. But public statements by senior executives made it clear that Walmart was equally committed to the complex, costly effort required to train its human workers.
“I want to be clear that we don’t believe technology is the answer to everything,” McMillon stated in a 2017 annual shareholder meeting. “The secret to success will always be our people. … It will be our humanity that drives our creativity, powers our competitive spirit, and keeps us out in front.”
Technology changes the nature of work
But at the same meeting, McMillon also acknowledged how technology changes the nature of work itself, a perspective echoed by Walmart Chief Sustainability Officer and Walmart Foundation President Kathleen McLaughlin. “…we’re now a tech company as much as a retail company,” Mc Laughlin said. “This digital transformation creates new jobs, but, more important, it changes the nature of jobs, even entry-level ones.”
Those demands require more of workers—and an equivalent commitment to re-skilling and compensation. In the case, Kerr cites Walmart’s investments in wages and training for employees of $1.2 billion and $1.5 billion in 2015 and 2016—part of a move that boosted starting pay for frontline associates from $9 per hour in 2015 to $10 in 2016 (it hit $11 per hour in early 2018). Yet in 2015, announcement of a wage increase resulted in a share price drop the following day of 10 percent, on news that the increase would cut earnings per share by 6 to 12 percent in 2016. It’s a dynamic that lays bare for MBA students the consequences of senior leadership’s choices, says Kerr.
“It’s easy to be critical and say that Walmart should be doing more, but when students review the company’s actions over the past five years, they have to confront the fact that every time the minimum wage went up, the stock price went down—and meanwhile, competitors have better margins.”
The case also outlines Walmart’s approach to training its workers, including its focus on building long-term, transferable skills through efforts such as Pathways, a program that teaches associates about the retail business model, explains the “why” behind the work they’re asked to do, and helps develop the soft skills that are useful in any field. Workers who completed the program received a raise and had increased job opportunities; however, many complained that it lacked clarity and that it took too long to move through the various modules. While Walmart planned for 500,000 employees to go through Pathways in 2016, the initial rollout was considerably lower; as a result, Walmart needed to revamp some parts of the program to speed up its completion rate. (Its Academies program, focused on training and empowering hourly supervisors to directly manage team members, faced similar challenges.)
In another move to build a more skilled, educated workforce, Walmart introduced a program in 2018 that offered workers the opportunity to enroll in online degree programs for $1 a day in business, technology, and supply chain management at three different universities; in June 2019, the program expanded to six universities and 14 areas of study, including cybersecurity and computer science. Widely hailed in the press for the opportunity it offers workers to graduate from college debt-free, the program has seen 7,500 employee enrollments in its first year.
“There’s so much to unpack in the choices that Walmart is making,” Kerr says, remarking that management has also introduced virtual reality goggles to train employees as well as an app, Spark City, that uses a game-type simulation to teach workers about store processes and customer service. Walmart has even crossed over with the gig economy by partnering with platforms including DoorDash, Postmates, Uber, and Lyft for package and grocery delivery.
‘You’re the CEO of Walmart’
So, is Walmart making the right investments for its future? “We spend a lot of time in conversation in this class,” says Kerr. “I’ll say, ‘You’re the CEO of Walmart. What would you have done differently? In 2030, what will your workforce look like? How much of your sales will be in-store, and how much online?
“An early indication of the uncertainty of the future is that, with a bunch of smart MBAs, we had a wide, wide range of opinions as to what the future looks like. From some putting all their chips on ecommerce to others who see Walmart as having a powerful position, particularly in more rural areas, where it can be the one place you go to get your prescriptions, do your shopping, and pick up your ecommerce packages—so building on that, rather than trying to become Amazon.”
Analysts generally give Walmart strong marks for how its investments in technology and training have set it up to compete.
“The progress that they’ve made and the strength they still possess has been working out for them to a good degree,” says Kerr. But it’s too soon to tell whether they have established themselves in a way that will allow them to truly excel. “That’s where the jury is still out. They are still defining the Walmart of the future.”
