

Quantum books

Past Year papers

Youtube channels
(for each subject), quantum books.

Engineering Physics
Quantum book

Engineering Chemistry

Engineering Mathematics-I

Fundamentals of Electronics Engineering

Engineering Mathematics-II

Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering

Programming for Problem Solving

Fundamentals of Mechanical Engineering

Soft skills
Past year papers, previous year papers.
These are previous year question papers for solutions prefer last pages of quantum and some youtube channels
- ENGINEERING-CHEMISTRY-BAS-102
- ENGINEERING-MATHEMATICS-I-BAS-103
- ENGINEERING-PHYSICS-BAS-101
- ENVIRONMENT-AND-ECOLOGY-BAS-104
- Fundamentals-of-Electrical-Engineering-BEE-101
- FUNDAMENTALS-OF-ELECTRONICS-ENGINEERING-BEC-101
- Fundamentals-of-Mechanical-Engineering-BME-101
- PROGRAMMING-FOR-PROBLEM-SOLVING-BCS-101
- SOFT-SKILLS-BAS-105
- PHYSICS-KAS-101-1
- ENGINEERING-MATHEMATICS-I-KAS-103T-1
- ENGINEERING-CHEMISTRY-KAS-102T-1
- FUNDAMENTALS-OF-MECHANICAL-ENGINEERING-MECHATRONICS-KME-101T-1
- AI-FOR-ENGINEERING-KMC101
- BASIC-ELECTRICAL-ENGG-KEE-101
- BASIC-ELECTRICAL-ENGINEERING-KEE-101T
- MATHEMATICS-I-KAS-103-2
- PROGRAMMING-FOR-PROBLEM-SOLVING-KCS-101-2
- SOFT-SKILL-I-KNC-101
- ARTIFICIAL-INTELLIGENCE-FOR-ENGINEERS-KMC-101
- BASIC-OF-ELECTRICAL-ENGINEERING-KEE-101T
- ENGINEERING-MATHEMATICS-I-KAS-103T
- EMERGING-DOMAIN-IN-ELECTRONICS-ENGINEERING-KEC-101T
- EMERGING-TECHNOLOGY-FOR-ENGINEERING-KMC-102
- ENGINEERING-CHEMISTRY-KAS-102T
- ENGINEERING-PHYSICS-KAS-101T-1
- PROGRAMMING-FOR-PROBLEM-SOLVING-KCS-101T-1
- SOFT-SKILLS-I-KNC-101
- BASIC-ELECTRICAL-ENGG.-KEE-101
- CHEMISTRY-KAS-102-1
- MATHEMATICS-I-KAS-103-1
- PHYSICS-KAS-101-
- PROGRAMMING-FOR-PROBLEM-SOLVING-KCS-101-1
- BASIC-ELECTRICAL-ENGINEERING-KEE-101
- CHEMISTRY-KAS-102
- MATHEMATICS-I-KAS-103
- PHYSICS-KAS-101
- PROGRAMMING-FOR-PROBLEM-SOLVING-KCS-101
For notes prefer this site: click here
Youtube channels.
FEARLESS INNOCENT MATH
Vaibhav Jain (For ECE )
Chemistry by Dr. Anjali Ssaxena
University Academy (For FEE)
gatewayclasses (For all subjects)

AKTU Question Paper
Download btech 2 sem programming for problem solving kcs201 2022, question paper links, important links, examination links.
C-programming notes Aktu B-tech 1st year
Download c-programming notes aktu b-tech 1st year in pdf format free.
C-Programming is a fundamental programming language that forms the basis for many other programming languages. It is widely used in various domains, including software development, system programming, and embedded systems. Learning C-Programming will not only enhance your problem-solving skills but also pave the way for a successful career in the field of computer science.
Hand written C-programming notes
Download now

