

Chapter 11. Interviewing
Introduction.
Interviewing people is at the heart of qualitative research. It is not merely a way to collect data but an intrinsically rewarding activity—an interaction between two people that holds the potential for greater understanding and interpersonal development. Unlike many of our daily interactions with others that are fairly shallow and mundane, sitting down with a person for an hour or two and really listening to what they have to say is a profound and deep enterprise, one that can provide not only “data” for you, the interviewer, but also self-understanding and a feeling of being heard for the interviewee. I always approach interviewing with a deep appreciation for the opportunity it gives me to understand how other people experience the world. That said, there is not one kind of interview but many, and some of these are shallower than others. This chapter will provide you with an overview of interview techniques but with a special focus on the in-depth semistructured interview guide approach, which is the approach most widely used in social science research.
An interview can be variously defined as “a conversation with a purpose” ( Lune and Berg 2018 ) and an attempt to understand the world from the point of view of the person being interviewed: “to unfold the meaning of peoples’ experiences, to uncover their lived world prior to scientific explanations” ( Kvale 2007 ). It is a form of active listening in which the interviewer steers the conversation to subjects and topics of interest to their research but also manages to leave enough space for those interviewed to say surprising things. Achieving that balance is a tricky thing, which is why most practitioners believe interviewing is both an art and a science. In my experience as a teacher, there are some students who are “natural” interviewers (often they are introverts), but anyone can learn to conduct interviews, and everyone, even those of us who have been doing this for years, can improve their interviewing skills. This might be a good time to highlight the fact that the interview is a product between interviewer and interviewee and that this product is only as good as the rapport established between the two participants. Active listening is the key to establishing this necessary rapport.
Patton ( 2002 ) makes the argument that we use interviews because there are certain things that are not observable. In particular, “we cannot observe feelings, thoughts, and intentions. We cannot observe behaviors that took place at some previous point in time. We cannot observe situations that preclude the presence of an observer. We cannot observe how people have organized the world and the meanings they attach to what goes on in the world. We have to ask people questions about those things” ( 341 ).
Types of Interviews
There are several distinct types of interviews. Imagine a continuum (figure 11.1). On one side are unstructured conversations—the kind you have with your friends. No one is in control of those conversations, and what you talk about is often random—whatever pops into your head. There is no secret, underlying purpose to your talking—if anything, the purpose is to talk to and engage with each other, and the words you use and the things you talk about are a little beside the point. An unstructured interview is a little like this informal conversation, except that one of the parties to the conversation (you, the researcher) does have an underlying purpose, and that is to understand the other person. You are not friends speaking for no purpose, but it might feel just as unstructured to the “interviewee” in this scenario. That is one side of the continuum. On the other side are fully structured and standardized survey-type questions asked face-to-face. Here it is very clear who is asking the questions and who is answering them. This doesn’t feel like a conversation at all! A lot of people new to interviewing have this ( erroneously !) in mind when they think about interviews as data collection. Somewhere in the middle of these two extreme cases is the “ semistructured” interview , in which the researcher uses an “interview guide” to gently move the conversation to certain topics and issues. This is the primary form of interviewing for qualitative social scientists and will be what I refer to as interviewing for the rest of this chapter, unless otherwise specified.
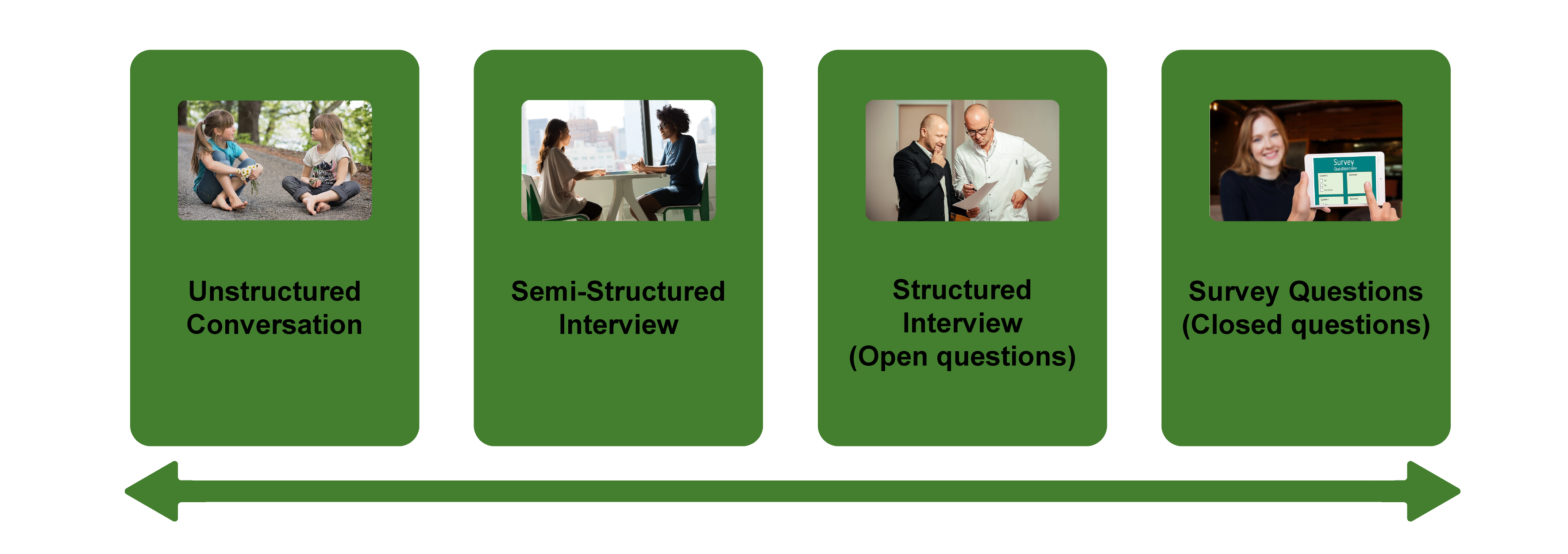
Informal (unstructured conversations). This is the most “open-ended” approach to interviewing. It is particularly useful in conjunction with observational methods (see chapters 13 and 14). There are no predetermined questions. Each interview will be different. Imagine you are researching the Oregon Country Fair, an annual event in Veneta, Oregon, that includes live music, artisan craft booths, face painting, and a lot of people walking through forest paths. It’s unlikely that you will be able to get a person to sit down with you and talk intensely about a set of questions for an hour and a half. But you might be able to sidle up to several people and engage with them about their experiences at the fair. You might have a general interest in what attracts people to these events, so you could start a conversation by asking strangers why they are here or why they come back every year. That’s it. Then you have a conversation that may lead you anywhere. Maybe one person tells a long story about how their parents brought them here when they were a kid. A second person talks about how this is better than Burning Man. A third person shares their favorite traveling band. And yet another enthuses about the public library in the woods. During your conversations, you also talk about a lot of other things—the weather, the utilikilts for sale, the fact that a favorite food booth has disappeared. It’s all good. You may not be able to record these conversations. Instead, you might jot down notes on the spot and then, when you have the time, write down as much as you can remember about the conversations in long fieldnotes. Later, you will have to sit down with these fieldnotes and try to make sense of all the information (see chapters 18 and 19).
Interview guide ( semistructured interview ). This is the primary type employed by social science qualitative researchers. The researcher creates an “interview guide” in advance, which she uses in every interview. In theory, every person interviewed is asked the same questions. In practice, every person interviewed is asked mostly the same topics but not always the same questions, as the whole point of a “guide” is that it guides the direction of the conversation but does not command it. The guide is typically between five and ten questions or question areas, sometimes with suggested follow-ups or prompts . For example, one question might be “What was it like growing up in Eastern Oregon?” with prompts such as “Did you live in a rural area? What kind of high school did you attend?” to help the conversation develop. These interviews generally take place in a quiet place (not a busy walkway during a festival) and are recorded. The recordings are transcribed, and those transcriptions then become the “data” that is analyzed (see chapters 18 and 19). The conventional length of one of these types of interviews is between one hour and two hours, optimally ninety minutes. Less than one hour doesn’t allow for much development of questions and thoughts, and two hours (or more) is a lot of time to ask someone to sit still and answer questions. If you have a lot of ground to cover, and the person is willing, I highly recommend two separate interview sessions, with the second session being slightly shorter than the first (e.g., ninety minutes the first day, sixty minutes the second). There are lots of good reasons for this, but the most compelling one is that this allows you to listen to the first day’s recording and catch anything interesting you might have missed in the moment and so develop follow-up questions that can probe further. This also allows the person being interviewed to have some time to think about the issues raised in the interview and go a little deeper with their answers.
Standardized questionnaire with open responses ( structured interview ). This is the type of interview a lot of people have in mind when they hear “interview”: a researcher comes to your door with a clipboard and proceeds to ask you a series of questions. These questions are all the same whoever answers the door; they are “standardized.” Both the wording and the exact order are important, as people’s responses may vary depending on how and when a question is asked. These are qualitative only in that the questions allow for “open-ended responses”: people can say whatever they want rather than select from a predetermined menu of responses. For example, a survey I collaborated on included this open-ended response question: “How does class affect one’s career success in sociology?” Some of the answers were simply one word long (e.g., “debt”), and others were long statements with stories and personal anecdotes. It is possible to be surprised by the responses. Although it’s a stretch to call this kind of questioning a conversation, it does allow the person answering the question some degree of freedom in how they answer.
Survey questionnaire with closed responses (not an interview!). Standardized survey questions with specific answer options (e.g., closed responses) are not really interviews at all, and they do not generate qualitative data. For example, if we included five options for the question “How does class affect one’s career success in sociology?”—(1) debt, (2) social networks, (3) alienation, (4) family doesn’t understand, (5) type of grad program—we leave no room for surprises at all. Instead, we would most likely look at patterns around these responses, thinking quantitatively rather than qualitatively (e.g., using regression analysis techniques, we might find that working-class sociologists were twice as likely to bring up alienation). It can sometimes be confusing for new students because the very same survey can include both closed-ended and open-ended questions. The key is to think about how these will be analyzed and to what level surprises are possible. If your plan is to turn all responses into a number and make predictions about correlations and relationships, you are no longer conducting qualitative research. This is true even if you are conducting this survey face-to-face with a real live human. Closed-response questions are not conversations of any kind, purposeful or not.
In summary, the semistructured interview guide approach is the predominant form of interviewing for social science qualitative researchers because it allows a high degree of freedom of responses from those interviewed (thus allowing for novel discoveries) while still maintaining some connection to a research question area or topic of interest. The rest of the chapter assumes the employment of this form.
Creating an Interview Guide
Your interview guide is the instrument used to bridge your research question(s) and what the people you are interviewing want to tell you. Unlike a standardized questionnaire, the questions actually asked do not need to be exactly what you have written down in your guide. The guide is meant to create space for those you are interviewing to talk about the phenomenon of interest, but sometimes you are not even sure what that phenomenon is until you start asking questions. A priority in creating an interview guide is to ensure it offers space. One of the worst mistakes is to create questions that are so specific that the person answering them will not stray. Relatedly, questions that sound “academic” will shut down a lot of respondents. A good interview guide invites respondents to talk about what is important to them, not feel like they are performing or being evaluated by you.
Good interview questions should not sound like your “research question” at all. For example, let’s say your research question is “How do patriarchal assumptions influence men’s understanding of climate change and responses to climate change?” It would be worse than unhelpful to ask a respondent, “How do your assumptions about the role of men affect your understanding of climate change?” You need to unpack this into manageable nuggets that pull your respondent into the area of interest without leading him anywhere. You could start by asking him what he thinks about climate change in general. Or, even better, whether he has any concerns about heatwaves or increased tornadoes or polar icecaps melting. Once he starts talking about that, you can ask follow-up questions that bring in issues around gendered roles, perhaps asking if he is married (to a woman) and whether his wife shares his thoughts and, if not, how they negotiate that difference. The fact is, you won’t really know the right questions to ask until he starts talking.
There are several distinct types of questions that can be used in your interview guide, either as main questions or as follow-up probes. If you remember that the point is to leave space for the respondent, you will craft a much more effective interview guide! You will also want to think about the place of time in both the questions themselves (past, present, future orientations) and the sequencing of the questions.
Researcher Note
Suggestion : As you read the next three sections (types of questions, temporality, question sequence), have in mind a particular research question, and try to draft questions and sequence them in a way that opens space for a discussion that helps you answer your research question.
Type of Questions
Experience and behavior questions ask about what a respondent does regularly (their behavior) or has done (their experience). These are relatively easy questions for people to answer because they appear more “factual” and less subjective. This makes them good opening questions. For the study on climate change above, you might ask, “Have you ever experienced an unusual weather event? What happened?” Or “You said you work outside? What is a typical summer workday like for you? How do you protect yourself from the heat?”
Opinion and values questions , in contrast, ask questions that get inside the minds of those you are interviewing. “Do you think climate change is real? Who or what is responsible for it?” are two such questions. Note that you don’t have to literally ask, “What is your opinion of X?” but you can find a way to ask the specific question relevant to the conversation you are having. These questions are a bit trickier to ask because the answers you get may depend in part on how your respondent perceives you and whether they want to please you or not. We’ve talked a fair amount about being reflective. Here is another place where this comes into play. You need to be aware of the effect your presence might have on the answers you are receiving and adjust accordingly. If you are a woman who is perceived as liberal asking a man who identifies as conservative about climate change, there is a lot of subtext that can be going on in the interview. There is no one right way to resolve this, but you must at least be aware of it.
Feeling questions are questions that ask respondents to draw on their emotional responses. It’s pretty common for academic researchers to forget that we have bodies and emotions, but people’s understandings of the world often operate at this affective level, sometimes unconsciously or barely consciously. It is a good idea to include questions that leave space for respondents to remember, imagine, or relive emotional responses to particular phenomena. “What was it like when you heard your cousin’s house burned down in that wildfire?” doesn’t explicitly use any emotion words, but it allows your respondent to remember what was probably a pretty emotional day. And if they respond emotionally neutral, that is pretty interesting data too. Note that asking someone “How do you feel about X” is not always going to evoke an emotional response, as they might simply turn around and respond with “I think that…” It is better to craft a question that actually pushes the respondent into the affective category. This might be a specific follow-up to an experience and behavior question —for example, “You just told me about your daily routine during the summer heat. Do you worry it is going to get worse?” or “Have you ever been afraid it will be too hot to get your work accomplished?”
Knowledge questions ask respondents what they actually know about something factual. We have to be careful when we ask these types of questions so that respondents do not feel like we are evaluating them (which would shut them down), but, for example, it is helpful to know when you are having a conversation about climate change that your respondent does in fact know that unusual weather events have increased and that these have been attributed to climate change! Asking these questions can set the stage for deeper questions and can ensure that the conversation makes the same kind of sense to both participants. For example, a conversation about political polarization can be put back on track once you realize that the respondent doesn’t really have a clear understanding that there are two parties in the US. Instead of asking a series of questions about Republicans and Democrats, you might shift your questions to talk more generally about political disagreements (e.g., “people against abortion”). And sometimes what you do want to know is the level of knowledge about a particular program or event (e.g., “Are you aware you can discharge your student loans through the Public Service Loan Forgiveness program?”).
Sensory questions call on all senses of the respondent to capture deeper responses. These are particularly helpful in sparking memory. “Think back to your childhood in Eastern Oregon. Describe the smells, the sounds…” Or you could use these questions to help a person access the full experience of a setting they customarily inhabit: “When you walk through the doors to your office building, what do you see? Hear? Smell?” As with feeling questions , these questions often supplement experience and behavior questions . They are another way of allowing your respondent to report fully and deeply rather than remain on the surface.
Creative questions employ illustrative examples, suggested scenarios, or simulations to get respondents to think more deeply about an issue, topic, or experience. There are many options here. In The Trouble with Passion , Erin Cech ( 2021 ) provides a scenario in which “Joe” is trying to decide whether to stay at his decent but boring computer job or follow his passion by opening a restaurant. She asks respondents, “What should Joe do?” Their answers illuminate the attraction of “passion” in job selection. In my own work, I have used a news story about an upwardly mobile young man who no longer has time to see his mother and sisters to probe respondents’ feelings about the costs of social mobility. Jessi Streib and Betsy Leondar-Wright have used single-page cartoon “scenes” to elicit evaluations of potential racial discrimination, sexual harassment, and classism. Barbara Sutton ( 2010 ) has employed lists of words (“strong,” “mother,” “victim”) on notecards she fans out and asks her female respondents to select and discuss.
Background/Demographic Questions
You most definitely will want to know more about the person you are interviewing in terms of conventional demographic information, such as age, race, gender identity, occupation, and educational attainment. These are not questions that normally open up inquiry. [1] For this reason, my practice has been to include a separate “demographic questionnaire” sheet that I ask each respondent to fill out at the conclusion of the interview. Only include those aspects that are relevant to your study. For example, if you are not exploring religion or religious affiliation, do not include questions about a person’s religion on the demographic sheet. See the example provided at the end of this chapter.
Temporality
Any type of question can have a past, present, or future orientation. For example, if you are asking a behavior question about workplace routine, you might ask the respondent to talk about past work, present work, and ideal (future) work. Similarly, if you want to understand how people cope with natural disasters, you might ask your respondent how they felt then during the wildfire and now in retrospect and whether and to what extent they have concerns for future wildfire disasters. It’s a relatively simple suggestion—don’t forget to ask about past, present, and future—but it can have a big impact on the quality of the responses you receive.
Question Sequence
Having a list of good questions or good question areas is not enough to make a good interview guide. You will want to pay attention to the order in which you ask your questions. Even though any one respondent can derail this order (perhaps by jumping to answer a question you haven’t yet asked), a good advance plan is always helpful. When thinking about sequence, remember that your goal is to get your respondent to open up to you and to say things that might surprise you. To establish rapport, it is best to start with nonthreatening questions. Asking about the present is often the safest place to begin, followed by the past (they have to know you a little bit to get there), and lastly, the future (talking about hopes and fears requires the most rapport). To allow for surprises, it is best to move from very general questions to more particular questions only later in the interview. This ensures that respondents have the freedom to bring up the topics that are relevant to them rather than feel like they are constrained to answer you narrowly. For example, refrain from asking about particular emotions until these have come up previously—don’t lead with them. Often, your more particular questions will emerge only during the course of the interview, tailored to what is emerging in conversation.
Once you have a set of questions, read through them aloud and imagine you are being asked the same questions. Does the set of questions have a natural flow? Would you be willing to answer the very first question to a total stranger? Does your sequence establish facts and experiences before moving on to opinions and values? Did you include prefatory statements, where necessary; transitions; and other announcements? These can be as simple as “Hey, we talked a lot about your experiences as a barista while in college.… Now I am turning to something completely different: how you managed friendships in college.” That is an abrupt transition, but it has been softened by your acknowledgment of that.
Probes and Flexibility
Once you have the interview guide, you will also want to leave room for probes and follow-up questions. As in the sample probe included here, you can write out the obvious probes and follow-up questions in advance. You might not need them, as your respondent might anticipate them and include full responses to the original question. Or you might need to tailor them to how your respondent answered the question. Some common probes and follow-up questions include asking for more details (When did that happen? Who else was there?), asking for elaboration (Could you say more about that?), asking for clarification (Does that mean what I think it means or something else? I understand what you mean, but someone else reading the transcript might not), and asking for contrast or comparison (How did this experience compare with last year’s event?). “Probing is a skill that comes from knowing what to look for in the interview, listening carefully to what is being said and what is not said, and being sensitive to the feedback needs of the person being interviewed” ( Patton 2002:374 ). It takes work! And energy. I and many other interviewers I know report feeling emotionally and even physically drained after conducting an interview. You are tasked with active listening and rearranging your interview guide as needed on the fly. If you only ask the questions written down in your interview guide with no deviations, you are doing it wrong. [2]
The Final Question
Every interview guide should include a very open-ended final question that allows for the respondent to say whatever it is they have been dying to tell you but you’ve forgotten to ask. About half the time they are tired too and will tell you they have nothing else to say. But incredibly, some of the most honest and complete responses take place here, at the end of a long interview. You have to realize that the person being interviewed is often discovering things about themselves as they talk to you and that this process of discovery can lead to new insights for them. Making space at the end is therefore crucial. Be sure you convey that you actually do want them to tell you more, that the offer of “anything else?” is not read as an empty convention where the polite response is no. Here is where you can pull from that active listening and tailor the final question to the particular person. For example, “I’ve asked you a lot of questions about what it was like to live through that wildfire. I’m wondering if there is anything I’ve forgotten to ask, especially because I haven’t had that experience myself” is a much more inviting final question than “Great. Anything you want to add?” It’s also helpful to convey to the person that you have the time to listen to their full answer, even if the allotted time is at the end. After all, there are no more questions to ask, so the respondent knows exactly how much time is left. Do them the courtesy of listening to them!
Conducting the Interview
Once you have your interview guide, you are on your way to conducting your first interview. I always practice my interview guide with a friend or family member. I do this even when the questions don’t make perfect sense for them, as it still helps me realize which questions make no sense, are poorly worded (too academic), or don’t follow sequentially. I also practice the routine I will use for interviewing, which goes something like this:
- Introduce myself and reintroduce the study
- Provide consent form and ask them to sign and retain/return copy
- Ask if they have any questions about the study before we begin
- Ask if I can begin recording
- Ask questions (from interview guide)
- Turn off the recording device
- Ask if they are willing to fill out my demographic questionnaire
- Collect questionnaire and, without looking at the answers, place in same folder as signed consent form
- Thank them and depart
A note on remote interviewing: Interviews have traditionally been conducted face-to-face in a private or quiet public setting. You don’t want a lot of background noise, as this will make transcriptions difficult. During the recent global pandemic, many interviewers, myself included, learned the benefits of interviewing remotely. Although face-to-face is still preferable for many reasons, Zoom interviewing is not a bad alternative, and it does allow more interviews across great distances. Zoom also includes automatic transcription, which significantly cuts down on the time it normally takes to convert our conversations into “data” to be analyzed. These automatic transcriptions are not perfect, however, and you will still need to listen to the recording and clarify and clean up the transcription. Nor do automatic transcriptions include notations of body language or change of tone, which you may want to include. When interviewing remotely, you will want to collect the consent form before you meet: ask them to read, sign, and return it as an email attachment. I think it is better to ask for the demographic questionnaire after the interview, but because some respondents may never return it then, it is probably best to ask for this at the same time as the consent form, in advance of the interview.
What should you bring to the interview? I would recommend bringing two copies of the consent form (one for you and one for the respondent), a demographic questionnaire, a manila folder in which to place the signed consent form and filled-out demographic questionnaire, a printed copy of your interview guide (I print with three-inch right margins so I can jot down notes on the page next to relevant questions), a pen, a recording device, and water.
After the interview, you will want to secure the signed consent form in a locked filing cabinet (if in print) or a password-protected folder on your computer. Using Excel or a similar program that allows tables/spreadsheets, create an identifying number for your interview that links to the consent form without using the name of your respondent. For example, let’s say that I conduct interviews with US politicians, and the first person I meet with is George W. Bush. I will assign the transcription the number “INT#001” and add it to the signed consent form. [3] The signed consent form goes into a locked filing cabinet, and I never use the name “George W. Bush” again. I take the information from the demographic sheet, open my Excel spreadsheet, and add the relevant information in separate columns for the row INT#001: White, male, Republican. When I interview Bill Clinton as my second interview, I include a second row: INT#002: White, male, Democrat. And so on. The only link to the actual name of the respondent and this information is the fact that the consent form (unavailable to anyone but me) has stamped on it the interview number.
Many students get very nervous before their first interview. Actually, many of us are always nervous before the interview! But do not worry—this is normal, and it does pass. Chances are, you will be pleasantly surprised at how comfortable it begins to feel. These “purposeful conversations” are often a delight for both participants. This is not to say that sometimes things go wrong. I often have my students practice several “bad scenarios” (e.g., a respondent that you cannot get to open up; a respondent who is too talkative and dominates the conversation, steering it away from the topics you are interested in; emotions that completely take over; or shocking disclosures you are ill-prepared to handle), but most of the time, things go quite well. Be prepared for the unexpected, but know that the reason interviews are so popular as a technique of data collection is that they are usually richly rewarding for both participants.
One thing that I stress to my methods students and remind myself about is that interviews are still conversations between people. If there’s something you might feel uncomfortable asking someone about in a “normal” conversation, you will likely also feel a bit of discomfort asking it in an interview. Maybe more importantly, your respondent may feel uncomfortable. Social research—especially about inequality—can be uncomfortable. And it’s easy to slip into an abstract, intellectualized, or removed perspective as an interviewer. This is one reason trying out interview questions is important. Another is that sometimes the question sounds good in your head but doesn’t work as well out loud in practice. I learned this the hard way when a respondent asked me how I would answer the question I had just posed, and I realized that not only did I not really know how I would answer it, but I also wasn’t quite as sure I knew what I was asking as I had thought.
—Elizabeth M. Lee, Associate Professor of Sociology at Saint Joseph’s University, author of Class and Campus Life , and co-author of Geographies of Campus Inequality
How Many Interviews?
Your research design has included a targeted number of interviews and a recruitment plan (see chapter 5). Follow your plan, but remember that “ saturation ” is your goal. You interview as many people as you can until you reach a point at which you are no longer surprised by what they tell you. This means not that no one after your first twenty interviews will have surprising, interesting stories to tell you but rather that the picture you are forming about the phenomenon of interest to you from a research perspective has come into focus, and none of the interviews are substantially refocusing that picture. That is when you should stop collecting interviews. Note that to know when you have reached this, you will need to read your transcripts as you go. More about this in chapters 18 and 19.
Your Final Product: The Ideal Interview Transcript
A good interview transcript will demonstrate a subtly controlled conversation by the skillful interviewer. In general, you want to see replies that are about one paragraph long, not short sentences and not running on for several pages. Although it is sometimes necessary to follow respondents down tangents, it is also often necessary to pull them back to the questions that form the basis of your research study. This is not really a free conversation, although it may feel like that to the person you are interviewing.
Final Tips from an Interview Master
Annette Lareau is arguably one of the masters of the trade. In Listening to People , she provides several guidelines for good interviews and then offers a detailed example of an interview gone wrong and how it could be addressed (please see the “Further Readings” at the end of this chapter). Here is an abbreviated version of her set of guidelines: (1) interview respondents who are experts on the subjects of most interest to you (as a corollary, don’t ask people about things they don’t know); (2) listen carefully and talk as little as possible; (3) keep in mind what you want to know and why you want to know it; (4) be a proactive interviewer (subtly guide the conversation); (5) assure respondents that there aren’t any right or wrong answers; (6) use the respondent’s own words to probe further (this both allows you to accurately identify what you heard and pushes the respondent to explain further); (7) reuse effective probes (don’t reinvent the wheel as you go—if repeating the words back works, do it again and again); (8) focus on learning the subjective meanings that events or experiences have for a respondent; (9) don’t be afraid to ask a question that draws on your own knowledge (unlike trial lawyers who are trained never to ask a question for which they don’t already know the answer, sometimes it’s worth it to ask risky questions based on your hypotheses or just plain hunches); (10) keep thinking while you are listening (so difficult…and important); (11) return to a theme raised by a respondent if you want further information; (12) be mindful of power inequalities (and never ever coerce a respondent to continue the interview if they want out); (13) take control with overly talkative respondents; (14) expect overly succinct responses, and develop strategies for probing further; (15) balance digging deep and moving on; (16) develop a plan to deflect questions (e.g., let them know you are happy to answer any questions at the end of the interview, but you don’t want to take time away from them now); and at the end, (17) check to see whether you have asked all your questions. You don’t always have to ask everyone the same set of questions, but if there is a big area you have forgotten to cover, now is the time to recover ( Lareau 2021:93–103 ).
Sample: Demographic Questionnaire
ASA Taskforce on First-Generation and Working-Class Persons in Sociology – Class Effects on Career Success
Supplementary Demographic Questionnaire
Thank you for your participation in this interview project. We would like to collect a few pieces of key demographic information from you to supplement our analyses. Your answers to these questions will be kept confidential and stored by ID number. All of your responses here are entirely voluntary!
What best captures your race/ethnicity? (please check any/all that apply)
- White (Non Hispanic/Latina/o/x)
- Black or African American
- Hispanic, Latino/a/x of Spanish
- Asian or Asian American
- American Indian or Alaska Native
- Middle Eastern or North African
- Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander
- Other : (Please write in: ________________)
What is your current position?
- Grad Student
- Full Professor
Please check any and all of the following that apply to you:
- I identify as a working-class academic
- I was the first in my family to graduate from college
- I grew up poor
What best reflects your gender?
- Transgender female/Transgender woman
- Transgender male/Transgender man
- Gender queer/ Gender nonconforming
Anything else you would like us to know about you?
Example: Interview Guide
In this example, follow-up prompts are italicized. Note the sequence of questions. That second question often elicits an entire life history , answering several later questions in advance.
Introduction Script/Question
Thank you for participating in our survey of ASA members who identify as first-generation or working-class. As you may have heard, ASA has sponsored a taskforce on first-generation and working-class persons in sociology and we are interested in hearing from those who so identify. Your participation in this interview will help advance our knowledge in this area.
- The first thing we would like to as you is why you have volunteered to be part of this study? What does it mean to you be first-gen or working class? Why were you willing to be interviewed?
- How did you decide to become a sociologist?
- Can you tell me a little bit about where you grew up? ( prompts: what did your parent(s) do for a living? What kind of high school did you attend?)
- Has this identity been salient to your experience? (how? How much?)
- How welcoming was your grad program? Your first academic employer?
- Why did you decide to pursue sociology at the graduate level?
- Did you experience culture shock in college? In graduate school?
- Has your FGWC status shaped how you’ve thought about where you went to school? debt? etc?
- Were you mentored? How did this work (not work)? How might it?
- What did you consider when deciding where to go to grad school? Where to apply for your first position?
- What, to you, is a mark of career success? Have you achieved that success? What has helped or hindered your pursuit of success?
- Do you think sociology, as a field, cares about prestige?
- Let’s talk a little bit about intersectionality. How does being first-gen/working class work alongside other identities that are important to you?
- What do your friends and family think about your career? Have you had any difficulty relating to family members or past friends since becoming highly educated?
- Do you have any debt from college/grad school? Are you concerned about this? Could you explain more about how you paid for college/grad school? (here, include assistance from family, fellowships, scholarships, etc.)
- (You’ve mentioned issues or obstacles you had because of your background.) What could have helped? Or, who or what did? Can you think of fortuitous moments in your career?
- Do you have any regrets about the path you took?
- Is there anything else you would like to add? Anything that the Taskforce should take note of, that we did not ask you about here?
Further Readings
Britten, Nicky. 1995. “Qualitative Interviews in Medical Research.” BMJ: British Medical Journal 31(6999):251–253. A good basic overview of interviewing particularly useful for students of public health and medical research generally.
Corbin, Juliet, and Janice M. Morse. 2003. “The Unstructured Interactive Interview: Issues of Reciprocity and Risks When Dealing with Sensitive Topics.” Qualitative Inquiry 9(3):335–354. Weighs the potential benefits and harms of conducting interviews on topics that may cause emotional distress. Argues that the researcher’s skills and code of ethics should ensure that the interviewing process provides more of a benefit to both participant and researcher than a harm to the former.
Gerson, Kathleen, and Sarah Damaske. 2020. The Science and Art of Interviewing . New York: Oxford University Press. A useful guidebook/textbook for both undergraduates and graduate students, written by sociologists.
Kvale, Steiner. 2007. Doing Interviews . London: SAGE. An easy-to-follow guide to conducting and analyzing interviews by psychologists.
Lamont, Michèle, and Ann Swidler. 2014. “Methodological Pluralism and the Possibilities and Limits of Interviewing.” Qualitative Sociology 37(2):153–171. Written as a response to various debates surrounding the relative value of interview-based studies and ethnographic studies defending the particular strengths of interviewing. This is a must-read article for anyone seriously engaging in qualitative research!
Pugh, Allison J. 2013. “What Good Are Interviews for Thinking about Culture? Demystifying Interpretive Analysis.” American Journal of Cultural Sociology 1(1):42–68. Another defense of interviewing written against those who champion ethnographic methods as superior, particularly in the area of studying culture. A classic.
Rapley, Timothy John. 2001. “The ‘Artfulness’ of Open-Ended Interviewing: Some considerations in analyzing interviews.” Qualitative Research 1(3):303–323. Argues for the importance of “local context” of data production (the relationship built between interviewer and interviewee, for example) in properly analyzing interview data.
Weiss, Robert S. 1995. Learning from Strangers: The Art and Method of Qualitative Interview Studies . New York: Simon and Schuster. A classic and well-regarded textbook on interviewing. Because Weiss has extensive experience conducting surveys, he contrasts the qualitative interview with the survey questionnaire well; particularly useful for those trained in the latter.
- I say “normally” because how people understand their various identities can itself be an expansive topic of inquiry. Here, I am merely talking about collecting otherwise unexamined demographic data, similar to how we ask people to check boxes on surveys. ↵
- Again, this applies to “semistructured in-depth interviewing.” When conducting standardized questionnaires, you will want to ask each question exactly as written, without deviations! ↵
- I always include “INT” in the number because I sometimes have other kinds of data with their own numbering: FG#001 would mean the first focus group, for example. I also always include three-digit spaces, as this allows for up to 999 interviews (or, more realistically, allows for me to interview up to one hundred persons without having to reset my numbering system). ↵
A method of data collection in which the researcher asks the participant questions; the answers to these questions are often recorded and transcribed verbatim. There are many different kinds of interviews - see also semistructured interview , structured interview , and unstructured interview .
A document listing key questions and question areas for use during an interview. It is used most often for semi-structured interviews. A good interview guide may have no more than ten primary questions for two hours of interviewing, but these ten questions will be supplemented by probes and relevant follow-ups throughout the interview. Most IRBs require the inclusion of the interview guide in applications for review. See also interview and semi-structured interview .
A data-collection method that relies on casual, conversational, and informal interviewing. Despite its apparent conversational nature, the researcher usually has a set of particular questions or question areas in mind but allows the interview to unfold spontaneously. This is a common data-collection technique among ethnographers. Compare to the semi-structured or in-depth interview .
A form of interview that follows a standard guide of questions asked, although the order of the questions may change to match the particular needs of each individual interview subject, and probing “follow-up” questions are often added during the course of the interview. The semi-structured interview is the primary form of interviewing used by qualitative researchers in the social sciences. It is sometimes referred to as an “in-depth” interview. See also interview and interview guide .
The cluster of data-collection tools and techniques that involve observing interactions between people, the behaviors, and practices of individuals (sometimes in contrast to what they say about how they act and behave), and cultures in context. Observational methods are the key tools employed by ethnographers and Grounded Theory .
Follow-up questions used in a semi-structured interview to elicit further elaboration. Suggested prompts can be included in the interview guide to be used/deployed depending on how the initial question was answered or if the topic of the prompt does not emerge spontaneously.
A form of interview that follows a strict set of questions, asked in a particular order, for all interview subjects. The questions are also the kind that elicits short answers, and the data is more “informative” than probing. This is often used in mixed-methods studies, accompanying a survey instrument. Because there is no room for nuance or the exploration of meaning in structured interviews, qualitative researchers tend to employ semi-structured interviews instead. See also interview.
The point at which you can conclude data collection because every person you are interviewing, the interaction you are observing, or content you are analyzing merely confirms what you have already noted. Achieving saturation is often used as the justification for the final sample size.
An interview variant in which a person’s life story is elicited in a narrative form. Turning points and key themes are established by the researcher and used as data points for further analysis.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Interviews can be defined as a qualitative research technique which involves “conducting intensive individual interviews with a small number of respondents to explore their perspectives on a particular idea, program or situation.” [1]
There are three different formats of interviews: structured, semi-structured and unstructured.
Structured interviews consist of a series of pre-determined questions that all interviewees answer in the same order. Data analysis usually tends to be more straightforward because researcher can compare and contrast different answers given to the same questions.
Unstructured interviews are usually the least reliable from research viewpoint, because no questions are prepared prior to the interview and data collection is conducted in an informal manner. Unstructured interviews can be associated with a high level of bias and comparison of answers given by different respondents tends to be difficult due to the differences in formulation of questions.
Semi-structured interviews contain the components of both, structured and unstructured interviews. In semi-structured interviews, interviewer prepares a set of same questions to be answered by all interviewees. At the same time, additional questions might be asked during interviews to clarify and/or further expand certain issues.
Advantages of interviews include possibilities of collecting detailed information about research questions. Moreover, in in this type of primary data collection researcher has direct control over the flow of process and she has a chance to clarify certain issues during the process if needed. Disadvantages, on the other hand, include longer time requirements and difficulties associated with arranging an appropriate time with perspective sample group members to conduct interviews.
When conducting interviews you should have an open mind and refrain from displaying disagreements in any forms when viewpoints expressed by interviewees contradict your own ideas. Moreover, timing and environment for interviews need to be scheduled effectively. Specifically, interviews need to be conducted in a relaxed environment, free of any forms of pressure for interviewees whatsoever.
Respected scholars warn that “in conducting an interview the interviewer should attempt to create a friendly, non-threatening atmosphere. Much as one does with a cover letter, the interviewer should give a brief, casual introduction to the study; stress the importance of the person’s participation; and assure anonymity, or at least confidentiality, when possible.” [2]
There is a risk of interviewee bias during the primary data collection process and this would seriously compromise the validity of the project findings. Some interviewer bias can be avoided by ensuring that the interviewer does not overreact to responses of the interviewee. Other steps that can be taken to help avoid or reduce interviewer bias include having the interviewer dress inconspicuously and appropriately for the environment and holding the interview in a private setting. [3]
My e-book, The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: a step by step assistance offers practical assistance to complete a dissertation with minimum or no stress. The e-book covers all stages of writing a dissertation starting from the selection to the research area to submitting the completed version of the work within the deadline.John Dudovskiy

