Reported Questions
Reported questions are one form of reported speech .
| direct question | reported question |
|---|---|
| She said: "Are you cold?" | She asked me if I was cold. |
| He said: "Where's my pen?" | He asked where his pen was. |
We usually introduce reported questions with the verb "ask":
- He asked (me) if / whether ... (YES/NO questions)
- He asked (me) why / when / where / what / how ... (question-word questions)
As with reported statements , we may need to change pronouns and tense (backshift) as well as time and place in reported questions.
But we also need to change the word order . After we report a question, it is no longer a question (and in writing there is no question mark). The word order is like that of a normal statement (subject-verb-object).

Reported YES/NO questions
We introduce reported YES/NO questions with ask + if :
| direct question | She said, | |
|---|---|---|
| reported question | She asked | . |
Note that in the above example the reported question has no auxiliary "do". But there is pronoun change and backshift.
Note that we sometimes use "whether" instead of "if". The meaning is the same. "Whether" is a little more formal and more usual in writing:
- They asked us if we wanted lunch.
- They asked us whether we wanted lunch.
Reported question-word questions
We introduce reported question-word questions with ask + question word :
| direct question | He said, | "Where | do you live?" |
|---|---|---|---|
| reported question | He asked me | where | I lived. |
Note that in the above example the reported question has no auxiliary "do". But there is pronoun change and backshift.
- YES/NO questions: Do you want tea?
- Question Word questions: Where did you drink tea?
- Choice questions: Do you prefer tea or coffee?
Look at these example sentences:
| direct question | reported question | |
|---|---|---|
| YES/NO questions | I said: "Can I help you?" | I asked if I could help her. |
| She said to us: "Did you feel cold?" | She asked if we had felt cold. | |
| He said: "Are your hands cold?" | He asked whether my hands were cold. | |
| question-word questions | He said: "Where are you going?" | He asked me where I was going. |
| He said: "Why didn't you say something?" | He asked me why I hadn't said anything. | |
| He said: "When will they come?" | He asked when they would come. | |
| He said: "Who has seen Avatar?" | He asked me who had seen Avatar. | |
| He said: "How much might it cost?" | He asked me how much it might cost. | |
| She said to me: "Where is the station?" | She asked me where the station was. | |
| choice questions | He asked, "Do you want tea or coffee?" | He asked whether I wanted tea or coffee. |
| He said, "Is the car new or second-hand?" | He asked whether the car was new or second-hand. |


What is Reported Speech and how to use it? with Examples
Published by
Olivia Drake
Reported speech and indirect speech are two terms that refer to the same concept, which is the act of expressing what someone else has said.
On this page:
Reported speech is different from direct speech because it does not use the speaker’s exact words. Instead, the reporting verb is used to introduce the reported speech, and the tense and pronouns are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. There are two main types of reported speech: statements and questions.
1. Reported Statements: In reported statements, the reporting verb is usually “said.” The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and any pronouns referring to the speaker or listener are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. For example, “I am going to the store,” becomes “He said that he was going to the store.”
2. Reported Questions: In reported questions, the reporting verb is usually “asked.” The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and the word order changes from a question to a statement. For example, “What time is it?” becomes “She asked what time it was.”
It’s important to note that the tense shift in reported speech depends on the context and the time of the reported speech. Here are a few more examples:
- Direct speech: “I will call you later.”Reported speech: He said that he would call me later.
- Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?”Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework.
- Direct speech: “I love pizza.”Reported speech: They said that they loved pizza.
When do we use reported speech?
Reported speech is used to report what someone else has said, thought, or written. It is often used in situations where you want to relate what someone else has said without quoting them directly.
Reported speech can be used in a variety of contexts, such as in news reports, academic writing, and everyday conversation. Some common situations where reported speech is used include:
News reports: Journalists often use reported speech to quote what someone said in an interview or press conference.
Business and professional communication: In professional settings, reported speech can be used to summarize what was discussed in a meeting or to report feedback from a customer.
