
Thinkers and theories
Rawls the redeemer
For John Rawls, liberalism was more than a political project: it is the best way to fashion a life that is worthy of happiness
Alexandre Lefebvre

Meaning and the good life
‘Everydayness is the enemy’ – excerpts from the existentialist novel ‘The Moviegoer’

Beyond authenticity
In her final unfinished work, Hannah Arendt mounted an incisive critique of the idea that we are in search of our true selves
Samantha Rose Hill

Philosophy was once alive
I was searching for meaning and purpose so I became an academic philosopher. Reader, you might guess what happened next
Pranay Sanklecha

Learning to be happier
In order to help improve my students’ mental health, I offered a course on the science of happiness. It worked – but why?

Biography and memoir
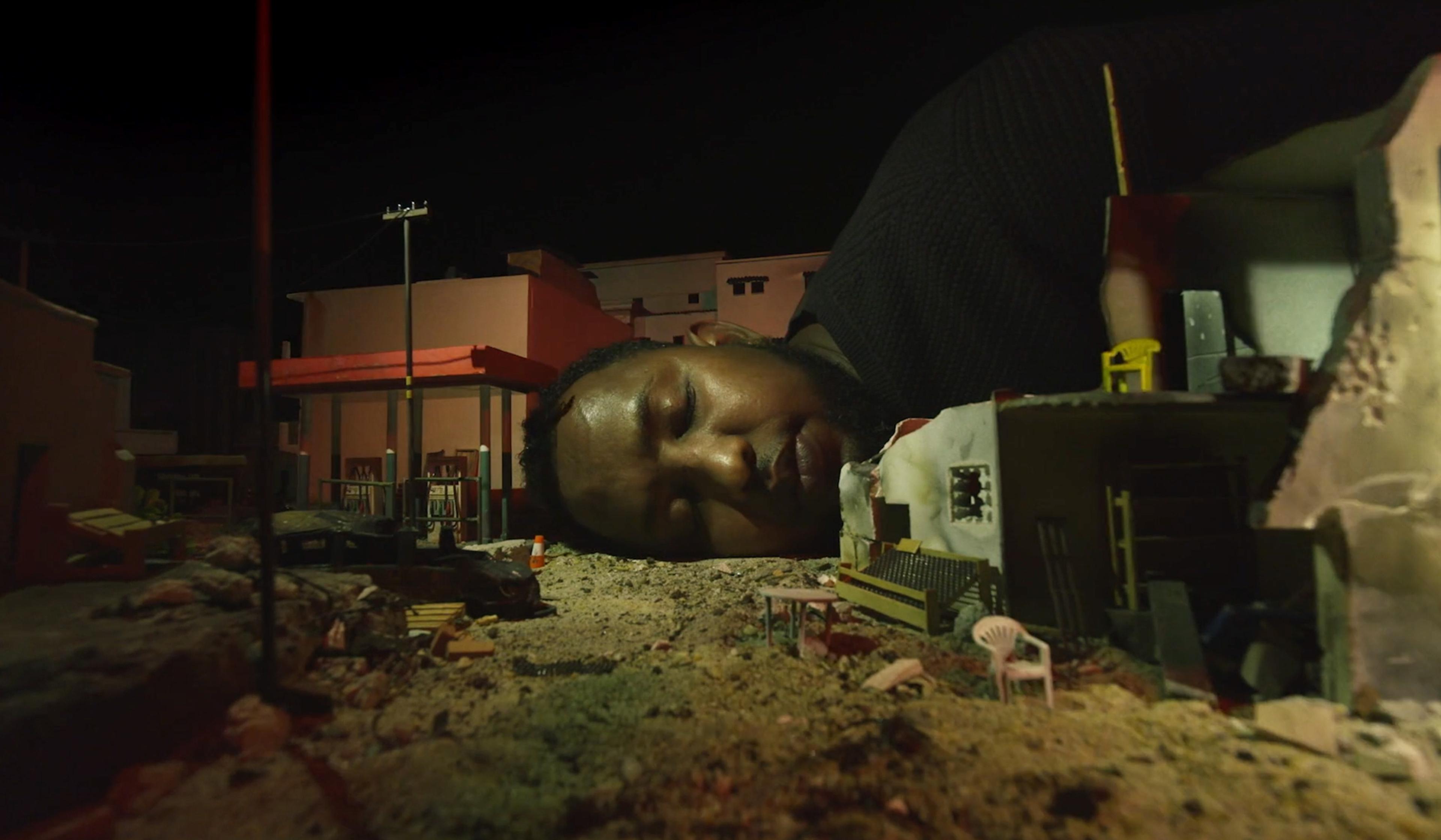
The unique life philosophy of Abdi, born in Somalia, living in the Netherlands
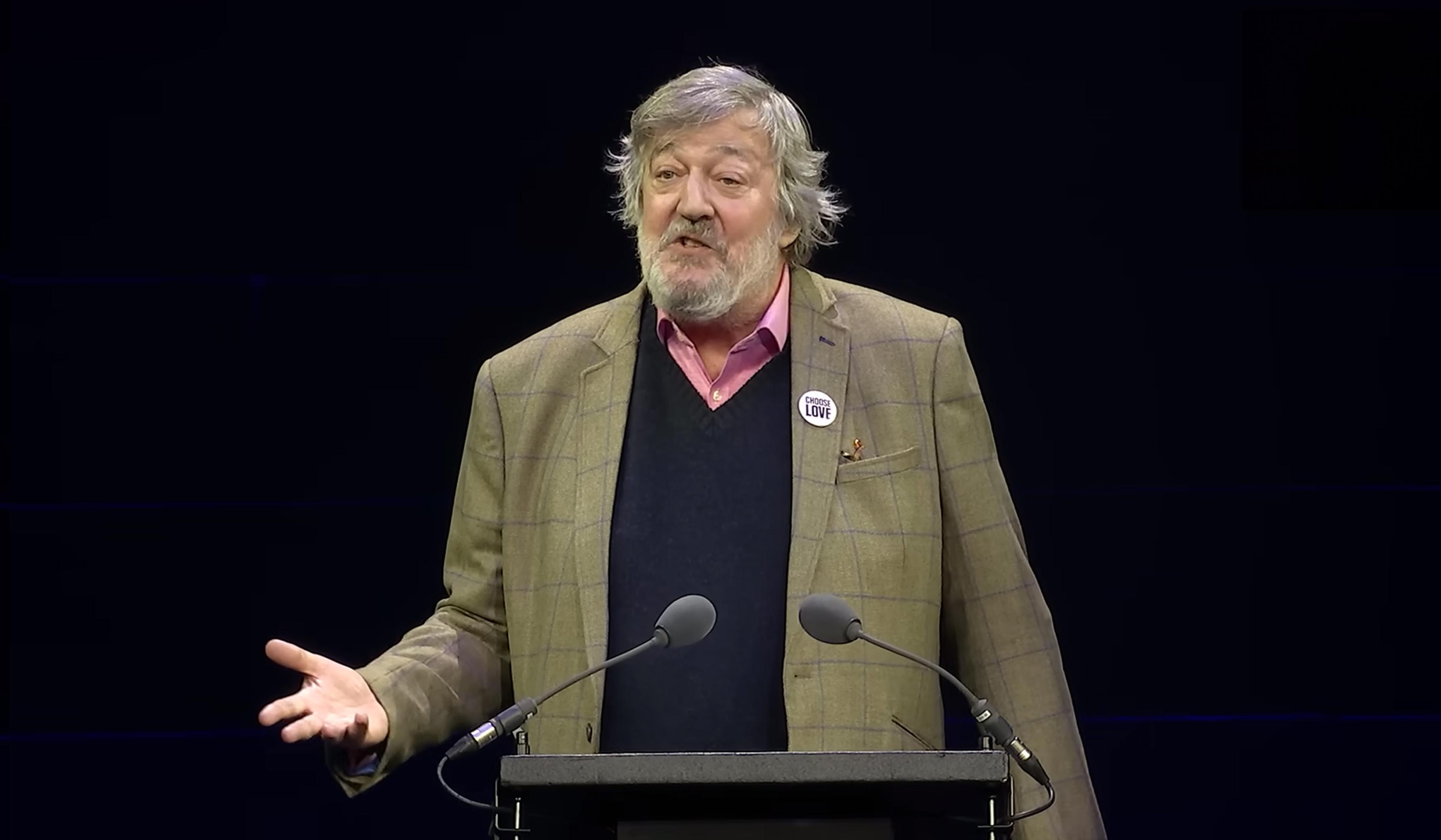

Why strive? Stephen Fry reads Nick Cave’s letter on the threat of computed creativity

Beauty and aesthetics
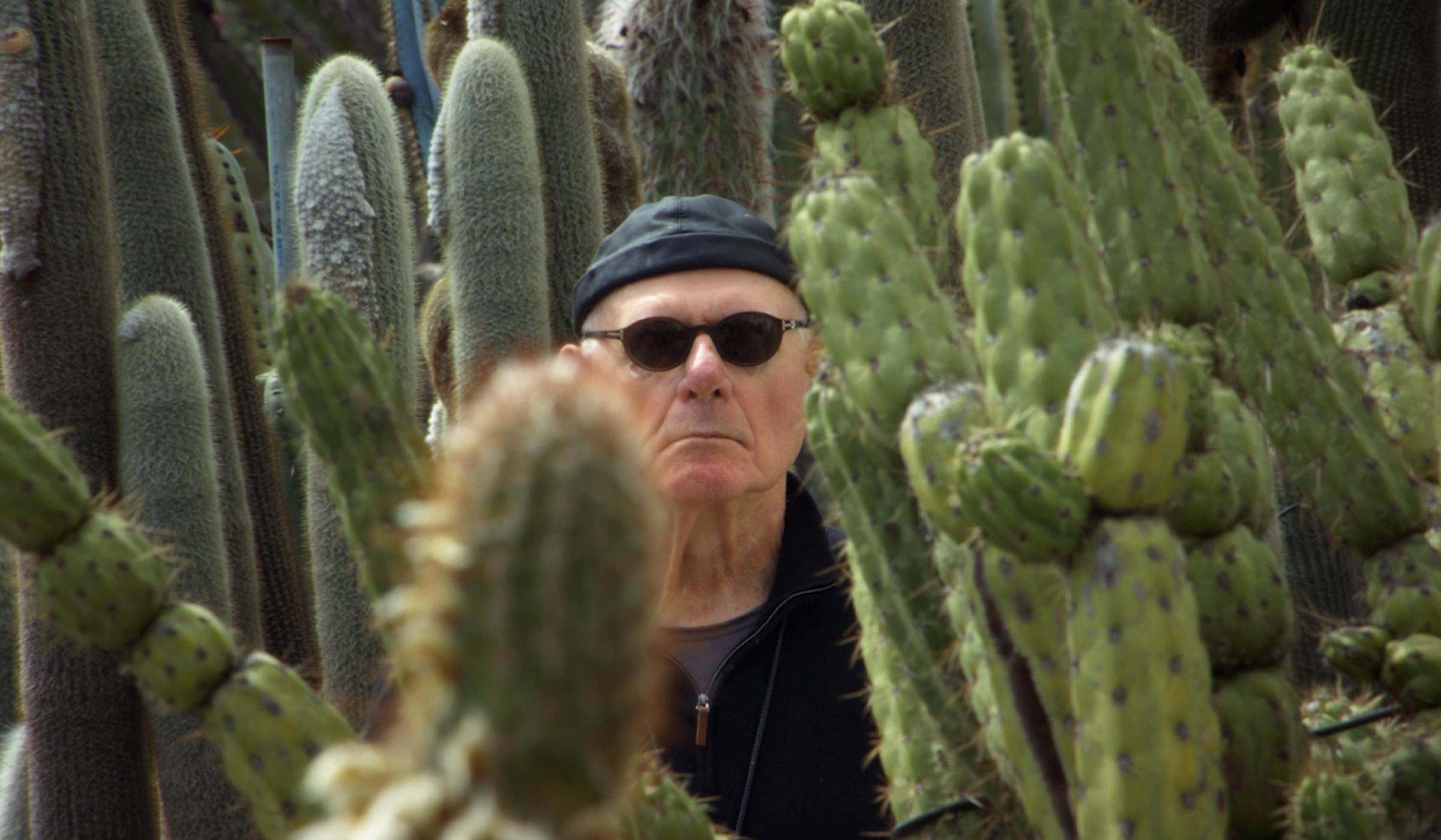
The grit of cacti and the drumbeat of time shape a sculptor’s life philosophy

Ageing and death
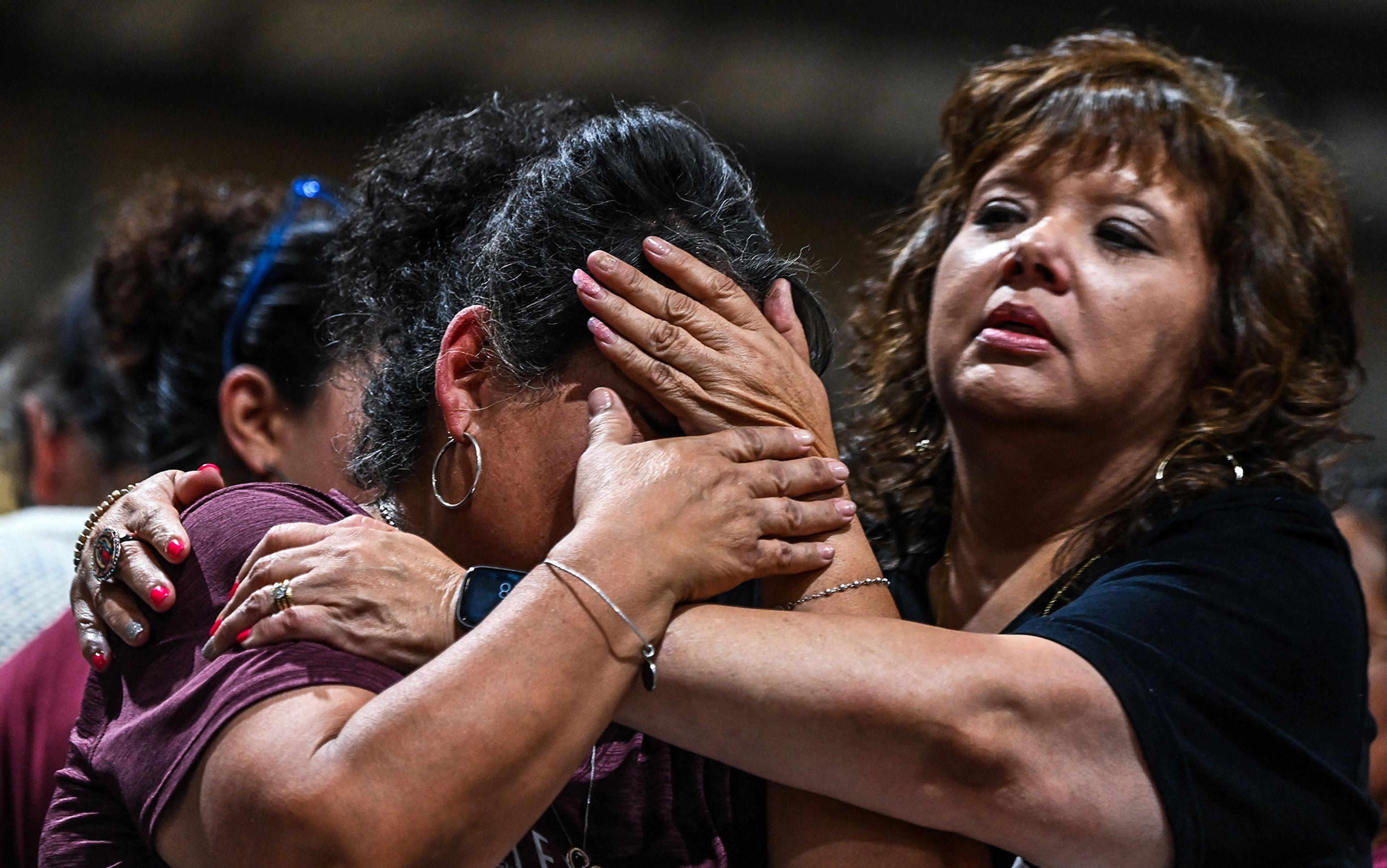
Witness the pain
When loved ones are traumatically lost, bereaved families become accidental activists by turning grief into grievance
Chris Bobel
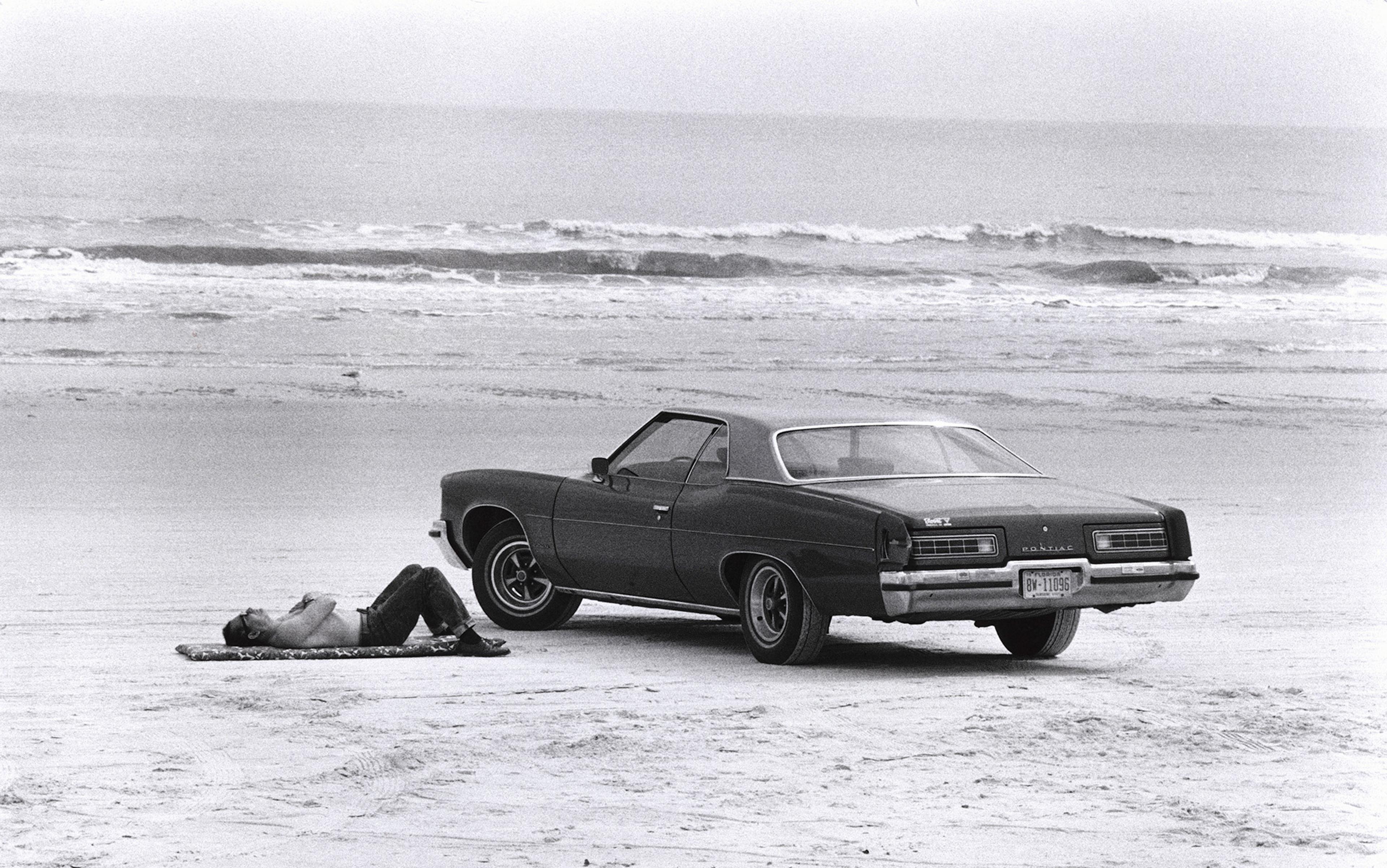

Modern life subjects us to all-consuming demands. That’s why we should reflect on what it means to step away from it all
David J Siegel

Cognition and intelligence
Are you an artistic genius?
Maybe not, but if that’s the threshold you use for creativity in your life, you are coming at the problem all wrong
James C Kaufman

Even in modern secular societies, belief in an afterlife persists. Why?

