- Find journals
- My journals
Register Sign in
Register or sign-in in order to manage your journal lists

Sign in or register to save a journal
To save a journal and create lists, you need to sign in to your Elsevier account.
Find the right journal for your research
Looking for the best journal match for your paper? Search the world's leading source of academic journals using your abstract or your keywords and other details.
Check if you're eligible for open access (OA) savings.
How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal
- Open access
- Published: 30 April 2020
- Volume 36 , pages 909–913, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Clara Busse ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0178-1000 1 &
- Ella August ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5151-1036 1 , 2
282k Accesses
17 Citations
708 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Communicating research findings is an essential step in the research process. Often, peer-reviewed journals are the forum for such communication, yet many researchers are never taught how to write a publishable scientific paper. In this article, we explain the basic structure of a scientific paper and describe the information that should be included in each section. We also identify common pitfalls for each section and recommend strategies to avoid them. Further, we give advice about target journal selection and authorship. In the online resource 1 , we provide an example of a high-quality scientific paper, with annotations identifying the elements we describe in this article.
Similar content being viewed by others

How to Choose the Right Journal

The Point Is…to Publish?

Writing and publishing a scientific paper
Explore related subjects.
- Artificial Intelligence
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Writing a scientific paper is an important component of the research process, yet researchers often receive little formal training in scientific writing. This is especially true in low-resource settings. In this article, we explain why choosing a target journal is important, give advice about authorship, provide a basic structure for writing each section of a scientific paper, and describe common pitfalls and recommendations for each section. In the online resource 1 , we also include an annotated journal article that identifies the key elements and writing approaches that we detail here. Before you begin your research, make sure you have ethical clearance from all relevant ethical review boards.
Select a Target Journal Early in the Writing Process
We recommend that you select a “target journal” early in the writing process; a “target journal” is the journal to which you plan to submit your paper. Each journal has a set of core readers and you should tailor your writing to this readership. For example, if you plan to submit a manuscript about vaping during pregnancy to a pregnancy-focused journal, you will need to explain what vaping is because readers of this journal may not have a background in this topic. However, if you were to submit that same article to a tobacco journal, you would not need to provide as much background information about vaping.
Information about a journal’s core readership can be found on its website, usually in a section called “About this journal” or something similar. For example, the Journal of Cancer Education presents such information on the “Aims and Scope” page of its website, which can be found here: https://www.springer.com/journal/13187/aims-and-scope .
Peer reviewer guidelines from your target journal are an additional resource that can help you tailor your writing to the journal and provide additional advice about crafting an effective article [ 1 ]. These are not always available, but it is worth a quick web search to find out.
Identify Author Roles Early in the Process
Early in the writing process, identify authors, determine the order of authors, and discuss the responsibilities of each author. Standard author responsibilities have been identified by The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) [ 2 ]. To set clear expectations about each team member’s responsibilities and prevent errors in communication, we also suggest outlining more detailed roles, such as who will draft each section of the manuscript, write the abstract, submit the paper electronically, serve as corresponding author, and write the cover letter. It is best to formalize this agreement in writing after discussing it, circulating the document to the author team for approval. We suggest creating a title page on which all authors are listed in the agreed-upon order. It may be necessary to adjust authorship roles and order during the development of the paper. If a new author order is agreed upon, be sure to update the title page in the manuscript draft.
In the case where multiple papers will result from a single study, authors should discuss who will author each paper. Additionally, authors should agree on a deadline for each paper and the lead author should take responsibility for producing an initial draft by this deadline.
Structure of the Introduction Section
The introduction section should be approximately three to five paragraphs in length. Look at examples from your target journal to decide the appropriate length. This section should include the elements shown in Fig. 1 . Begin with a general context, narrowing to the specific focus of the paper. Include five main elements: why your research is important, what is already known about the topic, the “gap” or what is not yet known about the topic, why it is important to learn the new information that your research adds, and the specific research aim(s) that your paper addresses. Your research aim should address the gap you identified. Be sure to add enough background information to enable readers to understand your study. Table 1 provides common introduction section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.

The main elements of the introduction section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Methods Section
The purpose of the methods section is twofold: to explain how the study was done in enough detail to enable its replication and to provide enough contextual detail to enable readers to understand and interpret the results. In general, the essential elements of a methods section are the following: a description of the setting and participants, the study design and timing, the recruitment and sampling, the data collection process, the dataset, the dependent and independent variables, the covariates, the analytic approach for each research objective, and the ethical approval. The hallmark of an exemplary methods section is the justification of why each method was used. Table 2 provides common methods section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Results Section
The focus of the results section should be associations, or lack thereof, rather than statistical tests. Two considerations should guide your writing here. First, the results should present answers to each part of the research aim. Second, return to the methods section to ensure that the analysis and variables for each result have been explained.
Begin the results section by describing the number of participants in the final sample and details such as the number who were approached to participate, the proportion who were eligible and who enrolled, and the number of participants who dropped out. The next part of the results should describe the participant characteristics. After that, you may organize your results by the aim or by putting the most exciting results first. Do not forget to report your non-significant associations. These are still findings.
Tables and figures capture the reader’s attention and efficiently communicate your main findings [ 3 ]. Each table and figure should have a clear message and should complement, rather than repeat, the text. Tables and figures should communicate all salient details necessary for a reader to understand the findings without consulting the text. Include information on comparisons and tests, as well as information about the sample and timing of the study in the title, legend, or in a footnote. Note that figures are often more visually interesting than tables, so if it is feasible to make a figure, make a figure. To avoid confusing the reader, either avoid abbreviations in tables and figures, or define them in a footnote. Note that there should not be citations in the results section and you should not interpret results here. Table 3 provides common results section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Discussion Section
Opposite the introduction section, the discussion should take the form of a right-side-up triangle beginning with interpretation of your results and moving to general implications (Fig. 2 ). This section typically begins with a restatement of the main findings, which can usually be accomplished with a few carefully-crafted sentences.
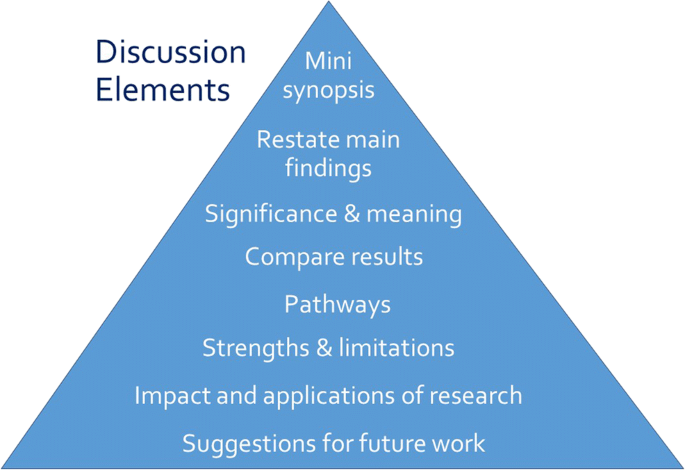
Major elements of the discussion section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Next, interpret the meaning or explain the significance of your results, lifting the reader’s gaze from the study’s specific findings to more general applications. Then, compare these study findings with other research. Are these findings in agreement or disagreement with those from other studies? Does this study impart additional nuance to well-accepted theories? Situate your findings within the broader context of scientific literature, then explain the pathways or mechanisms that might give rise to, or explain, the results.
Journals vary in their approach to strengths and limitations sections: some are embedded paragraphs within the discussion section, while some mandate separate section headings. Keep in mind that every study has strengths and limitations. Candidly reporting yours helps readers to correctly interpret your research findings.
The next element of the discussion is a summary of the potential impacts and applications of the research. Should these results be used to optimally design an intervention? Does the work have implications for clinical protocols or public policy? These considerations will help the reader to further grasp the possible impacts of the presented work.
Finally, the discussion should conclude with specific suggestions for future work. Here, you have an opportunity to illuminate specific gaps in the literature that compel further study. Avoid the phrase “future research is necessary” because the recommendation is too general to be helpful to readers. Instead, provide substantive and specific recommendations for future studies. Table 4 provides common discussion section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Follow the Journal’s Author Guidelines
After you select a target journal, identify the journal’s author guidelines to guide the formatting of your manuscript and references. Author guidelines will often (but not always) include instructions for titles, cover letters, and other components of a manuscript submission. Read the guidelines carefully. If you do not follow the guidelines, your article will be sent back to you.
Finally, do not submit your paper to more than one journal at a time. Even if this is not explicitly stated in the author guidelines of your target journal, it is considered inappropriate and unprofessional.
Your title should invite readers to continue reading beyond the first page [ 4 , 5 ]. It should be informative and interesting. Consider describing the independent and dependent variables, the population and setting, the study design, the timing, and even the main result in your title. Because the focus of the paper can change as you write and revise, we recommend you wait until you have finished writing your paper before composing the title.
Be sure that the title is useful for potential readers searching for your topic. The keywords you select should complement those in your title to maximize the likelihood that a researcher will find your paper through a database search. Avoid using abbreviations in your title unless they are very well known, such as SNP, because it is more likely that someone will use a complete word rather than an abbreviation as a search term to help readers find your paper.
After you have written a complete draft, use the checklist (Fig. 3 ) below to guide your revisions and editing. Additional resources are available on writing the abstract and citing references [ 5 ]. When you feel that your work is ready, ask a trusted colleague or two to read the work and provide informal feedback. The box below provides a checklist that summarizes the key points offered in this article.