Conversational English: In everyday conversations, reported speech is used to relate what someone else said. For example, “She told me that she was running late.”
Narration: In written narratives or storytelling, reported speech can be used to convey what a character said or thought.
How to make reported speech?
1. Change the pronouns and adverbs of time and place: In reported speech, you need to change the pronouns, adverbs of time and place to reflect the new speaker or point of view. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the store now,” she said. Reported speech: She said she was going to the store then.
In this example, the pronoun “I” is changed to “she” and the adverb “now” is changed to “then.”
2. Change the tense: In reported speech, you usually need to change the tense of the verb to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I will meet you at the park tomorrow,” he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet me at the park the next day.
In this example, the present tense “will” is changed to the past tense “would.”
3. Change reporting verbs: In reported speech, you can use different reporting verbs such as “say,” “tell,” “ask,” or “inquire” depending on the context of the speech. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework.
In this example, the reporting verb “asked” is changed to “said” and “did” is changed to “had.”
Overall, when making reported speech, it’s important to pay attention to the verb tense and the changes in pronouns, adverbs, and reporting verbs to convey the original speaker’s message accurately.
How do I change the pronouns and adverbs in reported speech?
1. Changing Pronouns: In reported speech, the pronouns in the original statement must be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. Generally, the first person pronouns (I, me, my, mine, we, us, our, ours) are changed according to the subject of the reporting verb, while the second and third person pronouns (you, your, yours, he, him, his, she, her, hers, it, its, they, them, their, theirs) are changed according to the object of the reporting verb. For example:
Direct speech: “I love chocolate.” Reported speech: She said she loved chocolate.
Direct speech: “You should study harder.” Reported speech: He advised me to study harder.
Direct speech: “She is reading a book.” Reported speech: They noticed that she was reading a book.
2. Changing Adverbs: In reported speech, the adverbs and adverbial phrases that indicate time or place may need to be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. For example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the cinema tonight.” Reported speech: She said she was going to the cinema that night.
Direct speech: “He is here.” Reported speech: She said he was there.
Note that the adverb “now” usually changes to “then” or is omitted altogether in reported speech, depending on the context.
It’s important to keep in mind that the changes made to pronouns and adverbs in reported speech depend on the context and the perspective of the new speaker. With practice, you can become more comfortable with making these changes in reported speech.
How do I change the tense in reported speech?
In reported speech, the tense of the reported verb usually changes to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here are some guidelines on how to change the tense in reported speech:
Present simple in direct speech changes to past simple in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I like pizza.” Reported speech: She said she liked pizza.
Present continuous in direct speech changes to past continuous in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I am studying for my exam.” Reported speech: He said he was studying for his exam.
Present perfect in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I have finished my work.” Reported speech: She said she had finished her work.
Past simple in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I visited my grandparents last weekend.” Reported speech: She said she had visited her grandparents the previous weekend.
Will in direct speech changes to would in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I will help you with your project.” Reported speech: He said he would help me with my project.
Can in direct speech changes to could in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I can speak French.” Reported speech: She said she could speak French.
Remember that the tense changes in reported speech depend on the tense of the verb in the direct speech, and the tense you use in reported speech should match the time frame of the new speaker’s perspective. With practice, you can become more comfortable with changing the tense in reported speech.
Do I always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech?
No, you do not always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech. However, using a reporting verb can help to clarify who is speaking and add more context to the reported speech.
In some cases, the reported speech can be introduced by phrases such as “I heard that” or “It seems that” without using a reporting verb. For example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the cinema tonight.” Reported speech with a reporting verb: She said she was going to the cinema tonight. Reported speech without a reporting verb: It seems that she’s going to the cinema tonight.
However, it’s important to note that using a reporting verb can help to make the reported speech more formal and accurate. When using reported speech in academic writing or journalism, it’s generally recommended to use a reporting verb to make the reporting more clear and credible.
Some common reporting verbs include say, tell, explain, ask, suggest, and advise. For example:
Direct speech: “I think we should invest in renewable energy.” Reported speech with a reporting verb: She suggested that they invest in renewable energy.