Spirituality
Trek alongside spiritual pilgrims on a treacherous journey across Pakistan

Freedom at work
There is always a demand for more jobs. But what makes a job good? For that, Immanuel Kant has an answer

The world turns vivid, strange and philosophical for one plane crash survivor

Stories and literature
Solace and saudade
In the face of an inscrutable, indifferent universe, Pessoa suggests we cultivate a certain longing for the elusive horizon
Jonardon Ganeri & Sarah Seymour

Philosophy of religion
A new paganism
Now is the time to revitalise our relationship with nature and immerse ourselves in the little wonders of the universe

Why Aristotle believed that philosophy was humanity’s highest purpose

Comparative philosophy
How to become wise
Practice is at the heart of Korean philosophy. In order to lead a good life, hone your daily rituals of self-cultivation
Kevin Cawley
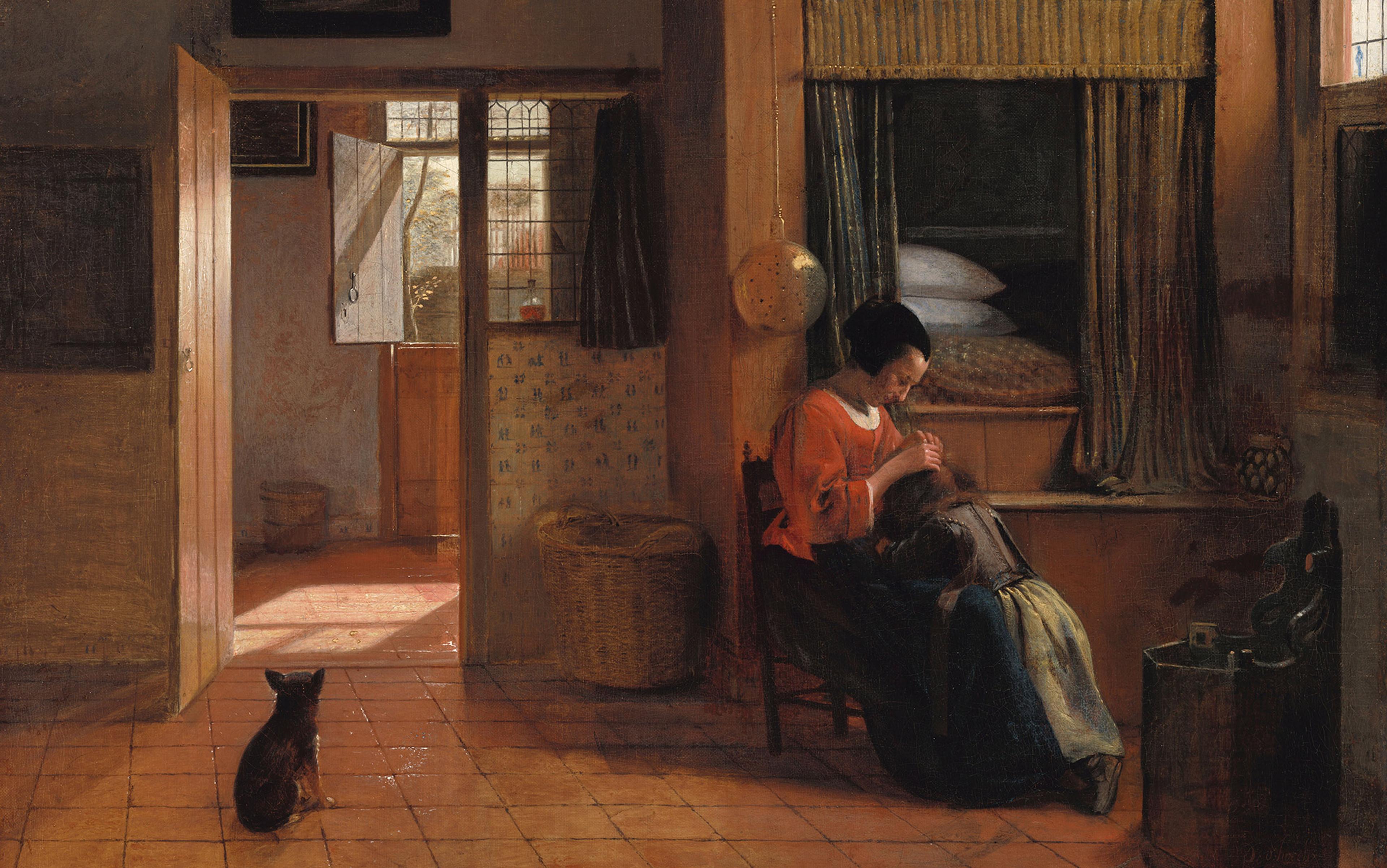

Attuned to the aesthetic
The ultimate value of the world can be discovered if you are sensitive to what is beautiful
Tom Cochrane
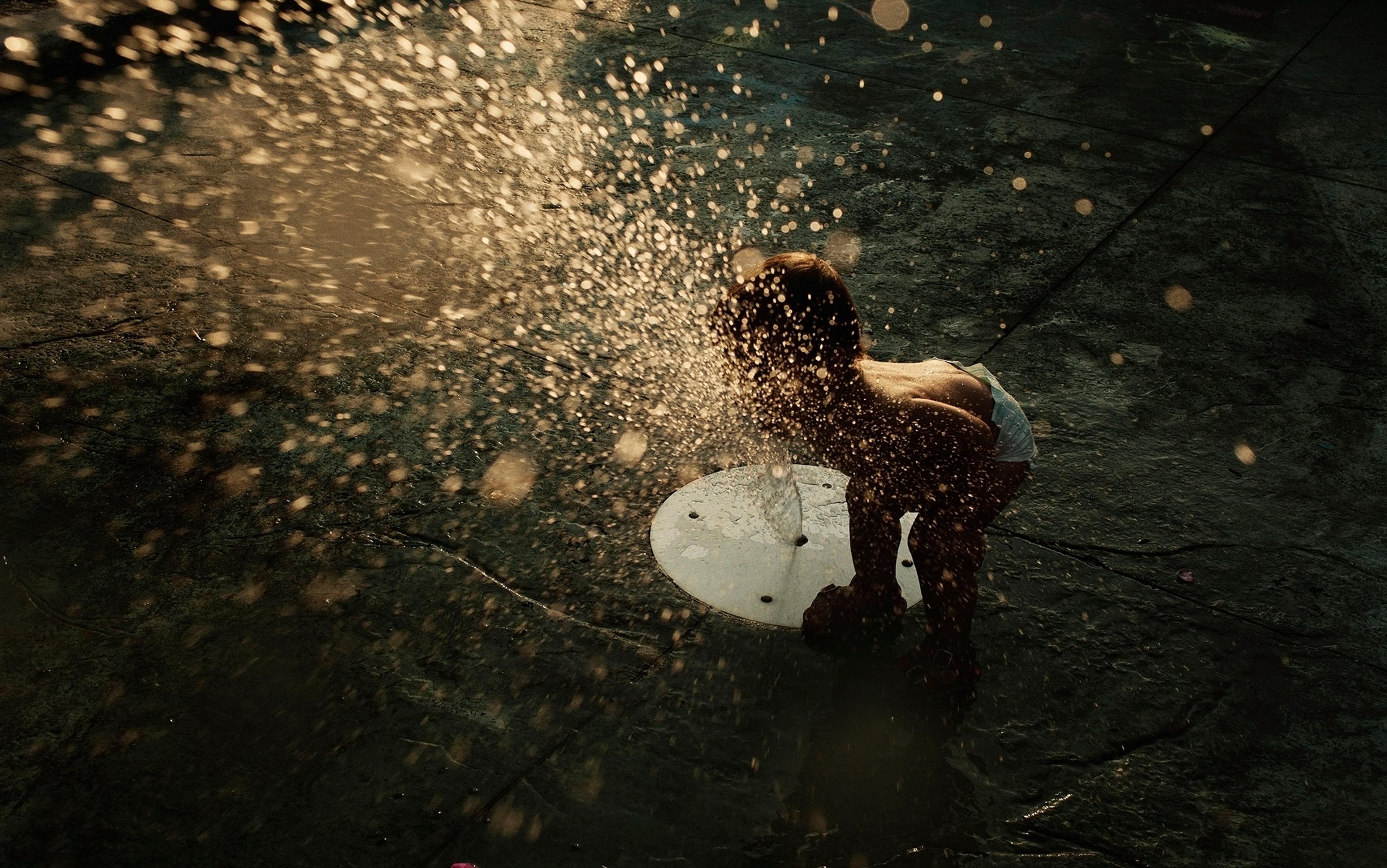

You’re astonishing!
Life can be better appreciated when you remember how wonderfully and frighteningly unlikely it is that you exist at all
Timm Triplett
Virtues and vices
Look on the dark side
We must keep the flame of pessimism burning: it is a virtue for our deeply troubled times, when crude optimism is a vice
Mara van der Lugt
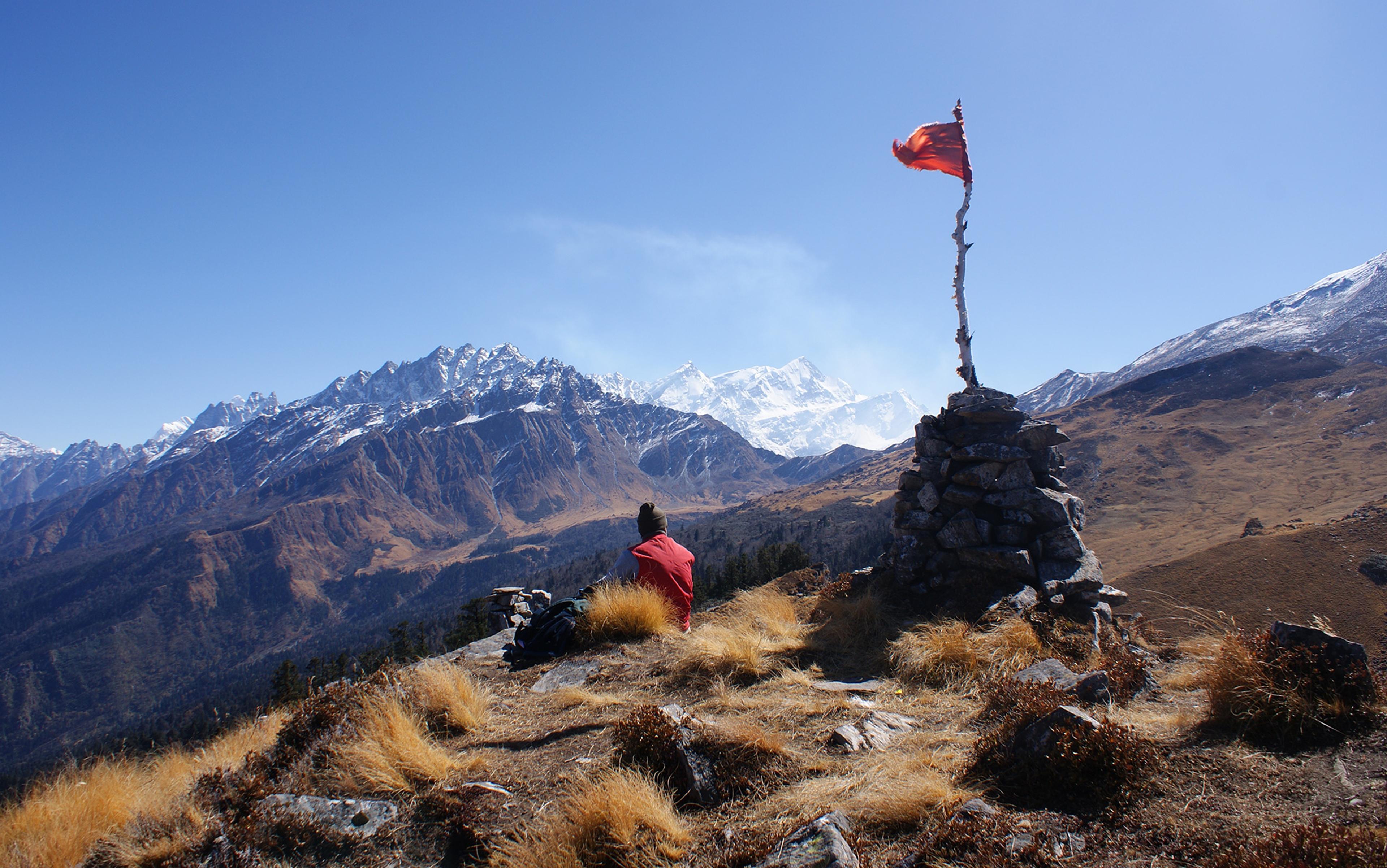

The end of travel
Driven by the need for a storied life, I relished the opportunity for endless travel. Is that a moment in time, now over?
Henry Wismayer

To know or not to know? Lillian weighs the costs of a life-changing genetic test

Your complimentary articles
You’ve read one of your four complimentary articles for this month.
You can read four articles free per month. To have complete access to the thousands of philosophy articles on this site, please