Checklist for manuscript quality
Data Availability
Michalek AM (2014) Down the rabbit hole…advice to reviewers. J Cancer Educ 29:4–5
Article Google Scholar
International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Defining the role of authors and contributors: who is an author? http://www.icmje.org/recommendations/browse/roles-and-responsibilities/defining-the-role-of-authosrs-and-contributors.html . Accessed 15 January, 2020
Vetto JT (2014) Short and sweet: a short course on concise medical writing. J Cancer Educ 29(1):194–195
Brett M, Kording K (2017) Ten simple rules for structuring papers. PLoS ComputBiol. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005619
Lang TA (2017) Writing a better research article. J Public Health Emerg. https://doi.org/10.21037/jphe.2017.11.06
Download references
Acknowledgments
Ella August is grateful to the Sustainable Sciences Institute for mentoring her in training researchers on writing and publishing their research.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Maternal and Child Health, University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health, 135 Dauer Dr, 27599, Chapel Hill, NC, USA
Clara Busse & Ella August
Department of Epidemiology, University of Michigan School of Public Health, 1415 Washington Heights, Ann Arbor, MI, 48109-2029, USA
Ella August
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ella August .
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
(PDF 362 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Busse, C., August, E. How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal. J Canc Educ 36 , 909–913 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
Download citation
Published : 30 April 2020
Issue Date : October 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Manuscripts
- Scientific writing
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Insights blog
How to publish your research
A step-by-step guide to getting published.
Publishing your research is an important step in your academic career. While there isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach, this guide is designed to take you through the typical steps in publishing a research paper.
Discover how to get your paper published, from choosing the right journal and understanding what a peer reviewed article is, to responding to reviewers and navigating the production process.
Step 1: Choosing a journal

Choosing which journal to publish your research paper in is one of the most significant decisions you have to make as a researcher. Where you decide to submit your work can make a big difference to the reach and impact your research has.
It’s important to take your time to consider your options carefully and analyze each aspect of journal submission – from shortlisting titles to your preferred method of publication, for example open access .
Don’t forget to think about publishing options beyond the traditional journals format – for example, open research platform F1000Research , which offers rapid, open publication for a wide range of outputs.
Why choose your target journal before you start writing?
The first step in publishing a research paper should always be selecting the journal you want to publish in. Choosing your target journal before you start writing means you can tailor your work to build on research that’s already been published in that journal. This can help editors to see how a paper adds to the ‘conversation’ in their journal.
In addition, many journals only accept specific manuscript formats of article. So, by choosing a journal before you start, you can write your article to their specifications and audience, and ultimately improve your chances of acceptance.
To save time and for peace of mind, you can consider using manuscript formatting experts while you focus on your research.

How to select the journal to publish your research in
Choosing which journal to publish your research in can seem like an overwhelming task. So, for all the details of how to navigate this important step in publishing your research paper, take a look at our choosing a journal guide . This will take you through the selection process, from understanding the aims and scope of the journals you’re interested in to making sure you choose a trustworthy journal.
Don’t forget to explore our Journal Suggester to see which Taylor & Francis journals could be right for your research.
Go to guidance on choosing a journal
Step 2: Writing your paper
Writing an effective, compelling research paper is vital to getting your research published. But if you’re new to putting together academic papers, it can feel daunting to start from scratch.
The good news is that if you’ve chosen the journal you want to publish in, you’ll have lots of examples already published in that journal to base your own paper on. We’ve gathered advice on every aspect of writing your paper, to make sure you get off to a great start.
How to write your paper
How you write your paper will depend on your chosen journal, your subject area, and the type of paper you’re writing. Everything from the style and structure you choose to the audience you should have in mind while writing will differ, so it’s important to think about these things before you get stuck in.
Our writing your paper guidance will take you through everything you need to know to put together your research article and prepare it for submission. This includes getting to know your target journal, understanding your audiences, and how to choose appropriate keywords.
You can also use this guide to take you through your research publication journey .

You should also make sure you’re aware of all the Editorial Policies for the journal you plan to submit to. Don’t forget that you can contact our editing services to help you refine your manuscript.
Discover advice and guidance for writing your paper
Step 3: Making your submission
Once you’ve chosen the right journal and written your manuscript, the next step in publishing your research paper is to make your submission .
Each journal will have specific submission requirements, so make sure you visit Taylor & Francis Online and carefully check through the instructions for authors for your chosen journal.
How to submit your manuscript
To submit your manuscript you’ll need to ensure that you’ve gone through all the steps in our making your submission guide. This includes thoroughly understanding your chosen journal’s instructions for authors, writing an effective cover letter, navigating the journal’s submission system, and making sure your research data is prepared as required.
You can also improve your submission experience with our guide to avoid obstacles and complete a seamless submission.

To make sure you’ve covered everything before you hit ‘submit’ you can also take a look at our ‘ready to submit’ checklist (don’t forget, you should only submit to one journal at a time).
Understand the process of making your submission
Step 4: Navigating the peer review process
Now you’ve submitted your manuscript, you need to get to grips with one of the most important parts of publishing your research paper – the peer review process .
What is peer review?
Peer review is the independent assessment of your research article by independent experts in your field. Reviewers, also sometimes called ‘referees’, are asked to judge the validity, significance, and originality of your work.
This process ensures that a peer-reviewed article has been through a rigorous process to make sure the methodology is sound, the work can be replicated, and it fits with the aims and scope of the journal that is considering it for publication. It acts as an important form of quality control for research papers.