Overall, while using a reporting verb is not always required, it can be helpful to make the reported speech more clear and accurate
How to use reported speech to report questions and commands?
1. Reporting Questions: When reporting questions, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “asked” or “wondered” followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “What time is the meeting?” Reported speech: She asked what time the meeting was.
Note that the question mark is not used in reported speech.
2. Reporting Commands: When reporting commands, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “ordered” or “told” followed by the person, to + infinitive, and any additional information. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “Clean your room!” Reported speech: She ordered me to clean my room.
Note that the exclamation mark is not used in reported speech.
In both cases, the tense of the reported verb should be changed accordingly. For example, present simple changes to past simple, and future changes to conditional. Here are some examples:
Direct speech: “Will you go to the party with me?”Reported speech: She asked if I would go to the party with her. Direct speech: “Please bring me a glass of water.”Reported speech: She requested that I bring her a glass of water.
Remember that when using reported speech to report questions and commands, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
How to make questions in reported speech?
To make questions in reported speech, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “asked” or “wondered” followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here are the steps to make questions in reported speech:
Identify the reporting verb: The first step is to identify the reporting verb in the sentence. Common reporting verbs used to report questions include “asked,” “inquired,” “wondered,” and “wanted to know.”
Change the tense and pronouns: Next, you need to change the tense and pronouns in the sentence to reflect the shift from direct to reported speech. The tense of the verb is usually shifted back one tense (e.g. from present simple to past simple) in reported speech. The pronouns should also be changed as necessary to reflect the shift in perspective from the original speaker to the reporting speaker.
Use an appropriate question word: If the original question contained a question word (e.g. who, what, where, when, why, how), you should use the same question word in the reported question. If the original question did not contain a question word, you can use “if” or “whether” to introduce the reported question.
Change the word order: In reported speech, the word order of the question changes from the inverted form to a normal statement form. The subject usually comes before the verb, unless the original question started with a question word.
Here are some examples of reported questions:
Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?”Reported speech: He wanted to know if I had finished my homework. Direct speech: “Where are you going?”Reported speech: She wondered where I was going.
Remember that when making questions in reported speech, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
Here you can find more examples of direct and indirect questions
What is the difference between reported speech an indirect speech?
In reported or indirect speech, you are retelling or reporting what someone said using your own words. The tense of the reported speech is usually shifted back one tense from the tense used in the original statement. For example, if someone said, “I am going to the store,” in reported speech you would say, “He/she said that he/she was going to the store.”
The main difference between reported speech and indirect speech is that reported speech usually refers to spoken language, while indirect speech can refer to both spoken and written language. Additionally, indirect speech is a broader term that includes reported speech as well as other ways of expressing what someone else has said, such as paraphrasing or summarizing.
Examples of direct speech to reported
- Direct speech: “I am hungry,” she said. Reported speech: She said she was hungry.
- Direct speech: “Can you pass the salt, please?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked her to pass the salt.
- Direct speech: “I will meet you at the cinema,” he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet her at the cinema.
- Direct speech: “I have been working on this project for hours,” she said. Reported speech: She said she had been working on the project for hours.
- Direct speech: “What time does the train leave?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked what time the train left.
- Direct speech: “I love playing the piano,” she said. Reported speech: She said she loved playing the piano.
- Direct speech: “I am going to the grocery store,” he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to the grocery store.
- Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?” the teacher asked. Reported speech: The teacher asked if he had finished his homework.
- Direct speech: “I want to go to the beach,” she said. Reported speech: She said she wanted to go to the beach.
- Direct speech: “Do you need help with that?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked if she needed help with that.
- Direct speech: “I can’t come to the party,” he said. Reported speech: He said he couldn’t come to the party.
- Direct speech: “Please don’t leave me,” she said. Reported speech: She begged him not to leave her.
- Direct speech: “I have never been to London before,” he said. Reported speech: He said he had never been to London before.
- Direct speech: “Where did you put my phone?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked where she had put her phone.
