
Fast Food Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Business Plan Outline
- Fast Food Business Plan Home
- 1. Executive Summary
- 2. Company Overview
- 3. Industry Analysis
- 4. Customer Analysis
- 5. Competitive Analysis
- 6. Marketing Plan
- 7. Operations Plan
- 8. Management Team
- 9. Financial Plan
Fast Food Restaurant Business Plan & Template
You’ve come to the right place to create your fast food business plan.
We have helped over 100,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their fast food businesses.
Fast Food Business Plan Example
Below are links to each section of a fast food restaurant business plan sample:
Next Section: Executive Summary >
Fast Food Business Plan FAQs
What is a fast food business plan.
A fast food business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your fast food restaurant. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your fast food business plan using our Fast Food Business Plan Template here .
What Are the Main Types of Fast Food Businesses?
There are many types of fast food businesses. The most common fast food restaurants serve hamburgers, fries, and soft drinks. Other common fast food establishments serve chicken, Chinese food, Mexican food, and pizza. There is a recent trend in fast food restaurants serving healthier options such as smoothies, wraps, sandwiches, and salads. A fast food restaurant can be centered around any food genre that is able to be prepared fast and in large quantities to serve multiple customers daily.
What Are the Main Sources of Revenue and Expenses for a Fast Food Restaurant?
The primary source of revenue for a fast food restaurant are the food and drink items sold at the establishment.
The key expenses are the costs to source the ingredients for the menu items, kitchen equipment and supplies, overhead expenses for the staff and rent, and any marketing costs the restaurant chooses to partake in.
What is the Difference Between a Franchise and Non-Franchise Fast Food Restaurant?
A franchise fast food restaurant is a business that is owned and operated by someone who has a contract with a larger company. That company provides the products, training, and marketing for the smaller business. A non-franchise fast food restaurant is a business that is independently owned and operated.
Franchise fast-food restaurants have a set of guidelines and standards to which they must adhere in order to use the franchise name. Non-franchise fast food restaurants do not have these guidelines and can vary greatly in terms of quality, cleanliness, and customer service.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Fast Food Business?
Fast food businesses are most likely to receive funding from banks. Typically you will find a local bank and present your business plan to them. Another option for a fast food business is to obtain a small business loan. SBA loans are a popular option as they offer longer loan terms with lower interest rates. Outside investors, crowdfunding, and/or friends or family are other typical funding options. This is true for a fast casual restaurant business plan or a takeout restaurant business plan.
What are the Steps To Start a Fast Food Business?
Starting a fast food restaurant can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a successful fast food business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Write A Fast Food Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed fast food business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include market research on the fast food industry and potential target market size, information on your fast food menu, marketing strategy, pricing strategy and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your fast food business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your fast food business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Fast Food Restaurant - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your fast food business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your fast food business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Fast Food Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your fast food business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your fast food business. Marketing efforts includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising to reach your target audience.
Where Can I Get a Fast Food Business Plan PDF?
You can download our free fast food business plan template PDF here. This is a sample fast food business plan template you can use in PDF format.

Fast Food Business Plan Template
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 7,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their fast food restaurants.
How To Write a Business Plan for a Fast Food Restaurant
Below are links to each of the key components of a comprehensive business plan for a fast food restaurant:
- Executive Summary – The Executive Summary is the first and most important section of your fast food restaurant business plan. It provides a concise overview of the entire document and should be written last to ensure it accurately reflects the rest of the plan.
- Company Overview – In this section, you will introduce your fast food restaurant, including its mission, vision, and goals. Explain the business concept, legal structure, its unique selling proposition, and the target market you intend to serve.
- Industry Analysis – In the Industry Analysis, conduct a thorough analysis of the fast food industry, including market trends, growth potential, and key players. Identify any challenges or opportunities that may impact your fast food restaurant.
- Customer Analysis – Define your target market in detail. Who are your ideal customers? What are their demographics, preferences, and behaviors? Understanding your customer spending habits will help you tailor your products, marketing, and operations to meet their needs.
- Competitive Analysis – In the Competitive Analysis, evaluate your direct and indirect competitors. Identify their strengths, weaknesses, and fast food market share. This analysis will help you understand the competitive landscape and develop strategies to differentiate your restaurant.
- Marketing Plan – The Marketing Plan section is where you will outline your marketing strategy, including your target audience, messaging, branding, advertising, social media marketing, and promotional activities. This section should clearly articulate how you will attract customers, the pricing strategy you will use, and the loyalty programs to keep them coming back.
- Operations Plan – The Operations Plan will describe the day-to-day operations of your restaurant, including staffing, training, inventory management, food preparation, online ordering, and customer service. This section should outline your procedures for ensuring efficiency and quality.
- Management Team – In the Management Team section, introduce the key members of your management team and their qualifications. This section should demonstrate that you have the necessary expertise to successfully run the restaurant.
- Financial Plan – In the Financial Plan section, develop detailed financial projections, including projected revenue, expenses, profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet. This section will help you assess the financial viability of your fast food business and secure funding.
- Appendix – In the Appendix, include any supporting documents, such as market research data, resumes, permits, licenses, and fast food menu items. This section can be used as a reference for investors, lenders, and other stakeholders.
Next Section: Executive Summary >
Fast Food Business Plan FAQs
What is a fast food business plan.
A business plan provides a snapshot of your fast food restaurant concept as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why Do You Need a Business Plan for a Fast Food Restaurant?
If you’re looking to start a successful fast food restaurant or grow your existing one you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth in order to improve your chances of a successful fast food business . Your fast food business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your business grows and changes
What Are the Sources of Funding for a Fast Food Restaurant?
Fast Food restaurants are usually funded through small business loans, personal savings, credit card financing and/or angel investors.
This is true for a traditional fast food restaurant, a quick service restaurant and a takeout restaurant business plan.
How Do I Download a Free Fast Food Business Plan PDF?
You can download our fast food restaurant business plan pdf and use our sample fast food business plan to write your own business plan. This is a business plan template you can use in PDF format. If you are looking for the quickest and easiest way to complete your business plan, Growthink’s Ultimate Fast Food Business Plan Template has numerous features not available in the free template including its financial projections template which automatically calculates your complete five-year financial projections including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
FAST FOOD BUSINESS PLAN OUTLINE
- Fast Food Business Plan Home
- 1. Executive Summary
- 2. Company Overview
- 3. Industry Analysis
- 4. Customer Analysis
- 5. Competitive Analysis
- 6. Marketing Plan
- 7. Operations Plan
- 8. Management Team
- 9. Financial Plan
- 10. Appendix
- Fast Food Business Plan Summary
Start Your Fast Food Plan Here
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

- Sample Business Plans
- Food, Beverage & Restaurant
Fast Food Restaurant Business Plan
Planning on starting a fast food restaurant? It can be an excellent way to create a niche business, serve a diverse customer base, and make a great career in the food service industry, but you need detailed planning for it.
That’s where you need a business plan; it will not only help you secure funding but will also provide a roadmap for seamless business operations.
Need help writing a business plan for your fast food restaurant business? You’re at the right place. Our fast food restaurant business plan template will help you get started.

Free Business Plan Template
Download our free fast food restaurant business plan template now and pave the way to success. Let’s turn your vision into an actionable strategy!
- Fill in the blanks – Outline
- Financial Tables
How To Write A Fast Food Restaurant Business Plan?
Writing a fast food restaurant business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan:
1. Executive Summary
An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan. However, it is written after the whole business plan is ready and summarizes each section of your plan.
Here are a few key components to include in your executive summary:
- Market Opportunity: Summarize your market research, including market size, growth potential, and marketing trends. Highlight the opportunities in the market and how your business will fit in to fill the gap.
- Products and Services: Highlight your food menu and the services you will offer to your customers. Describe any special dishes you serve.
- For instance, your products and services may include menu items, combo meals, takeout and delivery services, combo meals, and catering services.
- Marketing & Sales Strategies: Outline your sales and marketing strategies—what marketing platforms you use, how you plan on acquiring customers, etc.
- Financial Highlights: Briefly summarize your financial projections for the initial years of business operations. Include any capital or investment requirements, associated startup costs, projected revenues, and profit forecasts.
- Call to Action: Summarize your executive summary section with a clear CTA, for example, inviting angel investors to discuss the potential business investment.
Ensure your executive summary is clear, concise, easy to understand, and jargon-free.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

2. Business Overview
The business overview section of your business plan offers detailed information about your restaurant. The details you add will depend on how important they are to your business. Yet, business name, location, business history, and future goals are some of the foundational elements you must consider adding to this section:
- Business Description: Describe your business in this section by providing all the basic information:
- Vegetarian fast food restaurants
- Pizza chains
- Mexican fast food restaurants
- Asian fast food restaurants
- Sandwich shops
- Fried seafood restaurants
Describe the legal structure of your fast food restaurant, whether it is a sole proprietorship, LLC, partnership, or others.
- Owners: List the founders or owners of your fast food restaurant. Describe what shares they own and their responsibilities for efficiently managing the business.
- Mission Statement: Summarize your business’ objective, core principles, and values in your mission statement. This statement needs to be memorable, clear, and brief.
- Business History: If you’re an established fast food restaurant business, briefly describe your business history, like—when it was founded, how it evolved over time, etc.
- Additionally, If you have received any awards or recognition for excellent work, describe them.
- Future Goals: It’s crucial to convey your aspirations and vision. Mention your short-term and long-term goals; they can be specific targets for revenue, market share, or expanding your services.
This section should provide a thorough understanding of your business, its history, and its future plans. Keep this section engaging, precise, and to the point.
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section of your business plan should offer a thorough understanding of the industry with the target market, competitors, and growth opportunities. You should include the following components in this section.
- Target market: Start this section by describing your target market. Define your ideal customer and explain what types of services they prefer. Creating a buyer persona will help you easily define your target market to your readers.
- For instance, young adults, millennials, and busy professionals can be an ideal target market for a fast food restaurant.
- Market size and growth potential: Describe your market size and growth potential and whether you will target a niche or a much broader market.
- Competitive Analysis: Identify and analyze your direct and indirect competitors. Identify their strengths and weaknesses, and describe what differentiates your fast food restaurant from them. Point out how you have a competitive edge in the market.
- Market Trends: Analyze emerging trends in the industry, such as technology disruptions, changes in customer behavior or preferences, etc. Explain how your business will cope with all the trends.
- For instance, there is an increasing demand for healthier food options; explain how you plan to cater to this growing market.
- Regulatory Environment: List regulations and licensing requirements affecting fast food restaurants, such as business registration, insurance, food service license, employment, and environmental regulations.
Here are a few tips for writing the market analysis section of your fast food business plan:
- Conduct market research, industry reports, and surveys to gather data.
- Provide specific and detailed information whenever possible.
- Illustrate your points with charts and graphs.
- Write your business plan keeping your target audience in mind.
4. Products And Services
The product and services section should describe the specific services and products that will be offered to customers. To write this section should include the following:
- Fast Food Menu: Start this section by offering an overview of your fast food menu. Include the details about the types of cuisine, dietary options you provide, and any signature dishes.
- Beverages and Desserts: Besides the fast food items, mention if your restaurant serves any other beverages such as tea, coffee, soft drinks, juices, and desserts or treats. For instance, dramatic style involves using longer & thicker lashes for a glamorous look.
- Food Preparation and Safety Measures: This section should explain your food preparation process, cooking methods, and how your business aligns with food safety regulations.Your safety measures may include maintaining cleanliness, regular sanitization, and conducting regular staff training programs.
- Special Services: Mention if your fast food restaurant offers any additional services. You may include services like online ordering, drive-thru, and valet parking.
In short, this section of your fast food restaurant plan must be informative, precise, and client-focused. By providing a clear and compelling description of your offerings, you can help potential investors and readers understand the value of your business.
5. Sales And Marketing Strategies
Writing the sales and marketing strategies section means a list of strategies you will use to attract and retain your clients. Here are some key elements to include in your sales & marketing plan:
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Define your business’s USPs depending on the market you serve, the equipment you use, and the unique services you provide. Identifying USPs will help you plan your marketing strategies.
- For example, fresh and quality ingredients, unique menu items, sustainability, and ethical practices could be some of the great USPs for a fast-food restaurant.
- Pricing Strategy: Describe your pricing strategy—how you plan to price your products and services and stay competitive in the local market. You can mention any discounts you plan on offering to attract new customers.
- Marketing Strategies: Discuss your marketing strategies to market your services. You may include some of these marketing strategies in your business plan—social media marketing, Google ads, brochures, email marketing, content marketing, and print marketing.
- Sales Strategies: Outline the strategies you’ll implement to maximize your sales. Your sales strategies may include offering loyalty programs, online food delivery services, and creating corporate accounts.
- Customer Retention: Describe your customer retention strategies and how you plan to execute them. For instance, introducing loyalty programs, focusing on personalized service, offering promotions, etc
Overall, this section of your fast food restaurant business plan should focus on customer acquisition and retention.
Have a specific, realistic, and data-driven approach while planning sales and marketing strategies for your fast food restaurant, and be prepared to adapt or make strategic changes in your strategies based on feedback and results.
6. Operations Plan
The operations plan section of your business plan should outline the processes and procedures involved in your business operations, such as staffing requirements and operational processes. Here are a few components to add to your operations plan:
- Staffing & Training: Mention your restaurant’s staffing requirements, including the number of employees or kitchen staff needed. Include their qualifications, the training required, and the duties they will perform.
- Operational Process: Outline the processes and procedures you will use to run your fast food restaurant. Your operational processes may include restaurant opening, staff assignments, food preparation and cooking, order fulfillment, cleanliness and sanitization, and closing procedures.
- Equipment & Machinery: Include the list of equipment and machinery required for fast food restaurants, such as refrigerators, coffee machines, ice machines, POS systems, Utensils and kitchen tools, and food preparation equipment.
- Explain how these technologies help you maintain quality standards and improve the efficiency of your business operations.
Adding these components to your operations plan will help you lay out your business operations, which will eventually help you manage your business effectively.
7. Management Team
The management team section provides an overview of your fast food restaurant’s management team. This section should provide a detailed description of each manager’s experience and qualifications, as well as their responsibilities and roles.
- Founders/CEO: Mention the founders and CEO of your fast food restaurant, and describe their roles and responsibilities in successfully running the business.
- Key managers: Introduce your management and key members of your team, and explain their roles and responsibilities.
- It should include key executives, master chefs, senior management, and other department managers (e.g. operations manager.) involved in the fast food restaurant operations, including their education, professional background, and any relevant experience in the food industry.
- Organizational structure: Explain the organizational structure of your management team. Include the reporting line and decision-making hierarchy.
- Compensation Plan: Describe your compensation plan for the management and staff. Include their salaries, incentives, and other benefits.
This section should describe the key personnel for your fast food restaurant, highlighting how you have the perfect team to succeed.
8. Financial Plan
Your financial plan section should provide a summary of your business’s financial projections for the first few years. Here are some key elements to include in your financial plan:
- Profit & loss statement: Describe details such as projected revenue, operational costs, and service costs in your projected profit and loss statement . Make sure to include your business’s expected net profit or loss.
- Cash flow statement: The cash flow for the first few years of your operation should be estimated and described in this section. This may include billing invoices, payment receipts, loan payments, and any other cash flow statements.
- Balance Sheet: Create a projected balance sheet documenting your business’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Break-even point: Determine and mention your business’s break-even point—the point at which your business costs and revenue will be equal.
- This exercise will help you understand how much revenue you need to generate to sustain or be profitable.
- Financing Needs: Calculate costs associated with starting a fast food restaurant, and estimate your financing needs and how much capital you need to raise to operate your business. Be specific about your short-term and long-term financing requirements, such as investment capital or loans.
Be realistic with your financial projections, and make sure you offer relevant information and evidence to support your estimates.
9. Appendix
The appendix section of your plan should include any additional information supporting your business plan’s main content, such as market research, legal documentation, financial statements, and other relevant information.
- Add a table of contents for the appendix section to help readers easily find specific information or sections.
- In addition to your financial statements, provide additional financial documents like tax returns, a list of assets within the business, credit history, and more. These statements must be the latest and offer financial projections for at least the first three or five years of business operations.
- Provide data derived from market research, including stats about the restaurant industry, user demographics, and industry trends.
- Include any legal documents such as permits, licenses, and contracts.
- Include any additional documentation related to your business plan, such as product brochures, marketing materials, operational procedures, etc.
Use clear headings and labels for each section of the appendix so that readers can easily find the necessary information.
Remember, the appendix section of your fast food restaurant business plan should only include relevant and important information supporting your plan’s main content.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
This sample fast food restaurant business plan will provide an idea for writing a successful fast food restaurant plan, including all the essential components of your business.
After this, if you still need clarification about writing an investment-ready business plan to impress your audience, download our fast food restaurant business plan pdf .
Related Posts
Pizza Shop Business Plan
Food Cafe Business Plan
Library of Sample Business Plans
Top AI Business Plan Generators
Restaurant Business Plan
Business Plan Outline for Small Business
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do you need a fast food restaurant business plan.
A business plan is an essential tool for anyone looking to start or run a successful fast food restaurant business. It helps to get clarity in your business, secures funding, and identifies potential challenges while starting and growing your business.
Overall, a well-written plan can help you make informed decisions, which can contribute to the long-term success of your fast food restaurant.
How to get funding for your fast food restaurant business?
There are several ways to get funding for your fast food restaurant business, but self-funding is one of the most efficient and speedy funding options. Other options for funding are:
- Bank loan – You may apply for a loan in government or private banks.
- Small Business Administration (SBA) loan – SBA loans and schemes are available at affordable interest rates, so check the eligibility criteria before applying for it.
- Crowdfunding – The process of supporting a project or business by getting a lot of people to invest in your business, usually online.
- Angel investors – Getting funds from angel investors is one of the most sought startup options.
Apart from all these options, there are small business grants available, check for the same in your location and you can apply for it.
Where to find business plan writers for your fast food restaurant business?
There are many business plan writers available, but no one knows your business and ideas better than you, so we recommend you write your fast food restaurant business plan and outline your vision as you have in your mind.
What is the easiest way to write your fast food restaurant business plan?
A lot of research is necessary for writing a business plan, but you can write your plan most efficiently with the help of any fast food restaurant business plan example and edit it as per your need. You can also quickly finish your plan in just a few hours or less with the help of our business plan software .
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more

Turn your business idea into a solid business plan
Explore Plan Builder
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .


Expert business plan and financial models

Fast Food Restaurant Business Plan Template & PDF Example
- September 4, 2024
- Business Plan

Creating a comprehensive business plan is crucial for launching and running a successful fast food restaurant. This plan serves as your roadmap, detailing your vision, operational strategies, and financial plan. It helps establish your fast food restaurant’s identity, navigate the competitive market, and secure funding for growth.
This article not only breaks down the critical components of a fast food restaurant business plan, but also provides an example of a business plan to help you craft your own.
Whether you’re an experienced entrepreneur or new to the food and beverage industry, this guide, complete with a business plan example, lays the groundwork for turning your fast food restaurant concept into reality. Let’s dive in!
Our fast food restaurant business plan is structured to cover all essential aspects needed for a comprehensive strategy. It outlines the restaurant’s operations, marketing strategy, market environment, competitors, management team, and financial forecasts.
- Executive Summary : Offers a snapshot of your fast food restaurant’s business idea, market study, team, and money plan.
- Restaurant & Location: Talks about the restaurant’s look, features, and why the spot is good for customers.
- Menu & Pricing: Shows what food your place serves and how much it costs.
- Key Stats: Tells about how big the market is, how it’s growing, and important numbers for fast food.
- Key Trends : Points out new changes in fast food, like healthier options or tech for ordering.
- Key Competitors: Look at the main other fast food places and how your restaurant is different.
- SWOT : Lists your restaurant’s strengths, weaknesses, chances, and risks.
- Marketing Plan : Plans for how to get and keep customers.
- Timeline : Important steps and goals from starting to the first year.
- Management: Gives information on who runs the restaurant and their jobs.
- Financial Plan: Shows how your restaurant might do money-wise over 5 years, including sales, profit, and costs.

Fast Food Restaurant Business Plan

Fully editable 30+ slides Powerpoint presentation business plan template.
Download an expert-built 30+ slides Powerpoint business plan template
Executive Summary
The Executive Summary introduces the business plan for your fast food restaurant , providing a concise overview of your establishment and its offerings. It should highlight your market positioning, the variety of fast food items and services you provide, its location, size, and a summary of daily operations.
This section should also delve into how your fast food restaurant will fit into the local market, including the number of direct competitors in the vicinity, identifying who they are, along with your restaurant’s unique selling points that set it apart from these competitors.
Moreover, it should include information about the management and co-founding team, outlining their roles and contributions to the restaurant’s success. Additionally, a synopsis of your financial projections, including revenue and profits for the next five years, should be included here to give a clear overview of your restaurant’s financial strategy.
Fast Food Restaurant Business Plan Executive Summary Example

Business Overview
The business overview should clearly define the restaurant’s key features, including its specific cuisine or theme, strategic location, facility design, and menu offerings. Highlighting what sets your restaurant apart in the competitive fast food market, such as unique culinary concepts or sustainable practices, is key for attracting interest and investment.
Example: “FlavorFusion,” a fast food restaurant specializing in fusion tacos, is located in the lively Midtown area, known for its vibrant food scene. The restaurant boasts a modern, 2,000 square-foot space with an energetic and contemporary vibe, seating for 50 patrons, and an additional outdoor area. The menu features a variety of gourmet fusion tacos made with high-quality, locally-sourced ingredients, catering to a diverse clientele.
Market Overview
This section should analyze the fast food market’s size, growth trends, and key industry developments. It positions your restaurant within the industry and highlights its potential to capitalize on current consumer trends like online ordering and plant-based options.
Example: FlavorFusion enters a market valued at $331 billion, growing at a 5.1% CAGR. Amidst intense competition from five local fast food outlets, FlavorFusion stands out with its unique fusion menu and focus on sustainability, aligning with the growing demand for innovative and eco-friendly dining options.
Management Team
Detailing the management team’s background and roles is essential. This part of the summary should emphasize their experience in the food and beverage industry and their roles in ensuring the restaurant’s operational excellence and financial health.
Example: The CEO/CFO of FlavorFusion, with extensive experience in business strategy and financial management, oversees the restaurant’s overall strategy and financial planning. The General Manager, responsible for day-to-day operations, ensures efficient restaurant functioning and high customer satisfaction.
Financial Plan
Clearly outlining the financial goals and projections is key. This section should include revenue targets and profit margins, offering insight into the restaurant’s financial health and growth potential.
Example: FlavorFusion aims to achieve $1.5 million in annual revenue with an 18% EBITDA margin by 2028. Supported by a strong business model, innovative menu, and effective marketing strategies , the restaurant is positioned for significant growth in the dynamic fast food market.
For a Fast Food Restaurant, the Business Overview section can be effectively divided into 2 main categories:
Restaurant & Location
Provide a detailed description of the restaurant’s physical environment, focusing on its design, ambiance, and welcoming atmosphere that appeals to customers. Mention the restaurant’s location, emphasizing its accessibility and convenience for customers, such as proximity to busy shopping areas or availability of parking. Explain why this location is particularly beneficial in attracting your target customer base.
Menu & Pricing
Describe the variety of fast food items and beverages offered, ranging from classic favorites to unique specialties that differentiate your restaurant from competitors. Detail your pricing strategy , ensuring it aligns with the quality of food served and appeals to the market segment you are targeting. Highlight any special deals, combo offers, or loyalty programs that add value for customers, promoting frequent visits and customer loyalty.

Industry Size & Growth
In the Market Overview of your fast food restaurant business plan, start by looking at how big the fast food industry is and how much it could grow. This helps you see how much room there is in the market and where you might grow.
Key Market Trends
Talk about what’s new in the fast food world, like how people want different and healthy options, meals they can get quickly, and new kinds of food. Mention how people are looking for good food that fits their busy lives and how they like to try new flavors from different places.
Competitive Landscape
A competitive analysis is a crucial component of your fast food restaurant’s business plan. It provides insights into how your restaurant compares to its competitors in the market. This analysis is instrumental in identifying your restaurant’s unique selling points and understanding the competitive landscape.
A thorough competitive analysis helps in shaping a well-informed business plan, ensuring that your restaurant is positioned to meet market demands and customer expectations effectively.
Identifying Your Competitors in the Fast Food Industry
Identifying competitors is the first step in understanding your position in the fast food market. Start by mapping out local fast food restaurants. For instance, if your restaurant specializes in burgers, your direct competitors include nearby burger joints like McDonald’s or Burger King , as well as local favorites like “Bob’s Burgers.” Don’t overlook indirect competitors such as Subway or Chipotle, which offer alternative fast dining options.
Use online tools like Google Maps to get a geographical sense of competitor distribution. Platforms like Yelp and TripAdvisor offer customer reviews and ratings, providing insights into competitors’ strengths and weaknesses . For example, if several reviews mention the quick service at “Fast Eats,” this is a key strength of your competitor.