Peer review is also a very useful source of feedback, helping you to improve your paper before it’s published. It is intended to be a collaborative process, where authors engage in a dialogue with their peers and receive constructive feedback and support to advance their work.
Almost all research articles go through peer review, although in some cases the journal may operate post-publication peer review, which means that reviews and reader comments are invited after the paper is published.
If you’ll like to feel more confident before getting your work peer reviewed by the journal, you may want to consider using an in-depth technical review service from experts.
Understanding peer review
Peer review can be a complex process to get your head around. That’s why we’ve put together a comprehensive guide to understanding peer review . This explains everything from the many different types of peer review to the step-by-step peer review process and how to revise your manuscript. It also has helpful advice on what to do if your manuscript is rejected.
Visit our peer review guide for authors
Step 5: The production process
If your paper is accepted for publication, it will then head into production . At this stage of the process, the paper will be prepared for publishing in your chosen journal.
A lot of the work to produce the final version of your paper will be done by the journal production team, but your input will be required at various stages of the process.
What do you need to do during production?
During production, you’ll have a variety of tasks to complete and decisions to make. For example, you’ll need to check and correct proofs of your article and consider whether or not you want to produce a video abstract to accompany it.
Take a look at our guide to the production process to find out what you’ll need to do in this final step to getting your research published.
Your research is published – now what?
You’ve successfully navigated publishing a research paper – congratulations! But the process doesn’t stop there. Now your research is published in a journal for the world to see, you’ll need to know how to access your article and make sure it has an impact .
Here’s a quick tip on how to boost your research impact by investing in making your accomplishments stand out.
Below you’ll find helpful tips and post-publication support. From how to communicate about your research to how to request corrections or translations.
How to access your published article
When you publish with Taylor & Francis, you’ll have access to a new section on Taylor & Francis Online called Authored Works . This will give you and all other named authors perpetual access to your article, regardless of whether or not you have a subscription to the journal you have published in.
You can also order print copies of your article .
How to make sure your research has an impact
Taking the time to make sure your research has an impact can help drive your career progression, build your networks, and secure funding for new research. So, it’s worth investing in.
Creating a real impact with your work can be a challenging and time-consuming task, which can feel difficult to fit into an already demanding academic career.
To help you understand what impact means for you and your work, take a look at our guide to research impact . It covers why impact is important, the different types of impact you can have, how to achieve impact – including tips on communicating with a variety of audiences – and how to measure your success.

Keeping track of your article’s progress
Through your Authored Works access , you’ll be able to get real-time insights about your article, such as views, downloads and citation numbers.
In addition, when you publish an article with us, you’ll be offered the option to sign up for email updates. These emails will be sent to you three, six and twelve months after your article is published to let you know how many views and citations the article has had.
Corrections and translations of published articles
Sometimes after an article has been published it may be necessary to make a change to the Version of Record . Take a look at our dedicated guide to corrections, expressions of concern, retractions and removals to find out more.
You may also be interested in translating your article into another language. If that’s the case, take a look at our information on article translations .
Go to your guide on moving through production
Explore related posts
Insights topic: Get published
Use a trusted editing service to help you get published
5 practical tips for writing an academic article

5 ways to avoid the wrong journal and find the right one

Publishing in a scholarly journal: Part one, the publishing process
As a psychology student or early career psychologist, you might be thinking about publishing your first paper in a scholarly journal. There are several important steps and points to consider as you embark on your publishing journey. Not sure where to start? We’ve got you covered!
Recognizing that not all young academics get all of their questions about publication answered in their respective training programs, we crowdsourced from trainees and early career psychologists using an anonymous Twitter poll and direct solicitation from various students and colleagues known to the authors, this three-part article series includes frequently asked questions about the publication process with answers from the Editor-in-Chief of Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology ( ECP ), William Stoops, the Associate Editor of ECP , Raina Pang, and a past ECP Editorial Fellow, Daniel Bradford. Part one focuses on crucial publishing insights for future authors; part two examines the role of the editorial board; and part three sheds light on peer review.
Choosing a journal
How does one choose a journal in which to publish and what factors (impact factor, journal content) should be considered?
In general, the most important factor to consider when choosing where to submit your article is the fit of the manuscript to the scope and profile of the journal; Aside from the quality of the science and writing, this is the largest factor that will determine whether a manuscript is accepted to a journal. To determine fit, one should examine the journal description, usually found on the journal website.
Additionally, it is helpful to browse the journal to see whether it has published articles on the same topic and with similar methods to the manuscript you are submitting.
In addition to the above, you may also consider online search engines, which can help generate a list of journals that may be appropriate for the manuscript being submitted:
- JournalFinder
- Springer Nature: Journal suggester
- Enago’s Open Access Journal Finder
- Journal/Author Name Estimator
Can you submit a paper to multiple journals at once?
No. Submitting a paper to multiple journals at once contravenes publishing guidelines and presents serious ethical concerns.
Is there a uniform format that I should submit my manuscript in?
Make sure to carefully read the manuscript submission instructions available on every journal’s webpage. Although there are certain rules that most journals follow (e.g. formatting in APA Style), each journal provides specific guidelines about certain aspects, for example the information that must be included within the manuscript.
What’s a predatory journal?
A predatory journal is a counterfeit publication that imitates that of a legitimate, respected publisher. Predatory publishers use various techniques to trick scholars into submitting their article for publication. A predatory publisher will usually solicit articles via email, emphasizing a publishing fee and touting a quick turnaround that often omits peer review.
Although the publishing fee is a red flag when it comes to identifying a predatory journal, not all journals that charge a publishing fee are predatory (see next question for more information). For tips on how to identify a predatory journal, see the following resources:
- Scholars beware
- How to avoid predatory publishers
Publishing fees
Does it usually cost money to publish?
It’s important to note that many journals do not charge the author(s) or their institution to publish an article. There are exceptions, however.
Some journals may charge a fee for publishing the article in a particular format. For example, some authors prefer or require their figures to be printed in color. Because printing in color costs more to the publisher, some journals may require a fee for each figure to be printed in color. Other journals may print one color figure for free, but charge for every additional color figure.
An increasing number of journals are also adding open access options which, when chosen, require fees paid by the author or their institution. Further, some reputable journals have recently gone entirely open access and thus require a fee to publish (the fee varies by journal). Open access journals are free to read for all and do not receive revenue from journal subscriptions—therefore, in many cases, an article publishing fee is charged to offset the cost of publishing (e.g., peer review management, production costs).
For example, APA’s open access journal Technology, Mind, and Behavior charges a $1,200 article processing charge (APC), however an author may apply for an APC waiver if they are unable to pay via grant, institutional funding, or by other means outlined on the journal website.
As such, it is important to recognize that journals charging a fee are not necessarily “predatory”—it’s crucial to consider other factors to figure out the legitimacy of the publication.
What is the difference between an open access journal and the open science movement?
Open access is a publishing model in which the author pays a fee to publish; the reader is able to access the article for free. Some journals are entirely open access, while others are “hybrid”—providing both a subscription as well as an open access publishing option.
Open science , on the other hand, is a movement towards increased transparency in publishing. It goes beyond open access, offering guidelines on the type of information that authors should include in their manuscript: for example, APA Style JARS provide guidelines for the details that authors should include in their methods section. Open science initiatives include data sharing, preregistration, preprints, registered reports, and more. The goals of open science initiatives are to increase openness and collaboration, and to improve reproducibility of science and research discovery.
Licensing and copyright
How does licensing and copyright work?
Authors usually own the copyright of their original work and are free to share, without limitation, any version of their articles prior to the final text (after the journal proofing / copy editing process). However, licensing of article versions and individual publisher stances on sharing of accepted articles vary and change frequently. Fortunately, there are many resources to help authors keep track of individual policies. For example, the Sherpa Romeo website includes a conveniently searchable tool of journals’ copyright and open access policies on a journal-by-journal basis.
The Open Science Knowledge Base provides detailed information and recommendations about licensing content .
Publishing tips
Expert insights on key topics and best practices in publishing.
Read insights
- APA Journals ™ Publishing Resource Center
- Author resource center
- Reviewer Resource Center
- Editor resource center
- APA and Affiliated Journals
APA Publishing Insider
APA Publishing Insider is a free monthly newsletter with tips on APA Style, open science initiatives, active calls for papers, research summaries, and more.
Contact Journals
- Privacy Policy

Home » How to Publish a Research Paper – Step by Step Guide
How to Publish a Research Paper – Step by Step Guide
Table of Contents