Benefits of C-Programming Notes
The C-Programming notes provided by Aktu offer several advantages for B-Tech 1st year students:
- Comprehensive Content: The notes cover the entire C-Programming syllabus, ensuring you have access to all the necessary information.
- Organized Structure: The notes are well-structured, making it easier for you to follow along and grasp the concepts effectively.
- Supplementary Examples: The notes often include relevant examples and code snippets to illustrate key concepts and aid in understanding.
- Reference for Assignments and Exams: The notes serve as a valuable resource for completing assignments and preparing for exams.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Programming for Problem-Solving Aktu Quantum PDF Download free
AKTU Quantum Programming for Problem-Solving : You’ve found the correct place if you’re trying to get a free download of the AKTU Quantum Programming for Problem-Solving PDF. You can download AKTU Quantum’s Programming for Problem-Solving in PDF format for free. For the first year, you can download the most recent edition of Aktu Notes for Programming for Problem-Solving for free from our website. There is a thorough explanation of the entire syllabus.
Programming for Problem-Solving AKTU Quantum Download PDF
Download Programming for Problem-Solving Aktu Quantum PDF:- Download
If you are looking for all AKTU Quantum downloads:- Click Here
Programming is not merely about writing lines of code; it’s a creative and strategic process aimed at solving real-world problems. In the realm of problem-solving, programming serves as a dynamic tool, empowering individuals to tackle challenges across diverse domains.
At its core, programming instills a structured approach to problem-solving. It encourages breaking down complex issues into smaller, more manageable tasks. Through the logical flow of code, programmers devise solutions, leveraging the power of algorithms and data structures.
One of the key strengths of programming in problem-solving lies in its versatility. From automating repetitive tasks to optimizing intricate algorithms, code becomes a problem-solver’s best friend. Whether in scientific research, business analytics, or creative endeavors, programming provides a means to transform abstract ideas into functional solutions.
The iterative nature of programming promotes a mindset of continuous improvement. As developers encounter obstacles, they refine and enhance their code, learning from each challenge. This adaptive process not only resolves immediate issues but also hones problem-solving skills for future endeavors.
Programming languages serve as the languages of problem-solving, each with its unique strengths. From the simplicity of Python to the efficiency of C++ or the web development prowess of JavaScript, choosing the right language is akin to selecting the perfect tool for the job at hand.
Moreover, programming fosters collaboration and knowledge-sharing within a global community. Online forums, open-source projects, and collaborative platforms enable programmers to learn from one another, contributing to a collective pool of problem-solving expertise.
In essence, programming for problem-solving is a dynamic journey where logic meets creativity. It empowers individuals to transform challenges into opportunities, providing a skill set that transcends industries and fuels innovation. As technology continues to evolve, the ability to code for problem-solving remains a valuable asset, opening doors to a world of endless possibilities.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
AKTU 1st Year Sem 1 Solved Paper 2017-18 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec C
Paper download link : Paper | Sem 1 | 2017-18
B.Tech. (SEM-I) THEORY EXAMINATION 2017-18 COMPUTER SYSTEM & PROGRAMMING IN C
Time: 3hrs Total Marks : 100 Note :-
- There are three sections. Section A carries 20 marks, Section B carries 30 marks and Section C carries 50 marks.
- Attempt all questions. Marks are indicated against each question.
- Assume suitable data wherever necessary.
Section – C
3. Attempt any two of the following: (2*5 = 10)
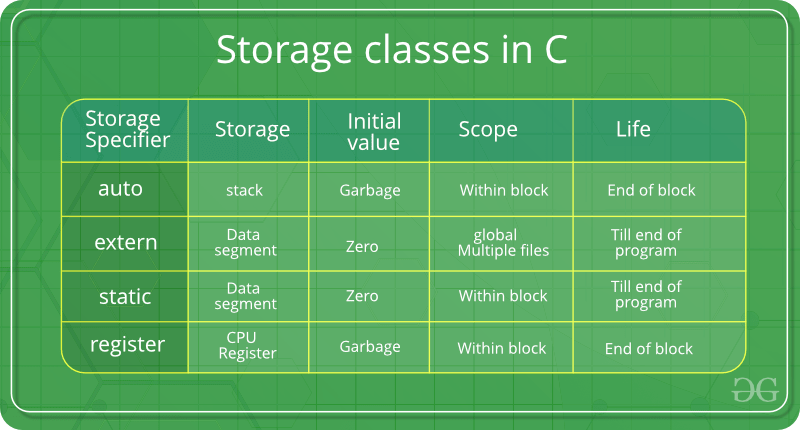
- auto : This is the default storage class for all the variables declared inside a function or a block. Hence, the keyword auto is rarely used while writing programs in C language. Auto variables can be only accessed within the block/function they have been declared and not outside them (which defines their scope). Of course, these can be accessed within nested blocks within the parent block/function in which the auto variable was declared. However, they can be accessed outside their scope as well using the concept of pointers given here by pointing to the very exact memory location where the variables resides. They are assigned a garbage value by default whenever they are declared.
- extern : Extern storage class simply tells us that the variable is defined elsewhere and not within the same block where it is used. Basically, the value is assigned to it in a different block and this can be overwritten/changed in a different block as well. So an extern variable is nothing but a global variable initialized with a legal value where it is declared in order to be used elsewhere. It can be accessed within any function/block. Also, a normal global variable can be made extern as well by placing the ‘extern’ keyword before its declaration/definition in any function/block. This basically signifies that we are not initializing a new variable but instead we are using/accessing the global variable only. The main purpose of using extern variables is that they can be accessed between two different files which are part of a large program. For more information on how extern variables work, have a look at this link .
- static : This storage class is used to declare static variables which are popularly used while writing programs in C language. Static variables have a property of preserving their value even after they are out of their scope! Hence, static variables preserve the value of their last use in their scope. So we can say that they are initialized only once and exist till the termination of the program. Thus, no new memory is allocated because they are not re-declared. Their scope is local to the function to which they were defined. Global static variables can be accessed anywhere in the program. By default, they are assigned the value 0 by the compiler.