Fast food competitors’ strategies
Analyzing the strategies of these competitors involves several aspects. Start with their menu offerings. For example, if “Healthy Bites” down the street is gaining popularity with its vegan options, it indicates a market trend towards healthier fast food.
Pricing strategy is another crucial aspect. Compare your prices with those of “Dollar Saver Menu” at McDonald’s or the premium options at “Shake Shack.” This comparison will help you understand where your restaurant fits in the market.
Marketing tactics in fast food can range from social media campaigns, like Wendy’s witty Twitter presence, to local billboard advertising. Pay attention to how competitors engage with customers online and the types of promotions they run.
Customer experience is also key. For instance, Chick-fil-A is renowned for its customer service. Visit competitors and note the service speed, order accuracy, and overall customer satisfaction.
Operational efficiency, especially in fast food, is a game-changer. Observe if competitors like Domino’s are using technology, like their pizza tracking system, to enhance efficiency and customer experience.
What’s your fast food restaurant’s value proposition?
Now, reflect on your restaurant’s unique value proposition . Perhaps your restaurant offers a unique fusion cuisine that isn’t available elsewhere in your area, or maybe you use locally sourced ingredients, which appeals to health-conscious consumers.
Identify market gaps through customer feedback and market trends . For example, the growing popularity of plant-based diets has led to the success of chains like “Beyond Meat.” If there’s a rising demand for plant-based fast food in your area that competitors aren’t meeting, this could be a niche for your restaurant.
Consider your location: A fast food restaurant located near a university might cater to students with budget-friendly deals, unlike a restaurant in a business district that might focus on quick service for office workers.

First, do a SWOT analysis for your fast food restaurant . Talk about Strengths (like a great menu and quick service), Weaknesses (like lots of competition or high costs), Opportunities (like more people wanting fast, tasty food), and Threats (like changes in what people want to eat or less money to spend on eating out).

Marketing Plan
Next, make a marketing plan that shows how you’ll get and keep customers. You can use ads, special deals, fun posts on social media, and events in the community.
Marketing Channels
Selecting the right marketing channels enables effective communication with potential customers and helps drive foot traffic to your restaurant. Employing diverse channels aids in enhancing brand visibility and engagement.
Digital Marketing
Utilize the digital landscape to your advantage:
- Social Media Presence: Utilize Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, TikTok, and other relevant platforms to showcase menu items, engage with followers through interactive content, host contests, and share user-generated content.
- Online Ordering Platforms: Partner with popular food delivery apps and maintain a user-friendly website with a seamless ordering system. Highlight exclusive online deals and promotions to attract online customers.
- Content Marketing : Produce engaging content such as blog posts, videos, or infographics about your recipes, behind-the-scenes kitchen stories, or spotlighting local ingredients. This content can be shared on your website and social media platforms to captivate your audience.
Local Advertising
Connect with the community through various local marketing strategies:
- Geo-targeted Ads: Invest in targeted online advertisements focused on your restaurant’s vicinity to capture the attention of nearby residents and commuters.
- Community Engagement: Participate in local events, sponsor local sports teams, or host charity fundraisers to increase community involvement and foster a positive brand image.
- Collaborations and Partnerships: Forge partnerships with local businesses, gyms, schools, or corporate offices for joint promotional events or meal deals.
Promotional Activities
Entice potential customers with compelling offers and promotions:
- Limited-time Offers: Introduce seasonal specials, combo deals, or promotional menu items to generate excitement and attract new customers.
- Customer Loyalty Programs: Implement loyalty cards or digital reward systems where frequent diners can earn points redeemable for discounts, free items, or exclusive perks.
- Referral Incentives : Encourage existing customers to refer friends and family by providing incentives such as discounts on their next order or free add-ons.

Sales Channels
Strategically employing various sales channels ensures efficient transactions and enhances customer satisfaction.
In-Store Upselling
Maximize sales during customer visits:
- Upsize Options: Offer upsized meals or meal add-ons for a nominal price increase to increase average order value.
- Combo Deals: Create bundled meal deals comprising popular items at a discounted price to encourage customers to spend more.
- Limited-time Add-ons : Introduce temporary add-ons or upgrades to entice customers into trying new menu items.
Online Ordering and Delivery
Enhance convenience and accessibility for customers:
- Efficient Online Ordering: Ensure a user-friendly online ordering system on your website and partnering delivery platforms, enabling customers to place orders seamlessly.
- Delivery Services: Optimize delivery operations to provide timely and efficient service, ensuring the food quality matches the in-store experience.
- Curbside Pickup: Offer a convenient pickup option for customers who prefer a quick in-and-out experience.
Subscription Services or Meal Plans
Encourage repeat business and secure recurring revenue streams:
- Subscription Plans: Create subscription-based meal plans offering weekly or monthly meal bundles at discounted rates for loyal customers.
- Meal Packages: Develop curated meal packages for families, individuals, or specific dietary preferences that customers can subscribe to for regular delivery or pickup.
Strategy Timeline
Lastly, make a clear timeline with important steps for starting your restaurant, getting the word out, getting more customers, and growing your business. This helps you stay on track and focused.
The Management section focuses on the fast food restaurant’s management and their direct roles in daily operations and strategic direction. This part is crucial for understanding who is responsible for making key decisions and driving the fast food restaurant towards its financial and operational goals.
For your fast food restaurant business plan, list the core team members, their specific responsibilities, and how their expertise supports the business.

The Financial Plan section is a comprehensive analysis of your financial projections for revenue, expenses, and profitability. It lays out your fast food restaurant’s approach to securing funding, managing cash flow, and achieving breakeven.
This section typically includes detailed forecasts for the first 5 years of operation, highlighting expected revenue, operating costs and capital expenditures.
For your fast food restaurant business plan, provide a snapshot of your financial statement (profit and loss, balance sheet, cash flow statement), as well as your key assumptions (e.g. number of customers and prices, expenses, etc.).
Make sure to cover here _ Profit and Loss _ Cash Flow Statement _ Balance Sheet _ Use of Funds

Related Posts

Steakhouse Business Plan Template & PDF Example
Bubble Tea Business Plan Template & PDF Example

Bar Business Plan Template & PDF Example
Privacy overview.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BIGipServerwww_ou_edu_cms_servers | session | This cookie is associated with a computer network load balancer by the website host to ensure requests are routed to the correct endpoint and required sessions are managed. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie is used to record the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category . |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| CookieLawInfoConsent | 1 year | Records the default button state of the corresponding category & the status of CCPA. It works only in coordination with the primary cookie. |
| elementor | never | This cookie is used by the website's WordPress theme. It allows the website owner to implement or change the website's content in real-time. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | 30 minutes | This cookie, set by Cloudflare, is used to support Cloudflare Bot Management. |
| language | session | This cookie is used to store the language preference of the user. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _ga | 2 years | The _ga cookie, installed by Google Analytics, calculates visitor, session and campaign data and also keeps track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognize unique visitors. |
| _ga_QP2X5FY328 | 2 years | This cookie is installed by Google Analytics. |
| _gat_UA-189374473-1 | 1 minute | A variation of the _gat cookie set by Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager to allow website owners to track visitor behaviour and measure site performance. The pattern element in the name contains the unique identity number of the account or website it relates to. |
| _gid | 1 day | Installed by Google Analytics, _gid cookie stores information on how visitors use a website, while also creating an analytics report of the website's performance. Some of the data that are collected include the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. |
| browser_id | 5 years | This cookie is used for identifying the visitor browser on re-visit to the website. |
| WMF-Last-Access | 1 month 18 hours 11 minutes | This cookie is used to calculate unique devices accessing the website. |
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Fast Food Restaurant Business Plan
Start your own fast food restaurant business plan
Fresin Fries
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">, opportunity.
There is an increasing demand for snack-type fast food, to be consumed while window shopping and walking around inside a shopping mall.
Fresin Fries will entice youngsters to bring their friends and family with our innovative environment, fresh-cut Belgian fries, and selection of unique signature dipping sauces.
Fresin Fries intends to cater to the bulk of teenagers and youngsters in Singapore. We have chosen this group for several important reasons. It is our goal to be "the extraordinary fast food place" and we believe that the age group from 15 to 25 is the primary age where brand building efforts could take place. They are on limited or fixed incomes and seek a value/price relationship that will not stretch their budgets.
Our secondary target is between the ages of 25 and 37, which are a heavy lounge/restaurant user group. They are more flexible in budgets and seek more than a value/price relationship.
Competition
Our main competitors in this segment are any food outlets within the 300 meter radius along the Orchard Road. In our location, there are Tori-Q, Pizza Walker, Starbucks, Bread Talk, and Rotiboy.
Our customers will have the total experience when visiting our outlet(s) and website as they will learn about this fascinating new "pop culture." We will sell merchandise from pre-packaged sauces and t-shirts, to potato cutters, all with our official brand attached to them.
Expectations
This plan is prepared to obtain a location for the initial launch of this concept. We plan to finance the costs with two investments of $100,000 total, one at startup and the other at the beginning of the second year. We expect strong growth for all three years, and profitability beginning in the third year.
Financial Highlights by Year
Financing needed.
The company is owned by the original 4 founders, who each will contribute $25,000 for the same amount of share, 25%, and $100,000 in paid-in capital at the start. This will cover start-up requirements. We expect to contribute a second $100,000 at the beginning of the second year.
Problem & Solution
Problem worth solving.
There is an increasing demand for snack-type fast food, to be consumed while window shopping and walking around inside a shopping mall.
Our Solution
Our main focus will be serving high-quality food at a great value. Fries will strive to be a premier local fast food brand in the local marketplace. We want our customers to have the total experience when visiting our outlet(s) and website as they will learn about this fascinating new “pop culture.” We will sell merchandise from pre-packaged sauces and t-shirts, to potato cutters, all with our official brand attached to them.
Target Market
Market size & segments.
We are targeting young Singaporeans as our primary market. Orchard Road is the place to meet and hang out after school. Due to heavy extra-curricular activities among Singapore’s youth, it is common for high schoolers to have lunch inside shopping malls, and not at home. They tend to flock to fast food joints inside shopping malls across Orchard Road.
Our secondary market segment is the "Working Singaporeans." With so many shopping malls in the vicinity, Orchard Road is the haven for shoppers and job seekers alike. In the new Paragon Shopping Centre, there are more than 8,000 workers currently working as sales persons and boutique staff. There are more than 10 major shopping malls across Orchard Road, including Ngee Ann City, the biggest shopping mall in the nation, employing more than 50,000 workers.
Lastly, Orchard Road is also the destination for tourists staying in the area. The Meritus Mandarin, Crown Prince Hotel, the Hilton, and Popular Hotel are a few of the biggest accommodations in Singapore. Tourists will stroll Orchard Road, hunting for the latest trend in fashion and have no time to stop for a full meal during shopping. Fresin Fries is the alternative for a quick bite while shopping the fancy boutiques in the area
Current Alternatives
More details on our competitors:
Tori-Q Tori-Q is locally owned franchise who sells Japanese BBQ skewers. Established in 1998, Tori-Q had expanded its operation into neighboring countries, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand. Tori-Q is popular among local teenagers as it offers fast service to its customers. Commonly, Tori-Q outlets are rather small, and can only serve a maximum of 6 guests. It is a choice for those who are in a hurry and would like to grab a quick lunch on the way.
Pizza Walker Pizza Walker is a joint venture positioned as gourmet pizza joint in Singapore. Most of its retail outlets are decorated with welcoming ambience, such as flowers and see-through kitchens. Pizza Walker is a good place to hang out, and the place is always full during lunch hour. It has more than enough tables to serve a maximum of 55 guests. Its specialty is all-you-can-eat pizza!
Starbucks Starbucks’ strategy entering the lunch market had made some impact in Singapore. Usually, a lunch menu in Singapore consists of "fried and BBQ stuff" such as roast pork with rice or the Big Mac. Starbucks is one of the first food retailers that popularized "light and healthy" alternatives such as salad or lean sandwich as an options for Singapore’s lunch accommodations.
Bread Talk As the most successful franchiser in Singapore, Bread Talk is surely becoming a threat for most food retailers. Bread Talk not only rented most of the retail space along Orchard Road, but now they are doing delivery to offices and apartments nearby. Bread Talk outlets usually consist of a huge see-through kitchen, and bread trays ready for pick-up by customers, with three or four cashiers at front, to speed up the queue. Rumor has it that Bread Talk sold more than 35,000 breads each day in just one of their retail outlets.
Rotiboy A Malaysian franchise. Rotiboy is quite popular in the region as it is now expanding into several cities in Indonesia, Vietnam, Thailand, and the Philippines. Rotiboy offers simplicity for quick lunch franchiser, and often considered alternatives for its long queueing rivals.
Our Advantages
We will provide a combination of excellent food at value pricing, with fun packaging and atmosphere. Fresin Fries is the answer to an increasing demand for snack-type fast food, to be consumed while window shopping and walking around inside a shopping mall.
Keys to Success
This is what it will take to make us successful:
- Create a unique, innovative, entertaining menu that will differentiate us from the rest of the competition.
- Control costs at all times, in all areas and implement a conservative approach to growth policy. Although, we provide more than enough fund to open more than one outlet, we want to be on the safe side of the business.
- Sell the products that are of the highest quality, as well as keeping the customers happy with all of our product categories from food to store merchandising.
- Provide 100% satisfaction to our customers and maintaining the level of excellent services among other competitors.
- Encourage the two most important values in fast food business: brand and image, as these two ingredients are a couple of main drivers in marketing communications.
- Get access to high-traffic shopping malls near the target market.
- Promote good values of company culture and business philosophy.
Marketing & Sales
Marketing plan.

The sales strategy is to build and open new locations in order to increase revenue. However, this plan will be implemented when the one "market tester" outlet showed potential growth. As each individual location will continue to build its local customer base over the first three years of operation, the goal of each store is shown on the graph as well as annual sales of our flagship store
Locations & Facilities
Fresin Fries locations will range in size from 50 – 70 meter square and will seat from 15 – 25 guests. Our first location will be on the larger end of this range. The location will feature its own originality in merchandise display and other brand building attributes. We will equip the outlet with modern furniture and aim for cleanliness and an open feeling. We are currently looking at several possible sites in shopping malls along Orchard Road.
The space selection will be chosen based upon the following criteria:
- Community size: minimum of 800,000 people within a radius of 8 kilometers.
- Tourist destination.
- Easy access.
- Large percentage of teenagers in the community.
All of these qualities are consistent with Fresin Fries’ goal of providing a top quality fast food experience. We want "word-of-mouth" to be our best form of marketing, where our customers value our brand as something exciting and cannot wait to tell their friends and neighbors. And of course these days word of mouth is amplified word of mouth, via social media.
Milestones & Metrics
Milestones table.
| Milestone | Due Date | Who’s Responsible | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sept 12, 2018 | Harry Hip | ||
| Sept 13, 2018 | Sam Sauce | ||
| Sept 13, 2018 | Sam Sauce | ||
| Sept 13, 2018 | Guy Fry | ||
| Sept 13, 2018 | |||
| Sept 13, 2018 | Harry Hip | ||
| Sept 21, 2018 | |||
| Sept 24, 2018 | |||
| Sept 24, 2018 | Guy Fry | ||
| Oct 09, 2018 | Carl Cone | ||
| Nov 15, 2018 | Carl Cone | ||
| Jan 01, 2019 | Carl Cone | ||
| Jan 01, 2020 | Carl Cone |
Key Metrics
Our key metrics that will help us succeed are:
- Detailed operational metrics for the flagship operations. We need to make the sales forecast and gross margin, plus sales per square foot. The original has to be running smoothly and be operationally solid before we go to second location.
- Sales per employee. We need to watch this variable very closely. We can’t expand without making sure that this model works with the planned amount of employees.
Ownership & Structure
Fresin Fries is a privately held company. It will be registered as a Limited company, with ownership 25% – Guy Fry, 25% – Sam Sauce, 25% – Carl Cone, 25% – Harry Hip.
Management Team
Guy Fry and Sam Sauce have more than 10 years of experience in the food industry. Both are currently employed as Corporate Staff of Company A.
Sam Sauce holds an MBA degree from University V. A true entrepreneur by heart, his latest entrepreneurial project is a diamond store in the heart of Singapore.
Guy Fry holds a BA degree in Graphic Design from the Academy of Arts. His projects are widely varied from product design to brand development of several reputable companies.
Harry Hip holds a MS degree from Institute Y. He completed several projects and served as project manager for multi-national companies in Singapore.
Carl Cone holds a BS degree from University Z, majoring in Management and Information Technology. Prior to his return to Singapore, he has held several management positions in a U.S.-based IT company.
Personnel Table
| FY2019 | FY2020 | FY2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Site Managers | $60,000 | $96,000 | |
| Cashiers (7.67) | $36,000 | $100,800 | $158,760 |
| Busboys (7.67) | $23,400 | $65,520 | $103,200 |
| Cooks (7.67) | $28,800 | $80,640 | $127,008 |
| Totals | $88,200 | $306,960 | $484,968 |
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
Key assumptions.
- Status quo regarding regulation
- No major change in macro-economic or political situation.
- We assume our product, product quality, and social media marketing will generate healthy growth in buzz and steady increase in sales
- We assume efficient management of multiple sites
- We will make the first site work before moving to the second.
- We will not add sites while any site is not working well
- We expect expansion will cause a loss in our second year, but that it will be an acceptable loss and we will have working capital to finance it.
Expenses by Month
Net profit (or loss) by year, use of funds.
Our startup funding of $100,000 will cover both startup expenses and initial assets. specifically:
Startup expenses of $54,500 incurred before launch:
These pre-launch, pre-revenue expenses show up in our financials as negative retained earnings in the Balance Sheet at launch.
- Legal: $3,000
- Furniture and interior: 17,000 (We discussed calling these assets, but we think we can legitimately expense them instead; that’s better for tax treatment)
- Rent: $15,000. We need five weeks in the location for fixup and such before we launch.
- Branding: $3,500. Includes imagery, website, logo, social media accounts, etc.
- Location fixup: $10,000
- Other: $2,000
- Total: $50,500
Current assets required:
- Cash: $50,000 to cover early deficits, working capital, etc.
- Inventory: $10,000
- Plates, napkins, etc. $4,000 (other current assets in starting balance)
Long-term Assets
- Kitchen and fixtures: $22,000
Total Startup Costs:
- $54,500 in expenses incurred before launch
- $86,000 in assets required at launch, including $50K cash reserve.
- Total: $140,500 startup cost
Sources of Funds
Investment will be in equal parts from all four founders. We expect to invest $100,000 to start and an additional $100,000 at the beginning of the second year. We plan to avoid commercial borrowing.
Projected Profit & Loss
| FY2019 | FY2020 | FY2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | $543,909 | $1,018,600 | $1,917,500 |
| Direct Costs | $212,125 | $397,254 | $747,825 |
| Gross Margin | $331,784 | $621,346 | $1,169,675 |
| Gross Margin % | 61% | 61% | 61% |
| Operating Expenses | |||
| Salaries & Wages | $88,200 | $306,960 | $484,968 |
| Employee Related Expenses | $17,640 | $61,392 | $96,994 |
| Rent | $174,000 | $248,000 | $298,000 |
| Utilities | $9,000 | $15,000 | $24,000 |
| Marketing expenses | $21,756 | $40,744 | $76,700 |
| Amortization of Other Current Assets | $11,000 | $31,000 | $50,250 |
| Total Operating Expenses | $321,596 | $703,096 | $1,030,912 |
| Operating Income | $10,188 | ($81,750) | $138,764 |
| Interest Incurred | |||
| Depreciation and Amortization | $3,143 | $4,045 | $5,713 |
| Gain or Loss from Sale of Assets | |||
| Income Taxes | $1,761 | ($1,761) | $13,575 |
| Total Expenses | $538,625 | $1,102,634 | $1,798,024 |
| Net Profit | $5,284 | ($84,034) | $119,476 |
| Net Profit/Sales | 1% | (8%) | 6% |
Projected Balance Sheet
| Starting Balances | FY2019 | FY2020 | FY2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cash | $50,000 | $26,029 | $26,361 | $159,099 |
| Accounts Receivable | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Inventory | $10,000 | $33,104 | $62,319 | $62,319 |
| Other Current Assets | $4,000 | $6,500 | $11,500 | $15,250 |
| Total Current Assets | $64,000 | $65,634 | $100,180 | $236,669 |
| Long-Term Assets | $22,000 | $22,000 | $27,000 | $32,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $0 | ($3,143) | ($7,188) | ($12,901) |
| Total Long-Term Assets | $22,000 | $18,857 | $19,812 | $19,099 |
| Total Assets | $86,000 | $84,491 | $119,991 | $255,768 |
| Accounts Payable | $32,500 | $26,647 | $43,816 | $47,772 |
| Income Taxes Payable | ($3,107) | ($1,761) | $8,033 | |
| Sales Taxes Payable | $2,167 | $3,187 | $5,737 | |
| Short-Term Debt | ||||
| Prepaid Revenue | ||||
| Total Current Liabilities | $32,500 | $25,707 | $45,242 | $61,542 |
| Long-Term Debt | ||||
| Long-Term Liabilities | ||||
| Total Liabilities | $32,500 | $25,707 | $45,242 | $61,542 |
| Paid-In Capital | $100,000 | $100,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($46,500) | ($46,500) | ($41,216) | ($125,250) |
| Earnings | $5,284 | ($84,035) | $119,476 | |
| Total Owner’s Equity | $53,500 | $58,784 | $74,750 | $194,226 |
| Total Liabilities & Equity | $86,000 | $84,491 | $119,991 | $255,768 |
Projected Cash Flow Statement
| FY2019 | FY2020 | FY2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | |||
| Net Profit | $5,284 | ($84,034) | $119,476 |
| Depreciation & Amortization | $14,143 | $35,046 | $55,962 |
| Change in Accounts Receivable | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Change in Inventory | ($23,104) | ($29,215) | $0 |
| Change in Accounts Payable | ($5,853) | $17,169 | $3,956 |
| Change in Income Tax Payable | ($3,107) | $1,346 | $9,794 |
| Change in Sales Tax Payable | $2,167 | $1,020 | $2,550 |
| Change in Prepaid Revenue | |||
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | ($10,471) | ($58,669) | $191,739 |
| Investing & Financing | |||
| Assets Purchased or Sold | ($13,500) | ($41,000) | ($59,000) |
| Net Cash from Investing | ($13,500) | ($41,000) | ($59,000) |
| Investments Received | $100,000 | ||
| Dividends & Distributions | |||
| Change in Short-Term Debt | |||
| Change in Long-Term Debt | |||
| Net Cash from Financing | $100,000 | ||
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $50,000 | $26,029 | $26,361 |
| Net Change in Cash | ($23,971) | $331 | $132,739 |
| Cash at End of Period | $26,029 | $26,361 | $159,099 |

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

Fast Food Restaurant Business Plan

Starting or growing a fast food business? Use this fast food restaurant business plan example as your guide to create your own custom plan to start a food truck, kiosk, or fast food franchise. You can even download it for quick editing.
After all, it’s always easier to edit something that to write it from scratch. That’s why we provide this fast food business restaurant plan free for downloading. You can modify the concepts presented in this plan to fit your specific needs and goals.
Download this Fast Food Business Plan free for easy editing in Google Docs or Microsoft Word:
Table of Contents
1.0 Fast Food Business Plan – Executive Summary
1.1 company & industry.
Nudlez, a Washington Corporation, is in the fast-food service industry. The company has developed a unique business model that reduces overhead by utilizing mobile vending units as opposed to brick and mortar stores. This is a very popular alternative to dining in larger business centric cities.
1.2 PRODUCTS & SERVICES
Nudlez provides high quality, fast-served Asian-styled meals, based on a central theme of noodles. The meals cater for variety and are delivered fresh faster than other noodle-based products. The meals are provided to the consumer initially through mobile Noodle Vending Units (NVU’s), which provide widespread point of sale coverage. The NVU’s are state-of-the-art, complying with health regulations. The first trial NVU was tested in Seattle in July 20XX, receiving great response. The NVU will become a product in itself, as Nudlez expands rapidly through franchising. Nudlez is a globally transportable business.
1.3 FAST FOOD RESTAURANT BUSINESS PLAN: MARKET ANALYSIS

1.4 STRATEGY & IMPLEMENTATION
Nudlez will build brand recognition through its Noodle Vending Units being placed strategically throughout large cities’ business districts. Once brand recognition has been achieved, catering services will be offered, and the Nudlez products will be available in supermarkets. Additionally, Nudlez offers franchise opportunities to help further expand its reach, along with adding an additional revenue stream.
1.5 MANAGEMENT
The owners have significant experience in: the hospitality industry, advertising, and business management. The founder previously owned two very successful Thai restaurants in Seattle but grew tired of paying exorbitant rent hoping customers would turn up each night. His Nudlez concept takes the product to the street!
1.6 FINANCIAL PLAN
Nudlez has strong financials, and is always cash flow positive. Revenues are projected to grow to nearly $58,000,000 by Year 5, with EBITDA totaling $15,000,000. An initial analysis indicates that only 100 meals per day per NVU must be sold to break even. The strong financial plan ensures that the company will be attractive as an acquisition for exit.
1.7 FUNDS REQUIRED & USE
The purpose of this business plan is to raise $1,500,000 from an investor, in the form of a convertible and redeemable note, providing a 32% compound annual return. Nudlez is committed to the rollout of its ‘wok-fresh’ fast food business in 20XX.
2.0 Company Summary
2.1 legal entity & ownership.
Nudlez is trademark registered. Nudlez Inc. was incorporated in the State of Washington in March 20XX. Nudlez is currently equally owned by Mr. Dan Billings and Mr. Bill Cook. They have already spent over $75,000 in direct costs of product testing and development, and will commit a further $200,000 in 20XX, prior to funds being required from the investor. Both owners will each hold two voting rights on the Board with the investor holding one.
2.2 HISTORY

For a start, shop fronts in good locations are expensive. The key to making such a venture successful domestically would be to ensure that the vendor outlets are very hygienic, comply with health standards, serviced by an efficient re-supply network producing consistent meals, with professionalism and quality paramount. He spent considerable time designing a purpose built Noodle Vending Unit. He also moved back to Seattle and renewed his ties in the culinary community to elicit the design of fresh and tasty meals to be served from the NVU. The Nudlez brand was born! Realizing the opportunity to seize a market niche through rapid expansion, the inventor also joined forces with an experienced international business team to develop and implement that initiative.
2.3 FACILITIES & LOCATIONS
During the start-up phase of the business, food sales revenue will come from NVU lunchtime customers in busy Seattle CBD locations. A small office will be setup in Seattle that will serve as the headquarters of the company.
3.0 Mobile Cooking Unit (Food Truck) Products and Services
3.1 product description.