About the Author
Julia Hanna is an associate editor of the HBS Alumni Bulletin [Image: artran]
Related Reading:
Are You a Digital Manager? Why Employers Must Stop Requiring College Degrees For Middle-Skill Jobs How to Hire a Millennial
What’s your take on the future of work?
Share your insights below.
- 25 Jun 2024
- Research & Ideas
Rapport: The Hidden Advantage That Women Managers Bring to Teams
- 11 Jun 2024
- In Practice
The Harvard Business School Faculty Summer Reader 2024
How transparency sped innovation in a $13 billion wireless sector.
- 24 Jan 2024
Why Boeing’s Problems with the 737 MAX Began More Than 25 Years Ago
- 27 Jun 2016
These Management Practices, Like Certain Technologies, Boost Company Performance
- Working Conditions
- Supply Chain Management
- Change Management
- Selection and Staffing
- Organizational Change and Adaptation
- Performance Productivity
- United States
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Strategic Management: Analyzing Walmart's Growth Strategies
- Perspectives
- Best Practices
- Inside Amplitude
- Customer Stories
- Contributors
Digital Transformation Case Studies: 3 Successful Brand Examples
Learn how three companies—Walmart, Ford, and Anheuser-Busch InBev—successfully transformed their business through digital initiatives to improve the customer experience.

Originally published on March 30, 2022
3 digital transformation case studies
Overcoming common digital transformation challenges, tips for building a digital transformation strategy, always focus on your customers.
Digital transformation is a process in which a company invests in new digital products and services to position it for growth and competition. A successful digital transformation improves the customer experience and enhances the way a company operates behind the scenes.
During a digital transformation, your business deploys new products and technologies and develops new ways to connect with your customers. Once the investment in digital begins, your business can use feedback and data to identify growth opportunities.
The three case studies below—from Ford, Walmart, and Anheuser-Busch InBev (AB InBev)—show how legendary companies went beyond simply creating an app and truly re-thought how digital transformation efforts supported sustainable growth for the business.
- A digital transformation is a major business transformation that employs technology to meet business goals and fundamentally change how companies operate.
- A digital transformation drives new products and services that improve the customer experience.
- A digital transformation gives you more informative behavioral data and more touchpoints with the customer.
- AB InBev, Walmart, and Ford invested in digital technology to accelerate internal processes and develop new digital products, which gave them valuable data on the customer experience and influenced future business investments.
Here are three examples of digital transformation. These leading companies carefully considered how new technology could generate data that made internal processes more efficient and produced insights about how to grow customer value.
Brewing company AB InBev underwent a digital transformation while compiling its network of independent breweries into a unified powerhouse . One of the team’s priorities was moving all their data to the cloud . By doing so, AB InBev enabled all employees to quickly and easily pull global insights and use them to make data-backed decisions.
For example, more accurate demand forecasting means AB InBev teams can match supply with demand, which is essential for such a large company with a complex supply chain. Access to big data from all the breweries means employees can experiment faster and roll out changes that improve business processes.
Gathering more data and opening up that data to internal teams was just the first step of the process, though. AB InBev capitalized on its digital investments by launching an e-commerce marketplace called BEES for its SMB customers—the “mom-and-pop shops”—to order products from. With the BEES platform, AB InBev found that their small and medium-sized businesses browsed the store on the mobile app and added items to their cart throughout the day. However, they only made the final purchases later in the evening.
Based on this behavioral data, the BEES team started sending push notifications after 6:00 p.m. recommending relevant products, which led to increased sales and greater customer satisfaction. Through these efforts, BEES gained over 1.8 million monthly active users and captured over $7.5B in Gross Merchandise Volume.
By closely monitoring metrics such as user engagement and purchasing patterns on the BEES platform, AB InBev has made a big impact with its marketing strategies and improved customer retention.