- register : This storage class declares register variables which have the same functionality as that of the auto variables. The only difference is that the compiler tries to store these variables in the register of the microprocessor if a free register is available. This makes the use of register variables to be much faster than that of the variables stored in the memory during the runtime of the program. If a free register is not available, these are then stored in the memory only. Usually few variables which are to be accessed very frequently in a program are declared with the register keyword which improves the running time of the program. An important and interesting point to be noted here is that we cannot obtain the address of a register variable using pointers.
- Write a program to multiply two matrices ( read size and number of element of matrices from the keyboard).
- char: The most basic data type in C. It stores a single character and requires a single byte of memory in almost all compilers.
- int: As the name suggests, an int variable is used to store an integer.
- float: It is used to store decimal numbers (numbers with floating point value) with single precision.
- double: It is used to store decimal numbers (numbers with floating point value) with double precision.
4. Attempt any two of the following: (2*5 = 10)
- What is recursion? Write a recursive program to find factorial of a number. Recursion : The process in which a function calls itself directly or indirectly is called recursion and the corresponding function is called as recursive function. Using recursive algorithm, certain problems can be solved quite easily. Examples of such problems are Towers of Hanoi (TOH) , Inorder/Preorder/Postorder Tree Traversals , DFS of Graph , etc. Base condition in recursion : In recursive program, the solution to base case is provided and solution of bigger problem is expressed in terms of smaller problems. Program to find factorial of a number:
- Explain the difference between parameter passing mechanism call by value and call by reference. Which is more efficient and why? There are different ways in which parameter data can be passed into and out of methods and functions. Let us assume that a function B() is called from another function A() . In this case A is called the “caller function” and B is called the “called function or callee function” . Also, the arguments which A sends to B are called actual arguments and the parameters of B are called formal arguments .
Terminology
- Formal Parameter : A variable and its type as they appear in the prototype of the function or method.
- Actual Parameter : The variable or expression corresponding to a formal parameter that appears in the function or method call in the calling environment.
- IN: Passes info from caller to callee.
- OUT: Callee writes values in caller.
- IN/OUT: Caller tells callee value of variable, which may be updated by callee.
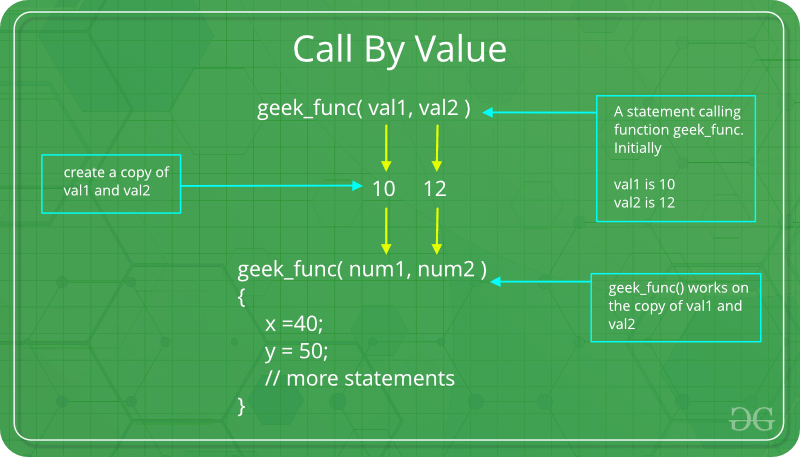
- Inefficiency in storage allocation
- For objects and arrays, the copy semantics are costly
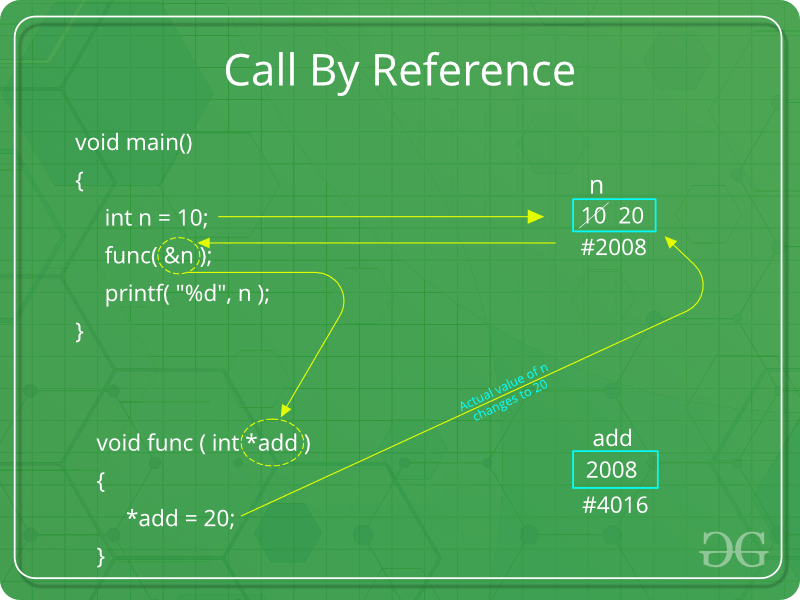
- Many potential scenarios can occur
- Programs are difficult to understand sometimes
- Write a program to check a number is prime number or not. Program to check a number is prime or not:
5. Attempt any two of the following: (2*5 = 10)
- Creating areaperi.h : Write the below code and then save the file as areaperi.h . The extension should be .h indicating its a header file.
- Including the areaperi.h file in other program : Now as we need to include stdio.h as #include in order to use printf() function. We will also need to include the above header file areaperi.h as #include”areaperi.h” . The ” ” here are used to instructs the preprocessor to look into the present folder and into the standard folder of all header files if not found in present folder. So, if you wish to use angular brackets instead of ” ” to include your header file you can save it in the standard folder of header files otherwise. If you are using ” ” you need to ensure that the header file you created is saved in the same folder in which you will save the C file using this header file.
- Using the created header file :
- “r” – Searches file. If the file is opened successfully fopen( ) loads it into memory and sets up a pointer which points to the first character in it. If the file cannot be opened fopen( ) returns NULL.
- “w” – Searches file. If the file exists, its contents are overwritten. If the file doesn’t exist, a new file is created. Returns NULL, if unable to open file.
- “a” – Searches file. If the file is opened successfully fopen( ) loads it into memory and sets up a pointer that points to the last character in it. If the file doesn’t exist, a new file is created. Returns NULL, if unable to open file.
- “r+” – Searches file. If is opened successfully fopen( ) loads it into memory and sets up a pointer which points to the first character in it. Returns NULL, if unable to open the file.
- “w+” – Searches file. If the file exists, its contents are overwritten. If the file doesn’t exist a new file is created. Returns NULL, if unable to open file.
- “a+” – Searches file. If the file is opened successfully fopen( ) loads it into memory and sets up a pointer which points to the last character in it. If the file doesn’t exist, a new file is created. Returns NULL, if unable to open file.
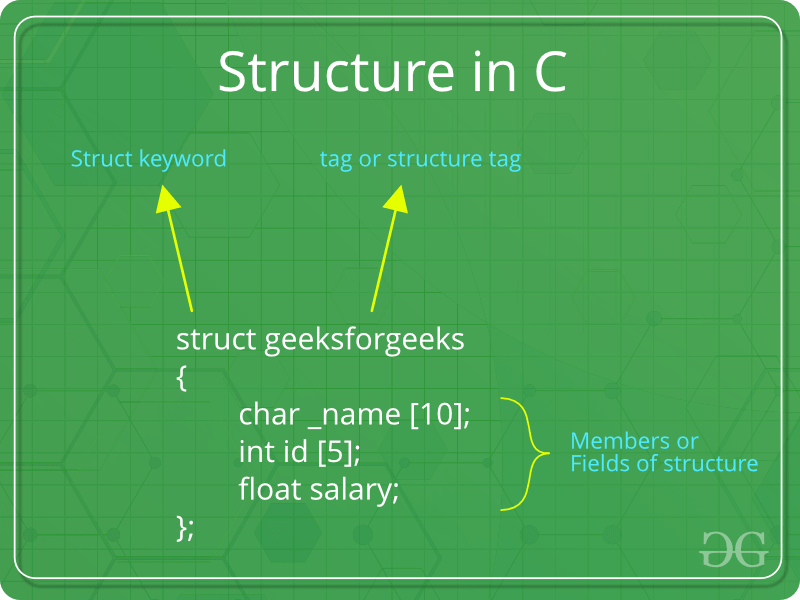
- How to declare structure variables? A structure variable can either be declared with structure declaration or as a separate declaration like basic types.
- Note: In C++, the struct keyword is optional before in declaration of a variable. In C, it is mandatory. Program that compares two given dates:
6. Attempt any two of the following: (2*5 = 10)
- Suppose a file contains student’s records with each record containing name and age of a student. Write a C program to read these records and display them in sorted order by name.
- Write a program to sort a set of names stored in an array in alphabetical order .
- Write a user define function to compare two strings where they are identical or not.
7. Attempt any two of the following: (2*5 = 10)
- Define the concept of pointer> Also define the dynamic memory allocation and various functions for dynamic memory allocation, with suitable examples. Pointers are symbolic representation of addresses. They enable programs to simulate call-by-reference as well as to create and manipulate dynamic data structures. It’s general declaration in C/C++ has the format: Syntax:
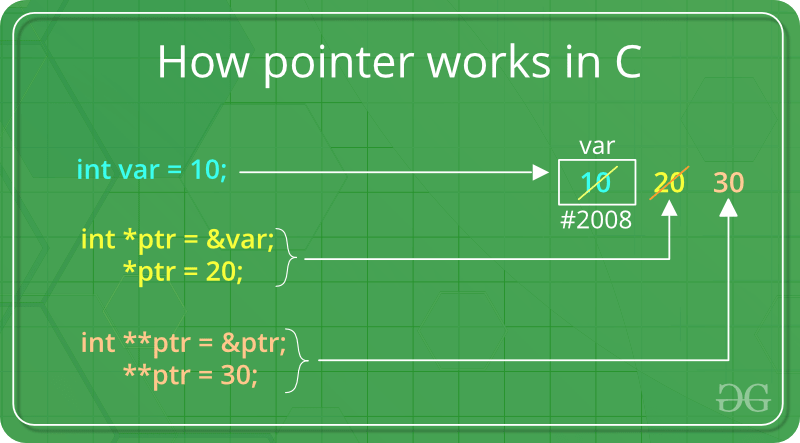
- Define a pointer variable
- Assigning the address of a variable to a pointer using unary operator (&) which returns the address of that variable.
- Accessing the value stored in the address using unary operator (*) which returns the value of the variable located at the address specified by its operand.
- malloc() “malloc” or “memory allocation” method is used to dynamically allocate a single large block of memory with the specified size. It returns a pointer of type void which can be cast into a pointer of any form. Syntax:

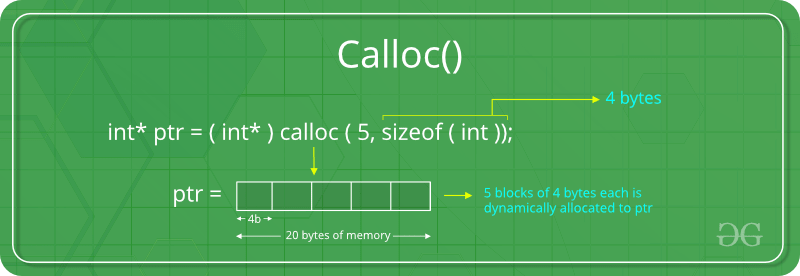
- calloc() “calloc” or “contiguous allocation” method is used to dynamically allocate the specified number of blocks of memory of the specified type. It initializes each block with a default value ‘0’. Syntax:
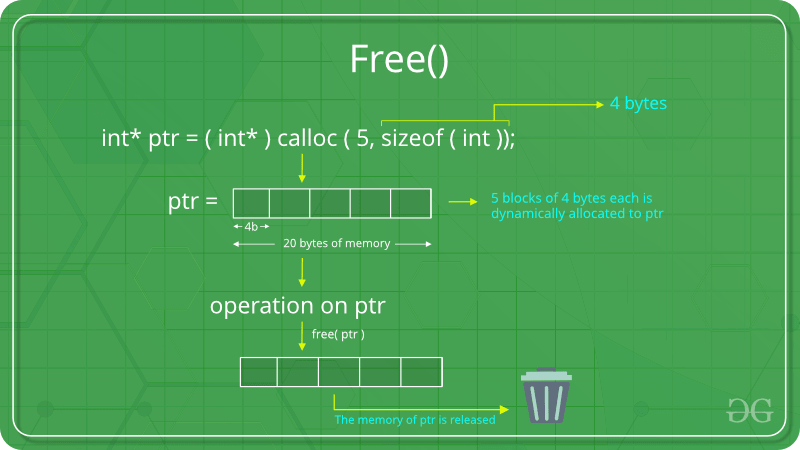
- free() “free” method is used to dynamically de-allocate the memory. The memory allocated using functions malloc() and calloc() are not de-allocated on their own. Hence the free() method is used, whenever the dynamic memory allocation takes place. It helps to reduce wastage of memory by freeing it. Syntax:
- realloc() “realloc” or “re-allocation” method is used to dynamically change the memory allocation of a previously allocated memory. In other words, if the memory previously allocated with the help of malloc or calloc is insufficient, realloc can be used to dynamically re-allocate memory . Syntax:

- strcat : The strcat() function will append a copy of the source string to the end of destination string. The strcat() function takes two arguments: 1) dest 2) src It will append copy of the source string in the destination string. The terminating character at the end of dest is replaced by the first character of src . Return value: The strcat() function returns dest, the pointer to the destination string.
- strchr : In C/C++, strrchr() is a predefined function used for string handling. cstring is the header file required for string functions. This function Returns a pointer to the last occurrence of a character in a string. The character whose last occurrence we want to find in passed as the second argument to the function and the string in which we have to find the character is passed as the first argument to the function. Syntax
- Here, str is the string and c is the character to be located. It is passed as its int promotion, but it is internally converted back to char.
- strcmp : strcmp() is a built-in library function and is declared in <string.h> header file. This function takes two strings as arguments and compare these two strings lexicographically. Syntax: :
- strcmp() compares the two strings lexicographically means it starts comparison character by character starting from the first character until the characters in both strings are equal or a NULL character is encountered.
- If first character in both strings are equal, then this function will check the second character, if this is also equal then it will check the third and so on
- This process will be continued until a character in either string is NULL or the characters are unequal.
- strcpy : strcpy() is a standard library function in C/C++ and is used to copy one string to another. In C it is present in string.h header file and in C++ it is present in cstring header file. Syntax:
- dest : Pointer to the destination array where the content is to be copied.
- src: string which will be copied.
- strlen : The strlen() function calculates the length of a given string.The strlen() function is defined in string.h header file. It doesn’t count null character ‘\0’. Syntax:
- str: It represents the string variable whose length we have to find.
- the strings overlap.
- the dest array is not large enough to append the contents of src.
- dest : the string where we want to append.
- src : the string from which ‘n’ characters are going to append.
- n : represents maximum number of character to be appended. size_t is an unsigned integral type.
- This function takes two strings and a number num as arguments and compare at most first num bytes of both the strings.
- num should be at most equal to the length of the longest string. If num is defined greater than the string length then comparison is done till the null-character(‘\0’) of either string.
- This function compares the two strings lexicographically. It starts comparison from the first character of each string. If they are equal to each other, it continues and compare the next character of each string and so on.
- This process of comparison stops until a terminating null-character of either string is reached or num characters of both the strings matches.
- strncpy : The strncpy() function is similar to strcpy() function, except that at most n bytes of src are copied. If there is no NULL character among the first n character of src, the string placed in dest will not be NULL-terminated. If the length of src is less than n, strncpy() writes additional NULL character to dest to ensure that a total of n character are written. Syntax:
- src: The string which will be copied.
- dest: Pointer to the destination array where the content is to be copied.
- n: The first n character copied from src to dest.
- strrchr : The strrchr() function in C/C++ locates the last occurrence of a character in a string. It returns a pointer to the last occurrence in the string. The terminating null character is considered part of the C string. Therefore, it can also be located to retrieve a pointer to the end of a string. It is defined in cstring header file. Syntax :
- str : specifies the pointer to the null terminated string to be searched for.
- ch: specifies the character to be search for.
- (i) Stack with push and pop operation : Stack is a linear data structure which follows a particular order in which the operations are performed. The order may be LIFO(Last In First Out) or FILO(First In Last Out).
Mainly the following three basic operations are performed in the stack:
- Push: Adds an item in the stack. If the stack is full, then it is said to be an Overflow condition.
- Pop: Removes an item from the stack. The items are popped in the reversed order in which they are pushed. If the stack is empty, then it is said to be an Underflow condition.
- Peek or Top: Returns top element of stack.
- isEmpty: Returns true if stack is empty, else false.
- Balancing of symbols
- Infix to Postfix /Prefix conversion
- Redo-undo features at many places like editors, photoshop.
- Forward and backward feature in web browsers
- Used in many algorithms like Tower of Hanoi, tree traversals , stock span problem , histogram problem .
- Other applications can be Backtracking, Knight tour problem , rat in a maze , N queen problem and sudoku solver
- In Graph Algorithms like Topological Sorting and Strongly Connected Components
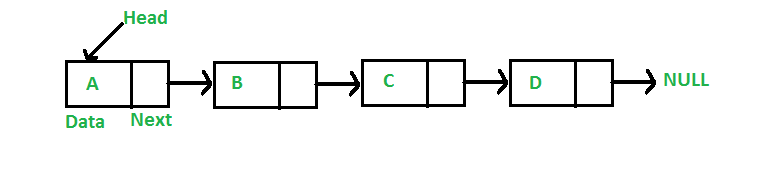
- Using array
- Using linked list
- Command line argument : The most important function of C/C++ is main() function. It is mostly defined with a return type of int and without parameters :
- We can also give command-line arguments in C and C++. Command-line arguments are given after the name of the program in command-line shell of Operating Systems. To pass command line arguments, we typically define main() with two arguments : first argument is the number of command line arguments and second is list of command-line arguments.
- argc (ARGument Count) is int and stores number of command-line arguments passed by the user including the name of the program. So if we pass a value to a program, value of argc would be 2 (one for argument and one for program name)
- The value of argc should be non negative.
- argv(ARGument Vector) is array of character pointers listing all the arguments.
- If argc is greater than zero, the array elements from argv[0] to argv[argc-1] will contain pointers to strings.
- Argv[0] is the name of the program, After that till argv[argc-1] every element is command -line arguments.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- AKTU-question-papers
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
LearningYouth
Stay ahead in AI with LearningYouth.com! Explore in-depth tutorials, the latest AI technology updates, and insightful case studies. Your ultimate resource for mastering AI concepts and tracking cutting-edge advancements.
- Share To Facebook Share To Twitter Share To Pinterest Share To WhatsApp Share To LinkedIn Share To Tumblr Share To Telegram Share To Reddit Share To Gmail
Programming For Problem Solving Handwritten notes pdf 1st Year AKTU university