These two products symbiotically solidify the Nudlez brand name. Nudlez is a state-of-the-art stir-fry noodle street vending system. While Nudlez’s footprint in the three major metropolitan cities in Washington will be underpinned by the NVU fleet and a smaller number of strategically placed Nudlez stores, the aim in year-3 is to diversify the revenue stream by selling the meal product alone in supermarkets for home preparation and consumption.
3.2 FEATURES & BENEFITS
Fast & affordable meals.
The NVU operator cooks the meals in front of the customer within sixty seconds, using fresh ingredients. As implied by the Nudlez tagline ‘wok fresh’, each serving of noodles is a taste sensation, freshly cooked-to-order and served piping hot in a convenient cardboard pail. Customers are invited to create their own noodle dish following three easy steps: Step 1: Select Noodle Type; Step 2: Add Sauce; Step 3: Choose Protein. Compared to the meals offered by competitors, Nudlez offers a fresh, tasty, nutritious alternative. Nudlez may be slower than some fast food from the point of order, but it is significantly fresher, more nutritious, and almost 50% more profitable.
One secret to the speed of Nudlez meals is that the meats and vegetables are pre-blanched and hygienically sealed in the same pail that the customer eventually receives. The operator simply removes from the fridge, and combines with noodles and sauce in the wok.
Noodle Vending Unit

Each NVU cart is immaculately presented in stainless steel and branded in strong colorful graphics. At night the noodle stand benefits from its own internal lighting. Construction is of the highest quality kitchen-grade stainless steel. It is designed to be versatile for use in just about any place where it is legal to sell food from a temporary stall. In comparison to standard ‘caravan-type’ vendor units, the NVU has major advantages in that it is: cheaper to produce, smaller size for better site access, self-sustaining power (no mains required short-term), easily moved by one person, unique look, hygienic and cheap to service.
3.3 COMPETITION
The range of competitors spans the market dominants like McDonalds to sandwich and sushi bars to ‘vendor’ foods like kebabs. However, when looking for closer similarity to Nudlez’s offering, we arrive at the specialized noodle-based products provided by such companies as ‘Noodlist’. A storefront operation located close to Pioneer Square in Seattle, the meal variety at ‘Noodlist’ is slightly broader. However speed of preparation is significantly slower than Nudlez, necessitating the addition of standard pre-cooked, oily and somewhat bland Asian fare to satisfy the ‘time-poor’ consumers. It is only this time constraint that is satisfied though, as taste and nutrition are compromised. The lack of speed in the fresh cooked Asian fast food market is emphasized by another competitor, ‘Hot Wok’, offering noodle-based meals in the Sea-Tac International Airport, where a sign on the counter informs consumers that meals may take up to thirty minutes to prepare. A captive consumer group is not being exploited here. Nudlez will change that.
‘Wok in a Box’ is an Oregon competitor that intends to open stores in Washington beginning in 20XX. The company currently operates 16 stores in the Pacific Northwest. Market research indicates company revenue for 20XX reached $5 million, representing a growth rate of 78 percent over the prior year. This growth is encouraging to Nudlez, which through the use of its NVU’s and its other competitive advantages will gain broader exposure. The existence of such competitors makes Nudlez an attractive acquisition or merger proposition.

3.4 COMPETITIVE EDGE/BARRIERS TO ENTRY
- Unique modality of fast-food availability, with unmatched preparation times
- Lower capital costs and overheads and high margin unit sales through broad exposure.
- Healthy, fresh, fast, quality, price competitive alternative
- New funky, identifiable brand, professional approach and solid management
- Aimed at segment of large market not currently exploited by the competition
3.5 DEVELOPMENT
The founders of Nudlez have invested a total of $75,000 in development of the NVU, and plan to spend an additional $200,000 over the next year on development of the second generation NVU. The ‘Generation-2’ NVU is currently under design, maintaining versatility yet improving with the introduction of inventions such as the Nudle-Rac.
4.0 Food Truck Market Analysis Summary
4.1 target market.
With Nudlez, the term “customer” holds two meanings; firstly as a reference to “consumers” who may purchase a meal from a Nudlez point of presence, and secondly as “entities” with an interest in owning a Nudlez franchise. The primary target “consumer” group for the first phase of Nudlez fits the profile of a medium to high-income earner, with a healthy and fresh lifestyle orientation. The first phase of the business plan is about growing brand awareness quickly with customers of this profile. Shortly after growing the brand awareness, as part of the Nudlez rapid growth plans, franchisee customers looking for a self-employment opportunity providing good income relative to the hours worked will be targeted. Institutions such as university campuses will also be targeted as potential franchisees.
The profile will then extend through catering to the customer who is looking for a relatively low cost, value-adding product to support private or corporate events. This customer will be served at both the supermarket (DIY) and event catering levels.
4.2 MARKET SIZE
With sales in excess of $105 billion, the market for fast food is substantial, and the opportunity to build and grow a new exciting product with a strong brand is real. Asian style food represented approximately 35% of this revenue. Although the market is mature with heavy buyer/seller saturation, it is heavily segmented on quality, style, modality and price, presenting opportunity for niche market products such as Nudlez. Customers’ perception of ‘healthier’ is an important value proposition. Nudlez provides this, with the added bonus of serving the meal quickly.
The idea that desirable food could be prepared in a quick fashion appeals to a sizeable portion of the market; those in tourism, people engaged in a commercial capacity, busy homemakers and students. These few examples are indicative of a large and growing collection of “time poor” individuals placing increasing value on every spare moment of their day. Nudlez has the ability to match the ravenous need for convenience with the utility that modern, fast paced lifestyles drive. Nudlez negates boundaries of culture, age and preference, through a daily mission to satiate appetites.
4.3 MARKET TRENDS

The economic environment for the successful outlet will take into account the factors and conditions that influence the ability of its target market to afford its product. Consumers today, particularly in business-centric cites, have a relatively high disposable income. Nudlez will be priced competitively with existing alternatives and will strive to attract market share through product differentiation.
4.4 FAST FOOD RESTAURANT SWOT ANALYSIS
The following represents our strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats for this fast food business plan:
- Strong product supported by great tasking meals with a strong focus on quality, healthy and competitively priced meals in addition to the speed of producing meals
- Strong brand, which has been tested before full implementation. Emphasis on a fund brand culture
- Market conditions are favorable with Nudlez offering new niche spark in an otherwise static market
- Low development risk as the product currently exists
- Easy, low risk growth through short time to market and short time for NVU construction as well as low cost per unit
- Transferable business model as a result of similarities in trends and the US culture of street style food vending. Ability to capitalize on brand and concept with expansion through franchise and other market segments
- Low management risk due to experienced team and the strong diversification of skills and expertise = holistic results
- High gross margins on meal products, which can be maximized by negotiating bulk purchase agreements with wholesalers.
- Defendability of concept as the meal products cannot be patented; this needs to be addressed by building strong brand awareness and establishing copyright on total quality system. Focus also on rapid growth and securing prime sites in target markets
- NVU restocking logistics is being addressed through NVU design, which ensures breakeven results for a day’s trade without restocking. Central production facilities also being established to support restocking
- Site permits for street vending need to be established before implementation of NVU’s, but also private sites will be secured to reduce exposure to local government issues
- Product may be vulnerable to weaken over time, which can be minimized through product innovation and diversification
Opportunities
- Niche-specific opportunities through monopolizing niche market by building strong brand awareness and leading the street food vending culture through being vigilant with other vending business opportunities.
- Low restriction to NVU operating hours means there can be diversity of venues and access to a very diverse target customer group
- Capitalize on diversity of venues and consumer groups to promote and market expansion through event catering and franchise ownership
- International expansion to Europe, which has a strong culture for street food vending and pre-prepared meals. Target strategic partner for joint venture, master franchise or sale of Nudlez
- Local government regulations in relation to street vendors means permits secured have minimum life period, however change in this area is slow
- Vulnerability to imitation products from competitors will be reduced through rapid development of Nudlez products and brand.
- Short-term site permits means the Nudlez brand needs to be diversified through catering, franchise and supermarket placement
- Seasonal demand for NVU’s meaning inconsistent returns. This can be minimized through diversifying brand through catering, franchising and a supermarket product line.
5.0 Fast Food Restaurant Business Plan Strategy & Implementation
5.1 philosophy.
“To forge a new, vibrant, high quality brand in the fast-food sector; to challenge the established market by offering a fresh, tasty and professional alternative; and to build a robust business model founded on high-yield, low capital outlay products.”
It is our vision that Nudlez will expand predominantly through franchising domestically and then to appropriate international markets. It will diversify through catering and product placement in supermarkets. The possibility of trade acquisition or merger also exists.
5.2 MARKETING STRATEGY

5.3 SALES STRATEGY
The marketing objective of Nudlez is to position itself so that consumers of fast food are confident they are purchasing and consuming a healthy and fresh product, enhanced by the overall delivery experience. The marketing objectives are to:
- Rapidly establish a recognized brand through street vendor points of sale supported by a smaller number of strategically placed hardstand stores
- Position itself as a fresh, tasty and healthy alternative to traditional fast food
- Maintain high gross margins on meal products
- Capitalize on the brand through expansion using franchising and product diversification, which will include catering and supermarket placement
Nudlez’s initial strategy will be focused within Washington, commencing in Seattle then within 18 months expansion into Spokane and the Vancouver/Portland metropolis. Beginning with company owned NVU’s and central production facilities, rapid expansion will then be achieved through franchising in all target areas.
5.4 OPERATIONS
NVU production will be outsourced to a manufacturer in Seattle and has been estimated at $12,500 per NVU. Each city will have company owned NVU’s, shops, a central kitchen premises and support kitchens (hubs).
Product Production and Preparation
Raw product has been sourced from selected Seattle suppliers. It is a competitive quality market, with room for a number of suppliers to diversify risk. The secret to Nudlez’ fast delivery to the customer from moment of order is the blanching and preparation process of the raw product at the central kitchen premises and hub sites. This will be overseen by our master-chef teams, adhering to strict health regulations. All ordering, stocking and quality controls will be managed on an in-house computer based system enabling usage patterns to be monitored maintaining ordering efficiency and minimizing wastage.
5.5 NVU Stocking
A unique system for NVU and store restocking, the Nudle-Rac is currently under design. Essentially providing completely removable internal sectioning to the refrigerators to hold the different meals available, it is spring-loaded so that when one meal is removed, the next meal raises to the top for easy access. At the beginning of each day, a franchisee will arrive at their support kitchen where the Nudle-Rac, preloaded with the day’s meals, will be loaded directly into the NVU’s fridge without having to remove the NVU from the van providing an efficient stocking system and minimizing the time meals spend out of refrigeration. For large catering events, support vans will provide additional pre-stocked Nudle-Racs to onsite NVU’s.
5.6 FAST FOOD RESTAURANT EXIT STRATEGY
It is Nudlez objective to be acquired by another fast food company within five years by posting large revenues and a substantial EBITDA. Additionally, merger options, as well as an IPO may be considered at that time.
6.0 Management Summary
6.1 organizational structure.
Nudlez will be lead by Bill Cook, CEO. He will report to the founders and investors, which will make up the board. The CEO will oversee the CFO, CIO, Food and Human Resources departments.
6.2 MANAGEMENT TEAM
With over 80 years of sector diverse, international strategic and operational combined experience, professionally qualified and with energetic personalities critical to ensuring the Nudlez values, the owners and the management provide the skills to deliver:
- Bill Cook has run start-up business operations, with broad management skills
- Dan Billings has owned and managed 2 successful restaurants and an advertising firm
- David Noor is a financial wiz with broad entrepreneurial appreciation
- Angela Gates is not your typical CIO, with a creative flair and eye for efficiency
- Sheila Arch brings the important HR skills combined with a marketing bent
Bill Cook – CEO & Director (Systems, Strategy & Finance)
Bill is a Seattle boy, born and bred, with an intimate knowledge of the cultural and niche diversities of Seattle. Originally with an honors degree in Civil Engineering, Bill worked in the Seattle construction industry from the 80’s boom time through the recession of the early 90’s. From there he traveled overseas working in such places as the UK, Bosnia (during the war), Romania and Holland. The bulk of his experience in these eight years centered on strategic management of start-up ventures. These ranged from establishing critical engineering support facilities for the UN in Bosnia, to expending Shell’s retail network across Eastern Europe, to property development ventures in Romania. Bill returned to Seattle in 20XX to utilize this broad strategic experience on home soil, initially focusing on the property sector. Bill has known Dan for over 20 years and quickly assessed the potential of his Nudlez idea, convincing Dan that rapid expansion was key to securing the market niche. Bill graduated his MBA with High Distinction in 20XX.
Dan Billings – Director (Marketing & Food Technology)
After a successful career in advertising culminating in the establishment of his own Seattle based agency, Dan entered the hospitality industry. His first venture, Pad Real Thai, a Thai restaurant and takeaway situated on bustling Pine Street, was an instant hit. An innovative and funky menu, supported with clever marketing (including the use of real Bangkok Pad’s for delivery vehicles) saw the business achieve critical acclaim. Rave reviews in Short Black and Cheap Eats to name a few, were followed by televised appearances on ‘Seattle Weekly’ and Seattle’s Food Lover’s Guide. A second Pad restaurant opened in Bellevue, and was awarded the prestigious ‘Bent Fork” award. Dan sold the Pad enterprise in 20XX to pursue business interests in Thailand. It was here, while enjoying Bangkok’s vibrant street food culture, where the Nudlez concept was born. Dan has a degree in Science from the University of Washington.
6.3 PERSONNEL NEEDS
In the long term, the employee/income ratio will be approximately $125,000 per employee. Nudlez will run a lean operation with an emphasis on sales and food production. In years two and three the sales staff will grow from 20 to 110 people, and the production staff will grow from 12 to 277 people. Administration will grow as needed to support this fast food business plan.
7.0 Fast Food Restaurant Financial Plan
7.1 requirements.

The investor’s $1,500,000 will be structured as a redeemable note, convertible to 15% shareholding in Nudlez at the end of year-3. Alternatively, redemption can be done at this time providing a return of $3,450,000 (2.3 times investment), equating to a compound annual return of approximately 32%. The end of year-3 is good point for possible investor exit, as decisions on product expansion into supermarkets will be made at this time.
7.2 USE OF FUNDS
Funds will be used to initially finish development of the NVU and to establish fit out central premises in Seattle, including IT infrastructure. 5 hubs and 5 sites will initially be established in Seattle, following that expansion into Vancouver/Portland and Spokane will begin.
7.3 INCOME STATEMENT PROJECTIONS
Nudlez will be profitable by the end of its first fiscal year, as shown in the attached financial statements. The business will grow dramatically in years two and three.
Break Even Analysis
A break even analysis, assuming zero catering and acquisition stores, reveals less than 100 meals per NVU and 150 per store need to be sold per trading day to achieve break even.
7.4 FAST FOOD BUSINESS PLAN ASSUMPTIONS
We are using the following assumptions in this fast food business plan:
- Number of average rain days for the 3 cities is 12 per month. This equates to approximately 40% of the month, which we have conservatively applied, despite its low probability. The conservatism also allows for logistics accidents, staff truancy, etc. to arrive at 13 trading days/month for NVU’s. (Exclude catering)
- Total employment in the expanded Seattle CBD areas is estimated at over 350,000. Nudlez expects to capture less than 2% of this daily market from CBD NVU’s and stores
- Seattle and Portland/Vancouver are similar sized markets, with Spokane being approximately half the size. Revenue estimates reflect these ratios.
- Gen-1 and first Gen-2 NVU, testing and development costs totaling around $75,000 already spent by inventor are not included in financials.
- First Gen-2 NVU will obtain homologation, meaning that the design has blanket pre-approval with local government, reducing time and cost for individual site permits.
- First 10 NVU’s cost $125,000, including homologation.
- Wastage is estimated at 15% across all food related product (validated in Seattle trials). This will reduce once the ‘Nudle-Rac’ and associated IT systems are in place
- Training, Quality Management Systems and Franchise Operations Manuals will be completed effectively for $220,000 by the end of year 1.
Like this? Share it with your network:
I need help with:, popular topics:.
- Learning SEO
- Generating Sales
- Writing a Marketing Plan
- Writing a Business Plan
- Leading My Team
- Free Marketing Webinars
- Starting My First Business
Got a Question?
Get personalized expert answers to your business questions – free.
Affiliate Disclosure : This post may contain affiliate links, meaning we get a commission if you decide to purchase something using one of our links at no extra cost to you.
You Might Also Like...

Should I Give a Discount on My Consulting Fees?

SEO Title Tag Makeover: 4 Powerful Examples

5 Steps to Design an Effective Employee Engagement Action Plan

4 Actionable Steps to Find a Mentor for Your Business

5 Effective Scheduling Tips To Boost Your Productivity

Business Coaching vs Executive Coaching: 10 Examples

7 Employee Satisfaction Secrets: Nurturing a Happy Small Business Team

Secure Your First 10 Investors: Step-by-Step Startup Guide

SEO Coaching and Marketing Courses
Get More Business
Marketing tools.
- SEO Keyword Tool
- MSP Website Content Kit
- Done-for-You Content
- Graphic Design Tool
- Webinar Automation
- Getting Referrals
- Hubspot Marketing Automation
Popular Downloads
- Marketing Plan Example
- MSP Marketing Plan
- Life Coach Business Plan
- Consulting Business Plan
- How to Write a Business Plan
- Clothing Line Business Plan
- Restaurant Business Plan
- Personal Trainer Business Plan
- Trucking Business Plan
- Pizza Restaurant Business Plan
Free Guides
- B2B SaaS SEO Best Practices
- MSP SEO Marketing Playbook
- Buyer Persona Examples
- How to Increase Google Rankings
- New Client Welcome Package
- How to Create a Happy Customer
- Brand Development Guide
- SaaS Metrics Dashboard
- Marketing and SEO Videos
- Salary Calculator
- Executive Coaching Newsletter
- Contributing Content
- Affiliate Disclosure
- Restaurant Type

- Reports & Guides
- Tools & Templates
- Case Studies
- BentoBox vs. Competitors
- Become a Partner

- Design Inspiration
- Diner Relationships
New Openings
- Product Updates
How to Write a Restaurant Business Plan [Free Template]
Start creating your restaurant’s business plan with BentoBox’s free business plan template.
The restaurant business plan is a crucial first step in turning an idea for a restaurant into an actual business. Without it, investors and lenders will have no way of knowing if the business is feasible or when the restaurant will become profitable. Business plans span dozens (or even hundreds) of pages, and due to the stakes that lie within the document and the work required to write it, the process of writing a restaurant business plan can threaten to overwhelm.
That’s why BentoBox has created a restaurant business plan template for aspiring restaurant owners. With section prompts for business plan essentials like financial projections, market analysis and a restaurant operations overview, this template makes creating a business plan significantly more manageable.
Included is a professionally designed, customizable version of the template on Google Docs. Restaurants can download the template below, make a copy and tailor it to their specific concept. For design inspiration, download here .

Restaurant Business Plan Template
Download the Free Restaurant Business Plan Template from BentoBox
Recommended

How to Open a Bakery: The 6 Key Steps
June 20, 2023
A step-by-step guide to planning, financing, designing, staffing, and marketing a new bakery.

How To Expand Into A Multi-Unit Concept
June 30, 2017
Advice from The Meatball Shop, Tacolicious and Next Door on growing your restaurant business

How to Find Restaurant Investors
June 14, 2017
Here are some tips and tricks from pros who’ve done it themselves.
Eat App for
How it works

Free Restaurant Business Plan Template
Opening a restaurant or looking to improve operations at your existing business? Download our free restaurant business plan template to make the process easier.
What is a restaurant business plan?
A restaurant business plan is a document you begin with when setting up or opening a new restaurant. It's a framework that brings together financials, menus, and marketing that helps you turn your restaurant ideas into a reality.
Professional business template
A professional-grade restaurant business plan valued at $159 completely FREE.
Step-by-step instructions
This template includes step-by-step instructions for each section of the business plan with examples.
Printable worksheets
Each section in this template contains fillable worksheets to help you plan out your restaurant business plan.
Check out our other guides

Customer acquisition strategy ebook

Ultimate guide to Google reservations

Instagram booking widget checklist

SWOT analysis bundle
-1.webp?width=1000&height=729&name=Free%20reservation%20email%20template%20(1)-1.webp)
Reservation email templates

Waitlist management manual
Get your restaurant business plan.
Our free-to-download restaurant business plan PDF template includes all the sections you need to get started with opening a restaurant.
Join the future of restaurant operations today

Empowering restaurants, one table at a time Discover seamless dining with Eat App
- Reservation system
- Table management
- CRM and guest profiles
- Reports & trends
- WhatsApp messaging
- Integrations
- Privacy policy
- Terms of service
- The 16 Best Reservation Systems
- Guide to Restaurant Marketing
- Guide to Customer Service
- Guide to Making a Restaurant Website
- All articles
"> "> Compare us
- Compare All
© Eat App. All rights reserved.
Sling is now Sling by Toast! Learn more
More Features

- Restaurants
- Get Started


Restaurant Business Plan: What To Include, Plus 8 Examples
- Business Growth & Management , Templates & Guides
Do you want to ensure the success of your new foodservice endeavor? Write a restaurant business plan.
In this article, the experts at Sling tell you why a business plan is vital for both new and existing businesses and give you tips on what to include.
Table Of Contents
What Is A Restaurant Business Plan?
Why is a restaurant business plan important, questions to ask first, what to include in an effective restaurant business plan, how to format a restaurant business plan, efficient workforce management is essential for success.

At its most basic, a restaurant business plan is a written document that describes your restaurant’s goals and the steps you will take to make those goals a reality.
This business plan also describes the nature of the business itself, financial projections, background information, and organizational strategies that govern the day-to-day activity of your restaurant.

A restaurant business plan is vital for the success of your endeavor because, without one, it is very difficult — sometimes even impossible — to obtain funding from an investor or a bank.
Without that all-important starting or operational capital, you may not be able to keep your doors open for long, if at all.
Even if funding isn’t a primary concern, a business plan provides you — the business owner or manager — with clear direction on how to translate general strategies into actionable plans for reaching your goals.
The plan can help solidify everything from the boots-on-the-ground functional strategy to the mid-level business strategy all the way up to the driving-force corporate strategy .
Think of this plan as a roadmap that guides your way when things are going smoothly and, more importantly, when they aren’t.
If you want to give your restaurant the best chance for success, start by writing a business plan.

Sitting down to write a restaurant business plan can be a daunting task.
As you’ll see in the What To Include In An Effective Restaurant Business Plan section below, you’ll need a lot of information and detail to ensure that the final document is both complete and effective.
Instead of starting with word one, it is hugely beneficial to answer a number of general questions first.
These questions will help you narrow down the information to include in your plan so the composition process feels less difficult.
The questions are:
- What problem does the business’s product or service solve?
- What niche will the business fill?
- What is the business’s solution to the problem?
- Who are the business’s customers?
- How will the business market and sell its products to them?
- What is the size of the market for this solution?
- What is the business model for the business?
- How will the business make money?
- Who are the competitors?
- How will the business maintain a competitive advantage?
- How does the business plan to manage growth?
- Who will run the business?
- What makes those individuals qualified to do so?
- What are the risks and threats confronting the business?
- What can you do to mitigate those risks and threats?
- What are the business’s capital and resource requirements?
- What are the business’s historical and projected financial statements?
Depending on your business, some of these questions may not apply or you may not have applicable answers.
Nevertheless, it helps to think about, and try to provide details for, the whole list so your finished restaurant business plan is as complete as possible.
Once you’ve answered the questions for your business, you can transfer a large portion of that information to the business plan itself.
We’ll discuss exactly what to include in the next section.
In this section, we’ll show you what to include in an effective restaurant business plan and provide a brief example of each component.
1) Executive Summary
You should always start any business plan with an executive summary. This gives the reader a brief introduction into common elements, such as:
- Mission statement
- Overhead costs
- Labor costs
- Return on investment (ROI)
This portion of your plan should pique the reader’s interest and make them want to read more.
Fanty & Mingo’s is a 50-seat fine-dining restaurant that will focus on Sweruvian (Swedish/Peruvian) fusion fare.
We will keep overhead and labor costs low thanks to simple but elegant decor , highly skilled food-prep staff, and well-trained servers.
Because of the location and surrounding booming economy, we estimate ROI at 20 percent per annum.
2) Mission Statement
A mission statement is a short description of what your business does for its customers, employees, and owners.
This is in contrast to your business’s vision statement which is a declaration of objectives that guide internal decision-making.
While the two are closely related and can be hard to distinguish, it often helps to think in terms of who, what, why, and where.
The vision statement is the where of your business — where you want your business to be and where you want your customers and community to be as a result.
The mission statement is the who , what , and why of your business — it’s an action plan that makes the vision statement a reality
Here’s an example of a mission statement for our fictional company:
Fanty and Mingo’s takes pride in making the best Sweruvian food, providing fast, friendly, and accurate service. It is our goal to be the employer of choice and offer team members opportunities for growth, advancement, and a rewarding career in a fun and safe working environment.
3) Company Description

In this section of your restaurant business plan, you fully introduce your company to the reader. Every business’s company description will be different and include its own pertinent information.
Useful details to include are:
- Owner’s details
- Brief description of their experience
- Legal standing
- Short-term goals
- Long-term goals
- Brief market study
- An understanding of the trends in your niche
- Why your business will succeed in these market conditions
Again, you don’t have to include all of this information in your company description. Choose the ones that are most relevant to your business and make the most sense to communicate to your readers.
Fanty & Mingo’s will start out as an LLC, owned and operated by founders Malcolm Reynolds and Zoe Washburne. Mr. Reynolds will serve as managing partner and Ms. Washburne as general manager.
We will combine atmosphere, friendly and knowledgeable staff, and menu variety to create a unique experience for our diners and to reach our goal of high value in the fusion food niche.
Our gross margin is higher than industry average, but we plan to spend more on payroll to attract the best team.
We estimate moderate growth for the first two years while word-of-mouth about our restaurant spreads through the area.
4) Market Analysis
A market analysis is a combination of three different views of the niche you want to enter:
- The industry as a whole
- The competition your restaurant will face
- The marketing you’ll execute to bring in customers
This section should be a brief introduction to these concepts. You can expand on them in other sections of your restaurant business plan.
The restaurant industry in our chosen location is wide open thanks in large part to the revitalization of the city’s center.
A few restaurants have already staked their claim there, but most are bars and non-family-friendly offerings.
Fanty & Mingo’s will focus on both tourist and local restaurant clientele. We want to bring in people that have a desire for delicious food and an exotic atmosphere.
We break down our market into five distinct categories:
- High-end singles
- Businessmen and businesswomen
We will target those markets to grow our restaurant by up to 17 percent per year.