Question of the Month
What is life, the following answers to this fundamental question each win a random book..
Life is the aspect of existence that processes, acts, reacts, evaluates, and evolves through growth (reproduction and metabolism). The crucial difference between life and non-life (or non-living things) is that life uses energy for physical and conscious development. Life is anything that grows and eventually dies, i.e., ceases to proliferate and be cognizant. Can we say that viruses, for example, are cognizant? Yes, insofar as they react to stimuli; but they are alive essentially because they reproduce and grow. Computers are non-living because even though they can cognize, they do not develop biologically (grow), and cannot produce offspring. It is not cognition that determines life, then: it is rather proliferation and maturation towards a state of death; and death occurs only to living substances.
Or is the question, ‘What is the meaning (purpose) of life?’ That’s a real tough one. But I think that the meaning of life is the ideals we impose upon it, what we demand of it. I’ve come to reaffirm my Boy Scout motto, give or take a few words, that the meaning of life is to: Do good, Be Good, but also to Receive Good. The foggy term in this advice, of course, is ‘good’; but I leave that to the intuitive powers that we all share.
There are, of course, many intuitively clear examples of Doing Good: by retrieving a crying baby from a dumpster; by trying to rescue someone who’s drowning. Most of us would avoid murdering; and most of us would refrain from other acts we find intuitively wrong. So our natural intuitions determine the meaning of life for us; and it seems for other species as well, for those intuitions resonate through much of life and give it its purpose.
Tom Baranski, Somerset, New Jersey
The ceramic artist Edmund de Waal places an object in front of him and begins to tell a story. Even if the patina, chips and signs of repair of the inanimate object hint at its history, the story is told by a living observer. A living thing is an object that contains its story within itself. Life’s story is held in the genome, based in DNA. Maybe other ways for memorising the story may be discovered, but in environments subject to common chemical processes, common methods are likely to emerge.
Although we have only the example of the Earth, it shows that life will evolve to fill every usable niche, and to secure and further diversify those niches. This should not be thought of as purposeful. Life embodies a ‘plan’, but one that does not specify ends, only methods acquired iteratively. Inanimate processes can be cyclic but not iterative: they do not learn from past mistakes.
Life exists at many levels. Life is also a process through which energy and materials are transformed; but so is non-life. The difference is that the process of life is intimately linked to story it contains, whereas non-life is indifferent to the story we impose upon it. Yet life is only a story, so it can act only through matter. Therefore life is by nature a toolmaker. Its tools are potentially everything that exists, and its workshop is potentially the whole universe. So why do humans risk undermining the life of which they are part? Because they try to impose upon it a story of their own making. Yet humans, the ‘tool-making animals’, are themselves tools of life, in an unplanned experiment.
Nicholas Taylor, Little Sandhurst, Berkshire
First the technical definition. Life is self-organising chemistry which reproduces itself and passes on its evolved characteristics, encoded in DNA. In thermodynamics terms, it has the ability to reduce local entropy or disorganisation, thus locally contravening the third law of thermodynamics.
But what is life really about , if anything? The two possibilities are, life is either a meaningless accident arising from the laws of physics operating in a meaningless universe, or it is a step in a planned ‘experiment’. I say ‘step’, because this cannot be the end. The current state of life is as yet too unstable and undeveloped for it to be the end. And I say ‘experiment’ because the evolutionary nature of life suggests that its future is not known. If therefore the universe itself has a purpose, it seems most likely to be to explore what the outcome of the evolutionary experiment would be.
But what will be the outcome? If, as many physicists now believe, the universe is only information, then harnessing all the resources of the universe in one giant evolutionary process could plausibly provide a useful outcome for a species clever enough to create the universe in the first place. On this interpretation, life will ultimately organise all the physical resources of the universe into a single self-conscious intelligence, which in turn will then be able to interact with its creator(s).
Dr Harry Fuchs, Flecknoe, Warwickshire
Life is the embodiment of selfishness! Life is selfish because it is for itself in two ways: it is for its own survival, and it is for its own reproduction. This desire is embodied in an adaptive autocatalytic chemical system, forming life’s embodied mind.
Anything that is not itself is the other; and the collection of others constitute its environment. The organism must destructively use the other to satisfy its reproductive desire, but on achieving this, it produces an additional other – but now one that also embodies its own selfish aim and the means to satisfy this aim. Therefore, even by an organism satisfying its desire, it makes the continuing satisfaction of its desires ever more difficult to achieve. A partial solution to this dilemma is for genetically-related entities to form a cooperating society.
The underlying mechanism of evolution is therefore the iteration of the embodied desire within an ever more complex competitive and social environment. Over vast numbers of iterations, this process forces some life-forms along a pathway that solves the desire for survival and reproduction by developing ever more complex and adaptable minds. This is achieved by supplementing their underlying cellular embodied chemistry with a specialist organ (although still based on chemistry) that we call its brain, able to rapidly process electrical signals. Advanced minds can collect and process vast inputs of data by ‘projecting’ the derived output back onto its environmental source, that is by acting. However advanced it might be, an organism is still driven by the same basic needs for survival and reproduction. The creative process, however, leads the organism towards an increasingly aesthetic experience of the world. This is why for us the world we experience is both rich and beautiful.
Dr Steve Brewer, St Ives, Cornwall
In our scientific age, we look to the biologists to define ‘life’ for us. After all, it is their subject matter. I believe they have yet to reach consensus, but a biological definition would be something like, ‘Life is an arrangement of molecules with qualities of self-sustenance and self-replication’. This kind of definition might serve the purposes of biologists, but for me, it has five deficiencies. First, any definition of life by biologists would have little utility outside biology because of its necessary inclusiveness. We humans would find ourselves in a class of beings that included the amoeba. ‘Life’ would be the limited common properties of all organisms, including the lowest. Second, the scientific definition of life is necessarily an external one. I think that knowing what life is, as opposed to defining it, requires knowing it from within. Non-sentient organisms live, but they do not know life. Third, in the scientific definition, there is no place for life having value. However, many would say that life has value in its own right – that it is not simply that we humans value life and so give it value, but that it has value intrinsically. Fourth, there is the question of life as a whole having a purpose or goal. This notion is not scientific, but one wonders if the tools of science are fit to detect any evolutionary purpose, if there is one. Fifth, for the scientists, life is a set of biological conditions and processes. However, everywhere and always, people have conceived of a life after biological death, a life of spirit not necessarily dependent on the physical for existence.
The scientific definition of life is valid in its context, but otherwise I find it impoverished. I believe there is a hierarchy of living beings from the non-sentient, to the sentient, to humans, and perhaps up to God. When I ask, ‘What is life? I want to know what life is at its highest form. I believe life at its best is spirit: it is active, sentient, feeling, thinking, purposive, valuing, social, other-respecting, relating, and caring.
John Talley, Rutherfordton, NC
I listen enthralled to scientific debate on what, how, when and where life was created. However, questions remain which may never be resolved. In this vacuum, philosophers and religious thinkers have attempted to give meaning to life by suggesting goals: Plato suggested the acquisition of knowledge, Aristotle to practice virtue, and the Stoics, mental fortitude and self-control. Today’s philosophers echo the existentialist view that life is full of absurdity, although they also tell us that we must put meaning into life by making our own values in an indifferent world. But if life is just a journey from womb to tomb, will such ‘meaning’ be sufficient to allow the traveller at journey’s end to feel that it was worthwhile?
Perhaps the hypothesis upon which Ivan Tyrrell and Joe Griffin have based their therapy could help (see Human Givens , 2003). They describe that we are born with evolved needs that seek satisfaction from our environment. These are physical and emotional needs, which, when enough of them are met, ensure the health of the individual, maximising his or her ability to achieve meaning in life. Griffin and Tyrrell have proven empirically that when sufficient needs are met an individual will enjoy mental and physical health, unless there is damage or toxicity in the environment. Some of these needs were identified by Maslow in his ‘Hierarchy of Needs’ in his 1943 paper ‘A Theory of Human Motivation’, Psychological Review , 50 (4), but Griffin and Tyrrell focus more clearly on emotional needs such as:
• To achieve, and to feel competent
• To fulfil our sense of autonomy and control
• To be emotionally connected to other people and part of a larger community
• To have a sense of status within social groupings
• For privacy and rest, to reflect and consolidate learning
• And yes – to have meaning in one’s life
Meaning becomes difficult, if not impossible, to achieve if these needs are insufficiently satisfied. Unfortunately, modern society seeks meaning to life through materialism, to the detriment of our biological needs, leading to dissatisfaction and a consequent inability to find meaning. The result is an exponential increase in mental ill-health. Sadly, then, many of us will not experience the satisfaction of a meaningful life journey.
Caryl A. Fuchs, Flecknoe, Warwickshire
Life is the eternal and unbroken flow of infinite rippling simultaneous events that by a fortuitous chain has led to this universe of elements we are all suspended in, that has somehow led to this present experience of sentient existence. Animal life (excluding that of humans) shows that life is a simple matter of being, by means of a modest routine of eating, sleeping and reproducing. Animals balance their days between these necessities, doing only what their bodies ask of them. The life of vegetation is not far from that of animals. They eat and sleep and reproduce in their own way, for the same result. So life is a beautiful and naturally harmonious borrowing of energy.
Yet we have taken it for granted. We have lost the power to simply be happy eating, sleeping, reproducing, believing we need a reason to be alive, a purpose and a goal to reach, so that on our deathbeds (something we have been made to fear) we can look back and tell ourselves we have done something with our lives. Life has lost its purpose because we have tried to give it one. The truth is that we are no more significant than the sand by the sea or the clouds in the sky. No more significant. But as significant.
No matter what your race, religion or gender, when you first step outside your door in the morning and feel the fresh air in your lungs and the morning sun on your face, you close your eyes and smile. In that moment you are feeling life as it should be. No defining, no understanding, no thinking. Just that feeling of pure bliss. For that is what life is.
Courtney Walsh, Farnborough, Hampshire
Of all Webster’s definitions of ‘life’, the one for me that best covers it is, “the sequence of physical and mental experiences that make up the existence of an individual.” Indeed, life is a continuum of accomplishment, failure, discovery, dilemma, challenge, boredom, sadness, disappointment, appreciation, the giving and receipt of grace, empathy, peace, and our reactions to all sorts of stimuli – touch, love, friendship, loss… One can either merely exist or try to achieve, working through the difficult times, perhaps learning a thing or two. Everyone has a story. I’ve been surprised when learning something new about an acquaintance or friend that must have been very difficult to manage or survive; but there they are in front of me. It’s how you come out on the other side of those challenging times that is important. How you land, get on with it, and keep on truckin’.
Life cannot be planned: there’s fate, and there’s simple bad luck. Failure can bring crushing disappointment, or you can try and make a new plan. A person can waste an inordinate amount of time mourning what they don’t have, or plans that don’t work out. But who wants to waste that much time regretting?
Life has happy surprises, small moments to cherish. It’s a matter of weighing the good and bad times – the challenge is to balance both, ending up with a life looked back on that was worth the mighty effort. I’m not meaning to sound like a Pollyanna – I assure you I’m not – it’s just more pleasant to strive for a modicum of equilibrium. If I can manage that, I’m good.
Cheryl Anderson, Kenilworth, Illinois
“Life’s but a walking shadow, a poor player, That struts and frets his hour upon the stage And then is heard no more. It is a tale Told by an idiot, full of sound and fury, Signifying nothing.” ( Macbeth , Act V, Scene V)
These words of Shakespeare’s Macbeth summarize interesting ideas about the nature of life. The first line expresses two of the three marks of existence as per Buddhist thinking, Anicca , impermanence, and Anatta , non-self: a “walking shadow” is as insubstantial and impermanent as anything imaginable; a “poor player” neither creates nor directs his role, and the character being played only exists because of an author. Macbeth’s entire statement, particularly the last sentence, expresses the third Buddhist mark of existence: Dukkha , dissatisfaction.
The stage metaphor in the second line represents boundaries or limits. Scientific research into the nature of life often focuses on the material, energetic, and temporal limitations within which life can exist. The temporal limit of life is known as death. In the spirit of this interpretation, the idea of being “heard no more” could imply that life constantly evolves new forms while discarding older ones.
Macbeth hints at the wisdom of mystery traditions while anticipating the revelations of genetic science by stating that life “is a tale”. Now, this refers to the language-based, or code-based, nature of life. Readers may consider this in relation to DNA and RNA, and also in relation to John’s Gospel: “In the beginning was the Word, and the Word was with God, and the Word was God.” (The implications of the phrase “told by an idiot” exceed the scope of this inquiry.)
In five concise and poetic lines, Shakespeare defined life as an impermanent, non-self-directed, unsatisfactory, limited, ever-changing, and ultimately insignificant code.
Devon Hall, Albuquerque, New Mexico
Life is the realisation of its own contingency. But that’s not the end of it; it’s merely the means towards the creation of meaning. Life is thus a constant process of becoming, through creating values and meaning. Life is therefore perpetual transcendence, always moving into the future, creating the present. Life is also acceptance: the acceptance of finitude; acceptance of one’s responsibilities; acceptance of other human beings’ existence and choices. Life is neither fixed nor absolute, it is ambiguous; life is the possibilities entailed by existence. Life is the consciousness of humanity; it is perception of the world and the universe. So life is sadness; life is death. Life is suffering and destruction. But life is also happiness; life is living. Life is joy and creativity. Life is finding a cause to survive, a reason not to die – not yet. It is youth and old age, with everything in between. Overall, life is beautiful – ugliness is fleeting. Corpses and skeletons are lugubrious; living flesh is resplendent, all bodies are statuesque. Human life is love and hate, but it can only be life when we are with others. Life as fear and hatred is not real life at all. For some, life is God. We would all then be His children. We are nevertheless the spawn of the Earth.
Human existence is freedom – an edifice of plurality.
Greg Chatterton, Cupar, Fife
If the ancients could do philosophy in the marketplace, maybe I can too. So I employed some modern technology by texting the question ‘What is Life?’ to all my contacts. I didn’t explain the context of the question, to avoid lyrical waxing. Here are a sample of replies. Life is: being conscious of yourself and others; a being with a soul; experience; what you make it; your chance to be a success; family; living as long as you can; not being dead; greater than the sum of its parts; complex chemical organisation; different things to different people; a mystery; a journey; don’t know; a quote from a song, “baby don’t hurt me”; life begins after death. I asked a regular in my favourite café. They said, “man’s chief end is to glorify God and enjoy him forever.” A person suffering from a degenerative disease answered: “life is sh** then you die.” Another with the same illness interviewed in our local newspaper said, “My life is a mission to help other sufferers.” A colleague said “some would want to shoot themselves if they had my life, but I’m happy.” I posed the question at my art club and we did no painting that day…
I was surprised to find that I had no immediate definition of life myself (hence the idea to ask) and that there is no consensus (only one reply was repeated), but then, that also is life.
I sometimes catch myself considering life when I arrive at the turning point on my evening walk. It’s a dark spot which makes stargazing easier, and the heavens are a good place to start, since life as we know it began there (the heavier atoms like carbon which make up our bodies initially formed in dying Red Giant stars). This makes me feel two things about my life: it’s a dot because the cosmos is immense; but it’s an important dot in the cosmos because I can consider it.
Kristine Kerr, Gourock, Renfrewshire
Next Question of the Month
Now we know what life is, the next question is, How Should I Live? Please give and justify your ethical advice in less than 400 words. The prize is a semi-random book from our book mountain. Subject lines or envelopes should be marked ‘Question of the Month’, and must be received by 9th June. If you want a chance of getting a book, please include your physical address. Submission implies permission to reproduce your answer physically and electronically. Thank you.
This site uses cookies to recognize users and allow us to analyse site usage. By continuing to browse the site with cookies enabled in your browser, you consent to the use of cookies in accordance with our privacy policy . X
- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section The Meaning of Life
Introduction, introductory works.
- General Overviews
- Anthologies
- Precursors to the Contemporary Debate
- The Meaning of “Meaning”
- God-based Theories
- Soul-based Theories
- Subjectivism
- Intersubjectivism
- Objectivism
- Non-Naturalism
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Anti-Natalism
- God and Possible Worlds
- Philosophy of Boredom
- Philosophy of Religion
- The Problem of Evil
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- Alfred North Whitehead
- Feminist Aesthetics and Feminist Philosophy of Art
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
The Meaning of Life by Thaddeus Metz LAST REVIEWED: 10 May 2010 LAST MODIFIED: 10 May 2010 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780195396577-0070
For millennia, thinkers have addressed the question of what, if anything, makes a life meaningful in some form or other. This article concentrates nearly exclusively on approaches to the question taken by analytic philosophers in the postwar era, by and large omitting reference to prewar Anglo-American works, texts from other traditions such as Continental or African philosophy, and writings from nonphilosophical but related fields such as religion and psychology. Much of the contemporary analytic discussion has sought to articulate and evaluate theories of meaning in life, i.e., general and fundamental principles of what all meaningful conditions have in common as distinct from meaningless ones. This entry accordingly focuses largely on these theories, which are distinguished according to the kind of property that is held to constitute meaning in life (see Supernaturalism , Naturalism , and Non-Naturalism ).
These texts are more introductory or have been written in a way that would likely be accessible to those not thoroughly trained in analytic philosophy. Baggini 2004 and Eagleton 2007 are pitched at a very wide, popular audience; Thomson 2003 and Belshaw 2005 would be best for undergraduate philosophy majors; and Belliotti 2001 , Martin 2002 , and Cottingham 2003 are probably most apt for those with some kind of university education or other intellectual development, not necessarily in Anglo-American philosophy.
Baggini, Julian. What’s It All About? Philosophy and the Meaning of Life . London: Granta, 2004.
Defends the view that meaning in life is largely a function of love; addresses approaches or maxims (e.g., Carpe diem ) more than it does principles.
Belliotti, Raymond Angelo. What Is the Meaning of Human Life? Amsterdam: Rodopi, 2001.
A thoughtful treatment of a variety of issues; defends an objective naturalist approach to meaning in the context of critical discussion of classic thinkers such as Aristotle, Nietzsche, and Schopenhauer.
Belshaw, Christopher. Ten Good Questions about Life and Death . Malden, MA: Blackwell, 2005.
Engagingly written, analytic treatments of several key “life and death” issues, many of which bear on meaningfulness, which the author cashes out objectively in terms of relationships and projects.
Cottingham, John. On the Meaning of Life . Thinking in Action. London: Routledge, 2003.
An elegantly written book that defends an Aristotelian, God-based (but not soul-based) approach to meaning in life.
Eagleton, Terry. The Meaning of Life: A Very Short Introduction . Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2007.
A light and lively essay on a variety of facets of the question of life’s meaning, often addressing linguistic and literary themes. Rejects subjective or “postmodern” approaches to meaning in favor of a need for harmonious or loving relationships.
Martin, Michael. Atheism, Morality, and Meaning . Amherst, NY: Prometheus, 2002.
A vigorous defense of a naturalist approach to morality, in the first half of the book, and to meaning, in the second. Very critical of Christian approaches to both.
Thomson, Garrett. On the Meaning of Life . London: Thompson/Wadsworth, 2003.
Argues that nine common views on meaning in life (e.g., that an infinite being is necessary for meaning or that meaning is exhausted by happiness) are flawed. Emphasizes that meaning must reside largely in activities we engage in, lest our lives be reduced to “tools” for the sake of ends beyond us.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Philosophy »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- A Priori Knowledge
- Abduction and Explanatory Reasoning
- Abstract Objects
- Addams, Jane
- Adorno, Theodor
- Aesthetic Hedonism
- Aesthetics, Analytic Approaches to
- Aesthetics, Continental
- Aesthetics, Environmental
- Aesthetics, History of
- African Philosophy, Contemporary
- Alexander, Samuel
- Analytic/Synthetic Distinction
- Anarchism, Philosophical
- Animal Rights
- Anscombe, G. E. M.
- Anthropic Principle, The
- Applied Ethics
- Aquinas, Thomas
- Argument Mapping
- Art and Emotion
- Art and Knowledge
- Art and Morality
- Astell, Mary
- Aurelius, Marcus
- Austin, J. L.
- Bacon, Francis
- Bayesianism
- Bergson, Henri
- Berkeley, George
- Biology, Philosophy of
- Bolzano, Bernard
- Boredom, Philosophy of
- British Idealism
- Buber, Martin
- Buddhist Philosophy
- Burge, Tyler
- Business Ethics
- Camus, Albert
- Canterbury, Anselm of
- Carnap, Rudolf
- Cavendish, Margaret
- Chemistry, Philosophy of
- Childhood, Philosophy of
- Chinese Philosophy
- Cognitive Ability
- Cognitive Phenomenology
- Cognitive Science, Philosophy of
- Coherentism
- Communitarianism
- Computational Science
- Computer Science, Philosophy of
- Computer Simulations
- Comte, Auguste
- Conceptual Role Semantics
- Conditionals
- Confirmation
- Connectionism
- Consciousness
- Constructive Empiricism
- Contemporary Hylomorphism
- Contextualism
- Contrastivism
- Cook Wilson, John
- Cosmology, Philosophy of
- Critical Theory
- Culture and Cognition
- Daoism and Philosophy
- Davidson, Donald
- de Beauvoir, Simone
- de Montaigne, Michel
- Decision Theory
- Deleuze, Gilles
- Derrida, Jacques
- Descartes, René
- Descartes, René: Sensory Representations
- Descriptions
- Dewey, John
- Dialetheism
- Disagreement, Epistemology of
- Disjunctivism
- Dispositions
- Divine Command Theory
- Doing and Allowing
- du Châtelet, Emilie
- Dummett, Michael
- Dutch Book Arguments
- Early Modern Philosophy, 1600-1750
- Eastern Orthodox Philosophical Thought
- Education, Philosophy of
- Engineering, Philosophy and Ethics of
- Environmental Philosophy
- Epistemic Basing Relation
- Epistemic Defeat
- Epistemic Injustice
- Epistemic Justification
- Epistemic Philosophy of Logic
- Epistemology
- Epistemology and Active Externalism
- Epistemology, Bayesian
- Epistemology, Feminist
- Epistemology, Internalism and Externalism in
- Epistemology, Moral
- Epistemology of Education
- Ethical Consequentialism
- Ethical Deontology
- Ethical Intuitionism
- Eugenics and Philosophy
- Events, The Philosophy of
- Evidence-Based Medicine, Philosophy of
- Evidential Support Relation In Epistemology, The
- Evolutionary Debunking Arguments in Ethics
- Evolutionary Epistemology
- Experimental Philosophy
- Explanations of Religion
- Extended Mind Thesis, The
- Externalism and Internalism in the Philosophy of Mind
- Faith, Conceptions of
- Feminist Philosophy
- Feyerabend, Paul
- Fichte, Johann Gottlieb
- Fictionalism
- Fictionalism in the Philosophy of Mathematics
- Film, Philosophy of
- Foot, Philippa
- Foreknowledge
- Forgiveness
- Formal Epistemology
- Foucault, Michel
- Frege, Gottlob
- Gadamer, Hans-Georg
- Geometry, Epistemology of
- God, Arguments for the Existence of
- God, The Existence and Attributes of
- Grice, Paul
- Habermas, Jürgen
- Hart, H. L. A.
- Heaven and Hell
- Hegel, Georg Wilhelm Friedrich: Aesthetics
- Hegel, Georg Wilhelm Friedrich: Metaphysics
- Hegel, Georg Wilhelm Friedrich: Philosophy of History
- Hegel, Georg Wilhelm Friedrich: Philosophy of Politics
- Heidegger, Martin: Early Works
- Hermeneutics
- Higher Education, Philosophy of
- History, Philosophy of
- Hobbes, Thomas
- Horkheimer, Max
- Human Rights
- Hume, David: Aesthetics
- Hume, David: Moral and Political Philosophy
- Husserl, Edmund
- Idealizations in Science
- Identity in Physics
- Imagination
- Imagination and Belief
- Immanuel Kant: Political and Legal Philosophy
- Impossible Worlds
- Incommensurability in Science
- Indian Philosophy
- Indispensability of Mathematics
- Inductive Reasoning
- Instruments in Science
- Intellectual Humility
- Intentionality, Collective
- James, William
- Japanese Philosophy
- Kant and the Laws of Nature
- Kant, Immanuel: Aesthetics and Teleology
- Kant, Immanuel: Ethics
- Kant, Immanuel: Theoretical Philosophy
- Kierkegaard, Søren
- Knowledge-first Epistemology
- Knowledge-How
- Kristeva, Julia
- Kuhn, Thomas S.
- Lacan, Jacques
- Lakatos, Imre
- Langer, Susanne
- Language of Thought
- Language, Philosophy of
- Latin American Philosophy
- Laws of Nature
- Legal Epistemology
- Legal Philosophy
- Legal Positivism
- Leibniz, Gottfried Wilhelm
- Levinas, Emmanuel
- Lewis, C. I.
- Literature, Philosophy of
- Locke, John
- Locke, John: Identity, Persons, and Personal Identity
- Lottery and Preface Paradoxes, The
- Machiavelli, Niccolò
- Martin Heidegger: Later Works
- Martin Heidegger: Middle Works
- Material Constitution
- Mathematical Explanation
- Mathematical Pluralism
- Mathematical Structuralism
- Mathematics, Ontology of
- Mathematics, Philosophy of
- Mathematics, Visual Thinking in
- McDowell, John
- McTaggart, John
- Meaning of Life, The
- Mechanisms in Science
- Medically Assisted Dying
- Medicine, Contemporary Philosophy of
- Medieval Logic
- Medieval Philosophy
- Mental Causation
- Merleau-Ponty, Maurice
- Meta-epistemological Skepticism
- Metaepistemology
- Metametaphysics
- Metaphilosophy
- Metaphysical Grounding
- Metaphysics, Contemporary
- Metaphysics, Feminist
- Midgley, Mary
- Mill, John Stuart
- Mind, Metaphysics of
- Modal Epistemology
- Models and Theories in Science
- Montesquieu
- Moore, G. E.
- Moral Contractualism
- Moral Naturalism and Nonnaturalism
- Moral Responsibility
- Multiculturalism
- Murdoch, Iris
- Music, Analytic Philosophy of
- Nationalism
- Natural Kinds
- Naturalism in the Philosophy of Mathematics
- Naïve Realism
- Neo-Confucianism
- Neuroscience, Philosophy of
- Nietzsche, Friedrich
- Nonexistent Objects
- Normative Ethics
- Normative Foundations, Philosophy of Law:
- Normativity and Social Explanation
- Objectivity
- Occasionalism
- Ontological Dependence
- Ontology of Art
- Ordinary Objects
- Other Minds
- Panpsychism
- Particularism in Ethics
- Pascal, Blaise
- Paternalism
- Peirce, Charles Sanders
- Perception, Cognition, Action
- Perception, The Problem of
- Perfectionism
- Persistence
- Personal Identity
- Phenomenal Concepts
- Phenomenal Conservatism
- Phenomenology
- Philosophy for Children
- Photography, Analytic Philosophy of
- Physicalism
- Physicalism and Metaphysical Naturalism
- Physics, Experiments in
- Political Epistemology
- Political Obligation
- Political Philosophy
- Popper, Karl
- Pornography and Objectification, Analytic Approaches to
- Practical Knowledge
- Practical Moral Skepticism
- Practical Reason
- Probabilistic Representations of Belief
- Probability, Interpretations of
- Problem of Divine Hiddenness, The
- Problem of Evil, The
- Propositions
- Psychology, Philosophy of
- Quine, W. V. O.
- Racist Jokes
- Rationalism
- Rationality
- Rawls, John: Moral and Political Philosophy
- Realism and Anti-Realism
- Realization
- Reasons in Epistemology
- Reductionism in Biology
- Reference, Theory of
- Reid, Thomas
- Reliabilism
- Religion, Philosophy of
- Religious Belief, Epistemology of
- Religious Experience
- Religious Pluralism
- Ricoeur, Paul
- Risk, Philosophy of
- Rorty, Richard
- Rousseau, Jean-Jacques
- Rule-Following
- Russell, Bertrand
- Ryle, Gilbert
- Sartre, Jean-Paul
- Schopenhauer, Arthur
- Science and Religion
- Science, Theoretical Virtues in
- Scientific Explanation
- Scientific Progress
- Scientific Realism
- Scientific Representation
- Scientific Revolutions
- Scotus, Duns
- Self-Knowledge
- Sellars, Wilfrid
- Semantic Externalism
- Semantic Minimalism
- Senses, The
- Sensitivity Principle in Epistemology
- Shepherd, Mary
- Singular Thought
- Situated Cognition
- Situationism and Virtue Theory
- Skepticism, Contemporary
- Skepticism, History of
- Slurs, Pejoratives, and Hate Speech
- Smith, Adam: Moral and Political Philosophy
- Social Aspects of Scientific Knowledge
- Social Epistemology
- Social Identity
- Sounds and Auditory Perception
- Space and Time
- Speech Acts
- Spinoza, Baruch
- Stebbing, Susan
- Strawson, P. F.
- Structural Realism
- Supererogation
- Supervenience
- Tarski, Alfred
- Technology, Philosophy of
- Testimony, Epistemology of
- Theoretical Terms in Science
- Thomas Aquinas' Philosophy of Religion
- Thought Experiments
- Time and Tense
- Time Travel
- Transcendental Arguments
- Truth and the Aim of Belief
- Truthmaking
- Turing Test
- Two-Dimensional Semantics
- Understanding
- Uniqueness and Permissiveness in Epistemology
- Utilitarianism
- Value of Knowledge
- Vienna Circle
- Virtue Epistemology
- Virtue Ethics
- Virtues, Epistemic
- Virtues, Intellectual
- Voluntarism, Doxastic
- Weakness of Will
- Weil, Simone
- William of Ockham
- Williams, Bernard
- Wittgenstein, Ludwig: Early Works
- Wittgenstein, Ludwig: Later Works
- Wittgenstein, Ludwig: Middle Works
- Wollstonecraft, Mary
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [91.193.111.216]
- 91.193.111.216