[1] Boyce, C. & Neale, P. (2006) “Conducting in-depth Interviews: A Guide for Designing and Conducting In-Depth Interviews”, Pathfinder International Tool Series
[2] Connaway, L.S.& Powell, R.P.(2010) “Basic Research Methods for Librarians” ABC-CLIO
[3] Connaway, L.S.& Powell, R.P.(2010) “Basic Research Methods for Librarians” ABC-CLIO
- University Libraries
- Research Guides
- Topic Guides
- Research Methods Guide
- Interview Research
Research Methods Guide: Interview Research
- Introduction
- Research Design & Method
- Survey Research
- Data Analysis
- Resources & Consultation
Tutorial Videos: Interview Method
Interview as a Method for Qualitative Research

Goals of Interview Research
- Preferences
- They help you explain, better understand, and explore research subjects' opinions, behavior, experiences, phenomenon, etc.
- Interview questions are usually open-ended questions so that in-depth information will be collected.
Mode of Data Collection
There are several types of interviews, including:
- Face-to-Face
- Online (e.g. Skype, Googlehangout, etc)
FAQ: Conducting Interview Research
What are the important steps involved in interviews?
- Think about who you will interview
- Think about what kind of information you want to obtain from interviews
- Think about why you want to pursue in-depth information around your research topic
- Introduce yourself and explain the aim of the interview
- Devise your questions so interviewees can help answer your research question
- Have a sequence to your questions / topics by grouping them in themes
- Make sure you can easily move back and forth between questions / topics
- Make sure your questions are clear and easy to understand
- Do not ask leading questions
- Do you want to bring a second interviewer with you?
- Do you want to bring a notetaker?
- Do you want to record interviews? If so, do you have time to transcribe interview recordings?
- Where will you interview people? Where is the setting with the least distraction?
- How long will each interview take?
- Do you need to address terms of confidentiality?
Do I have to choose either a survey or interviewing method?
No. In fact, many researchers use a mixed method - interviews can be useful as follow-up to certain respondents to surveys, e.g., to further investigate their responses.
Is training an interviewer important?
Yes, since the interviewer can control the quality of the result, training the interviewer becomes crucial. If more than one interviewers are involved in your study, it is important to have every interviewer understand the interviewing procedure and rehearse the interviewing process before beginning the formal study.
- << Previous: Survey Research
- Next: Data Analysis >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 10:42 AM

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 13: Interviews
Danielle Berkovic
Learning outcomes
Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to:
- Understand when to use interviews in qualitative research.
- Develop interview questions for an interview guide.
- Understand how to conduct an interview.
What are interviews?
An interviewing method is the most commonly used data collection technique in qualitative research. 1 The purpose of an interview is to explore the experiences, understandings, opinions and motivations of research participants. 2 Interviews are conducted one-on-one with the researcher and the participant. Interviews are most appropriate when seeking to understand a participant’s subjective view of an experience and are also considered suitable for the exploration of sensitive topics.
What are the different types of interviews?
There are four main types of interviews:
- Key stakeholder: A key stakeholder interview aims to explore one issue in detail with a person of interest or importance concerning the research topic. 3 Key stakeholder interviews seek the views of experts on some cultural, political or health aspects of the community, beyond their personal beliefs or actions. An example of a key stakeholder is the Chief Health Officer of Victoria (Australia’s second-most populous state) who oversaw the world’s longest lockdowns in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Dyad: A dyad interview aims to explore one issue in a level of detail with a dyad (two people). This form of interviewing is used when one participant of the dyad may need some support or is not wholly able to articulate themselves (e.g. people with cognitive impairment, or children). Independence is acknowledged and the interview is analysed as a unit. 4
- Narrative: A narrative interview helps individuals tell their stories, and prioritises their own perspectives and experiences using the language that they prefer. 5 This type of interview has been widely used in social research but is gaining prominence in health research to better understand person-centred care, for example, negotiating exercise and food abstinence whilst living with Type 2 diabetes. 6,7
- Life history: A life history interview allows the researcher to explore a person’s individual and subjective experiences within a history of the time framework. 8 Life history interviews challenge the researcher to understand how people’s current attitudes, behaviours and choices are influenced by previous experiences or trauma. Life history interviews have been conducted with Holocaust survivors 9 and youth who have been forcibly recruited to war. 10
Table 13.4 provides a summary of four studies, each adopting one of these types of interviews.
Interviewing techniques
There are two main interview techniques:
- Semi-structured: Semi-structured interviewing aims to explore a few issues in moderate detail, to expand the researcher’s knowledge at some level. 11 Semi-structured interviews give the researcher the advantage of remaining reasonably objective while enabling participants to share their perspectives and opinions. The researcher should create an interview guide with targeted open questions to direct the interview. As examples, semi-structured interviews have been used to extend knowledge of why women might gain excess weight during pregnancy, 12 and to update guidelines for statin uptake. 13
- In-depth: In-depth interviewing aims to explore a person’s subjective experiences and feelings about a particular topic. 14 In-depth interviews are often used to explore emotive (e.g. end-of-life care) 15 and complex (e.g. adolescent pregnancy) topics. 16 The researcher should create an interview guide with selected open questions to ask of the participant, but the participant should guide the direction of the interview more than in a semi-structured setting. In-depth interviews value participants’ lived experiences and are frequently used in phenomenology studies (as described in Chapter 6) .
When to use the different types of interview s
The type of interview a researcher uses should be determined by the study design, the research aims and objectives, and participant demographics. For example, if conducting a descriptive study, semi-structured interviews may be the best method of data collection. As explained in Chapter 5 , descriptive studies seek to describe phenomena, rather than to explain or interpret the data. A semi-structured interview, which seeks to expand upon some level of existing knowledge, will likely best facilitate this.
Similarly, if conducting a phenomenological study, in-depth interviews may be the best method of data collection. As described in Chapter 6 , the key concept of phenomenology is the individual. The emphasis is on the lived experience of that individual and the person’s sense-making of those experiences. Therefore, an in-depth interview is likely best placed to elicit that rich data.
While some interview types are better suited to certain study designs, there are no restrictions on the type of interview that may be used. For example, semi-structured interviews provide an excellent accompaniment to trial participation (see Chapter 11 about mixed methods), and key stakeholder interviews, as part of an action research study, can be used to define priorities, barriers and enablers to implementation.
How do I write my interview questions?
An interview aims to explore the experiences, understandings, opinions and motivations of research participants. The general rule is that the interviewee should speak for 80 per cent of the interview, and the interviewer should only be asking questions and clarifying responses, for about 20 per cent of the interview. This percentage may differ depending on the interview type; for example, a semi-structured interview involves the researcher asking more questions than in an in-depth interview. Still, to facilitate free-flowing responses, it is important to use open-ended language to encourage participants to be expansive in their responses. Examples of open-ended terms include questions that start with ‘who’, ‘how’ and ‘where’.
The researcher should avoid closed-ended questions that can be answered with yes or no, and limit conversation. For example, asking a participant ‘Did you have this experience?’ can elicit a simple ‘yes’, whereas asking them to ‘Describe your experience’, will likely encourage a narrative response. Table 13.1 provides examples of terminology to include and avoid in developing interview questions.
Table 13.1. Interview question formats to use and avoid
| Use | Avoid |
|---|---|
| Tell me about… | Do you think that… |
| What happened when… | Will you do this… |
| Why is this important? | Did you believe that… |
| How did you feel when…How do you… | Were there issues from your perspective… |
| What are the…What does... |
How long should my interview be?
There is no rule about how long an interview should take. Different types of interviews will likely run for different periods of time, but this also depends on the research question/s and the type of participant. For example, given that a semi-structured interview is seeking to expand on some previous knowledge, the interview may need no longer than 30 minutes, or up to one hour. An in-depth interview seeks to explore a topic in a greater level of detail and therefore, at a minimum, would be expected to last an hour. A dyad interview may be as short as 15 minutes (e.g. if the dyad is a person with dementia and a family member or caregiver) or longer, depending on the pairing.
Designing your interview guide
To figure out what questions to ask in an interview guide, the researcher may consult the literature, speak to experts (including people with lived experience) about the research and draw on their current knowledge. The topics and questions should be mapped to the research question/s, and the interview guide should be developed well in advance of commencing data collection. This enables time and opportunity to pilot-test the interview guide. The pilot interview provides an opportunity to explore the language and clarity of questions, the order and flow of the guide and to determine whether the instructions are clear to participants both before and after the interview. It can be beneficial to pilot-test the interview guide with someone who is not familiar with the research topic, to make sure that the language used is easily understood (and will be by participants, too). The study design should be used to determine the number of questions asked and the duration of the interview should guide the extent of the interview guide. The participant type may also determine the extent of the interview guide; for example, clinicians tend to be time-poor and therefore shorter, focused interviews are optimal. An interview guide is also likely to be shorter for a descriptive study than a phenomenological or ethnographic study, given the level of detail required. Chapter 5 outlined a descriptive study in which participants who had undergone percutaneous coronary intervention were interviewed. The interview guide consisted of four main questions and subsequent probing questions, linked to the research questions (see Table 13.2). 17
Table 13.2. Interview guide for a descriptive study
| Research question | Open questions | Probing questions and topics |
|---|---|---|
| How does the patient feel, physically and psychologically, after their procedure? | From your perspective, what would be considered a successful outcome of the procedure? | Did the procedure meet your expectations? How do you define whether the procedure was successful? |
| How did you feel after the procedure?
| How did you feel one week after the procedure and how does that compare with how you feel now? | |
| How does the patient function after their procedure? | After your procedure, tell me about your ability to do your daily activities? | Prompt for activities including gardening, housework, personal care, work-related and family-related tasks.Did you attend cardiac rehabilitation? Can you tell us about your experience of cardiac rehabilitation? What effect has medication had on your recovery?
|
| What are the long-term effects of the procedure? | What, if any, lifestyle changes have you made since your procedure? |
Table 13.3 is an example of a larger and more detailed interview guide, designed for the qualitative component of a mixed-methods study aiming to examine the work and financial effects of living with arthritis as a younger person. The questions are mapped to the World Health Organization’s International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health, which measures health and disability at individual and population levels. 18
Table 13.3. Detailed interview guide
| Research questions | Open questions | Probing questions |
|---|---|---|
| How do young people experience their arthritis diagnosis? | Tell me about your experience of being diagnosed with arthritis.How did being diagnosed with arthritis make you feel?Tell me about your experience of arthritis flare ups what do they feel like?What impacts arthritis flare ups or feeling like your arthritis is worse?What circumstances lead to these feelings?Based on your experience, what do you think causes symptoms of arthritis to become worse? | When were you diagnosed with arthritis?What type of arthritis were you diagnosed with?Does anyone else in your family have arthritis? What relation are they to you? |
| What are the work impacts of arthritis on younger people? | What is your field of work, and how long have you been in this role?How frequently do you work (full-time/part-time/casual)? | How has arthritis affected your work-related demands or career? How so?Has arthritis led you to reconsider your career? How so?Has arthritis affected your usual working hours each week? How so?How have changes to work or career because of your arthritis impacted other areas of life, i.e. mental health or family role? |
| What are the financial impacts of living with arthritis as a younger person? | Has your arthritis led to any financial concerns? | Financial concerns pertaining to:• Direct costs: rheumatologist, prescribed and non-prescribed medications (as well as supplements), allied health costs (rheumatology, physiotherapy, chiropractic, osteopathy, myotherapy), Pilates, and gym/personal trainer fees, complementary therapies.• Indirect costs: workplace absenteeism, productivity, loss of wages, informal care, cost of different types of insurance: health insurance (joint replacements) |
It is important to create an interview guide, for the following reasons:
- The researcher should be familiar with their research questions.
- Using an interview guide will enable the incorporation of feedback from the piloting process.
- It is difficult to predict how participants will respond to interview questions. They may answer in a way that is anticipated or they may provide unanticipated insights that warrant follow-up. An interview guide (a physical or digital copy) enables the researcher to note these answers and follow-up with appropriate inquiry.
- Participants will likely have provided heterogeneous answers to certain questions. The interview guide enables the researcher to note similarities and differences across various interviews, which may be important in data analysis.
- Even experienced qualitative researchers get nervous before an interview! The interview guide provides a safety net if the researcher forgets their questions or needs to anticipate the next question.
Setting up the interview
In the past, most interviews were conducted in person or by telephone. Emerging technologies promote easier access to research participation (e.g. by people living in rural or remote communities, or for people with mobility limitations). Even in metropolitan settings, many interviews are now conducted electronically (e.g. using videoconferencing platforms). Regardless of your interview setting, it is essential that the interview environment is comfortable for the participant. This process can begin as soon as potential participants express interest in your research. Following are some tips from the literature and our own experiences of leading interviews:
- Answer questions and set clear expectations . Participating in research is not an everyday task. People do not necessarily know what to expect during a research interview, and this can be daunting. Give people as much information as possible, answer their questions about the research and set clear expectations about what the interview will entail and how long it is expected to last. Let them know that the interview will be recorded for transcription and analysis purposes. Consider sending the interview questions a few days before the interview. This gives people time and space to reflect on their experiences, consider their responses to questions and to provide informed consent for their participation.
- Consider your setting . If conducting the interview in person, consider the location and room in which the interview will be held. For example, if in a participant’s home, be mindful of their private space. Ask if you should remove your shoes before entering their home. If they offer refreshments (which in our experience many participants do), accept it with gratitude if possible. These considerations apply beyond the participant’s home; if using a room in an office setting, consider privacy and confidentiality, accessibility and potential for disruption. Consider the temperature as well as the furniture in the room, who may be able to overhear conversations and who may walk past. Similarly, if interviewing by phone or online, take time to assess the space, and if in a house or office that is not quiet or private, use headphones as needed.
- Build rapport. The research topic may be important to participants from a professional perspective, or they may have deep emotional connections to the topic of interest. Regardless of the nature of the interview, it is important to remember that participants are being asked to open up to an interviewer who is likely to be a stranger. Spend some time with participants before the interview, to make sure that they are comfortable. Engage in some general conversation, and ask if they have any questions before you start. Remember that it is not a normal part of someone’s day to participate in research. Make it an enjoyable and/or meaningful experience for them, and it will enhance the data that you collect.
- Let participants guide you. Oftentimes, the ways in which researchers and participants describe the same phenomena are different. In the interview, reflect the participant’s language. Make sure they feel heard and that they are willing and comfortable to speak openly about their experiences. For example, our research involves talking to older adults about their experience of falls. We noticed early in this research that participants did not use the word ‘fall’ but would rather use terms such as ‘trip’, ‘went over’ and ‘stumbled’. As interviewers we adopted the participant’s language into our questions.
- Listen consistently and express interest. An interview is more complex than a simple question-and-answer format. The best interview data comes from participants feeling comfortable and confident to share their stories. By the time you are completing the 20th interview, it can be difficult to maintain the same level of concentration as with the first interview. Try to stay engaged: nod along with your participants, maintain eye contact, murmur in agreement and sympathise where warranted.
- The interviewer is both the data collector and the data collection instrument. The data received is only as good as the questions asked. In qualitative research, the researcher influences how participants answer questions. It is important to remain reflexive and aware of how your language, body language and attitude might influence the interview. Being rested and prepared will enhance the quality of the questions asked and hence the data collected.
- Avoid excessive use of ‘why’. It can be challenging for participants to recall why they felt a certain way or acted in a particular manner. Try to avoid asking ‘why’ questions too often, and instead adopt some of the open language described earlier in the chapter.
After your interview
When you have completed your interview, thank the participant and let them know they can contact you if they have any questions or follow-up information they would like to provide. If the interview has covered sensitive topics or the participant has become distressed throughout the interview, make sure that appropriate referrals and follow-up are provided (see section 6).
Download the recording from your device and make sure it is saved in a secure location that can only be accessed by people on the approved research team (see Chapters 35 and 36).
It is important to know what to do immediately after each interview is completed. Interviews should be transcribed – that is, reproduced verbatim for data analysis. Transcribing data is an important step in the process of analysis, but it is very time-consuming; transcribing a 60-minute interview can take up to 8 hours. Data analysis is discussed in Section 4.
Table 13.4. Examples of the four types of interviews
| Title | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC Licence | ||||
| First author and year | Cuthbertson, 2019 | Bannon, 2021 | McGranahan, 2020 | Gutierrez-Garcia, 2021 |
| Interview type | Key stakeholder | Dyad | Narrative | Life history |
| Interview guide | Appendix A | eAppendix Supplement | Not provided, but the text states that ‘qualitative semi-structured narrative interviews’ were conducted.’ [methods] | Not provided, but the text states that ‘an open and semi-structured question guide was designed for use.' [methods] |
| Study design | Convergent mixed-methods study | Qualitative dyadic study | Narrative interview study | Life history and lifeline techniques |
| Number of participants | 30Key stakeholders were emergency management or disaster healthcare practitioners, academics specialising in disaster management in the Oceania region, and policy managers. | 23 dyads | 28 | 7 |
| Aim | ‘To investigate threats to the health and well-being of societies associated with disaster impact in Oceania.’ [abstract] | ‘To explore the lived experiences of couples managing young-onset dementia using an integrated dyadic coping model.’[abstract] | ‘To explore the experiences and views of people with psychotic experiences who have not received any treatment or other support from mental health services for the past 5 years.’ [abstract] | ‘To analyse the use of life histories and lifelines in the study of female genital mutilation in the context of cross-cultural research in participants with different languages.’ [abstract] |
| Country | Australia, Fiji, Indonesia, Aotearoa New Zealand, Timor Leste and Tonga | United States | England | Spain |
| Length of interview | 45–60 minutes | 60 minutes | 40-120 minutes | 3 sessionsSession 1: life history interviewSession 2: Lifeline activity where participants used drawings to complement or enhance their interviewSession 3: The researchers and participants worked together to finalise the lifeline. The life history interviews ran for 40 – 60 minutes. The timing for sessions 2 and 3 is not provided. |
| Sample of interview questions from interview guide | 1. What do you believe are the top five disaster risks or threats in the Oceania region today?2. What disaster risks do you believe are emerging in the Oceania region over the next decade?3. Why do you think these are risks?4. What are the drivers of these risks?5. Do you have any suggestions on how we can improve disaster risk assessment?6. Are the current disaster risk plans and practices suited to the future disaster risks? If not, why? If not, what do you think needs to be done to improve them?7. What are the key areas of disaster practice that can enhance future community resilience to disaster risk?8. What are the barriers or inhibitors to facilitating this practice?9. What are the solutions or facilitators to enhancing community resilience?[Appendix A]
| 1. We like to start by learning more about what you each first noticed that prompted the evaluations you went through to get to the diagnosis.• Can you each tell me about the earliest symptoms you noticed?2. What are the most noticeable or troubling symptoms that you have experienced since the time of diagnosis?• How have your changes in functioning impacted you?• Emotionally, how do you feel about your symptoms and the changes in functioning you are experiencing?3. Are you open with your friends and family about the diagnosis?• Have you experienced any stigma related to your diagnosis?4. What is your understanding of the diagnosis?• What is your understanding about the how this condition will affect you both in the future? How are you getting information about this diagnosis?[eAppendix Supplement]
| Not provided. | Not provided. |
| Analysis | Thematic analysis guided by The Hazard and Peril Glossary for describing and categorising disasters applied by the Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters Emergency Events Database | Thematic analysis guided by the Dyadic Coping Theoretical Framework | Inductive thematic analysis outlined by Braun and Clarke. | Phenomenological method proposed by Giorgi (sense of the whole):1. Reading the entire description to obtain a general sense of the discourse2. The researcher goes back to the beginning and reads the text again, with the aim of distinguishing the meaning units by separating the perspective of the phenomenon of interest3. The researcher expresses the contents of the units of meaning more clearly by creating categories4. The researcher synthesises the units and categories of meaning into a consistent statement that takes into account the participant’s experience and language. |
| Main themes | 1. Climate change is observed as a contemporary and emerging disaster risk2. Risk is contextual to the different countries, communities and individuals in Oceania.3. Human development trajectories and their impact, along with perceptions of a changing world, are viewed as drivers of current and emerging risks.4. Current disaster risk plans and practices are not suited to future disaster risks.5. Increased education and education of risk and risk assessment at a local level to empower community risk ownership.[Results, Box 1] | 1. Stress communication2. Positive individual dyadic coping3. Positive conjoint dyadic coping4. Negative individual dyadic coping5. Negative conjoint dyadic coping[Abstract] | 1. Perceiving psychosis as positive2. Making sense of psychotic experiences3. Finding sources of strength4. Negative past experiences of mental health services5. Positive past experiences with individual clinicians[Abstract] | 1. Important moments and their relationship with female genital mutilation2. The ritual knife: how sharp or blunt it is at different stages, where and how women are subsequently held as a result3. Changing relationships with family: how being subject to female genital mutilation changed relationships with mothers4. Female genital mutilation increases the risk of future childbirth complications which change relationships with family and healthcare systems5. Managing experiences with early exposure to physical and sexual violence across the lifespan. |
Interviews are the most common data collection technique in qualitative research. There are four main types of interviews; the one you choose will depend on your research question, aims and objectives. It is important to formulate open-ended interview questions that are understandable and easy for participants to answer. Key considerations in setting up the interview will enhance the quality of the data obtained and the experience of the interview for the participant and the researcher.
- Gill P, Stewart K, Treasure E, Chadwick B. Methods of data collection in qualitative research: interviews and focus groups. Br Dent J . 2008;204(6):291-295. doi:10.1038/bdj.2008.192
- DeJonckheere M, Vaughn LM. Semistructured interviewing in primary care research: a balance of relationship and rigour. Fam Med Community Health . 2019;7(2):e000057. doi:10.1136/fmch-2018-000057
- Nyanchoka L, Tudur-Smith C, Porcher R, Hren D. Key stakeholders’ perspectives and experiences with defining, identifying and displaying gaps in health research: a qualitative study. BMJ Open . 2020;10(11):e039932. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039932
- Morgan DL, Ataie J, Carder P, Hoffman K. Introducing dyadic interviews as a method for collecting qualitative data. Qual Health Res . 2013;23(9):1276-84. doi:10.1177/1049732313501889
- Picchi S, Bonapitacola C, Borghi E, et al. The narrative interview in therapeutic education. The diabetic patients’ point of view. Acta Biomed . Jul 18 2018;89(6-S):43-50. doi:10.23750/abm.v89i6-S.7488
- Stuij M, Elling A, Abma T. Negotiating exercise as medicine: Narratives from people with type 2 diabetes. Health (London) . 2021;25(1):86-102. doi:10.1177/1363459319851545
- Buchmann M, Wermeling M, Lucius-Hoene G, Himmel W. Experiences of food abstinence in patients with type 2 diabetes: a qualitative study. BMJ Open . 2016;6(1):e008907. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2015-008907
- Jessee E. The Life History Interview. Handbook of Research Methods in Health Social Sciences . 2018:1-17:Chapter 80-1.
- Sheftel A, Zembrzycki S. Only Human: A Reflection on the Ethical and Methodological Challenges of Working with “Difficult” Stories. The Oral History Review . 2019;37(2):191-214. doi:10.1093/ohr/ohq050
- Harnisch H, Montgomery E. “What kept me going”: A qualitative study of avoidant responses to war-related adversity and perpetration of violence by former forcibly recruited children and youth in the Acholi region of northern Uganda. Soc Sci Med . 2017;188:100-108. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2017.07.007
- Ruslin., Mashuri S, Rasak MSA, Alhabsyi M, Alhabsyi F, Syam H. Semi-structured Interview: A Methodological Reflection on the Development of a Qualitative Research Instrument in Educational Studies. IOSR-JRME . 2022;12(1):22-29. doi:10.9790/7388-1201052229
- Chang T, Llanes M, Gold KJ, Fetters MD. Perspectives about and approaches to weight gain in pregnancy: a qualitative study of physicians and nurse midwives. BMC Pregnancy & Childbirth . 2013;13(47)doi:10.1186/1471-2393-13-47
- DeJonckheere M, Robinson CH, Evans L, et al. Designing for Clinical Change: Creating an Intervention to Implement New Statin Guidelines in a Primary Care Clinic. JMIR Hum Factors . 2018;5(2):e19. doi:10.2196/humanfactors.9030
- Knott E, Rao AH, Summers K, Teeger C. Interviews in the social sciences. Nature Reviews Methods Primers . 2022;2(1)doi:10.1038/s43586-022-00150-6
- Bergenholtz H, Missel M, Timm H. Talking about death and dying in a hospital setting – a qualitative study of the wishes for end-of-life conversations from the perspective of patients and spouses. BMC Palliat Care . 2020;19(1):168. doi:10.1186/s12904-020-00675-1
- Olorunsaiye CZ, Degge HM, Ubanyi TO, Achema TA, Yaya S. “It’s like being involved in a car crash”: teen pregnancy narratives of adolescents and young adults in Jos, Nigeria. Int Health . 2022;14(6):562-571. doi:10.1093/inthealth/ihab069
- Ayton DR, Barker AL, Peeters G, et al. Exploring patient-reported outcomes following percutaneous coronary intervention: A qualitative study. Health Expect . 2018;21(2):457-465. doi:10.1111/hex.12636
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF). WHO. https://www.who.int/standards/classifications/international-classification-of-functioning-disability-and-health#:~:text=ICF%20is%20the%20WHO%20framework,and%20measure%20health%20and%20disability.
- Cuthbertson J, Rodriguez-Llanes JM, Robertson A, Archer F. Current and Emerging Disaster Risks Perceptions in Oceania: Key Stakeholders Recommendations for Disaster Management and Resilience Building. Int J Environ Res Public Health . 2019;16(3)doi:10.3390/ijerph16030460
- Bannon SM, Grunberg VA, Reichman M, et al. Thematic Analysis of Dyadic Coping in Couples With Young-Onset Dementia. JAMA Netw Open . 2021;4(4):e216111. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.6111
- McGranahan R, Jakaite Z, Edwards A, Rennick-Egglestone S, Slade M, Priebe S. Living with Psychosis without Mental Health Services: A Narrative Interview Study. BMJ Open . 2021;11(7):e045661. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-045661
- Gutiérrez-García AI, Solano-Ruíz C, Siles-González J, Perpiñá-Galvañ J. Life Histories and Lifelines: A Methodological Symbiosis for the Study of Female Genital Mutilation. Int J Qual Methods . 2021;20doi:10.1177/16094069211040969
Qualitative Research – a practical guide for health and social care researchers and practitioners Copyright © 2023 by Danielle Berkovic is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Exploring the Definition and Dynamics of Interviews in Research