Every restaurant needs a good menu, and this is the section within your restaurant business plan that you describe the food you’ll serve in as much detail as possible.
You may not have your menu design complete, but you’ll likely have at least a handful of dishes that serve as the foundation of your offerings.
It’s also essential to discuss pricing and how it reflects your overall goals and operating model. This will give potential investors and partners a better understanding of your business’s target price point and profit strategy.
We don’t have room to describe a sample menu in this article, but for more information on menu engineering, menu pricing, and even a menu template, check out these helpful articles from the Sling blog:
- Menu Engineering: What It Is And How It Can Increase Profits
- Restaurant Menu Pricing: 7 Tips To Maximize Profitability
- How To Design Your Menu | Free Restaurant Menu Template
6) Location
In this section, describe your potential location (or locations) so that you and your investors have a clear image of what the restaurant will look like.
Include plenty of information about the location — square footage, floor plan , design , demographics of the area, parking, etc. — to make it feel as real as possible.
We will locate Fanty & Mingo’s in the booming and rapidly expanding downtown sector of Fort Wayne, Indiana.
Ideally, we will secure at least 2,000 square feet of space with a large, open-plan dining room and rich color scheme near the newly built baseball stadium to capitalize on the pre- and post-game traffic and to appeal to the young urban professionals that live in the area.
Parking will be available along side streets and in the 1,000-vehicle parking garage two blocks away.
7) Marketing

The marketing section of your restaurant business plan is where you should elaborate on the information you introduced in the Market Analysis section.
Go into detail about the plans you have to introduce your restaurant to the public and keep it at the top of their mind.
Fanty & Mingo’s will employ three distinct marketing tactics to increase and maintain customer awareness:
- Word-of-mouth/in-restaurant marketing
- Partnering with other local businesses
- Media exposure
We will direct each tactic at a different segment of our potential clientele in order to maximize coverage.
In the process of marketing to our target audience, we will endeavor to harness the reach of direct mail and broadcast media, the exclusivity of the VIP party, and the elegance of a highly trained sommelier and wait staff.
8) Financials
Even though the Financials section is further down in your restaurant business plan, it is one of the most important components for securing investors and bank funding.
We recommend hiring a trained accountant to help you prepare this section so that it will be as accurate and informative as possible.
Fanty & Mingo’s needs $250,000 of capital investment over the next year and a half for the following:
- Renovations to leased space
- Dining room furniture
- Kitchen and food-prep equipment
- Liquor license
Projected profit and loss won’t jump drastically in the first year, but, over time, Fanty & Mingo’s will develop its reputation and client base. This will lead to more rapid growth toward the third and fourth years of business.

Most entrepreneurs starting a new business find it valuable to have multiple formats of their business plan.
The information, data, and details remain the same, but the length and how you present them will change to fit a specific set of circumstances.
Below we discuss the four most common business plan formats to cover a multitude of potential situations.
Elevator Pitch
An elevator pitch is a short summary of your restaurant business plan’s executive summary.
Rather than being packed full of details, the elevator pitch is a quick teaser of sorts that you use on a short elevator ride (hence the name) to stimulate interest in potential customers, partners, and investors
As such, an effective elevator pitch is between 30 and 60 seconds and hits the high points of your restaurant business plan.
A pitch deck is a slide show and oral presentation that is designed to stimulate discussion and motivate interested parties to investigate deeper into your stakeholder plan (more on that below).
Most pitch decks are designed to cover the executive summary and include key graphs that illustrate market trends and benchmarks you used (and will use) to make decisions about your business.
Some entrepreneurs even include time and space in their pitch deck to demonstrate new products coming down the pipeline.
This won’t necessarily apply to a restaurant business plan, but, if logistics permit, you could distribute small samples of your current fare or tasting portions of new dishes you’re developing.
Stakeholder Plan (External)
A stakeholder plan is the standard written presentation that business owners use to describe the details of their business model to customers, partners, and potential investors.
The stakeholder plan can be as long as is necessary to communicate the current and future state of your business, but it must be well-written, well-formatted, and targeted at those looking at your business from the outside in.
Think of your stakeholder plan as a tool to convince others that they should get involved in making your business a reality. Write it in such a way that readers will want to partner with you to help your business grow.
Management Plan (Internal)
A management plan is a form of your restaurant business plan that describes the details that the owners and managers need to make the business run smoothly.
While the stakeholder plan is an external document, the management plan is an internal document.
Most of the details in the management plan will be of little or no interest to external stakeholders so you can write it with a higher degree of candor and informality.
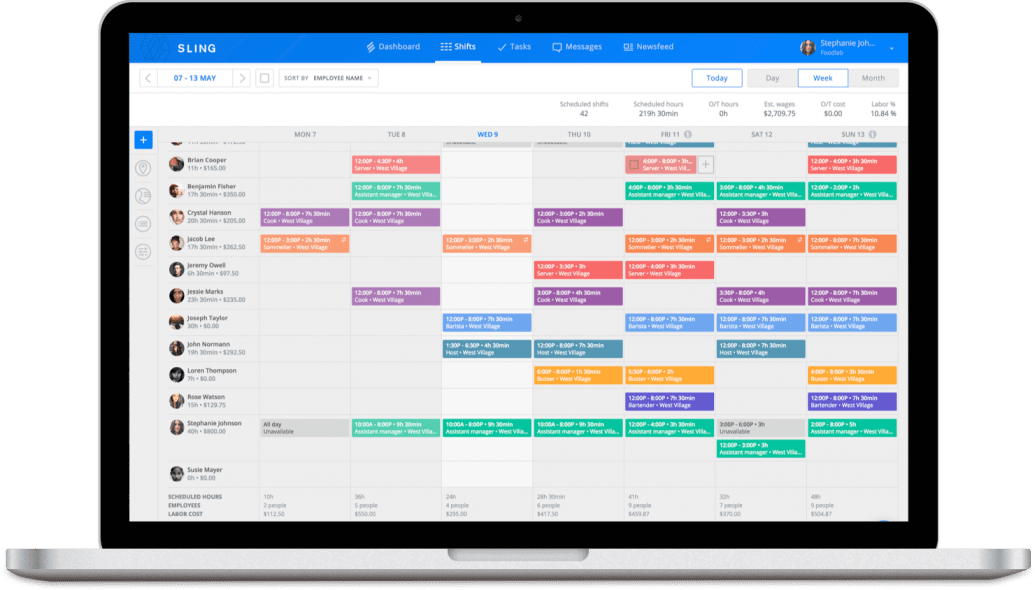
After you’ve created your restaurant business plan, it’s time to take steps to make it a reality.
One of the biggest challenges in ensuring that your business runs smoothly and successfully is managing and optimizing your team. The Sling app can help.
Sling not only includes powerful and intuitive artificial-intelligence-based scheduling tools but also many other features to help make your workforce management more efficient, including:
- Time and attendance tracking
- Built-in time clock
- Labor cost optimization
- Data analysis and reporting
- Messaging and communication
- And much more…
With Sling, you can schedule faster, communicate better, and organize and manage your work from a single, integrated platform. And when you use Sling for all of your scheduling needs, you’ll have more time to focus on bringing your restaurant business plan to life.
For more free resources to help you manage your business better, organize and schedule your team, and track and calculate labor costs, visit GetSling.com today.
See Here For Last Updated Dates: Link
This content is for informational purposes and is not intended as legal, tax, HR, or any other professional advice. Please contact an attorney or other professional for specific advice.
Find the article useful? Share with others:
Related articles

How To Write Your Ideal Restaurant Mission Statement + 15 Inspiring Examples
Whether you run a one-person food cart, a small eatery with fewer than five empl...

12 Examples of Small Business Goals, Plus How to Achieve Your Own
Want to improve the way your business operates? Learn some of the more common bu...

55 Restaurant Marketing Tips To Win Your Market
Discover the best restaurant marketing tips and learn how you can harness onlin...
Get started today
Schedule faster, communicate better, get things done.

Restaurant Business Plan Template [Updated 2024]
Restaurant Business Plan
If you want to start a new restaurant or expand your current restaurant, you need a business plan.
Fortunately, you’re in the right place. Our team has helped develop over 100,000 business plans over the past 20 years, including thousands of restaurant business plans.
The following restaurant business plan template and example gives you the key elements you must include in your plan. A business plan template for a restaurant can be used to create a small restaurant business plan, a business for a fine dining restaurant, fast casual restaurant, and many other types of restaurant businesses. In our experience speaking with lenders and investors, the template is organized in the precise format they want.
You can download our Restaurant business plan template (including a full, customizable financial model) to your computer here.
Sample Restaurant Business Plan
I. executive summary, business overview.
[Company Name], located at [insert location here] is a new, upscale restaurant focusing on providing organic, healthy and/or premium food and beverage products. Our product line fits nicely with health trends nationwide – as individuals are seeking healthier lifestyles complimented by natural, low-fat, and organic foods.
Products Served
[Company Name] will offer a full menu of appetizers, salads, soups, sandwiches, entrees and desserts. All products will use 100% all natural and organic ingredients. Several products on the menu will be highlighted as being lower in fat, cholesterol, or sodium.
In addition to a full menu of food items, [Company Name] will offer beer, wine, coffee, tea, and soft drinks.
Customer Focus
[Company Name] will primarily serve the residents within a 15 mile radius of our restaurant. The demographics of these customers are as follows:
- 27,827 residents
- Average income of $74,700
- 58.9% married
- 49.6% in Mgt./Professional occupations
- Median age: 38 years
In addition to this prime adult demographic for an upscale and healthy restaurant, there are five elementary school, a middle school, and a high school. This will make [Company Name] an ideal location for parents to spend time while waiting for their children or to bring their children to after school.
Management Team
[Company Name] is led by [Founder’s Name] who has been in the restaurant business for 20 years. While [Founder] has never run a restaurant himself, he has taught cooking classes at the local culinary institute for 20 years and has worked as a sous-chef at some of the most upscale restaurants in the community over the past 10 years. As such [Founder] has an in-depth knowledge of the restaurant business including the operations side (e.g., running day-to-day operations) and the business management side (e.g., staffing, marketing, etc.).
Success Factors
[Company Name] is uniquely qualified to succeed due to the following reasons:
- There is currently no upscale and healthy restaurant in the community we are entering. In addition, we have surveyed the local population and received extremely positive feedback saying that they explicitly want to frequent our business when launched.
- Our location is in a high-volume area with little direct traffic, and will thus be highly convenient to significant numbers of passerby’s each day.
- The management team has a track record of success in the restaurant business.
- The upscale and healthy restaurant business is a proven business and has succeeded in communities throughout the United States.
- Market trends such as healthy and organic living support our business opportunity as well as growing awareness about the obesity epidemic and repercussions of non-nutritious eating
Financial Highlights
[Company Name] is currently seeking $370,000 to launch. Specifically, these funds will be used as follows:
- Store design/build: $250,000
- Working capital: $120,000 to pay for Marketing, salaries, and lease costs until [Company Name] reaches break-even
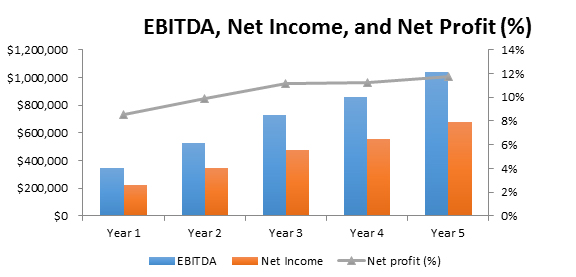
II. Company Overview
Who is [company name].
[Company Name], located at [insert location here] is a new, upscale and healthy restaurant focusing on providing organic and delicious foods to the local community.
[Company Name] was founded by [Founder’s Name]. While [Founder’s Name] has been in the restaurant business for some time, it was in [month, date] that he decided to launch [Company Name]. Specifically, during this time, [Founder] took a trip to Fort Lauderdale, FL. During his trip, [Founder’s Name] frequented a restaurant that enjoyed tremendous success. After several discussions with the owner of the restaurant, [Founder’s Name] clearly understood that a similar business would enjoy significant success in his hometown.
Specifically the customer demographics and competitive situations in the Fort Lauderdale location and in [insert location here] were so similar that he knew it would work. Furthermore, after surveying the local population, this theory was proven.
[Company Name]’s History
Upon returning from Fort Lauderdale, surveying the local customer base, and finding potential location, [Founder’s Name] incorporated [Company Name] as an S-Corporation on [date of incorporation].
[Founder’s Name] has selected three initial locations and is currently undergoing due diligence on each property and the local market to assess which will be the most desirable location for the restaurant.
Since incorporation, the company has achieved the following milestones:
- Developed the company’s name, logo and website located at www…
- Created the menu
- Determined equipment and inventory requirements
- Began recruiting key employees with experience in the restaurant industry
[Company Name]’s Products
Below is [Company Name]’s initial menu. All items will be 100% natural and organic. As you can see all items are classified under the following six main categories:
The location has 40 dedicated parking spots which should suffice even in peak hours.
[Company Name] plans to be open 7 days a week, from 12PM to11PM. As demand dictates, we may extend or reduce our hours. Likewise, as demand dictates, we may offer delivery service.
III. Industry Analysis
The following industry trends and statistics bode well for [Company Name].
According to a recent National Restaurant Association Restaurant Industry Forecast, annual restaurant industry sales are expected to reach $566 billion.
Full-service restaurants are expected to reach $182.9 billion; in contrast, quick service restaurants are expected to grow to $163.8 billion, a gain of 4.0 percent over last year. Eating-and-drinking places will see an increase in sales from of 2.2 percent from last year, totaling $395 billion.
The forecast projects that while overall restaurant industry sales will increase in current dollars by 2.5 percent over recent figures; the numbers translate to an inflation-adjusted decline of 1.0 percent. The industry will remain a cornerstone of the economy, representing 4 percent of the U.S. gross domestic product.
Consumer and Menu Trends Among top trends restaurateurs see are an expanded focus on value, healthy options in kids’ meals, locally sourced items and green initiatives.
- Among 1,600 of American Culinary Federation member chefs, it was decided that balanced children’s meals was number 4 on list of the most popular recent trends and fruit/vegetable side items for kids ranked sixth. In a separate survey, quick-service operators named healthy options in kids meals as the No. 1 food trend in the segment.
- Overall, chefs ranked nutrition/health as the No. 11 trend on restaurant menus—this includes healthy foods, produce and fruit, smaller dishes, fish and gluten-free/ allergy According to Association consumer research, three in four adults say they are trying to eat healthier now at restaurants than they did two years ago. Nearly three in 10 adults – 27 percent – have gone online to search for nutrition information about restaurant food, up from 24 percent a year ago.
- Restaurateurs will also continue to show increasing leadership in becoming “greener”— by taking action such as reducing energy and water use—in step with patrons’ interest in environmental issues. About four in 10 full-service-restaurant operators and nearly three in 10 quick service operators say they plan to devote more of their budgets to green initiatives. Restaurant patrons like the idea: 44 percent surveyed recently said they are likely to make a restaurant choice based on an operation’s practices in the areas of energy and water conservation.
IV. Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
[Company Name] will serve the residents of [company location] and the immediately surrounding areas as well as those who work in [company location].
The area we serve is affluent and has an affinity to healthy and organic foods and beverages like we will be offering.
| Wilmette | Winnetka | |
|---|---|---|
| Total Population | 26,097 | 10,725 |
| Square Miles | 6.89 | 3.96 |
| Population Density | 3,789.20 | 2,710.80 |
| Population Male | 48.04% | 48.84% |
| Population Female | 51.96% | 51.16% |
| Target Population by Age Group | ||
| Age 18-24 | 3.68% | 3.52% |
| Age 25-34 | 5.22% | 4.50% |
| Age 35-44 | 13.80% | 13.91% |
| Age 45-54 | 18.09% | 18.22% |
| Target Population by Income | ||
| Income $50,000 to $74,999 | 11.16% | 6.00% |
| Income $75,000 to $99,999 | 10.91% | 4.41% |
| Income $100,000 to $124,999 | 9.07% | 6.40% |
| Income $125,000 to $149,999 | 9.95% | 8.02% |
| Income $150,000 to $199,999 | 12.20% | 11.11% |
| Income $200,000 and Over | 32.48% | 54.99% |
Customer Segmentation
We will primarily target the following customer segments:
- Local office workers: approximately 5,000 individuals work in offices within a quarter mile of our location and we expect a fair portion of these individuals to frequent us during lunch hours.
- Students: there is a middle school and a high school in the town and the high school are within one half mile. Students from these schools will be targeted to frequent [Company Name].
- Families and Couples: We expect couples and families to frequent our restaurant and enjoy our dinner atmosphere.
V. Competitive Analysis
Direct & indirect competitors.
The following restaurants are located within a 2 mile radius of [Company Name], thus providing either direct or indirect competition for customers:
Joe’s Tavern
Joe’s Tavern is the town’s leading local restaurant and has been in business for 32 years. Joe’s offers a wide array of foods, with local bands as entertainment, and is a highly family friendly environment. .
Joe’s has an extensive menu, with some healthy options and some fried foods and bar favorites. While it has an established clientele, Joe’s Tavern does not differentiate itself as a healthy food choice.
Old Time Organics
Old Time Organics has been in business for 5 years. Old Time offers a variety of baked goods, organic teas and coffees, and sandwiches served to-go.
While Old Time Organics’ food is entirely organic, they have a very limited selection of items and are not open for dinner. The location only has four sit down tables and is thus targeting to-go customers that are either stopping for a quick breakfast or picking up baked goods and coffee for work.
Freddy’s Deli
Freddy’s Deli is a recently opened restaurant. Freddy’s offers breakfast, lunch, and dinner and is open until 1am nightly.
[Company Name] has several advantages over Freddy’s Deli including:
- Freddy’s Deli does not offer products, including pastries, sandwiches, soups and more, made with organic ingredients
- Freddy’s has very little ambience and due to enormous portion sizes and low quality ingredients, the food is largely unhealthy
While we expect that Freddy’s Deli will continue to thrive based on its location and excitement about a new restaurant, we expect that more and more customers will frequent [Company Name] based on the high-quality and organic ingredients we use and product selection.
Competitive Advantage
[Company Name] enjoys several advantages over its competitors. These advantages include:
- 100% Natural/Organic/High-Quality Ingredients: getting 100% Natural/Organic baked goods, soups, sandwiches and more in the local market is challenging and is being increasingly demanded by the local community
- Management: Our management team has years of business and marketing experience that allows us to market and serve customers in a much more sophisticated manner than our competitors.
- Relationships: Having lived in the community for 25 years, [Founder’s Name] knows all of the local leaders, newspapers and other influencers. As such, it will be relatively easy for us to build branding and awareness of our restaurant.
VI. Marketing Plan
The Marketing Plan describes the type of brand [Company Name] seeks to create and the Company’s planned promotions and pricing strategies.
The [Company Name] Brand
The [Company Name] brand will focus on the Company’s unique value proposition:
- Offering organic, high-quality food items including baked goods, sandwiches, soups, salads and more
- Offering a convenient location that offers both eat-in or take-out options
- Providing excellent customer service
Promotions Strategy
[Company Name] expects its target market to be individuals working and/or living within a 15-mile radius of each of its store. The Company’s promotions strategy to reach these individuals includes:
Direct Mail
[Company Name] will blanket neighborhoods surrounding its locations with direct mail pieces. These pieces will provide general information on [Company Name], offer discounts and/or provide other inducements for people to frequent the restaurant.
Public Relations
We will contact all local and area newspapers and television stations to tell them about the opening and unique value proposition of [Company Name].
Advertising
[Company Name] will initially advertise in local newspapers and sponsor community events in order to gain awareness.
[Company Name] employees will initially give free food samples to passerby’s to enable them to taste the quality of our products and learn about us.
Ongoing Customer Communications
[Company Name] will maintain a website and publish a monthly email newsletter to tell customers about new events, products, and more.
Pre-Opening Events
Before opening the store, [Company Name] will organize pre-opening events designed for prospective customers, local merchants and press contacts. These events will create buzz and awareness for [Company Name] in the area.
Pricing Strategy
[Company Name]’s pricing will be moderate so customers feel they receive great value when patronizing the stores.
VII. Operations Plan
Functional roles.
In order to execute on [Company Name]’s business model, the Company needs to perform many functions including the following:
Administrative Functions
- General & administrative functions including legal, marketing, bookkeeping, etc.
- Sourcing and storing ingredients
- Hiring and training staff
Kitchen Functions
- Food preparation
- Ongoing menu creation and modification
Restaurant Service Functions
- Order taking and fulfillment (for take-out and dine-in)
- Customer service
- Janitor/maintenance personnel to keep the restaurant clean
[Company Name] expects to achieve the following milestones in the following [] months:
| Date | Milestone |
|---|---|
| [Date 1] | Finalize lease agreement |
| [Date 2] | Design and build out [Company Name] |
| [Date 3] | Hire and train initial staff |
| [Date 4] | Launch [Company Name] store |
| [Date 5] | Reach break-even |
VIII. Management Team
Management team members.
[Company Name] is led by [Founder’s Name] who has been in the restaurant business for 20 years.
While [Founder] has never ran a restaurant himself, he has taught cooking classes as the local culinary institute for 20 years. Two courses that he taught included:
1. How To Cook for Everyday Eating This course was designed to give students an overall understanding of basic dishes that could be cooked for everyday healthy home-style meals
2. Vegetarian Cooking This course was designed to give students an overall understanding of how to cook with the necessary vitamins and proteins needed to enrich a vegetarian diet without compromising on taste.
[Founder] has also worked part-time at restaurants throughout the region. Specifically, he has worked for Giana’s Patisserie and Mike’s Place, where he was responsible for overseeing kitchen quality.
[Founder] graduated from the University of ABC where he majored in Communications.
Hiring Plan
[Founder] will serve as the restaurant manager. In order to launch the restaurant, we need to hire the following personnel:
- Wait staff (4 full-time equivalents to start)
- Chefs (3 to start)
- Sous-chefs (2 to start)
- Assistant Restaurant Manager (will manage cash register and other administrative functions)
IX. Financial Plan
Revenue and cost drivers.
[Company Name]’s revenues will come from the sale of natural and organic food products to its customers.
The Company will have dine-in, takeout, and possibly delivery systems to cater to a broad spectrum of customers in its target market.
The major costs for the company will be food production costs and salaries of the staff. In the initial years, the company’s marketing spend will be high, as it establishes itself in the market.
Capital Requirements and Use of Funds
[Company Name] is seeking a total funding of $370,000 to launch its restaurant. The capital will be used for funding capital expenditures, manpower costs, marketing expenses and working capital.
Specifically, these funds will be used as follows:
- Working capital: $120,000 to pay for marketing, salaries, and lease costs until [Company Name] reaches break-even
Key Assumptions & Forecasts
Below please find the key assumptions that went into the financial forecast and a summary of the financial projections over the next five years. Please see the Appendix for more detailed financial forecasting information.
| Menu Items | % of Sales | Quantity | Average Price Point | Cost of Goods Sold |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beer | 25% | 2.25 | $7.33 | 16% |
| Cocktails | 20% | 2.25 | $7.00 | 19% |
| Wine by Glass | 10% | 2.25 | $8.67 | 25% |
| Food Items | 45% | 1 | $17.67 | 30% |
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenues | ||||||
| Product/Service A | $151,200 | $333,396 | $367,569 | $405,245 | $446,783 | |
| Product/Service B | $100,800 | $222,264 | $245,046 | $270,163 | $297,855 | |
| Total Revenues | $252,000 | $555,660 | $612,615 | $675,408 | $744,638 | |
| Expenses & Costs | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | $57,960 | $122,245 | $122,523 | $128,328 | $134,035 | |
| Lease | $60,000 | $61,500 | $63,038 | $64,613 | $66,229 | |
| Marketing | $20,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | |
| Salaries | $133,890 | $204,030 | $224,943 | $236,190 | $248,000 | |
| Other Expenses | $3,500 | $4,000 | $4,500 | $5,000 | $5,500 | |
| Total Expenses & Costs | $271,850 | $412,775 | $435,504 | $454,131 | $473,263 | |
| EBITDA | ($19,850) | $142,885 | $177,112 | $221,277 | $271,374 | |
| Depreciation | $36,960 | $36,960 | $36,960 | $36,960 | $36,960 | |
| EBIT | ($56,810) | $105,925 | $140,152 | $184,317 | $234,414 | |
| Interest | $23,621 | $20,668 | $17,716 | $14,763 | $11,810 | |
| PRETAX INCOME | ($80,431) | $85,257 | $122,436 | $169,554 | $222,604 | |
| Net Operating Loss | ($80,431) | ($80,431) | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Income Tax Expense | $0 | $1,689 | $42,853 | $59,344 | $77,911 | |
| NET INCOME | ($80,431) | $83,568 | $79,583 | $110,210 | $144,693 | |
| Net Profit Margin (%) | - | 15.00% | 13.00% | 16.30% | 19.40% |
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASSETS | ||||||
| Cash | $16,710 | $90,188 | $158,957 | $258,570 | $392,389 | |
| Accounts receivable | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Inventory | $21,000 | $23,153 | $25,526 | $28,142 | $31,027 | |
| Total Current Assets | $37,710 | $113,340 | $184,482 | $286,712 | $423,416 | |
| Fixed assets | $246,450 | $246,450 | $246,450 | $246,450 | $246,450 | |
| Depreciation | $36,960 | $73,920 | $110,880 | $147,840 | $184,800 | |
| Net fixed assets | $209,490 | $172,530 | $135,570 | $98,610 | $61,650 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $247,200 | $285,870 | $320,052 | $385,322 | $485,066 | |
| LIABILITIES & EQUITY | ||||||
| Debt | $317,971 | $272,546 | $227,122 | $181,698 | $136,273 | |
| Accounts payable | $9,660 | $10,187 | $10,210 | $10,694 | $11,170 | |
| Total Liabilities | $327,631 | $282,733 | $237,332 | $192,391 | $147,443 | |
| Share Capital | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Retained earnings | ($80,431) | $3,137 | $82,720 | $192,930 | $337,623 | |
| Total Equity | ($80,431) | $3,137 | $82,720 | $192,930 | $337,623 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES & EQUITY | $247,200 | $285,870 | $320,052 | $385,322 | $485,066 |
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASH FLOW FROM OPERATIONS | |||||
| Net Income (Loss) | ($80,431) | $83,568 | $79,583 | $110,210 | $144,693 |
| Change in working capital | ($11,340) | ($1,625) | ($2,350) | ($2,133) | ($2,409) |
| Depreciation | $36,960 | $36,960 | $36,960 | $36,960 | $36,960 |
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | ($54,811) | $118,902 | $114,193 | $145,037 | $179,244 |
| CASH FLOW FROM INVESTMENTS | |||||
| Investment | ($246,450) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Net Cash Flow from Investments | ($246,450) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| CASH FLOW FROM FINANCING | |||||
| Cash from equity | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Cash from debt | $317,971 | ($45,424) | ($45,424) | ($45,424) | ($45,424) |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $317,971 | ($45,424) | ($45,424) | ($45,424) | ($45,424) |
| SUMMARY | |||||
| Net Cash Flow | $16,710 | $73,478 | $68,769 | $99,613 | $133,819 |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $0 | $16,710 | $90,188 | $158,957 | $258,570 |
| Cash at End of Period | $16,710 | $90,188 | $158,957 | $258,570 | $392,389 |
Comments are closed.