- Direct speech: “I’m sorry for being late,” he said. Reported speech: He apologized for being late.
- Direct speech: “I need some help with this math problem,” she said. Reported speech: She said she needed some help with the math problem.
- Direct speech: “I am going to study abroad next year,” he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to study abroad the following year.
- Direct speech: “Can you give me a ride to the airport?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked him to give her a ride to the airport.
- Direct speech: “I don’t know how to fix this,” he said. Reported speech: He said he didn’t know how to fix it.
- Direct speech: “I hate it when it rains,” she said. Reported speech: She said she hated it when it rained.
If you've read this far, you likely found value in our content. We measure the quality of our articles in various ways, and one significant metric is the number of shares. If you appreciated this piece, please spread the word.
Leave a reply cancel reply, i’m olivia.

Welcome to my virtual classroom! Join me on a journey of language and learning, where we explore the wonders of English together. Let’s discover the joy of words and education!
Let’s connect
Join the fun!
Stay updated with our latest tutorials and ideas by joining our newsletter.
Type your email…
Recent posts
Modal verbs in conditional sentences with examples, questions in future perfect continuous tense with examples, questions in future perfect tense with examples, questions in future continuous tense with examples, questions in future indefinite (simple) tense with examples, questions in past perfect continuous tense with examples, discover more from fluent english grammar.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
Reported Speech – Rules, Examples
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
They say gossip is a natural part of human life. That’s why language has evolved to develop grammatical rules about the “he said” and “she said” statements. We call them reported speech.
Every time we use reported speech in English, we are talking about something said by someone else in the past. Thinking about it brings me back to high school, when reported speech was the main form of language!
Learn all about the definition, rules, and examples of reported speech as I go over everything. I also included a worksheet at the end of the article so you can test your knowledge of the topic.
What Does Reported Speech Mean?
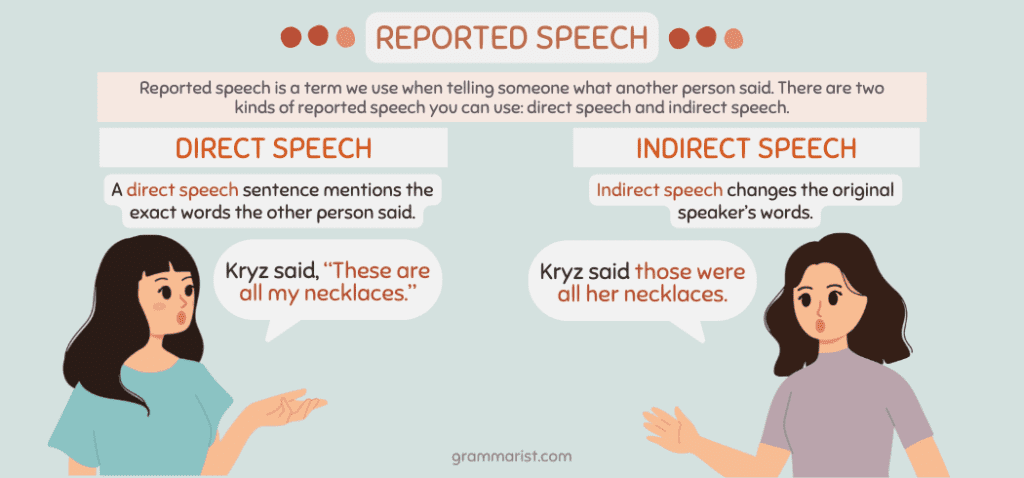
Reported speech is a term we use when telling someone what another person said. You can do this while speaking or writing.
There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I’ll break each down for you.
A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example:
- Kryz said, “These are all my necklaces.”
Indirect speech changes the original speaker’s words. For example:
- Kryz said those were all her necklaces.
When we tell someone what another individual said, we use reporting verbs like told, asked, convinced, persuaded, and said. We also change the first-person figure in the quotation into the third-person speaker.