Publishing a research paper is an important step for researchers to disseminate their findings to a wider audience and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in their field. Whether you are a graduate student, a postdoctoral fellow, or an established researcher, publishing a paper requires careful planning, rigorous research, and clear writing. In this process, you will need to identify a research question , conduct a thorough literature review , design a methodology, analyze data, and draw conclusions. Additionally, you will need to consider the appropriate journals or conferences to submit your work to and adhere to their guidelines for formatting and submission. In this article, we will discuss some ways to publish your Research Paper.
How to Publish a Research Paper
To Publish a Research Paper follow the guide below:
- Conduct original research : Conduct thorough research on a specific topic or problem. Collect data, analyze it, and draw conclusions based on your findings.
- Write the paper : Write a detailed paper describing your research. It should include an abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
- Choose a suitable journal or conference : Look for a journal or conference that specializes in your research area. You can check their submission guidelines to ensure your paper meets their requirements.
- Prepare your submission: Follow the guidelines and prepare your submission, including the paper, abstract, cover letter, and any other required documents.
- Submit the paper: Submit your paper online through the journal or conference website. Make sure you meet the submission deadline.
- Peer-review process : Your paper will be reviewed by experts in the field who will provide feedback on the quality of your research, methodology, and conclusions.
- Revisions : Based on the feedback you receive, revise your paper and resubmit it.
- Acceptance : Once your paper is accepted, you will receive a notification from the journal or conference. You may need to make final revisions before the paper is published.
- Publication : Your paper will be published online or in print. You can also promote your work through social media or other channels to increase its visibility.
How to Choose Journal for Research Paper Publication
Here are some steps to follow to help you select an appropriate journal:
- Identify your research topic and audience : Your research topic and intended audience should guide your choice of journal. Identify the key journals in your field of research and read the scope and aim of the journal to determine if your paper is a good fit.
- Analyze the journal’s impact and reputation : Check the impact factor and ranking of the journal, as well as its acceptance rate and citation frequency. A high-impact journal can give your paper more visibility and credibility.
- Consider the journal’s publication policies : Look for the journal’s publication policies such as the word count limit, formatting requirements, open access options, and submission fees. Make sure that you can comply with the requirements and that the journal is in line with your publication goals.
- Look at recent publications : Review recent issues of the journal to evaluate whether your paper would fit in with the journal’s current content and style.
- Seek advice from colleagues and mentors: Ask for recommendations and suggestions from your colleagues and mentors in your field, especially those who have experience publishing in the same or similar journals.
- Be prepared to make changes : Be prepared to revise your paper according to the requirements and guidelines of the chosen journal. It is also important to be open to feedback from the editor and reviewers.
List of Journals for Research Paper Publications
There are thousands of academic journals covering various fields of research. Here are some of the most popular ones, categorized by field:
General/Multidisciplinary
- Nature: https://www.nature.com/
- Science: https://www.sciencemag.org/
- PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS): https://www.pnas.org/
- The Lancet: https://www.thelancet.com/
- JAMA (Journal of the American Medical Association): https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama
Social Sciences/Humanities
- Journal of Personality and Social Psychology: https://www.apa.org/pubs/journals/psp
- Journal of Consumer Research: https://www.journals.uchicago.edu/journals/jcr
- Journal of Educational Psychology: https://www.apa.org/pubs/journals/edu
- Journal of Applied Psychology: https://www.apa.org/pubs/journals/apl
- Journal of Communication: https://academic.oup.com/joc
- American Journal of Political Science: https://ajps.org/
- Journal of International Business Studies: https://www.jibs.net/
- Journal of Marketing Research: https://www.ama.org/journal-of-marketing-research/
Natural Sciences
- Journal of Biological Chemistry: https://www.jbc.org/
- Cell: https://www.cell.com/
- Science Advances: https://advances.sciencemag.org/
- Chemical Reviews: https://pubs.acs.org/journal/chreay
- Angewandte Chemie: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/15213765
- Physical Review Letters: https://journals.aps.org/prl/
- Journal of Geophysical Research: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/2156531X
- Journal of High Energy Physics: https://link.springer.com/journal/13130
Engineering/Technology
- IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/RecentIssue.jsp?punumber=5962385
- IEEE Transactions on Power Systems: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/RecentIssue.jsp?punumber=59
- IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/RecentIssue.jsp?punumber=42
- IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/RecentIssue.jsp?punumber=87
- Journal of Engineering Mechanics: https://ascelibrary.org/journal/jenmdt
- Journal of Materials Science: https://www.springer.com/journal/10853
- Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan: https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/browse/jcej
- Journal of Mechanical Design: https://asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/mechanicaldesign
Medical/Health Sciences
- New England Journal of Medicine: https://www.nejm.org/
- The BMJ (formerly British Medical Journal): https://www.bmj.com/
- Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA): https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama
- Annals of Internal Medicine: https://www.acpjournals.org/journal/aim
- American Journal of Epidemiology: https://academic.oup.com/aje
- Journal of Clinical Oncology: https://ascopubs.org/journal/jco
- Journal of Infectious Diseases: https://academic.oup.com/jid
List of Conferences for Research Paper Publications
There are many conferences that accept research papers for publication. The specific conferences you should consider will depend on your field of research. Here are some suggestions for conferences in a few different fields:
Computer Science and Information Technology:
- IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM): https://www.ieee-infocom.org/
- ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Data Communication: https://conferences.sigcomm.org/sigcomm/
- IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP): https://www.ieee-security.org/TC/SP/
- ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS): https://www.sigsac.org/ccs/
- ACM Conference on Human-Computer Interaction (CHI): https://chi2022.acm.org/
Engineering:
- IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA): https://www.ieee-icra.org/
- International Conference on Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (ICMAE): http://www.icmae.org/
- International Conference on Civil and Environmental Engineering (ICCEE): http://www.iccee.org/
- International Conference on Materials Science and Engineering (ICMSE): http://www.icmse.org/
- International Conference on Energy and Power Engineering (ICEPE): http://www.icepe.org/
Natural Sciences:
- American Chemical Society National Meeting & Exposition: https://www.acs.org/content/acs/en/meetings/national-meeting.html
- American Physical Society March Meeting: https://www.aps.org/meetings/march/
- International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology (ICEST): http://www.icest.org/
- International Conference on Natural Science and Environment (ICNSE): http://www.icnse.org/
- International Conference on Life Science and Biological Engineering (LSBE): http://www.lsbe.org/
Social Sciences:
- Annual Meeting of the American Sociological Association (ASA): https://www.asanet.org/annual-meeting-2022
- International Conference on Social Science and Humanities (ICSSH): http://www.icssh.org/
- International Conference on Psychology and Behavioral Sciences (ICPBS): http://www.icpbs.org/
- International Conference on Education and Social Science (ICESS): http://www.icess.org/
- International Conference on Management and Information Science (ICMIS): http://www.icmis.org/
How to Publish a Research Paper in Journal
Publishing a research paper in a journal is a crucial step in disseminating scientific knowledge and contributing to the field. Here are the general steps to follow:
- Choose a research topic : Select a topic of your interest and identify a research question or problem that you want to investigate. Conduct a literature review to identify the gaps in the existing knowledge that your research will address.
- Conduct research : Develop a research plan and methodology to collect data and conduct experiments. Collect and analyze data to draw conclusions that address the research question.
- Write a paper: Organize your findings into a well-structured paper with clear and concise language. Your paper should include an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. Use academic language and provide references for your sources.
- Choose a journal: Choose a journal that is relevant to your research topic and audience. Consider factors such as impact factor, acceptance rate, and the reputation of the journal.
- Follow journal guidelines : Review the submission guidelines and formatting requirements of the journal. Follow the guidelines carefully to ensure that your paper meets the journal’s requirements.
- Submit your paper : Submit your paper to the journal through the online submission system or by email. Include a cover letter that briefly explains the significance of your research and why it is suitable for the journal.
- Wait for reviews: Your paper will be reviewed by experts in the field. Be prepared to address their comments and make revisions to your paper.
- Revise and resubmit: Make revisions to your paper based on the reviewers’ comments and resubmit it to the journal. If your paper is accepted, congratulations! If not, consider revising and submitting it to another journal.
- Address reviewer comments : Reviewers may provide comments and suggestions for revisions to your paper. Address these comments carefully and thoughtfully to improve the quality of your paper.
- Submit the final version: Once your revisions are complete, submit the final version of your paper to the journal. Be sure to follow any additional formatting guidelines and requirements provided by the journal.
- Publication : If your paper is accepted, it will be published in the journal. Some journals provide online publication while others may publish a print version. Be sure to cite your published paper in future research and communicate your findings to the scientific community.
How to Publish a Research Paper for Students
Here are some steps you can follow to publish a research paper as an Under Graduate or a High School Student:
- Select a topic: Choose a topic that is relevant and interesting to you, and that you have a good understanding of.
- Conduct research : Gather information and data on your chosen topic through research, experiments, surveys, or other means.
- Write the paper : Start with an outline, then write the introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion sections of the paper. Be sure to follow any guidelines provided by your instructor or the journal you plan to submit to.
- Edit and revise: Review your paper for errors in spelling, grammar, and punctuation. Ask a peer or mentor to review your paper and provide feedback for improvement.
- Choose a journal : Look for journals that publish papers in your field of study and that are appropriate for your level of research. Some popular journals for students include PLOS ONE, Nature, and Science.
- Submit the paper: Follow the submission guidelines for the journal you choose, which typically include a cover letter, abstract, and formatting requirements. Be prepared to wait several weeks to months for a response.
- Address feedback : If your paper is accepted with revisions, address the feedback from the reviewers and resubmit your paper. If your paper is rejected, review the feedback and consider revising and resubmitting to a different journal.
How to Publish a Research Paper for Free
Publishing a research paper for free can be challenging, but it is possible. Here are some steps you can take to publish your research paper for free:
- Choose a suitable open-access journal: Look for open-access journals that are relevant to your research area. Open-access journals allow readers to access your paper without charge, so your work will be more widely available.
- Check the journal’s reputation : Before submitting your paper, ensure that the journal is reputable by checking its impact factor, publication history, and editorial board.
- Follow the submission guidelines : Every journal has specific guidelines for submitting papers. Make sure to follow these guidelines carefully to increase the chances of acceptance.
- Submit your paper : Once you have completed your research paper, submit it to the journal following their submission guidelines.
- Wait for the review process: Your paper will undergo a peer-review process, where experts in your field will evaluate your work. Be patient during this process, as it can take several weeks or even months.
- Revise your paper : If your paper is rejected, don’t be discouraged. Revise your paper based on the feedback you receive from the reviewers and submit it to another open-access journal.
- Promote your research: Once your paper is published, promote it on social media and other online platforms. This will increase the visibility of your work and help it reach a wider audience.
Journals and Conferences for Free Research Paper publications
Here are the websites of the open-access journals and conferences mentioned:
Open-Access Journals:
- PLOS ONE – https://journals.plos.org/plosone/
- BMC Research Notes – https://bmcresnotes.biomedcentral.com/
- Frontiers in… – https://www.frontiersin.org/
- Journal of Open Research Software – https://openresearchsoftware.metajnl.com/
- PeerJ – https://peerj.com/
Conferences:
- IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM) – https://globecom2022.ieee-globecom.org/
- IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM) – https://infocom2022.ieee-infocom.org/
- IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM) – https://www.ieee-icdm.org/
- ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Data Communication (SIGCOMM) – https://conferences.sigcomm.org/sigcomm/
- ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS) – https://www.sigsac.org/ccs/CCS2022/
Importance of Research Paper Publication
Research paper publication is important for several reasons, both for individual researchers and for the scientific community as a whole. Here are some reasons why:
- Advancing scientific knowledge : Research papers provide a platform for researchers to present their findings and contribute to the body of knowledge in their field. These papers often contain novel ideas, experimental data, and analyses that can help to advance scientific understanding.
- Building a research career : Publishing research papers is an essential component of building a successful research career. Researchers are often evaluated based on the number and quality of their publications, and having a strong publication record can increase one’s chances of securing funding, tenure, or a promotion.
- Peer review and quality control: Publication in a peer-reviewed journal means that the research has been scrutinized by other experts in the field. This peer review process helps to ensure the quality and validity of the research findings.
- Recognition and visibility : Publishing a research paper can bring recognition and visibility to the researchers and their work. It can lead to invitations to speak at conferences, collaborations with other researchers, and media coverage.
- Impact on society : Research papers can have a significant impact on society by informing policy decisions, guiding clinical practice, and advancing technological innovation.
Advantages of Research Paper Publication
There are several advantages to publishing a research paper, including:
- Recognition: Publishing a research paper allows researchers to gain recognition for their work, both within their field and in the academic community as a whole. This can lead to new collaborations, invitations to conferences, and other opportunities to share their research with a wider audience.
- Career advancement : A strong publication record can be an important factor in career advancement, particularly in academia. Publishing research papers can help researchers secure funding, grants, and promotions.
- Dissemination of knowledge : Research papers are an important way to share new findings and ideas with the broader scientific community. By publishing their research, scientists can contribute to the collective body of knowledge in their field and help advance scientific understanding.
- Feedback and peer review : Publishing a research paper allows other experts in the field to provide feedback on the research, which can help improve the quality of the work and identify potential flaws or limitations. Peer review also helps ensure that research is accurate and reliable.
- Citation and impact : Published research papers can be cited by other researchers, which can help increase the impact and visibility of the research. High citation rates can also help establish a researcher’s reputation and credibility within their field.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Limitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