Jason Lambert, SVP of product at BEES, credits their success with the hard data that told them how their customers behaved and what they needed: “It turned out to be a thousand times better than any of our previous strategies or assumptions.” BEES used behavioral analytics to respond quickly, changing the buying experience to match the needs and habits of their retailers.
As a traditional brick-and-mortar retailer, Walmart began a digital transformation by opening an online marketplace. However, digital transformation is an ongoing process—it doesn’t end at the first website. A digital transformation means companies refocus their operations around digital technology. This usually happens both internally and in a customer-facing way.
To drive more customer value through digital touchpoints, Walmart set up mobile apps and a website to enable customers to purchase goods online. After analyzing customer behavioral information from its app, Walmart added more services such as same-day pickup, mobile ordering, and “buy now, pay later.”
These changes were made to meet customer expectations and improve the customer experience. Walmart’s introduction of a seamless online shopping experience represents a pivotal step in digital innovation, setting new standards for retail convenience and efficiency.
In 2024, Walmart announced an AI-powered logistics product called Route Optimization. This product uses AI to find the most straightforward driving routes, pack trailers efficiently, and reduce miles traveled. In addition to using this product internally, Walmart plans to offer it to other businesses that need to employ more efficient supply chain and logistic processes.
Aside from improving customer experience and logistics, Walmart’s head of mobile marketing , Sherry Thomas-Zon, also notes the importance of data—and access to data—in digital transformations. “Our marketing and product teams are always looking at numbers,” Thomas-Zon said. “It keeps our teams agile despite our size and the increasing amount of data we collect and analyze.”
Ford has embraced several digital transformation initiatives, including using technology to transform and improve manufacturing at one of its biggest automotive factories.
Not having the correct parts available holds up workers and slows down the production process. Ford introduced a material flow wireless parts system so they could track the quantities of different parts and make sure there were enough available. Ford’s use of automation has significantly improved its inventory management process by reducing manual tasks and enhancing worker efficiency.
In 2016, Ford also introduced a digital product for its customers: the FordPass app . It enables Ford owners to control their vehicles remotely. For example, drivers can check their battery or fuel levels and lock or unlock their cars from their phones.
In 2024, Ford took its digital transformation even further when it launched the Ford and Lincoln Digital Experience . Key features include personalized vehicle settings, real-time traffic updates, and seamless integration with smart home devices. The platform also provides advanced navigation, remote control of vehicle functions via the FordPass app, and in-depth vehicle health monitoring.
To capitalize on these digital touchpoints, Ford uses data from its app to improve user experiences . With the ability to capture and analyze data in real-time, Ford’s leadership can now make quicker, more informed decisions that directly enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Ford’s success is grounded in the same process as Walmart and AB InBev. They used their digital transformation to gather detailed information about how customers interact with their products. Then, they made data-driven decisions to provide more value.
It’s not called a transformation for no reason. You’re changing the way your business operates, which is no easy feat. Planning and effective change management strategies are key to overcoming digital transformation challenges.
Create a digital transformation strategy roadmap that outlines your integration strategy and details how this will affect your teams, processes, and workflows. Once you’ve created your plan, share it with the entire company so everyone can use it as a single reference point. Use a project management tool that enables team members to get a big-picture overview and see granular details like the tasks they’re responsible for.
It takes time for teams to onboard and move away from what was successful under the previous system, for example, shifting from heavyweight to lightweight project planning. Make sure you factor some breathing space into your roadmap—giving everyone a chance to get used to the new way of operating.
As part of a digital transformation, you’ll want your team to develop new skills as well. Upskill your team by incorporating digital skills into your employee development plans . Provide people with opportunities to learn and then track their progress. Promote platforms like LinkedIn Learning to help your teams understand the nuances of digital transformation and boost their skills.
If you believe there’s an end-state to digital transformation, more challenges will arise. New technology and consumer behaviors are always emerging, meaning digital transformation is ongoing. It’s not something you’ll complete in a week. Rather, it’s a continuous state of experimentation and improvement.