- Share on Facebook Share on X Share on Pinterest Share on Whatsapp Partager sur Linkedin Share on Tumblr Share on Telegram Share on Reddit Share on Gmail
Subscribe Our Newsletter
Recommandation
Post a comment, article center ads, article bottom ads.

Quantum Notes For B.tech 1st Year
All 1st Year Q uantum PDF Availble Here……. …
- This page contain all the Quantum Series B.tech All branch pdf available here
- Aktu Notes working hard to provide you best and good quality study materials.
Enigineering Physics Quantum PDF for B.Tech 1 ST Year
UNIT-1 RELATIVISTIC MECHANICS
FRAME OF REFERENCE, INERTIAL & NON-INERTIAL FRAMES, GALILEAN
TRANSFORMATIONS, MICHELSON- MORLEY EXPERIMENT, POSTULATES OF
SPECIAL THEORY OF RELATIVITY, LORENTZ TRANSFORMATIONS, LENGTH
CONTRACTION, TIME DILATION, VELOCITY ADDITION THEOREM, VARIATION OF
MASS WITH VELOCITY, EINSTEIN’S M ES ENERGY RELATION, RELATIVISTIC
RELATION BETWEEN ENERGY AND MOM.NTUM, MASSLESS PARTICLE.
UNIT-2: ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD THEORY
CONTINUITY EQUATION FOR CURRENT DENSITY, DISPLACEMENT CURRENT,
MODIFYING EQUATION FOR THE CURL OF MAGNETIC FIELD TO SATISFY
CONTINUITY EQUATION, MAXWELL’S EQUATIONS IN VACUUM AND IN NON
CONDUCTING MEDIUM, ENERGY IN AN ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD, POYNTING
VECTOR AND POYNTING THEOREM, PLANE ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN
VACUUM AND THEIR TRANSVERSE NATURE. RELATION BETWEEN ELECTRIC AND
MAGNETIC FIELDS OF AN ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE, ENERGY AND MOMENTUM
CARRIED BY ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES, RESULTANT PRESSURE, SKIN DEPTH.
UNIT-3 : QUANTUM MECHANICS
BLACK BODY RADIATION, STEFAN’S LAW, WIEN’S LAW, RAYLEIGH-JEANS LAW
AND PLANCK’S LAW, WAVE PARTICLE DUALITY, MATTER WAVES, TIME
DEPENDENT AND TIME-INDEPENDENT SCHRODINGER WAVE EQUATION, BOR
INTERPRETATION OF WAVE FUNCTION, SOLUTION TO STATIONARY STATE
SCHRODINGER WAVE EQUATION FOR ONE-DIMENSIONAL PARTICLE IN A BOX,
COMPTON EFFECT.
UNIT-4 : WAVE OPTICS
COHERENT SOURCES, INTERFERENCE IN UNIFORM AND WEDGE SHAPED THIN
FILMS, NECESSITY OF EXTENDED SOURCES, NEWTON’S RINGS AND ITS
APPLICATIONS. FRAUNHOFFER DIFFRACTION AT SINGLE SLIT AND AT DOUBLE SLIT,
ABSENT SPECTRA, DIFFRACTION GRATING SPECTRA WITH GRATING, DISPERSIVE
POWER, RESOLVING POWER OF GRATING, RAYLEIGH’S CRITERION OF RESOLUTION.
RESOLVING POWER OF GRATING.
UNIT-5: FIBER OPTICS AND LASER
FIBRE OPTICS: INTRODUCTION TO FIBRE OPTICS, ACCEPTANCE ANGLE,
NUMERICAL APERTURE, NORMALIZED FREQUENCY, CLASSIFICATION OF FIBRE,
ATTENUATION AND DISPERSION IN OPTICAL FIBRES,
LASER: ABSORPTION OF RADIATION, SPONTANEOUS AND STIMULATED
EMISSION OF RADIATION, EINSTEIN’ COEFFICIENTS, POPULATION INVERSION.
VARIOUS LEVELS OF LASER, RUBY LASER, HE-NE LASER, LASER APPLICATIONS.
DOWNLOAD NOW : CLICK HERE
Table of Contents
Enigineering Chemistry Quantum PDF for B.Tech 1 ST Year
UNIT-I: MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY
MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY AND ITS APPLICATIONS TO HOMO-NUCLEAR
DIATOMIC MOLECULES. BAND THEORY OF SOLIDS. LIQUID CRYSTALS AND ITS
APPLICATIONS. POINT DEFECTS IN SOLIDS. STRUCTURE AND APPLICATIONS OF
GRAPHITE AND FULLERENES. CONCEPTS OF NANO-MATERIALS AND ITS
APPLICATIONS.
UNIT-II: POLYMERS AND ORGANOMETALLICS
POLYMERS: BASIC CONCEPTS OF POLYMER- BLENDS AND COMPOSITES.
CONDUCTING AND BIODEGRADABLEPOLYMERS. PREPARATIONS AND
APPLICATIONS OF SOME INDUSTRIALLY IMPORTANT POLYMERS(BUNA N,
BUNA S, NEOPRENE, NYLON 6, NYLON 6,6 , TERYLENE). GENERAL METHODS
OF SYNTHESIS OF ORGANOMETALLIC COMPOUND (GRIGNARD REAGENT) AND
THEIR APPLICATIONS IN POLYMERIZATION.
UNIT-III : ELECTROCHEMISTRY
ELECTROCHEMISTRY: GALVANIC CEL, ELECTRODE POTENTIAL, LEAD STORAGE
BATTERY. CORROSION, CAUSES AND AS PREVENTION. SETTING AND HARDENING
OF CEMENT, APPLICATIONS OF CEMENT. PLASTER OF PARIS. LUBRICANTS-
CLASSIFICATION, MECHANISM AND APPLICATIONS.
UNIT-IV : WATER TREATMENT
HARDNESS OF WATER. DISADVANTAGE OF HARD WATER. BOILER TROUBLES,
TECHNIQUES FOR WATER SOFTENING; LIME-SODA, ZEOLITE, ION EXCHANGE RESIN,
REVERSE OSMOSIS. PHASE RULE AND ITS APPLICATION TO WATER SYSTEM.
UNIT-V : FUELS AND SPECTRAL TECHNIQUES
FUELS: CLASSIFICATION OF FUELS. ANALYSIS OF COAL. DETERMINATION OF
CALORIFIC VALUES (BOMB CALORIMETER & DULONG’S METHOD). BIOGAS.
ELEMENTARY IDEAS AND SIMPLE APPLICATIONS OF UV, VISIBLE, IR AND
HINMR SPECTRAL TECHNIQUES.
DOWNLOAD NOW: CLICK HERE
Enigineering Maths-I Quantum Notes for B.Tech 1 ST Year
UNIT-1 : DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS – I
SUCCESSIVE DIFFERENTIATION, LEIBNIZ’S THEOREM, LIMIT, CONTINUITY
AND DIFFERENTIABILITY OF FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES, PARTIAL
DERIVATIVES, EULER’, THEOREM FOR HOMOGENEOUS FUNCTIONS, TOTAL
DERIVATIVES, CHANGEBF VARIABLES, CURVE TRACING: CARTESIAN AND POLAR
COORDINATES,
UNIT-II : DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS – II
TAYLOR’S AND MACLAURIN’S THEOREM, EXPANSION OF FUNCTION OF SEVERAL
VARIABLES, JACOBIAN, APPROXIMATION OF ERRORS, EXTREMA OF FUNCTIONS
OF SEVERAL VARIABLES, LAGRANGE’S METHOD OF MULTIPLIERS (SIMPLE
APPLICATIONS).
UNIT-III : MATRIX ALGEBRA
TYPES OF MATRICES, INVERSE OF A MATRIX BY ELEMENTARY
TRANSFORMATIONS, RANK OF A MATRIX (ECHELON & NORMAL FORM), LINEAR
DEPENDENCE, CONSISTENCY OF LINEAR SYSTEM OF EQUATIONS AND THEIR
SOLUTION, CHARACTERISTIC EQUATION, EIGEN VALUES AND EIGEN VECTORS,
(CAYLEY-HAMILION THEOREM, DIAGONALIZATION, COMPLEXAND UNITARY
MATRICES AND ITS PROPERTIES.
Download Now
UNIT-IV: MULTIPLE INTEGRALS
DOUBLE AND TRIPLE INTEGRALS, CHANGE OF ORDER OF INTEGRATION, CHANGE
OF VARIABLES, APPLICATION OF INTEGRATION TO LENGTHS, SURFACE AREAS
AND VOLUMES -CARTESIAN AND POLAR COORDINATES. BETA AND GAMMA