Free Restaurant Business Plan Template
Create a restaurant business plan by customizing Venngage restaurant business plan template.
- Design style modern
- Colors light, dark
- Size Letter (8.5 x 11 in)
- File type PNG, PDF, PowerPoint
- Plan business
A restaurant business plan is a document for planning for any restaurant project. This document addresses the feasibility of opening and running a restaurant by exploring related market conditions, assessing financial risks and summarizing the opportunities and challenges that need to be faced. A restaurant business plan may be part of a more complex long-term business plan or may be a stand-alone document. A restaurant business plan is often prepared by the owner of a franchised outlet, but can also be prepared by an independent entrepreneur for submission to potential investors. Venngage has created a restaurant business plan template that you can use for free. You don't need to be a designer or have design experience and you don't need to download any tools because Venngage's restaurant business plan template is completely customizable through Venngage's webapp. Venngage can help you create restaurant business plan in minutes. Our web app has simple drag-and-drop tools, dozens of stock photos, and color options to make the restaurant business plan template your own. Now you can customize everything you see, from font styles, icon styles,
Read more >
Explore more
- Photography
Related plans

- Canada (EN)
- Canada (FR)
- Deutschland
- Netherlands
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Take reservations
- Market your restaurant
- Run smoother shifts
- Sell events & experiences
- Manage reviews
- Manage guest profiles
- View all restaurant solutions
- Robust reporting and insights
- The largest diner network
- 24/7 customer support
- For restaurants
- For restaurant groups & enterprise
- For bars & wineries
- For hotels & casinos
- Integrations
- Pricing and plans
- View all industry insights
- Industry expertise Get advice and tactics from top industry authorities.
- Hospitality Find out how the most successful restaurants make every guest feel like a VIP.
- Marketing Learn how to bring new guests to the table with the latest tech, tools, and ideas for every marketing budget.
- Operations How to iron out operations for shifts smooth as butter.
- Industry trends
- Product innovation
- Advisory board
- Case studies
- Get started
How to write a restaurant business plan

A small restaurant business plan is the roadmap you use to open a successful spot. As a first step to creating yours, ask your friends and colleagues to share restaurant business plan examples. Their restaurant business plan samples can inspire yours.
Once you’ve studied those examples, it’s time to start writing your own. No matter how much thought you’ve put into your concept or how many trusted colleagues have assured you of its greatness, you must write a restaurant business plan. It will prove the viability of your concept to potential investors and provide them with a clear and engaging answer to the question: “Why does the world need this restaurant?”
“The point of a business plan is to show that you’ve done your homework,” says Charles Bililies, owner of Souvla , a fine casual Greek restaurant in San Francisco that has received national acclaim since opening in the spring of 2014.
“You have to show any potential investor that you have an actual plan, you know what you’re talking about, it looks professional, and you’re not just screwing around.”
Quick links Branded cover Table of contents Concept Sample menu Service Management team Design Target market Location Market overview Marketing and publicity Specialists and consultants Business structure Financials
1. Branded cover
Include your logo (even if it’s not finalized), the date, and your name.
2. Table of contents
A table of contents in a restaurant business plan provides an organized overview of the document’s structure and content. It typically appears at the beginning of the plan and lists the major sections and subsections with their corresponding page numbers.
The table of contents is important for several reasons. Firstly, it allows readers to quickly navigate through the plan, enabling easy access to specific sections of interest. Secondly, it helps in presenting a professional and well-structured document, showing that you have carefully organized your thoughts and ideas. It also improves readability and comprehension, as readers can easily locate and refer back to relevant information

3. Restaurant concept
Describe your restaurant concept and get the reader excited about your idea. Specify whether the restaurant will be fine dining or more casual. Include an executive summary and go into detail about the food you’ll be serving, inspiration behind your concept, and an overview of service style.
Define clearly what will be unique about your restaurant and include your mission statement. This section should include a market analysis that shows how your restaurant will be similar and different from competing restaurants.
4. Sample menu
The menu is the most important touchpoint of any restaurant’s brand, so this should be more than just a simple list of items. Incorporate your logo and mock up a formatted menu design (tap a designer for help if needed).
Your sample menu should also include prices that are based on a detailed cost analysis. This will:
- Give investors a clear understanding of your targeted price point
- Provide the info needed to estimate check averages
- Show the numbers used create financial projections for starting costs
- Show investors that you’ve done the homework
- Prove you can stay within a budget
This section is most relevant for:
- Fine-dining concepts
- Concepts that have a unique service style
- Owners who have particularly strong feelings about what role service will play in their restaurant.
It can be a powerful way of conveying your approach to hospitality to investors by explaining the details of the guest’s service experience.
Will your restaurant have counter service and restaurant hostess software designed to get guests on their way as quickly as possible, or will it look more like a theater, with captains putting plates in front of guests simultaneously?
If an extensive wine program is an integral part of what you’re doing, will you have a sommelier? If you don’t feel that service is a noteworthy component of your operation, address it briefly in the concept section.

6. Management team
Write a brief overview of yourself and the team you have established so far. You want to show that your experience has provided you with the necessary skills to run a successful restaurant and act as a restaurant business owner.
Ideally, once you have described the strong suit of every member of your team, you’ll be presenting a full pitch deck. Most independent restaurant investors are in this for more than just money, so giving some indication of what you value and who you are outside of work may also be helpful.
Incorporate some visuals. Create a mood board that shows images related to the design and feeling of your restaurant.
Whether you’re planning to cook in a wood-burning oven or are designing an eclectic front-of-house, be sure to include those ideas. Photos of materials and snippets of other restaurants that you love that are similar to the brand you’re building are also helpful.
8. Target market
Who is going to eat at your restaurant? What do they do for a living, how old are they, and what’s their average income? Once you’ve described them in detail, reiterate why your specific concept will appeal to them.

9. Location
There should be a natural and very clear connection between the information you present in the “Target Market” section and this one. You probably won’t have a specific site identified at this point in the process, but you should talk about viable neighborhoods.
Don’t assume that potential investors will be familiar with the areas you’re discussing and who works or lives there—make the connections clear. You want readers to be confident that your restaurant’s “ideal” diner intersects with the neighborhood(s) you’re proposing as often as possible.
If you don’t have a site , this is a good place to discuss what you’re looking for in terms of square footage, foot traffic, parking, freeway accessibility, outdoor seating , and other important details.
10. Market overview
Address the micro and macro market conditions in your area and how they relate to licenses and permits. At a macro level, what are the local and regional economic conditions?
If restaurants are doing poorly, explain why yours won’t; if restaurants are doing well, explain how you’ll be able to compete in an already booming restaurant climate. At a micro level, discuss who your direct competitors are. Talk about what types of restaurants share your target market and how you’ll differentiate yourself.
11. Marketing and publicity
The restaurant landscape is only getting more competitive. Discuss your pre- and post-opening marketing plans to show investors how you plan to gain traction leading up to opening day, as well as how you’ll keep the momentum going.
If you’re going to retain a PR/marketing company, introduce them and explain why you’ve chosen them over other companies (including some of their best-known clients helps). If not, convey that you have a solid plan in place to generate attention on your own through social media, your website , and media connections.

12. Specialists and consultants
List any outside contractors you plan to retain, such as:
- General contractor
- PR and marketing
Briefly explain the services they’ll be providing for you, why you chose them, and any notable accomplishments.
13. Business structure
This section should be short and sweet. What type of business structure have you set up and why did you make that specific decision? You will need to work with an attorney to help you determine what business structure is best for you.
“Step one: write a business plan. Step two: hire a good attorney. In addition to helping me build a smart, sustainable business structure, my attorney was also a great resource for reviewing my business plan because she’s read thousands of them. She was a very helpful, experienced outside perspective for more than just legal matters,” says Charles Bililies.
14. Financial projections
Let your accountant guide you through this portion of your business plan. It is crucial that whoever you hire to help you with your finances has a wealth of restaurant experience (not just one or two places). They should be familiar with the financial specifics of starting a restaurant and know what questions to ask you.
Before creating realistic financial projections, your accountant will want to know:
- How many seats the restaurant will have
- What your average check will be
- How many covers per day you plan to do
Being conservative in these estimations is key. These three data points will be used as the basis for figuring out whether your concept is financially feasible.
Lou Guerrero, Principal at Kross, Baumgarten, Kniss & Guerrero, emphasizes, “You’ll get a lot of accountants that tell you that they’ve done a couple of restaurants, but you have to choose someone that has a deep expertise in what you’re doing. There’s nothing to gain from going with someone that doesn’t have a very restaurant-centric practice.”
A well-vetted accountant with restaurant experience will know exactly what you’ll need to have prepared to show investors.
The key projections you can expect to work on are:
- Pro forma profit and loss statement for the first three to five years of operation
- Break even analysis
- Capital requirements budget
Writing a comprehensive restaurant business plan is a crucial step towards opening a successful establishment. By seeking inspiration from examples, demonstrating your expertise, and addressing all the essential components, you can prove the viability of your concept to potential investors.
Remember, a well-prepared business plan demonstrates professionalism and a clear understanding of your goals, increasing your chances of achieving long-term success in the competitive restaurant industry.
Discover how OpenTable can take your business where you want to go
Take the Quiz
Explore more articles

- Restaurant reservation software
- Digital marketing solutions
- Restaurant table management
- Online ordering for restaurants
- Experiences
- Reputation and reviews
- Relationship management
- OpenTable integrations
- For restaurant groups
- For bars and wineries
- For hotels and casinos
- The best customer service
- Private dining
- Data & security
- Online waitlist
- Benchmark reporting
- Direct messaging
- About OpenTable
- New on OpenTable
Need help deciding which option is best for you? Give us a call at
(866) 951-7154
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Cookies and Interest-Based Ads
- Do Not Sell My Info (California)
Earn a $500 gift card when an eligible restaurant you refer joins OpenTable*
*terms and conditions apply
Business Plan Quick Builder
The takeaway business plan template, $3.33, per month - paid 3 monthly.

- Restaurant Business Plan
Article Index:
2.0 Company Description
3.0 daily operations and production, 4.0 market analysis, 5.0 marketing strategy and implementation, 6.0 organization and management, 7.0 financial plan.

1.0 Executive Summary
The Traditional Home-Style Restaurant (“THR”) will be a moderately priced 86 seat restaurant offering family style food and service. Broasted chicken, pot roast, steaks and pork chops along with classic hamburgers, wraps and generous salads are all on the menu. We will offer specialty selections including a lighter options and smaller portions for a children’s menu.
The restaurant will be family owned and operated by Jeff and Betty Wright. Together they have over 25+ collective years experience in the restaurant and catering industry.
The Wrights will be leasing a 3,400 square foot space located at West Roads Shopping Center, an existing retail center located in Benbrook, a suburb in Fort Worth, Texas. The site was previously leased as an Italian Restaurant. Although the location was previously utilized as a restaurant, the former tenant removed the majority of the furniture, fixtures and equipment which will need to be replaced. The location will also require some additional renovation to update the lavatories and increase table space in the dining area.
The décor will feature wood accented chairs with blue and white checked table cloths. Dinner style tables will be surrounded by wooden chairs with comfortable seating cushions.
Sales projections assume 1700 customers per week resulting in weekly sales of just over $19,777, or $1,028,000 annually. This equates to around $302 per square foot in sales annually which positions THR as a highly desirable concept for ownership in a table service market where $200 to $325 per square foot is considered moderately profitable and therefore a good investment. Total start up costs will be $363,000, $174,000 of which will be contributed by the owners and the remainder will be secured by a proposed bank loan.
1.1 Business Objectives
The primary objectives of the business plan for Restaurant are below:
- To be the premier home-style restaurant in western Fort Worth, Texas
- To provide quality meals at reasonable prices with exemplary service
- Achieve Cover ratios of 1.00X at each lunch and dinner serving
- To achieve Prime Cost Ratios lower than 65%
1.2 Mission Statement
Our Mission is to provide a unique and relaxing dining experience – similar to dining at home. We will strive to achieve this goal by: 1) by providing menu items incorporating quality ingredients at reasonable prices, and 2) we will be mindful of the well being of our customers and staff– treating each and everyone with dignity and respect – just like we would at our own home!
1.3 Guiding Principles
- Being Mindful of our Customers and our Staff Coinciding with our family values, we will treat both our customers and staff in a manner in which we ourselves would want to be treated (or better!).
- Gratitude “An attitude of gratitude” shown to our customers, employees and vendors – because without their input, service, labor and time, our business would not be here without them!
- Our Service Provide the warm and friendly service expected from a family-style restaurant creating an informal, comfortable environment which will make the customers satisfied and want to return again and again.
1.4 Keys to Success
- Repeat business. Every customer who comes in once should want to return, and recommend us. Word–of–mouth marketing is a powerful ally.
- Hire top notch chefs and offer training to keep the chef on top of his/her game, and pay top wages to ensure they stay with us.
- Location. Convenience is essential to us; we need to be close to our market because we are not trying to get people to travel to reach us.
- A variety of menu offerings with a “down home” theme, reasonably priced to establish credibility, but not so high as to limit customers.
The Traditional Home-Style Restaurant will be located 7950 Camp Bowie West Blvd, Fort Worth, Texas. The restaurant will be wholly owned and operated by Jeff and Betty Wright. The restaurant will serve a variety of classic home-style favorites from pot roast and mashed potatoes to patty melts and vanilla ice cream.
The restaurant will be open 7 days a week with hours as follows:
Monday 11:00 am – 9:00 pm Tuesday 11:00 am – 9:00 pm Wednesday 11:00 am – 9:00 pm Thursday 11:00 am – 9:00 pm Friday 11:00 am – 10:00 pm Saturday 11:00 am – 10:00 pm Sunday 12:00 pm – 5:00 pm
2.1 Ownership
The restaurant will be owned by Jeff Wright. Jeff began his restaurant career at the age of 15 working in a quick-service foodservice operation and earned his way through college as a server and bartender. After earning his degree, he worked for a regional restaurant chain and an independent fine dining restaurant. In these organizations he held the positions of Assistant Manager and then General Manager.
Betty Wright received her Culinary Degree from the Art Institute in Dallas. After graduation she was employed by a local chain restaurant and then at a Five Star Hotel in Dallas. Betty will be employed as the Kitchen Manager.
With the high turnover of help for startup restaurants, we will rely on family to fill in where required until we are off the ground and making a profit.
2.2 Legal Form
THR will be organized as a sole proprietorship, wholly owned and operated by Jeff Wright d/b/a Traditional Home-Style Restaurant. THR is registered in the state of Texas a community property state.
2.3 Start-Up Summary
The cost to open the restaurant is $363,000. The majority of the expenses are in furniture fixtures and equipment totally $110,000. The location requires some build-out and renovation totally $50,000 and will require approximately 30 days to complete. The Wrights will sub-contract the work themselves. Costs are detailed in a later section of this restaurant business plan.
$175,000 of the start-up costs will be funded by the owners. The owner’s source of funds is a combination of liquid assets and marketable securities, primarily from their existing catering business.
2.4 Location and Facilities
The 3,400 square foot restaurant will be located in a West Roads Shopping Center, a retail strip center located in the Benbrook suburb of Fort Worth, Texas. The restaurant is located in a major traffic area, at the intersection of Camp Bowie and Cherry Road.
Benbrook, a suburb of Fort Worth, Texas, has a population of over 51,000 according to the 2010 U.S. Census Report. The residential population in the immediate area is comprised of a mixture of single family and multi-family housing. The median household income is $46,532. Major employers include Union Pacific and Bank of America.
THR will be open 7 days a week for lunch and dinner requiring multiple shifts. Jeff will write the schedules. The schedules will be written in a manner that will allow the ability to increase or decrease hourly labor according to sales volume in order to maintain a consistent labor cost control.
Proper labeling and rotation techniques, accompanied by ample storage facilities will ensure that high quality prepared product will be sufficiently available to meet the demands during peak business hours. Replenishment and ongoing preparation will continue during off peak business hours.
Jeff Wright will be responsible for ordering, receiving and maintaining sufficient inventory to meet production demands. Ordering schedules will be staggered with perishable products being ordered multiple times per week to preserve freshness. Standard grocery and supply orders will be ordered less often, according to a predetermined schedule and storage capacity.
Mr. Wright will rely on operational checklists to verify that each work shift has been properly prepared for and to insure the operational standards are followed before, during and after work shifts.
The restaurant layout, including the dining room, kitchen and serving line, has been designed for efficiency and flexibility to accommodate the fluctuation in customer traffic and peak meal periods.
Upon arrival, guests will be greeted immediately by either the assistant manager or a server and asked for the seating preference. Drink orders will be taken and guests can munch on our complimentary rolls. Once the customer’s order is taken, the order will automatically be printed to a requisition printer located in the grill area. The grill cook will use the printed ticket to keep track of orders and place the meal under the heating lamps until the order is complete. The kitchen preparation line has been designed to be operated by a minimum staff of 1 line cook and a maximum of 4 cooks. This design allows line staffing to be adjusted to the business volume. Shift changes for all staff will involve cleanup, restocking and preparation. All monies will be settled at the end of each shift. The closing shift will involve designated closing duties that will leave the restaurant clean and fully prepared for the next day.
3.2 Competitive Comparison
The US restaurant industry includes about 480,000 restaurants with combined annual revenue of about $400 billion. Major companies include Brinker International which owns Chili’s Grill & Bar) and Maggiano’s, Ruby Tuesdays McDonald’s; YUM! Brands (KFC, Pizza Hut, Taco Bell); and Darden Restaurants (Olive Garden, Red Lobster). The industry is highly fragmented: the 50 largest companies hold just 20 percent of the market.
Local competitors within a five mile radius are as follows.
- Hedarys Restaurant – This is a full service family restaurant established in 1977. The 5,000 SF restaurant run as a sole proprietorship, has 17 employees and generates $1.7 million in revenue annually. Prices are higher than THR and range from $8.00-$20 per entrée.
- Applebee’s – this is a chain restaurant offering standard fare. The food quality is average. Entrées range from $6.99 – $20.
- Chili’s – this is a chain restaurant also offering standard fare. Food choices are varied and prices range for $8-$21.
- Barbeque Ben’s – This is sole proprietorship offering primarily barbeque item. Although the food offering does not compete directly with the subject, the restaurant targets the same neighborhood families and has been operating at the single location since 1978. Entrée range from $8.99-$12.
- Cracker Barrel – located along Interstate 30, the restaurant is not located within the target market area. However due to its menu offering of home comfort food, the restaurant attracts a similar market, although Cracker Barrel’s attract the tourist business as well. Entrées range in price from $7.99-$14.
3.3 Suppliers
Because of their years of experience combined with their existing catering business, Jeff and Betty Wright have established relationships with qualified suppliers. These suppliers can provide reasonably priced products, delivered according to the schedule.
3.4 Management Controls
The Wrights will practice sound management procedures in order to control costs, insure quality of product and provide friendly customer service. The following systems will be used by management:
Order Guide: The restaurant will use an item specific order guide to track order history and maintain designated levels of product in inventory.
Weekly Inventory: Management will conduct a weekly inventory to determine valuation for use in the preparation of weekly profit and loss reports.
Daily Inventory Tracking: Daily inventory will be taken on specific items. Movement will be compared to sales data to ensure designated products have been properly accounted for.
3.5 Administrative Systems
With a limited staff, it is crucial that the Wrights remain current with daily cash outlay. The purchase of a POS system will immensely help them with these daily administrative reports:
Daily Cash Control. Sales and receipts recorded by the POS system will be compared to actual cash and credit card deposits on a daily basis. Acceptable over/short amounts will be limited to $5.00 per day. Discrepancies greater than $5.00 will prompt management to conduct an immediate audit to account for the difference. Monthly totals will be compared to actual P&L statements for accuracy. Cash, debit card and credit card receipts will be deposited in a deposit.
Weekly Prime Cost Report. Jeff Wright will prepare a weekly report that shows the gross profit margin after cost of goods sold and labor cost has been deducted from the sales revenue. The prime cost for this type of restaurant is expected to range from 60% to 65%. Proper control of the prime cost is the single most effective measure of management’s ability to operate the restaurant.
Purchasing Records/Payables. A part time bookkeeper will process and record invoices and credits daily. Reports detailing cash expenditures, payments by check, and accounts payable transactions will be readily available. Check disbursements will be prepared by the bookkeeper. Check signing authority for the general operating account will be given to the general manager.
Payroll Processing. Payroll checks will be issued bi-monthly. Jeff Wright will run reports from the time & attendance system, make necessary adjustments, and prepare for transfer to the payroll system. Payroll will be processed by a payroll processing service.
3.6 Future Services
THR has future plans to provide catering services for family reunions, weddings and other events desiring a “home-style” menu. This could potentially become a large portion of gross sales. The Wrights are targeting Year 2 and at that point, a sales agent would be hired to directly market the products for daily delivery or catered functions.
The restaurant industry is a large and diverse business: Restaurant-industry sales are forecast to reach $580.1 billion in 2010 – an increase of 2.5 percent over 2009. Restaurant-industry sales are projected to total $604 billion in 2011 and equal 4 percent of the U.S. gross domestic product. The overall economic impact of the restaurant industry is expected to exceed $1.7 trillion in 2011. On a typical day in America in 2010, more than 130 million people will be foodservice patrons. Sales at full service restaurants reached $184.2 billion in 2010. Sales at limited service restaurants increased to $164.8 billion in 2010, while snack and non-alcoholic-beverage bar sales rose to $24.7 billion. (National Restaurant Association).
The US restaurant industry includes about 480,000 restaurants with combined annual revenue of about $400 billion. Major companies include McDonald’s; YUM! Brands (KFC, Pizza Hut, Taco Bell); and Darden Restaurants (Olive Garden, Red Lobster). The industry is highly fragmented: the 50 largest companies hold just 20 percent of the market. (First Research).
The industry consists of full-service restaurants (FSR) and limited service eating places, which include quick-service restaurants (QSR); cafeterias; buffets; snack bars; and nonalcoholic beverage bars. (First Research)
4.1 Industry Analysis
This analysis is based on the Standard Industry Code (“SIC”) 5812: Eating and Drinking Places Establishments primarily engaged in the retail sale of prepared food and drinks for on-premise or immediate consumption. It is also based on the North American Industry Classification System (“NAICS”) 722110 – Full-Service Restaurants.
This industry comprises establishments primarily engaged in providing food services to patrons who order and are served while seated (i.e., waiter/waitress services) and pay after eating. These establishments may provide food services to patrons in combination with selling alcoholic beverages, providing carry out services, or presenting live nontheatrical entertainment.
Demographics, consumer tastes, and personal income drive demand. The profitability of individual companies can vary: while QSRs rely on efficient operations and high volume sales, FSRs rely on high-margin items and effective marketing. Large companies have advantages in purchasing, finance, and marketing. Small companies can offer superior food or service. The industry is labor-intensive. (First Research)
Wages form a significant proportion of operating costs. The existence of a statutory minimum wage in most states increases the need for players to keep other costs as lean as possible, which in turn increases the importance of suppliers. A slight complication is that in some states, foodservice employers are able to treat tips received by their staff as contributing to their wages; in such states, this policy reduces the impact of the minimum wage from the employers’ perspective. (Data Monitor)
Annual revenue per worker is less than $50,000.
Restaurants compete with companies that serve meals or prepared foods, including grocery stores, warehouse clubs, delis, and convenience stores. In addition, restaurants compete with home cooking.
Among FSRs, most establishments focus on Italian cuisine, steak, or seafood. Hamburger joints make up a majority of QSR locations, along with pizza parlors and sub sandwich shops. Industry revenue is roughly evenly split between FSRs QSRs.
In FSRs, waiters take orders, serve beverages and meals, present the check, and process payment. FSRs include casual dining (full bar); family dining (limited bar); and fine dining establishments.
Annual sales average $860,000 for FSRs.
An FSR’s square footage and the number of seats and tables dictate how many patrons it can serve (also known as table turns or covers) directly affects sales. Because the restaurant industry is highly competitive, site selection is critical: companies may consider population density, household income, competition, visibility, accessibility, and traffic.
Companies carefully manage inventory of perishable food products, such as fresh seafood and dairy goods, to reduce losses due to spoilage.
Computerized information systems can improve and link food preparation and serving operations. Touch screen ordering programs ensure accurate communication of customer orders. Timing systems monitor meal progress and can alert staff if an order is running behind schedule. Reservations programs maximize traffic flow and seating. Inventory management systems track supply levels and can help reduce waste due to spoilage. Cost accounting programs help companies determine the profitability of individual menu items. Handheld point-of-sale (POS) devices allow servers to place orders and print checks tableside, improving accuracy and reducing ordering time. Some handhelds can also print customer checks and process credit card payments. (First Research)
4.1.1 Market Size
The US restaurant industry includes about 480,000 restaurants with combined annual revenue of about $400 billion.
4.1.2 Industry Participants
Major participants include Major companies include McDonald’s; YUM! Brands (KFC, Pizza Hut, Taco Bell); and Darden Restaurants (Olive Garden, Red Lobster).
4.1.3 Main Competitors
The following restaurants are located within a five mile radius of THR:
- Applebee’s – This is a chain restaurant offering standard fare. The food quality is average. Entrées range from $6.99 – $20.
- Chili’s – This is a chain restaurant also offering standard fare. Food choices are varied and prices range for $8-$21.
- Cracker Barrel – Located along Interstate 30, the restaurant is not located within the target market area. However due to its menu offering of home comfort food, the restaurant attracts a similar market, although Cracker Barrel’s attract the tourist business as well. Entrées range in price from $7.99-$14.
4.1.4 Market Segments
THR will appeal to a broad base of consumers in both the residential and business community. The location selected for THR was chosen primarily to appeal to the growing number of households in the area.
The suburb of Benbrook located in western Forth Worth, TX has a population of over 51,000 according to the 2010 U.S. Census Report. The residential population in the immediate area is comprised of a mixture of single family and multi-family housing. The median household income is $46,532 for 2010 and estimated to be $54,646 for 2015. (US Census).
Major employers include Union Pacific Railroad and Bank of America.