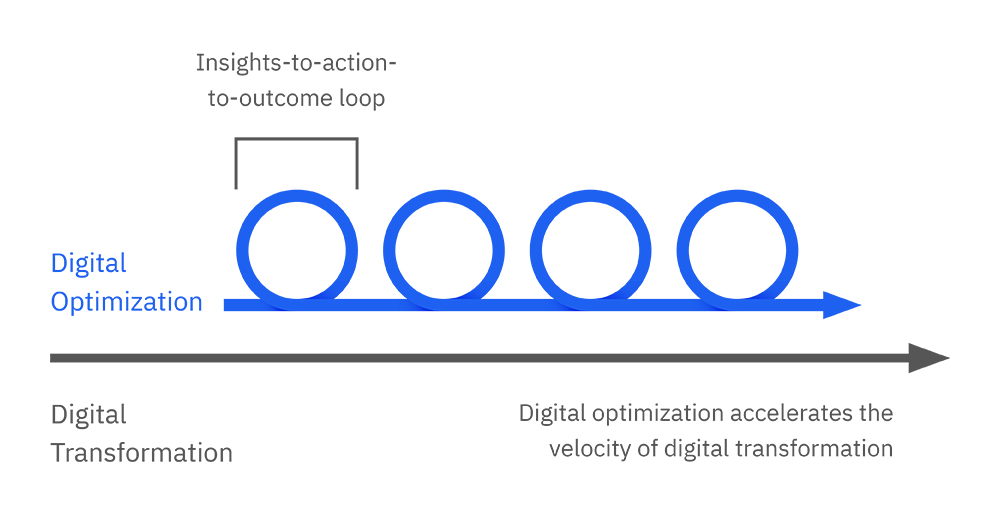
At Amplitude, we refer to this process as digital optimization . If digital transformation brings new products, services, and business models to the fold, then digital optimization is about improving these outputs. Both digital transformation and digital optimization are important—digital transformation signals the start of new investments, and digital optimization compounds them.
Examine how each part of the transformation will affect your customers and your employees. Then, you can be intentional and introduce initiatives that positively impact your business.
Diagnose what you want from a digital transformation first
There are different ways of approaching a digital transformation. Some companies prefer to implement an all-inclusive digital strategy, transforming all parts of their organization at the same time. Others opt for a less risky incremental strategy. Every company is different. To choose the best approach, examine your whole organization and analyze where digital systems could help.
Consider your business goals. Investigate how a digital transformation could impact the customer experience. What new products could you provide? How could you improve your services? For example, you might use artificial intelligence to create a chatbot that reduces customer service wait times—or purchase software that does the same.
You’ll also want to review your business processes. How could a digital transformation speed up your current workflows, improve your operations, or enable more collaboration between teams? Asking these questions lets you challenge the way you operate and will help you identify problems in your organization that you might not have noticed before. For example, perhaps your deliveries are often delayed, and you could make delivery smoother by digitizing elements of your supply chain .
Get cross-team involvement
Though different teams may work separately, your customers are affected by each department. Collaboration elevates everyone’s work because it means people can make informed decisions.
Make sure you get input from all of the right stakeholders when you create your digital transformation strategy. Ask:
- What processes hold you up?
- Where are the bottlenecks?
- What data would be useful for you?
Enable everyone to access the data they need without input from anyone else. Help your employees improve their data literacy . Start by training all your employees to use your organization’s data tools and software. To help everyone in your organization access and analyze data, adopt easy-to-use self-service tools (e.g., an analytics tool and a CRM). Then, lead by example. Provide inspiration by using data storytelling in your presentations to explain the decisions you make.
Encourage collaboration between teams by creating shared resources so they have spaces to present insights and submit suggestions. This could be as simple as creating a Google Doc for brainstorming that multiple teams can access or sharing charts directly within your analytics solution, like with Amplitude Notebooks . Then, you can start to experiment and make improvements to the digital customer experience like Walmart, Ford, and AB InBev did.