APA Table of Contents – Format and Example

Appendices – Writing Guide, Types and Examples

Research Objectives – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Introduction – Writing Guide and...

Chapter Summary & Overview – Writing Guide...
Unfortunately we don't fully support your browser. If you have the option to, please upgrade to a newer version or use Mozilla Firefox , Microsoft Edge , Google Chrome , or Safari 14 or newer. If you are unable to, and need support, please send us your feedback .
We'd appreciate your feedback. Tell us what you think! opens in new tab/window
7 steps to publishing in a scientific journal
April 5, 2021 | 10 min read
By Aijaz Shaikh, PhD
Before you hit “submit,” here’s a checklist (and pitfalls to avoid)
As scholars, we strive to do high-quality research that will advance science. We come up with what we believe are unique hypotheses, base our work on robust data and use an appropriate research methodology. As we write up our findings, we aim to provide theoretical insight, and share theoretical and practical implications about our work. Then we submit our manuscript for publication in a peer-reviewed journal. For many, this is the hardest part of research. In my seven years of research and teaching, I have observed several shortcomings in the manuscript preparation and submission process that often lead to research being rejected for publication. Being aware of these shortcomings will increase your chances of having your manuscript published and also boost your research profile and career progression.

Dr Aijaz Shaikh gives a presentation.
In this article, intended for doctoral students and other young scholars, I identify common pitfalls and offer helpful solutions to prepare more impactful papers. While there are several types of research articles, such as short communications, review papers and so forth, these guidelines focus on preparing a full article (including a literature review), whether based on qualitative or quantitative methodology, from the perspective of the management, education, information sciences and social sciences disciplines.
Writing for academic journals is a highly competitive activity, and it’s important to understand that there could be several reasons behind a rejection. Furthermore, the journal peer-review process is an essential element of publication because no writer could identify and address all potential issues with a manuscript.
1. Do not rush submitting your article for publication.
In my first article for Elsevier Connect – “Five secrets to surviving (and thriving in) a PhD program” – I emphasized that scholars should start writing during the early stages of your research or doctoral study career. This secret does not entail submitting your manuscript for publication the moment you have crafted its conclusion. Authors sometimes rely on the fact that they will always have an opportunity to address their work’s shortcomings after the feedback received from the journal editor and reviewers has identified them.
A proactive approach and attitude will reduce the chance of rejection and disappointment. In my opinion, a logical flow of activities dominates every research activity and should be followed for preparing a manuscript as well. Such activities include carefully re-reading your manuscript at different times and perhaps at different places. Re-reading is essential in the research field and helps identify the most common problems and shortcomings in the manuscript, which might otherwise be overlooked. Second, I find it very helpful to share my manuscripts with my colleagues and other researchers in my network and to request their feedback. In doing so, I highlight any sections of the manuscript that I would like reviewers to be absolutely clear on.
2. Select an appropriate publication outlet.
I also ask colleagues about the most appropriate journal to submit my manuscript to; finding the right journal for your article can dramatically improve the chances of acceptance and ensure it reaches your target audience.
Elsevier provides an innovative Journal Finder opens in new tab/window search facility on its website. Authors enter the article title, a brief abstract and the field of research to get a list of the most appropriate journals for their article. For a full discussion of how to select an appropriate journal see Knight and Steinbach (2008).
Less experienced scholars sometimes choose to submit their research work to two or more journals at the same time. Research ethics and policies of all scholarly journals suggest that authors should submit a manuscript to only one journal at a time. Doing otherwise can cause embarrassment and lead to copyright problems for the author, the university employer and the journals involved.
3. Read the aims and scope and author guidelines of your target journal carefully.
Once you have read and re-read your manuscript carefully several times, received feedback from your colleagues, and identified a target journal, the next important step is to read the aims and scope of the journals in your target research area. Doing so will improve the chances of having your manuscript accepted for publishing. Another important step is to download and absorb the author guidelines and ensure your manuscript conforms to them. Some publishers report that one paper in five does not follow the style and format requirements of the target journal, which might specify requirements for figures, tables and references.
Rejection can come at different times and in different formats. For instance, if your research objective is not in line with the aims and scope of the target journal, or if your manuscript is not structured and formatted according to the target journal layout, or if your manuscript does not have a reasonable chance of being able to satisfy the target journal’s publishing expectations, the manuscript can receive a desk rejection from the editor without being sent out for peer review. Desk rejections can be disheartening for authors, making them feel they have wasted valuable time and might even cause them to lose enthusiasm for their research topic. Sun and Linton (2014), Hierons (2016) and Craig (2010) offer useful discussions on the subject of “desk rejections.”
4. Make a good first impression with your title and abstract.
The title and abstract are incredibly important components of a manuscript as they are the first elements a journal editor sees. I have been fortunate to receive advice from editors and reviewers on my submissions, and feedback from many colleagues at academic conferences, and this is what I’ve learned:
The title should summarize the main theme of the article and reflect your contribution to the theory.
The abstract should be crafted carefully and encompass the aim and scope of the study; the key problem to be addressed and theory; the method used; the data set; key findings; limitations; and implications for theory and practice.
Dr. Angel Borja goes into detail about these components in “ 11 steps to structuring a science paper editors will take seriously .”
Learn more in Elsevier's free Researcher Academy opens in new tab/window
5. Have a professional editing firm copy-edit (not just proofread) your manuscript, including the main text, list of references, tables and figures.
The key characteristic of scientific writing is clarity. Before submitting a manuscript for publication, it is highly advisable to have a professional editing firm copy-edit your manuscript. An article submitted to a peer-reviewed journal will be scrutinized critically by the editorial board before it is selected for peer review. According to a statistic shared by Elsevier, between 30 percent and 50 percent of articles submitted to Elsevier journals are rejected before they even reach the peer-review stage, and one of the top reasons for rejection is poor language. A properly written, edited and presented text will be error free and understandable and will project a professional image that will help ensure your work is taken seriously in the world of publishing. On occasion, the major revisions conducted at the request of a reviewer will necessitate another round of editing. Authors can facilitate the editing of their manuscripts by taking precautions at their end. These include proofreading their own manuscript for accuracy and wordiness (avoid unnecessary or normative descriptions like “it should be noted here” and “the authors believe) and sending it for editing only when it is complete in all respects and ready for publishing. Professional editing companies charge hefty fees, and it is simply not financially viable to have them conduct multiple rounds of editing on your article. Applications like the spelling and grammar checker in Microsoft Word or Grammarly are certainly worth applying to your article, but the benefits of proper editing are undeniable. For more on the difference between proofreading and editing, see the description in Elsevier’s WebShop.

6. Submit a cover letter with the manuscript.
Never underestimate the importance of a cover letter addressed to the editor or editor-in-chief of the target journal. Last year, I attended a conference in Boston. A “meet the editors” session revealed that many submissions do not include a covering letter, but the editors-in-chief present, who represented renewed and ISI-indexed Elsevier journals, argued that the cover letter gives authors an important opportunity to convince them that their research work is worth reviewing.
Accordingly, the content of the cover letter is also worth spending time on. Some inexperienced scholars paste the article’s abstract into their letter thinking it will be sufficient to make the case for publication; it is a practice best avoided. A good cover letter first outlines the main theme of the paper; second, argues the novelty of the paper; and third, justifies the relevance of the manuscript to the target journal. I would suggest limiting the cover letter to half a page. More importantly, peers and colleagues who read the article and provided feedback before the manuscript’s submission should be acknowledged in the cover letter.
7. Address reviewer comments very carefully.
Editors and editors-in-chief usually couch the acceptance of a manuscript as subject to a “revise and resubmit” based on the recommendations provided by the reviewer or reviewers. These revisions may necessitate either major or minor changes in the manuscript. Inexperienced scholars should understand a few key aspects of the revision process. First, it important to address the revisions diligently; second, is imperative to address all the comments received from the reviewers and avoid oversights; third, the resubmission of the revised manuscript must happen by the deadline provided by the journal; fourth, the revision process might comprise multiple rounds. The revision process requires two major documents. The first is the revised manuscript highlighting all the modifications made following the recommendations received from the reviewers. The second is a letter listing the authors’ responses illustrating they have addressed all the concerns of the reviewers and editors. These two documents should be drafted carefully. The authors of the manuscript can agree or disagree with the comments of the reviewers (typically agreement is encouraged) and are not always obliged to implement their recommendations, but they should in all cases provide a well-argued justification for their course of action.
Given the ever increasing number of manuscripts submitted for publication, the process of preparing a manuscript well enough to have it accepted by a journal can be daunting. High-impact journals accept less than 10 percent of the articles submitted to them, although the acceptance ratio for special issues or special topics sections is normally over 40 percent. Scholars might have to resign themselves to having their articles rejected and then reworking them to submit them to a different journal before the manuscript is accepted.
The advice offered here is not exhaustive but it’s also not difficult to implement. These recommendations require proper attention, planning and careful implementation; however, following this advice could help doctoral students and other scholars improve the likelihood of getting their work published, and that is key to having a productive, exciting and rewarding academic career.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Professor Heikki Karjaluoto, Jyväskylä University School of Business and Economics for providing valuable feedback on this article.
Sun, H., & Linton, J. D. (2014).
Structuring papers for success: Making your paper more like a high impact publication than a desk reject opens in new tab/window
Technovation.
Craig, J. B. (2010).
Desk rejection: How to avoid being hit by a returning boomerang opens in new tab/window
Family Business Review
Hierons, R. M. (2016).
The dreaded desk reject opens in new tab/window
, Software Testing, Verification and Reliability .
Borja, A (2014):
11 steps to structuring a science paper editors will take seriously
Elsevier Connect
Knight, L. V., & Steinbach, T. A. (2008).
Selecting an appropriate publication outlet: a comprehensive model of journal selection criteria for researchers in a broad range of academic disciplines opens in new tab/window
, International Journal of Doctoral Studies .
Tewin, K. (2015).
How to Better Proofread An Article in 6 Simple Steps opens in new tab/window ,
Day, R, & Gastel, B: How to write and publish a scientific paper. Cambridge University Press (2012)
Contributor
Aijaz shaikh, phd.
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience. Learn more about DOAJ’s privacy policy.
Hide this message
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience and security.
The Directory of Open Access Journals
Directory of Open Access Journals
Find open access journals & articles.
Doaj in numbers.
80 languages
135 countries represented
13,738 journals without APCs
20,888 journals
10,433,665 article records
Quick search
About the directory.
DOAJ is a unique and extensive index of diverse open access journals from around the world, driven by a growing community, and is committed to ensuring quality content is freely available online for everyone.
DOAJ is committed to keeping its services free of charge, including being indexed, and its data freely available.
→ About DOAJ
→ How to apply
DOAJ is twenty years old in 2023.
Fund our 20th anniversary campaign
DOAJ is independent. All support is via donations.
82% from academic organisations
18% from contributors
Support DOAJ
Publishers don't need to donate to be part of DOAJ.
News Service
Meet the doaj team: head of editorial and deputy head of editorial (quality), vacancy: operations manager, press release: pubscholar joins the movement to support the directory of open access journals, new major version of the api to be released.
→ All blog posts
We would not be able to work without our volunteers, such as these top-performing editors and associate editors.
→ Meet our volunteers
Librarianship, Scholarly Publishing, Data Management
Brisbane, Australia (Chinese, English)
Adana, Türkiye (Turkish, English)
Humanities, Social Sciences
Natalia Pamuła
Toruń, Poland (Polish, English)
Medical Sciences, Nutrition
Pablo Hernandez
Caracas, Venezuela (Spanish, English)
Research Evaluation
Paola Galimberti
Milan, Italy (Italian, German, English)
Social Sciences, Humanities
Dawam M. Rohmatulloh
Ponorogo, Indonesia (Bahasa Indonesia, English, Dutch)
Systematic Entomology
Kadri Kıran
Edirne, Türkiye (English, Turkish, German)
Library and Information Science
Nataliia Kaliuzhna
Kyiv, Ukraine (Ukrainian, Russian, English, Polish)
WeChat QR code

- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write and Publish Your Research in a Journal
Last Updated: May 26, 2024 Fact Checked
Choosing a Journal
Writing the research paper, editing & revising your paper, submitting your paper, navigating the peer review process, research paper help.
This article was co-authored by Matthew Snipp, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Cheyenne Main . C. Matthew Snipp is the Burnet C. and Mildred Finley Wohlford Professor of Humanities and Sciences in the Department of Sociology at Stanford University. He is also the Director for the Institute for Research in the Social Science’s Secure Data Center. He has been a Research Fellow at the U.S. Bureau of the Census and a Fellow at the Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences. He has published 3 books and over 70 articles and book chapters on demography, economic development, poverty and unemployment. He is also currently serving on the National Institute of Child Health and Development’s Population Science Subcommittee. He holds a Ph.D. in Sociology from the University of Wisconsin—Madison. There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 706,683 times.
Publishing a research paper in a peer-reviewed journal allows you to network with other scholars, get your name and work into circulation, and further refine your ideas and research. Before submitting your paper, make sure it reflects all the work you’ve done and have several people read over it and make comments. Keep reading to learn how you can choose a journal, prepare your work for publication, submit it, and revise it after you get a response back.
Things You Should Know
- Create a list of journals you’d like to publish your work in and choose one that best aligns with your topic and your desired audience.
- Prepare your manuscript using the journal’s requirements and ask at least 2 professors or supervisors to review your paper.
- Write a cover letter that “sells” your manuscript, says how your research adds to your field and explains why you chose the specific journal you’re submitting to.

- Ask your professors or supervisors for well-respected journals that they’ve had good experiences publishing with and that they read regularly.
- Many journals also only accept specific formats, so by choosing a journal before you start, you can write your article to their specifications and increase your chances of being accepted.
- If you’ve already written a paper you’d like to publish, consider whether your research directly relates to a hot topic or area of research in the journals you’re looking into.

- Review the journal’s peer review policies and submission process to see if you’re comfortable creating or adjusting your work according to their standards.
- Open-access journals can increase your readership because anyone can access them.

- Scientific research papers: Instead of a “thesis,” you might write a “research objective” instead. This is where you state the purpose of your research.
- “This paper explores how George Washington’s experiences as a young officer may have shaped his views during difficult circumstances as a commanding officer.”
- “This paper contends that George Washington’s experiences as a young officer on the 1750s Pennsylvania frontier directly impacted his relationship with his Continental Army troops during the harsh winter at Valley Forge.”

- Scientific research papers: Include a “materials and methods” section with the step-by-step process you followed and the materials you used. [5] X Research source
- Read other research papers in your field to see how they’re written. Their format, writing style, subject matter, and vocabulary can help guide your own paper. [6] X Research source

- If you’re writing about George Washington’s experiences as a young officer, you might emphasize how this research changes our perspective of the first president of the U.S.
- Link this section to your thesis or research objective.
- If you’re writing a paper about ADHD, you might discuss other applications for your research.

- Scientific research papers: You might include your research and/or analytical methods, your main findings or results, and the significance or implications of your research.
- Try to get as many people as you can to read over your abstract and provide feedback before you submit your paper to a journal.

- They might also provide templates to help you structure your manuscript according to their specific guidelines. [11] X Research source

- Not all journal reviewers will be experts on your specific topic, so a non-expert “outsider’s perspective” can be valuable.

- If you have a paper on the purification of wastewater with fungi, you might use both the words “fungi” and “mushrooms.”
- Use software like iThenticate, Turnitin, or PlagScan to check for similarities between the submitted article and published material available online. [15] X Research source

- Header: Address the editor who will be reviewing your manuscript by their name, include the date of submission, and the journal you are submitting to.
- First paragraph: Include the title of your manuscript, the type of paper it is (like review, research, or case study), and the research question you wanted to answer and why.
- Second paragraph: Explain what was done in your research, your main findings, and why they are significant to your field.
- Third paragraph: Explain why the journal’s readers would be interested in your work and why your results are important to your field.
- Conclusion: State the author(s) and any journal requirements that your work complies with (like ethical standards”).
- “We confirm that this manuscript has not been published elsewhere and is not under consideration by another journal.”
- “All authors have approved the manuscript and agree with its submission to [insert the name of the target journal].”

- Submit your article to only one journal at a time.
- When submitting online, use your university email account. This connects you with a scholarly institution, which can add credibility to your work.

- Accept: Only minor adjustments are needed, based on the provided feedback by the reviewers. A first submission will rarely be accepted without any changes needed.
- Revise and Resubmit: Changes are needed before publication can be considered, but the journal is still very interested in your work.
- Reject and Resubmit: Extensive revisions are needed. Your work may not be acceptable for this journal, but they might also accept it if significant changes are made.
- Reject: The paper isn’t and won’t be suitable for this publication, but that doesn’t mean it might not work for another journal.

- Try organizing the reviewer comments by how easy it is to address them. That way, you can break your revisions down into more manageable parts.
- If you disagree with a comment made by a reviewer, try to provide an evidence-based explanation when you resubmit your paper.

- If you’re resubmitting your paper to the same journal, include a point-by-point response paper that talks about how you addressed all of the reviewers’ comments in your revision. [22] X Research source
- If you’re not sure which journal to submit to next, you might be able to ask the journal editor which publications they recommend.

Expert Q&A
You might also like.