Table of Contents
Have you ever wondered how researchers gather in-depth information on subjects that questionnaires can’t cover? Interviews are a fundamental tool in the kit of a psychologist , serving as the bridge between a research question and the rich, nuanced answers that lie within human experiences. But what sets an interview apart from a casual chat, and how does it unlock the stories and insights researchers are seeking? Let’s dive into the world of interviews and uncover their significance in psychological research.
The essence of an interview in psychological research
An interview, in its most distilled form, is a purposeful conversation. It’s an orchestrated verbal exchange designed to delve deep into a participant’s thoughts, feelings, and experiences. Unlike the spontaneous ebb and flow of a casual conversation, an interview is structured, with clear roles demarcated between the interviewer and the interviewee. This dynamic is not about idle chatter; it’s about purposeful exploration with the goal of gathering data that can illuminate psychological phenomena.
Types of interviews
Within the realm of research, interviews can take various forms, each tailored to the nature of the investigation:
- Structured interviews: These follow a script, ensuring that every participant is asked the same questions in the same way. This allows for easy comparison across different responses.
- Semi- structured interviews : While there’s a guide of topics the interviewer wants to cover, the conversation can flow more naturally, with room for follow-up questions based on the interviewee’s responses.
- Unstructured interviews: Resembling more of a guided conversation, these interviews are flexible and allow the participant to lead the direction of the talk, offering spontaneous insights.
Crafting the questions
The art of interviewing hinges on the questions posed. In structured interviews, questions are often closed-ended, seeking specific information. Semi-structured and unstructured interviews , however, thrive on open-ended questions that encourage participants to share their stories and perspectives, providing the researcher with a wealth of qualitative data . Crafting these questions requires skill and a deep understanding of human psychology to ensure they’re open, neutral, and capable of eliciting the desired depth of response.
Preparation and execution
Conducting an interview is more than just asking questions; it’s an intricate dance of preparation, rapport building , and active listening . Here’s how researchers prepare for and execute interviews:
- Preparation: Researchers must thoroughly understand their research question and the information they seek. This involves background research, question development, and logistical planning for the interview setting.
- Rapport building: A comfortable interviewee is more likely to share openly. Hence, building rapport is crucial. This can involve small talk or explaining the purpose and process of the interview to put the participant at ease.
- Active listening: Throughout the interview, the researcher must listen attentively, not just to the words but to the tone, pace, and emotion behind them. This helps in understanding the context and nuances of the responses.
Challenges faced during interviews
Interviews aren’t without their challenges. Participants may be reluctant to share sensitive information, or they might provide socially desirable responses rather than authentic ones. Interviewers must navigate these obstacles with sensitivity and ethical consideration, ensuring confidentiality and the comfort of the participant at all times.
After the interview
The interview might be over, but the researcher’s work has just begun. Post-interview, the following steps are crucial:
- Transcribing: Interviews are often recorded and then transcribed verbatim. This textual representation of the audio is vital for analysis.
- Analysis: Qualitative data from interviews can be analyzed in various ways, like thematic analysis or content analysis , to identify patterns, themes, and insights.
- Reflection: The interviewer reflects on their own performance and the interview’s process to refine their technique for future research.
Ensuring validity and reliability
Validity and reliability are pillars of sound research. Interviewers must remain aware of biases and ensure that their questions and demeanor don’t lead or influence the participant. They must also ensure the reliability of their methods so that the interview could be replicated under similar conditions with similar results.
Interviews as a window to the human psyche
Ultimately, interviews in psychological research are more than just a method; they’re a window into the complexities of the human psyche. They allow researchers to capture the vivid colors of human thought, emotion, and experience, turning them into data that can inform theories, practices, and our understanding of human behavior.
Interviews are an indispensable part of psychological research, offering a structured yet flexible way to extract rich qualitative data from participants. With careful design and execution, interviews can shed light on the intricacies of human nature in ways other methods cannot. They are not just conversations; they are carefully curated journeys into the human experience, guided by the researcher’s expertise and the participant’s willingness to share.
What do you think? How do you believe interviews contribute to the depth and breadth of psychological research? Can you think of a situation where an interview could uncover insights that a survey might not?
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
Research Methods in Psychology
1 Introduction to Psychological Research – Objectives and Goals, Problems, Hypothesis and Variables
- Nature of Psychological Research
- The Context of Discovery
- Context of Justification
- Characteristics of Psychological Research
- Goals and Objectives of Psychological Research
2 Introduction to Psychological Experiments and Tests
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Extraneous Variables
- Experimental and Control Groups
- Introduction of Test
- Types of Psychological Test
- Uses of Psychological Tests
3 Steps in Research
- Research Process
- Identification of the Problem
- Review of Literature
- Formulating a Hypothesis
- Identifying Manipulating and Controlling Variables
- Formulating a Research Design
- Constructing Devices for Observation and Measurement
- Sample Selection and Data Collection
- Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Hypothesis Testing
- Drawing Conclusion
4 Types of Research and Methods of Research
- Historical Research
- Descriptive Research
- Correlational Research
- Qualitative Research
- Ex-Post Facto Research
- True Experimental Research
- Quasi-Experimental Research
5 Definition and Description Research Design, Quality of Research Design
- Research Design
- Purpose of Research Design
- Design Selection
- Criteria of Research Design
- Qualities of Research Design
6 Experimental Design (Control Group Design and Two Factor Design)
- Experimental Design
- Control Group Design
- Two Factor Design
7 Survey Design
- Survey Research Designs
- Steps in Survey Design
- Structuring and Designing the Questionnaire
- Interviewing Methodology
- Data Analysis
- Final Report
8 Single Subject Design
- Single Subject Design: Definition and Meaning
- Phases Within Single Subject Design
- Requirements of Single Subject Design
- Characteristics of Single Subject Design
- Types of Single Subject Design
- Advantages of Single Subject Design
- Disadvantages of Single Subject Design
9 Observation Method
- Definition and Meaning of Observation
- Characteristics of Observation
- Types of Observation
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Observation
- Guides for Observation Method
10 Interview and Interviewing
- Definition of Interview
- Types of Interview
- Aspects of Qualitative Research Interviews
- Interview Questions
- Convergent Interviewing as Action Research
- Research Team
11 Questionnaire Method
- Definition and Description of Questionnaires
- Types of Questionnaires
- Purpose of Questionnaire Studies
- Designing Research Questionnaires
- The Methods to Make a Questionnaire Efficient
- The Types of Questionnaire to be Included in the Questionnaire
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Questionnaire
- When to Use a Questionnaire?
12 Case Study
- Definition and Description of Case Study Method
- Historical Account of Case Study Method
- Designing Case Study
- Requirements for Case Studies
- Guideline to Follow in Case Study Method
- Other Important Measures in Case Study Method
- Case Reports
13 Report Writing
- Purpose of a Report
- Writing Style of the Report
- Report Writing – the Do’s and the Don’ts
- Format for Report in Psychology Area
- Major Sections in a Report
14 Review of Literature
- Purposes of Review of Literature
- Sources of Review of Literature
- Types of Literature
- Writing Process of the Review of Literature
- Preparation of Index Card for Reviewing and Abstracting
15 Methodology
- Definition and Purpose of Methodology
- Participants (Sample)
- Apparatus and Materials
16 Result, Analysis and Discussion of the Data
- Definition and Description of Results
- Statistical Presentation
- Tables and Figures
17 Summary and Conclusion
- Summary Definition and Description
- Guidelines for Writing a Summary
- Writing the Summary and Choosing Words
- A Process for Paraphrasing and Summarising
- Summary of a Report
- Writing Conclusions
18 References in Research Report
- Reference List (the Format)
- References (Process of Writing)
- Reference List and Print Sources
- Electronic Sources
- Book on CD Tape and Movie
- Reference Specifications
- General Guidelines to Write References
Share on Mastodon
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Basic Clin Pharm
- v.5(4); September 2014-November 2014
Qualitative research method-interviewing and observation
Shazia jamshed.
Department of Pharmacy Practice, Kulliyyah of Pharmacy, International Islamic University Malaysia, Kuantan Campus, Pahang, Malaysia
Buckley and Chiang define research methodology as “a strategy or architectural design by which the researcher maps out an approach to problem-finding or problem-solving.”[ 1 ] According to Crotty, research methodology is a comprehensive strategy ‘that silhouettes our choice and use of specific methods relating them to the anticipated outcomes,[ 2 ] but the choice of research methodology is based upon the type and features of the research problem.[ 3 ] According to Johnson et al . mixed method research is “a class of research where the researcher mixes or combines quantitative and qualitative research techniques, methods, approaches, theories and or language into a single study.[ 4 ] In order to have diverse opinions and views, qualitative findings need to be supplemented with quantitative results.[ 5 ] Therefore, these research methodologies are considered to be complementary to each other rather than incompatible to each other.[ 6 ]
Qualitative research methodology is considered to be suitable when the researcher or the investigator either investigates new field of study or intends to ascertain and theorize prominent issues.[ 6 , 7 ] There are many qualitative methods which are developed to have an in depth and extensive understanding of the issues by means of their textual interpretation and the most common types are interviewing and observation.[ 7 ]
Interviewing
This is the most common format of data collection in qualitative research. According to Oakley, qualitative interview is a type of framework in which the practices and standards be not only recorded, but also achieved, challenged and as well as reinforced.[ 8 ] As no research interview lacks structure[ 9 ] most of the qualitative research interviews are either semi-structured, lightly structured or in-depth.[ 9 ] Unstructured interviews are generally suggested in conducting long-term field work and allow respondents to let them express in their own ways and pace, with minimal hold on respondents’ responses.[ 10 ]
Pioneers of ethnography developed the use of unstructured interviews with local key informants that is., by collecting the data through observation and record field notes as well as to involve themselves with study participants. To be precise, unstructured interview resembles a conversation more than an interview and is always thought to be a “controlled conversation,” which is skewed towards the interests of the interviewer.[ 11 ] Non-directive interviews, form of unstructured interviews are aimed to gather in-depth information and usually do not have pre-planned set of questions.[ 11 ] Another type of the unstructured interview is the focused interview in which the interviewer is well aware of the respondent and in times of deviating away from the main issue the interviewer generally refocuses the respondent towards key subject.[ 11 ] Another type of the unstructured interview is an informal, conversational interview, based on unplanned set of questions that are generated instantaneously during the interview.[ 11 ]
In contrast, semi-structured interviews are those in-depth interviews where the respondents have to answer preset open-ended questions and thus are widely employed by different healthcare professionals in their research. Semi-structured, in-depth interviews are utilized extensively as interviewing format possibly with an individual or sometimes even with a group.[ 6 ] These types of interviews are conducted once only, with an individual or with a group and generally cover the duration of 30 min to more than an hour.[ 12 ] Semi-structured interviews are based on semi-structured interview guide, which is a schematic presentation of questions or topics and need to be explored by the interviewer.[ 12 ] To achieve optimum use of interview time, interview guides serve the useful purpose of exploring many respondents more systematically and comprehensively as well as to keep the interview focused on the desired line of action.[ 12 ] The questions in the interview guide comprise of the core question and many associated questions related to the central question, which in turn, improve further through pilot testing of the interview guide.[ 7 ] In order to have the interview data captured more effectively, recording of the interviews is considered an appropriate choice but sometimes a matter of controversy among the researcher and the respondent. Hand written notes during the interview are relatively unreliable, and the researcher might miss some key points. The recording of the interview makes it easier for the researcher to focus on the interview content and the verbal prompts and thus enables the transcriptionist to generate “verbatim transcript” of the interview.
Similarly, in focus groups, invited groups of people are interviewed in a discussion setting in the presence of the session moderator and generally these discussions last for 90 min.[ 7 ] Like every research technique having its own merits and demerits, group discussions have some intrinsic worth of expressing the opinions openly by the participants. On the contrary in these types of discussion settings, limited issues can be focused, and this may lead to the generation of fewer initiatives and suggestions about research topic.
Observation
Observation is a type of qualitative research method which not only included participant's observation, but also covered ethnography and research work in the field. In the observational research design, multiple study sites are involved. Observational data can be integrated as auxiliary or confirmatory research.[ 11 ]
Research can be visualized and perceived as painstaking methodical efforts to examine, investigate as well as restructure the realities, theories and applications. Research methods reflect the approach to tackling the research problem. Depending upon the need, research method could be either an amalgam of both qualitative and quantitative or qualitative or quantitative independently. By adopting qualitative methodology, a prospective researcher is going to fine-tune the pre-conceived notions as well as extrapolate the thought process, analyzing and estimating the issues from an in-depth perspective. This could be carried out by one-to-one interviews or as issue-directed discussions. Observational methods are, sometimes, supplemental means for corroborating research findings.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 15 September 2022
Interviews in the social sciences
- Eleanor Knott ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9131-3939 1 ,
- Aliya Hamid Rao ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0674-4206 1 ,
- Kate Summers ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9964-0259 1 &
- Chana Teeger ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5046-8280 1
Nature Reviews Methods Primers volume 2 , Article number: 73 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
734k Accesses
77 Citations
190 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Interdisciplinary studies
In-depth interviews are a versatile form of qualitative data collection used by researchers across the social sciences. They allow individuals to explain, in their own words, how they understand and interpret the world around them. Interviews represent a deceptively familiar social encounter in which people interact by asking and answering questions. They are, however, a very particular type of conversation, guided by the researcher and used for specific ends. This dynamic introduces a range of methodological, analytical and ethical challenges, for novice researchers in particular. In this Primer, we focus on the stages and challenges of designing and conducting an interview project and analysing data from it, as well as strategies to overcome such challenges.
Similar content being viewed by others
The fundamental importance of method to theory