Once your digital transformation is moving, a digital optimization strategy is an opportunity to generate growth. Your digital transformation initiatives will continue in parallel, and the process will become a feedback loop:
- Deploy new digital systems and products.
- Analyze the data that comes forth from these investments. Use it to draw insights about your customers or processes.
- Make decisions based on the data and make changes.
Keep customer needs at the heart of your work. Let them guide you as you undergo digital transformation. As you gather more data about how your customers interact with your new digital products, use it to make the experience even better for them. This will lead to more trust and loyalty and, ultimately, more recurring revenue.
To continue your learning about digital transformation and optimization, join an Amplitude workshop or webinar or read our Guide to Digital Optimization .
- MIT Sloan. How to build data literacy in your company
- Ernst & Young. How global supply chain strategy is changing and what comes next
- Datanami. From Big Beer to Big Data: Inside AB InBev’s Digital Transformation
- Predictable Profits. How Ford Embraced Digital Transformation
- APMG International. Heavyweight vs Lightweight Management

About the Author
More best practices.

What is a Data Warehouse?
The guide to data accessibility, what is a product roadmap a definitive guide, new amplitude + snowflake integration delivers the modern data stack, digital optimization vs. digital transformation explained, 6 essential digital optimization skills you need, what is martech full guide and how to build your stack, recurring revenue 101: mrr vs. arr.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Walton was a man of simple tastes and took a keen interest in people. He believed in three guiding principles: 1. Customer value and service; 2. Partnership with its associates; 3. Community involvement. The Customer — The word "always" can be seen in virtually all of Wal-Mart's literature.
Conclusion. In conclusion, Walmart's business strategy is that of an growing Omnichannel marketplace, a multifaceted approach that combines physical and digital retail, competitive pricing, supply chain excellence, and a commitment to customer satisfaction. Understanding these elements provides insights into the retail giant's enduring ...
Walmart is one of the largest retail companies in the world. It was founded in 1962 by Sam Walton. The headquarter of this company is situated in the United States. The main aim of the company is to provide consistent discounts, loyal customer service, and fast friendly service. Walmart's targets to expand its business in large cities as well ...
The 10 Strategic Decision Areas of Operations Management at Walmart. 1. Design of Goods and Services. This decision area of operations management involves the strategic characterization of the retail company's products. In this case, the decision area covers Walmart's goods and services. As a retailer, the company offers retail services.
Going digital is a top priority—which is why Walmart recently paid $3 billion to acquire e-tailer Jet.com. But the company also wants to strengthen the in-store experience. "The reality ...
Just the mention of the name will bring about connotations of scale that are difficult to fathom in our modern context. Let's take a look at some of Walmart's astounding numbers. $524 Billion (USD) revenue in 2020, an increase of $9.6 Billion. Over 2.3 Million employees worldwide, 1.6 Million in the US alone. 4,743 Walmart stores in the US alone.
In 2019 Walmart was still the world's largest company, with over $500 billion in annual revenue and operations around the world. Although it had mostly vanquished its rival discount retailers in the U.S., it was struggling to find the right growth strategy. Facing a mature U.S. market, it had looked to ecommerce and international sales as an ...
Walmart's strategic planning must prioritize competition and new entry in the retail industry. Based on this Five Forces analysis, the business needs to continually improve its capabilities to sustain its competitive advantages. ... Walmart: A Business Case Study in Knowledge Management, Walmart's Secret Sauce - The Use of Machine ...
HBS Case No. 720-370. The (B) case describes Walmart's omnichannel strategy in 2018 as it battled Amazon for online retail market share. Walmart aimed to integrate its enormous brick and mortar footprint with its growing ecommerce business, e.g., through merchandise and grocery delivery and order online, pickup in store options.
This case describes Walmart's omnichannel strategy in 2018 as it battled Amazon for online retail market share. The case discusses Walmart's early forays into online retail, as well as its 2018 strategy, which aimed to integrate Walmart's enormous brick and mortar footprint with its growing ecommerce business, e.g., through merchandise and grocery delivery and order online, pickup in store ...