- Table of Contents
- New in this Archive
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
The Meaning of Life
Many major historical figures in philosophy have provided an answer to the question of what, if anything, makes life meaningful, although they typically have not put it in these terms. Consider, for instance, Aristotle on the human function, Aquinas on the beatific vision, and Kant on the highest good. While these concepts have some bearing on happiness and morality, they are straightforwardly construed as accounts of which final ends a person ought to realize in order to have a life that matters. Despite the venerable pedigree, it is only in the last 50 years or so that something approaching a distinct field on the meaning of life has been established in Anglo-American philosophy, and it is only in the last 30 years that debate with real depth has appeared. Concomitant with the demise of positivism and of utilitarianism in the post-war era has been the rise of analytical enquiry into non-hedonistic conceptions of value, including conceptions of meaning in life, grounded on relatively uncontroversial (but not certain or universally shared) judgments of cases, often called “intuitions.” English-speaking philosophers can be expected to continue to find life's meaning of interest as they increasingly realize that it is a distinct topic that admits of rational enquiry to no less a degree than more familiar ethical categories such as well-being, virtuous character, and right action.
This survey critically discusses approaches to meaning in life that are prominent in contemporary Anglo-American philosophical literature. To provide context, sometimes it mentions other texts, e.g., in Continental philosophy or from before the 20 th century. However, the central aim is to acquaint the reader with recent analytic work on life's meaning and to pose questions about it that are currently worthy of consideration.
When the topic of the meaning of life comes up, people often pose one of two questions: “So, what is the meaning of life?” and “What are you talking about?” The literature can be divided in terms of which question it seeks to answer. This discussion starts off with works that address the latter, abstract question regarding the sense of talk of “life's meaning,” i.e., that aim to clarify what we are asking when we pose the question of what, if anything, makes life meaningful. Afterward, it considers texts that provide answers to the more substantive question about the nature of meaning as a property. Some accounts of what make life meaningful provide particular ways to do so, e.g., by making certain achievements (James 2005), developing moral character (Thomas 2005), or learning from relationships with family members (Velleman 2005). However, most recent discussions of meaning in life are attempts to capture in a single principle all the variegated conditions that can confer meaning on life. This survey focuses heavily on the articulation and evaluation of these theories of what would make life meaningful. It concludes by examining nihilist views that the conditions necessary for meaning in life do not obtain for any of us, i.e., that all our lives are meaningless.
1. The Meaning of “Meaning”
- 2.1 God-Centered Views
- 2.2 Soul-Centered Views
3.1 Subjectivism
3.2 objectivism, 4. nihilism, works cited, collections, books for the general reader, other internet resources, related entries.
One part of the field of life's meaning consists of the systematic attempt to clarify what people mean when they ask in virtue of what life has meaning. This section addresses different accounts of the sense of talk of “life's meaning” (and of “significance,” “importance,” and other synonyms). A large majority of those writing on life's meaning deem talk of it centrally to indicate a positive final value that an individual's life can exhibit. That is, comparatively few believe either that a meaningful life is a merely neutral quality, or that what is of key interest is the meaning of the human species or universe as a whole (for discussions focused on the latter, see Edwards 1972; Munitz 1986; Seachris 2009). Most in the field have ultimately wanted to know whether and how the existence of one of us over time has meaning, a certain property that is desirable for its own sake.
Beyond drawing the distinction between the life of an individual and that of a whole, there has been very little discussion of life as the logical bearer of meaning. For instance, is the individual's life best understood biologically, qua human being, or instead as the existence of a person that may or may not be human (Flanagan 1996)? And if an individual is loved from afar, can it logically affect the meaningfulness of her “life” (Brogaard and Smith 2005, 449)?
Returning to topics on which there is consensus, most writing on meaning believe that it comes in degrees such that some periods of life are more meaningful than others and that some lives as a whole are more meaningful than others (perhaps contra Britton 1969, 192). Note that one can coherently hold the view that some people's lives are less meaningful than others, or even meaningless, and still maintain that people have an equal moral status. Consider a consequentialist view according to which each individual counts for one in virtue of having a capacity for a meaningful life (cf. Railton 1984), or a Kantian view that says that people have an intrinsic worth in virtue of their capacity for autonomous choices, where meaning is a function of the exercise of this capacity (Nozick 1974, ch. 3). On both views, morality could counsel an agent to help people with relatively meaningless lives, at least if the condition is not of their choosing.
Another uncontroversial element of the sense of “meaningfulness” is that it connotes a good that is conceptually distinct from happiness or rightness (something emphasized in Wolf 2010). First, to ask whether someone's life is meaningful is not one and the same as asking whether her life is happy or pleasant. A life in an experience or virtual reality machine could conceivably be happy but very few take it to be a prima facie candidate for meaningfulness (Nozick 1974: 42–45). Indeed, many would say that talk of “meaning” by definition excludes the possibility of it coming from time spent in an experience machine (although there have been a small handful who disagree and contend that a meaningful life just is a pleasant life. Goetz 2012, in particular, bites many bullets.) Furthermore, one's life logically could become meaningful precisely by sacrificing one's happiness, e.g., by helping others at the expense of one's self-interest.
Second, asking whether a person's existence is significant is not identical to considering whether she has been morally upright; there seem to be ways to enhance meaning that have nothing to do with morality, at least impartially conceived, for instance, making a scientific discovery.
Of course, one might argue that a life would be meaningless if (or even because) it were unhappy or immoral, particularly given Aristotelian conceptions of these disvalues. However, that is to posit a synthetic, substantive relationship between the concepts, and is far from indicating that speaking of “meaning in life” is analytically a matter of connoting ideas regarding happiness or rightness, which is what I am denying here. My point is that the question of what makes a life meaningful is conceptually distinct from the question of what makes a life happy or moral, even if it turns out that the best answer to the question of meaning appeals to an answer to one of these other evaluative questions.
If talk about meaning in life is not by definition talk about happiness or rightness, then what is it about? There is as yet no consensus in the field. One answer is that a meaningful life is one that by definition has achieved choice-worthy purposes (Nielsen 1964) or involves satisfaction upon having done so (Hepburn 1965; Wohlgennant 1981). However, for such an analysis to clearly demarcate meaningfulness from happiness, it would be useful to modify it to indicate which purposes are germane to the former. On this score, some suggest that conceptual candidates for grounding meaning are purposes that not only have a positive value, but also render a life coherent (Markus 2003), make it intelligible (Thomson 2003, 8–13), or transcend animal nature (Levy 2005).
Now, it might be that a focus on any kind of purpose is too narrow for ruling out the logical possibility that meaning could inhere in certain actions, experiences, states, or relationships that have not been adopted as ends and willed and that perhaps even could not be, e.g., being an immortal offshoot of an unconscious, spiritual force that grounds the physical universe, as in Hinduism. In addition, the above purpose-based analyses exclude as not being about life's meaning some of the most widely read texts that purport to be about it, namely, Jean-Paul Sartre's (1948) existentialist account of meaning being constituted by whatever one chooses, and Richard Taylor's (1970, ch. 18) discussion of Sisyphus being able to acquire meaning in his life merely by having his strongest desires satisfied. These are prima facie accounts of meaning in life, but do not essentially involve the attainment of purposes that foster coherence, intelligibility or transcendence.
The latter problem also faces the alternative suggestion that talk of “life's meaning” is not necessarily about purposes, but is rather just a matter of referring to goods that are qualitatively superior, worthy of love and devotion, and appropriately awed (Taylor 1989, ch. 1). It is implausible to think that these criteria are satisfied by subjectivist appeals to whatever choices one ends up making or to whichever desires happen to be strongest for a given person.
Although relatively few have addressed the question of whether there exists a single, primary sense of “life's meaning,” the inability to find one so far might suggest that none exists. In that case, it could be that the field is united in virtue of addressing certain overlapping but not equivalent ideas that have family resemblances (Metz 2013, ch. 2). Perhaps when we speak of “meaning in life,” we have in mind one or more of these related ideas: certain conditions that are worthy of great pride or admiration, values that warrant devotion and love, qualities that make a life intelligible, or ends apart from base pleasure that are particularly choice-worthy. Another possibility is that talk of “meaning in life” fails to exhibit even this degree of unity, and is instead a grab-bag of heterogenous ideas (Mawson 2010; Oakley 2010).
As the field reflects more on the sense of “life's meaning,” it should not only try to ascertain in what respect it admits of unity, but also try to differentiate the concept of life's meaning from other, closely related ideas. For instance, the concept of a worthwhile life is probably not identical to that of a meaningful one (Baier 1997, ch. 5; Metz 2012). For instance, one would not be conceptually confused to claim that a meaningless life full of animal pleasures would be worth living. Furthermore, it seems that talk of a “meaningless life” does not simply connote the concept of an absurd (Nagel 1970; Feinberg 1980), unreasonable (Baier 1997, ch. 5), futile (Trisel 2002), or wasted (Kamm 2003, 210–14) life.
Fortunately the field does not need an extremely precise analysis of the concept of life's meaning (or definition of the phrase “life's meaning”) in order to make progress on the substantive question of what life's meaning is. Knowing that meaningfulness analytically concerns a variable and gradient final good in a person's life that is conceptually distinct from happiness, rightness, and worthwhileness provides a certain amount of common ground. The rest of this discussion addresses attempts to theoretically capture the nature of this good.
2. Supernaturalism
Most English speaking philosophers writing on meaning in life are trying to develop and evaluate theories, i.e., fundamental and general principles that are meant to capture all the particular ways that a life could obtain meaning. These theories are standardly divided on a metaphysical basis, i.e., in terms of which kinds of properties are held to constitute the meaning. Supernaturalist theories are views that meaning in life must be constituted by a certain relationship with a spiritual realm. If God or a soul does not exist, or if they exist but one fails to have the right relationship with them, then supernaturalism—or the Western version of it (on which I focus)—entails that one's life is meaningless. In contrast, naturalist theories are views that meaning can obtain in a world as known solely by science. Here, although meaning could accrue from a divine realm, certain ways of living in a purely physical universe would be sufficient for it. Note that there is logical space for a non-naturalist theory that meaning is a function of abstract properties that are neither spiritual nor physical. However, only scant attention has been paid to this possibility in the Anglo-American literature (Williams 1999; Audi 2005).
Supernaturalist thinkers in the monotheistic tradition are usefully divided into those with God-centered views and soul-centered views. The former take some kind of connection with God (understood to be a spiritual person who is all-knowing, all-good, and all-powerful and who is the ground of the physical universe) to constitute meaning in life, even if one lacks a soul (construed as an immortal, spiritual substance). The latter deem having a soul and putting it into a certain state to be what makes life meaningful, even if God does not exist. Of course, many supernaturalists believe that certain relationships with God and a soul are jointly necessary and sufficient for a significant existence. However, the simpler view is common, and often arguments proffered for the more complex view fail to support it any more than the simpler view.
2.1 God-centered Views
The most widely held and influential God-based account of meaning in life is that one's existence is more significant, the better one fulfills a purpose God has assigned. The familiar idea is that God has a plan for the universe and that one's life is meaningful to the degree that one helps God realize this plan, perhaps in the particular way God wants one to do so (Affolter 2007). Fulfilling God's purpose by choice is the sole source of meaning, with the existence of an afterlife not necessary for it (Brown 1971; Levine 1987; Cottingham 2003). If a person failed to do what God intends him to do with his life, then, on the current view, his life would be meaningless.
What I call “purpose theorists” differ over what it is about God's purpose that makes it uniquely able to confer meaning on human lives. Some argue that God's purpose could be the sole source of invariant moral rules, where a lack of such would render our lives nonsensical (Craig 1994; Cottingham 2003). However, Euthyphro problems arguably plague this rationale; God's purpose for us must be of a particular sort for our lives to obtain meaning by fulfilling it (as is often pointed out, serving as food for intergalactic travelers won't do), which suggests that there is a standard external to God's purpose that determines what the content of God's purpose ought to be (but see Cottingham 2005, ch. 3). In addition, some critics argue that a universally applicable and binding moral code is not necessary for meaning in life, even if the act of helping others is (Ellin 1995, 327).
Other purpose theorists contend that having been created by God for a reason would be the only way that our lives could avoid being contingent (Craig 1994; cf. Haber 1997). But it is unclear whether God's arbitrary will would avoid contingency, or whether his non-arbitrary will would avoid contingency anymore than a deterministic physical world. Furthermore, the literature is still unclear what contingency is and why it is a deep problem. Still other purpose theorists maintain that our lives would have meaning only insofar as they were intentionally fashioned by a creator, thereby obtaining meaning of the sort that an art-object has (Gordon 1983). Here, though, freely choosing to do any particular thing would not be necessary for meaning, and everyone's life would have an equal degree of meaning, which are both counterintuitive implications (see Trisel 2012 for additional criticisms). Are all these objections sound? Is there a promising reason for thinking that fulfilling God's (as opposed to any human's) purpose is what constitutes meaning in life?
Not only does each of these versions of the purpose theory have specific problems, but they all face this shared objection: if God assigned us a purpose, then God would degrade us and thereby undercut the possibility of us obtaining meaning from fulfilling the purpose (Baier 1957, 118–20; Murphy 1982, 14–15; Singer 1996, 29). This objection goes back at least to Jean-Paul Sartre (1948, 45), and there are many replies to it in the literature that have yet to be assessed (e.g., Hepburn 1965, 271–73; Brown 1971, 20–21; Davis 1986, 155–56; Hanfling 1987, 45–46; Moreland 1987, 129; Walker 1989; Jacquette 2001, 20–21).
Robert Nozick presents a God-centered theory that focuses less on God as purposive and more on God as infinite (Nozick 1981, ch. 6, 1989, chs. 15–16; see also Cooper 2005). The basic idea is that for a finite condition to be meaningful, it must obtain its meaning from another condition that has meaning. So, if one's life is meaningful, it might be so in virtue of being married to a person, who is important. And, being finite, the spouse must obtain his or her importance from elsewhere, perhaps from the sort of work he or she does. And this work must obtain its meaning by being related to something else that is meaningful, and so on. A regress on meaningful finite conditions is present, and the suggestion is that the regress can terminate only in something infinite, a being so all-encompassing that it need not (indeed, cannot) go beyond itself to obtain meaning from anything else. And that is God.
The standard objection to this rationale is that a finite condition could be meaningful without obtaining its meaning from another meaningful condition; perhaps it could be meaningful in itself, or obtain its meaning by being related to something beautiful, autonomous or otherwise valuable for its own sake but not meaningful (Thomson 2003, 25–26, 48).
The purpose- and infinity-based rationales are the two most common instances of God-centered theory in the literature, and the naturalist can point out that they arguably face a common problem: a purely physical world seems able to do the job for which God is purportedly necessary. Nature seems able to ground a universal morality and the sort of final value from which meaning might spring. And other God-based views seem to suffer from this same problem. For two examples, some claim that God must exist in order for there to be a just world, where a world in which the bad do well and the good fare poorly would render our lives senseless (Craig 1994; cf. Cottingham 2003, pt. 3), and others maintain that God's remembering all of us with love is alone what would confer significance on our lives (Hartshorne 1984). However, the naturalist will point out that an impersonal, Karmic-like force of nature conceivably could justly distribute penalties and rewards in the way a retributive personal judge would, and that actually living together in loving relationships would seem to confer much more meaning on life than a loving fond remembrance.
A second problem facing all God-based views is the existence of apparent counterexamples. If we think of the stereotypical lives of Albert Einstein, Mother Teresa, and Pablo Picasso, they seem meaningful even if we suppose there is no all-knowing, all-powerful, and all-good spiritual person who is the ground of the physical world. Even religiously inclined philosophers find this hard to deny (Quinn 2000, 58; Audi 2005), though some of them suggest that a supernatural realm is necessary for a “deep” or “ultimate” meaning (Nozick 1981, 618; Craig 1994, 42). What is the difference between a deep meaning and a shallow one? And why think a spiritual realm is necessary for the former?
At this point, the supernaturalist could usefully step back and reflect on what it might be about God that would make Him uniquely able to confer meaning in life, perhaps as follows from the perfect being theological tradition. For God to be solely responsible for any significance in our lives, God must have certain qualities that cannot be found in the natural world, these qualities must be qualitatively superior to any goods possible in a physical universe, and they must be what ground meaning in it. Here, the supernaturalist could argue that meaning depends on the existence of a perfect being, where perfection requires properties such as atemporality, simplicity, and immutability that are possible only in a spiritual realm (Metz 2013, chs. 6–7; cf. Morris 1992; contra Brown 1971 and Hartshorne 1996). Meaning might come from loving a perfect being or orienting one's life toward it in other ways such as imitating it or even fulfilling its purpose, perhaps a purpose tailor-made for each individual (as per Affolter 2007).
Although this might be a promising strategy for a God-centered theory, it faces a serious dilemma. On the one hand, in order for God to be the sole source of meaning, God must be utterly unlike us; for the more God were like us, the more reason there would be to think we could obtain meaning from ourselves, absent God. On the other hand, the more God is utterly unlike us, the less clear it is how we could obtain meaning by relating to Him. How can one love a being that cannot change? How can one imitate such a being? Could an immutable, atemporal, simple being even have purposes? Could it truly be a person? And why think an utterly perfect being is necessary for meaning? Why would not a very good but imperfect being confer some meaning?
2.2 Soul-centered Views
A soul-centered theory is the view that meaning in life comes from relating in a certain way to an immortal, spiritual substance that supervenes on one's body when it is alive and that will forever outlive its death. If one lacks a soul, or if one has a soul but relates to it in the wrong way, then one's life is meaningless. There are two prominent arguments for a soul-based perspective.
The first one is often expressed by laypeople and is suggested by the work of Leo Tolstoy (1884; see also Hanfling 1987, 22–24; Morris 1992, 26; Craig 1994). Tolstoy argues that for life to be meaningful something must be worth doing, that nothing is worth doing if nothing one does will make a permanent difference to the world, and that doing so requires having an immortal, spiritual self. Many of course question whether having an infinite effect is necessary for meaning (e.g., Schmidtz 2001; Audi 2005, 354–55). Others point out that one need not be immortal in order to have an infinite effect (Levine 1987, 462), for God's eternal remembrance of one's mortal existence would be sufficient for that.
The other major rationale for a soul-based theory of life's meaning is that a soul is necessary for perfect justice, which, in turn, is necessary for a meaningful life. Life seems nonsensical when the wicked flourish and the righteous suffer, at least supposing there is no other world in which these injustices will be rectified, whether by God or by Karma. Something like this argument can be found in the Biblical chapter Ecclesiastes , and it continues to be defended (Davis 1987; Craig 1994). However, like the previous rationale, the inferential structure of this one seems weak; even if an afterlife were required for just outcomes, it is not obvious why an eternal afterlife should be thought necessary (Perrett 1986, 220).
Work has been done to try to make the inferences of these two arguments stronger, and the basic strategy has been to appeal to the value of perfection (Metz 2013, ch. 7). Perhaps the Tolstoian reason why one must live forever in order to make the relevant permanent difference is an agent-relative need for one to honor an infinite value, something qualitatively higher than the worth of, say, pleasure. And maybe the reason why immortality is required in order to mete out just deserts is that rewarding the virtuous requires satisfying their highest free and informed desires, one of which would be for eternal flourishing of some kind (Goetz 2012). While far from obviously sound, these arguments at least provide some reason for thinking that immortality is necessary to satisfy the major premise about what is required for meaning.
However, both arguments are still plagued by a problem facing the original versions; even if they show that meaning depends on immortality, they do not yet show that it depends on having a soul . By definition, if one has a soul, then one is immortal, but it is not clearly true that if one is immortal, then one has a soul. Perhaps being able to upload one's consciousness into an infinite succession of different bodies in an everlasting universe would count as an instance of immortality without a soul. Such a possibility would not require an individual to have an immortal spiritual substance (imagine that when in between bodies, the information constitutive of one's consciousness were temporarily stored in a computer). What reason is there to think that one must have a soul in particular for life to be significant?
The most promising reason seems to be one that takes us beyond the simple version of soul-centered theory to the more complex view that both God and a soul constitute meaning. The best justification for thinking that one must have a soul in order for one's life to be significant seems to be that significance comes from uniting with God in a spiritual realm such as Heaven, a view espoused by Thomas Aquinas, Leo Tolstoy (1884), and contemporary religious thinkers (e.g., Craig 1994). Another possibility is that meaning comes from honoring what is divine within oneself, i.e., a soul (Swenson 1949).
As with God-based views, naturalist critics offer counterexamples to the claim that a soul or immortality of any kind is necessary for meaning. Great works, whether they be moral, aesthetic, or intellectual, would seem to confer meaning on one's life regardless of whether one will live forever. Critics maintain that soul-centered theorists are seeking too high a standard for appraising the meaning of people's lives (Baier 1957, 124–29; Baier 1997, chs. 4–5; Trisel 2002; Trisel 2004). Appeals to a soul require perfection, whether it be, as above, a perfect object to honor, a perfectly just reward to enjoy, or a perfect being with which to commune. However, if indeed soul-centered theory ultimately relies on claims about meaning turning on perfection, such a view is attractive at least for being simple, and rival views have yet to specify in a principled and thoroughly defended way where to draw the line at less than perfection (perhaps a start is Metz 2013, ch. 8). What less than ideal amount of value is sufficient for a life to count as meaningful?
Critics of soul-based views maintain not merely that immortality is not necessary for meaning in life, but also that it is sufficient for a meaningless life. One influential argument is that an immortal life, whether spiritual or physical, could not avoid becoming boring, rendering life pointless (Williams 1973; Ellin 1995, 311–12; Belshaw 2005, 82–91; Smuts 2011). The most common reply is that immortality need not get boring (Fischer 1994; Wisnewski 2005; Bortolotti and Nagasawa 2009; Chappell 2009; Quigley and Harris 2009, 75–78). However, it might also be worth questioning whether boredom is truly sufficient for meaninglessness. Suppose, for instance, that one volunteers to be bored so that many others will not be bored; perhaps this would be a meaningful sacrifice to make.
Another argument that being immortal would be sufficient to make our lives insignificant is that persons who cannot die could not exhibit certain virtues (Nussbaum 1989; Kass 2001). For instance, they could not promote justice of any important sort, be benevolent to any significant degree, or exhibit courage of any kind that matters, since life and death issues would not be at stake. Critics reply that even if these virtues would not be possible, there are other virtues that could be. And of course it is not obvious that meaning-conferring justice, benevolence and courage would not be possible if we were immortal, perhaps if we were not always aware that we could not die or if our indestructible souls could still be harmed by virtue of intense pain, frustrated ends, and repetitive lives.
There are other, related arguments maintaining that awareness of immortality would have the effect of removing meaning from life, say, because our lives would lack a sense of preciousness and urgency (Lenman 1995; Kass 2001; James 2009) or because external rather than internal factors would then dictate their course (Wollheim 1984, 266). Note that the target here is belief in an eternal afterlife, and not immortality itself, and so I merely mention these rationales (for additional, revealing criticism, see Bortolotti 2010).
3. Naturalism
I now address views that even if there is no spiritual realm, meaning in life is possible, at least for many people. Among those who believe that a significant existence can be had in a purely physical world as known by science, there is debate about two things: the extent to which the human mind constitutes meaning and whether there are conditions of meaning that are invariant among human beings.
Subjectivists believe that there are no invariant standards of meaning because meaning is relative to the subject, i.e., depends on an individual's pro-attitudes such as desires, ends, and choices. Roughly, something is meaningful for a person if she believes it to be or seeks it out. Objectivists maintain, in contrast, that there are some invariant standards for meaning because meaning is (at least partly) mind-independent, i.e., is a real property that exists regardless of being the object of anyone's mental states. Here, something is meaningful (to some degree) in virtue of its intrinsic nature, independent of whether it is believed to be meaningful or sought.
There is logical space for an intersubjective theory according to which there are invariant standards of meaning for human beings that are constituted by what they would all agree upon from a certain communal standpoint (Darwall 1983, chs. 11–12). However, this orthogonal approach is not much of a player in the field and so I set it aside in what follows.
According to this view, meaning in life varies from person to person, depending on each one's variable mental states. Common instances are views that one's life is more meaningful, the more one gets what one happens to want strongly, the more one achieves one's highly ranked goals, or the more one does what one believes to be really important (Trisel 2002; Hooker 2008; Alexis 2011). Lately, one influential subjectivist has maintained that the relevant mental state is caring or loving, so that life is meaningful just to the extent that one cares about or loves something (Frankfurt 1982, 2002, 2004).
Subjectivism was dominant for much of the 20 th century when pragmatism, positivism, existentialism, noncognitivism, and Humeanism were quite influential (James 1900; Ayer 1947; Sartre 1948; Barnes 1967; Taylor 1970; Hare 1972; Williams 1976; Klemke 1981). However, in the last quarter of the 20 th century, “reflective equilibrium” became a widely accepted argumentative procedure, whereby more controversial normative claims are justified by virtue of entailing and explaining less controversial normative claims that do not command universal acceptance. Such a method has been used to defend the existence of objective value, and, as a result, subjectivism about meaning has lost its dominance.
Those who continue to hold subjectivism often are suspicious of attempts to justify beliefs about objective value (e.g., Frankfurt 2002, 250; Trisel 2002, 73, 79, 2004, 378–79). Theorists are primarily moved to accept subjectivism because the alternatives are unpalatable; they are sure that value in general and meaning in particular exists, but do not see how it could be grounded in something independent of the mind, whether it be the natural, the non-natural, or the supernatural. In contrast to these possibilities, it appears straightforward to account for what is meaningful in terms of what people find meaningful or what people want out of life. Wide-ranging meta-ethical debates in epistemology, metaphysics, and the philosophy of language are necessary to address this rationale for subjectivism.
There are two other, more circumscribed arguments for subjectivism. One is that subjectivism is plausible since it is reasonable to think that a meaningful life is an authentic one (Frankfurt 1982). If a person's life is significant insofar as she is true to herself or her deepest nature, then we have some reason to believe that meaning simply is a function of satisfying certain desires held by the individual or realizing certain ends of hers. Another argument is that meaning intuitively comes from losing oneself, i.e., in becoming absorbed in an activity or experience (Frankfurt 1982). Work that concentrates the mind and relationships that are engrossing seem central to meaning and to be so because of the subjective element involved, that is, because of the concentration and engrossment.
However, critics maintain that both of these arguments are vulnerable to a common objection: they neglect the role of objective value both in realizing oneself and in losing oneself (Taylor 1992, esp. ch. 4). One is not really being true to oneself if one intentionally harms others (Dahl 1987, 12), successfully maintains 3,732 hairs on one's head (Taylor 1992, 36), or, well, eats one's own excrement (Wielenberg 2005, 22), and one is also not losing oneself in a meaning-conferring way if one is consumed by these activities. There seem to be certain actions, relationships, states, and experiences that one ought to concentrate on or be engrossed in, if meaning is to accrue.
So says the objectivist, but many subjectivists also feel the pull of the point. Paralleling replies in the literature on well-being, subjectivists often respond by contending that no or very few individuals would desire to do such intuitively trivial things, at least after a certain idealized process of reflection (e.g., Griffin 1981). More promising, perhaps, is the attempt to ground value not in the responses of an individual valuer, but in those of a particular group (Brogaard and Smith 2005; Wong 2008). Would such an intersubjective move avoid the counterexamples? If so, would it do so more plausibly than an objective theory?