How ‘going online’ mediates the challenges of policy elite interviews
Participatory action research
Introduction.
In-depth interviews are a qualitative research method that follow a deceptively familiar logic of human interaction: they are conversations where people talk with each other, interact and pose and answer questions 1 . An interview is a specific type of interaction in which — usually and predominantly — a researcher asks questions about someone’s life experience, opinions, dreams, fears and hopes and the interview participant answers the questions 1 .
Interviews will often be used as a standalone method or combined with other qualitative methods, such as focus groups or ethnography, or quantitative methods, such as surveys or experiments. Although interviewing is a frequently used method, it should not be viewed as an easy default for qualitative researchers 2 . Interviews are also not suited to answering all qualitative research questions, but instead have specific strengths that should guide whether or not they are deployed in a research project. Whereas ethnography might be better suited to trying to observe what people do, interviews provide a space for extended conversations that allow the researcher insights into how people think and what they believe. Quantitative surveys also give these kinds of insights, but they use pre-determined questions and scales, privileging breadth over depth and often overlooking harder-to-reach participants.
In-depth interviews can take many different shapes and forms, often with more than one participant or researcher. For example, interviews might be highly structured (using an almost survey-like interview guide), entirely unstructured (taking a narrative and free-flowing approach) or semi-structured (using a topic guide ). Researchers might combine these approaches within a single project depending on the purpose of the interview and the characteristics of the participant. Whatever form the interview takes, researchers should be mindful of the dynamics between interviewer and participant and factor these in at all stages of the project.
In this Primer, we focus on the most common type of interview: one researcher taking a semi-structured approach to interviewing one participant using a topic guide. Focusing on how to plan research using interviews, we discuss the necessary stages of data collection. We also discuss the stages and thought-process behind analysing interview material to ensure that the richness and interpretability of interview material is maintained and communicated to readers. The Primer also tracks innovations in interview methods and discusses the developments we expect over the next 5–10 years.
We wrote this Primer as researchers from sociology, social policy and political science. We note our disciplinary background because we acknowledge that there are disciplinary differences in how interviews are approached and understood as a method.
Experimentation
Here we address research design considerations and data collection issues focusing on topic guide construction and other pragmatics of the interview. We also explore issues of ethics and reflexivity that are crucial throughout the research project.
Research design
Participant selection.
Participants can be selected and recruited in various ways for in-depth interview studies. The researcher must first decide what defines the people or social groups being studied. Often, this means moving from an abstract theoretical research question to a more precise empirical one. For example, the researcher might be interested in how people talk about race in contexts of diversity. Empirical settings in which this issue could be studied could include schools, workplaces or adoption agencies. The best research designs should clearly explain why the particular setting was chosen. Often there are both intrinsic and extrinsic reasons for choosing to study a particular group of people at a specific time and place 3 . Intrinsic motivations relate to the fact that the research is focused on an important specific social phenomenon that has been understudied. Extrinsic motivations speak to the broader theoretical research questions and explain why the case at hand is a good one through which to address them empirically.
Next, the researcher needs to decide which types of people they would like to interview. This decision amounts to delineating the inclusion and exclusion criteria for the study. The criteria might be based on demographic variables, like race or gender, but they may also be context-specific, for example, years of experience in an organization. These should be decided based on the research goals. Researchers should be clear about what characteristics would make an individual a candidate for inclusion in the study (and what would exclude them).
The next step is to identify and recruit the study’s sample . Usually, many more people fit the inclusion criteria than can be interviewed. In cases where lists of potential participants are available, the researcher might want to employ stratified sampling , dividing the list by characteristics of interest before sampling.
When there are no lists, researchers will often employ purposive sampling . Many researchers consider purposive sampling the most useful mode for interview-based research since the number of interviews to be conducted is too small to aim to be statistically representative 4 . Instead, the aim is not breadth, via representativeness, but depth via rich insights about a set of participants. In addition to purposive sampling, researchers often use snowball sampling . Both purposive and snowball sampling can be combined with quota sampling . All three types of sampling aim to ensure a variety of perspectives within the confines of a research project. A goal for in-depth interview studies can be to sample for range, being mindful of recruiting a diversity of participants fitting the inclusion criteria.
Study design
The total number of interviews depends on many factors, including the population studied, whether comparisons are to be made and the duration of interviews. Studies that rely on quota sampling where explicit comparisons are made between groups will require a larger number of interviews than studies focused on one group only. Studies where participants are interviewed over several hours, days or even repeatedly across years will tend to have fewer participants than those that entail a one-off engagement.
Researchers often stop interviewing when new interviews confirm findings from earlier interviews with no new or surprising insights (saturation) 4 , 5 , 6 . As a criterion for research design, saturation assumes that data collection and analysis are happening in tandem and that researchers will stop collecting new data once there is no new information emerging from the interviews. This is not always possible. Researchers rarely have time for systematic data analysis during data collection and they often need to specify their sample in funding proposals prior to data collection. As a result, researchers often draw on existing reports of saturation to estimate a sample size prior to data collection. These suggest between 12 and 20 interviews per category of participant (although researchers have reported saturation with samples that are both smaller and larger than this) 7 , 8 , 9 . The idea of saturation has been critiqued by many qualitative researchers because it assumes that meaning inheres in the data, waiting to be discovered — and confirmed — once saturation has been reached 7 . In-depth interview data are often multivalent and can give rise to different interpretations. The important consideration is, therefore, not merely how many participants are interviewed, but whether one’s research design allows for collecting rich and textured data that provide insight into participants’ understandings, accounts, perceptions and interpretations.
Sometimes, researchers will conduct interviews with more than one participant at a time. Researchers should consider the benefits and shortcomings of such an approach. Joint interviews may, for example, give researchers insight into how caregivers agree or debate childrearing decisions. At the same time, they may be less adaptive to exploring aspects of caregiving that participants may not wish to disclose to each other. In other cases, there may be more than one person interviewing each participant, such as when an interpreter is used, and so it is important to consider during the research design phase how this might shape the dynamics of the interview.
Data collection
Semi-structured interviews are typically organized around a topic guide comprised of an ordered set of broad topics (usually 3–5). Each topic includes a set of questions that form the basis of the discussion between the researcher and participant (Fig. 1 ). These topics are organized around key concepts that the researcher has identified (for example, through a close study of prior research, or perhaps through piloting a small, exploratory study) 5 .
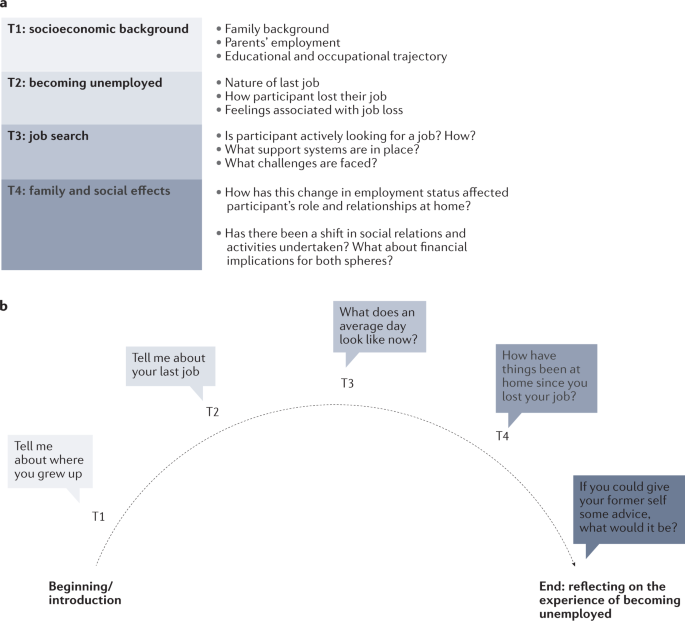
a | Elaborated topics the researcher wants to cover in the interview and example questions. b | An example topic arc. Using such an arc, one can think flexibly about the order of topics. Considering the main question for each topic will help to determine the best order for the topics. After conducting some interviews, the researcher can move topics around if a different order seems to make sense.
Topic guide
One common way to structure a topic guide is to start with relatively easy, open-ended questions (Table 1 ). Opening questions should be related to the research topic but broad and easy to answer, so that they help to ease the participant into conversation.
After these broad, opening questions, the topic guide may move into topics that speak more directly to the overarching research question. The interview questions will be accompanied by probes designed to elicit concrete details and examples from the participant (see Table 1 ).
Abstract questions are often easier for participants to answer once they have been asked more concrete questions. In our experience, for example, questions about feelings can be difficult for some participants to answer, but when following probes concerning factual experiences these questions can become less challenging. After the main themes of the topic guide have been covered, the topic guide can move onto closing questions. At this stage, participants often repeat something they have said before, although they may sometimes introduce a new topic.
Interviews are especially well suited to gaining a deeper insight into people’s experiences. Getting these insights largely depends on the participants’ willingness to talk to the researcher. We recommend designing open-ended questions that are more likely to elicit an elaborated response and extended reflection from participants rather than questions that can be answered with yes or no.
Questions should avoid foreclosing the possibility that the participant might disagree with the premise of the question. Take for example the question: “Do you support the new family-friendly policies?” This question minimizes the possibility of the participant disagreeing with the premise of this question, which assumes that the policies are ‘family-friendly’ and asks for a yes or no answer. Instead, asking more broadly how a participant feels about the specific policy being described as ‘family-friendly’ (for example, a work-from-home policy) allows them to express agreement, disagreement or impartiality and, crucially, to explain their reasoning 10 .
For an uninterrupted interview that will last between 90 and 120 minutes, the topic guide should be one to two single-spaced pages with questions and probes. Ideally, the researcher will memorize the topic guide before embarking on the first interview. It is fine to carry a printed-out copy of the topic guide but memorizing the topic guide ahead of the interviews can often make the interviewer feel well prepared in guiding the participant through the interview process.
Although the topic guide helps the researcher stay on track with the broad areas they want to cover, there is no need for the researcher to feel tied down by the topic guide. For instance, if a participant brings up a theme that the researcher intended to discuss later or a point the researcher had not anticipated, the researcher may well decide to follow the lead of the participant. The researcher’s role extends beyond simply stating the questions; it entails listening and responding, making split-second decisions about what line of inquiry to pursue and allowing the interview to proceed in unexpected directions.
Optimizing the interview
The ideal place for an interview will depend on the study and what is feasible for participants. Generally, a place where the participant and researcher can both feel relaxed, where the interview can be uninterrupted and where noise or other distractions are limited is ideal. But this may not always be possible and so the researcher needs to be prepared to adapt their plans within what is feasible (and desirable for participants).
Another key tool for the interview is a recording device (assuming that permission for recording has been given). Recording can be important to capture what the participant says verbatim. Additionally, it can allow the researcher to focus on determining what probes and follow-up questions they want to pursue rather than focusing on taking notes. Sometimes, however, a participant may not allow the researcher to record, or the recording may fail. If the interview is not recorded we suggest that the researcher takes brief notes during the interview, if feasible, and then thoroughly make notes immediately after the interview and try to remember the participant’s facial expressions, gestures and tone of voice. Not having a recording of an interview need not limit the researcher from getting analytical value from it.
As soon as possible after each interview, we recommend that the researcher write a one-page interview memo comprising three key sections. The first section should identify two to three important moments from the interview. What constitutes important is up to the researcher’s discretion 9 . The researcher should note down what happened in these moments, including the participant’s facial expressions, gestures, tone of voice and maybe even the sensory details of their surroundings. This exercise is about capturing ethnographic detail from the interview. The second part of the interview memo is the analytical section with notes on how the interview fits in with previous interviews, for example, where the participant’s responses concur or diverge from other responses. The third part consists of a methodological section where the researcher notes their perception of their relationship with the participant. The interview memo allows the researcher to think critically about their positionality and practice reflexivity — key concepts for an ethical and transparent research practice in qualitative methodology 11 , 12 .
Ethics and reflexivity
All elements of an in-depth interview can raise ethical challenges and concerns. Good ethical practice in interview studies often means going beyond the ethical procedures mandated by institutions 13 . While discussions and requirements of ethics can differ across disciplines, here we focus on the most pertinent considerations for interviews across the research process for an interdisciplinary audience.
Ethical considerations prior to interview
Before conducting interviews, researchers should consider harm minimization, informed consent, anonymity and confidentiality, and reflexivity and positionality. It is important for the researcher to develop their own ethical sensitivities and sensibilities by gaining training in interview and qualitative methods, reading methodological and field-specific texts on interviews and ethics and discussing their research plans with colleagues.
Researchers should map the potential harm to consider how this can be minimized. Primarily, researchers should consider harm from the participants’ perspective (Box 1 ). But, it is also important to consider and plan for potential harm to the researcher, research assistants, gatekeepers, future researchers and members of the wider community 14 . Even the most banal of research topics can potentially pose some form of harm to the participant, researcher and others — and the level of harm is often highly context-dependent. For example, a research project on religion in society might have very different ethical considerations in a democratic versus authoritarian research context because of how openly or not such topics can be discussed and debated 15 .
The researcher should consider how they will obtain and record informed consent (for example, written or oral), based on what makes the most sense for their research project and context 16 . Some institutions might specify how informed consent should be gained. Regardless of how consent is obtained, the participant must be made aware of the form of consent, the intentions and procedures of the interview and potential forms of harm and benefit to the participant or community before the interview commences. Moreover, the participant must agree to be interviewed before the interview commences. If, in addition to interviews, the study contains an ethnographic component, it is worth reading around this topic (see, for example, Murphy and Dingwall 17 ). Informed consent must also be gained for how the interview will be recorded before the interview commences. These practices are important to ensure the participant is contributing on a voluntary basis. It is also important to remind participants that they can withdraw their consent at any time during the interview and for a specified period after the interview (to be decided with the participant). The researcher should indicate that participants can ask for anything shared to be off the record and/or not disseminated.
In terms of anonymity and confidentiality, it is standard practice when conducting interviews to agree not to use (or even collect) participants’ names and personal details that are not pertinent to the study. Anonymizing can often be the safer option for minimizing harm to participants as it is hard to foresee all the consequences of de-anonymizing, even if participants agree. Regardless of what a researcher decides, decisions around anonymity must be agreed with participants during the process of gaining informed consent and respected following the interview.
Although not all ethical challenges can be foreseen or planned for 18 , researchers should think carefully — before the interview — about power dynamics, participant vulnerability, emotional state and interactional dynamics between interviewer and participant, even when discussing low-risk topics. Researchers may then wish to plan for potential ethical issues, for example by preparing a list of relevant organizations to which participants can be signposted. A researcher interviewing a participant about debt, for instance, might prepare in advance a list of debt advice charities, organizations and helplines that could provide further support and advice. It is important to remember that the role of an interviewer is as a researcher rather than as a social worker or counsellor because researchers may not have relevant and requisite training in these other domains.
Box 1 Mapping potential forms of harm
Social: researchers should avoid causing any relational detriment to anyone in the course of interviews, for example, by sharing information with other participants or causing interview participants to be shunned or mistreated by their community as a result of participating.
Economic: researchers should avoid causing financial detriment to anyone, for example, by expecting them to pay for transport to be interviewed or to potentially lose their job as a result of participating.
Physical: researchers should minimize the risk of anyone being exposed to violence as a result of the research both from other individuals or from authorities, including police.
Psychological: researchers should minimize the risk of causing anyone trauma (or re-traumatization) or psychological anguish as a result of the research; this includes not only the participant but importantly the researcher themselves and anyone that might read or analyse the transcripts, should they contain triggering information.
Political: researchers should minimize the risk of anyone being exposed to political detriment as a result of the research, such as retribution.
Professional/reputational: researchers should minimize the potential for reputational damage to anyone connected to the research (this includes ensuring good research practices so that any researchers involved are not harmed reputationally by being involved with the research project).
The task here is not to map exhaustively the potential forms of harm that might pertain to a particular research project (that is the researcher’s job and they should have the expertise most suited to mapping such potential harms relative to the specific project) but to demonstrate the breadth of potential forms of harm.
Ethical considerations post-interview
Researchers should consider how interview data are stored, analysed and disseminated. If participants have been offered anonymity and confidentiality, data should be stored in a way that does not compromise this. For example, researchers should consider removing names and any other unnecessary personal details from interview transcripts, password-protecting and encrypting files and using pseudonyms to label and store all interview data. It is also important to address where interview data are taken (for example, across borders in particular where interview data might be of interest to local authorities) and how this might affect the storage of interview data.
Examining how the researcher will represent participants is a paramount ethical consideration both in the planning stages of the interview study and after it has been conducted. Dissemination strategies also need to consider questions of anonymity and representation. In small communities, even if participants are given pseudonyms, it might be obvious who is being described. Anonymizing not only the names of those participating but also the research context is therefore a standard practice 19 . With particularly sensitive data or insights about the participant, it is worth considering describing participants in a more abstract way rather than as specific individuals. These practices are important both for protecting participants’ anonymity but can also affect the ability of the researcher and others to return ethically to the research context and similar contexts 20 .
Reflexivity and positionality
Reflexivity and positionality mean considering the researcher’s role and assumptions in knowledge production 13 . A key part of reflexivity is considering the power relations between the researcher and participant within the interview setting, as well as how researchers might be perceived by participants. Further, researchers need to consider how their own identities shape the kind of knowledge and assumptions they bring to the interview, including how they approach and ask questions and their analysis of interviews (Box 2 ). Reflexivity is a necessary part of developing ethical sensibility as a researcher by adapting and reflecting on how one engages with participants. Participants should not feel judged, for example, when they share information that researchers might disagree with or find objectionable. How researchers deal with uncomfortable moments or information shared by participants is at their discretion, but they should consider how they will react both ahead of time and in the moment.
Researchers can develop their reflexivity by considering how they themselves would feel being asked these interview questions or represented in this way, and then adapting their practice accordingly. There might be situations where these questions are not appropriate in that they unduly centre the researchers’ experiences and worldview. Nevertheless, these prompts can provide a useful starting point for those beginning their reflexive journey and developing an ethical sensibility.
Reflexivity and ethical sensitivities require active reflection throughout the research process. For example, researchers should take care in interview memos and their notes to consider their assumptions, potential preconceptions, worldviews and own identities prior to and after interviews (Box 2 ). Checking in with assumptions can be a way of making sure that researchers are paying close attention to their own theoretical and analytical biases and revising them in accordance with what they learn through the interviews. Researchers should return to these notes (especially when analysing interview material), to try to unpack their own effects on the research process as well as how participants positioned and engaged with them.
Box 2 Aspects to reflect on reflexively
For reflexive engagement, and understanding the power relations being co-constructed and (re)produced in interviews, it is necessary to reflect, at a minimum, on the following.
Ethnicity, race and nationality, such as how does privilege stemming from race or nationality operate between the researcher, the participant and research context (for example, a researcher from a majority community may be interviewing a member of a minority community)
Gender and sexuality, see above on ethnicity, race and nationality
Social class, and in particular the issue of middle-class bias among researchers when formulating research and interview questions
Economic security/precarity, see above on social class and thinking about the researcher’s relative privilege and the source of biases that stem from this
Educational experiences and privileges, see above
Disciplinary biases, such as how the researcher’s discipline/subfield usually approaches these questions, possibly normalizing certain assumptions that might be contested by participants and in the research context
Political and social values
Lived experiences and other dimensions of ourselves that affect and construct our identity as researchers
In this section, we discuss the next stage of an interview study, namely, analysing the interview data. Data analysis may begin while more data are being collected. Doing so allows early findings to inform the focus of further data collection, as part of an iterative process across the research project. Here, the researcher is ultimately working towards achieving coherence between the data collected and the findings produced to answer successfully the research question(s) they have set.
The two most common methods used to analyse interview material across the social sciences are thematic analysis 21 and discourse analysis 22 . Thematic analysis is a particularly useful and accessible method for those starting out in analysis of qualitative data and interview material as a method of coding data to develop and interpret themes in the data 21 . Discourse analysis is more specialized and focuses on the role of discourse in society by paying close attention to the explicit, implicit and taken-for-granted dimensions of language and power 22 , 23 . Although thematic and discourse analysis are often discussed as separate techniques, in practice researchers might flexibly combine these approaches depending on the object of analysis. For example, those intending to use discourse analysis might first conduct thematic analysis as a way to organize and systematize the data. The object and intention of analysis might differ (for example, developing themes or interrogating language), but the questions facing the researcher (such as whether to take an inductive or deductive approach to analysis) are similar.
Preparing data
Data preparation is an important step in the data analysis process. The researcher should first determine what comprises the corpus of material and in what form it will it be analysed. The former refers to whether, for example, alongside the interviews themselves, analytic memos or observational notes that may have been taken during data collection will also be directly analysed. The latter refers to decisions about how the verbal/audio interview data will be transformed into a written form, making it suitable for processes of data analysis. Typically, interview audio recordings are transcribed to produce a written transcript. It is important to note that the process of transcription is one of transformation. The verbal interview data are transformed into a written transcript through a series of decisions that the researcher must make. The researcher should consider the effect of mishearing what has been said or how choosing to punctuate a sentence in a particular way will affect the final analysis.
Box 3 shows an example transcript excerpt from an interview with a teacher conducted by Teeger as part of her study of history education in post-apartheid South Africa 24 (Box 3 ). Seeing both the questions and the responses means that the reader can contextualize what the participant (Ms Mokoena) has said. Throughout the transcript the researcher has used square brackets, for example to indicate a pause in speech, when Ms Mokoena says “it’s [pause] it’s a difficult topic”. The transcription choice made here means that we see that Ms Mokoena has taken time to pause, perhaps to search for the right words, or perhaps because she has a slight apprehension. Square brackets are also included as an overt act of communication to the reader. When Ms Mokoena says “ja”, the English translation (“yes”) of the word in Afrikaans is placed in square brackets to ensure that the reader can follow the meaning of the speech.
Decisions about what to include when transcribing will be hugely important for the direction and possibilities of analysis. Researchers should decide what they want to capture in the transcript, based on their analytic focus. From a (post)positivist perspective 25 , the researcher may be interested in the manifest content of the interview (such as what is said, not how it is said). In that case, they may choose to transcribe intelligent verbatim . From a constructivist perspective 25 , researchers may choose to record more aspects of speech (including, for example, pauses, repetitions, false starts, talking over one another) so that these features can be analysed. Those working from this perspective argue that to recognize the interactional nature of the interview setting adequately and to avoid misinterpretations, features of interaction (pauses, overlaps between speakers and so on) should be preserved in transcription and therefore in the analysis 10 . Readers interested in learning more should consult Potter and Hepburn’s summary of how to present interaction through transcription of interview data 26 .
The process of analysing semi-structured interviews might be thought of as a generative rather than an extractive enterprise. Findings do not already exist within the interview data to be discovered. Rather, researchers create something new when analysing the data by applying their analytic lens or approach to the transcripts. At a high level, there are options as to what researchers might want to glean from their interview data. They might be interested in themes, whereby they identify patterns of meaning across the dataset 21 . Alternatively, they may focus on discourse(s), looking to identify how language is used to construct meanings and therefore how language reinforces or produces aspects of the social world 27 . Alternatively, they might look at the data to understand narrative or biographical elements 28 .
A further overarching decision to make is the extent to which researchers bring predetermined framings or understandings to bear on their data, or instead begin from the data themselves to generate an analysis. One way of articulating this is the extent to which researchers take a deductive approach or an inductive approach to analysis. One example of a truly inductive approach is grounded theory, whereby the aim of the analysis is to build new theory, beginning with one’s data 6 , 29 . In practice, researchers using thematic and discourse analysis often combine deductive and inductive logics and describe their process instead as iterative (referred to also as an abductive approach ) 30 , 31 . For example, researchers may decide that they will apply a given theoretical framing, or begin with an initial analytic framework, but then refine or develop these once they begin the process of analysis.
Box 3 Excerpt of interview transcript (from Teeger 24 )
Interviewer : Maybe you could just start by talking about what it’s like to teach apartheid history.
Ms Mokoena : It’s a bit challenging. You’ve got to accommodate all the kids in the class. You’ve got to be sensitive to all the racial differences. You want to emphasize the wrongs that were done in the past but you also want to, you know, not to make kids feel like it’s their fault. So you want to use the wrongs of the past to try and unite the kids …
Interviewer : So what kind of things do you do?
Ms Mokoena : Well I normally highlight the fact that people that were struggling were not just the blacks, it was all the races. And I give examples of the people … from all walks of life, all races, and highlight how they suffered as well as a result of apartheid, particularly the whites… . What I noticed, particularly my first year of teaching apartheid, I noticed that the black kids made the others feel responsible for what happened… . I had a lot of fights…. A lot of kids started hating each other because, you know, the others are white and the others were black. And they started saying, “My mother is a domestic worker because she was never allowed an opportunity to get good education.” …
Interviewer : I didn’t see any of that now when I was observing.
Ms Mokoena : … Like I was saying I think that because of the re-emphasis of the fact that, look, everybody did suffer one way or the other, they sort of got to see that it was everybody’s struggle … . They should now get to understand that that’s why we’re called a Rainbow Nation. Not everybody agreed with apartheid and not everybody suffered. Even all the blacks, not all blacks got to feel what the others felt . So ja [yes], it’s [pause] it’s a difficult topic, ja . But I think if you get the kids to understand why we’re teaching apartheid in the first place and you show the involvement of all races in all the different sides , then I think you have managed to teach it properly. So I think because of my inexperience then — that was my first year of teaching history — so I think I — maybe I over-emphasized the suffering of the blacks versus the whites [emphasis added].
Reprinted with permission from ref. 24 , Sage Publications.
From data to codes
Coding data is a key building block shared across many approaches to data analysis. Coding is a way of organizing and describing data, but is also ultimately a way of transforming data to produce analytic insights. The basic practice of coding involves highlighting a segment of text (this may be a sentence, a clause or a longer excerpt) and assigning a label to it. The aim of the label is to communicate some sort of summary of what is in the highlighted piece of text. Coding is an iterative process, whereby researchers read and reread their transcripts, applying and refining their codes, until they have a coding frame (a set of codes) that is applied coherently across the dataset and that captures and communicates the key features of what is contained in the data as it relates to the researchers’ analytic focus.
What one codes for is entirely contingent on the focus of the research project and the choices the researcher makes about the approach to analysis. At first, one might apply descriptive codes, summarizing what is contained in the interviews. It is rarely desirable to stop at this point, however, because coding is a tool to move from describing the data to interpreting the data. Suppose the researcher is pursuing some version of thematic analysis. In that case, it might be that the objects of coding are aspects of reported action, emotions, opinions, norms, relationships, routines, agreement/disagreement and change over time. A discourse analysis might instead code for different types of speech acts, tropes, linguistic or rhetorical devices. Multiple types of code might be generated within the same research project. What is important is that researchers are aware of the choices they are making in terms of what they are coding for. Moreover, through the process of refinement, the aim is to produce a set of discrete codes — in which codes are conceptually distinct, as opposed to overlapping. By using the same codes across the dataset, the researcher can capture commonalities across the interviews. This process of refinement involves relabelling codes and reorganizing how and where they are applied in the dataset.
From coding to analysis and writing
Data analysis is also an iterative process in which researchers move closer to and further away from the data. As they move away from the data, they synthesize their findings, thus honing and articulating their analytic insights. As they move closer to the data, they ground these insights in what is contained in the interviews. The link should not be broken between the data themselves and higher-order conceptual insights or claims being made. Researchers must be able to show evidence for their claims in the data. Figure 2 summarizes this iterative process and suggests the sorts of activities involved at each stage more concretely.
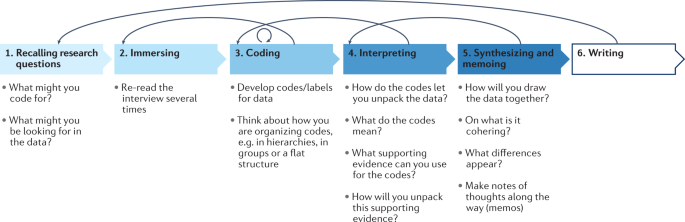
As well as going through steps 1 to 6 in order, the researcher will also go backwards and forwards between stages. Some stages will themselves be a forwards and backwards processing of coding and refining when working across different interview transcripts.
At the stage of synthesizing, there are some common quandaries. When dealing with a dataset consisting of multiple interviews, there will be salient and minority statements across different participants, or consensus or dissent on topics of interest to the researcher. A strength of qualitative interviews is that we can build in these nuances and variations across our data as opposed to aggregating them away. When exploring and reporting data, researchers should be asking how different findings are patterned and which interviews contain which codes, themes or tropes. Researchers should think about how these variations fit within the longer flow of individual interviews and what these variations tell them about the nature of their substantive research interests.
A further consideration is how to approach analysis within and across interview data. Researchers may look at one individual code, to examine the forms it takes across different participants and what they might be able to summarize about this code in the round. Alternatively, they might look at how a code or set of codes pattern across the account of one participant, to understand the code(s) in a more contextualized way. Further analysis might be done according to different sampling characteristics, where researchers group together interviews based on certain demographic characteristics and explore these together.
When it comes to writing up and presenting interview data, key considerations tend to rest on what is often termed transparency. When presenting the findings of an interview-based study, the reader should be able to understand and trace what the stated findings are based upon. This process typically involves describing the analytic process, how key decisions were made and presenting direct excerpts from the data. It is important to account for how the interview was set up and to consider the active part that the researcher has played in generating the data 32 . Quotes from interviews should not be thought of as merely embellishing or adding interest to a final research output. Rather, quotes serve the important function of connecting the reader directly to the underlying data. Quotes, therefore, should be chosen because they provide the reader with the most apt insight into what is being discussed. It is good practice to report not just on what participants said, but also on the questions that were asked to elicit the responses.
Researchers have increasingly used specialist qualitative data analysis software to organize and analyse their interview data, such as NVivo or ATLAS.ti. It is important to remember that such software is a tool for, rather than an approach or technique of, analysis. That said, software also creates a wide range of possibilities in terms of what can be done with the data. As researchers, we should reflect on how the range of possibilities of a given software package might be shaping our analytical choices and whether these are choices that we do indeed want to make.
Applications
This section reviews how and why in-depth interviews have been used by researchers studying gender, education and inequality, nationalism and ethnicity and the welfare state. Although interviews can be employed as a method of data collection in just about any social science topic, the applications below speak directly to the authors’ expertise and cutting-edge areas of research.
When it comes to the broad study of gender, in-depth interviews have been invaluable in shaping our understanding of how gender functions in everyday life. In a study of the US hedge fund industry (an industry dominated by white men), Tobias Neely was interested in understanding the factors that enable white men to prosper in the industry 33 . The study comprised interviews with 45 hedge fund workers and oversampled women of all races and men of colour to capture a range of experiences and beliefs. Tobias Neely found that practices of hiring, grooming and seeding are key to maintaining white men’s dominance in the industry. In terms of hiring, the interviews clarified that white men in charge typically preferred to hire people like themselves, usually from their extended networks. When women were hired, they were usually hired to less lucrative positions. In terms of grooming, Tobias Neely identifies how older and more senior men in the industry who have power and status will select one or several younger men as their protégés, to include in their own elite networks. Finally, in terms of her concept of seeding, Tobias Neely describes how older men who are hedge fund managers provide the seed money (often in the hundreds of millions of dollars) for a hedge fund to men, often their own sons (but not their daughters). These interviews provided an in-depth look into gendered and racialized mechanisms that allow white men to flourish in this industry.
Research by Rao draws on dozens of interviews with men and women who had lost their jobs, some of the participants’ spouses and follow-up interviews with about half the sample approximately 6 months after the initial interview 34 . Rao used interviews to understand the gendered experience and understanding of unemployment. Through these interviews, she found that the very process of losing their jobs meant different things for men and women. Women often saw job loss as being a personal indictment of their professional capabilities. The women interviewed often referenced how years of devaluation in the workplace coloured their interpretation of their job loss. Men, by contrast, were also saddened by their job loss, but they saw it as part and parcel of a weak economy rather than a personal failing. How these varied interpretations occurred was tied to men’s and women’s very different experiences in the workplace. Further, through her analysis of these interviews, Rao also showed how these gendered interpretations had implications for the kinds of jobs men and women sought to pursue after job loss. Whereas men remained tied to participating in full-time paid work, job loss appeared to be a catalyst pushing some of the women to re-evaluate their ties to the labour force.
In a study of workers in the tech industry, Hart used interviews to explain how individuals respond to unwanted and ambiguously sexual interactions 35 . Here, the researcher used interviews to allow participants to describe how these interactions made them feel and act and the logics of how they interpreted, classified and made sense of them 35 . Through her analysis of these interviews, Hart showed that participants engaged in a process she termed “trajectory guarding”, whereby they sought to monitor unwanted and ambiguously sexual interactions to avoid them from escalating. Yet, as Hart’s analysis proficiently demonstrates, these very strategies — which protect these workers sexually — also undermined their workplace advancement.
Drawing on interviews, these studies have helped us to understand better how gendered mechanisms, gendered interpretations and gendered interactions foster gender inequality when it comes to paid work. Methodologically, these studies illuminate the power of interviews to reveal important aspects of social life.
Nationalism and ethnicity
Traditionally, nationalism has been studied from a top-down perspective, through the lens of the state or using historical methods; in other words, in-depth interviews have not been a common way of collecting data to study nationalism. The methodological turn towards everyday nationalism has encouraged more scholars to go to the field and use interviews (and ethnography) to understand nationalism from the bottom up: how people talk about, give meaning, understand, navigate and contest their relation to nation, national identification and nationalism 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 . This turn has also addressed the gap left by those studying national and ethnic identification via quantitative methods, such as surveys.
Surveys can enumerate how individuals ascribe to categorical forms of identification 40 . However, interviews can question the usefulness of such categories and ask whether these categories are reflected, or resisted, by participants in terms of the meanings they give to identification 41 , 42 . Categories often pitch identification as a mutually exclusive choice; but identification might be more complex than such categories allow. For example, some might hybridize these categories or see themselves as moving between and across categories 43 . Hearing how people talk about themselves and their relation to nations, states and ethnicities, therefore, contributes substantially to the study of nationalism and national and ethnic forms of identification.
One particular approach to studying these topics, whether via everyday nationalism or alternatives, is that of using interviews to capture both articulations and narratives of identification, relations to nationalism and the boundaries people construct. For example, interviews can be used to gather self–other narratives by studying how individuals construct I–we–them boundaries 44 , including how participants talk about themselves, who participants include in their various ‘we’ groupings and which and how participants create ‘them’ groupings of others, inserting boundaries between ‘I/we’ and ‘them’. Overall, interviews hold great potential for listening to participants and understanding the nuances of identification and the construction of boundaries from their point of view.
Education and inequality
Scholars of social stratification have long noted that the school system often reproduces existing social inequalities. Carter explains that all schools have both material and sociocultural resources 45 . When children from different backgrounds attend schools with different material resources, their educational and occupational outcomes are likely to vary. Such material resources are relatively easy to measure. They are operationalized as teacher-to-student ratios, access to computers and textbooks and the physical infrastructure of classrooms and playgrounds.
Drawing on Bourdieusian theory 46 , Carter conceptualizes the sociocultural context as the norms, values and dispositions privileged within a social space 45 . Scholars have drawn on interviews with students and teachers (as well as ethnographic observations) to show how schools confer advantages on students from middle-class families, for example, by rewarding their help-seeking behaviours 47 . Focusing on race, researchers have revealed how schools can remain socioculturally white even as they enrol a racially diverse student population. In such contexts, for example, teachers often misrecognize the aesthetic choices made by students of colour, wrongly inferring that these students’ tastes in clothing and music reflect negative orientations to schooling 48 , 49 , 50 . These assessments can result in disparate forms of discipline and may ultimately shape educators’ assessments of students’ academic potential 51 .
Further, teachers and administrators tend to view the appropriate relationship between home and school in ways that resonate with white middle-class parents 52 . These parents are then able to advocate effectively for their children in ways that non-white parents are not 53 . In-depth interviews are particularly good at tapping into these understandings, revealing the mechanisms that confer privilege on certain groups of students and thereby reproduce inequality.
In addition, interviews can shed light on the unequal experiences that young people have within educational institutions, as the views of dominant groups are affirmed while those from disadvantaged backgrounds are delegitimized. For example, Teeger’s interviews with South African high schoolers showed how — because racially charged incidents are often framed as jokes in the broader school culture — Black students often feel compelled to ignore and keep silent about the racism they experience 54 . Interviews revealed that Black students who objected to these supposed jokes were coded by other students as serious or angry. In trying to avoid such labels, these students found themselves unable to challenge the racism they experienced. Interviews give us insight into these dynamics and help us see how young people understand and interpret the messages transmitted in schools — including those that speak to issues of inequality in their local school contexts as well as in society more broadly 24 , 55 .
The welfare state
In-depth interviews have also proved to be an important method for studying various aspects of the welfare state. By welfare state, we mean the social institutions relating to the economic and social wellbeing of a state’s citizens. Notably, using interviews has been useful to look at how policy design features are experienced and play out on the ground. Interviews have often been paired with large-scale surveys to produce mixed-methods study designs, therefore achieving both breadth and depth of insights.
In-depth interviews provide the opportunity to look behind policy assumptions or how policies are designed from the top down, to examine how these play out in the lives of those affected by the policies and whose experiences might otherwise be obscured or ignored. For example, the Welfare Conditionality project used interviews to critique the assumptions that conditionality (such as, the withdrawal of social security benefits if recipients did not perform or meet certain criteria) improved employment outcomes and instead showed that conditionality was harmful to mental health, living standards and had many other negative consequences 56 . Meanwhile, combining datasets from two small-scale interview studies with recipients allowed Summers and Young to critique assumptions around the simplicity that underpinned the design of Universal Credit in 2020, for example, showing that the apparently simple monthly payment design instead burdened recipients with additional money management decisions and responsibilities 57 .
Similarly, the Welfare at a (Social) Distance project used a mixed-methods approach in a large-scale study that combined national surveys with case studies and in-depth interviews to investigate the experience of claiming social security benefits during the COVID-19 pandemic. The interviews allowed researchers to understand in detail any issues experienced by recipients of benefits, such as delays in the process of claiming, managing on a very tight budget and navigating stigma and claiming 58 .
These applications demonstrate the multi-faceted topics and questions for which interviews can be a relevant method for data collection. These applications highlight not only the relevance of interviews, but also emphasize the key added value of interviews, which might be missed by other methods (surveys, in particular). Interviews can expose and question what is taken for granted and directly engage with communities and participants that might otherwise be ignored, obscured or marginalized.
Reproducibility and data deposition
There is a robust, ongoing debate about reproducibility in qualitative research, including interview studies. In some research paradigms, reproducibility can be a way of interrogating the rigour and robustness of research claims, by seeing whether these hold up when the research process is repeated. Some scholars have suggested that although reproducibility may be challenging, researchers can facilitate it by naming the place where the research was conducted, naming participants, sharing interview and fieldwork transcripts (anonymized and de-identified in cases where researchers are not naming people or places) and employing fact-checkers for accuracy 11 , 59 , 60 .
In addition to the ethical concerns of whether de-anonymization is ever feasible or desirable, it is also important to address whether the replicability of interview studies is meaningful. For example, the flexibility of interviews allows for the unexpected and the unforeseen to be incorporated into the scope of the research 61 . However, this flexibility means that we cannot expect reproducibility in the conventional sense, given that different researchers will elicit different types of data from participants. Sharing interview transcripts with other researchers, for instance, downplays the contextual nature of an interview.
Drawing on Bauer and Gaskell, we propose several measures to enhance rigour in qualitative research: transparency, grounding interpretations and aiming for theoretical transferability and significance 62 .
Researchers should be transparent when describing their methodological choices. Transparency means documenting who was interviewed, where and when (without requiring de-anonymization, for example, by documenting their characteristics), as well as the questions they were asked. It means carefully considering who was left out of the interviews and what that could mean for the researcher’s findings. It also means carefully considering who the researcher is and how their identity shaped the research process (integrating and articulating reflexivity into whatever is written up).
Second, researchers should ground their interpretations in the data. Grounding means presenting the evidence upon which the interpretation relies. Quotes and extracts should be extensive enough to allow the reader to evaluate whether the researcher’s interpretations are grounded in the data. At each step, researchers should carefully compare their own explanations and interpretations with alternative explanations. Doing so systematically and frequently allows researchers to become more confident in their claims. Here, researchers should justify the link between data and analysis by using quotes to justify and demonstrate the analytical point, while making sure the analytical point offers an interpretation of quotes (Box 4 ).
An important step in considering alternative explanations is to seek out disconfirming evidence 4 , 63 . This involves looking for instances where participants deviate from what the majority are saying and thus bring into question the theory (or explanation) that the researcher is developing. Careful analysis of such examples can often demonstrate the salience and meaning of what appears to be the norm (see Table 2 for examples) 54 . Considering alternative explanations and paying attention to disconfirming evidence allows the researcher to refine their own theories in respect of the data.
Finally, researchers should aim for theoretical transferability and significance in their discussions of findings. One way to think about this is to imagine someone who is not interested in the empirical study. Articulating theoretical transferability and significance usually takes the form of broadening out from the specific findings to consider explicitly how the research has refined or altered prior theoretical approaches. This process also means considering under what other conditions, aside from those of the study, the researcher thinks their theoretical revision would be supported by and why. Importantly, it also includes thinking about the limitations of one’s own approach and where the theoretical implications of the study might not hold.
Box 4 An example of grounding interpretations in data (from Rao 34 )
In an article explaining how unemployed men frame their job loss as a pervasive experience, Rao writes the following: “Unemployed men in this study understood unemployment to be an expected aspect of paid work in the contemporary United States. Robert, a white unemployed communications professional, compared the economic landscape after the Great Recession with the tragic events of September 11, 2001:
Part of your post-9/11 world was knowing people that died as a result of terrorism. The same thing is true with the [Great] Recession, right? … After the Recession you know somebody who was unemployed … People that really should be working.
The pervasiveness of unemployment rendered it normal, as Robert indicates.”
Here, the link between the quote presented and the analytical point Rao is making is clear: the analytical point is grounded in a quote and an interpretation of the quote is offered 34 .
Limitations and optimizations
When deciding which research method to use, the key question is whether the method provides a good fit for the research questions posed. In other words, researchers should consider whether interviews will allow them to successfully access the social phenomena necessary to answer their question(s) and whether the interviews will do so more effectively than other methods. Table 3 summarizes the major strengths and limitations of interviews. However, the accompanying text below is organized around some key issues, where relative strengths and weaknesses are presented alongside each other, the aim being that readers should think about how these can be balanced and optimized in relation to their own research.
Breadth versus depth of insight
Achieving an overall breadth of insight, in a statistically representative sense, is not something that is possible or indeed desirable when conducting in-depth interviews. Instead, the strength of conducting interviews lies in their ability to generate various sorts of depth of insight. The experiences or views of participants that can be accessed by conducting interviews help us to understand participants’ subjective realities. The challenge, therefore, is for researchers to be clear about why depth of insight is the focus and what we should aim to glean from these types of insight.
Naturalistic or artificial interviews
Interviews make use of a form of interaction with which people are familiar 64 . By replicating a naturalistic form of interaction as a tool to gather social science data, researchers can capitalize on people’s familiarity and expectations of what happens in a conversation. This familiarity can also be a challenge, as people come to the interview with preconceived ideas about what this conversation might be for or about. People may draw on experiences of other similar conversations when taking part in a research interview (for example, job interviews, therapy sessions, confessional conversations, chats with friends). Researchers should be aware of such potential overlaps and think through their implications both in how the aims and purposes of the research interview are communicated to participants and in how interview data are interpreted.
Further, some argue that a limitation of interviews is that they are an artificial form of data collection. By taking people out of their daily lives and asking them to stand back and pass comment, we are creating a distance that makes it difficult to use such data to say something meaningful about people’s actions, experiences and views. Other approaches, such as ethnography, might be more suitable for tapping into what people actually do, as opposed to what they say they do 65 .
Dynamism and replicability
Interviews following a semi-structured format offer flexibility both to the researcher and the participant. As the conversation develops, the interlocutors can explore the topics raised in much more detail, if desired, or pass over ones that are not relevant. This flexibility allows for the unexpected and the unforeseen to be incorporated into the scope of the research.
However, this flexibility has a related challenge of replicability. Interviews cannot be reproduced because they are contingent upon the interaction between the researcher and the participant in that given moment of interaction. In some research paradigms, replicability can be a way of interrogating the robustness of research claims, by seeing whether they hold when they are repeated. This is not a useful framework to bring to in-depth interviews and instead quality criteria (such as transparency) tend to be employed as criteria of rigour.
Accessing the private and personal
Interviews have been recognized for their strength in accessing private, personal issues, which participants may feel more comfortable talking about in a one-to-one conversation. Furthermore, interviews are likely to take a more personable form with their extended questions and answers, perhaps making a participant feel more at ease when discussing sensitive topics in such a context. There is a similar, but separate, argument made about accessing what are sometimes referred to as vulnerable groups, who may be difficult to make contact with using other research methods.
There is an associated challenge of anonymity. There can be types of in-depth interview that make it particularly challenging to protect the identities of participants, such as interviewing within a small community, or multiple members of the same household. The challenge to ensure anonymity in such contexts is even more important and difficult when the topic of research is of a sensitive nature or participants are vulnerable.
Increasingly, researchers are collaborating in large-scale interview-based studies and integrating interviews into broader mixed-methods designs. At the same time, interviews can be seen as an old-fashioned (and perhaps outdated) mode of data collection. We review these debates and discussions and point to innovations in interview-based studies. These include the shift from face-to-face interviews to the use of online platforms, as well as integrating and adapting interviews towards more inclusive methodologies.
Collaborating and mixing
Qualitative researchers have long worked alone 66 . Increasingly, however, researchers are collaborating with others for reasons such as efficiency, institutional incentives (for example, funding for collaborative research) and a desire to pool expertise (for example, studying similar phenomena in different contexts 67 or via different methods). Collaboration can occur across disciplines and methods, cases and contexts and between industry/business, practitioners and researchers. In many settings and contexts, collaboration has become an imperative 68 .
Cheek notes how collaboration provides both advantages and disadvantages 68 . For example, collaboration can be advantageous, saving time and building on the divergent knowledge, skills and resources of different researchers. Scholars with different theoretical or case-based knowledge (or contacts) can work together to build research that is comparative and/or more than the sum of its parts. But such endeavours also carry with them practical and political challenges in terms of how resources might actually be pooled, shared or accounted for. When undertaking such projects, as Morse notes, it is worth thinking about the nature of the collaboration and being explicit about such a choice, its advantages and its disadvantages 66 .
A further tension, but also a motivation for collaboration, stems from integrating interviews as a method in a mixed-methods project, whether with other qualitative researchers (to combine with, for example, focus groups, document analysis or ethnography) or with quantitative researchers (to combine with, for example, surveys, social media analysis or big data analysis). Cheek and Morse both note the pitfalls of collaboration with quantitative researchers: that quality of research may be sacrificed, qualitative interpretations watered down or not taken seriously, or tensions experienced over the pace and different assumptions that come with different methods and approaches of research 66 , 68 .
At the same time, there can be real benefits of such mixed-methods collaboration, such as reaching different and more diverse audiences or testing assumptions and theories between research components in the same project (for example, testing insights from prior quantitative research via interviews, or vice versa), as long as the skillsets of collaborators are seen as equally beneficial to the project. Cheek provides a set of questions that, as a starting point, can be useful for guiding collaboration, whether mixed methods or otherwise. First, Cheek advises asking all collaborators about their assumptions and understandings concerning collaboration. Second, Cheek recommends discussing what each perspective highlights and focuses on (and conversely ignores or sidelines) 68 .
A different way to engage with the idea of collaboration and mixed methods research is by fostering greater collaboration between researchers in the Global South and Global North, thus reversing trends of researchers from the Global North extracting knowledge from the Global South 69 . Such forms of collaboration also align with interview innovations, discussed below, that seek to transform traditional interview approaches into more participatory and inclusive (as part of participatory methodologies).
Digital innovations and challenges
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has centred the question of technology within interview-based fieldwork. Although conducting synchronous oral interviews online — for example, via Zoom, Skype or other such platforms — has been a method used by a small constituency of researchers for many years, it became (and remains) a necessity for many researchers wanting to continue or start interview-based projects while COVID-19 prevents face-to-face data collection.
In the past, online interviews were often framed as an inferior form of data collection for not providing the kinds of (often necessary) insights and forms of immersion face-to-face interviews allow 70 , 71 . Online interviews do tend to be more decontextualized than interviews conducted face-to-face 72 . For example, it is harder to recognize, engage with and respond to non-verbal cues 71 . At the same time, they broaden participation to those who might not have been able to access or travel to sites where interviews would have been conducted otherwise, for example people with disabilities. Online interviews also offer more flexibility in terms of scheduling and time requirements. For example, they provide more flexibility around precarious employment or caring responsibilities without having to travel and be away from home. In addition, online interviews might also reduce discomfort between researchers and participants, compared with face-to-face interviews, enabling more discussion of sensitive material 71 . They can also provide participants with more control, enabling them to turn on and off the microphone and video as they choose, for example, to provide more time to reflect and disconnect if they so wish 72 .
That said, online interviews can also introduce new biases based on access to technology 72 . For example, in the Global South, there are often urban/rural and gender gaps between who has access to mobile phones and who does not, meaning that some population groups might be overlooked unless researchers sample mindfully 71 . There are also important ethical considerations when deciding between online and face-to-face interviews. Online interviews might seem to imply lower ethical risks than face-to-face interviews (for example, they lower the chances of identification of participants or researchers), but they also offer more barriers to building trust between researchers and participants 72 . Interacting only online with participants might not provide the information needed to assess risk, for example, participants’ access to a private space to speak 71 . Just because online interviews might be more likely to be conducted in private spaces does not mean that private spaces are safe, for example, for victims of domestic violence. Finally, online interviews prompt further questions about decolonizing research and engaging with participants if research is conducted from afar 72 , such as how to include participants meaningfully and challenge dominant assumptions while doing so remotely.
A further digital innovation, modulating how researchers conduct interviews and the kinds of data collected and analysed, stems from the use and integration of (new) technology, such as WhatsApp text or voice notes to conduct synchronous or asynchronous oral or written interviews 73 . Such methods can provide more privacy, comfort and control to participants and make recruitment easier, allowing participants to share what they want when they want to, using technology that already forms a part of their daily lives, especially for young people 74 , 75 . Such technology is also emerging in other qualitative methods, such as focus groups, with similar arguments around greater inclusivity versus traditional offline modes. Here, the digital challenge might be higher for researchers than for participants if they are less used to such technology 75 . And while there might be concerns about the richness, depth and quality of written messages as a form of interview data, Gibson reports that the reams of transcripts that resulted from a study using written messaging were dense with meaning to be analysed 75 .
Like with online and face-to-face interviews, it is important also to consider the ethical questions and challenges of using such technology, from gaining consent to ensuring participant safety and attending to their distress, without cues, like crying, that might be more obvious in a face-to-face setting 75 , 76 . Attention to the platform used for such interviews is also important and researchers should be attuned to the local and national context. For example, in China, many platforms are neither legal nor available 76 . There, more popular platforms — like WeChat — can be highly monitored by the government, posing potential risks to participants depending on the topic of the interview. Ultimately, researchers should consider trade-offs between online and offline interview modalities, being attentive to the social context and power dynamics involved.
The next 5–10 years
Continuing to integrate (ethically) this technology will be among the major persisting developments in interview-based research, whether to offer more flexibility to researchers or participants, or to diversify who can participate and on what terms.
Pushing the idea of inclusion even further is the potential for integrating interview-based studies within participatory methods, which are also innovating via integrating technology. There is no hard and fast line between researchers using in-depth interviews and participatory methods; many who employ participatory methods will use interviews at the beginning, middle or end phases of a research project to capture insights, perspectives and reflections from participants 77 , 78 . Participatory methods emphasize the need to resist existing power and knowledge structures. They broaden who has the right and ability to contribute to academic knowledge by including and incorporating participants not only as subjects of data collection, but as crucial voices in research design and data analysis 77 . Participatory methods also seek to facilitate local change and to produce research materials, whether for academic or non-academic audiences, including films and documentaries, in collaboration with participants.
In responding to the challenges of COVID-19, capturing the fraught situation wrought by the pandemic and the momentum to integrate technology, participatory researchers have sought to continue data collection from afar. For example, Marzi has adapted an existing project to co-produce participatory videos, via participants’ smartphones in Medellin, Colombia, alongside regular check-in conversations/meetings/interviews with participants 79 . Integrating participatory methods into interview studies offers a route by which researchers can respond to the challenge of diversifying knowledge, challenging assumptions and power hierarchies and creating more inclusive and collaborative partnerships between participants and researchers in the Global North and South.
Brinkmann, S. & Kvale, S. Doing Interviews Vol. 2 (Sage, 2018). This book offers a good general introduction to the practice and design of interview-based studies.
Silverman, D. A Very Short, Fairly Interesting And Reasonably Cheap Book About Qualitative Research (Sage, 2017).
Yin, R. K. Case Study Research And Applications: Design And Methods (Sage, 2018).
Small, M. L. How many cases do I need?’ On science and the logic of case selection in field-based research. Ethnography 10 , 5–38 (2009). This article convincingly demonstrates how the logic of qualitative research differs from quantitative research and its goal of representativeness.
Google Scholar
Gerson, K. & Damaske, S. The Science and Art of Interviewing (Oxford Univ. Press, 2020).
Glaser, B. G. & Strauss, A. L. The Discovery Of Grounded Theory: Strategies For Qualitative Research (Aldine, 1967).
Braun, V. & Clarke, V. To saturate or not to saturate? Questioning data saturation as a useful concept for thematic analysis and sample-size rationales. Qual. Res. Sport Exerc. Health 13 , 201–216 (2021).
Guest, G., Bunce, A. & Johnson, L. How many interviews are enough? An experiment with data saturation and variability. Field Methods 18 , 59–82 (2006).
Vasileiou, K., Barnett, J., Thorpe, S. & Young, T. Characterising and justifying sample size sufficiency in interview-based studies: systematic analysis of qualitative health research over a 15-year period. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 18 , 148 (2018).
Silverman, D. How was it for you? The Interview Society and the irresistible rise of the (poorly analyzed) interview. Qual. Res. 17 , 144–158 (2017).
Jerolmack, C. & Murphy, A. The ethical dilemmas and social scientific tradeoffs of masking in ethnography. Sociol. Methods Res. 48 , 801–827 (2019).
MathSciNet Google Scholar
Reyes, V. Ethnographic toolkit: strategic positionality and researchers’ visible and invisible tools in field research. Ethnography 21 , 220–240 (2020).
Guillemin, M. & Gillam, L. Ethics, reflexivity and “ethically important moments” in research. Qual. Inq. 10 , 261–280 (2004).
Summers, K. For the greater good? Ethical reflections on interviewing the ‘rich’ and ‘poor’ in qualitative research. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 23 , 593–602 (2020). This article argues that, in qualitative interview research, a clearer distinction needs to be drawn between ethical commitments to individual research participants and the group(s) to which they belong, a distinction that is often elided in existing ethics guidelines.
Yusupova, G. Exploring sensitive topics in an authoritarian context: an insider perspective. Soc. Sci. Q. 100 , 1459–1478 (2019).
Hemming, J. in Surviving Field Research: Working In Violent And Difficult Situations 21–37 (Routledge, 2009).
Murphy, E. & Dingwall, R. Informed consent, anticipatory regulation and ethnographic practice. Soc. Sci. Med. 65 , 2223–2234 (2007).
Kostovicova, D. & Knott, E. Harm, change and unpredictability: the ethics of interviews in conflict research. Qual. Res. 22 , 56–73 (2022). This article highlights how interviews need to be considered as ethically unpredictable moments where engaging with change among participants can itself be ethical.
Andersson, R. Illegality, Inc.: Clandestine Migration And The Business Of Bordering Europe (Univ. California Press, 2014).
Ellis, R. What do we mean by a “hard-to-reach” population? Legitimacy versus precarity as barriers to access. Sociol. Methods Res. https://doi.org/10.1177/0049124121995536 (2021).
Article Google Scholar
Braun, V. & Clarke, V. Thematic Analysis: A Practical Guide (Sage, 2022).
Alejandro, A. & Knott, E. How to pay attention to the words we use: the reflexive review as a method for linguistic reflexivity. Int. Stud. Rev. https://doi.org/10.1093/isr/viac025 (2022).
Alejandro, A., Laurence, M. & Maertens, L. in International Organisations and Research Methods: An Introduction (eds Badache, F., Kimber, L. R. & Maertens, L.) (Michigan Univ. Press, in the press).
Teeger, C. “Both sides of the story” history education in post-apartheid South Africa. Am. Sociol. Rev. 80 , 1175–1200 (2015).
Crotty, M. The Foundations Of Social Research: Meaning And Perspective In The Research Process (Routledge, 2020).
Potter, J. & Hepburn, A. Qualitative interviews in psychology: problems and possibilities. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2 , 281–307 (2005).
Taylor, S. What is Discourse Analysis? (Bloomsbury Publishing, 2013).
Riessman, C. K. Narrative Analysis (Sage, 1993).
Corbin, J. M. & Strauss, A. Grounded theory research: Procedures, canons and evaluative criteria. Qual. Sociol. 13 , 3–21 (1990).
Timmermans, S. & Tavory, I. Theory construction in qualitative research: from grounded theory to abductive analysis. Sociol. Theory 30 , 167–186 (2012).
Fereday, J. & Muir-Cochrane, E. Demonstrating rigor using thematic analysis: a hybrid approach of inductive and deductive coding and theme development. Int. J. Qual. Meth. 5 , 80–92 (2006).
Potter, J. & Hepburn, A. Eight challenges for interview researchers. Handb. Interview Res. 2 , 541–570 (2012).
Tobias Neely, M. Fit to be king: how patrimonialism on Wall Street leads to inequality. Socioecon. Rev. 16 , 365–385 (2018).
Rao, A. H. Gendered interpretations of job loss and subsequent professional pathways. Gend. Soc. 35 , 884–909 (2021). This article used interview data from unemployed men and women to illuminate how job loss becomes a pivotal moment shaping men’s and women’s orientation to paid work, especially in terms of curtailing women’s participation in paid work.
Hart, C. G. Trajectory guarding: managing unwanted, ambiguously sexual interactions at work. Am. Sociol. Rev. 86 , 256–278 (2021).
Goode, J. P. & Stroup, D. R. Everyday nationalism: constructivism for the masses. Soc. Sci. Q. 96 , 717–739 (2015).
Antonsich, M. The ‘everyday’ of banal nationalism — ordinary people’s views on Italy and Italian. Polit. Geogr. 54 , 32–42 (2016).
Fox, J. E. & Miller-Idriss, C. Everyday nationhood. Ethnicities 8 , 536–563 (2008).
Yusupova, G. Cultural nationalism and everyday resistance in an illiberal nationalising state: ethnic minority nationalism in Russia. Nations National. 24 , 624–647 (2018).
Kiely, R., Bechhofer, F. & McCrone, D. Birth, blood and belonging: identity claims in post-devolution Scotland. Sociol. Rev. 53 , 150–171 (2005).
Brubaker, R. & Cooper, F. Beyond ‘identity’. Theory Soc. 29 , 1–47 (2000).
Brubaker, R. Ethnicity Without Groups (Harvard Univ. Press, 2004).
Knott, E. Kin Majorities: Identity And Citizenship In Crimea And Moldova From The Bottom-Up (McGill Univ. Press, 2022).
Bucher, B. & Jasper, U. Revisiting ‘identity’ in international relations: from identity as substance to identifications in action. Eur. J. Int. Relat. 23 , 391–415 (2016).
Carter, P. L. Stubborn Roots: Race, Culture And Inequality In US And South African Schools (Oxford Univ. Press, 2012).
Bourdieu, P. in Cultural Theory: An Anthology Vol. 1, 81–93 (eds Szeman, I. & Kaposy, T.) (Wiley-Blackwell, 2011).
Calarco, J. M. Negotiating Opportunities: How The Middle Class Secures Advantages In School (Oxford Univ. Press, 2018).
Carter, P. L. Keepin’ It Real: School Success Beyond Black And White (Oxford Univ. Press, 2005).
Carter, P. L. ‘Black’ cultural capital, status positioning and schooling conflicts for low-income African American youth. Soc. Probl. 50 , 136–155 (2003).
Warikoo, N. K. The Diversity Bargain Balancing Acts: Youth Culture in the Global City (Univ. California Press, 2011).
Morris, E. W. “Tuck in that shirt!” Race, class, gender and discipline in an urban school. Sociol. Perspect. 48 , 25–48 (2005).
Lareau, A. Social class differences in family–school relationships: the importance of cultural capital. Sociol. Educ. 60 , 73–85 (1987).
Warikoo, N. Addressing emotional health while protecting status: Asian American and white parents in suburban America. Am. J. Sociol. 126 , 545–576 (2020).
Teeger, C. Ruptures in the rainbow nation: how desegregated South African schools deal with interpersonal and structural racism. Sociol. Educ. 88 , 226–243 (2015). This article leverages ‘ deviant ’ cases in an interview study with South African high schoolers to understand why the majority of participants were reluctant to code racially charged incidents at school as racist.
Ispa-Landa, S. & Conwell, J. “Once you go to a white school, you kind of adapt” black adolescents and the racial classification of schools. Sociol. Educ. 88 , 1–19 (2015).
Dwyer, P. J. Punitive and ineffective: benefit sanctions within social security. J. Soc. Secur. Law 25 , 142–157 (2018).
Summers, K. & Young, D. Universal simplicity? The alleged simplicity of Universal Credit from administrative and claimant perspectives. J. Poverty Soc. Justice 28 , 169–186 (2020).
Summers, K. et al. Claimants’ Experiences Of The Social Security System During The First Wave Of COVID-19 . https://www.distantwelfare.co.uk/winter-report (2021).
Desmond, M. Evicted: Poverty And Profit In The American City (Crown Books, 2016).
Reyes, V. Three models of transparency in ethnographic research: naming places, naming people and sharing data. Ethnography 19 , 204–226 (2018).
Robson, C. & McCartan, K. Real World Research (Wiley, 2016).
Bauer, M. W. & Gaskell, G. Qualitative Researching With Text, Image And Sound: A Practical Handbook (SAGE, 2000).
Lareau, A. Listening To People: A Practical Guide To Interviewing, Participant Observation, Data Analysis And Writing It All Up (Univ. Chicago Press, 2021).
Lincoln, Y. S. & Guba, E. G. Naturalistic Inquiry (Sage, 1985).
Jerolmack, C. & Khan, S. Talk is cheap. Sociol. Methods Res. 43 , 178–209 (2014).
Morse, J. M. Styles of collaboration in qualitative inquiry. Qual. Health Res. 18 , 3–4 (2008).
ADS Google Scholar
Lamont, M. et al. Getting Respect: Responding To Stigma And Discrimination In The United States, Brazil And Israel (Princeton Univ. Press, 2016).
Cheek, J. Researching collaboratively: implications for qualitative research and researchers. Qual. Health Res. 18 , 1599–1603 (2008).
Botha, L. Mixing methods as a process towards indigenous methodologies. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 14 , 313–325 (2011).
Howlett, M. Looking at the ‘field’ through a zoom lens: methodological reflections on conducting online research during a global pandemic. Qual. Res. https://doi.org/10.1177/1468794120985691 (2021).
Reñosa, M. D. C. et al. Selfie consents, remote rapport and Zoom debriefings: collecting qualitative data amid a pandemic in four resource-constrained settings. BMJ Glob. Health 6 , e004193 (2021).
Mwambari, D., Purdeková, A. & Bisoka, A. N. Covid-19 and research in conflict-affected contexts: distanced methods and the digitalisation of suffering. Qual. Res. https://doi.org/10.1177/1468794121999014 (2021).
Colom, A. Using WhatsApp for focus group discussions: ecological validity, inclusion and deliberation. Qual. Res. https://doi.org/10.1177/1468794120986074 (2021).
Kaufmann, K. & Peil, C. The mobile instant messaging interview (MIMI): using WhatsApp to enhance self-reporting and explore media usage in situ. Mob. Media Commun. 8 , 229–246 (2020).
Gibson, K. Bridging the digital divide: reflections on using WhatsApp instant messenger interviews in youth research. Qual. Res. Psychol. 19 , 611–631 (2020).
Lawrence, L. Conducting cross-cultural qualitative interviews with mainland Chinese participants during COVID: lessons from the field. Qual. Res. https://doi.org/10.1177/1468794120974157 (2020).
Ponzoni, E. Windows of understanding: broadening access to knowledge production through participatory action research. Qual. Res. 16 , 557–574 (2016).
Kong, T. S. Gay and grey: participatory action research in Hong Kong. Qual. Res. 18 , 257–272 (2018).
Marzi, S. Participatory video from a distance: co-producing knowledge during the COVID-19 pandemic using smartphones. Qual. Res. https://doi.org/10.1177/14687941211038171 (2021).
Kvale, S. & Brinkmann, S. InterViews: Learning The Craft Of Qualitative Research Interviewing (Sage, 2008).
Rao, A. H. The ideal job-seeker norm: unemployment and marital privileges in the professional middle-class. J. Marriage Fam. 83 , 1038–1057 (2021).
Rivera, L. A. Ivies, extracurriculars and exclusion: elite employers’ use of educational credentials. Res. Soc. Stratif. Mobil. 29 , 71–90 (2011).
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the MY421 team and students for prompting how best to frame and communicate issues pertinent to in-depth interview studies.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Methodology, London School of Economics, London, UK
Eleanor Knott, Aliya Hamid Rao, Kate Summers & Chana Teeger
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The authors contributed equally to all aspects of the article.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Eleanor Knott .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Reviews Methods Primers thanks Jonathan Potter and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
A pre-written interview outline for a semi-structured interview that provides both a topic structure and the ability to adapt flexibly to the content and context of the interview and the interaction between the interviewer and participant. Others may refer to the topic guide as an interview protocol.
Here we refer to the participants that take part in the study as the sample. Other researchers may refer to the participants as a participant group or dataset.
This involves dividing a population into smaller groups based on particular characteristics, for example, age or gender, and then sampling randomly within each group.
A sampling method where the guiding logic when deciding who to recruit is to achieve the most relevant participants for the research topic, in terms of being rich in information or insights.
Researchers ask participants to introduce the researcher to others who meet the study’s inclusion criteria.
Similar to stratified sampling, but participants are not necessarily randomly selected. Instead, the researcher determines how many people from each category of participants should be recruited. Recruitment can happen via snowball or purposive sampling.
A method for developing, analysing and interpreting patterns across data by coding in order to develop themes.
An approach that interrogates the explicit, implicit and taken-for-granted dimensions of language as well as the contexts in which it is articulated to unpack its purposes and effects.
A form of transcription that simplifies what has been said by removing certain verbal and non-verbal details that add no further meaning, such as ‘ums and ahs’ and false starts.
The analytic framework, theoretical approach and often hypotheses, are developed prior to examining the data and then applied to the dataset.
The analytic framework and theoretical approach is developed from analysing the data.
An approach that combines deductive and inductive components to work recursively by going back and forth between data and existing theoretical frameworks (also described as an iterative approach). This approach is increasingly recognized not only as a more realistic but also more desirable third alternative to the more traditional inductive versus deductive binary choice.
A theoretical apparatus that emphasizes the role of cultural processes and capital in (intergenerational) social reproduction.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Knott, E., Rao, A.H., Summers, K. et al. Interviews in the social sciences. Nat Rev Methods Primers 2 , 73 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43586-022-00150-6
Download citation
Accepted : 14 July 2022
Published : 15 September 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s43586-022-00150-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
‘life minus illness = recovery’: a phenomenological study about experiences and meanings of recovery among individuals with serious mental illness from southern india.
- Srishti Hegde
- Shalini Quadros
- Vinita A. Acharya
Community Mental Health Journal (2024)
Is e-business breaking down barriers for Bangladesh’s young female entrepreneurs during the COVID-19 pandemic? A qualitative study
- Md. Fouad Hossain Sarker
- Sayed Farrukh Ahmed
- Md. Salman Sohel
SN Social Sciences (2024)
Between the dog and the wolf: an interpretative phenomenological analysis of bicultural, sexual minority people’s lived experiences
- Emelie Louise Miller
- Ingrid Zakrisson
Discover Psychology (2024)
Acknowledging that Men are Moral and Harmed by Gender Stereotypes Increases Men’s Willingness to Engage in Collective Action on Behalf of Women
- Alexandra Vázquez
- Lucía López-Rodríguez
- Marco Brambilla
Sex Roles (2024)
Supporting mid-career students’ psychological needs to improve motivation and retention in post-graduate courses
- Gillian Kirk
- Carly Sanbrook
The Australian Educational Researcher (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