Reported Speech Examples
We usually talk about the past every time we use reported speech. That’s because the time of speaking is already done. For example:
- Direct speech: The employer asked me, “Do you have experience with people in the corporate setting?”
Indirect speech: The employer asked me if I had experience with people in the corporate setting.
- Direct speech: “I’m working on my thesis,” I told James.
Indirect speech: I told James that I was working on my thesis.
Reported Speech Structure
A speech report has two parts: the reporting clause and the reported clause. Read the example below:
- Harry said, “You need to help me.”
The reporting clause here is William said. Meanwhile, the reported clause is the 2nd clause, which is I need your help.
What are the 4 Types of Reported Speech?
Aside from direct and indirect, reported speech can also be divided into four. The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative.
Reported Speech Rules
The rules for reported speech can be complex. But with enough practice, you’ll be able to master them all.
Choose Whether to Use That or If
The most common conjunction in reported speech is that. You can say, “My aunt says she’s outside,” or “My aunt says that she’s outside.”
Use if when you’re reporting a yes-no question. For example:
- Direct speech: “Are you coming with us?”
Indirect speech: She asked if she was coming with them.
Verb Tense Changes
Change the reporting verb into its past form if the statement is irrelevant now. Remember that some of these words are irregular verbs, meaning they don’t follow the typical -d or -ed pattern. For example:
- Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken.
Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken.
Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form.
Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting. This verb tense also works if the report is something someone would repeat. For example:
- Slater says they’re opening a restaurant soon.
- Maya says she likes dogs.
This rule proves that the choice of verb tense is not a black-and-white question. The reporter needs to analyze the context of the action.
Move the tense backward when the reporting verb is in the past tense. That means:
- Present simple becomes past simple.
- Present perfect becomes past perfect.
- Present continuous becomes past continuous.
- Past simple becomes past perfect.
- Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous.
Here are some examples:
- The singer has left the building. (present perfect)
He said that the singers had left the building. (past perfect)
- Her sister gave her new shows. (past simple)
- She said that her sister had given her new shoes. (past perfect)
If the original speaker is discussing the future, change the tense of the reporting verb into the past form. There’ll also be a change in the auxiliary verbs.
- Will or shall becomes would.
- Will be becomes would be.
- Will have been becomes would have been.
- Will have becomes would have.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I will be there in a moment.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would be there in a moment.
Do not change the verb tenses in indirect speech when the sentence has a time clause. This rule applies when the introductory verb is in the future, present, and present perfect. Here are other conditions where you must not change the tense:
- If the sentence is a fact or generally true.
- If the sentence’s verb is in the unreal past (using second or third conditional).
- If the original speaker reports something right away.
- Do not change had better, would, used to, could, might, etc.
Changes in Place and Time Reference
Changing the place and time adverb when using indirect speech is essential. For example, now becomes then and today becomes that day. Here are more transformations in adverbs of time and places.
- This – that.
- These – those.
- Now – then.
- Here – there.
- Tomorrow – the next/following day.
- Two weeks ago – two weeks before.
- Yesterday – the day before.
Here are some examples.
- Direct speech: “I am baking cookies now.”
Indirect speech: He said he was baking cookies then.
- Direct speech: “Myra went here yesterday.”
Indirect speech: She said Myra went there the day before.
- Direct speech: “I will go to the market tomorrow.”
Indirect speech: She said she would go to the market the next day.