Objective naturalists believe that meaning is constituted (at least in part) by something physical independent of the mind about which we can have correct or incorrect beliefs. Obtaining the object of some variable pro-attitude is not sufficient for meaning, on this view. Instead, there are certain inherently worthwhile or finally valuable conditions that confer meaning for anyone, neither merely because they are wanted, chosen, or believed to be meaningful, nor because they somehow are grounded in God.
Morality and creativity are widely held instances of actions that confer meaning on life, while trimming toenails and eating snow (and the other counterexamples to subjectivism above) are not. Objectivism is thought to be the best explanation for these respective kinds of judgments: the former are actions that are meaningful regardless of whether any arbitrary agent (whether it be an individual,her society, or even God) judges them to be meaningful or seeks to engage in them, while the latter actions simply lack significance and cannot obtain it if someone believes them to have it or engages in them. To obtain meaning in one's life, one ought to pursue the former actions and avoid the latter ones. Of course, meta-ethical debates about the nature of value are again relevant here.
A “pure” objectivist thinks that being the object of a person's mental states plays no role in making that person's life meaningful. Relatively few objectivists are pure, so construed. That is, a large majority of them believe that a life is more meaningful not merely because of objective factors, but also in part because of subjective ones such as cognition, affection, and emotion. Most commonly held is the hybrid view captured by Susan Wolf's pithy slogan: “Meaning arises when subjective attraction meets objective attractiveness” (Wolf 1997a, 211; see also Hepburn 1965; Kekes 1986, 2000; Wiggins 1988; Wolf 1997b, 2002, 2010; Dworkin 2000, ch. 6; Raz 2001, ch. 1; Schmidtz 2001; Starkey 2006; Mintoff 2008). This theory implies that no meaning accrues to one's life if one believes in, is satisfied by, or cares about a project that is not worthwhile, or if one takes up a worthwhile project but fails to judge it important, be satisfied by it, care about it or otherwise identify with it. Different versions of this theory will have different accounts of the appropriate mental states and of worthwhileness.
Pure objectivists deny that subjective attraction plays any constitutive role in conferring meaning on life. For instance, utilitarians with respect to meaning (as opposed to morality) are pure objectivists, for they claim that certain actions confer meaning on life regardless of the agent's reactions to them. On this view, the more one benefits others, the more meaningful one's life, regardless of whether one enjoys benefiting them, believes they should be aided, etc. (Singer 1993, ch. 12, 1995, chs. 10–11; Singer 1996, ch. 4). Midway between pure objectivism and the hybrid theory is the view that having certain propositional attitudes toward finally good activities would enhance the meaning of life without being necessary for it (Audi 2005, 344). For instance, might a Mother Teresa who is bored by her substantial charity work have a significant existence because of it, even if she would have an even more significant existence if she were excited by it?
There have been several attempts to theoretically capture what all objectively attractive, inherently worthwhile, or finally valuable conditions have in common insofar as they bear on meaning. Some believe that they can all be captured as actions that are creative (Taylor 1987), while others maintain that they are exhibit rightness or virtue and perhaps also involve reward proportionate to morality (Kant 1791, pt. 2; cf. Pogge 1997). Most objectivists, however, deem these respective aesthetic and ethical theories to be too narrow, even if living a moral life is necessary for a meaningful one (Landau 2011). It seems to most in the field not only that creativity and morality are independent sources of meaning, but also that there are sources in addition to these two. For just a few examples, consider making an intellectual discovery, rearing children with love, playing music, and developing superior athletic ability.
So, in the literature one finds a variety of principles that aim to capture all these and other (apparent) objective grounds of meaning. One can read the perfectionist tradition as proffering objective theories of what a significant existence is, even if their proponents do not frequently use contemporary terminology to express this. Consider Aristotle's account of the good life for a human being as one that fulfills its natural purpose qua rational, Marx's vision of a distinctly human history characterized by less alienation and more autonomy, culture, and community, and Nietzsche's ideal of a being with a superlative degree of power, creativity, and complexity.
More recently, some have maintained that objectively meaningful conditions are just those that involve: transcending the limits of the self to connect with organic unity (Nozick 1981, ch. 6, 1989, chs. 15–16); realizing human excellence in oneself (Bond 1983, chs. 6, 8); maximally promoting non-hedonist goods such as friendship, beauty, and knowledge (Railton 1984); exercising or promoting rational nature in exceptional ways (Hurka 1993; Smith 1997, 179–221; Gewirth 1998, ch. 5); substantially improving the quality of life of people and animals (Singer 1993, ch. 12, 1995, chs. 10–11; Singer 1996, ch. 4); overcoming challenges that one recognizes to be important at one's stage of history (Dworkin 2000, ch. 6); constituting rewarding experiences in the life of the agent or the lives of others the agent affects (Audi 2005); making progress toward ends that in principle can never be completely realized because one's knowledge of them changes as one approaches them (Levy 2005); realizing goals that are transcendent for being long-lasting in duration and broad in scope (Mintoff 2008); or contouring intelligence toward fundamental conditions of human life (Metz 2013).
One major test of these theories is whether they capture all experiences, states, relationships, and actions that intuitively make life meaningful. The more counterexamples of apparently meaningful conditions that a principle entails lack meaning, the less justified the principle. There is as yet no convergence in the field on any one principle or even cluster as accounting for commonsensical judgments about meaning to an adequate, convincing degree. Indeed, some believe the search for such a principle to be pointless (Wolf 1997b, 12–13; Kekes 2000; Schmidtz 2001). Are these pluralists correct, or does the field have a good chance of discovering a single, basic property that grounds all the particular ways to acquire meaning in life?
Another important way to criticize these theories is more comprehensive: for all that has been said so far, the objective theories are aggregative or additive, objectionably reducing life to a “container” of meaningful conditions (Brännmark 2003, 330). As with the growth of “organic unity” views in the context of debates about intrinsic value, it is becoming common to think that life as a whole (or at least long stretches of it) can substantially affect its meaning apart from the amount of meaning in its parts.
For instance, a life that has lots of beneficent and otherwise intuitively meaning-conferring conditions but that is also extremely repetitive (à la the movie Groundhog Day ) is less than maximally meaningful (Taylor 1987). Furthermore, a life that not only avoids repetition but also ends with a substantial amount of meaningful parts seems to have more meaning overall than one that has the same amount of meaningful parts but ends with few or none of them (Kamm 2003, 210–14). And a life in which its meaningless parts cause its meaningful parts to come about through a process of personal growth seems meaningful in virtue of this causal pattern or being a “good life-story” (Velleman 1991; Fischer 2005).
Extreme versions of holism are also present in the literature. For example, some maintain that the only bearer of final value is life as a whole, which entails that there are strictly speaking no parts or segments of a life that can be meaningful in themselves (Tabensky 2003; Levinson 2004). For another example, some accept that both parts of a life and a life as a whole can be independent bearers of meaning, but maintain that the latter has something like a lexical priority over the former when it comes to what to pursue or otherwise to prize (Blumenfeld 2009).
What are the ultimate bearers of meaning? What are all the fundamentally different ways (if any) that holism can affect meaning? Are they all a function of narrativity, life-stories, and artistic self-expression (as per Kauppinen 2012), or are there holistic facets of life's meaning that are not a matter of such literary concepts? How much importance should they be accorded by an agent seeking meaning in her life?
So far, I have addressed theoretical accounts that have been naturally understood to be about what confers meaning on life, which obviously assumes that some lives are in fact meaningful. However, there are nihilistic perspectives that question this assumption. According to nihilism (or pessimism), what would make a life meaningful either cannot obtain or as a matter of fact simply never does.
One straightforward rationale for nihilism is the combination of supernaturalism about what makes life meaningful and atheism about whether God exists. If you believe that God or a soul is necessary for meaning in life, and if you believe that neither exists, then you are a nihilist, someone who denies that life has meaning. Albert Camus is famous for expressing this kind of perspective, suggesting that the lack of an afterlife and of a rational, divinely ordered universe undercuts the possibility of meaning (Camus 1955; cf. Ecclesiastes ).
Interestingly, the most common rationales for nihilism these days do not appeal to supernaturalism. The idea shared among many contemporary nihilists is that there is something inherent to the human condition that prevents meaning from arising, even granting that God exists. For instance, some nihilists make the Schopenhauerian claim that our lives lack meaning because we are invariably dissatisfied; either we have not yet obtained what we seek, or we have obtained it and are bored (Martin 1993). Critics tend to reply that at least a number of human lives do have the requisite amount of satisfaction required for meaning, supposing that some is (Blackburn 2001, 74–77).
Other nihilists claim that life would be meaningless if there were no invariant moral rules that could be fully justified—the world would be nonsensical if, in (allegedly) Dostoyevskian terms, “everything were permitted”—and that such rules cannot exist for persons who can always reasonably question a given claim (Murphy 1982, ch. 1). While a number of philosophers agree that a universally binding and warranted morality is necessary for meaning in life (Kant 1791; Tännsjö 1988; Jacquette 2001, ch. 1; Cottingham 2003, 2005, ch. 3), some do not (Margolis 1990; Ellin 1995, 325–27). Furthermore, contemporary rationalist and realist work in meta-ethics has led many to believe that such a moral system exists.
In the past 10 years, some interesting new defences of nihilism have arisen that merit careful consideration. According to one rationale, for our lives to matter, we must in a position to add value to the world, which we are not since the value of the world is already infinite (Smith 2003). The key premises for this view are that every bit of space-time (or at least the stars in the physical universe) have some positive value, that these values can be added up, and that space is infinite. If the physical world at present contains an infinite degree of value, nothing we do can make a difference in terms of meaning, for infinity plus any amount of value must be infinity.
One way to question this argument is to suggest that even if one cannot add to the value of the universe, meaning plausibly obtains merely by being the source of value. Consider that one does not merely want one's child to be reared with love, but wants to be the one who rears one's child with love. And this desire remains even knowing that others would have reared one's child with love in one's absence, so that one's actions are not increasing the goodness of the state of the universe relative to what it would have had without them. Similar remarks might apply to cases of meaning more generally (for additional, and technical, discussion of whether an infinite universe entails nihilism, see Almeida 2010; Vohánka and Vohánková n.d.).
Another fresh argument for nihilism is forthcoming from certain defenses of anti-natalism, the view that it is immoral to bring new people into existence because doing so would be a harm to them. There are now a variety of rationales for anti-natalism, but most relevant to debates about whether life is meaningful is probably the following argument from David Benatar (2006, 18–59). According to him, the bads of existing (e.g., pains) are real disadvantages relative to not existing, while the goods of existing (pleasures) are not real advantages relative to not existing, since there is in the latter state no one to be deprived of them. If indeed the state of not existing is no worse than that of experiencing the benefits of existence, then, since existing invariably brings harm in its wake, existing is always a net harm compared to not existing. Although this argument is about goods such as pleasures in the first instance, it seems generalizable to non-experiential goods, including that of meaning in life.
The criticisms of Benatar that promise to cut most deep are those that question his rationale for the above judgments of good and bad. He maintains that these appraisals best explain, e.g., why it would be wrong for one to create someone whom one knows would suffer a torturous existence, and why it would not be wrong for one not to create someone whom one knows would enjoy a wonderful existence. The former would be wrong and the latter would not be wrong, for Benatar, because no pain in non-existence is better than pain in existence, and because no pleasure in non-existence is no worse than pleasure in existence. Critics usually grant the judgments of wrongness, but provide explanations of them that do not invoke Benatar's judgments of good and bad that apparently lead to anti-natalism (e.g., Boonin 2012; Weinberg 2012).
This survey closes by discussing the most well-known rationale for nihilism, namely, Thomas Nagel's (1986) invocation of the external standpoint that purportedly reveals our lives to be unimportant (see also Hanfling 1987, 22–24; Benatar 2006, 60–92; cf. Dworkin 2000, ch. 6). According to Nagel, we are capable of comprehending the world from a variety of standpoints that are either internal or external. The most internal perspective would be a particular human being's desire at a given instant, with a somewhat less internal perspective being one's interests over a life-time, and an even less internal perspective being the interests of one's family or community. In contrast, the most external perspective, an encompassing standpoint utterly independent of one's particularity, would be, to use Henry Sidgwick's phrase, the “point of view of the universe,” that is, the standpoint that considers the interests of all sentient beings at all times and in all places. When one takes up this most external standpoint and views one's finite—and even downright puny—impact on the world, little of one's life appears to matter. What one does in a certain society on Earth over an approximately 75 years just does not amount to much, when considering the billions of years and likely trillions of beings that are a part of space-time.
Very few accept the authority of the (most) external standpoint (Ellin 1995, 316–17; Blackburn 2001, 79–80; Schmidtz 2001) or the implications that Nagel believes it has for the meaning of our lives (Quinn 2000, 65–66; Singer 1993, 333–34; Wolf 1997b, 19–21). However, the field could use much more discussion of this rationale, given its persistence in human thought. It is plausible to think, with Nagel, that part of what it is to be a person is to be able to take up an external standpoint. However, what precisely is a standpoint? Must we invariably adopt one standpoint or the other, or is it possible not to take one up at all? Is there a reliable way to ascertain which standpoint is normatively more authoritative than others? These and the other questions posed in this survey still lack conclusive answers, another respect in which the field of life's meaning is tantalizingly open for substantial contributions.
- Affolter, J., 2007, “Human Nature as God's Purpose”, Religious Studies , 43: 443–55.
- Alexis., A., 2011, The Meaning of Life: A Modern Secular Answer to the Age-Old Fundamental Question , CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform.
- Almeida, M., 2010, “Two Challenges to Moral Nihilism”, The Monist , 93: 96–105.
- Audi, R., 2005, “Intrinsic Value and Meaningful Life”, Philosophical Papers , 34: 331–55.
- Ayer, A. J., 1947, “The Claims of Philosophy”, repr. in The Meaning of Life, 2 nd Ed. , E. D. Klemke (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, 2000: 219–32.
- Baier, K., 1957, “The Meaning of Life”, repr. in The Meaning of Life, 2 nd Ed. , E. D. Klemke (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, 2000: 101–32.
- –––, 1997, Problems of Life and Death: A Humanist Perspective , Amherst: Prometheus Books.
- Barnes, H., 1967, An Existentialist Ethics , New York: Alfred A. Knopf.
- Belshaw, C., 2005, 10 Good Questions about Life and Death , Malden, MA: Blackwell.
- Benatar, D., 2006, Better Never to Have Been: The Harm of Coming into Existence , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Blackburn, S., 2001, Being Good , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Blumenfeld, D., 2009, “Living Life Over Again”, Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 79: 357–86.
- Bond, E. J., 1983, Reason and Value , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Boonin, D., 2012, “Better to Be”, South African Journal of Philosophy , 31: 10–25.
- Bortolotti, L., 2010, “Agency, Life Extension, and the Meaning of Life”, The Monist , 92: 38–56.
- Bortolotti, L. and Nagasawa, Y., 2009, “Immortality Without Boredom”, Ratio , 22: 261–77.
- Brännmark, J., 2003, “Leading Lives”, Philosophical Papers , 32: 321–43.
- Britton, K., 1969, Philosophy and the Meaning of Life , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Brogaard, B. and Smith, B., 2005, “On Luck, Responsibility, and the Meaning of Life”, Philosophical Papers , 34: 443–58.
- Brown, D., 1971, “Process Philosophy and the Question of Life's Meaning”, Religious Studies , 7: 13–29.
- Camus, A., 1955, The Myth of Sisyphus , J. O'Brian (tr.), London: H. Hamilton.
- Chappell, T., 2009, “Infinity Goes Up on Trial: Must Immortality Be Meaningless?”, European Journal of Philosophy , 17: 30–44.
- Cooper, D., 2005, “Life and Meaning”, Ratio , 18: 125–37.
- Cottingham, J., 2003, On the Meaning of Life , London: Routledge.
- –––, 2005, The Spiritual Dimension: Religion, Philosophy and Human Value , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Craig, W., 1994, “The Absurdity of Life Without God”, repr. in The Meaning of Life, 2 nd Ed. , E. D. Klemke (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, 2000: 40–56.
- Dahl, N., 1987, “Morality and the Meaning of Life”, Canadian Journal of Philosophy , 17: 1–22.
- Darwall, S., 1983, Impartial Reason , Ithaca: Cornell University Press.
- Davis, W., 1986, “The Creation of Meaning”, Philosophy Today , 30: 151–67.
- –––, 1987, “The Meaning of Life”, Metaphilosophy , 18: 288–305.
- Dworkin, R., 2000, Sovereign Virtue , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Edwards, P., 1972, “Why”, in The Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Volumes 7– 8 , P. Edwards (ed.), New York: Macmillan Publishing Company: 296–302.
- Ellin, J., 1995. Morality and the Meaning of Life , Ft. Worth, TX: Harcourt Brace.
- Feinberg, J., 1980, “Absurd Self-Fulfillment,” repr. in Freedom and Fulfillment: Philosophical Essays , Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1992: 297–330.
- Fischer, J. M., 1994, “Why Immortality is Not So Bad”, International Journal of Philosophical Studies , 2: 257–70.
- –––, 2005, “Free Will, Death, and Immortality: The Role of Narrative”, Philosophical Papers , 34: 379–403.
- Flanagan, O., 1996, Self-Expressions: Mind, Morals, and the Meaning of Life , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Frankfurt, H., 1982, “The Importance of What We Care About”, Synthese , 53: 257–72.
- –––, 2002, “Reply to Susan Wolf”, in The Contours of Agency: Essays on Themes from Harry Frankfurt , S. Buss and L. Overton (eds.), Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press: 245–52.
- –––, 2004, The Reasons of Love , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Gewirth, A., 1998, Self-Fulfillment , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Goetz, S., 2012, The Purpose of Life: A Theistic Perspective , New York: Continuum.
- Gordon, J., 1983, “Is the Existence of God Relevant to the Meaning of Life?” The Modern Schoolman , 60: 227–46.
- Griffin, J., 1981, “On Life's Being Valuable”, Dialectics and Humanism , 8: 51–62.
- Haber, J., 1997, “Contingency and the Meaning of Life”, Philosophical Writings , 5: 32–44.
- Hanfling, O., 1987, The Quest for Meaning , New York: Basil Blackwell Inc.
- Hare, R. M., 1957, “Nothing Matters”, repr. in Applications of Moral Philosophy , London: Macmillan, 1972: 32–47.
- Hartshorne, C., 1984, “God and the Meaning of Life”, in Boston University Studies in Philosophy and Religion, Volume 6: On Nature , L. Rouner (ed.), Notre Dame: University of Notre Dame Press: 154–68.
- –––, 1996, “The Meaning of Life”, Process Studies , 25: 10–18.
- Hepburn, R., 1965, “Questions About the Meaning of Life”, repr. in The Meaning of Life, 2 nd Ed. , E. D. Klemke (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, 2000: 261–76.
- Hooker, B., 2008, “The Meaning of Life: Subjectivism, Objectivism, and Divine Support”, in The Moral Life: Essays in Honour of John Cottingham , N. Athanassoulis and S. Vice (eds.), New York: Palgrave Macmillan: 184–200.
- Hurka, T., 1993, Perfectionism , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Jacquette, D., 2001, Six Philosophical Appetizers , Boston: McGraw-Hill.
- James, L., 2005, “Achievement and the Meaningfulness of Life”, Philosophical Papers , 34: 429–42.
- –––, 2009, “Shape and the Meaningfulness of Life”, in Philosophy and Happiness , L. Bortolotti (ed.), New York: Palgrave Macmillan: 54–67.
- James, W., 1900, “What Makes a Life Significant?”, in On Some of Life's Ideals , New York: Henry Holt and Company: 49–94.
- Kamm, F. M., 2003, “Rescuing Ivan Ilych: How We Live and How We Die”, Ethics , 113: 202–33.
- Kant, I., 1791, Critique of Judgment .
- Kass, L., 2001, “ L'Chaim and Its Limits: Why not Immortality?”, First Things , 113: 17–24.
- Kauppinen, A., 2012, “Meaningfulness and Time”, Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 82: 345–77.
- Kekes, J., 1986, “The Informed Will and the Meaning of Life”, Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 47: 75–90.
- –––, 2000, “The Meaning of Life”, in Midwest Studies in Philosophy, Volume 24; Life and Death: Metaphysics and Ethics , P. French and H. Wettstein (eds.), Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers: 17–34.
- Klemke, E. D., 1981, “Living Without Appeal”, in The Meaning of Life, E. D. Klemke (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press.
- Landau, I., 2011, “Immorality and the Meaning of Life”, The Journal of Value Inquiry , 45: 309–17.
- Lenman, J., 1995, “Immortality: A Letter”, Cogito , 9: 164–69.
- Levine, M., 1987, “What Does Death Have to Do with the Meaning of Life?” Religious Studies , 23: 457–65.
- Levinson, J., 2004, “Intrinsic Value and the Notion of a Life”, The Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism , 62: 319–29.
- Levy, N., 2005, “Downshifting and Meaning in Life”, Ratio , 18: 176–89.
- Margolis, J., 1990, “Moral Realism and the Meaning of Life”, The Philosophical Forum , 22: 19–48.
- Markus, A., 2003, “Assessing Views of Life, A Subjective Affair?”, Religious Studies , 39: 125–43.
- Martin, R., 1993, “A Fast Car and a Good Woman”, in The Experience of Philosophy, 2 nd Ed. , D. Kolak and R. Martin (eds.), Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Publishing Company: 589–95.
- Mawson, T., 2010, “Sources of Dissatisfaction with Answers to the Question of the Meaning of Life”, European Journal for Philosophy of Religion , 2: 19–41.
- Metz, T., 2012, “The Meaningful and the Worthwhile: Clarifying the Relationships”, The Philosophical Forum , 43: 435–48.
- –––, 2013, Meaning in Life: An Analytic Study , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Mintoff, J., 2008, “Transcending Absurdity”, Ratio , 21: 64–84.
- Moreland, J. P., 1987, Scaling the Secular City: A Defense of Christianity , Grand Rapids: Baker Book House.
- Morris, T., 1992, Making Sense of It All: Pascal and the Meaning of Life , Grand Rapids: Willliam B. Eerdmans Publishing Company.
- Munitz, M., 1986, Cosmic Understanding , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Murphy, J., 1982, Evolution, Morality, and the Meaning of Life , Totowa: Rowman and Littlefield.
- Nagel, T., 1970, “The Absurd”, Journal of Philosophy , 68: 716–27.
- –––, 1986, The View from Nowhere , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Nielsen, K., 1964, “Linguistic Philosophy and ‘The Meaning of Life’”, rev. ed. in The Meaning of Life, E. D. Klemke (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, 1981: 177–204.
- Nozick, R., 1974, Anarchy, State and Utopia , New York: Basic Books.
- –––, 1981, Philosophical Explanations , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- –––, 1989, The Examined Life , New York: Simon & Schuster.
- Nussbaum, M., 1989, “Mortal Immortals: Lucretius on Death and the Voice of Nature”, Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 50: 303–51.
- Oakley, T., 2010, “The Issue is Meaninglessness”, The Monist , 93: 106–22.
- Perrett, R., 1986, “Regarding Immortality”, Religious Studies , 22: 219–33.
- Pogge, T., 1997, “Kant on Ends and the Meaning of Life”, in Reclaiming the History of Ethics: Essays for John Rawls , A. Reath et al. (eds.), New York: Cambridge University Press: 361–87.
- Quigley, M. and Harris, J., 2009, “Immortal Happiness”, in Philosophy and Happiness , L. Bortolotti (ed.), New York: Palgrave Macmillan: 68–81.
- Quinn, P., 2000, “How Christianity Secures Life's Meanings”, in The Meaning of Life in the World Religions , J. Runzo and N. Martin (eds.), Oxford: Oneworld Publications: 53–68.
- Railton, P., 1984, “Alienation, Consequentialism, and the Demands of Morality”, repr. in Consequentialism and Its Critics , S. Scheffler (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, 1988: 93–133.
- Raz, J., 2001, Value, Respect, and Attachment , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Sartre, J.-P., 1948, Existentialism is a Humanism , P. Mairet (tr.), London: Methuen & Co.
- Schmidtz, D., 2001, “The Meanings of Life”, in Boston University Studies in Philosophy and Religion, Volume 22; If I Should Die: Life, Death, and Immortality , L. Rouner (ed.), Notre Dame: University of Notre Dame Press: 170–88.
- Seachris, J., 2009, “The Meaning of Life as Narrative: A New Proposal for Interpreting Philosophy's ‘Primary’ Question”, Philo , 12: 5–23.
- Singer, I., 1996, Meaning in Life, Volume 1: The Creation of Value , Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
- Singer, P., 1993, Practical Ethics, 2 nd Ed ., New York: Cambridge University Press.
- –––, 1995, How are We to Live? Amherst, MA: Prometheus Books.
- Smith, Q., 1997, Ethical and Religious Thought in Analytic Philosophy of Language , New Haven: Yale University Press.
- –––, 2003, “Moral Realism and Infinite Spacetime Imply Moral Nihilism”, in Time and Ethics: Essays at the Intersection , H. Dyke (ed.), Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers: 43–54.
- Smuts, A., 2011, “Immortality and Significance”, Philosophy and Literature , 35: 134–49.
- Starkey, C., 2006, “Meaning and Affect”, The Pluralist , 1: 88–103.
- Swenson, D., 1949, “The Dignity of Human Life”, repr. in The Meaning of Life, 2 nd Ed. , E. D. Klemke (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, 2000: 21–30.
- Tabensky, P., 2003, “Parallels Between Living and Painting”, The Journal of Value Inquiry , 37: 59–68.
- Tännsjö, T., 1988, “The Moral Significance of Moral Realism”, The Southern Journal of Philosophy , 26: 247–61.
- Taylor, C., 1989, Sources of the Self , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- –––, 1992, The Ethics of Authenticity , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Taylor, R., 1970, Good and Evil , New York: Macmillan Publishing Co.
- –––, 1987, “Time and Life's Meaning”, The Review of Metaphysics , 40: 675–86.
- Thomas, L., 2005, “Morality and a Meaningful Life”, Philosophical Papers , 34: 405–27.
- Thomson, G., 2003, On the Meaning of Life , South Melbourne: Wadsworth.
- Tolstoy, L., 1884, A Confession .
- Trisel, B. A., 2002, “Futility and the Meaning of Life Debate”, Sorites , 70–84.
- –––, 2004, “Human Extinction and the Value of Our Efforts”, The Philosophical Forum , 35: 371–91.
- –––, 2012, “Intended and Unintended Life”, The Philosophical Forum , 43: 395–403.
- Velleman, J. D., 1991, “Well-Being and Time”, Pacific Philosophical Quarterly , 72: 48–77.
- Velleman, J. D., 2005, “Family History”, Philosophical Papers , 34: 357–78.
- Walker, L., 1989, “Religion and the Meaning of Life and Death”, in Philosophy: The Quest for Truth , L. Pojman (ed.), Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Publishing Co: 167–71.
- Weinberg, R., 2012, “Is Having Children Always Wrong?”, South African Journal of Philosophy , 31: 26–37.
- Wielenberg, E., 2005, Value and Virtue in a Godless Universe , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Wiggins, D., 1988, “Truth, Invention, and the Meaning of Life”, rev. ed. in Essays on Moral Realism , G. Sayre-McCord (ed.), Ithaca: Cornell University Press: 127-65.
- Williams, B., 1973, “The Makropulos Case: Reflections on the Tedium of Immortality”, in Problems of the Self , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 82–100.
- –––, 1976, “Persons, Character and Morality”, in The Identities of Persons , A. O. Rorty (ed.), Berkeley: University of California Press: 197–216.
- Williams, G., 1999, “Kant and the Question of Meaning”, The Philosophical Forum , 30: 115–31.
- Wisnewski, J. J., 2005, “Is the Immortal Life Worth Living?”, International Journal for Philosophy of Religion , 58: 27–36.
- Wohlgennant, R., 1981, “Has the Question About the Meaning of Life Any Meaning?” repr. in Life and Meaning: A Reader , O. Hanfling (ed.), Cambridge: Basic Blackwell Inc., 1987: 34–38.
- Wolf, S., 1997a, “Happiness and Meaning: Two Aspects of the Good Life”, Social Philosophy and Policy , 14: 207–25.
- –––, 1997b, “Meaningful Lives in a Meaningless World”, Quaestiones Infinitae , Volume 19 , Utrecht: Utrecht University: 1–22.
- –––, 2002, “The True, the Good, and the Lovable: Frankfurt's Avoidance of Objectivity”, in The Contours of Agency: Essays on Themes from Harry Frankfurt , S. Buss and L. Overton (eds.), Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press: 227–44.
- –––, 2010, Meaning in Life and Why It Matters , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Wollheim, R., 1984, The Thread of Life , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Wong, W., 2008, “Meaningfulness and Identities”, Ethical Theory and Moral Practice , 11: 123–48.
- Benatar, D. (ed.), 2004, Life, Death & Meaning , Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Inc.
- Cottingham, J. (ed.), 2007, Western Philosophy: An Anthology , Oxford: Blackwell: pt. 12.
- Hanfling, O. (ed.), 1987, Life and Meaning: A Reader , Cambridge: Basic Blackwell Inc.
- Klemke, E. D. and Cahn, S. M. (eds.), 2007, The Meaning of Life: A Reader, 3 rd Ed. , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Metz, T. (ed.), 2005, Special Issue: Meaning in Life, Philosophical Papers , 34: 330–463.
- Runzo, J. and Martin, N. (eds.), 2000, The Meaning of Life in the World Religions , Oxford: Oneworld Publications.
- Sanders, S. and Cheney, D. (eds.), 1980, The Meaning of Life: Questions, Answers, and Analysis , Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, Inc.
- Seachris, J. (ed.), 2012, Exploring the Meaning of Life: An Anthology and Guide , Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell.
- Smith, Q. (ed.), 2010, Special Issue: The Meaning of Life, The Monist , 93: 3–165.
- Westphal, J. and Levenson, C. A. (eds.), 1993, Life and Death , Indianapolis: Hackett.
- Baggini, J., 2004, What's It All About?: Philosophy and the Meaning of Life , London: Granta Books.
- Belliotti, R., 2001, What Is the Meaning of Life? , Amsterdam: Rodopi.
- Eagleton, T., 2007, The Meaning of Life: A Very Short Introduction , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Ford, D., 2007, The Search for Meaning: A Short History , Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Martin, M., 2002, Atheism, Morality, and Meaning , Amherst, NY: Prometheus Books.
- Messerly, J., 2012, The Meaning of Life: Religious, Philosophical, Transhumanist, and Scientific Approaches , Seattle: Darwin and Hume Publishers.
- Young, J., 2003, The Death of God and the Meaning of Life , New York: Routledge.
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up this entry topic at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- Seachris, J., 2011, “ Meaning of Life: The Analytic Perspective ”, in Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy , J. Fieser and B. Dowden (eds.)
- Vohánka, V. and Vohánková, P., n.d., “ On Nihilism Driven by the Magnitude of the Universe ”.
afterlife | death | ethics: ancient | existentialism | friendship | love | perfectionism, in moral and political philosophy | value: intrinsic vs. extrinsic | well-being
Copyright © 2013 by Thaddeus Metz < tmetz @ uj . ac . za >
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites

The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2016 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Center for the Study of Language and Information (CSLI), Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
- Essay Samples
- College Essay
- Writing Tools
- Writing guide

↑ Return to College Essay
My Personal Philosophy of Life
Introduction We all have a philosophy of life, even if we don’t know how to put it into words. Some of us are cynics, some are optimists. Some think the world owes us; others want to give back. I have a few sayings or mottos that I live by.
Live in the now
I used to worry about what was going to happen next, some distant time in the future. I would lie awake at night and make up all sorts of what ifs. Usually the scenes in my mind ended badly, with something terrible happening. I also used to have a lot of regret and even shame about the past. I’d think about silly things I’d said or done, and cringe. Even when I was sleeping, my mind would replay these things.
Then someone told me about mindfulness. It’s about being alive to what is happening to you right now, and giving your all to that moment. Like right now, I’m writing this essay and I’m giving it 100% of my attention. I could be distracted by my cell phone ringing, but I switched it off so I can focus on just one thing.
When I’m with my boyfriend, I’m truly with him. I try to really engage with him. So often, we’re in the presence of someone, but our minds are elsewhere. Especially with a partner. Because we spend a lot of time with our partners, we start to take them for granted. We often “talk” to other people via social media when we’re lying in bed with our partner, rather than talking to them. This leads to disengagement. I try and live in the now.
Amnesia by choice
I used to hold terrible grudges against people who did me wrong. They actually did do me wrong, it was not just in my head, but the point is I would spend hours dwelling on the bad things they did to me, feeling hurt and sorry for myself. I’d even fantasize about possible types of revenge, which I’m not going to mention in this essay or you might have to report me to the police!
I had a boyfriend who cheated on me with my close friend. It hurt me very badly, understandably so. I fell to pieces, lay in bed for weeks and lost a lot of weight. I was devastated.
Instead of moving on, I’d think about it all the time. How could they! I lost my boyfriend and my good friend at the same time.
One day, another friend who had been patiently listening to me for months ranting and raving said to me: You know, you don’t have to forgive them. But you can just forget about it.
That made sense to me. Everyone else had been telling me to forgive them, but I felt what they did was unforgiveable. But now I had a way of moving on without having to forgive. I could just forget about it.
And that’s what I’ve done. I call it amnesia by choice, and I’m a much happier person for it.
Conclusion I know people who have chosen philosophies related to being the richest; being more successful or effective; or winning at everything they do. Others choose to be pessimistic, and believe that you need to step on others to survive. The two philosophies of life I included in this essay help me live a more fulfilled, happier life.