Research Interviews: An effective and insightful way of data collection
Research interviews play a pivotal role in collecting data for various academic, scientific, and professional endeavors. They provide researchers with an opportunity to delve deep into the thoughts, experiences, and perspectives of an individual, thus enabling a comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena. It is important for researchers to design an effective and insightful method of data collection on a particular topic. A research interview is typically a two-person meeting conducted to collect information on a certain topic. It is a qualitative data collection method to gain primary information.
The three key features of a research interview are as follows:
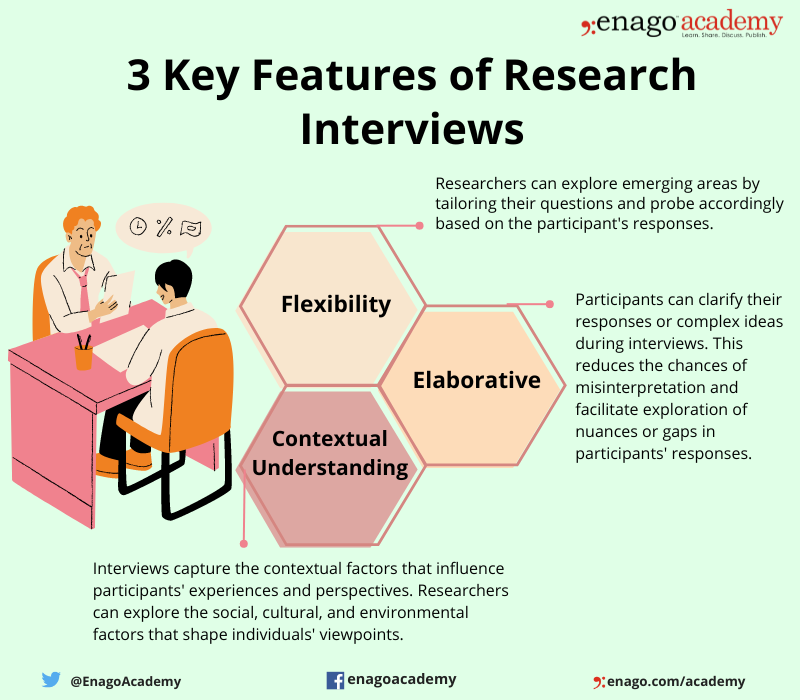
Table of Contents
The Significance of Research Interviews in Gathering Primary Data
The role of research interviews in gathering first-hand information is invaluable. Additionally, they allow researchers to interact directly with participants, enabling them to collect unfiltered primary data.
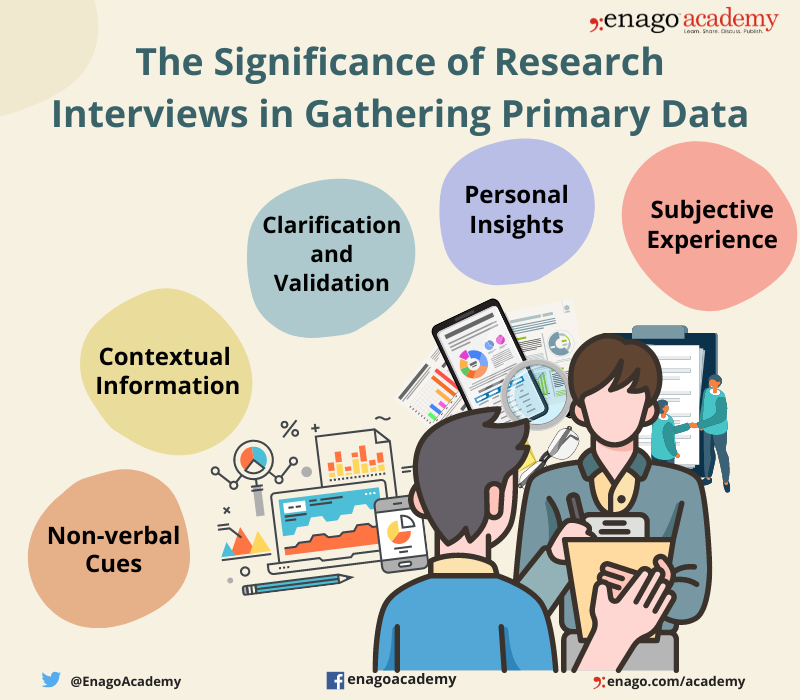
1. Subjective Experience
Research interviews facilitate in-depth exploration of a research topic. Thus, by engaging in one-to-one conversation with participants, researchers can delve into the nuances and complexities of their experiences, perspectives, and opinions. This allows comprehensive understanding of the research subject that may not be possible through other methods. Also, research interviews offer the unique advantage of capturing subjective experiences through personal narratives. Moreover, participants can express their thoughts, feelings, and beliefs, which add depth to the findings.
2. Personal Insights
Research interviews offer an opportunity for participants to share their views and opinions on the objective they are being interviewed for. Furthermore, participants can express their thoughts and experiences, providing rich qualitative data . Consequently, these personal narratives add a human element to the research, thus enhancing the understanding of the topic from the participants’ perspectives. Research interviews offer the opportunity to uncover unanticipated insights or emerging themes. Additionally, open-ended questions and active listening can help the researchers to identify new perspectives, ideas, or patterns that may not have been initially considered. As a result, these factors can lead to new avenues for exploration.

3. Clarification and Validation
Researchers can clarify participants’ responses and validate their understanding during an interview. This ensures accurate data collection and interpretation. Additionally, researchers can probe deeper into participants’ statements and seek clarification on any ambiguity in the information.
4. Contextual Information
Research interviews allow researchers to gather contextual information that offers a comprehensive understanding of the research topic. Additionally, participants can provide insights into the social, cultural, or environmental factors that shape their experiences, behaviors, and beliefs. This contextual information helps researchers place the data in a broader context and facilitates a more nuanced analysis.
5. Non-verbal Cues
In addition to verbal responses, research interviews allow researchers to observe non-verbal cues such as body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice. Additionally, non-verbal cues can convey information, such as emotions, attitudes, or levels of comfort. Furthermore, integrating non-verbal cues with verbal responses provides a more holistic understanding of participants’ experiences and enriches the data collection process.
Research interviews offer several advantages, making them a reliable tool for collecting information. However, choosing the right type of research interview is essential for collecting useful data.
Types of Research Interviews
There are several types of research interviews that researchers can use based on their research goals , the nature of their study, and the data they aim to collect. Here are some common types of research interviews:
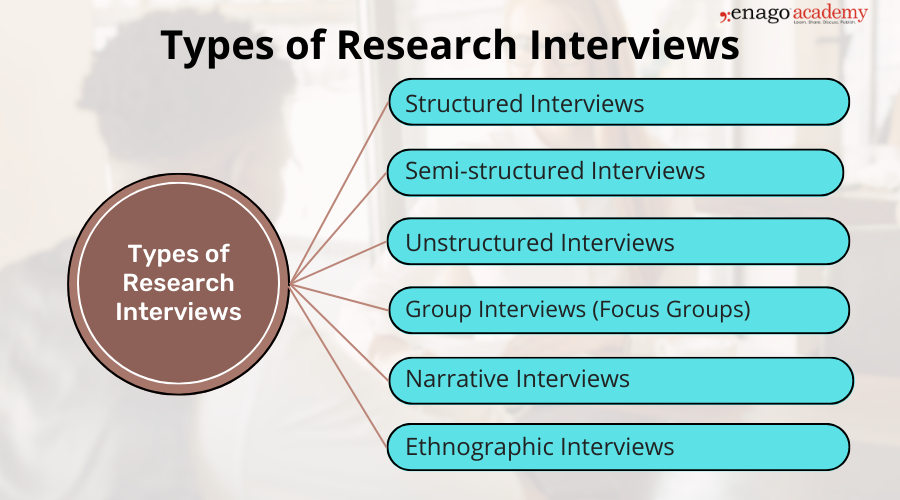
1. Structured Interviews
- Structured interviews are standardized and follow a fixed format.
- Therefore, these interviews have a pre-determined set of questions.
- All the participants are asked the same set of questions in the same order.
- Therefore, this type of interview facilitates standardization and allows easy comparison and quantitative analysis of responses.
- As a result, structured interviews are used in surveys or studies which aims for a high level of standardization and comparability.
2. Semi-structured Interviews
- Semi-structured interviews offer a flexible framework by combining pre-determined questions.
- So, this gives an opportunity for follow-up questions and open-ended discussions.
- Researchers have a list of core questions but can adapt the interview depending on the participant’s responses.
- Consequently, this allows for in-depth exploration while maintaining some level of consistency across interviews.
- As a result, semi-structured interviews are widely used in qualitative research, where content-rich data is desired.
3. Unstructured Interviews
- Unstructured interviews provide the greatest flexibility and freedom in the interview process.
- This type do not have a pre-determined set of questions.
- Thus, the conversation flows naturally based on the participant’s responses and the researcher’s interests.
- Moreover, this type of interview allows for open-ended exploration and encourages participants to share their experiences, thoughts, and perspectives freely.
- Unstructured interviews useful to explore new or complex research topics, with limited preconceived questions.
4. Group Interviews (Focus Groups)
- Group interviews involve multiple participants who engage in a facilitated discussion on a specific topic.
- This format allows the interaction and exchange of ideas among participants, generating a group dynamic.
- Therefore, group interviews are beneficial for capturing diverse perspectives, and generating collective insights.
- They are often used in market research, social sciences, or studies demanding shared experiences.
5. Narrative Interviews
- Narrative interviews focus on eliciting participants’ personal stories, views, experiences, and narratives. Researchers aim to look into the individual’s life journey.
- As a result, this type of interview allows participants to construct and share their own narratives, providing rich qualitative data.
- Qualitative research, oral history, or studies focusing on individual experiences and identities uses narrative interviews.
6. Ethnographic Interviews
- Ethnographic interviews are conducted within the context of ethnographic research, where researchers immerse themselves in a specific social or cultural setting.
- These interviews aim to understand participants’ experiences, beliefs, and practices within their cultural context, thereby understanding diversity in different ethnic groups.
- Furthermore, ethnographic interviews involve building rapport, observing the participants’ daily lives, and engaging in conversations that capture the nuances of the culture under study.
It must be noted that these interview types are not mutually exclusive. Therefore, researchers often employ a combination of approaches to gather the most comprehensive data for their research. The choice of interview type depends on the research objectives and the nature of the research topic.
Steps of Conducting a Research Interview
Research interviews offer several benefits, and thus careful planning and execution of the entire process are important to gather in-depth information from the participants. While conducting an interview, it is essential to know the necessary steps to follow for ensuring success. The steps to conduct a research interview are as follows:
- Identify the objectives and understand the goals
- Select an appropriate interview format
- Organize the necessary materials for the interview
- Understand the questions to be addressed
- Analyze the demographics of interviewees
- Select the interviewees
- Design the interview questions to gather sufficient information
- Schedule the interview
- Explain the purpose of the interview
- Analyze the interviewee based on his/her responses
Considerations for Research Interviews
Since the flexible nature of research interviews makes them an invaluable tool for data collection, researchers must consider certain factors to make the process effective. They should avoid bias and preconceived notion against the participants. Furthermore, researchers must comply with ethical considerations and respect the cultural differences between them and the participants. Also, they should ensure careful tailoring of the questions to avoid making them offensive or derogatory. The interviewers must respect the privacy of the participants and ensure the confidentiality of their details.