- If reviewers suspect that your submitted manuscript plagiarizes another work, they may refer to a Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) flowchart to see how to move forward. [23] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- ↑ https://www.wiley.com/en-us/network/publishing/research-publishing/choosing-a-journal/6-steps-to-choosing-the-right-journal-for-your-research-infographic
- ↑ https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
- ↑ https://libguides.unomaha.edu/c.php?g=100510&p=651627
- ↑ https://www.canberra.edu.au/library/start-your-research/research_help/publishing-research
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/conclusions
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/writing-an-abstract-for-your-research-paper/
- ↑ https://www.springer.com/gp/authors-editors/book-authors-editors/your-publication-journey/manuscript-preparation
- ↑ https://apus.libanswers.com/writing/faq/2391
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/library/keyword/search-strategy
- ↑ https://ifis.libguides.com/journal-publishing-guide/submitting-your-paper
- ↑ https://www.springer.com/kr/authors-editors/authorandreviewertutorials/submitting-to-a-journal-and-peer-review/cover-letters/10285574
- ↑ https://www.apa.org/monitor/sep02/publish.aspx
- ↑ Matthew Snipp, PhD. Research Fellow, U.S. Bureau of the Census. Expert Interview. 26 March 2020.
About This Article

To publish a research paper, ask a colleague or professor to review your paper and give you feedback. Once you've revised your work, familiarize yourself with different academic journals so that you can choose the publication that best suits your paper. Make sure to look at the "Author's Guide" so you can format your paper according to the guidelines for that publication. Then, submit your paper and don't get discouraged if it is not accepted right away. You may need to revise your paper and try again. To learn about the different responses you might get from journals, see our reviewer's explanation below. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
RAMDEV GOHIL
Oct 16, 2017
Did this article help you?
David Okandeji
Oct 23, 2019
Revati Joshi
Feb 13, 2017
Shahzad Khan
Jul 1, 2017
Apr 7, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Journals By Subject | Journals A - Z
Architecture / Design
Biomedicine, business and management, computer science, earth sciences, engineering, environment, life sciences, materials science, mathematics, medicine & public health, science, humanities and social sciences, multidisciplinary, social sciences.
Browse article collections by subject.
- Built Heritage
- Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology
- Future Business Journal
- International Journal of Corporate Social Responsibility
- Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship
- Journal of Shipping and Trade
- Schmalenbach Journal of Business Research
- Applied Biological Chemistry
- Bioresources and Bioprocessing
- Fashion and Textiles
- Journal of Analytical Science and Technology
- Journal of Umm Al-Qura University for Applied Sciences
- Applied Network Science
- Brain Informatics
- Cybersecurity
- Energy Informatics
- EPJ Data Science
- International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education
- Journal of Big Data
- Journal of Cloud Computing
- Visual Computing for Industry, Biomedicine, and Art
- International Journal of Implant Dentistry
- Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Progress in Orthodontics
- Earth, Planets and Space
- Geoscience Letters
- Geothermal Energy
- Progress in Earth and Planetary Science
- Swiss Journal of Geosciences
- Swiss Journal of Palaeontology
- Agricultural and Food Economics
- Financial Innovation
- Journal for Labour Market Research
- Journal of Economic Structures
- Marine Development
- Swiss Journal of Economics and Statistics
- Asian-Pacific Journal of Second and Foreign Language Education
- Disciplinary and Interdisciplinary Science Education Research
- Empirical Research in Vocational Education and Training
- International Journal of Child Care and Education Policy
- International Journal of STEM Education
- Language Testing in Asia
- Large-scale Assessments in Education
- Smart Learning Environments
- Sustainable Energy Research
- Advanced Modeling and Simulation in Engineering Sciences
- Advances in Aerodynamics
- Advances in Bridge Engineering
- AI Perspectives & Advances
- Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering
- EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing
- EURASIP Journal on Audio, Speech, and Music Processing
- EURASIP Journal on Image and Video Processing
- EURASIP Journal on Information Security
- EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking
- European Transport Research Review
- International Journal of Concrete Structures and Materials
- Journal of Electrical Systems and Information Technology
- Journal of Engineering and Applied Science
- Journal of Infrastructure Preservation and Resilience
- Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Engineering
- Journal of Umm Al-Qura University for Engineering and Architecture
- Micro and Nano Systems Letters
- Moore and More
- ROBOMECH Journal
- Satellite Navigation
- Ecological Processes
- Environmental Sciences Europe
- Environmental Systems Research
- Geoenvironmental Disasters
- City, Territory and Architecture
- European Journal of Futures Research
- Journal of International Humanitarian Action
- AMB Express
- Botanical Studies
- Cell Regeneration
- Chemical and Biological Technologies in Agriculture
- Egyptian Journal of Biological Pest Control
- Fire Ecology
- Horticulture Advances
- Journal of Wood Science
- Natural Products and Bioprospecting
- The Journal of Basic and Applied Zoology
- Applied Microscopy
- Collagen and Leather
- Functional Composite Materials
- Heritage Science
- Journal of Materials Science: Materials Theory
- Microplastics and Nanoplastics
- Nano Convergence
- Advances in Continuous and Discrete Models
- Boundary Value Problems
- Fixed Point Theory and Algorithms for Sciences and Engineering
- Journal of Inequalities and Applications
- Journal of Mathematics in Industry
- African Journal of Urology
- Annals of Intensive Care
- Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences
- Blood Research
- Bulletin of Faculty of Physical Therapy
- Clinical Phytoscience
- CVIR Endovascular Open peer review
- Egyptian Journal of Forensic Sciences
- Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics
- Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery
- Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine
- Egyptian Liver Journal
- Egyptian Pediatric Association Gazette
- Egyptian Rheumatology and Rehabilitation
- EJNMMI Physics
- EJNMMI Radiopharmacy and Chemistry
- EJNMMI Reports
- EJNMMI Research
- European Radiology Experimental
- Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences
- Insights into Imaging
- Intensive Care Medicine Experimental
- International Journal of Bipolar Disorders
- JA Clinical Reports
- Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection
- Journal of Orthopaedics and Traumatology
- Journal of Patient-Reported Outcomes
- Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute
- Journal of the Egyptian Public Health Association
- Middle East Current Psychiatry
- Middle East Fertility Society Journal
- Molecular and Cellular Pediatrics
- Sports Medicine - Open
- Surgical Case Reports
- The Cardiothoracic Surgeon
- The Egyptian Heart Journal
- The Egyptian Journal of Bronchology
- The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine
- The Egyptian Journal of Neurology, Psychiatry and Neurosurgery
- The Egyptian Journal of Otolaryngology
- The Ultrasound Journal
- eLight Transparent peer review
- EPJ Quantum Technology
- EPJ Techniques and Instrumentation
- Surface Science and Technology
- Cognitive Research: Principles and Implications
- Psicologia: Reflexão e Crítica
- Bulletin of the National Research Centre
- Comparative Migration Studies
- International Journal of Anthropology and Ethnology
- The Journal of Chinese Sociology

Explore millions of high-quality primary sources and images from around the world, including artworks, maps, photographs, and more.
Explore migration issues through a variety of media types
- Part of The Streets are Talking: Public Forms of Creative Expression from Around the World
- Part of The Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 34, No. 1 (Winter 2020)
- Part of Cato Institute (Aug. 3, 2021)
- Part of University of California Press
- Part of Open: Smithsonian National Museum of African American History & Culture
- Part of Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Winter 2012)
- Part of R Street Institute (Nov. 1, 2020)
- Part of Leuven University Press
- Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016)
- Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 (August 2018)
- Part of Leveraging Lives: Serbia and Illegal Tunisian Migration to Europe, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (Mar. 1, 2023)
- Part of UCL Press
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR.
Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals.
Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world’s leading museums, archives, and scholars.
- Submit Paper
- Check Paper Status
- Download Certificate/Paper

- --> --> --> --> --> E-mail [email protected] --> -->