(www.Business Decision. Info)
4.2 Market Tests
For the past 10 years, Jeff and Betty have been catering part-time. Their home-style menu is very popular with family reunions. More often than not, the couple gets asked to open a restaurant full-time so that patrons can return again and again.
Through Constant Contact (an online marketing program) the couple has stayed in touch with their host and hostesses, and has been asked to return to provide catering services to several repeat events. Home-Style Catering as also grown by word of mouth.
The couple also co-authors a home-style blog – attracting foodies nationwide and globally, swapping recipes, compiling the most sought after home-style comfort recipes, and identifying current trends, for example, providing expanded menus for children and for those with food allergies.
The Wrights already have a customer base through their catering business and local blog visitors. These customers will be the first to be contacted when they announce the grand opening of the brick and mortar restaurant.
4.3 Target Market Segment Strategy
Jeff and Betty Wright selected the subject area for its restaurant primarily because of its location to the very busy intersection of Cherry Street and Camp Bowie. The restaurant located in a retail strip center is located on “going home” side of Camp Bowie. This will encourage families tired from a day of work to stop in for a home cooked meal they can enjoy – without the cleanup!
Cherry Road which runs North and South is connected to the busy Interstate 30 corridor, 1/2 mile north of the shopping center. Camp Bowie which runs East and West connects to the newer western suburbs of Fort Worth.
4.3.1 Market Needs
The Benbrook area is in great need of a family style restaurant. This section of Camp Bowie is commonly referred to as “fast food alley” The selection of fast food is vast however; the area is limited on its family restaurant choices. THR’s nearest competitor, The Hedary Restaurant is located over 5 miles away from the location. Further, established in the 1970’s the Hedary Restaurant’s customers are older than the targeted family group THR focuses on.
4.3.2 Market Trends
According to the National Restaurant Association, the top 10 trends for are:
- locally sourced meats and seafood,
- locally grown produce,
- sustainability as a culinary theme,
- nutritious kids’ dishes,
- hyper-local items, (networked locally grown – like a Craigslist for restaurants)
- children’s nutrition as a culinary theme,
- sustainable seafood,
- gluten-free allergy conscious items,
- back to basics cuisine, and
- farm brand ingredients.
4.3.3 Market Growth
US consumer spending on services, an indicator of restaurant sales, rose 1.8 percent in November 2011 compared to the same month in 2010. The average US retail price for diesel and regular gas, which influences discretionary consumer spending on eating out, rose 13.1 percent and 9.3 percent respectively in the week ending January 16, 2012, compared to the same week in 2011. US tourism spending for food services and drinking places, an indicator for restaurant revenues, increased 6.1 percent in the third quarter of 2011 compared to the same period in 2010. (First Research)
4.4 Positioning
Consumers believe that meals at home are healthier and higher quality than eating at restaurants. At THR, we will position ourselves as the premier home-style restaurant by preparing quality home cooked meals with simple wholesome ingredients. Jeff and Betty Wright will also provide home cooked fare that appeals to the current trends of healthier food and offer menu selections which will appeal to this group. THR will be positioned as the premier traditional home-style restaurant.
THR will position itself as the premier home-style restaurant in the Benbrook suburb of Fort Worth, Texas. We will do this by providing quality home style meals, prepared with quality ingredients at a reasonable prices. Customers will enjoy the quaint surroundings inside with the wood tables and checkered table cloths. Our restaurant will provide a relaxed atmosphere and when customers walk in they will be greeted by warm smiles and greeted just as they were arriving home.
The chains have tried to create home-style restaurants but where they have failed is in the personal aspect of the business. The POS system known as “The Expediter” used to monitor inventories and time meals has replaced one of the most important aspects of a restaurant – the friendliness of the staff! And in light of this, a handful of chain restaurants are beta testing self-pay tables!
Our customers will enjoy our standard menu fare, along with seasonal menus so that we can better take advantage of cost savings and stay current with some of the food industry trends.
At THR we plan to be the premier restaurant to work for as well. We believe that the restaurant industry is a great place to begin one’s career or pursue full-time. In fact, according to the Restaurant Association, nearly half of all adults have worked in the restaurant industry at some point during their lives, and more than one out of four adults got their first job experience in a restaurant. At THR we believe that our restaurant will provide job opportunities both for the entry level applicant was well as for the part-time worker searching for flexibly in job hours. We will pay our employees a competitive salary and believe we can do so by meticulously keeping our records, including daily review of the Prime Cost Report, and utilize Cost Accounting Systems, to prevent inventory shortfalls. We will be proactive with our employees by scheduling regular performance reviews, and provide bonuses and other incentives to motivate our staff. We will also provide our employees with the most current training programs regarding safe food handling, and worker protection. (Additional information regarding our employees is explained in Section 6.1 which follows).
THR will also remain current with current industry marketing tends. In addition to a website with our menu, map and driving directions, we will also have a Facebook page and utilize other social media such as Twitter. We will team up with Groupon and Yelp. We will offer a loyalty club and birthday club which recent reports indicate increases earnings as much as 15%.
5.1.1 Strengths
- Prime location with easy access from Interstate 30
- Exceptional staff with the can do attitude. Combined 25 years in the restaurant industry
- Because owner has catering industry experience, he already has established a customer market and approved vendors
- Due to our small size, we believe we can provide exceptional quality by hand selecting our market specials when compared to our larger corporate competitors
- The same concept holds true in our staffing requirements, by hand selecting our employees we will strive to offer unsurpassed service when compared to our larger competitors
5.1.2 Weaknesses
- Recruiting and retaining quality employees
- Tight margins will allow little wiggle room for error
5.1.3 Opportunities
- Little barriers to entry allows for immediate business opportunities
- Offer additional catering services
5.1.4 Threats
- Government mandates (restaurant operation, food safety, and worker protection at the federal level and health, sanitation, safety, fire at the local level)
- Rising operating costs
- Building/maintaining sales volume
- Supermarkets and convenience stores
- Consumers that believe that meals at home are healthier than those prepared in restaurants.
5.2 Strategy Pyramid
Strategy: Be the Benbrook area’s premier Home-Style Food Restaurant in Customer Satisfaction.
Tactics: First create awareness– our signage on the front of restaurant will bring customers to us and once inside, we will immediately acknowledge the customer with the warmest and most sincere greeting and begin the service process anticipating repeat customers.
Programs: Provide employee training on customer service and retention; offer ongoing training programs for employees keeping them current on industry trends and food safety. Keep track of employee’s progress through performance reviews and offer employees incentives attracting and retailing customers. Employ Mystery Shoppers. Employ the use of surveys both at the table and online.
5.3 Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
THR will be able to offer home-style meals for a reasonable price in a comfortable ‘home-like’ setting. The average check price is expected to be between $8-$15 which appears in line with industry standards below $25.00 (First Research). Because of our current expertise with vendors, and our excellent credit, we can negotiate better credit terms than say someone brand new starting a restaurant. We will also be able to keep our menu reasonably priced by offering menu items that take advantage of seasonal produce further reducing price. Finally we will keep our prices in check by meticulous monitoring of our controllable expenses – keeping close eye on our Prime Cost Report and Inventory. By initially employing family members who will work for lower and reduced wagers, for example, we can further reduce our controllable expenses.
5.4 Competitive Edge
THR’s competitive edge is in its people. We truly believe that your business is not only as good as your products (meals) but the quality of your staff as well. Our staff is a reflection of us. Initially, we intend to employ our family members who will work for lower and reduced wages. Our long term goal is to hire team members that are truly hand selected and have the same honest to goodness family values we do. And unlike our big chain competitors, because of our lean size, we can turn on a dime when economically pushed and make changes quickly allowing us to be proactive. (Whereas our corporate competitors have to adhere more closely to their company policies thus impeding their reaction time)
5.5 Marketing Strategy and Positioning
We realize the success of THR will have to be achieved by doing more that serving great food, and providing friendly service. We will utilize a restaurant marketing plan to build customer traffic. At THR we will continually strive to win more customers by being proactive rather than reactive in our marketing efforts and stay current with popular industry trends. We will achieve these goals by using the following:
- Database: We will begin our campaign by marketing to our existing database of customers. We will email fliers announcing our grand opening. We will continually update our database by providing a fishbowl for business cards in the lobby and offer a weekly or monthly drawing.
- Loyalty Program/Birthday Program. THR will offer a birthday/loyalty club proving a complimentary hamburger or chicken sandwich or wrap to the for the birthday person. A recent report from the National Restaurant Association explained how this simple technique can increase revenues as much as 15% due to repeat business.
- Our restaurant team will also be active in the local community and we plan to take an active role by participating, sponsoring, and donating to local churches, sports clubs or teams in the market area.
- We will also strive to develop rapport with local business as a quick, comfortable lunch choice. In the future, we plan on establishing a marketing campaign to call on the local business in the market area, deliver samples, and encourage them to consider our restaurant as the restaurant of choice for their next business luncheon
5.5.1 Positioning Statement
THR will be the premier home-style dining restaurant in western Fort Worth. We will offer reasonably priced meals, in a warm, relaxed and comfortable setting. We have a wide selection on our menu and also have menu options for lighter fare as well as a children’s menu. We are open 7 days a week and unlike our chain competitors, our servers won’t try to be your best friend our rush you thought your meal. Our name says it all “Traditional Home-Style Restaurant – – honest to goodness food served to you by honest to goodness people!”
5.5.2 Pricing Strategy
At THR, cost accounting is important, since the profitability of individual dishes can vary significantly and will initially determine the cost of the menu items. We will take advantage of our excellent credit terms with our suppliers and will also update our menu to take advantage of seasonality for example in local produce items. We will also closely monitor the Prime Cost Report which focuses on the controllable expenses of Cost of Goods Sold and Labor. As a new start-up we can currently control employee cost by hiring family members who will work for low and reduced wages.
5.5.3 Promotion and Advertising Strategy
- Location- The restaurant will be located in a strip center at the busy intersection of Cherry road and Camp Bowie. With easy access to Interstate 30 (less than ½ mile south) and located on the “going home side” (Western Corner) of the intersection. We will have Signage on the West Roads Shopping Plaza as well as signage over our entrance
- Word of Mouth – We already have a database of existing catering customers and will rely heavily on this method to attract and grow new business.
- Participate with Costco as Small Business of the Month – We will leave our menu, a fishbowl for business cards and a small ‘homey’ display with the retailer announcing us as new entrants in the local restaurant arena.
- Direct Mail – Bulk mailing either directly to potential customers or by including a postcard in a value-pack-type mailing.
- Event Marketing -We plan on joining our local chamber of commerce and utilizing their networking services for our grand opening
5.5.4 Website
- We will stay current with industry trends and have a webpage, Facebook page and Twitter site. Our menu, map, and hours of operation will be easily accessed. In the future we may consider fax or email orders as well a phone application.
5.5.5 Marketing Programs
- Our initial marketing campaign will consist of contacting our databases clients and notifying them of our grand opening. We will seek the use of a local mailing service program to assist us in the implementation of the campaign.
- Ongoing- we will meticulously keep our database current and use the Constant Contact program
- Loyalty and Birthday Club members will notified of upcoming special menu items and to alert them of our catering service.
5.6 Sales Strategy
Customer service is of the utmost importance. Customer surveys estimate that only 1 in 20 customers that have a problem in a restaurant will tell management about it. It will be our goal to provide a wonderful home-style meal combined with superior customer service. Training programs will include teaching materials to train our employees about service attitudes, customer perception and how to handle guest complaints. Jeff and Betty will conduct periodic staff meetings intended to review policy, increase guest satisfaction and to keep a general line of communication between staff and management. All guest complaints will be acknowledged by the staff and referred to management. Programs will be in place for all types of guest complaints. More serious complaints will be documented and kept on file. Customer feedback will be accomplished by customer surveys or the use of mystery shoppers.
5.6.1 Sales Forecast
We are expecting a conservative 5% increase in sales revenues annually over the next 3 years. The growth is adjusted for inflation. With the addition of catering revenues, sales will increase by 12.93% in Year 2 and 6.02% in Year 3.
The following table shows expected Sales Forecast for the next 3 years:

5.6.2 Sales Programs
We will encourage our employees to grow our customer base and provide incentives and regular bonuses to employees for referrals and repeat customers. These initiatives are still in the planning stages as we gear up to hire and staff. They will play an active role in our employee culture.
It is also anticipated that as we grow our catering business, along with our lunch business group, we will hire a sales director to facilitate this portion of the business. The sales director will be compensated similarly to their national peers (national Restaurant Association)
Initially we will be formed a sole proprietor: Jeff Wright d/b/a Traditional Home Style Restaurant. The State of Texas is a community property state. Over time, the couple plans to form a Limited Liability Company.
5.8 Milestones
Our initial milestones are as follows:

6.1 Organizational Structure
THR expects to hire 19 employees. Together, Jeff and Betty Wright will personally select each candidate. They’ve adopted an effective interview process designed to staff the restaurant with highly qualified people for each position. Each applicant will be rated and evaluated according to a pre-defined set of standards designed for each position. Background checks will be utilized for designated positions. Recruiting efforts will always center on referrals.
6.2 Management Team
Betty Wright received her Culinary Degree from the Art Institute in Dallas. After graduation she was employed by a local chain restaurant and then at a Five Star Hotel in Dallas. Betty will initially be employed as the Kitchen Manager.
6.3 Management Team Gaps
Initially Jeff and Betty will fill in many of the management gaps. Jeff has been responsible for developing the restaurant business plan and will be developing the marketing plan. Over time, they have plans to hire a sales director, a general manager, and a kitchen manager.
To meet the gaps associated in payroll, inventory management, and cost accounting, the Wrights will purchase have considered a POS (point of sale system) that it simplifies communications between the kitchen and the wait staff. Orders go through the computer, directly to the kitchen printer. Another benefit of a restaurant POS programs is that it can track everything from food usage, to the most popular menu items. Because the POS system acts as a time clock, it can also help prepare payroll – which will save some money in the bookkeeping department. Along with the daily operations of running a restaurant, a POS system can organize profit and loss statement and sales tax.
6.4 Personnel Plan

The following sections outline our financial plan:
- Required Cost of Start-Up
- Profit and Loss
- Balance Sheet
- Financial Ratios
- Hourly Labor Costs
- Weekly Sales Projections
7.1 Important Assumptions
- Meal Price range from $8.00 – $15.00
- Average lunch price: 8.79
- Average dinner price: 13.74
- The restaurant is located in the West Roads Shopping Center and is comprised of 3,400 square feet
- The dining room will be comprised of 20 tables with a seating capacity of 86 seats and 40 available parking spaces to meet the needs of the customers.
- The restaurant will employ 19 employees
- $860,000 -1,200,000 revenue target; Industry average for casual restaurant average of $860,000.
- Annual 3% increase for inflation and 5% annual increase in revenues
- Year 2 Assumes Catering Business in Place. Assumes 4 parties monthly @ $15 per plate and $50 persons. Catering will escalate to 8 parties monthly in month 20 and then 10 parties monthly thereafter. Also assumes additional increase in staffing (4 persons to be hired at 6 hours @ $8.00 per hour.
7.2 Start-Up Costs
Total start up costs will be $363,000, $174,000 of which will be contributed by the owners and the remainder will be secured through a proposed bank loan.

7.3 Source and Use of Funds
Total start-up costs are estimated to be $363,000. The majority of the costs are associated with the restaurant equipment, inventory and furniture and furnishings for the dining room. Total costs for these items are reported to be $110,500. The costs are associated with build out and renovation of the restaurant to provide updated plumbing and creating additional space in the dining area by removing a non-supporting wall: $50,000. Additional start up expenses are in the form of working capital and contingency $182,500.
Jeff and Betty Wright will contribute $174, 000 and are requesting an additional $189,000 in the form of a bank loan. The loan is expected to be a fully amortizing 5 year term note secured by UCC filings on all furniture fixtures and equipment.

7.4 Break-Even Analysis
Total fixed costs associated with the restaurant are $669,186 and represent the annual expenses. The variable cost (overhead) is estimated to be $4.51 per meal. Based on the assumption of $11.37 as the average meal price, the breakeven revenue then is $1,108,970 or 97,535 meals (units). This is further depicted in the Table Below and the Graph that follow:

7.5 Projections
7.5.1 projected profit and loss.
The profit and loss demonstrates modest increases in revenues over the three expected years with adjustments for inflation.

7.5.2 Projected Cash Flow
The statement of cash flow shows the incoming and outgoing cash of the business.

7.5.3 Projected Balance Sheet
Table 7.5.3 Pro Forma Balance Sheet

7.6 Business Ratios

7.7 Hourly Labor Schedule

7.8 Weekly Sales Projections

Free A3 Six Sigma Templates
We’ve gathered the most useful A3 Six Sigma templates in all formats. You’ll learn all about the different types of A3 templates. Included on this page, you’ll find a basic A3 problem-solving template, an A3 strategic planning template, an A3 status report template, an A3 project charter template, and more.
By Lulu Richter Updated September 4, 2024