The Business Strategy of Walmart - A Case study Introduction: Walmart has continued to retain the top position on the Fortune 500 list consecutively for several years. The brand's growth is driven mainly by its 'everyday low prices' strategy and the large assortment of merchandise it offers. Its online sales in the United States have ...
It is clear to see that the business strategy Walmart is ... A longitudinal case study of Amazon's financial situation during the 2016-2020 period, and time-series analysis, ratio analysis ...
Quantifying Walmart's Sources of Advantage*. Humberto Brea-Solís† November 6, 2012. Ramon Casadesus-Masanell‡. A B S T R A C T. Emili Grifell-Tatjé§. In recent years, the concept of the business model has received substantial attention in the strategy literature, where a number of qualitative approaches to describe, represent, and ...
Scott announced that Wal-Mart was launching a sweeping business sustainability strategy to dramatically reduce the company's impact on the global environment and thus become "the most competitive and innovative company in the world.". He argued that, "Being a good steward of the environment and being profitable are not mutually exclusive.
Walmart's industry position comes with a dominant brick-and-mortar retail presence, which is a business strength in this SWOT analysis. This strength enables the company to maintain a stable market share, despite aggressive competitors, like Amazon and Target. The large brick-and-mortar presence, along with the operations of the subsidiary, Sam's Club, helps protect Walmart from ...
(I) Marketing Strategies: An Integral Part of Walmart Case Study Creating a winning marketing plan is key for survival in today's market, and Walmart has a unique strategy to make its mark. Walmart plays the game of business marketing with a powerful approach called market penetration.
In the case, Kerr cites Walmart's investments in wages and training for employees of $1.2 billion and $1.5 billion in 2015 and 2016—part of a move that boosted starting pay for frontline associates from $9 per hour in 2015 to $10 in 2016 (it hit $11 per hour in early 2018). Yet in 2015, announcement of a wage increase resulted in a share ...
Walmart has achieved tremendous success through a strategy of cost leadership and technological innovation. At the core of its business model is an "everyday low prices" strategy, achieved through large sales volumes, an efficient supply chain system, and bargaining power over suppliers. This strategy has helped Walmart grow to operate over 11,000 stores globally. It continues investing ...
About Walmart Walmart Inc. (NYSE: WMT) is a people-led, tech-powered omnichannel retailer helping people save money and live better - anytime and anywhere - in stores, online, and through their mobile devices. Each week, approximately 240 million customers and members visit more than 10,500 stores and numerous eCommerce websites in 20 countries.
Business The Business Strategy of Walmart - A Case study Introduction: Walmart has continued to retain the top position on the Fortune 500 list for a consecutive fifth year. The brand has continued to grow based on its everyday low prices strategy and has taken fast advances into the digital market. The brand that
Case Study: Business Strategy Analysis of Wal-Mart. Sam Walton, a leader with an innovative vision, started his own company and made it into the leader in discount retailing that it is today. Through his savvy, and sometimes unusual, business practices, he and his associates led the company forward for thirty years.
walmart business strategy case study.docx - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. 1) Walmart has emerged as the largest company in the world through decades of successfully implementing a cost leadership strategy of offering everyday low prices. 2) Key elements of Walmart's strategy included developing economies of scale, reducing ...
Business document from Columbia Southern University, 7 pages, Running Head: UNIT VII CASE Zellars 1 Unit VII Case Study Shynice Zellars BUS 5302: Strategic Management and Business Policy Instructor: David Qiu May 17, 2024 Running Head: UNIT VII CASE Zellars 2 Walmart is one of the biggest multi-channel retail store
The three case studies below—from Ford, Walmart, and Anheuser-Busch InBev (AB InBev)—show how legendary companies went beyond simply creating an app and truly re-thought how digital transformation efforts supported sustainable growth for the business. ... A digital transformation is a major business transformation that employs technology to ...