FUNCTIONS, DIRICHLET’S INTEGRAL AND ITS APPLICATIONS.
UNIT-V : VECTOR CALCULUS
POINT FUNCTION, GRADIENT, DIVERGENCE AND CURL OF A VECTOR AND THEIR
PHYSICAL INTERPRETATIONS, VECTOR IDENTITIES, TANGENT AND NORMAL,
DIRECTIONAL DERIVATIVES. LINE, SURFACE AND VOLUME INTEGRALS,
APPLICATIONS OF GREEN’S, STOKE’S AND GAUSS DIVERGENCE THEOREMS
(WITHOUT PROOF).
Basic Electrical Engineering Quantum Notes for B.Tech 1 ST Year
UNIT-1 : DC CIRCUITS
AT J ELECTRICAL FIREUIT DLEFMENTS (R, L AND C), CONCEPT OF ACTIVE AND PASSIVE*
DEMENTS, VOLTAGE AND CURRENT SOURCES, CONCEPT OF LINEARITY AND LINEAR
-NETORK, UNILATERAL, AND BILATERAL, ELEMENTS, KIRCHHOFF’S LAWS, LOOP AND
NODAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS, STAR-DELTA TRANSFORMATION, SUPERPOSITION
(C% – (NEORÉM THEVENIN THEOREM, NORTON THEOREM
UNIT-2 : STEADY-STATE ANALYSIS OF 1-& AC CIRCUITS
SINUSCIDALLY VARYING VOLTÄGE AND CURRENT.
ANALYSIS OF SINGLE PHASE AC CIRCUITS CONSISTING OF R, L. C, RL, RC. RICINU
COMBINATIONS (SERIES AND PARALLEL), APPARENT, ACTIVE & REACTIVE POWER,
POWER FACTOR, POWER FACTOR IMPROVEMENT CONCEPT OF RESONANCE IN SERIES
DE PARALLEL CIRCUITS, BANDWIDTH AND QUALITY FACTOR. THREE PHASE BALANCED
CIRCUITS, VOLTAGE AND CURRENT RELATIONS IN STAR AND DELTA CONNECTIONS
UNIT-3 : TRANSFORMERS
MAGNETIC MATERIALS, BI CHARACTERISTICS, IDEAL AND PRACTICAL TRANSLORMER,
EQUIVALENT CIRRUIT, LOSSES IN TRANSFORMERS, REGULATION AND EFFICIENCY, AUTO .
TRANSFORMER AND THREE-PHASE TRANSFORMER CONNECTIONS.
UNIT-4 : ELECTRICAL MACHINES
DC MACHINES: PRINDPLE & CONSTRUCTION, TYPES, EMF EQUATION OF GENERATOR
AND TORQUE EQUATION OF MOTOR, *PPLICATIONS OF DC MOTORS (SIMPLE NUMERICAL
/ PROBLEMS)
THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR. PRINCIPLE & CORSTRUCTION, TYPES, SLIP-TORQUE
(CITE. CHARACTERISTIOS, APPLICATIONS (NUMERICAL PROBLEMS RELATED TO SLIP ONLY)
SINGLE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR: PRINDPLE OF OPERATION AND INTRODUCTION F749
METHODS OF STARTING, APPLICATIONS
THREE PHASE SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION @F ALTERNATOR AND
SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR AND THEIR APPLICATIONS.
UNIT-S : ELECTRICAL INSTALLATIONS
(AR_ COMPONENT OF LT SWILCHGEAR: SWITCH FUSE UNIT (SFU), MCB, ELCB, MOCB
TYPES OF WIRES AND CABLES, IMPORTANCE OF EARTHING TYPES OF BATTERLES,
IMPORTANT CHARACTERISTICS FOR BALTERIES ELEMENTARY CALCULATIONS FOR ENERGY .L.E
CONSUMPTION AND SAVINGS, BATTERY BACKUP.
Programming for Problem Solving Quantum Notes
UNIT-1 : INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING
INTRODUCTION TO COMPONENTS OF A COMPUTER SYSTEM: MEMORY,
PROCESSOR. 1/0 DEVICES, STORAGE, OPERATING SYSTEM, CONCEPT OF
ASSEMBLER, COMPILER, INTERPRETER, LOADER AND LINKER.
IDEA OF ALGORITHM: REPRESENTATION OF ALGORITHM, FLOWCHART, PSEUDO
CODE WITH EXAMPLES, FROM ALGORITHMS TO PROGRAMS, SOURCE CODE
PROGRAMMING BASICS: STRUCTURE OF C PROGRAM, WRITING AND
EXECUTING THE FIRST C. PROGRAM, SYNTAX AND LOGICAL ERRORS IN
COMPILATION, OBJECT AND EXECUTABLE CODE. COMPONENTS OF C
LANGUAGE, STANDARD 1/0 IN C, FUNDAMENTAL DATA TYPES, YARIABLES
AND MEMORY LOCATIONS, STORAGE CLASSES.
UNIT-2: ARITHMETIC EXPRESSIONS
ARITHMETIC EXPRESSIONS AND PRECEDENCE:OPERATORS AND EXPRESSION USING
NUMERIC AND RELATIONAL OPERATORS, MIXED OPERANDS, TYPE CONVERSION
LOGICIT OPERATORS, BIT OPERATIONS, APSIGNMENT OPERATOR, OPERATOR
PRECEDENCE AND ASSOCIATIVITY,
CONDITIONAL BRANCHING2APPLYING IF AND SWITCH STATEMENTS, NESTING
IF AND ELSE, USE OF BREAK AND DEFAULT WITH SWITCH.
UNIT-3: LOOPS & FUNCTIONS
ITERATION AND LOOPS: USE OF WHILE, DO WHILE AND FOR LOOPS, MULTIPLE
LOOP VARIABLES, USE OF BREAK AND CONTINUE STATEMENTS.
FUNCTIONS: INTRODUCTION, TYPES OF FUNCTIONS, FUNCTIONS WITH ARRAY,
PASSING PARAMETERS TO FUNCTIONS, CALL BY VALUE, CALL BY REFERENCE,
RECURSIVE FUNCTIONS.
UNIT-4 : ARRAYS & BASIC ALGORITHM
ARRAYS: ARRAY NOTATION AND REPRESENTATION, MANIPULATING ARRAY
ELEMENTS, USING MULTI DIMENSIONAL ARRAYS. CHARACTER ARRAYS AND STRINGS,
STRUCTURE, UNION, ENUMERATED DATA TYPES, ARRAY OF STRUCTURES, PASSING
ARRAYS TO FUNCTIONS. BASIC ALGORITHMS: SEARCHING & BASIC SORTING
ALGORITHMS (BUBBLE, INSERTION AND SELECTION), FINDING ROOTS OF
EQUATIONS, NOTION OF ORDER OF COMPLEXITY.
UNIT-5: POINTERS AND FILE HANDLING
POINTERS: INTRODUCTION, DECLARATION, APPLICATIONS, INTRODUCTION TO
DYNAMIC MEMORY ALLOCATION (MALLOC, CALLOC, REALLOC, FREE), USE OF POINTERS
IN SELF-REFERENTIAL STRUCTURES, NOTION OF LINKED LIST (NO IMPLEMENTATION).
FIE HANDLING: FILE 1/0 FUNCTIONS, STANDARD C PREPROCESSORS, DEFINING
AND CALLING MACROS, COMMAND-LINE ARGUMENTS.
DOWNLOAD NOW : Click Here
Professional Communication FOR 1 ST YEAR
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Download Programming for Problem Solving Notes Aktu B-tech 1st year Handwritten Notes Introduction. C programming is a fundamental skill for students pursuing a B.Tech degree from AKTU (Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University) or any other university. This article aims to provide an overview of C programming for problem solving and offers ...
AKTU; Programming For Problem Solving; Programming For Problem Solving (KCS101T) 39 39 documents. 0 0 questions 8 8 students. Follow this course. Programming For Problem Solving (KCS101T) Follow. ... PPS Handwritten Notes Unit 5 watermark. Other 100% (1) 5. Simple interest and compound interest. Lecture notes 100% (1) 10. Unit 1 - PPS notes of ...
A one-stop destination for AKTU students, offering free PDF quantum books , past year papers, and study notes , for first year students . Aktu Resources . home; Year. First Year ... PROGRAMMING-FOR-PROBLEM-SOLVING-KCS-101T-1 SOFT-SKILLS-I-KNC-101 2019-20. BASIC-ELECTRICAL-ENGG.-KEE-101 ...