Detailed A3 Problem-Solving Template
Create a comprehensive A3 report for targeted issues or improvement projects with this editable template. It includes an integrated fishbone diagram to help you analyze root causes, as well as columns for listing activities, owners, start and end dates, status, and required resources. Other template sections include a problem statement, current and target states, countermeasures, results, and more.
Download Template for
Excel Microsoft Word Google Docs Google Sheets
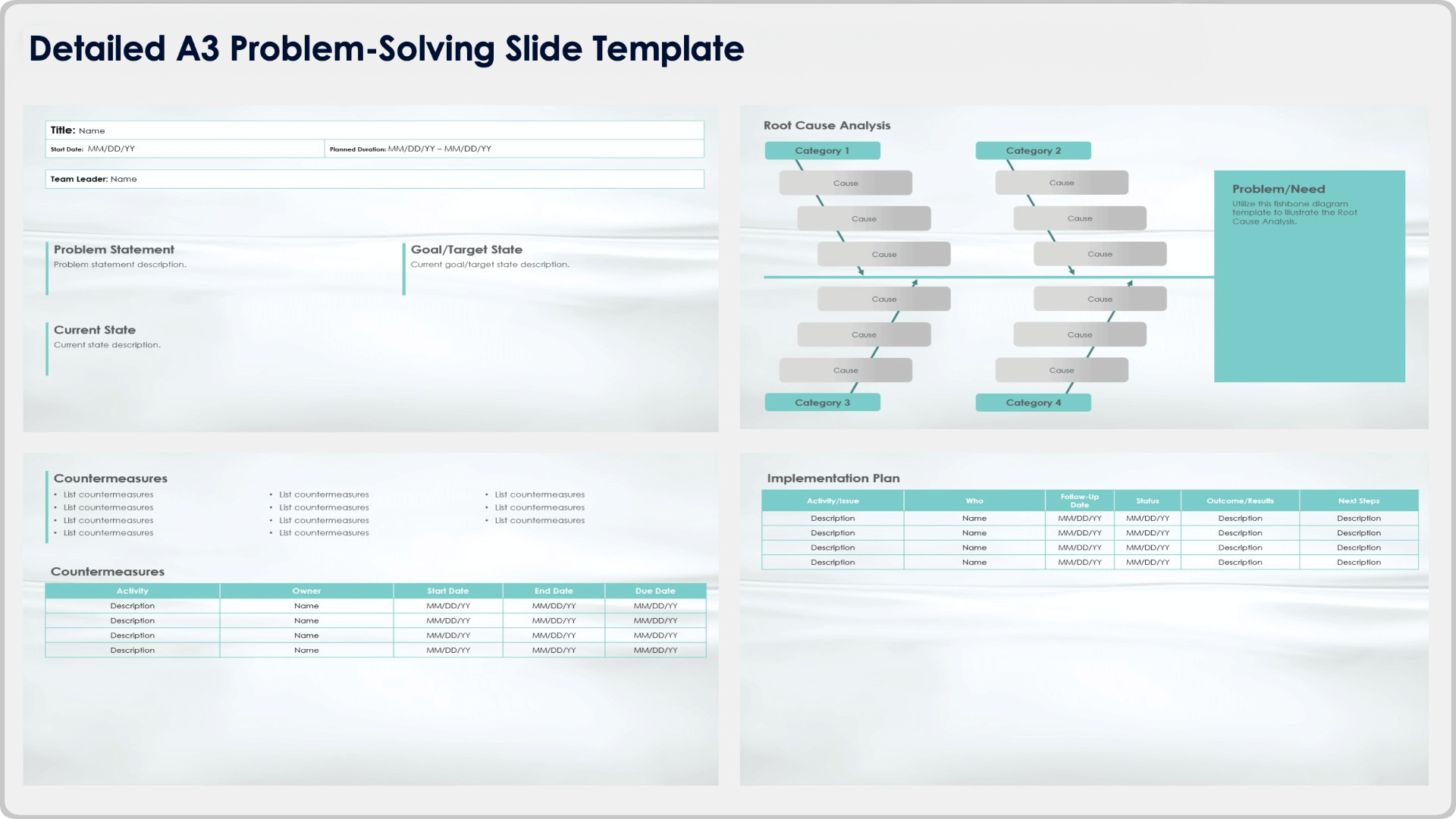
Detailed A3 Problem-Solving Slide Template
This problem-solving slide template is perfect when you need a detailed A3 analysis for presentations and team meetings. It condenses a detailed A3 report into a convenient slide format with sections for describing the problem, goals, root cause analysis, proposed solutions, actions, and follow-up. A built-in fishbone diagram and preformatted tables make it easy to present information systematically.
PowerPoint Google Slides
Basic A3 Problem-Solving Template
Choose this basic template when your team needs to create a streamlined A3 report that is easy to customize and share. This template provides a simplified layout with sufficient room for adding customized images and text. For users who want additional guidance, the free download also comes with an example version that is pre-filled with sample text, as well as an FAQ page with additional tips.
Microsoft Word Adobe PDF Google Docs
Basic A3 Problem-Solving Slide Template
Use this A3 problem-solving slide template in planning sessions or close-out reviews, or when creating a high-level project overview. This template provides a basic layout to focus attention on key details during stakeholder presentations. The template includes a blank A3 slide, as well as a template completed with sample text and an FAQ page for additional guidance.
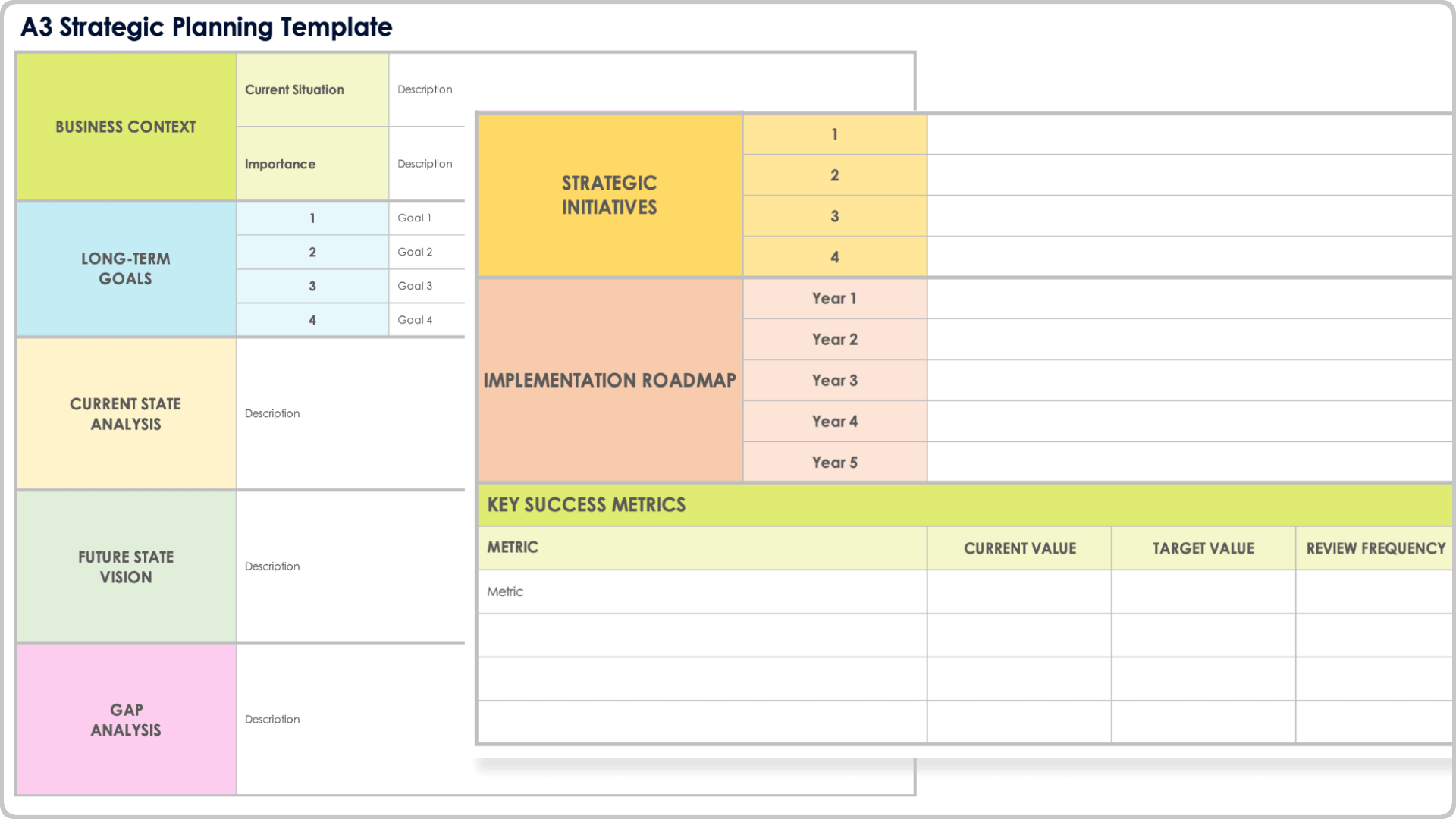
A3 Strategic Planning Template
This template is designed for organizational strategy development, long-term product development, and other high-level strategic planning. This template blends a strategic planning document with an A3 report. The template focuses on developing a future vision, with long-term goals, strategic initiatives, and an implementation roadmap that covers five years.
A3 Strategy Slide Template
Use this A3 strategy template when you or your team needs to present a high-level strategic plan to senior leaders, company executives, team members, and other stakeholders. This customizable template includes a multiyear plan for strategic initiatives, analysis of current conditions, future state vision, long-term objectives, and metrics for measuring success.
A3 Status Report Template
Use this editable A3 status report template for project management updates, executive reporting, team coordination, and milestone reviews. This template offers a comprehensive yet concise format, with a project overview, a progress summary comparing planned versus actual status, performance metrics, risk management details, resources needed, and next steps.
A3 Status Report Slide Template
Use this template for stakeholder presentations, project reviews, client updates, and other scenarios requiring a quick project overview. This A3 template helps you create an organized and visually engaging status report. The template includes sections for a project summary, a color-coded status column to highlight the progress of key milestones, and more.
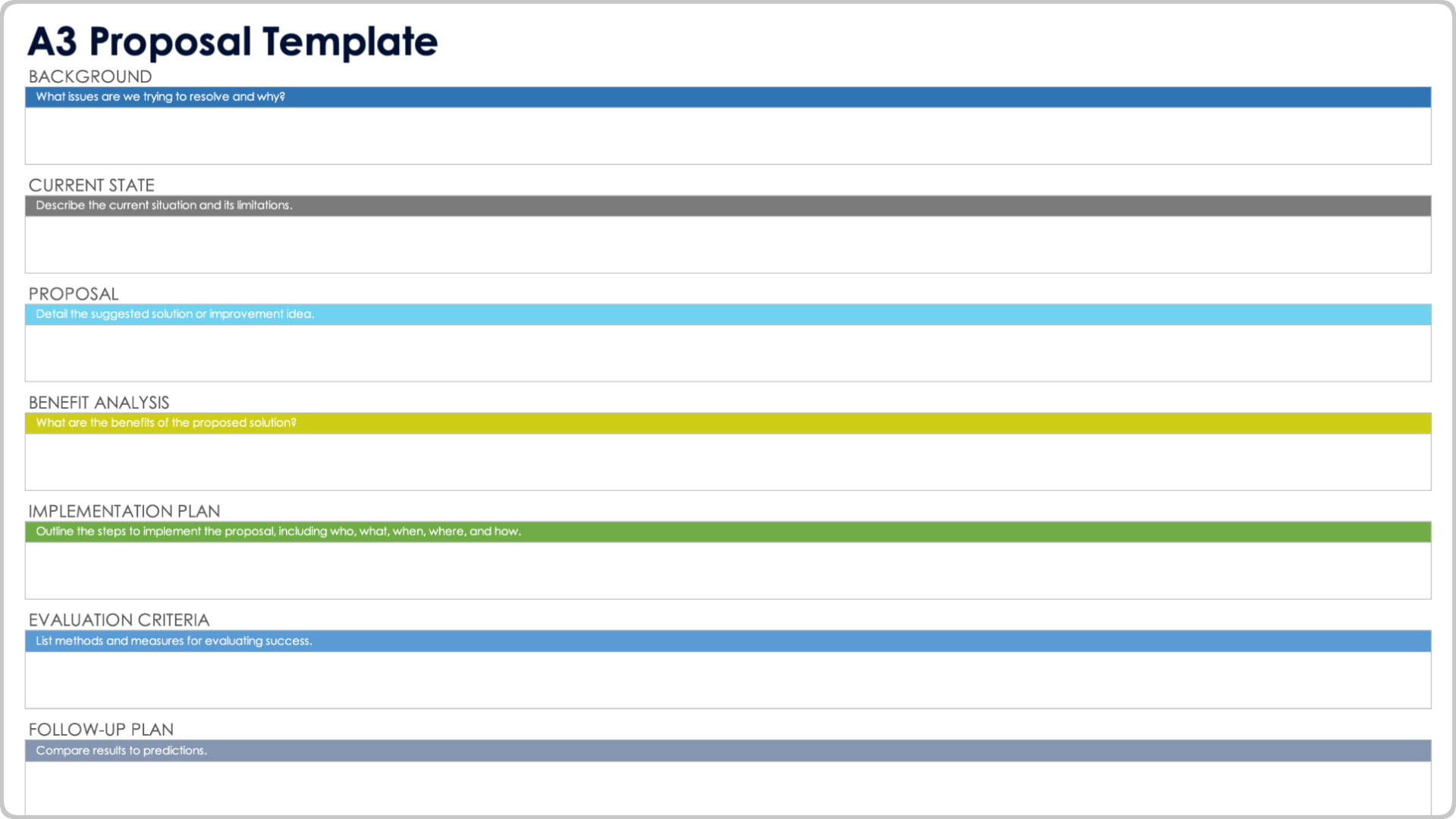
A3 Proposal Template
Use this A3 template for problem-solving proposals, new product proposals, process improvement or strategic initiatives, and more. This template offers a vertical outline rather than the typical horizontal A3 format, while including other A3 elements, such as proposed solutions, anticipated benefits, implementation plan, approval fields, follow-up, and more.
Excel Microsoft Word Adobe PDF Google Docs Google Sheets
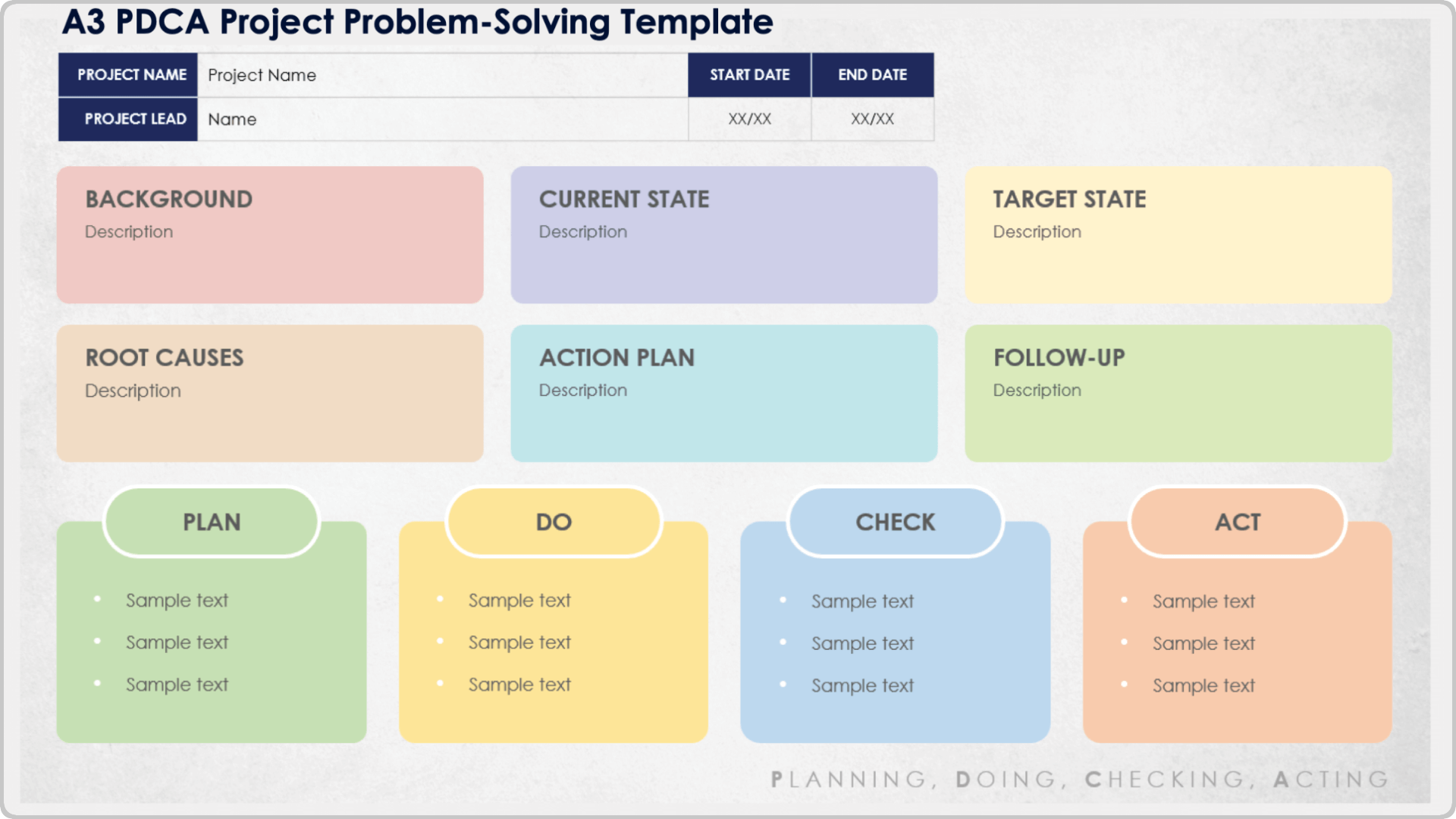
A3 PDCA Project Problem-Solving Template
Use this template to simplify complex information, engage your audience, and emphasize the plan-do-check-act (PDCA) cycle. The color-coded, modular design is easy to customize for any project.
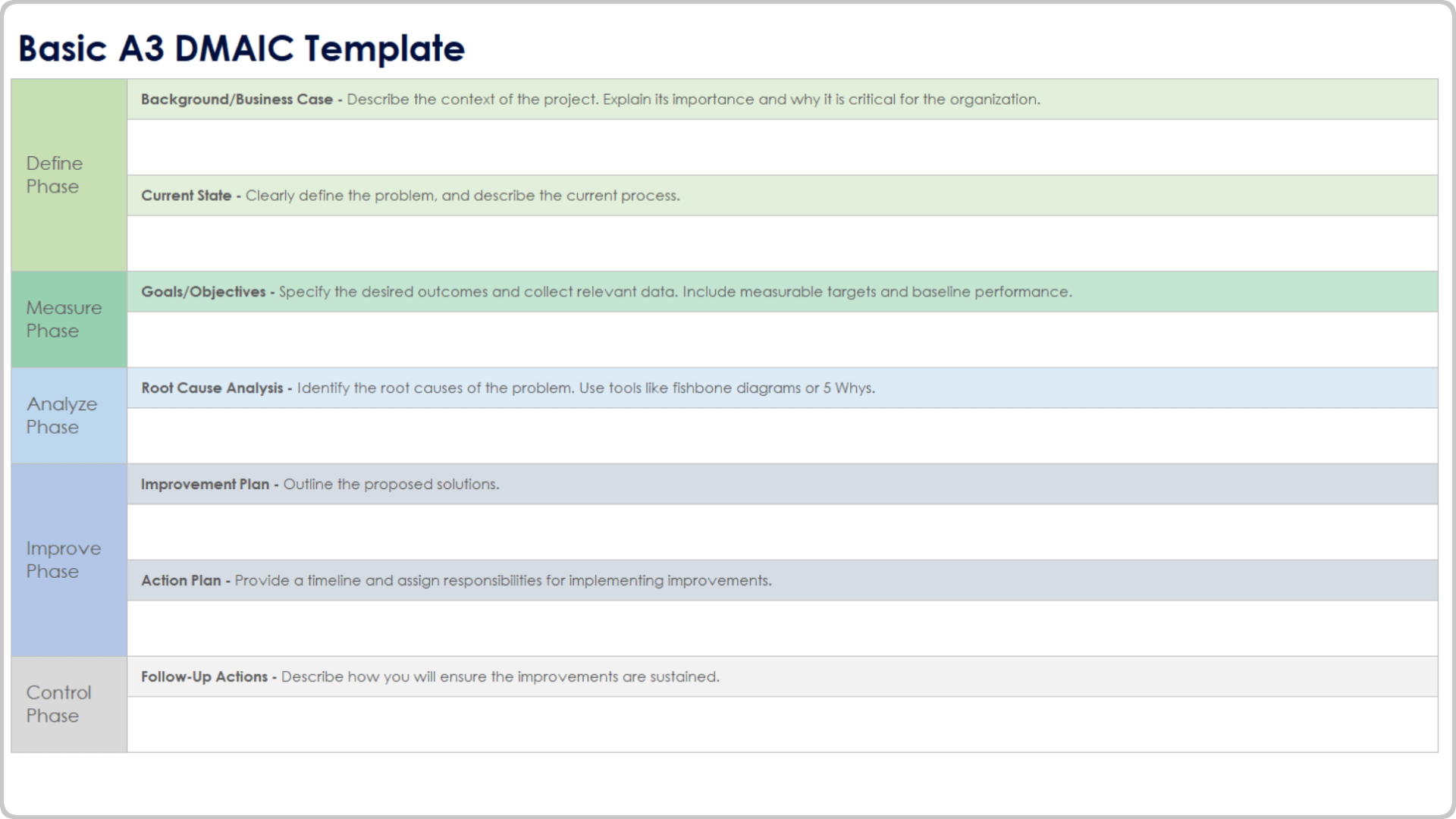
Basic A3 DMAIC Template
This template focuses on the key elements of the DMAIC process for small-scale projects or internal process reviews. With less detail than other A3 templates, it is quicker to complete and review.
Excel Google Sheets
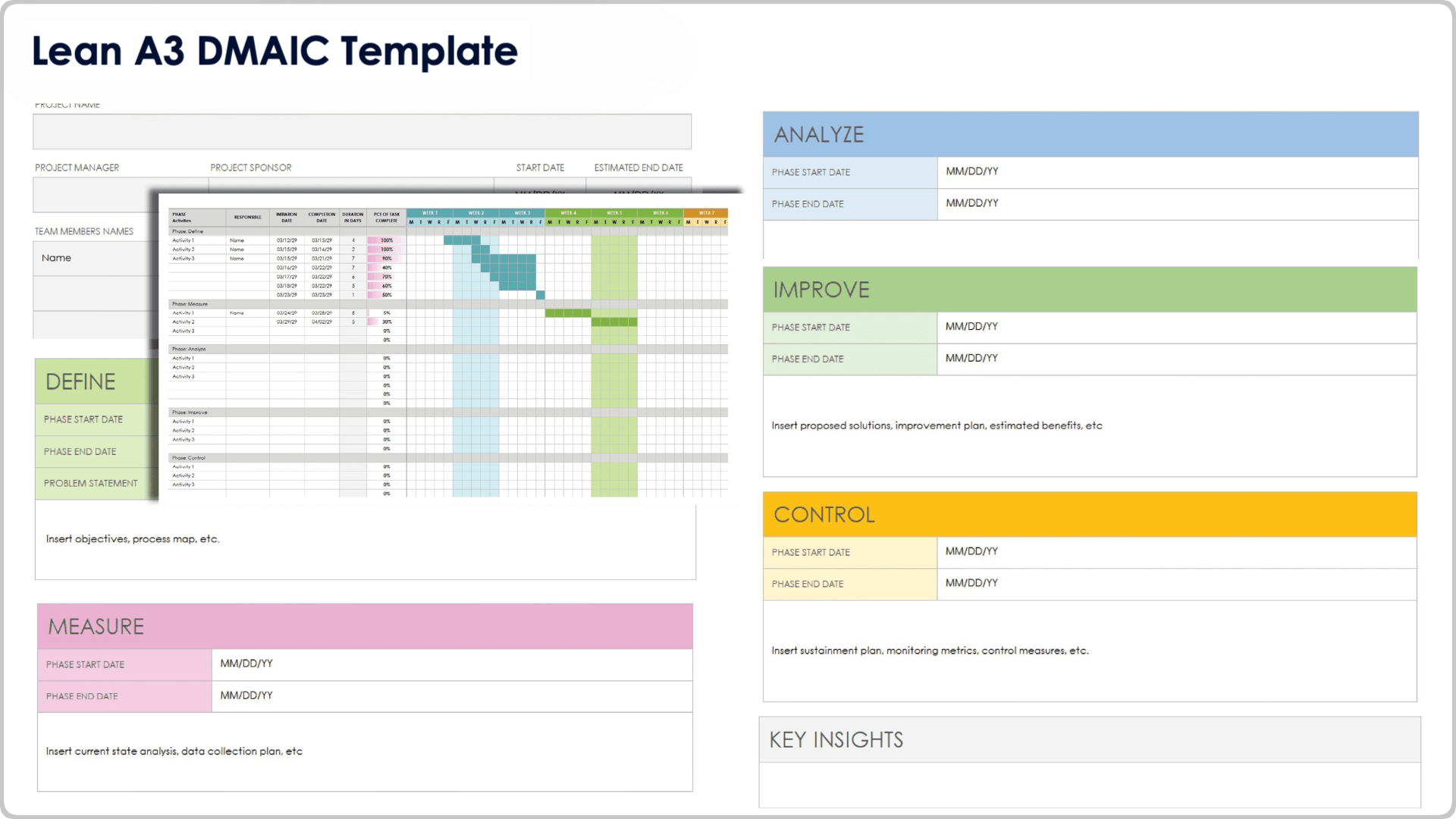
Lean A3 DMAIC Template
This template is perfect for complex projects. In addition to the A3 report, it features a Gantt chart for assigning activities, setting task due dates, and tracking the progress of DMAIC phases.
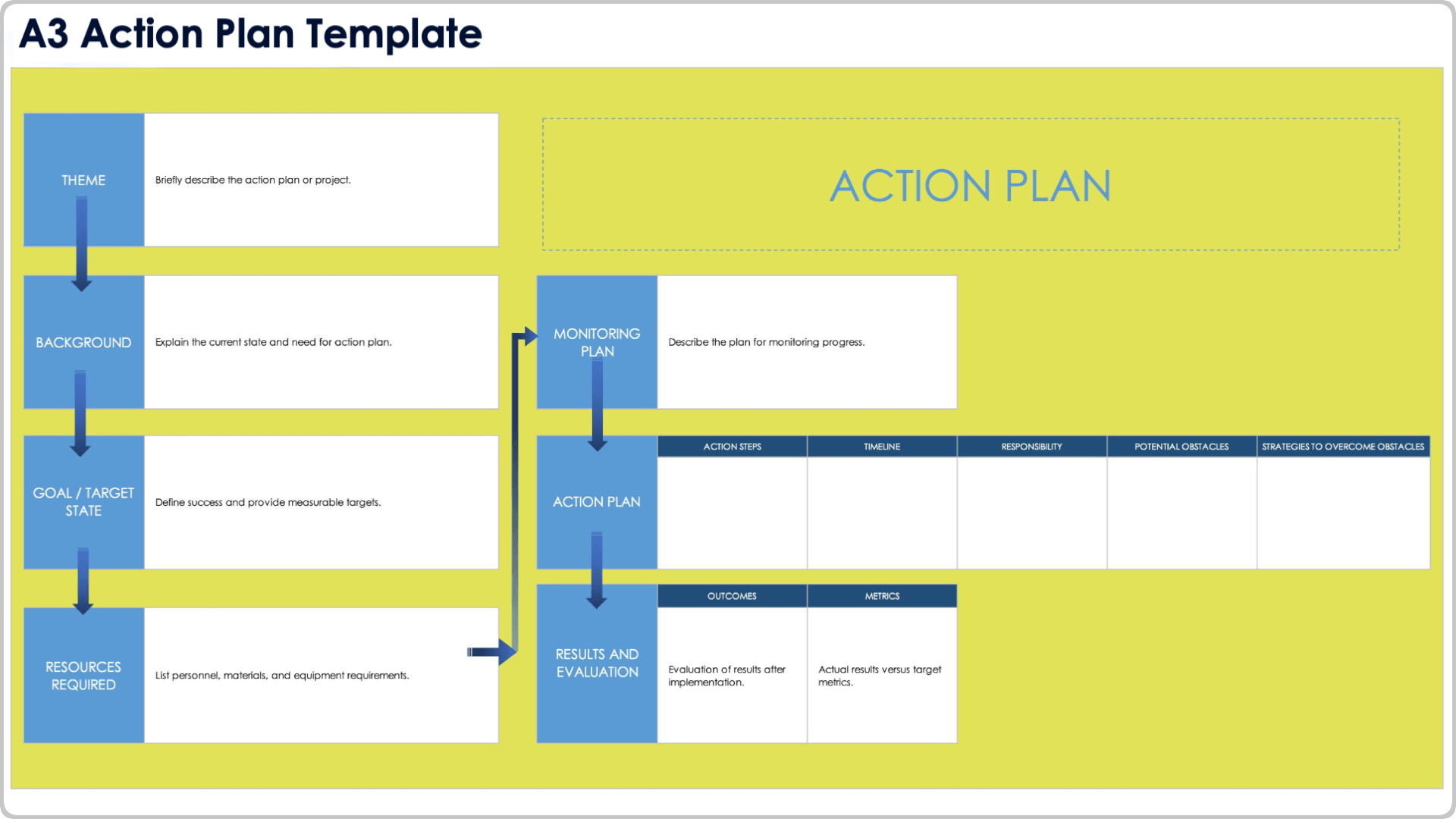
A3 Action Plan Template
Use this A3 action plan template to create a clear, actionable roadmap. It allows you to assign responsibilities, identify potential roadblocks, monitor progress, evaluate results, and more.
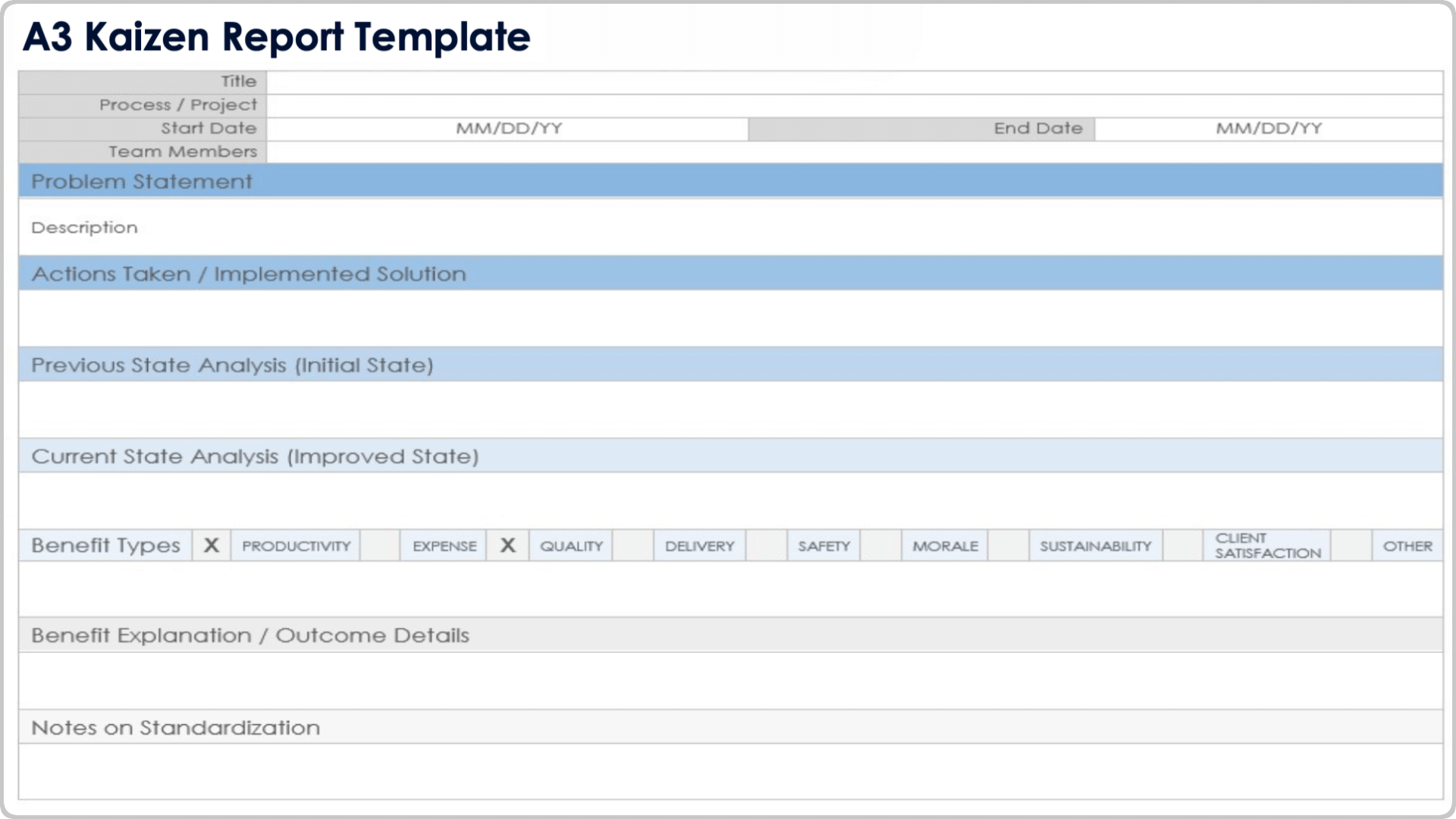
A3 Kaizen Report Template
Use this Kaizen report form to capture before-and-after conditions, implemented changes, and resulting benefits. You can also insert diagrams, pictures, and text to complete the Kaizen report.
Microsoft Word Adobe PDF
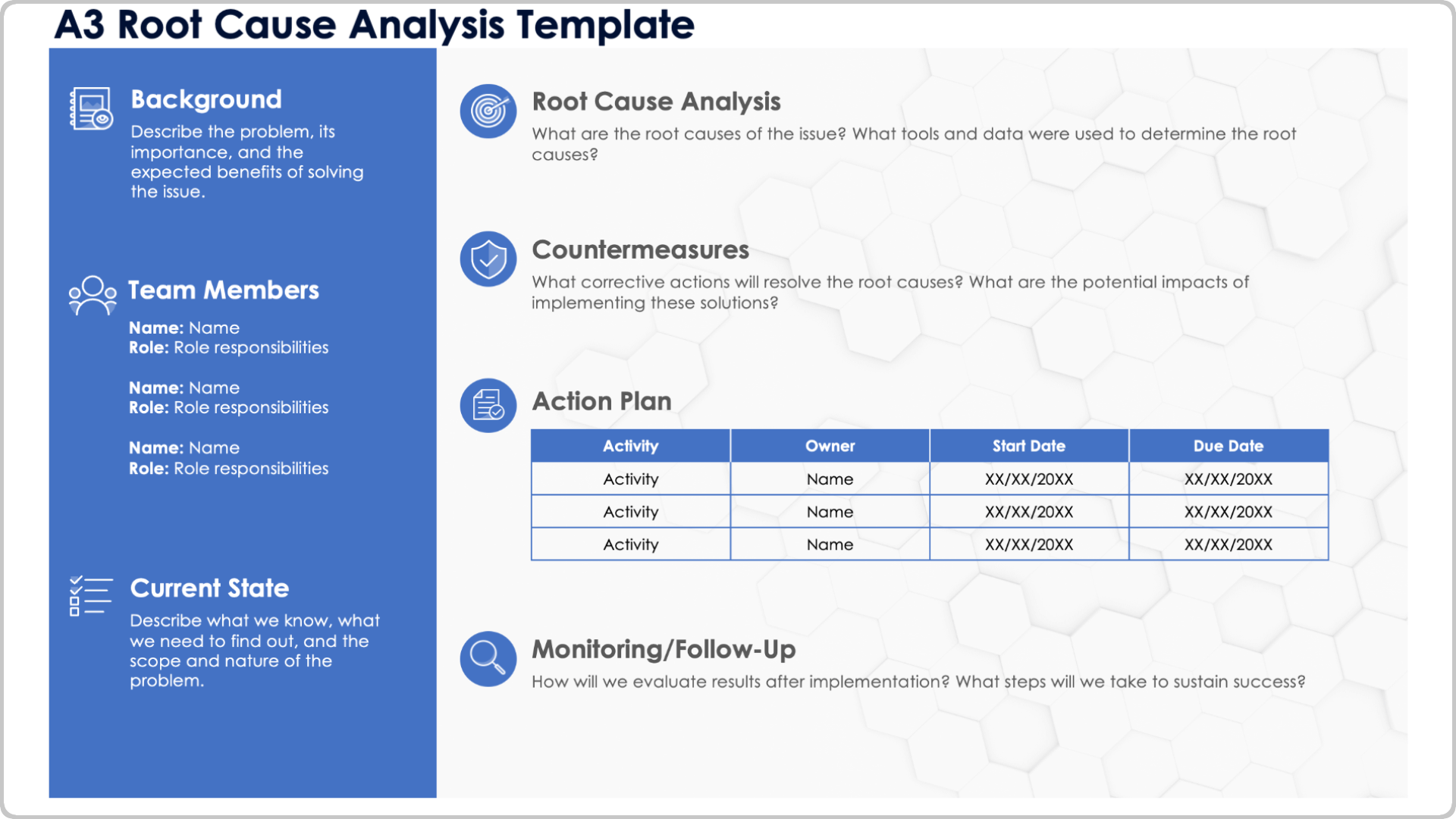
A3 Root Cause Analysis Template
This customizable template guides users through the critical stages of root cause analysis. It also includes a section for listing team members and identifying internal and external stakeholders.
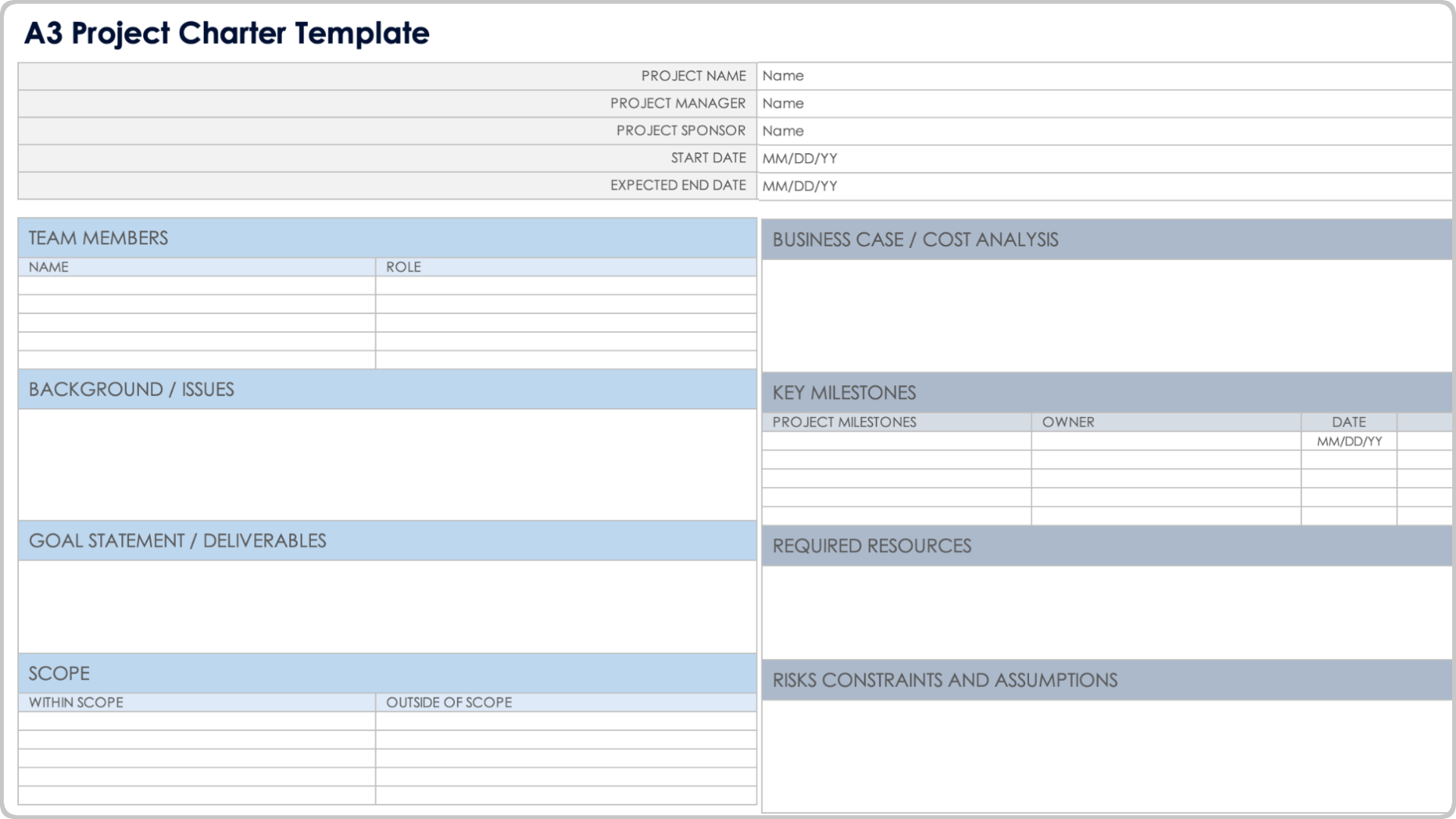
A3 Project Charter Template
Use this editable template to distill project information down to the most critical elements. The template includes sections for problem identification, goal setting, business justification, and more.
A3 Hoshin Kanri Template
Use this template to align your organization’s activities with its long-term vision using the Hoshin Kanri process. It provides space for performance analysis, current business conditions, and more.
Microsoft Word Google Docs
Expertly Address Your Business Problems with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Types of A3 Templates
A3 templates generally follow a similar format and include elements based on Lean management and the PDCA cycle. They can serve diverse purposes, from strategic alignment and project management to problem-solving and team coordination.
Here are several A3 template types:
- Simple A3 Template: This is a streamlined version of the A3 template that focuses on essential elements, making it ideal for quick problem-solving or communication. A simple A3 typically includes basic sections — such as the problem statement template, analysis, and action steps — without requiring extensive detail.
- Detailed A3 Template: This is a comprehensive A3 template that includes in-depth sections for analysis, data collection, and detailed action plans. Use this template type for complex problems requiring thorough exploration and documentation of the process.
- PDCA A3 Template: This template is an iterative tool that follows the PDCA cycle, guiding teams through continuous improvement by planning and implementing actions, checking results, and making necessary adjustments. Learn more in this guide to continuous improvement .
- Problem-Solving A3 Template: Designed to guide teams through the problem-solving process, this template emphasizes root cause analysis, countermeasures, and results for a structured approach to identifying and resolving issues.
- Project Planning A3 Template: A tool for planning and managing projects, this template includes sections for defining objectives, timelines, resources, and risks.
- Proposal A3 Template: Used to present proposals or recommendations to gain buy-in from stakeholders, this template outlines the problem, proposed solutions, expected benefits, and implementation plan.
- Status A3 Template: This template is used to report on the current status of a project or initiative, including progress, challenges, and next steps.
- Strategic A3 Template: Designed for strategic planning, this template aligns long-term goals with specific initiatives, outlining strategic objectives, key actions, and expected outcomes.
- Team Charter A3 Template: This template outlines the team’s mission, objectives, and working agreements. The charter serves as a foundational document that guides team dynamics and performance.
For more Lean resources, see our collection of free Lean Six Sigma templates , as well as these complete guides to Lean project management and Lean process improvement .
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