By ensuring due diligence of these considerations associated with research interviews, researchers can maximize the validity and reliability of the collected data, leading to robust and meaningful research outcomes.
Have you ever conducted a research interview? What was your experience? What factors did you consider when conducting a research interview? Share it with researchers worldwide by submitting your thought piece on Enago Academy’s Open Blogging Platform .
Frequently Asked Questions
• Identify the objectives of the interview • State and explain the purpose of the interview • Select an appropriate interview format • Organize the necessary materials for the Interview • Check the demographics of the participants • Select the Interviewees or the participants • Prepare the list of questions to gather maximum useful data from the participants • Schedule the Interview • Analyze the participant based on his/ her Responses
Interviews are important in research as it helps to gather elaborative first-hand information. It helps to draw conclusions from the non-verbal views and personal experiences. It reduces the ambiguity of data through detailed discussions.
The advantages of research interviews are: • It offers first-hand information • Offers detailed assessment which can result in elaborate conclusions • It is easy to conduct • Provides non-verbal cues The disadvantages of research interviews are: • There is a risk of personal bias • It can be time consuming • The outcomes might be unpredictable
The difference between structured and unstructured interview are: • Structured interviews have well-structured questions in a pre-determined order; while unstructured interviews are flexible and do not have a pre-planned set of questions. • Structured interview is more detailed; while unstructured interviews are exploratory in nature. • Structured interview is easier to replicate as compared to unstructured interview.
Focus groups is a group of multiple participants engaging in a facilitated discussion on a specific topic. This format allows for interaction and exchange of ideas among participants.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Publishing Research
10 Tips to Prevent Research Papers From Being Retracted
Research paper retractions represent a critical event in the scientific community. When a published article…

- Industry News
Google Releases 2024 Scholar Metrics, Evaluates Impact of Scholarly Articles
Google has released its 2024 Scholar Metrics, assessing scholarly articles from 2019 to 2023. This…
![interviewing research methods definition What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Trending Now
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Demystifying the Role of Confounding Variables in Research

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- AI in Academia
- Promoting Research
- Career Corner
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Peer-Review Week 2023
- Open Access Week 2023
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

In your opinion, what is the most effective way to improve integrity in the peer review process?
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Types of Interviews in Research and Methods

There are more types of interviews than most people think. An interview is generally a qualitative research technique that involves asking open-ended questions to converse with respondents and collect elicit data about a subject.
The interviewer, in most cases, is the subject matter expert who intends to understand respondent opinions in a well-planned and executed series of star questions and answers .
Interviews are similar to focus groups and surveys for garnering information from the target market but are entirely different in their operation – focus groups are restricted to a small group of 6-10 individuals, whereas surveys are quantitative.
Interviews are conducted with a sample from a population, and the key characteristic they exhibit is their conversational tone.
LEARN ABOUT: telephone survey
What is An Interview?
An interview is a way to get information from a person by asking questions and hearing their answers.
An interview is a question-and-answer session where one person asks questions, and the other person answers those questions. It can be a one-on-one, two-way conversation, or there can be more than one interviewer and more than one participant.
The interview is the most important part of the whole selection bias process. It is used to decide if a person should be interviewed further, hired, or taken out of consideration. It is the main way to learn more about applicants and the basis for judging their job-related knowledge, research skills , and abilities.
Fundamental Types of Interviews in Research
A researcher has to conduct interviews with a group of participants at a juncture in the research where information can only be obtained by meeting and personally connecting with a section of their target audience. Interviews offer the researchers a platform to prompt their participants and obtain inputs in the desired detail. There are three fundamental types of interviews in research:
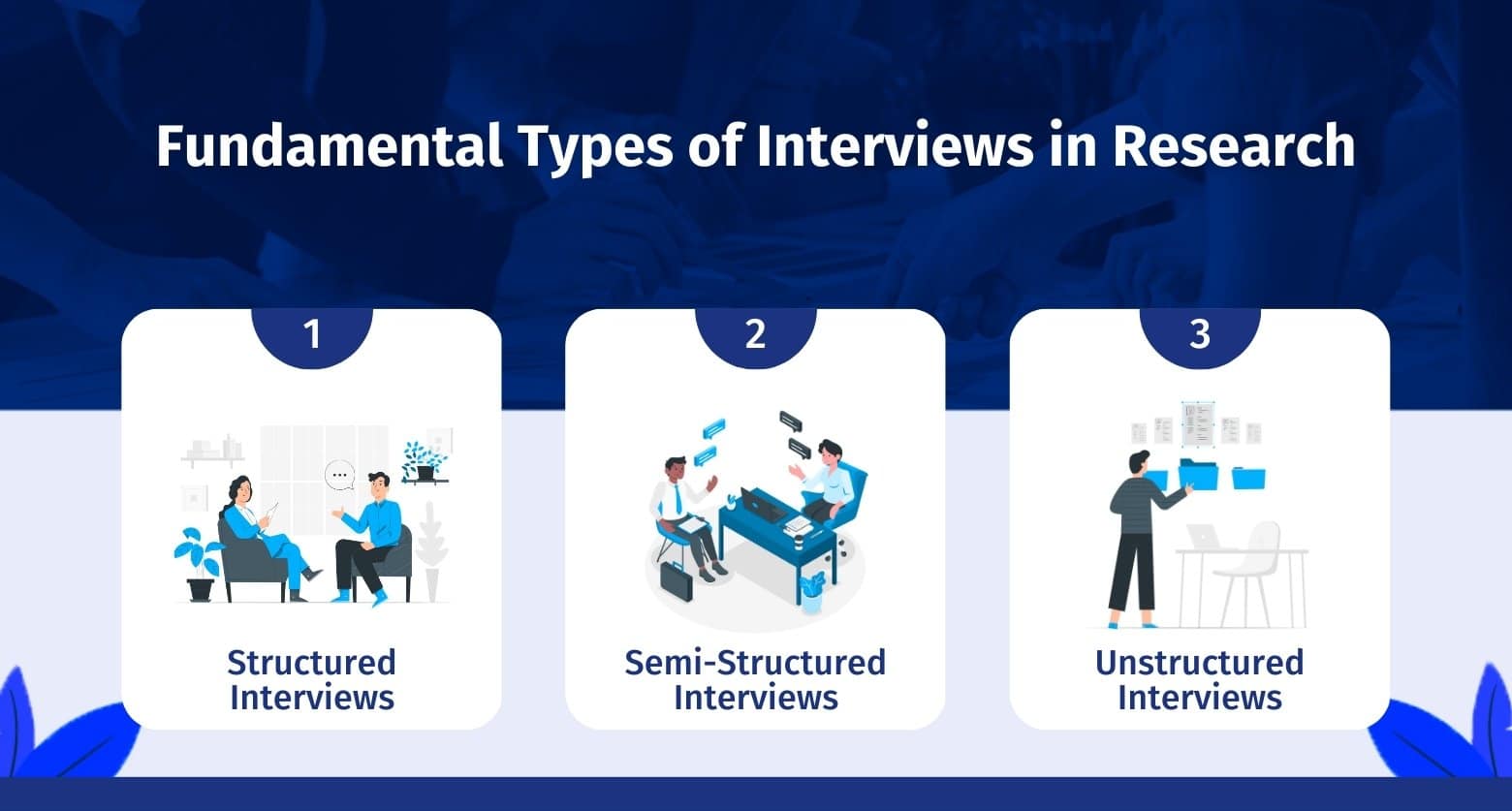
1. Structured Interviews:
Structured interviews are defined as research tools that could be more flexible in their operations are allow more or no scope of prompting the participants to obtain and analyze results. It is thus also known as a standardized interview and is significantly quantitative in its approach.
Questions in this interview are pre-decided according to the required detail of information. This can be used in a focus group interview and an in-person interview.
These interviews are excessively used in survey research with the intention of maintaining uniformity throughout all the interview sessions.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
They can be closed-ended and open-ended – according to the type of target population. Closed-ended questions can be included to understand user preferences from a collection of answer options. In contrast, open-ended ones can be included to gain details about a particular section in the interview.
Example of a structured interview question:
Here’s an example of a structured question for a job interview for a customer service job:
- Can you talk about what it was like to work in customer service?
- How do you deal with an angry or upset customer?
- How do you ensure that the information you give customers is correct?
- Tell us about when you went out of your way to help a customer.
- How do you handle a lot of customers or tasks at once?
- Can you talk about how you’ve used software or tools for customer service?
- How do you set priorities and use your time well while giving good customer service?
- Can you tell us about when you had to get a customer to calm down?
- How do you deal with a customer who wants something that goes against your company’s rules?
- Tell me about a time when you had to deal with a hard customer or coworker.
Advantages of structured interviews:
- It focuses on the accuracy of different responses, due to which extremely organized data can be collected. Different respondents have different types of answers to the same structure of questions – answers obtained can be collectively analyzed.
- They can be used to get in touch with a large sample of the target population.
- The interview procedure is made easy due to the standardization offered by it.
- Replication across multiple samples becomes easy due to the same structure of the interview.
- As the scope of detail is already considered while designing the interview questions, better information can be obtained. The researcher can analyze the research problem comprehensively by asking accurate research questions .
- Since the structure of the interview is fixed, it often generates reliable results and is quick to execute.
- The relationship between the researcher and the respondent is not formal, due to which the researcher can clearly understand the margin of error in case the respondent either degree to be a part of the survey or is just not interested in providing the right information.
Disadvantages of structured interviews:
- The limited scope of assessment of obtained results.
- The accuracy of information overpowers the detail of information.
- Respondents are forced to select from the provided answer options.
- The researcher is expected to always adhere to the list of decided questions, irrespective of how interesting the conversation is turning out to be with the participants.
- A significant amount of time is required for a structured interview.
Learn more: Market Research
2. Semi-Structured Types of Interviews:
Semi-structured interviews offer a considerable amount of leeway to the researcher to probe the respondents, along with maintaining a basic interview structure. Even if it is a guided conversation between researchers and interviewees – appreciable flexibility is offered to the researchers. A researcher can be assured that multiple interview rounds will not be required in the presence of structure in this type of research interview.
Keeping the structure in mind, the researcher can follow any idea or take creative advantage of the entire interview. Additional respondent probing is always necessary to garner information for a research study. The best application of semi-structured interviews is when the researcher doesn’t have time to conduct research and requires detailed information about the topic.
Example of a semi-structured interview question:
Here’s an example of a semi-structured marketing job interviews question:
- Can you tell us about the marketing work you’ve done?
- What do you think are the most important parts of a marketing campaign that works?
- Tell me about a campaign you worked on that you’re very proud of.
- How do you do research on the market and look at data to help you make marketing decisions?
- Can you tell us about a time when you had to change your marketing plan because of something that didn’t go as planned?
- How do you figure out if a marketing campaign worked?
- Can you talk about how you’ve used social media to market?
- How do you ensure your marketing message gets through to the people you want to hear it?
- Can you tell us about a time when you had to run a marketing campaign on a small budget?
- How do you keep up with changes and trends in marketing?
Advantages of semi-structured interviews:
- Questions from semi-structured interview questions are prepared before the scheduled interview, giving the researcher time to prepare and analyze the questions.
- It is flexible to an extent while maintaining the research guidelines.
- Unlike a structured interview, researchers can express the interview questions in the preferred format.
- Reliable qualitative data can be collected via these interviews.
- The flexible structure of the interview.
Learn more: Quantitative Data
Disadvantages of semi-structured interviews:
- Participants may question the reliability factor of these interviews due to the flexibility offered.
- Comparing two different answers becomes difficult as the guideline for conducting interviews is not entirely followed. No two questions will have the exact same structure, and the result will be an inability to compare are infer results.
3. Unstructured Interviews:
Also called in-depth interviews , unstructured interviews are usually described as conversations held with a purpose in mind – to gather data about the research study. These interviews have the least number of questions as they lean more towards a normal conversation but with an underlying subject.
The main objective of most researchers using unstructured interviews is to build a bond with the respondents, due to which there is a high chance that the respondents will be 100% truthful with their answers. There are no guidelines for the researchers to follow. So they can approach the participants ethically to gain as much information as possible about their research topic.
Since there are no guidelines for these interviews, a researcher is expected to keep their approach in check so that the respondents do not sway away from the main research motive.
For a researcher to obtain the desired outcome, he/she must keep the following factors in mind:
- The intent of the interview.
- The interview should primarily take into consideration the participant’s interests and skills.
- All the conversations should be conducted within the permissible limits of research, and the researcher should try and stick by these limits.
- The researcher’s skills and knowledge should match the interview’s purpose.
- Researchers should understand the dos and don’ts of it.
Example of an unstructured interview question:
Here’s an example of a question asked in an unstructured interview:
- Can you tell me about when you had to deal with something hard and how you did it?
- What are some of the things you’re most proud of, and what did you learn from them?
- How do you deal with ambiguity or not knowing what to do at work?
- Can you describe how you lead and how you get your team going?
- Tell me about a time when you had to take a chance and how it turned out.
- What do you think are the most important qualities for success in this role?
- How do you deal with setbacks or failures, and what do you learn from them?
- Can you tell me about a time when you had to solve a problem by thinking outside the box?
- What do you think makes you different from the other people who want this job?
- Can you tell me about a time when you had to make a hard choice and how you made that choice?
Advantages of Unstructured Interviews:
- Due to this type of interview’s informal nature, it becomes extremely easy for researchers to try and develop a friendly rapport with the participants. This leads to gaining insights in extreme detail without much conscious effort.
- The participants can clarify all their doubts about the questions, and the researcher can take each opportunity to explain his/her intention for better answers.
- There are no questions that the researcher has to abide by, and this usually increases the flexibility of the entire research process.
Disadvantages of Unstructured Interviews:
- Researchers take time to execute these interviews because there is no structure to the interview process.
- The absence of a standardized set of questions and guidelines indicates that its reliability of it is questionable.
- The ethics involved in these interviews are often considered borderline upsetting.
Learn more: Qualitative Market Research & Qualitative Data Collection
Other Types of Interviews
Besides the 3 basic interview types, we have already mentioned there are more. Here are some other interview types that are commonly used in a job interview:
Behavioral Interview
During this type of interview, candidates are asked to give specific examples of how they have acted in the past. The idea behind this kind of interview is that what someone did in the past can be a sign of how they will act in the future. And by this interview, the company can also understand the interviewee’s behavior through body language.
Panel Interview
During a panel interview, three or more interviewers usually ask questions and evaluate the candidate’s answers as a group. This is a good way to get a full picture of a candidate’s skills and suitability for the job.
Group Types of Interviews
Multiple people are interviewed at the same time in group interviews. This form of interview often focus groups that are utilized on entry-level positions or employment in customer service to examine how well candidates get along with others and function as a team.
Case Interview
During a case interview, candidates are given a business problem or scenario and asked to think about how to solve it. In the consulting and finance fields, this kind of interview is common.
Technical Interview
A candidate’s technical skills and knowledge are tested during a technical interview, usually in fields like engineering or software development. Most of the time, candidates are asked to solve problems or complete technical tasks.
Stress Interview
During a stress interview, candidates are put under pressure or asked difficult or confrontational questions on purpose to see how they react in stressful situations. This kind of interview is used to see how well a candidate can deal with stress and hard situations.
Methods of Research Interviews:
There are four methods to conduct research interviews, each of which is peculiar in its application and can be used according to the research study requirement.
Personal Interviews:
Personal interviews are one of the most used types of interviews, where the questions are asked personally directly to the respondent as a form of an individual interview. One of the many in-person interviews is a lunch interview, which is frequently better suited for casual inquiries and discussions.
For this, a researcher can have a guide to online surveys to take note of the answers. A researcher can design his/her survey in such a way that they take notes of the comments or points of view that stands out from the interviewee. It can be a one-on-one interview as well.
- Higher response rate.
- When the interviewees and respondents are face-to-face, there is a way to adapt the questions if this is not understood.
- More complete answers can be obtained if there is doubt on both sides or a remarkable piece of information is detected.
- The researcher has an opportunity to detect and analyze the interviewee’s body language at the time of asking the questions and taking notes about it.
Disadvantages:
- They are time-consuming and extremely expensive.
- They can generate distrust on the part of the interviewee since they may be self-conscious and not answer truthfully.
- Contacting the interviewees can be a real headache, either scheduling an appointment in workplaces or going from house to house and not finding anyone.
- Therefore, many interviews are conducted in public places like shopping centers or parks. Even consumer studies take advantage of these sites to conduct interviews or surveys and give incentives, gifts, and coupons. In short, There are great opportunities for online research in shopping centers.
- Among the advantages of conducting such types of interviews is that the respondents will have more fresh information if the interview is conducted in the context and with the appropriate stimuli so that researchers can have data from their experience at the scene of the events immediately and first hand. The interviewer can use an online survey through a mobile device that will undoubtedly facilitate the entire process.
Telephonic Type of Interviews:
Phonic interviews are widely used and easily combined with online surveys to conduct research effectively.
Advantages:
- To find the interviewees, it is enough to have their phone numbers on hand.
- They are usually lower cost.
- The information is collected quickly.
- Having a personal contact can also clarify doubts or give more details of the questions.
- Many times researchers observe that people do not answer phone calls because it is an unknown number for the respondent or simply already changed their place of residence and they cannot locate it, which causes a bias in the interview.
- Researchers also face that they simply do not want to answer and resort to pretexts such as they are busy to answer, they are sick, they do not have the authority to answer the questions asked, they have no interest in answering, or they are afraid of putting their security at risk.
- One of the aspects that should be taken care of in these types of interviews is the kindness with which the interviewers address the respondents in order to get them to cooperate more easily with their answers. Good communication is vital for the generation of better answers.
Learn More: Data Collection Methods: Types & Examples
Email or Web Page Types of Interviews:
Online research is growing more and more because consumers are migrating to a more virtual world, and it is best for each researcher to adapt to this change.
The increase in people with Internet access has made it popular that interviews via email or web page stand out among the types of interviews most used today. For this nothing better than an online survey.
More and more consumers are turning to online shopping, which is why they are a great niche to be able to carry out an interview that will generate information for the correct decision-making.
Advantages of email surveys:
- Speed in obtaining data
- The respondents respond according to their time, when they want, and where they decide.
- Online surveys can be mixed with other research methods or using some of the previous interview models. They are tools that can perfectly complement and pay for the project.
- A researcher can use a variety of questions and logic to create graphs and reports immediately.
Disadvantages of email survey:
- Low response rates
- Limited access to certain populations
- Potential for spam filters
- Lack of personal touch
What to Avoid in Different Types of Interviews
Try not to do any of the following things when you’re in an interview:
- Don’t blame your previous managers, coworkers, or companies. This will make a bad impression on the interviewer and show that you are not accountable.
- Do not go to the interview without knowing anything about the company you are interviewing for. Interviewers will think you don’t care about learning about the company if you don’t know anything.
- Don’t fidget with things because that shows you lack self-confidence and focus.
- Stop checking the time because it shows that you have something more important to do and that you don’t give the interview much importance.
Related Questions of Interviews
After the interview is over, you might also get a chance to ask some questions. You should make the most of this chance to learn useful things from the interviewer. Based on what you’ve learned, you can then decide if the company and the job are a good fit for you. You can ask the interviewer questions about the company or about the job role.
Here are some common but important questions to ask in an interview:
- What do you anticipate from team members in this role?
- What does a typical day look like for an employee in this role?
- What qualities are essential for success in this position?
- How is success measured for this position?
- How does this job profile relate to the organization’s overarching objectives?
- What are your company’s guiding principles?
- Which departments will I work closely with throughout my time in this profile?
Learn more: Quantitative Research
To summarize the discussion, an effective interview will be one that provides researchers with the necessary data to know the object of study and that this information is applicable to the decisions researchers make.
Undoubtedly, the objective of the research will set the pattern of what types of interviews are best for data collection. Based on the research design , a researcher can plan and test the questions, for instance, if the questions are correct and if the survey flows in the best way.
LEARN ABOUT: Best Data Collection Tools
In addition, other types of research can be used under specific circumstances.
For example, there are no connections or adverse situations to carry out surveyors. In these types of occasions, it is necessary to conduct field research, which can not be considered an interview if not rather a completely different methodology.
QuestionPro is a flexible online survey platform that can help researchers do different kinds of interviews, like structured, semi-structured, unstructured, phone interview, group interview, etc. It gives researchers a flexible platform that can be changed to fit their needs and the needs of their research project.
QuestionPro can help researchers get detailed and useful information from participants using features like skip logic, piping, and live chat. Also, the platform is easy to use and get to, making it a useful tool for researchers to use in their work.
LEARN ABOUT: Candidate Experience Survey
Overall, QuestionPro can be helpful for researchers who want to do good interviews and collect good project data.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
The 3 main types of interviews are 1. Structured interviews 2. Semi-structured interviews 3. Unstructured interviews
There are different ways to conduct an interview, and each one can add depth and substance to the information the interviewer gathers by asking questions. We discuss four interview methods: situational, professional behavior profiling, stress, and behavioral.
Face-to-face means in-person interviews are the most common type of interview. It’s about getting a good sense of the candidate by focusing on them directly. But it also allows the person interviewed to talk freely and ask questions.
Personal interviews, phone interviews, email or web page interviews, and a combination of these methods are the four types of research interviews.
MORE LIKE THIS

Customer Experience Lessons from 13,000 Feet — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Aug 20, 2024