Using Modals
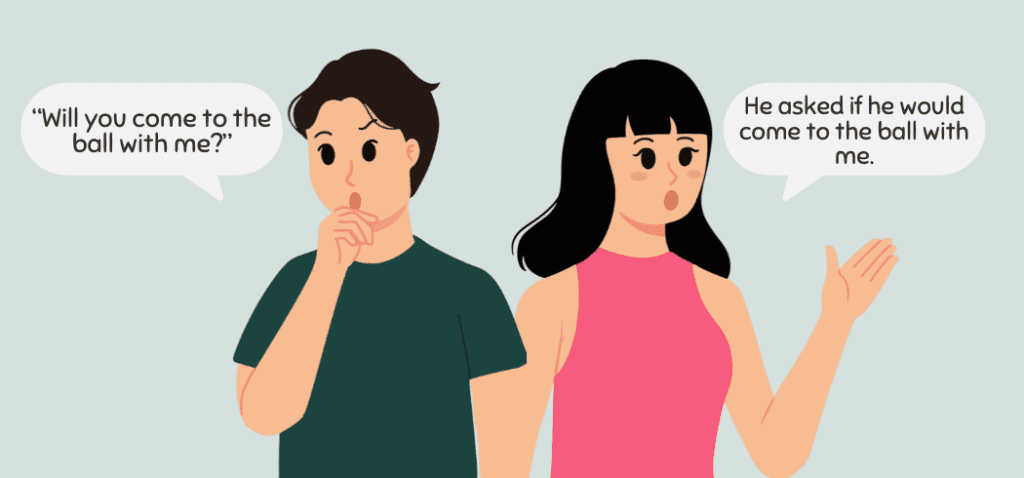

If the direct speech contains a modal verb, make sure to change them accordingly.
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- Shall becomes should or would.
- Direct speech: “Will you come to the ball with me?”
Indirect speech: He asked if he would come to the ball with me.
- Direct speech: “Gina can inspect the room tomorrow because she’s free.”
Indirect speech: He said Gina could inspect the room the next day because she’s free.
However, sometimes, the modal verb should does not change grammatically. For example:
- Direct speech: “He should go to the park.”
Indirect speech: She said that he should go to the park.
Imperative Sentences
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please . Instead, say request or say. For example:
- “Please don’t interrupt the event,” said the host.
The host requested them not to interrupt the event.
- Jonah told her, “Be careful.”
- Jonah ordered her to be careful.
Reported Questions
When reporting a direct question, I would use verbs like inquire, wonder, ask, etc. Remember that we don’t use a question mark or exclamation mark for reports of questions. Below is an example I made of how to change question forms.
- Incorrect: He asked me where I live?
Correct: He asked me where I live.
Here’s another example. The first sentence uses direct speech in a present simple question form, while the second is the reported speech.
- Where do you live?
She asked me where I live.
Wrapping Up Reported Speech
My guide has shown you an explanation of reported statements in English. Do you have a better grasp on how to use it now?
Reported speech refers to something that someone else said. It contains a subject, reporting verb, and a reported cause.
Don’t forget my rules for using reported speech. Practice the correct verb tense, modal verbs, time expressions, and place references.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.

Reported Speech: Important Grammar Rules and Examples
Reported speech is a very common aspect of the English language. You use it nearly every day, both in conversations and in writing. This reference covers key sections about reported speech, including what it is, examples, rules, and verb tense changes. You’ll also learn about modal verbs, changes in time and place, and different reporting verbs.
Reported Speech

What Is Reported Speech?
Reported speech is simply when you tell somebody what someone else said. You can do this in your writing, or in speech. Reported speech is very different from direct speech , which is when you show what somebody said in the exact way that they said it . In reported speech though, you do not need to quote somebody directly.
Instead, you use a reporting verb, such as ‘say’ or ‘ask’. These reporting verbs are used to report the speech to someone else. There are many different reporting verbs that can be used.
In short, reported speech is the linguistic technique that you use to tell somebody what someone else’s direct speech was. In reported speech though, you may need to make certain changes to the grammar to make the sentence make sense. Some examples below highlight what needs to be changed.
Reported Speech Examples
When using reported speech, you are usually talking about the past. The verbs, therefore, usually have to be in the past too.
For example :
- Direct speech: I’ve lost my umbrella .
- Reported speech: He said (that) he had lost his umbrella.
Another example :
- Direct speech: She is doing her homework .
- Reported speech: He said (that) she was doing her homework.
Table of Changes :
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| I am | He said he was |
| I have | She said she had |
| I will | They said they would |
Reported Speech Rules
Verb tense changes in reported speech.
When the reporting verb is in the present tense, only small changes are needed.
- Direct speech: I like dogs.