Follow Us on Social Media
Get more free essays

Send via email
Most useful resources for students:.
- Free Essays Download
- Writing Tools List
- Proofreading Services
- Universities Rating
Contributors Bio


Find more useful services for students
Free plagiarism check, professional editing, online tutoring, free grammar check.
- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring
My Personal Philosophy of Life, Essay Example
Pages: 6
Words: 1689
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
I am the third of five children: I have two older sisters and two younger brothers. My big family helped me to realize the importance of family relations and it has been a basis of my future convictions. Person is an indivisible part of the family. Another thing about my childhood is that I have been involved in the nursing field from the time I could work. I started my nursing practice as a nurse aid at the age of sixteen. Strange as it may seem, I never seriously thought about being a nurse until many years later and many failed attempts at other careers. My transcript speaks for itself. I went a long way to nursing: I did not become a nurse until I was thirty one and pregnant at the time with twins. My professional choice is thoughtful and I do know what I want to get from the course.
I am not a light-minded girl and I have my own life principle, and I always try to adhere to it. My philosophy of life is “life is not always easy and you have to work hard for what you want.” Though for someone it may sound like a commonplace, in fact it is not. Such philosophy came as a result of my life, of my experience, and I believe that it helps me to withstand difficult situations.
As English proverb claims, if wishes were horses, beggars would ride, and I totally agree with it. Usually, tangible achievements come as a result of long and hard work. I perceive difficult tasks just like challenges and I understand that they are beneficial to my skills and my experience. Nursing school was not easy, studying in Framingham state college is not easy, but I know that I will reap the benefits in the end. It takes some doing to achieve good results, but I know it is the way it always happens. And everyone has to work hard for what they have ‘everyone’. Nursing is not an easy profession but I do believe that it is a way to help people understand that they should work for their wellness too, they should cooperate with nurses and then any results are achievable.
My Professional Philosophy of Nursing
When I think back now as to why I went into nursing school, I cannot come up with any clear reason. May be, it was a moment of inspiration, because then I had no strong intention of being a nurse. However, now I know that this is what I was destined to do with my life. All careers I have tried failed to provide that certainty.
I have my own perception of nursing practice, and it is my own professional philosophy. I am here to help people live a healthier, happier, and longer life. I am not striving for lofty aims; neither do I resort to common knowledge. I just feel that it is the very thing that nurses should do. Though I have come up with this idea, it is difficult to adhere to it. I feel that frequently I fail to promote this philosophy and focus on the immediate task. And that is why I study more and hone my skills.
I work as an emergency room nurse now. Actually, it is rather hard to stand back and look at the patient as a whole when you are trying to fix him or her. When they are broken, say, their blood pressure is 70/40 and you need to focus on the I.V., fluids, and blood products, it is hardly impossible to concentrate on their integrity and reasons of their illness. Current and urgent actions outweigh philosophical questions and perceptual issues.
Now I realize that helping people to recover their health does not come to just fixing their blood pressure or their broken arm. While having them in the emergency room it is teaching that I perform to help them cope with their illness or limitations. In order to better serve the patient and the family I need to consider the person as a physiological, psychological, sociocultural, and developmental being. This concept is difficult in itself, but to make people think that they are able to recover, to communicate with their relatives, to provide help and support I should embody this concept.
Just corresponding to my nursing career my philosophy of nursing is always changing and evolving. New circumstances and new cases help me to concentrate on important psychological aspects of nursing, to realize needs of ill people and make necessary decisions. They make my understanding of human needs more profound, and this enables me to help them to live healthy, happy and long lives.
My Personal and Professional Philosophy Integrated With the Framingham State
Conceptual Framework
The Framingham state college philosophy states that we need to focus “on the person as a physiological, psychological, sociocultural, and developmental being who progresses through the life cycle as a unified whole within the environment.” I do believe that we need to look at the person and the family as a whole. According to the Framingham State College Philosophy “the faculty believes that the goal of nursing is to promote the person’s movement along the wellness-illness continuum toward high-level wellness.” The way we promote the movement along the wellness-illness continuum is through education of out patients. We as nurses do not necessarily need to change the patient or family environment. To say the least, it is a difficult task. But what we can do is help them to cope with the environment that they live in to promote wellness. But we must inform our patients about what the way to wellness looks like. We do need to let patient know that it is not always easy. There is no one pill that cures everything.
Here my own life philosophy coincides with the Framingham state college idea. I think that there are no easy ways to deal with serious illness or limitation. So in order to evaluate some compromise way to recover that would be easy to follow I explore the patient as a whole: his or her lifestyle, habits, environment, etc. I usually try to persuade people that in order to get better or prevent their illness they should change something: say, their behavior, habits, diet, or lifestyles.
As prevention is better that cure, the college emphasizes the importance of prevention. Whether prevention means reduction of risk of being ill or general promotion of wellness or it means in-time detection and prevention of further worsening, or even prevention of consequences of the existing illness, it is achieved through promotion of wellness. The philosophy of college claims that promotion of wellness is an important part of the cure, and my personal philosophy also supports this idea. Everyone has an ability to withstand the illness being provided with a professional and timely help. And then it is necessary to understand that nurses are able to provide that kind of help, but not everything can be done by nurses. Something is always left for the patient’s work.
The Framingham college course underlines the importance of nurses in preventive health care. Nurses can influence people and make decisions concerning their health conditions. It is not a part of usual nursing course, and it is important to integrate these principles of preventive health care into usual working practice. As I have mentioned, it is not that easy but in the long run worth doing. It requires new skills and knowledge of behavioral and natural sciences and change of attitude to the patient sometimes.
What is really important for the college philosophy is not just taking care of health, but providing education, assistance and advocacy to people. Nurses should not be just medical profession, they should communicate with their patients and involve them into decision making if necessary. But the role of nurse must be leading as nurses are responsible for all decisions. Also, nurses should hone their skills constantly in communities, within collectives, and strive for betterment of their nursing practice. Actually, promoting wellness is a complex mission and it requires certain skills and approaches.
I think that in general my personal philosophy does comply with the philosophy of the college. College philosophy requires nurses to learn constantly and to improve their skills, to change the professional attitude to patients from the medical to more humanistic, socioeconomic, etc. I understand that it is necessary and in the long run it will improve my nursing skills noticeably. Professional nurses should be able to help patients to withstand their illnesses, and not only by means of pills and injections. Promoting wellness is a part of prevention of future diseases. For me, this idea is really great and it is the very thing I need to study and promote. It corresponds to my idea of providing wellness through nursing, and to my philosophy of life.
Life is not easy, work is not easy, but we as nurses can ease lives of our patients and help them to recover. We are able to make the patient’s life healthier and better on the other level. All we need is improvement of nursing skills with social and humanities studies. Then patients face the reality and come up with idea that nothing comes without efforts. They realize that they are provided with extraordinary help but their wellness depends on their own efforts, too. So the philosophy of college, my personal professional philosophy and my philosophy of life are interwoven; though college idea of nursing is stable, my own convictions change as I learn more and improve my experience.
We as nurses are always working towards the highest level of wellness, either in our family, in our careers, or in our self. And we need to do the same for our patients, as we possess knowledge that is unavailable to our patients. We as nurses have an extraordinary influence on our patients and the public. We need to promote education and have the ability to promote compliance. We need to look at the patient or family as a whole and remember that at some point in time we will have someone in the health care system and could only wish the same care we would give.
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
The Role of Modern Governor, Essay Example
Carter G. Woodson, Research Paper Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Pages: 1
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371