Insight: Definition & meaning, types and examples
Aug 19, 2024

Employee Loyalty: Strategies for Long-Term Business Success
Jotform vs SurveyMonkey: Which Is Best in 2024
Aug 15, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Structured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
Structured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
Published on January 27, 2022 by Tegan George and Julia Merkus. Revised on June 22, 2023.
A structured interview is a data collection method that relies on asking questions in a set order to collect data on a topic. It is one of four types of interviews .
In research, structured interviews are often quantitative in nature. They can also be used in qualitative research if the questions are open-ended, but this is less common.
While structured interviews are often associated with job interviews, they are also common in marketing, social science, survey methodology, and other research fields.
- Semi-structured interviews : A few questions are predetermined, whereas the other questions aren’t planned.
- Unstructured interviews : None of the questions are predetermined.
- Focus group interviews : The questions are presented to a group instead of one individual.
Table of contents
What is a structured interview, when to use a structured interview, advantages of structured interviews, disadvantages of structured interviews, structured interview questions, how to conduct a structured interview, how to analyze a structured interview, presenting your results, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about structured interviews.
Structured interviews are the most systematized type of interview. In contrast to semi-structured or unstructured interviews, the interviewer uses predetermined questions in a set order.
Structured interviews are often closed-ended. They can be dichotomous, which means asking participants to answer “yes” or “no” to each question, or multiple-choice. While open-ended structured interviews do exist, they are less common.
Asking set questions in a set order allows you to easily compare responses between participants in a uniform context. This can help you see patterns and highlight areas for further research, and it can be a useful explanatory or exploratory research tool.
Structured interviews are best used when:
- You already have a very clear understanding of your topic, so you possess a baseline for designing strong structured questions.
- You are constrained in terms of time or resources and need to analyze your data efficiently.
- Your research question depends on strong parity between participants, with environmental conditions held constant.
A structured interview is straightforward to conduct and analyze. Asking the same set of questions mitigates potential biases and leads to fewer ambiguities in analysis. It is an undertaking you can likely handle as an individual, provided you remain organized.
Differences between different types of interviews
Make sure to choose the type of interview that suits your research best. This table shows the most important differences between the four types.
| Fixed questions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed order of questions | ||||
| Fixed number of questions | ||||
| Option to ask additional questions |
Reduced bias
Increased credibility, reliability and validity, simple, cost-effective and efficient, formal in nature, limited flexibility, limited scope.
It can be difficult to write structured interview questions that approximate exactly what you are seeking to measure. Here are a few tips for writing questions that contribute to high internal validity :
- Define exactly what you want to discover prior to drafting your questions. This will help you write questions that really zero in on participant responses.
- Avoid jargon, compound sentences, and complicated constructions.
- Be as clear and concise as possible, so that participants can answer your question immediately.
- Do you think that employers should provide free gym memberships?
- Did any of your previous employers provide free memberships?
- Does your current employer provide a free membership?
- a) 1 time; b) 2 times; c) 3 times; d) 4 or more times
- Do you enjoy going to the gym?
Structured interviews are among the most straightforward research methods to conduct and analyze. Once you’ve determined that they’re the right fit for your research topic , you can proceed with the following steps.
Step 1: Set your goals and objectives
Start with brainstorming some guiding questions to help you conceptualize your research question, such as:
- What are you trying to learn or achieve from a structured interview?
- Why are you choosing a structured interview as opposed to a different type of interview, or another research method?
If you have satisfying reasoning for proceeding with a structured interview, you can move on to designing your questions.
Step 2: Design your questions
Pay special attention to the order and wording of your structured interview questions . Remember that in a structured interview they must remain the same. Stick to closed-ended or very simple open-ended questions.
Step 3: Assemble your participants
Depending on your topic, there are a few sampling methods you can use, such as:
- Voluntary response sampling : For example, posting a flyer on campus and finding participants based on responses
- Convenience sampling of those who are most readily accessible to you, such as fellow students at your university
- Stratified sampling of a particular age, race, ethnicity, gender identity, or other characteristic of interest to you
- Judgment sampling of a specific set of participants that you already know you want to include
Step 4: Decide on your medium
Determine whether you will be conducting your interviews in person or whether your interview will take pen-and-paper format. If conducted live, you need to decide if you prefer to talk with participants in person, over the phone, or via video conferencing.
Step 5: Conduct your interviews
As you conduct your interviews, be very careful that all conditions remain as constant as possible.
- Ask your questions in the same order, and try to moderate your tone of voice and any responses to participants as much as you can.
- Pay special attention to your body language (e.g., nodding, raising eyebrows), as this can bias responses.
After you’re finished conducting your interviews, it’s time to analyze your results.
- Assign each of your participants a number or pseudonym for organizational purposes.
- Transcribe the recordings manually or with the help of transcription software.
- Conduct a content or thematic analysis to look for categories or patterns of responses. In most cases, it’s also possible to conduct a statistical analysis to test your hypotheses .
Transcribing interviews
If you have audio-recorded your interviews, you will likely have to transcribe them prior to conducting your analysis. In some cases, your supervisor might ask you to add the transcriptions in the appendix of your paper.
First, you will have to decide whether to conduct verbatim transcription or intelligent verbatim transcription. Do pauses, laughter, or filler words like “umm” or “like” affect your analysis and research conclusions?
- If so, conduct verbatim transcription and include them.
- If not, conduct intelligent verbatim transcription, which excludes fillers and fixes any grammar issues, and is often easier to analyze.
The transcription process is a great opportunity for you to cleanse your data as well, spotting and resolving any inconsistencies or errors that come up as you listen.
Coding and analyzing structured interviews
After transcribing, it’s time to conduct your thematic or content analysis . This often involves “coding” words, patterns, or themes, separating them into categories for more robust analysis.
Due to the closed-ended nature of many structured interviews, you will most likely be conducting content analysis, rather than thematic analysis.
- You quantify the categories you chose in the coding stage by counting the occurrence of the words, phrases, subjects or concepts you selected.
- After coding, you can organize and summarize the data using descriptive statistics .
- Next, inferential statistics allows you to come to conclusions about your hypotheses and make predictions for future research.
When conducting content analysis, you can take an inductive or a deductive approach. With an inductive approach, you allow the data to determine your themes. A deductive approach is the opposite, and involves investigating whether your data confirm preconceived themes or ideas.
Content analysis has a systematic procedure that can easily be replicated , yielding high reliability to your results. However, keep in mind that while this approach reduces bias, it doesn’t eliminate it. Be vigilant about remaining objective here, even if your analysis does not confirm your hypotheses .
After your data analysis, the next step is to combine your findings into a research paper .
- Your methodology section describes how you collected the data (in this case, describing your structured interview process) and explains how you justify or conceptualize your analysis.
- Your discussion and results sections usually address each of your coded categories, describing each in turn, as well as how often they occurred.
If you conducted inferential statistics in addition to descriptive statistics, you would generally report the test statistic , p -value , and effect size in your results section. These values explain whether your results justify rejecting your null hypothesis and whether the result is practically significant .
You can then conclude with the main takeaways and avenues for further research.
Example of interview methodology for a research paper
Let’s say you are interested in healthcare on your campus. You attend a large public institution with a lot of international students, and you think there may be a difference in perceptions based on country of origin.
Specifically, you hypothesize that students coming from countries with single-payer or socialized healthcare will find US options less satisfying.
There is a large body of research available on this topic, so you decide to conduct structured interviews of your peers to see if there’s a difference between international students and local students.
You are a member of a large campus club that brings together international students and local students, and you send a message to the club to ask for volunteers.
Here are some questions you could ask:
- Do you find healthcare options on campus to be: excellent; good; fair; average; poor?
- Does your home country have socialized healthcare? Yes/No
- Are you on the campus healthcare plan? Yes/No
- Have you ever worried about your health insurance? Yes/No
- Have you ever had a serious health condition that insurance did not cover? Yes/No
- Have you ever been surprised or shocked by a medical bill? Yes/No
After conducting your interviews and transcribing your data, you can then conduct content analysis, coding responses into different categories. Since you began your research with the theory that international students may find US healthcare lacking, you would use the deductive approach to see if your hypotheses seem to hold true.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Student’s t -distribution
- Normal distribution
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Quartiles & Quantiles
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Data cleansing
- Reproducibility vs Replicability
- Peer review
- Prospective cohort study
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Placebo effect
- Hawthorne effect
- Hindsight bias
- Affect heuristic
- Social desirability bias
A structured interview is a data collection method that relies on asking questions in a set order to collect data on a topic. They are often quantitative in nature. Structured interviews are best used when:
- You already have a very clear understanding of your topic. Perhaps significant research has already been conducted, or you have done some prior research yourself, but you already possess a baseline for designing strong structured questions.
- You are constrained in terms of time or resources and need to analyze your data quickly and efficiently.
More flexible interview options include semi-structured interviews , unstructured interviews , and focus groups .
The four most common types of interviews are:
- Structured interviews : The questions are predetermined in both topic and order.
- Semi-structured interviews : A few questions are predetermined, but other questions aren’t planned.
The interviewer effect is a type of bias that emerges when a characteristic of an interviewer (race, age, gender identity, etc.) influences the responses given by the interviewee.
There is a risk of an interviewer effect in all types of interviews , but it can be mitigated by writing really high-quality interview questions.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. & Merkus, J. (2023, June 22). Structured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 21, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/structured-interview/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, semi-structured interview | definition, guide & examples, unstructured interview | definition, guide & examples, what is a focus group | step-by-step guide & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section Interview Methodology
Introduction, general overviews.
- Interview Styles
- Focused Interviews and Focus Groups
- Sensitive Topics
- Recording the Data
- Transcribing Interviews
- Coding and Analysis of Interview Data
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Interview Methodology by Heather Hamill LAST REVIEWED: 27 March 2014 LAST MODIFIED: 27 March 2014 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199756384-0105
Interview methodology is perhaps the oldest of all the social science methodologies. Asking interview participants a series of informal questions to obtain knowledge has been a common practice among anthropologists and sociologists since the inception of their disciplines. Within sociology, the early-20th-century urban ethnographers of the Chicago School did much to prompt interest in the method. In essence, interviewing is a method of eliciting information. It is a “conversation between people in which one person has the role of the researcher” ( Arksey and Knight 1999 , cited under General Overviews ; p. 2). Interviews can be carried out face to face, over the telephone and Internet, or in a group setting. The interview can vary from a spontaneous conversation to a highly structured, closed interview style associated with social survey research. Semistructured or open-ended interviews are commonly used in qualitative research. They are often aided by an interview guide, schedule, or aide memoire that contains topics, themes, or issues to be covered during the course of the interview rather than a sequence of standardized questions. The intention is that the interviewer remains flexible and responsive throughout the interview so that the sequence of questions can change, their content can evolve, and the interviewer can probe more deeply into initial responses to gain a more detailed or “in-depth” answer to the question. Interviews may also vary considerably in length. Thus the elicitation skills of the interviewer have a strong effect on the quality and richness of the interview data. Interview data is often recorded and then transcribed to produce text that can be analyzed using qualitative and quantitative methods of data analysis. In general, the overall sample size of an interview study is relatively small because of the amount of data that is generated in great depth and detail from interviewing. Thus, when thinking about who to interview and how many interviews to carry out, a non-probabilistic sampling strategy is generally most appropriate, and while empirical generalizations cannot be made, theory can be generated from this kind of data. Interview methodology is particularly useful for researchers who take a phenomenological approach. That is, they are concerned with the way in which individuals interpret and assign meaning to their social world. It is also commonly used in more open-ended inductive research whereby the researcher observes specific patterns within the interview data, formulates hypotheses to be explored with additional data, and finally develops theory.
Although sociologists had been carrying out interviewed-based research for some time, it was the work of Barney Glaser and Anselm Strauss (see Glaser and Strauss 1967 ) that pioneered the integration of qualitative interviews into their field studies and subsequently developed the grounded theory approach to qualitative data analysis. There are a large number of very high quality ethnographic monographs that contain detailed accounts of how researchers negotiated access to research groups and individuals, the relationship between researcher and respondent, ethical concerns, what questions were asked and how they were framed, and the general highs and lows of interviewing. First published in 1943, Whyte 1993 is supremely well written and remains a classic ethnography, and the appendix contains rich and relevant details as to how the author elicited information from his respondents. Spradley 1979 was among the first to systematically outline interviewing as a distinct methodology, and this was followed by a plethora of methodology textbooks, such as Arksey and Knight 1999 , Patton 2002 , Hammersley and Atkinson 2007 (cited under Interview Styles ), and Kvale and Brinkmann 2009 , that all provide very detailed guidance on how to design an interview-based piece of research and how to best elicit information by interviewing respondents. Fielding’s edited four-volume Interviewing II ( Fielding 2009 ) and Gubrium, et al. 2012 both provide comprehensive overviews of the method.
Arksey, Hilary, and Peter Knight. 1999. Interviewing for social scientists: An introductory resource with examples . London: SAGE.
This practical guide to interviewing covers a wide range of issues such as theories of interviewing, research design, and application and interpretation of interview data. Aimed at undergraduate and graduate students, it mainly focuses on interviewing within the context of small-scale studies with tight time and resource constraints.
Fielding, Nigel G., ed. 2009. Interviewing II . London: SAGE.
A four-volume collection of essays of which the wide-ranging contributions comprehensively cover all the theoretical and practical aspects of interviewing methodology.
Glaser, Barney G., and Anselm L. Strauss. 1967. The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research . Chicago: Aldine.
The principles of grounded theory were first articulated in this book. The authors contrast grounded theories derived directly from the data with theories derived from a deductive approach.
Gubrium, Jaber F., James A. Holstein, Amir B. Marvasti, and Karyn D. McKinney, eds. 2012. The SAGE handbook of interview research: The complexity of the craft . 2d ed. Thousand Oaks, CA, and London: SAGE.
A comprehensive guide to interviewing, this second edition emphasizes the dynamic, interactional, and reflexive aspects of the research interview.
Kvale, Steinar, and Svend Brinkmann. 2009. InterViews: Learning the craft of qualitative research interviewing . 2d ed. Los Angeles and London: SAGE.
An easy-to-read guide to interviewing. The authors propose that interviewing is a craft rather than just a method. The book emphasizes learning from “best practice,” and there are numerous examples and learning exercises to help facilitate that goal.
Patton, Michael Q. 2002. Qualitative research and evaluation methods . 3d ed. Thousand Oaks, CA, and London: SAGE.
In chapter 7, Patton provides a comprehensive guide to qualitative interviewing. This chapter highlights the variations in qualitative interviews and the interview guides or schedules that can be used. It provides a very useful guide as to how to formulate and ask questions and offers practical tips about recording and transcribing interviews. The chapter also covers focus groups, group interviews, ethics, and the relationship between researcher and interview participants.
Spradley, James P. 1979. The ethnographic interview . New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
A guide to ethnography informed by symbolic interactionism. Chapters 1 to 5 remain a very relevant and useful guide to interviewing.
Whyte, William Foote. 1993. Street corner society: The social structure of an Italian slum . 4th ed. Chicago and London: Univ. of Chicago Press.
DOI: 10.7208/chicago/9780226922669.001.0001
The appendix describes in great detail how Whyte carried out his ethnographic research. He writes about how he had to learn not only when it was appropriate to ask questions, but also how to ask those questions—and that, once he was established in the neighborhood, much of his data was gathered during casual conversations.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Sociology »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- Actor-Network Theory
- Adolescence
- African Americans
- African Societies
- Agent-Based Modeling
- Analysis, Spatial
- Analysis, World-Systems
- Anomie and Strain Theory
- Arab Spring, Mobilization, and Contentious Politics in the...
- Asian Americans
- Assimilation
- Authority and Work
- Bell, Daniel
- Biosociology
- Bourdieu, Pierre
- Catholicism
- Causal Inference
- Chicago School of Sociology
- Chinese Cultural Revolution
- Chinese Society
- Citizenship
- Civil Rights
- Civil Society
- Cognitive Sociology
- Cohort Analysis
- Collective Efficacy
- Collective Memory
- Comparative Historical Sociology
- Comte, Auguste
- Conflict Theory
- Conservatism
- Consumer Credit and Debt
- Consumer Culture
- Consumption
- Contemporary Family Issues
- Contingent Work
- Conversation Analysis
- Corrections
- Cosmopolitanism
- Crime, Cities and
- Cultural Capital
- Cultural Classification and Codes
- Cultural Economy
- Cultural Omnivorousness
- Cultural Production and Circulation
- Culture and Networks
- Culture, Sociology of
- Development
- Discrimination
- Doing Gender
- Du Bois, W.E.B.
- Durkheim, Émile
- Economic Globalization
- Economic Institutions and Institutional Change
- Economic Sociology
- Education and Health
- Education Policy in the United States
- Educational Policy and Race
- Empires and Colonialism
- Entrepreneurship
- Environmental Sociology
- Epistemology
- Ethnic Enclaves
- Ethnomethodology and Conversation Analysis
- Exchange Theory
- Families, Postmodern
- Family Policies
- Feminist Theory
- Field, Bourdieu's Concept of
- Forced Migration
- Foucault, Michel
- Frankfurt School
- Gender and Bodies
- Gender and Crime
- Gender and Education
- Gender and Health
- Gender and Incarceration
- Gender and Professions
- Gender and Social Movements
- Gender and Work
- Gender Pay Gap
- Gender, Sexuality, and Migration
- Gender Stratification
- Gender, Welfare Policy and
- Gendered Sexuality
- Gentrification
- Gerontology
- Global Inequalities
- Globalization and Labor
- Goffman, Erving
- Historic Preservation
- Human Trafficking
- Immigration
- Indian Society, Contemporary
- Institutions
- Intellectuals
- Intersectionalities
- Interview Methodology
- Job Quality
- Knowledge, Critical Sociology of
- Labor Markets
- Latino/Latina Studies
- Law and Society
- Law, Sociology of
- LGBT Parenting and Family Formation
- LGBT Social Movements
- Life Course
- Lipset, S.M.
- Markets, Conventions and Categories in
- Marriage and Divorce
- Marxist Sociology
- Masculinity
- Mass Incarceration in the United States and its Collateral...
- Material Culture
- Mathematical Sociology
- Medical Sociology
- Mental Illness
- Methodological Individualism
- Middle Classes
- Military Sociology
- Money and Credit
- Multiculturalism
- Multilevel Models
- Multiracial, Mixed-Race, and Biracial Identities
- Nationalism
- Non-normative Sexuality Studies
- Occupations and Professions
- Organizations
- Panel Studies
- Parsons, Talcott
- Political Culture
- Political Economy
- Political Sociology
- Popular Culture
- Proletariat (Working Class)
- Protestantism
- Public Opinion
- Public Space
- Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA)
- Race and Sexuality
- Race and Violence
- Race and Youth
- Race in Global Perspective
- Race, Organizations, and Movements
- Rational Choice
- Relationships
- Religion and the Public Sphere
- Residential Segregation
- Revolutions
- Role Theory
- Rural Sociology
- Scientific Networks
- Secularization
- Sequence Analysis
- Sex versus Gender
- Sexual Identity
- Sexualities
- Sexuality Across the Life Course
- Simmel, Georg
- Single Parents in Context
- Small Cities
- Social Capital
- Social Change
- Social Closure
- Social Construction of Crime
- Social Control
- Social Darwinism
- Social Disorganization Theory
- Social Epidemiology
- Social History
- Social Indicators
- Social Mobility
- Social Movements
- Social Network Analysis
- Social Networks
- Social Policy
- Social Problems
- Social Psychology
- Social Stratification
- Social Theory
- Socialization, Sociological Perspectives on
- Sociolinguistics
- Sociological Approaches to Character
- Sociological Research on the Chinese Society
- Sociological Research, Qualitative Methods in
- Sociological Research, Quantitative Methods in
- Sociology, History of
- Sociology of Manners
- Sociology of Music
- Sociology of War, The
- Suburbanism
- Survey Methods
- Symbolic Boundaries
- Symbolic Interactionism
- The Division of Labor after Durkheim
- Tilly, Charles
- Time Use and Childcare
- Time Use and Time Diary Research
- Tourism, Sociology of
- Transnational Adoption
- Unions and Inequality
- Urban Ethnography
- Urban Growth Machine
- Urban Inequality in the United States
- Veblen, Thorstein
- Visual Arts, Music, and Aesthetic Experience
- Wallerstein, Immanuel
- Welfare, Race, and the American Imagination
- Welfare States
- Women’s Employment and Economic Inequality Between Househo...
- Work and Employment, Sociology of
- Work/Life Balance
- Workplace Flexibility
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [81.177.180.204]
- 81.177.180.204
- Usability testing
Run remote usability tests on any digital product to deep dive into your key user flows
- Product analytics
Learn how users are behaving on your website in real time and uncover points of frustration
- Research repository
A tool for collaborative analysis of qualitative data and for building your research repository and database.
Trymata Blog
How-to articles, expert tips, and the latest news in user testing & user experience
Knowledge Hub
Detailed explainers of Trymata’s features & plans, and UX research terms & topics
- Plans & Pricing
Get paid to test
- For UX & design teams
- For product teams
- For marketing teams
- For ecommerce teams
- For agencies
- For startups & VCs
- Customer Stories
How do you want to use Trymata?
Conduct user testing, desktop usability video.
You’re on a business trip in Oakland, CA. You've been working late in downtown and now you're looking for a place nearby to grab a late dinner. You decided to check Zomato to try and find somewhere to eat. (Don't begin searching yet).
- Look around on the home page. Does anything seem interesting to you?
- How would you go about finding a place to eat near you in Downtown Oakland? You want something kind of quick, open late, not too expensive, and with a good rating.
- What do the reviews say about the restaurant you've chosen?
- What was the most important factor for you in choosing this spot?
- You're currently close to the 19th St Bart station, and it's 9PM. How would you get to this restaurant? Do you think you'll be able to make it before closing time?
- Your friend recommended you to check out a place called Belly while you're in Oakland. Try to find where it is, when it's open, and what kind of food options they have.
- Now go to any restaurant's page and try to leave a review (don't actually submit it).
What was the worst thing about your experience?
It was hard to find the bart station. The collections not being able to be sorted was a bit of a bummer
What other aspects of the experience could be improved?
Feedback from the owners would be nice
What did you like about the website?
The flow was good, lots of bright photos
What other comments do you have for the owner of the website?
I like that you can sort by what you are looking for and i like the idea of collections
You're going on a vacation to Italy next month, and you want to learn some basic Italian for getting around while there. You decided to try Duolingo.
- Please begin by downloading the app to your device.
- Choose Italian and get started with the first lesson (stop once you reach the first question).
- Now go all the way through the rest of the first lesson, describing your thoughts as you go.
- Get your profile set up, then view your account page. What information and options are there? Do you feel that these are useful? Why or why not?
- After a week in Italy, you're going to spend a few days in Austria. How would you take German lessons on Duolingo?
- What other languages does the app offer? Do any of them interest you?
I felt like there could have been a little more of an instructional component to the lesson.
It would be cool if there were some feature that could allow two learners studying the same language to take lessons together. I imagine that their screens would be synced and they could go through lessons together and chat along the way.
Overall, the app was very intuitive to use and visually appealing. I also liked the option to connect with others.
Overall, the app seemed very helpful and easy to use. I feel like it makes learning a new language fun and almost like a game. It would be nice, however, if it contained more of an instructional portion.
All accounts, tests, and data have been migrated to our new & improved system!
Use the same email and password to log in:
Legacy login: Our legacy system is still available in view-only mode, login here >
What’s the new system about? Read more about our transition & what it-->
What is Formative Research? Definition, Methods, Example and Process
What is Formative Research?
Formative research is defined as a type of research that is used to gather insights and data during the initial stages of developing a program or intervention.
Unlike summative research, which evaluates the outcomes after a program’s completion, formative research focuses on understanding the needs, behaviors, and contexts of the target audience to tailor interventions more effectively.
The primary purpose of formative research is to ensure that a final program is well-suited to the target audience’s characteristics and needs. By collecting qualitative and quantitative data, researchers can identify barriers and facilitators to behavior change, understand cultural and contextual factors, and test preliminary concepts or materials. This process helps in developing strategies that are not only theoretically sound but also practically feasible and culturally appropriate. Formative research is crucial for minimizing risks and enhancing the effectiveness and sustainability of programs.
Formative research employs various methodologies to gather comprehensive data. These methods can include focus group discussions, in-depth interviews, surveys, observations, and community assessments etc.
For example, consider a public health campaign aimed at increasing vaccination rates among a hesitant population:
- Formative research would begin with exploratory focus groups to understand the community’s beliefs, fears, and misconceptions about vaccines.
- Researchers might also conduct surveys to quantify the prevalence of these attitudes.
- In-depth interviews with key informants, such as community leaders and healthcare providers, could provide insights into local influences and potential messaging strategies.
- Observational studies at healthcare facilities might reveal practical barriers to accessing vaccines, such as long wait times or inconvenient clinic hours.
By synthesizing this data, the research team could design a tailored intervention addressing specific concerns, leveraging trusted messengers, and improving accessibility, thereby increasing the likelihood of the campaign’s success.
When is Formative Research Used?
- Early Stages of Program Development
When designing a new intervention, policy, or program, it is essential to gather relevant data to ensure the initiative is tailored to the target audience’s needs and contexts. This stage involves understanding the problem, identifying target behaviors, and gathering insights about the population. By using formative research at this stage, developers can design more effective and relevant programs that are likely to achieve their intended outcomes.
- Program Planning and Strategy Development
Formative research is also used during the program planning and strategy development phases. This involves developing specific strategies, messages, and materials for the program. Researchers gather detailed information about the target audience’s preferences, motivations, and barriers to inform the creation of effective communication strategies and interventions. For example, in a public health campaign, formative research might identify the most effective channels for reaching different audience segments, the types of messages that resonate best, and the potential barriers to behavior change.
- Pre-Implementation Testing
Before a program is fully implemented, formative research is used for pretesting various elements of the intervention. This can include testing messages, materials, delivery methods, and strategies with a sample of the target audience. Pretesting helps identify any issues or misunderstandings that might arise and allows for adjustments to be made. This step ensures that the program components are well-received and effective before broader rollout. For instance, in an educational campaign, pretesting might reveal that certain messages are confusing or that particular delivery methods are not engaging the audience.
- Continuous Improvement During Implementation
Formative research is not limited to the initial stages of program development but is also used for continuous improvement during implementation. As the program is rolled out, ongoing feedback is gathered from participants and other stakeholders to identify areas for refinement and improvement. This iterative process allows for real-time adjustments based on the target audience’s responses and changing contexts.
For example, in a community health program, ongoing formative research might reveal new barriers or emerging needs, prompting timely adjustments to the intervention strategy.
Key Components of Formative Research
Formative research comprises several critical components that collectively contribute to the development of effective programs and interventions. These components include needs assessment, audience segmentation, pretesting, and continuous feedback.
1. Needs Assessment
This process helps to ensure that the intervention addresses real and pressing issues. The assessment is done using surveys, focus groups, evaluating existing data etc. By understanding the specific needs and priorities of the target audience, researchers can tailor interventions to be more relevant and impactful.
2. Audience Segmentation
Audience segmentation involves dividing the target population into distinct groups based on specific characteristics such as demographics, behaviors, attitudes, or psychographics. This component is crucial because it allows researchers to develop targeted strategies for different segments of the population. For instance, an intervention may need to be customized differently for teenagers than for older adults, or for urban residents compared to rural residents. Effective segmentation ensures that the intervention resonates with each subgroup, enhancing its overall effectiveness.
3. Pretesting
Pretesting refers to the process of testing various elements of the intervention before its full-scale implementation. This can include pretesting messages, materials, methods, and strategies with a sample of the target audience. Pretesting helps to identify any issues or misunderstandings that might arise and allows for adjustments to be made before the intervention is rolled out more broadly. Techniques used in pretesting can include focus groups, pilot studies, and cognitive interviews. The feedback obtained from pretesting is invaluable in refining and optimizing the intervention.
4. Continuous Feedback and Iteration
Continuous feedback and iteration are essential to the formative research process. As the intervention is developed and implemented, ongoing feedback is gathered from the target audience and other stakeholders. This feedback loop allows for continuous refinement and improvement of the intervention. Methods for obtaining feedback can include follow-up surveys, monitoring and evaluation reports, and regular stakeholder meetings. The iterative nature of formative research ensures that the intervention remains responsive to the evolving needs and contexts of the target population, ultimately enhancing its effectiveness and sustainability.
Key Steps in the Formative Research Process
The formative research process involves a series of systematic steps to gather insights and data, ensuring that a program or intervention is well-informed and tailored to the target audience. These steps include defining objectives, designing the research plan, data collection, data analysis, and applying findings.
1. Defining Objectives
This involves identifying what specific information is needed to inform the program or intervention. Objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For example, objectives might include understanding the target audience’s knowledge and attitudes about a health issue, identifying barriers to behavior change, or determining the most effective communication channels.
2. Designing the Research Plan
This includes selecting the appropriate research methods (qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods), determining the sample size and characteristics, and developing data collection instruments such as surveys, interview guides, or observation checklists. The research plan should also include a timeline and budget, as well as considerations for ethical approval and data confidentiality.
3. Data Collection
This step can include various methods such as focus groups, in-depth interviews, surveys, observations, and review of existing data. Effective data collection requires skilled researchers who can elicit honest and comprehensive responses from participants. It is also important to pilot test data collection instruments to ensure they are clear and effective.
4. Data Analysis
Qualitative data analysis involves identifying themes, patterns, and trends from textual or visual data, while quantitative data analysis involves statistical analysis to determine the prevalence and relationships between variables. Tools and software such as NVivo for qualitative data and SPSS or Excel for quantitative data can be used to assist in this process.
5. Applying Findings
The final step in the formative research process is to apply the findings to inform the development and implementation of the program or intervention. The findings should be communicated to stakeholders in a clear and accessible manner, often through reports, presentations, and workshops. Based on the insights gained, the program can be designed or adjusted to better meet the needs of the target audience, improve effectiveness, and ensure sustainability.
Formative Research Methods
Formative research employs a variety of methods to gather comprehensive data and insights about the target population and context. These methods can be broadly categorized into qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches, each providing unique insights and complementing each other to create a well-rounded understanding.
- Qualitative Methods
– Focus Groups
Focus groups involve guided discussions with a small group of people from the target population. This method helps in exploring attitudes, perceptions, and motivations in a social context. Focus groups are particularly useful for generating in-depth insights into how a community or group perceives an issue or intervention.
– In-Depth Interviews
This method is useful for gaining a deep understanding of complex behaviors and underlying reasons that may not be evident in group settings.
– Observations
This approach helps to understand the context and environment in which the target population operates, providing insights into actual behaviors and social dynamics.
– Case Studies
Case studies are useful for understanding the intricacies and particularities of a situation, providing detailed contextual insights that can inform program design.
- Quantitative Methods
This method is useful for collecting standardized data on knowledge, attitudes, behaviors, and demographics.
– Structured Observations
Structured observations involve using predefined criteria and checklists to systematically observe and record specific behaviors or events. This method provides quantitative data on the frequency, duration, or occurrence of particular behaviors, which can be used to identify patterns and trends.
- Mixed Methods
– Combining Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches
Mixed methods research involves integrating qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis techniques in a single study. For example, a study might use qualitative focus groups to explore perceptions and then design a quantitative survey to measure the prevalence of these perceptions in the larger population.
– Sequential and Concurrent Designs
This approach allows for the initial qualitative findings to inform the design of the subsequent quantitative phase, or vice versa. Concurrent designs involve collecting both qualitative and quantitative data simultaneously and integrating the findings during the analysis phase, providing a comprehensive view of the research problem.
By employing a variety of formative research methods, researchers can gather rich, multi-faceted data that provides a thorough understanding of the target population, context, and issues at hand.
Examples of Formative Research
Here are some examples of how formative research has been used in different contexts:
1. Public Health Campaigns
Example: Increasing HPV Vaccination Rates
A public health organization aiming to increase HPV vaccination rates among adolescents might conduct formative research to understand the barriers and facilitators to vaccination. This could involve:
- Focus Groups: Conducting discussions with parents, teenagers, and healthcare providers to explore their attitudes, beliefs, and knowledge about the HPV vaccine.
- Surveys: Administering surveys to a larger sample of parents and teens to quantify the prevalence of different beliefs and identify key demographic differences.
- In-Depth Interviews: Interviewing healthcare providers to understand their experiences and challenges in recommending and administering the vaccine.
- Observations: Observing interactions in clinics to identify practical barriers to vaccination, such as long wait times or lack of privacy.
Based on these insights, the organization might develop targeted messaging that addresses specific concerns, create educational materials tailored to different audience segments, and implement changes in clinic processes to make vaccination more convenient.
2. Education Programs
Example: Improving Literacy Rates
An educational NGO aiming to improve literacy rates among elementary school children in a rural area might use formative research to design an effective literacy program. This could involve:
- Needs Assessment: Assessing the current literacy levels and identifying gaps in existing educational resources and support.
- Focus Groups: Conducting discussions with teachers, parents, and students to understand their perceptions of literacy challenges and potential solutions.
- Surveys: Surveying teachers to identify common barriers to effective literacy instruction and the types of support they need.
- Classroom Observations: Observing literacy instruction in classrooms to identify effective practices and areas for improvement.
The findings might lead to the development of teacher training programs focused on literacy instruction, the creation of culturally relevant reading materials, and the implementation of parent engagement initiatives to support literacy at home.
3. Social Marketing Campaigns
Example: Reducing Plastic Waste
A government agency aiming to reduce plastic waste might conduct formative research to design a social marketing campaign that encourages recycling and the use of reusable products. This could involve:
- Surveys: Administering surveys to understand public awareness, attitudes, and behaviors related to plastic use and recycling.
- Focus Groups: Conducting discussions with different demographic groups to explore motivations and barriers to reducing plastic use and adopting reusable products.
- In-Depth Interviews: Interviewing stakeholders such as retailers, waste management professionals, and environmental activists to gather insights on effective strategies and potential challenges.
- Community Assessments: Assessing community infrastructure and resources available for recycling and waste management.
Interested in learning more about the fields of product, research, and design? Search our articles here for helpful information spanning a wide range of topics!
14 Best Performance Testing Tools for Application Reliability
A complete guide to usability testing methods for better ux, ux mapping methods and how to create effective maps, a guide to the system usability scale (sus) and its scores.
In‐Depth Interviews
- September 2020

- Fielding Graduate University

Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Vivian I Buhain

- Slamet Riyadi
- Siska Armawati Sufa

- Theo Jhoni Hartanto

- Nawshin Farzana Eva
- Amare Setie Alebel
- Adugna Abebe Bihonegn

- BMC PUBLIC HEALTH

- Blessings Chiwosi
- Rumbidzai H. C.
- Tapiwa G. S.

- Dustin I. Bessette

- Inform Comm Soc

- Karyn D. McKinney
- INT J ADVERT

- J APPL DEV PSYCHOL

- Cliff Lampe
- L.-P Morency
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