Learn about Shopify
Sales Planning: How To Create a Sales Plan (+ Template)
Sales planning helps you set goals, forecast revenue, and chart a course to growth. With an easy-to-use sales planning template, you’ll be set up for success.

You can buy and hire all the resources to build a house. But without blueprints, you’ll end up with a stack of boards, piles of nails, and construction workers twiddling their thumbs.
Sales teams need a blueprint, too. It’s called sales planning. Like a construction blueprint, sales planning ensures your resources are put to their best use, and team members are focused on what’s most important.
“If you’re not looking at the sales data and making a plan, you might be giving equal weight to all of your products when there are a few that are really the workhorses,” says Shawn Khemsurov, cofounder of strategic design and development agency Electric Eye . “ Those are the products you should invest in and focus on.”
Learn how to create an effective sales plan that aligns with your business objectives, and keeps your sales team driving growth.
What is sales planning?
Sales planning is a set of processes to drive sales for a business—specifically, setting sales goals and outlining the actions needed to achieve them.
The sales planning process helps leaders understand market conditions, analyze customers and trends, allocate resources effectively, and set realistic sales targets.
Sales plan template
Sales planning templates can provide a good framework for you to get started with sales planning. Shopify’s free sales plan template makes it easy to visualize your goals for the year or quarter and keep your team on track.
Sales planning process
- Analyze market conditions and historical performance
- Identify and understand your target audience
- Determine sales goals
- Set strategy
- Allocate budget and resources
- Create action plans
- Monitor sales performance and adjust accordingly
Create a sales plan by following these steps:
1. Analyze market conditions and historical performance
To position your products well and set appropriate goals, you’ll first need to understand what’s going on both inside and outside of your company.
Pull data from your preferred ecommerce analytics tools to analyze your company’s past performance and your customers’ behavior, looking at key performance indicators (KPIs) like conversion rate , session length, and average order value (AOV). This will help you identify areas of strength and opportunities to improve within your sales process.

Also, perform external market research to understand trends, evolving customer needs, and the competitive landscape. Shawn recommends asking yourself a series of questions to help dig deeper into the market and your brand’s place within it.
“Who else is selling in this category? How much are they charging?” says Shawn. “Is the market saturated? If so, what’s our differentiator that we can play up? Or is there a niche that isn’t being served that we can develop something around?”
2. Identify and understand your target audience
Once you’ve identified some overall business and market trends, you can use the same analytics reports to learn more about your target customers. You can divide your target market into smaller customer segments based on details like geography, preferences, and pain points.
Deeply understanding these different audiences can help you market effectively and identify your best customers, both of which can fuel sales and, ultimately, business growth.
3. Determine sales goals
Armed with both internal and market data, you can set clear goals for your sales reps. Consider using the SMART goals framework to ensure your sales objectives are strategic, measurable, actionable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (i.e., SMART).
Most sales teams have revenue goals, but you might set sales goals that involve market share, the number of new customers acquired, a reduction in customer churn , or channel-specific sales.
4. Set strategy
Identify specific methods and sales techniques that your team will leverage to achieve sales goals. Depending on your business, you can leverage a variety of sales tools and marketing strategies including:
- Email marketing campaigns
- Influencer partnerships
- Search engine optimization
- Retargeting ads
- Content marketing
- Social media advertising
- Sales automation
- Website redesigns
Your data analysis and market research can help guide you to the best techniques for your needs. For example, you might find that your average order value is solid, but you need to market more widely to draw more people to visit the site. Or perhaps your site traffic is good, but people drop off rather than convert with a purchase—suggesting an update of your product page or checkout process may be in order.
Market your business with Shopify’s customer marketing tools
Shopify has everything you need to capture more leads, send email campaigns, automate key marketing moments, segment your customers, and analyze your results. Plus, it’s all free for your first 10,000 emails sent per month.
5. Allocate budget and resources
Focus is important not only to avoid being overwhelmed, but to allocate resources accordingly. Sales teams rarely have unlimited budgets, so you’ll need to decide how much to invest in each of your sales activities, including marketing campaigns , promotions, partnerships , and staffing.
6. Create action plans
Outline and assign the specific actions required to execute each sales strategy. A successful sales plan lays out clear timelines and expectations.
For example, a set of sales representatives may be called on to contact 25 leads and set 10 sales appointments by the end of the month. Or, sales managers could assign them to check in with all existing customers on their accounts to ensure retention and attempt to upsell with new complementary services.
Depending on your strategies, action plans may include delegating tasks to people outside the sales organization. For example, an email newsletter or content marketing strategy requires looping in the marketing team to create these assets. Marketing and sales alignment is crucial in this example to ensure sales messaging is maintained.
7. Monitor sales performance and adjust strategies accordingly
Effective sales planning involves keeping track of what works and what doesn’t to inform future plans.
Define the metrics you’ll use to measure the effectiveness of each sales strategy you choose, and identify data sources and tools to help you track sales success. You may find one strategic process isn’t as successful as others, or that you need to swap strategies over time.
Tips for sales planning
Set realistic goals, focus on what’s most impactful.
- Allocate resources to get the most bang for your buck
Align planning and goals to overall business objectives
Here are a few tips sales leaders can use to create effective sales plans:
Dream big, yet not too big. “Reach” goals can help your team strive to achieve more, but be careful to strike a balance.
There’s a fine line between aspirational and unrealistic, and if you’re on the wrong side of things, your sales team will end up frustrated.
Setting impossible revenue targets and other goals helps no one. Ensure your objectives are realistic based on past sales efforts, historical performance, and market research.
Dig enough, and you’ll find seemingly endless tools, strategies, and potential ways to boost future sales. But not every method is right for your business, right now.
“It’s easy to get overwhelmed,” Shawn says. “Simplify your focus to the few key areas that have the biggest impact on your sales, and figure out how you can attack those hard.”
Allocate resources to get the bang for your buck
Monitor your sales and strategies to see which efforts have the greatest impact, and put your resources into them.
For example, you may find promotions or abandoned-cart email campaigns tend to bring customers to the site. In other cases, factors like supply chain issues and low inventory might be denting your sales.
“Some shops are surprised to find it’s a small number of products that are really pulling the weight—so in that case, you want to make sure you’re always in stock,” Shawn says.
“If a customer on your site can’t make that purchase, it’s frustrating for them and a lost sale for you. Fixing that problem can have a massive effect on your sales, because even the best marketing messaging doesn’t help if you don’t have a product to ship.”
As you perform sales planning activities—whether it’s conducting an in-depth competitive analysis, reorganizing the sales team structure, or forecasting sales—never lose sight of the overall business plan .
Not every company is necessarily focused on how much revenue they can generate or increasing the sales quota. Instead, they may be looking to break into new geographic areas, reach new target markets, or overcome the sales team’s challenges in explaining the product’s differentiators. You define what sales success means, based on your company’s overall goals right now.
Sales planning FAQ
What is the first step in the sales planning process.
Analyze internal data and external market trends to better understand sales opportunities and your customers. This will help you develop informed, clear, realistic sales forecasts and goals.
Why is sales planning important?
Sales planning is important because it provides a structured approach to achieving sales goals. It helps companies set data-based goals, select appropriate sales techniques, allocate resources effectively, track progress toward sales goals, and adjust strategies over time.
What should be included in a sales plan?
A sales planning template often includes an executive summary, sales goals, market trends and historical sales data, audience data, sales strategies, budget and allocations, action plans, and monitoring.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
10 Sept 2024
9 Sept 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn how to create a fast food business plan with a template and a sample. Find out the types, sources, and steps of fast food businesses, and how to get funding and marketing strategies.
Learn how to write a compelling business plan for your fast food restaurant with this step-by-step guide and free template. Find out how to conduct market analysis, fund your venture, create a marketing strategy, and project your financials.
Download a customizable fast food business plan template with financial model and market research. Learn how to start or grow your fast food restaurant with a comprehensive guide and tips.
Download a free template and learn how to write a business plan for your fast food restaurant. The template covers executive summary, business overview, market analysis, products and services, marketing and sales, and financial projections.
Learn how to create a comprehensive business plan for your fast food restaurant, covering operations, marketing, strategy, and financials. Download a fully editable PowerPoint template and see an example of a fast food restaurant business plan.
The following Fast Food business plan template gives you the key elements to include in a winning Fast Food restaurant business plan. It can be used to create a takeout restaurant business plan, a quick service restaurant business plan or a traditional fast food plan.
Download a pre-filled example of a fast food restaurant business plan in Word format and customize it to your needs. Learn how to use this template to create a plan that fits your goals and get professional support in LivePlan.
Learn how to start your own fast food restaurant business with this sample plan. Find out the opportunity, problem, solution, market, competition, and financial highlights of Fresin Fries, a snack-type fast food concept in Singapore.
Download a free sample fast food restaurant business plan for a mobile noodle vending unit. Learn how to start a food truck, kiosk, or franchise with this guide.
Learn how to write a comprehensive business plan for your fast food restaurant, including an executive summary, market analysis, financial projections, and more. Use a template and follow the step-by-step guide to create a roadmap for your success.
Learn how to create a comprehensive and professional restaurant business plan with a free template. Find out the key elements, tips and examples for a successful restaurant concept, location, market analysis and financial projections.
Download a 15-page editable template to write a restaurant business plan and secure investor funding. Learn how to use the nine customizable sections, including market analysis, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Download a free, customizable template for writing a restaurant business plan from BentoBox, a hospitality technology company. The template includes prompts for financial projections, market analysis and restaurant operations overview.
Free Restaurant Business Plan Template Download
It's helpful to look at another restaurant business plan example to see how these types of documents are written. 7. Use Visuals, Charts, and Tables. Use images, graphics, tables, and charts to explain complex ideas, add color to your document - both literally and figuratively - and present specific information. 8.
Learn how to write a restaurant business plan that covers your goals, strategies, finances, and market analysis. See 8 examples of effective restaurant business plans and download free templates.
Learn the key elements of a restaurant business plan and download a free template to organize your vision and secure investors. Find out how to describe your concept, market, location, operations, and financials in this comprehensive guide.
Full-service restaurants are expected to reach $182.9 billion; in contrast, quick service restaurants are expected to grow to $163.8 billion, a gain of 4.0 percent over last year. Eating-and-drinking places will see an increase in sales from of 2.2 percent from last year, totaling $395 billion.
Venngage can help you create restaurant business plan in minutes. Our web app has simple drag-and-drop tools, dozens of stock photos, and color options to make the restaurant business plan template your own. Now you can customize everything you see, from font styles, icon styles, Venngage offers restaurant business plan template. Save your time ...
Learn the essential components of a restaurant business plan and get expert insights for success. Find out how to create a concept, menu, service, design, target market, location, market overview, marketing and publicity, specialists and consultants, business structure, and financials.
Templates. $3.33. Per month - Paid 3 monthly. AI Automated Business Planning. Full professional plan for your Takeaway business. 350,000 Users. 350K entrepreneurs have used our business plan template. Rating: 4.7 - 3167 reviews. Our business plan template has a rating of 4.7 out of 5 on Google Play.
Learn how to write a restaurant business plan with this sample and template. Find out the key elements, objectives, market analysis, financial projections and more for your own restaurant concept.
When you're using business plan templates, keep the following four tips in mind. 1. Know your audience. Remember who you're writing for - is the business plan primarily for your own use, or are you looking for a loan, or even equity investment? Keeping your audience in mind will help you stay on track. 2. Keep it concise
How to write a business proposal. To help with sending future proposals, you might want to create a business proposal template. You can then edit it each time to make it specific to the business you're pitching to.. For a business proposal to help you get the work you're bidding for, it'll usually need to include the following points.
Proposal A3 Template: Used to present proposals or recommendations to gain buy-in from stakeholders, this template outlines the problem, proposed solutions, expected benefits, and implementation plan. Status A3 Template: This template is used to report on the current status of a project or initiative, including progress, challenges, and next steps.
Sales planning is a set of processes to drive sales for a business—specifically, setting sales goals and outlining the actions needed to achieve them. The sales planning process helps leaders understand market conditions, analyze customers and trends, allocate resources effectively, and set realistic sales targets. Sales plan template