1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
Philosophy, One Thousand Words at a Time
Welcome to 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology , an ever-growing set of over 180 original 1000-word essays on philosophical questions, theories, figures, and arguments.
We publish new essays frequently, so please check back for updates, follow us on Facebook , Twitter / X , and Instagram , and subscribe by email on this page to receive notifications of new essays.
All of our essays are now available in audio format; many of our essays are available as videos .
Select Recent Essays
Moral Education: Teaching Students to Become Better People by Dominik Balg
Gödel’s Incompleteness Theorems by Jon Charry
Objects and their Parts: The Problem of Material Composition by Jeremy Skrzypek
Artificial Intelligence: The Possibility of Artificial Minds by Thomas Metcalf
The Mind-Body Problem: What Are Minds? by Jacob Berger
Seemings: Justifying Beliefs Based on How Things Seem by Kaj André Zeller
Form and Matter: Hylomorphism by Jeremy W. Skrzypek
Kant’s Theory of the Sublime by Matthew Sanderson
Philosophy of Color by Tiina Carita Rosenqvist
On Karl Marx’s Slogan “From Each According to their Ability, To Each According to their Need” by Sam Badger
Philosophy as a Way of Life by Christine Darr
Philosophy of Mysticism: Do Mystical Experiences Justify Religious Beliefs? by Matthew Sanderson
Ancient Cynicism: Rejecting Civilization and Returning to Nature by G. M. Trujillo, Jr.
“Properly Basic” Belief in God: Believing in God without an Argument by Jamie B. Turner
Philosophy of Time: Time’s Arrow by Dan Peterson
W.D. Ross’s Ethics of “Prima Facie” Duties by Matthew Pianalto
Aristotle on Friendship: What Does It Take to Be a Good Friend? by G. M. Trujillo, Jr.
Plato’s Allegory of the Cave: the Journey Out of Ignorance by Spencer Case
Epistemic Justification: What is Rational Belief? by Todd R. Long
The Doctrine of Double Effect: Do Intentions Matter to Ethics? by Gabriel Andrade
The Buddhist Theory of No-Self (Anātman/Anattā) by Daniel Weltman
Self-Knowledge: Knowing Your Own Mind by Benjamin Winokur
The Meaning of Life: What’s the Point? and Meaning in Life: What Makes Our Lives Meaningful? by Matthew Pianalto
The Philosophy of Humor: What Makes Something Funny? by Chris A. Kramer
Karl Marx’s Theory of History by Angus Taylor
Saving the Many or the Few: The Moral Relevance of Numbers by Theron Pummer
Philosophy of Space and Time: What is Space? and Philosophy of Space and Time: Are the Past and Future Real ? by Dan Peterson
What Is Misogyny? by Odelia Zuckerman and Clair Morrissey
Philosophy and Race: An Introduction to Philosophy of Race by Thomas Metcalf
“Can They Suffer?”: Bentham on our Obligations to Animals by Daniel Weltman
Ursula Le Guin’s “The Ones who Walk Away from Omelas”: Would You Walk Away? by Spencer Case
Indoctrination: What is it to Indoctrinate Someone? by Chris Ranalli
Agnosticism about God’s Existence by Sylwia Wilczewska
African American Existentialism: DuBois, Locke, Thurman, and King by Anthony Sean Neal
Conspiracy Theories by Jared Millson
Philosophical Inquiry in Childhood by Jana Mohr Lone
Essay Categories
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Africana Philosophy
- Buddhist Philosophy
- Chinese Philosophy
- Epistemology, or Theory of Knowledge
- Historical Philosophy
- Islamic Philosophy
- Logic and Reasoning
- Metaphilosophy, or Philosophy of Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Phenomenology and Existentialism
- Philosophy of Education
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Mind and Language
- Philosophy of Race
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Sex and Gender
- Social and Political Philosophy
* New categories are added as the project expands.
Popular Essays
* This is a selection of some of our most popular essays.
Descartes’ “I think, therefore I am” by Charles Miceli and Descartes’ Meditations by Marc Bobro
Marx’s Conception of Alienation by Dan Lowe
John Rawls’ ‘A Theory of Justice’ by Ben Davies
The Ethics of Abortion by Nathan Nobis
Aristotle’s Defense of Slavery by Dan Lowe
“God is Dead”: Nietzsche and the Death of God by Justin Remhof
Philosophy and Its Contrast with Science : Comparing Philosophical and Scientific Understanding by Thomas Metcalf
Happiness: What is it to be Happy? by Kiki Berk
Pascal’s Wager: A Pragmatic Argument for Belief in God by Liz Jackson
The African Ethic of Ubuntu by Thaddeus Metz
New to philosophy?! Perhaps begin with these essays:
What is Philosophy? by Thomas Metcalf,
Critical Thinking: What is it to be a Critical Thinker? by Carolina Flores,
Arguments: Why Do You Believe What You Believe? by Thomas Metcalf, and
Is it Wrong to Believe Without Sufficient Evidence? W.K. Clifford’s “The Ethics of Belief” by Spencer Case.
We have resources for students on How to Write a Philosophical Essay and How to Read Philosophy by the Editors of 1000-Word Philosophy .
A teaching units page has resources to help instructors develop course modules.
2023 and 2022 End of Year Reports are available here .
Follow 1000-Word Philosophy on Facebook , Twitter / X , and Instagram and subscribe to receive email notifications of new essays at 1000WordPhilosophy.com
Share this:.
Home — Essay Samples — Philosophy — Personal Philosophy — I Am Who I Am: My Personal Philosophy
I Am Who I Am: My Personal Philosophy
- Categories: Me Myself and I Personal Philosophy
About this sample

Words: 503 |
Published: Feb 8, 2022
Words: 503 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Works Cited:
- Calder, L. D., & Krueger, A. B. (1993). The effect of the minimum wage on employment and unemployment: A survey of the evidence from micro data. National Bureau of Economic Research.
- Deere, D. R., Murphy, K. M., & Welch, F. (1995). Employment and the 1990-1991 minimum-wage hike. ILR Review, 48(4), 792-809.
- Grossman, J. B. (2019). Minimum wage laws. Salem Press Encyclopedia.
- Hess, F. M., & Byker, T. (2016). The impact of minimum wage rates on body weight in the United States. Social Science & Medicine, 150, 19-24.
- Holtz-Eakin, D., & Sherman, R. (2019). The Congressional Budget Office’s analysis of the Raise the Wage Act of 2019. American Action Forum.
- Krugman, P. (2019). A minimum-wage review: Up with wages. The New York Times.
- Neumark, D., & Wascher, W. (2007). Minimum wages and employment. Foundations and Trends® in Microeconomics, 3(1–2), 1-182.
- Stone, C., & Trisi, D. (2019). Raising the minimum wage to $15 by 2025 would lift wages for 17 million workers but would also cut 1.3 million jobs. Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
- Ziliak, J. P. (2019). Minimum wage increases are flawed policy. The Hill.
- Zucman, G. (2019). The case for a progressive national sales tax. The New York Times.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: Life Philosophy

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 1004 words
4 pages / 1991 words
2 pages / 844 words
3 pages / 1234 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Personal Philosophy
Education is a powerful force that shapes the future of individuals and societies. As an educator, my personal philosophy of education serves as the guiding compass for my teaching practices and the principles that underpin my [...]
Developing a personal teaching philosophy is essential to defining the way an educator shapes the minds of their students. My teaching philosophy essay reflects my belief that the role of education extends far beyond the [...]
Life is how we go about day by day, month by month, year by year. Our actions, even the slightest, can twist and turn our paths like a labyrinth. Life is quite unpredictable, though it is what we make of it. Whatever happens in [...]
Philosophy in nursing stems from providing competent and optimal care to patients and communities. These values are the stepping stones to be a successful nurse. For as long as I can remember I have been overwhelmed with a [...]
Understanding the thoughts of Bertrand Russell“To fear love is to fear life and those who fear life are already three parts dead” Russell focuses on this line of thought to define love through his Analytic Philosophy which gives [...]
The wind whipped around the corner, moaning and warning me that torrential rain awaited me. Without hesitating, I shut all the windows in my room. I fumbled down the stairs to the living room and sat on a couch. The sound of the [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

College Life Is Unpredictable–And That’s Okay
Written by lauren smyth.
“Why are you here?”
My first instinct was to justify myself. To come up with a college-counselor-approved, resume-stamped, yes-I-want-this-job reason. Because I need the credit hours. Because I think everyone should know these skills. Because I’m taking a health economics course in the fall, so I should know something about health, right…?
The truth was, I’d signed up for the EMT class just because I wanted to. Which is a seriously underrated reason to sign up for anything, but also doesn’t sound like much of an answer.
“It’s a useful skill,” I told my instructor. She just looked more puzzled, so I added: “And it sounded fun.”
In other words: Why not?
I came to college to study politics. I’ll leave with economics and journalism degrees. I argued with the family members who told me to try out radio as an extracurricular, and I’m now running news coverage at WRFH Radio Free Hillsdale. (Thanks, Mom + Dad). Working at the State Department had been a lifelong pre-college dream, and now I’m hoping to fly medical rescue helicopters and become a news anchor.
The point is, things change. Being in college is like being a loaf of bread. Your margins expand and you rise to the challenge.
One of the most important lessons you’ll learn in college—especially a liberal arts school like Hillsdale, where opportunities and career choices abound—is that you don’t always know what’s best for you. As long as you remain willing to listen and course-correct accordingly, you’ll end up not only where you need to be, but where you’re meant to be.
“If you know what God has gifted you with and desired you to pursue, awesome—stick with it and don’t be ashamed that you can see His vision already,” said Caitlin Filep, ’25. “If you have no clue about your future, or He begins to change what you thought you wanted, then let Him lead you to things you might not have considered!”
Caitlin, now in her final year of college, found herself somewhere between those two extremes. She recognized from the start that she wanted to be a teacher, but it wasn’t until she’d completed part of her college experience that she began considering grad school.
“I’m definitely open to whatever else God might have for me if He wants to keep changing my plans,” she added.
It’s exactly the right mindset to have. But if you’re one of those people who requires a five-year plan for peace of mind, it can be difficult to exist in what feels like limbo. It can be even harder when every scholarship questionnaire and job application demands to know where you think you’ll be in ten years.
Once you write down an answer (I see myself as the CEO of a Fortune 500 company right out of college, which I know isn’t realistic but sounds like a great resume-builder), it can feel like failure if you don’t end up meeting your self-imposed goal.
All that pressure stilts discovery. And it makes you less receptive to adventures you might never have imagined without a little more advice and experience.
Like Caitlin, Lydia Chenoweth, ’25, also knew she wanted to be a teacher. Instead of working with elementary students like she’d always imagined, however, she now dreams of becoming a professor.
“It’s all subject to change,” Lydia said. “At the end of the day, I want to learn as much as I can surrounded by peers and students who share my interests.”
One way to leave room for new interests and discoveries, Lydia suggests, is to take as many of the required core courses as possible during freshman and sophomore year. With Hillsdale’s broad and varied core curriculum, you’ll sample a buffet of classes from across departments.
“That way, [freshmen] will find something they like eventually, without committing to anything too soon and limiting their options,” Lydia said.
Senior Lindsey Larkin agrees, adding: “Whatever career aspirations you have, learn as much as you can about that field before you’re on the job hunt. Have discussions with professionals, seek internships, and research your desired career to learn whether it’s a good fit for you. You don’t know what you don’t know!”
Lindsey’s own goals changed dramatically during her college career, leading her away from her original dream of attending law school to a new mission in conservative media.
“In my own experience, my interests shifted as I grew academically, personally, and professionally,” Lindsey said. “I entered college dead set on a politics degree and law school, then completely changed my mind. You might too!”
Didn’t like the bread analogy? Sorry, but here’s another: College is like a mystery novel. You don’t get all the answers upfront, and that’s okay. The process of discovery is rewarding for its own sake, just like unraveling a fictional mystery is a rainy afternoon’s delight.
Don’t let your plan be an anchor tethering you to something you’ve realized isn’t for you. Be open, be flexible. Let yourself be surprised.
Here’s the good news: The mystery will be solved. You will do great things. Perhaps most importantly, you will have the opportunity to change the lives of everyone you interact with—at work, at play, in college, in the “real world,” and beyond.

Published in August 2024

COMMENTS
My Personal Philosophy of Life. Life is a complex journey filled with ups and downs, challenges and opportunities. As individuals, we often find ourselves searching for meaning and purpose in this vast and mysterious existence. In this essay, I will share my personal philosophy of life, which is shaped by my experiences, values, and beliefs.
3. Naturalism. Recall that naturalism is the view that a physical life is central to life's meaning, that even if there is no spiritual realm, a substantially meaningful life is possible. Like supernaturalism, contemporary naturalism admits of two distinguishable variants, moderate and extreme (Metz 2019).
The meaning of life might be the true story of life's origins and significance.[7] In this sense, life cannot be meaningless, but its meaning might be pleasing or disappointing to us. When people like Tolstoy regard life as meaningless, they seem to be thinking that the truth about life is bad news.[8] 2.
I have known people who strongly believe in a positive viewpoint, for instance. Their life philosophies are based on seeking the good in the world around them, and I am certainly not about to argue with such beliefs. At the same time, I feel that such a way of thinking creates borders. It is a philosophy as a focus, and I do not believe that ...
Journal of Philosophy of Life Vol.5, No.1 (July 2015):1-18 [Essay] Philosophy for Everyday Life Finn Janning* Abstract The aim of this essay is two-sided. The first is to illustrate to what extent philosophy can contribute to our everyday living. The second is to illustrate how. The implicit thesis that I try to unfold in this experimental ...
Ernie Johns, Owen Sound, Ontario. 'Meaning' is a word referring to what we have in mind as 'signification', and it relates to intention and purpose. 'Life' is applied to the state of being alive; conscious existence. Mind, consciousness, words and what they signify, are thus the focus for the answer to the question.
Journal of Philosophy of Life Vol.5, No.2 (August 2015):82-90 [Essay] Life and the Pursuit of Happiness Ben G. Yacobi* Abstract Humans strive for some kind of happiness in a world that is not conducive to it. As each human life is a collection of random thoughts, choices, experiences, memories, and their interpretations, a
Lillian weighs the costs of a life-changing genetic test. Philosophy Essays from Aeon. World-leading thinkers explore life's big questions and the history of ideas from Socrates to Simone de Beauvoir, political philosophy to philosophy of mind, the Western canon and the non-Western world.
The term 'life' is important outside of biology. Often, the focus is not on the concept of life or life in general, but on the status of individual living entities. Typically, the focus is on the beginning and end stages of individual lives, which raises legal, religious, and moral questions.
This volume presents thirty-two essays on a wide array of topics in modern philosophical meaning in life research. The essays are organized into six parts. Part I, Understanding Meaning in Life, focuses on various ways of conceptualizing meaning in life. Among other issues, it discusses whether meaning in life should be understood objectively ...
Author: Matthew Pianalto Category: Ethics, Phenomenology and Existentialism, Philosophy of Religion Word Count: 997. Editors' note: this essay and its companion essay, The Meaning of Life: What's the Point? both explore the concept of meaning in relation to human life. This essay focuses on meaning in individual human lives, whereas the other addresses the meaning of life as a whole.
Life is neither fixed nor absolute, it is ambiguous; life is the possibilities entailed by existence. Life is the consciousness of humanity; it is perception of the world and the universe. So life is sadness; life is death. Life is suffering and destruction. But life is also happiness; life is living.
In 1931 a volume of Living Philosophies was published by Simon & Schuster and includes short essays about their philosophy on life from notable figures including Albert Einstein. These insightful essays capture their perspective on the world including their beliefs and ideals. ... Your life philosophy can help you better understand yourself and ...
The Meaning of Life: A Very Short Introduction. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2007. A light and lively essay on a variety of facets of the question of life's meaning, often addressing linguistic and literary themes. Rejects subjective or "postmodern" approaches to meaning in favor of a need for harmonious or loving relationships.
1. The Meaning of "Meaning". One part of the field of life's meaning consists of the systematic attempt to clarify what people mean when they ask in virtue of what life has meaning. This section addresses different accounts of the sense of talk of "life's meaning" (and of "significance," "importance," and other synonyms).
My philosophy in life essay. This topic is all about my philosophy in life together with the understanding of the philosopher named Socrates. Before I start to tell something of Socrates's philosophy and his belief, I would like to share to you the ups and downs of my life and all the hardships that I have encountered. ...
My Personal Philosophy of Life. Introduction. We all have a philosophy of life, even if we don't know how to put it into words. Some of us are cynics, some are optimists. Some think the world owes us; others want to give back. I have a few sayings or mottos that I live by. Live in the now. I used to worry about what was going to happen next ...
n philosophical writing:Avoid direct quotes. If you need to quote, quote sparingly, and follow your quotes by expla. ning what the author means in your own words. (There are times when brief direct quotes can be helpful, for example when you want to present and interpret a potential amb.
My philosophy of life is "life is not always easy and you have to work hard for what you want.". Though for someone it may sound like a commonplace, in fact it is not. Such philosophy came as a result of my life, of my experience, and I believe that it helps me to withstand difficult situations. As English proverb claims, if wishes were ...
One must remain active because a sedentary lifestyle is not beneficial to one's health. The "good life" is simply success though stability, accomplished goals and dreams, and a balanced lifestyle. Peace comes with contentment. Harmony is achieved through balance. Stability revolves around rationalization.
Welcome to 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology, an ever-growing set of over 180 original 1000-word essays on philosophical questions, theories, figures, and arguments.. We publish new essays frequently, so please check back for updates, follow us on Facebook, Twitter / X, and Instagram, and subscribe by email on this page to receive notifications of new essays.
But thinking about myself, it entails the meaning of who I am. With that, all philosophers drawn much of my life's reflection. I am conscious of my surroundings, my peers, my family, my future and so many things. Deep in my thoughts, I could say I wish I were a…and I want to be…..It's quite ridiculous, I know there's only constant ...
Final Philosophy 101 Essay Life Argument begins with the assertion that life is good for its subject. He goes on to present several supporting ideas for this, such as the features of the human experience constitute us as human beings and therefore allows us to do things. Furthermore, these characteristics are good for human life, and though ...
"May earth be better and heaven be richer because of the life and labor of Hillsdale College." Prayer in Bible placed inside the cornerstone of Central Hall, 1853; ... Outside of starting arguments in philosophy class, she enjoys curling up on a bench outdoors (sun, rain, or snow) to write novels or articles for her blog, www.laurensmythbooks ...