- The Chicago School
- The Chicago School Library
- Research Guides
Quantitative Research Methods
What is quantitative research, about this guide, introduction, quantitative research methodologies.
- Key Resources
- Quantitative Software
- Finding Qualitative Studies
The purpose of this guide is to provide a starting point for learning about quantitative research. In this guide, you'll find:
- Resources on diverse types of quantitative research.
- An overview of resources for data, methods & analysis
- Popular quantitative software options
- Information on how to find quantitative studies
Research involving the collection of data in numerical form for quantitative analysis. The numerical data can be durations, scores, counts of incidents, ratings, or scales. Quantitative data can be collected in either controlled or naturalistic environments, in laboratories or field studies, from special populations or from samples of the general population. The defining factor is that numbers result from the process, whether the initial data collection produced numerical values, or whether non-numerical values were subsequently converted to numbers as part of the analysis process, as in content analysis.
Citation: Garwood, J. (2006). Quantitative research. In V. Jupp (Ed.), The SAGE dictionary of social research methods. (pp. 251-252). London, England: SAGE Publications. doi:10.4135/9780857020116
Watch the following video to learn more about Quantitative Research:
(Video best viewed in Edge and Chrome browsers, or click here to view in the Sage Research Methods Database)
Correlational
Researchers will compare two sets of numbers to try and identify a relationship (if any) between two things.
Descriptive
Researchers will attempt to quantify a variety of factors at play as they study a particular type of phenomenon or action. For example, researchers might use a descriptive methodology to understand the effects of climate change on the life cycle of a plant or animal.
Experimental
To understand the effects of a variable, researchers will design an experiment where they can control as many factors as possible. This can involve creating control and experimental groups. The experimental group will be exposed to the variable to study its effects. The control group provides data about what happens when the variable is absent. For example, in a study about online teaching, the control group might receive traditional face-to-face instruction while the experimental group would receive their instruction virtually.
Quasi-Experimental/Quasi-Comparative
Researchers will attempt to determine what (if any) effect a variable can have. These studies may have multiple independent variables (causes) and multiple dependent variables (effects), but this can complicate researchers' efforts to find out if A can cause B or if X, Y, and Z are also playing a role.
Surveys can be considered a quantitative methodology if the researchers require their respondents to choose from pre-determined responses.
- Next: Key Resources >>
- Last Updated: Aug 20, 2024 5:29 PM
- URL: https://library.thechicagoschool.edu/quantitative
- Open access
- Published: 19 August 2024
Updating a conceptual model of effective symptom management in palliative care to include patient and carer perspective: a qualitative study
- Emma J. Chapman 1 ,
- Carole A. Paley 1 ,
- Simon Pini 2 &
- Lucy E. Ziegler 1
BMC Palliative Care volume 23 , Article number: 208 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
64 Accesses
Metrics details
A conceptual model of effective symptom management was previously developed from interviews with multidisciplinary healthcare professionals (HCP) working in English hospices. Here we aimed to answer the question; does a HCP data-derived model represent the experience of patients and carers of people with advanced cancer?
Semi-structured interviews were undertaken with six patients with advanced cancer and six carers to gain an in-depth understanding of their experience of symptom management. Analysis was based on the framework method; transcription, familiarisation, coding, applying analytical framework (conceptual model), charting, interpretation. Inductive framework analysis was used to align data with themes in the existing model. A deductive approach was also used to identify new themes.
The experience of patients and carers aligned with key steps of engagement, decision making, partnership and delivery in the HCP-based model. The data aligned with 18 of 23 themes. These were; Role definition and boundaries, Multidisciplinary team decision making, Availability of services/staff, Clinician-Patient relationship/rapport, Patient preferences, Patient characteristics, Quality of life versus treatment need, Staff time/burden, Psychological support -informal, Appropriate understanding, expectations, acceptance and goals- patients, Appropriate understanding, expectations, acceptance and goals-HCPs, Appropriate understanding, expectations, acceptance and goals- family friends, carers, Professional, service and referral factors, Continuity of care, Multidisciplinary team working, Palliative care philosophy and culture, Physical environment and facilities, Referral process and delays. Four additional patient and carer-derived themes were identified: Carer Burden, Communication, Medicines management and COVID-19. Constructs that did not align were Experience (of staff), Training (of staff), Guidelines and evidence, Psychological support (for staff) and Formal psychological support (for patients).
Conclusions
A healthcare professional-based conceptual model of effective symptom management aligned well with the experience of patients with advanced cancer and their carers. Additional domains were identified. We make four recommendations for change arising from this research. Routine appraisal and acknowledgement of carer burden, medicine management tasks and previous experience in healthcare roles; improved access to communication skills training for staff and review of patient communication needs. Further research should explore the symptom management experience of those living alone and how these people can be better supported.
Peer Review reports
A conceptual model of effective symptom management was previously developed from qualitative data derived from interviews with healthcare professionals working in English hospices to elicit their views about the barriers and facilitators of effective symptom management [ 1 ]. The model delineated the successful symptom management experience into four steps of: engagement, decision-making, partnership and delivery. Constructs contributing to these were identified (Table 1 ).
Our original model was based solely on Healthcare professional (HCP) input. However, the perception of professionals may vary from that of patients and carers. A recent patient and professional survey of needs assessments in an oncology inpatient unit showed discrepancies between perception of unmet needs between staff and patients [ 2 ]. For this reason, we were concerned that what was deemed important by HCP working in palliative care may not mirror the concerns and experience of patients and carers.
Here we aimed to answer the question; does an HCP data-derived model represent the experience of patients and carers of people with advanced cancer?. If necessary, the original conceptual model of effective symptom management will be updated.
Qualitative, semi-structured interviews were chosen to gain an in-depth understanding of the experience from the perspective of a range of patients and carers. All methods were carried out in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical approval was granted by a UK research ethics committee ( North of Scotland [ 2 ] Research Ethics Committee (20/NS/0086)). Verbal, recorded informed consent was given using a verbal consent script (Supplementary information 1). Our original intention had been to conduct interviews face to face facilitated by a set of laminated prompt cards based upon those used in the HCP interviews. However, adaptation to telephone interviews in patient’s homes was necessary due to COVID-19 restrictions and it became apparent that the card exercise did not work well remotely. We continued interviews based on the interview schedule but without the use of prompt cards. EC is a female, non-clinical senior research fellow in palliative care. She has experience of qualitative interviews and led the development of the original HCP-based model of effective symptom management [ 1 ]. Audio recordings were transcribed verbatim by a senior academic secretary.
Recruitment
Participants who met the inclusion criteria were identified by a research nurse at the participating hospice. Eligible patients were those who met all 5 criteria:
Diagnosed with advanced disease (i.e., cancer that is considered to be incurable).
Had been referred to the participating hospice.
Were 18 years of age or over.
Were able to speak and understand English.
Were able to give informed consent.
Eligible carers were people who met all 4 criteria:
Were the informal carer of an eligible patient (who may or may not also be participating in the study).
Patients or carers were excluded if they:
Exhibited cognitive dysfunction which would impede their being able to give informed consent and take part in the study.
Were deemed by hospice staff to be too ill or distressed.
Access to the inpatient unit was not possible at this time due to Covid-19 restrictions. The research nurse introduced the study, provided a participant information sheet and completed a consent to contact form. The first contact with the researcher was made by telephone to confirm (or not) interest in participation and answer questions. An interview time not less than 48 h after provision of the participant information sheet, was scheduled. The researcher and the participant information sheet explained the overall aim of the RESOLVE research programme to improve health status and symptom experience for people living with advanced cancer (Supplementary information 2). The verbal consent statements made it clear that this was a conversation for research purposes only and would not have any impact on the care the patient received (Supplementary information 3). Permission was granted that the researcher may contact the clinical team at the hospice if there was a serious concern for welfare that required urgent attention. Verbal informed consent was collected, and audio recorded at the start of the interview with participants answering yes or no to each of the statements in the verbal consent script (Supplementary information 3). Participants were told that we had already interviewed HCPs about what helped or hindered effective symptom management and now we wanted to understand their perspective too.
Data Collection
Interview topic guides (Supplementary information 4 and 5) were used. Interviews were conducted by EC over the telephone and audio recorded onto an encrypted Dictaphone. Files were downloaded onto a secure University of Leeds drive and then deleted from the Dictaphone. No video was recorded. The researcher made brief field notes directly after the interview on impression, emotion and participant backgrounds that were disclosed.
An Excel spreadsheet was used to facilitate data management. We explored the constructs of patient and carer experience as defined by our existing model. An inductive framework analysis was used to align data with themes in the existing conceptual model. A deductive approach was also used to identify new themes not included in the original model. Two researchers (EC and CP) independently conducted framework analysis on all transcripts. Data was then compared and discussed until a consensus data set was developed. The study is reported in accordance with Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) recommendations [ 11 ].
Twelve participants were interviewed in their own homes by telephone. In five interviews a family member or friend was also present, and they were interviewed as a dyad. One interview was with a carer of a patient (patient not interviewed) and one interview was with a patient alone. Interviews lasted between 21 and 45 min. Basic self-declared demographic information was collected (Table 2 ).
One person was approached by a research nurse and provided with participant information sheet. However, when they spoke with the researcher on the telephone it was clear that they had not read the participant information sheet. The individual declined for the information to be read out loud with them. Informed consent could therefore not be given and an interview was not carried out. Upon reflection, this person was keen to informally chat to the researcher but was perhaps seeking social interaction rather than research participation. All other participants completed the interview as planned.
Participant background was relevant as one carer and one patient, had experience of working in healthcare and this may have shaped their experience and understanding. Analysis was based on the framework method; transcription, familiarisation, coding, applying analytical framework (conceptual model), charting, interpretation.
Data aligned with 18 of 23 constructs in the professional based model (Table 3 ). Pseudonyms are used to protect confidentiality.
Four constructs that had featured in the healthcare professional based model did not feature in the patient and carer derived data. These were perhaps not unexpectedly related to characteristics of staff; Experience (of staff), Training (of staff), Psychological support (for staff) and the provision of formal psychological support (for patients). One construct ‘Guidelines and Evidence’ was not explicitly mentioned by patients and carers. However, a carer did comment that at time of referral to the hospice, the patient had been on two different does of co-codamol simultaneously ‘ You were on co-codamol, the 500/8 plus co-codamol 500/30’ (Patricia, carer) which suggested to the researchers that the patient had been taking the medication in a way contrary to guidelines. Medications were then optimised by hospice staff. Four additional patient and carer-derived themes were identified: Carer Burden, Communication, Medicines management and Impact of COVID-19 (Fig. 1 ).
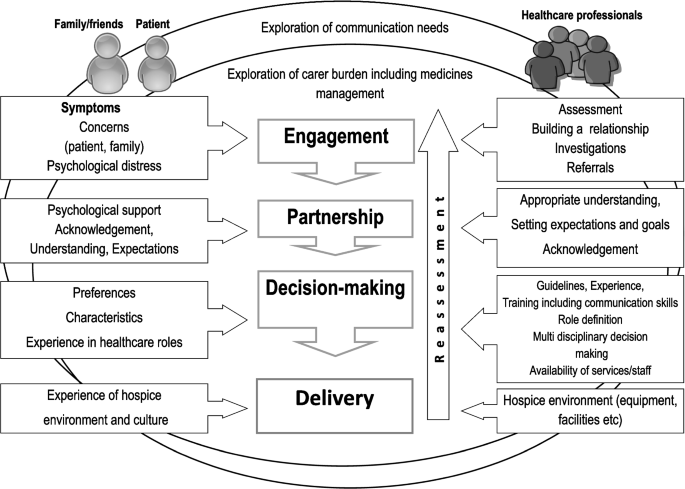
The conceptual model of effective symptom management in palliative care was updated to also reflect patient and carer perspective. Specifically, the need for support with communication and medicines management plus consideration of the carer burden were included
Carer burden
Our HCP-based conceptual model identified a role for the carer in shaping symptom management experience in either a positive or negative way [ 1 ]. The patient and carer derived data presented here provides additional insight into their role and the activities required of them. Carer burden is a multifaceted experience, however our interview schedule specifically asked about symptom management experience.
The carer was sometimes responsible for raising concerns and initiating the referral for specialist palliative cares support ‘it was at some stage earlier in this year when I was a little anxious about your health and contacted the chemo wing at (hospital) and one of the nurses there thought it would be helpful to me and Patient to put us in touch with (the hospice) (Kathleen, carer).
Carers were enmeshed into the disease and symptom experience of the patient, referring to ‘we’ when talking about the patient’s cancer treatment, pain and referral to hospice.
Olivia (carer): Immune therapy we’d had a reaction to and we’d resolved the reaction but it concluded in stopping any treatment and we then went to a situation where we were not able to manage the pain from the cancer successfully and it was recommended by our oncologist that (the hospice) may have some expertise that we could….
Olivia (carer): Tap into…as I say that was a difficult decision for us to agree for Anthony to go into (the hospice).
However, on occasion the insight from the carer was not acted upon leading to a delay in support for distressing symptoms ‘ I kept saying to people, he’s losing weight, he’s in pain and they just kept saying well he shouldn’t be in this amount of pain ‘cos of what his bloods are like. And I kept saying well what you’re saying he should be like, I can tell you he’s not like and we’re not ones to you know erm (he) isn’t one to be bothering the doctor.’ (Sandra, carer).
Once the patient was receiving palliative care the carer took responsibility for obtaining and retaining knowledge either because the patient could not, due to memory problems from medication, or their condition, or they were not willing to do this for themselves.
Martin (patient): ‘she knows better than me ‘cos I’m always, I’m not very good at remembering stuff’
Martin (patient): I’m not interested no I understand you do have a very important role and she’s taken the lead on it now, that’s definitely the case’
And with another couple
Terry (patient): Sorry I’ve got my wife at the side of me ‘cos she knows better than me ‘cos I’m always, I’m not very good at remembering stuff.
Stacey (carer): I’m usually present yeah, I’m usually around. I tend to be the one that asks more questions.
However, in our interviews occasionally discordance between patient and carer opinion was seen with the carer rating the symptoms more troublesome than the patient’s recollection.
Interviewer: So was it (the pain) stopping you doing any activities that you had been able to do?
Marti, (patient): Oh I see, not particularly no
Mary (carer): I would probably disagree with that sorry. I would say that Martin’s management of the pain and our management of the pain and everything was kind of a constant thing, that’s all we, you know if felt like we were talking about it all the time, his pain’.
Despite an integral role in facilitating effective symptom management carers could feel unacknowledged, specifically by hospital staff. ‘ at the same time they’re telling me I’m not a carer and yet you know Wendy would be in a very sorry state if I wasn’t on the ball all the time’ (Patricia, carer). Specialist palliative care staff were better at providing acknowledgement and consideration of individual capabilities.
Patricia (carer): ‘So they understand that I’m not sort of hale and hearty and I’ve got my limitations….and it’s just lovely them knowing and actually accepting that I am caring for patient, we are doing the best that we can and that they are there for us.’. This simple step of acknowledgement was appreciated and a factor in allowing the carer to continue to support the patient.
Olivia (carer): ‘You know I do feel that it’s about me as well, it’s not just about Anthony which, it is really all about Anthony but you know it’s important that I continue with my wellbeing in order that I can support and look after him’ .
Communication
The impact of communication of effective symptom management occurred at different levels. As would be expected, communication needed to be tailored to the background, previous experience and outlook of the individual. In particular, we noted that a patient who had a healthcare background themselves welcomed more in-depth discussion and input into decision making.
Andrew (patient): I’ve dealt with people with cancers and terminal illnesses. Yeah, I know about syringe drives and everything…The important thing is to be able to discuss it and with my knowledge of medication as well, I mean I can discuss it in depth.’ .
Interestingly, this person also equated being admitted to the hospice with the use of a syringe driver and end of life, illustrating that regardless of the patient’s professional background, a thorough explanation without any assumptions on understanding would still be necessary. Andrew (patient): ‘I mean I could go into (the hospice) at any time knowing this but with my work record and everything else, I know what it all entails I mean I’d probably go in and they’d probably want to put me on a syringe drive with Oramorph and Midazolam and Betamethasone and everything else and I know that is the beginning of the end once you start on the syringe driver and everything because it just puts you to sleep and just makes you comfortable and you don’t really have no quality of life’ .
Patients and carers valued being able to get in contact with someone when difficulties arose. Kathleen (carer): ‘Ease of communication is important to us so it’s easy to get in touch with somebody’ .
For some people, at the earlier stages after referral to the palliative care team, the only support that they required was just telephone contact.
Kathleen (carer): ‘What we have at the moment is a phone number to call and another lady, a nurse who actually rings us probably about once a fortnight yeah to check if we have any anxieties, problems.’ .
Palliative care professionals had a key role in mediating communication between patients and carers and other services. Kathleen (carer): ‘she said yes, do you think Harry would mind us contacting the GP you know and I said I’m sure he would, if I think it’s a good idea he’d go along with it so that’s what we did, she did, she contacted our GP which meant that we got a telephone appointment and something happened very quickly’ .
This extended to explaining the purpose and results of tests such as X-rays.
Stacey (carer): Yeah he went when he was admitted he went for an Xray and that was the hospice, it was (clinical nurse specialist) that had organised that. We didn’t really know what was happening in the hospital but we came home again and he didn’t really know why he’d had the Xray or anything.
So when he spoke to the nurse at (the hospice), she sort of went through it all with him and talked him through it and that was really informative and helpful
There was a feeling that communication was better in specialist palliative care compared to the general National Health Service (NHS).
Olivia (carer): ‘There is an awful lot to be learned from the NHS about liaising and communications they could learn an awful lot from the way that the palliative care is operating and running’.
The carer also became an advocate for the patient’s needs and relaying information about symptoms and concerns to the healthcare professionals which the patient may not have themselves. Andrew (patient): ‘ I mean she (partner) tells (hospice nurse) things that I don’t’ cos‘ I mean I sometimes bottle quite a few things up and don’t say nothing but (partner) notices these things and then she will tell (hospice nurse) about them’.
This was also seen during a research interview, where the patient was willing for the carer to ‘tell the story’ on their behalf.
Mary (carer): Sorry I’m doing all the talking.
Martin (patient): Well no you need to because I’m useless.
We identified that patients had unmet needs in communicating about their condition ‘ Yeah, erm, again it’s, people are very reticent to use the word cancer. So they balk at saying the word’ (Wendy, patient) and symptom experience with family and friends other than their regular carer.
Wendy (patient): I don’t know where she’s (my sister) at in terms of knowing about my symptoms and about the treatment I’m having, well no I do tell her actually, it’s not that I don’t but she has very bad arthritis…so I don’t push that too much because I’m thinking she’s actually in as much pain as I might be.’
This lack of communication could come from a position of wishing to protect the feelings of family members:
Wendy (patient): ‘Oh it’s been very difficult with family. You don’t know how much you want to tell them and you don’t know how far down the line you are anyway. I think over the years, I’ve been protecting my family’ )
Sometimes there were other important conversations that had not been held with family members.
Martin (patient): ‘I suppose my point in bringing up was because they’re particularly good kids and they are particularly, although I wouldn’t like them to hear me say it but they are, very good’ .
The work of medicines management
Medicines management was a time consuming and complex task, even for carers who has a background working in healthcare.
Sandra (carer): ‘I’m having to ring back my fourth phone call today to see is it a week off or have they forgotten to give him it. The communication isn’t great and I kind of think you know I’m kind of used to the NHS I’m, I know to ring and that sort of thing but I do think, I think if someone isn’t, got a health background or that sort of background there’s a lot of left to guesswork’ .
Commonly, the responsibility of managing the medicines could be delegated to the carer due to the side effects of the medication on the patient’s memory. It was felt that the patient would not have been able to manage by themselves. Mary (carer): ‘ a lot of the medication has made him not so aware, maybe a little bit muddled at times and his memory’s not as good as it was….you know he does forget quite easily so I wouldn’t, I have to say I wouldn’t trust him with his medication at all.’.
Carers took responsibility for ensuring medications were taken on time. As previously reported, this carer viewed this a joint endeavour with the patient.
Patricia (carer): I wake (patient) at 9 o’clock and make sure that she has her Lansoprazole and that she has her 12 hourly Longtech tablet. I generally am doing everything and as I say, we put the injection in at lunchtime every day and at night I remind her, not that she doesn’t, she doesn’t really need reminding but at 9 o’clock, I say have you had your tablets?’ .
The carer (who did not have a healthcare background) had developed an understanding of complex concepts such as the different modes of metabolism of medication for pain.
Patricia (carer): ‘So she’s now on a different set of pain relief which, the morphine was better but not better for her. So the pain killing stuff that she’s on is processed through the liver rather than through the kidneys and the kidney function has stabilised.’ .
Impact of COVID-19
Interviewees were asked about whether COVID-19 had impacted upon their experience. It seemed that for this selected group of patients and carers the impact was minimal.
Patricia (carer): ‘Can I just add that Covid seems to have, people have been complaining that this has stopped and that’s stopped whereas with Wendy her appointments, they’ve always wanted face to face and we’ve done phone appointments when it’s been appropriate and the care has been absolutely marvelous’.
Availably of hospice staff sometimes filled the gap in other services.
Kathleen (carer): ‘Because of lockdown and the virus and everything obviously all that (GP support) changed and you did start to feel a bit isolated and alone ‘cos you don’t always want to have to get in the car and drive to (hospital) for something if it’s not absolutely necessary and so therefore having someone else to talk to who knew more about things because obviously we’re learning as we go along Harry and I, it was very helpful’.
Problems were attributed to the general NHS system rather than being COVID-19 specific.
Sandra (carer): ‘I think as far as forthcoming information, I don’t think Covid has any bearing on that to be honest. You know, it just, I think it’s just an age-old problem in the NHS is communication.’ .
The close alignment of this patient and carer data with our HCP-based conceptual model provides additional reinforcement of the importance of multidisciplinary working and continuity of care in shaping symptom management experience. Indeed, the ability to see preferred member of general practices staff was recently reported as a factor associated with satisfaction with ends of life care in England [ 3 ].
Palliative care takes a holistic view of the patient and carer, the concerns of both being intertwined and interdependent. The observation that carers and patients viewed themselves as a single unit and talked about ‘we’ when describing the experience of symptoms and service referral, aligns with the dimension of the carer ‘living in the patients world’ and living in ‘symbiosis’ recently described by Borelli et al [ 4 ] and in earlier qualitative work with advanced cancer patients [ 5 ]. Carer opinion can be a close but not always perfect proxy of patient voice, even in this small sample we observed some discordance between patient and carer perception of symptom burden. However, carers were vitally important for communication with healthcare providers, relaying concerns, managing medication and generally advocating for the patient when they were unable or willing to do so. In the UK in 2022, the number of people living alone was 8.3 million. Since 2020, the number of people over 65 years old living alone has also increased [ 6 ]. Household composition is not a general indicator of wider social support networks, but these data do suggest that there could be a considerable number of people with palliative care needs without live-in carer support. This raises the questions of whether the experience of those living without a supportive carer can be equitable and how services might better facilitate this.
Home-based palliative care is thought to reduce symptom burden for patients with cancer [ 7 ]. To enable this, it is therefore vital that carers are adequately supported. Carer burden is a multifaceted experience, however our interview schedule specifically asked about symptom management experience. In agreement with the term ‘role strain’ in the review by Choi and Seo [ 8 ] we saw carers involvement in symptom management and in mediating communication between the patient and healthcare providers. Additional aspects reported by Choi et Seo include physical symptoms of the carer, psychological distress, impaired social relationships, spiritual distress, financial crisis, disruption of daily life and uncertainty [ 8 ] and these will not have all been probed by our interview topic guide.
Although in our original study HCPs talked about medicines from their perspective, the role of the carer was not discussed. Medicines management was an important way that carers facilitated effective symptom management but is a complex task. One carer commented: ‘I have to say that would be a nightmare if I wasn’t a nurse by background’ . Our data on the difficulties with medicine management are not novel and closely mirror the report of Pollock et al., [ 9 ]. Our findings echo and support their conclusions that managing medicine at home during end-of-life care could be improved by reducing the work of medicines management and improving co-ordination and communication in health care and we echo their calls for further research in the area.
We identified that patients and carers viewed mediating communication as an important role for healthcare professionals. This could be enabling communication between patients and carers and other healthcare professionals, for example arranging follow-up care or explaining information received. There was also a need for better communication between patients and their family members. As reviewed and synthesised by Murray et al., (2014) the importance of effective communication in palliative care has been long recognised [ 10 ]. In our study, an opportunity for HCPs to facilitate better communication about symptom experience between patients and their wider family was identified. Our previous survey of English hospices found that healthcare professionals, particularly nurses and allied health professionals felt that they needed more training in basic and advanced communication skills [ 11 ]. Having relevant experience and if the appropriate training was provided, staff may be well placed to support patients with developing an approach to these potentially difficult conversations. Participants were offered a choice of joint or individual interviews, but most chose to be interviewed as a dyad. It is possible that being interviewed as a pair may have altered the information disclosed. Although the aim was to discuss factors that impacted upon effective symptom management, discussions at times deviated to a more general appraisal of a participant’s experiences and all data collected may not be relevant to the research question.
When data was collected that lead to the development of the HCP-based model of effective symptom management (May to November 2019) a global pandemic was unforeseen. At the time of the patient and carer interview described here (October to December 2020), COVID-19 restrictions were in place in the UK. The patients and carers we interviewed were already receiving specialist palliative care support as outpatients. For these individuals it appeared that the impact of COVID-19 pandemic had had minimal impact on their care. The availability and reassurance of telephone support from hospice staff seemed in part to ameliorate the reduced support available from other services such as GPs. This contrasts sharply with the negative impact of COVID-19 on the experience of patients and carers in the more immediate end of life phase [ 12 ], receiving oncology care [ 13 ] or with cancer more generally [ 14 ]. Selection bias is likely as patients and carers with the capacity and willingness to participate in our research study possibly reflect those where the illness is in a more stable phase and immediate needs were being met. Indeed, participants talked about difficulties before referral to specialist palliative care and with other services but were overwhelmingly positive about the support currently being provided by the hospice.
Limitations
Due to the constraints of conducting a research study during the COVID-19 lockdown, more purposive sampling was not possible, this led to a lack of diversity in our sample. All participants identified themselves as of white British or white Scottish ethnicity which potentially means issues related to diverse ethnicities were not captured. All the patients who participated (and the non-participating patient whose carer was interviewed) lived with another person and had carer/family support. The experience of those managing their symptoms in isolation was therefore not captured. All participants were currently accessing support from a single hospice, the experience of those not yet receiving specialist support or receiving support from a different organisation may differ. The sample were diverse in age and included males and females, but all carers were female. Demographic information was not collected on socioeconomic background. COVID-19 restrictions necessitated the use of telephone interviews which may have lost subtle communications cues such as body language or conversely may have facilitated candid description. The transcripts do suggest that participants felt comfortable to tell their experience and they mostly spoke freely with limited prompting. One participant mentioned that he found it very difficult to leave the house, and therefore a telephone interview might have facilitated his inclusion. In some interviews more data was derived from the opinion of the carer than the patient, with the pair agreeing that the carer took responsibility for many tasks involved in managing the condition. We cannot be certain that carer interpretation accurately matches patient experience for all symptoms [ 15 ].
We set out to answer the question; does a healthcare professional data derived model represent the experience of patients and carers of people with advanced cancer? Overall, the answer was yes, as our healthcare professional based conceptual model of effective symptom management aligned well with the experience of patients with advanced cancer and their carers. Domains that did not align were those specifically related to professionals; experience (of staff), training (of staff), guidelines and evidence, psychological support (for staff) and the provision of formal psychological support (for patients), a resource patients and carers might be unaware of. Additional domains of carer burden, communication, medicine management and the impact of COVID-19 were identified. We make four recommendations arising from this research.
Routine appraisal and acknowledgement of carer burden, medicine management tasks and previous experience in healthcare roles.
Increased access to communication skills training for staff caring for palliative care patients and their families.
Review of patient communication needs with support provided where needed.
Further research into the symptom management experience of those living alone and exploration of how these people can be better supported.
Availability of data and materials
Original recordings generated and analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to protection of confidentiality. Anonymised transcripts with identifiable information removed may be available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Coronavirus disease 2019
Healthcare professional
National Health Service
United Kingdom
Chapman EJ, Pini S, Edwards Z, Elmokhallalati Y, Murtagh FEM, Bennett MI. Conceptualising effective symptom management in palliative care: a novel model derived from qualitative data. BMC Palliat Care. 2022;21(1):17.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cosgrove D, Connolly M, Monnery D. Holistic care needs in an inpatient oncology unit: patients versus professionals. BMJ Support Palliat Care. 2023. Published Online First: https://doi.org/10.1136/spcare-2023-004617 .
ElMokhallalati Y, Chapman E, Relton SD, Bennett MI, Ziegler L. Characteristics of good home-based end-of-life care: analysis of 5-year data from a nationwide mortality follow-back survey in England. Br J Gen Pract. 2023;73(731):e443–50.
Borelli E, Bigi S, Potenza L, Gilioli F, Efficace F, Porro CA, et al. Caregiver’s quality of life in advanced cancer: validation of the construct in a real-life setting of early palliative care. Front Oncol. 2023;13:1213906.
McDonald J, Swami N, Pope A, Hales S, Nissim R, Rodin G, et al. Caregiver quality of life in advanced cancer: Qualitative results from a trial of early palliative care. Palliat Med. 2018;32(1):69–78.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Office for National Statistics (ONS). Statitical bulletin, Familes and households in the UK:2022 2023 [updated 18th May 2023. Available from: https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/birthsdeathsandmarriages/families/bulletins/familiesandhouseholds/2022 .
Gomes B, Calanzani N, Curiale V, McCrone P, Higginson IJ. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of home palliative care services for adults with advanced illness and their caregivers. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;2013(6):CD007760. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD007760.pub2 .
Choi S, Seo J. Analysis of caregiver burden in palliative care: an integrated review. Nurs Forum. 2019;54(2):280–90.
Pollock K, Wilson E, Caswell G, Latif A, Caswell A, Avery A, et al. Family and health-care professionals managing medicines for patients with serious and terminal illness at home: a qualitative study. NIHR J Libr. 2021.
Atkin H, McDonald C, Murray CD. The communication experiences of patients with palliative care needs: a systematic review and meta-synthesis of qualitative findings. Palliat Support Care. 2015;13(2):369–83.
Paley CA, Keshwala V, Farfan Arango M, Hodgson E, Chapman EJ, Birtwistle J. Evaluating provision of psychological assessment and support in palliative care: A national survey of hospices in England. Progress in Palliative Care. 2024;32(1):11–21.
Article Google Scholar
Bailey C, Guo P, MacArtney J, Finucane A, Meade R, Swan S, Wagstaff E. “Palliative care is so much more than that”: a qualitative study exploring experiences of hospice staff and bereaved carers during the COVID-19 pandemic. Front Public Health. 2023;11:1139313.
de Joode K, Dumoulin DW, Engelen V, Bloemendal HJ, Verheij M, van Laarhoven HWM, et al. Impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on cancer treatment: the patients’ perspective. Eur J Cancer. 2020;136:132–9.
Moraliyage H, De Silva D, Ranasinghe W, Adikari A, Alahakoon D, Prasad R, et al. Cancer in lockdown: impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on patients with cancer. Oncologist. 2021;26(2):e342–4.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar
McPherson CJ, Addington-Hall JM. Judging the quality of care at the end of life: can proxies provide reliable information? Soc Sci Med. 2003;56(1):95–109.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the patients and carers who in giving valuable time to share their experiences, made this research possible. We thank research nurses Kath Black and Angela Wray for their support with recruitment.
The authors disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: this work was supported by Yorkshire Cancer Research programme grant L412, RESOLVE: “Improving health status and symptom experience for people living with advanced cancer”. The sponsor had no role in study design or the collection, analysis and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the article for publication.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Academic Unit of Palliative Care, Worsley Building, University of Leeds, Clarendon Way, LS2 9NL, UK
Emma J. Chapman, Carole A. Paley & Lucy E. Ziegler
Division of Psychological and Social Medicine, Worsley Building, University of Leeds, Clarendon Way, LS2 9NL, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Original idea, EC and SP; Data collection, EC; Data Analysis, EC and CP; Data interpretation, All, Methodological oversight, SP and LZ; writing the manuscript, All. All authors contributed to the development of the updated conceptual model and approved the final submission.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Emma J. Chapman .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethical approval was granted by a UK research ethics committee ( North of Scotland (2) Research Ethics Committee (20/NS/0086)). All participants gave informed consent for participation and for the use of their direct quotations in research publications.
Consent for publication
Participants gave consent for publication of their direct quotations.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1, supplementary material 2, supplementary material 3, supplementary material 4, supplementary material 5, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Chapman, E.J., Paley, C.A., Pini, S. et al. Updating a conceptual model of effective symptom management in palliative care to include patient and carer perspective: a qualitative study. BMC Palliat Care 23 , 208 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12904-024-01544-x
Download citation
Received : 08 March 2024
Accepted : 08 August 2024
Published : 19 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12904-024-01544-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Symptom management
- Conceptual model
- Communication skills
- Medicines management
BMC Palliative Care
ISSN: 1472-684X
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
COMMENTS
An interview is a qualitative research method that relies on asking questions in order to collect data. Interviews involve two or more people, one of whom is the interviewer asking the questions. ... Unstructured interviews are by definition open-ended. This flexibility can help you gather detailed information on your topic, while still ...
Introduction. Interviewing people is at the heart of qualitative research. It is not merely a way to collect data but an intrinsically rewarding activity—an interaction between two people that holds the potential for greater understanding and interpersonal development. Unlike many of our daily interactions with others that are fairly shallow ...
Interviews can be defined as a qualitative research technique which involves "conducting intensive individual interviews with a small number of respondents to explore their perspectives on a particular idea, program or situation." There are three different formats of interviews: structured, semi-structured and unstructured.
Develop an interview guide. Introduce yourself and explain the aim of the interview. Devise your questions so interviewees can help answer your research question. Have a sequence to your questions / topics by grouping them in themes. Make sure you can easily move back and forth between questions / topics. Make sure your questions are clear and ...
A structured interview is a quantitative research method where the interviewer a set of prepared closed-ended questions in the form of an interview schedule, which he/she reads out exactly as worded. Interviews schedules have a standardized format, meaning the same questions are asked to each interviewee in the same order (see Fig. 1). Figure 1.
This section explores the diversity of interviews including informal conversational types, general interview guides, standardized open-ended interviews, closed fixed-response interviews, and telephone interviews. Each type serves different research needs, offering a range of structure and flexibility to suit the investigation's objectives.
What are interviews? An interviewing method is the most commonly used data collection technique in qualitative research. 1 The purpose of an interview is to explore the experiences, understandings, opinions and motivations of research participants. 2 Interviews are conducted one-on-one with the researcher and the participant. Interviews are most appropriate when seeking to understand a ...
Interviews are face-to-face verbal exchanges where a researcher or interviewer seeks to elicit information from a respondent. Unlike casual conversations, interviews are purpose-driven, structured, and maintain defined roles for the interviewer and the interviewee, aimed at gathering insights on specific research topics.
Qualitative research method-interviewing and observation. Buckley and Chiang define research methodology as "a strategy or architectural design by which the researcher maps out an approach to problem-finding or problem-solving.". [ 1] According to Crotty, research methodology is a comprehensive strategy 'that silhouettes our choice and ...
Interviews will often be used as a standalone method or combined with other qualitative methods, such as focus groups or ethnography, or quantitative methods, such as surveys or experiments.
Researchers aim to look into the individual's life journey. As a result, this type of interview allows participants to construct and share their own narratives, providing rich qualitative data. Qualitative research, oral history, or studies focusing on individual experiences and identities uses narrative interviews. 6.
There are more types of interviews than most people think. An interview is generally a qualitative research technique that involves asking open-ended questions to converse with respondents and collect elicit data about a subject.. The interviewer, in most cases, is the subject matter expert who intends to understand respondent opinions in a well-planned and executed series of star questions ...
Revised on June 22, 2023. A structured interview is a data collection method that relies on asking questions in a set order to collect data on a topic. It is one of four types of interviews. In research, structured interviews are often quantitative in nature. They can also be used in qualitative research if the questions are open-ended, but ...
In essence, interviewing is a method of eliciting information. It is a "conversation between people in which one person has the role of the researcher" ( Arksey and Knight 1999, cited under General Overviews; p. 2). Interviews can be carried out face to face, over the telephone and Internet, or in a group setting.
Vancouver, Canada. Abstract. Interviews are one of the most promising ways of collecting qualitative data throug h establishment of a. communication between r esearcher and the interviewee. Re ...
Definitions. The qualitative research interview seeks to describe and the meanings of central themes in the life world of the subjects. The main task in interviewing is to understand the meaning of what the interviewees say. (Kvale,1996) participant's experiences. The interviewer can information around the topic.
An offer of a copy of the final research report can help in some cases. Ensure that the questionnaire can be returned with the minimum of trouble and expense (e.g. by including a reply paid envelope). Keep the questionnaire short and easy to answer. Ensure that you send it to people for whom it is relevant.
7 interview methods in research. Here's a list of seven major interview methods that you can use in your research: 1. Focus group. One popular research interview method is conducting a focus group interview, which involves a group of individuals interviewed at the same time.
Abstract. The interview is an important data gathering technique involving verbal communication between the researcher and the subject. Interviews are commonly used in survey designs and in ...
The main purpose of the case study in this research is to test and get feedback on the established assessment model. Case study data collection used the one-on-one interview method by Ryan et al ...
An interview is a conversation for gathering information. A research interview involves an interviewer, who coordinates the process of the conversation and asks questions, and an interviewee, who responds to those questions. Interviews can be conducted face-to-face or over the telephone. The internet is also emerging as a tool for interviewing.
We have shown in this paper that DMI provides an analytical procedure for methodically controlled interpretations of interview accounts in all domains of qualitative social research because it also allows to re-interpret interviewees' everyday theories and justifications presented in interviews against the background of their 'a theoretical ...
Formative Research Methods. Formative research employs a variety of methods to gather comprehensive data and insights about the target population and context. These methods can be broadly categorized into qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches, each providing unique insights and complementing each other to create a well-rounded ...
An in -depth interview is a qualitative research technique that is used to conduct detailed. interviews with a small number of participants. In contrast to other forms of qualitative. research ...
Research involving the collection of data in numerical form for quantitative analysis. The numerical data can be durations, scores, counts of incidents, ratings, or scales. Quantitative data can be collected in either controlled or naturalistic environments, in laboratories or field studies, from special populations or from samples of the ...
A conceptual model of effective symptom management was previously developed from qualitative data derived from interviews with healthcare professionals working in English hospices to elicit their views about the barriers and facilitators of effective symptom management [].The model delineated the successful symptom management experience into four steps of: engagement, decision-making ...