CO 4 To decompose a problem into functions and synthesize a complete program using divide and conquer approach. K 4 CO 5 To use arrays, pointers and structures to develop algorithms and programs. K 2, K 3 K 1 - Remember, K 2 - Understand, K 3 - Apply, K 4 - Analyze , K 5 - Evaluate , K 6 - Create KCS101/KCS 201: Programming for Problem Solving ...
Studying Problem Solving Using C KCA102 at Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University? On Studocu you will find 16 lecture notes, practice materials, summaries, ... AKTU; Problem Solving Using C; Problem Solving Using C (KCA102) ... Problem solving & c programming. 28 pages. 2023/2024. None. 2023/2024 None. Save. Input output statement. 12 ...
In this video, we cover an introduction to The C Programming For Problem Solving Course playlist and we are over the course syllabus. | C Programming AKTU fu...
unit-1 Introduction to Components of a Computer System: Memory, Processor, I/O Devices, Storage, Operating System, Concept of Assembler, Compiler, Interprete...
In this video, we cover a unit-1 of Introduction to components of a computer system and the idea of algorithm | Introduction to Components of a Computer Syst...
AKTU; Programming For Problem Solving / Fundamentals Of Mechanical Engineering & Mechatronics; ... 0 0 questions 1 1 student. Follow this course. Programming For Problem Solving / Fundamentals Of Mechanical Engineering & Mechatronics (KCS201T/KME201T) Follow. Lecture notes. Date Rating. year. Ratings. Module 4 - pratical works. 50 pages. 2017/ ...
AKTU btech-1-sem-programming-for-problem-solving-bcs101-2023.pdf question paper with solutions, Notes pdf download AKTU Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow
Programming for Problem Solving: Download PDF: BME201: Fundamentals of Mechanical Engineering: Download PDF: BAS204: Environment and Ecology: Not Available: BAS205: Soft Skills: Download PDF 1 Download PDF 2: FAQs for AKTU BTech 1st Year Notes PDF Free Download: 1. Are the AKTU BTech 1st Year Notes PDF available for free download? Yes, you can ...
Outcomes:Demonstrate the basic knowledge of computer hardware and. ftware.To formulate simple algorithms for arithmetic a. logical problems.To translate the algorithms to programs (in C langu. e).To test and execute the programs and correct syntax and logical errors.Ability to apply solvin.
The "C Programming for Problem Solving Quantum PDF" offers numerous benefits to AKTU B-Tech 1st year students. It provides a comprehensive overview of C programming, highlighting its relevance in problem-solving and its integration with quantum computing. The PDF covers practical examples, algorithms, and coding techniques specific to ...
AKTU btech-2-sem-programming-for-problem-solving-kcs201-2022.pdf question paper with solutions, Notes pdf download AKTU Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow
In this video, we cover a unit-1 of Introduction to components of a computer system and the idea of algorithm | Programming Basics | Structure of C Program |...
SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec A; AKTU 1st Year Sem 1 Solved Paper 2014-15 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec B; Semester 2: AKTU 1st Year Sem 2 Solved Paper 2014-15 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec A; AKTU 1st Year Sem 2 Solved Paper 2014-15 | COMP. SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec B; Register Here for Free. Fundamentals of Programming with C
Learning C-Programming will not only enhance your problem-solving skills but also pave the way for a successful career in the field of computer science. Hand written C-programming notes. Download now. Benefits of C-Programming Notes. The C-Programming notes provided by Aktu offer several advantages for B-Tech 1st year students:
UNIT 2 - COMPILE DESIGN UNIT 2 NOTES AKTU; ... PROBLEM SOLVING AND PROGRAMMING UNIT-I Introduction to Computer Problem Solving Steps Involved in Problem Solving. A computer cannot solve a problem on its own. One has to provide step by step solutions of the. problem to the computer. In fact, the task of problem solving is not that of the computer.
For the first year, you can download the most recent edition of Aktu Notes for Programming for Problem-Solving for free from our website. There is a thorough explanation of the entire syllabus. Programming for Problem-Solving AKTU Quantum Download PDF
SYSTEM & C PROGRAMMING | Sec C. Last Updated : 01 Mar, 2023. Paper download link: Paper | Sem 1 | 2017-18. B.Tech. (SEM-I) THEORY EXAMINATION 2017-18 COMPUTER SYSTEM & PROGRAMMING IN C. Time: 3hrs Total Marks: 100 Note :-. There are three sections. Section A carries 20 marks, Section B carries 30 marks and Section C carries 50 marks.
Programming For Problem Solving Handwritten notes pdf 1st Year AKTU university last Update 2024-04-30T16:18:41Z Comment If you're just starting your journey at AKTU University, you're probably taking a course called Problem Solving in Programming. ... These notes explain programming concepts in a simple way and provide solutions to common ...
UNIT - 3 | C PROGRAMMING MR. ASHUTOSH PANDEY. 1- Write a program in C to read n number of values in an array and display it in reverse order. 2. Write a program in C to find the sum of all elements of the array. 3. Write a program in C to find the maximum and minimum element in an array. Assignment: UNIT - 3 | C PROGRAMMING MR.
programming for problem solving quantum notes. unit-1 : introduction to programming. introduction to components of a computer system: memory, processor. 1/0 devices, storage, operating system, concept of. assembler, compiler, interpreter, loader and linker. idea of algorithm: representation of algorithm, flowchart, pseudo