- Reported speech: She says she likes dogs.
When the reporting verb is in the past tense, you need to change the tense of both the reporting verb and the main verb.
- Reported speech: She said she liked dogs.
The tenses generally move backward as follows:
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Past Simple | |
| Present Continuous | Past Continuous |
| Past Perfect | |
| Past Simple | Past Perfect |
| Past Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous |
| Past Perfect | Past Perfect (remains unchanged) |
For sentences about the future, you also need to change the future verbs.
- Direct speech: I shall leave in a moment.
- Reported speech: She said that she would leave in a moment.
Here are the changes for future tenses:
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Will | Would |
| Will be | Would be |
| Will have | Would have |
| Will have been | Would have been |
Modal Verbs and Reported Speech
Modal verbs also change when used in reported speech.
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Can | Could |
| Could | Could (unchanged) |
| Have to | Had to |
| Must | Must/Had to |
| May | Might |
| Might | Might (unchanged) |
| Should | Should (unchanged) |
- Direct speech: Will I see you later?
- Reported speech: He asked if he would see me later.
Some modal verbs do not need to change tense because they fit naturally.
- Direct speech: I should go to the park.
- Reported speech: He told me he should go to the park.
Here are both correct and incorrect examples of reported speech for clarity:
- Reported speech: He told me he should go to the park.
- Reported speech: He said he should go to the park.
- Incorrect reported speech: He told he should go to the park.
- Incorrect reported speech: He said me he should go to the park.
To correct these:
- Add ‘me’: He told me he should go to the park.
- Remove ‘me’ or add ‘to’: He said he should go to the park or He said to me he should go to the park.
Direct and Indirect Speech
Changes in time and place in reported speech.
References to time and place often need to change when you use indirect speech. Here is a useful guide to these changes:
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
|---|---|
| Now | Then |
| Today | That day |
| Here | There |
| This | That |
| Tomorrow | The following day/ The next day |
| Next week | The following week/ The week after |
| Yesterday | The previous day/ The day before |
| Last week | The previous week/ The week before |
| Ago | Previously/ Before |
| Tonight | That night |
No Change in Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
In some cases, verb tenses do not change when you report speech indirectly. Here are the key instances:
- When the introductory verb is in the present , present perfect , or future .
- When the reported sentence deals with a fact or general truth .
- When the reported sentence contains a time clause .
- If the verb of the sentence is in the unreal past (the second or the third conditional ).
- The subjunctive stays unchanged in the subordinate clause .
- Had better , could , would , used to , should , might , ought to , and mustn’t remain unchanged.
- If the speaker reports something immediately or soon after it was said .
Reporting Verbs in Indirect Speech
Reporting verbs are crucial in indirect speech. Here is a list categorized by their usage:
- Basic Verbs : Tell, say, ask
- Verb + that + clause : Complain, deny, explain, exclaim, remark, promise, boast, inform somebody, claim, agree, suggest
- Verb + to + infinitive : Agree, offer, refuse, demand, threaten, promise, claim
- Verb + indirect object + to + infinitive : Advise, allow, beg, command, encourage, forbid, invite, want, instruct, permit, urge, order, remind, warn
- Verb + “ing” form : Admit (to), accuse somebody of, apologize for, boast about/of, complain to somebody of, deny, insist on, suggest
- Verb + how : Explain to somebody
Reported Questions
When converting questions from direct to indirect speech, you follow rules similar to those for statements. Verbs used include inquire, wonder, want to know, ask.
Reported Commands and Requests
Commands and requests in Indirect Speech are formed using the to-infinitive and not to-infinitive . Common reporting verbs include order, shout, demand, warn, beg, command, tell, insist, beseech , threaten, implore, ask, propose, forbid.
Pronoun and tense changes are needed when shifting from direct to indirect speech.
Reported Speech Video
- Latest Posts
- Active vs. Passive Voice Exercises – Active vs. Passive Voice Worksheet - December 25, 2023
- Phrase Exercises – Phrase Worksheet - December 23, 2023
- Sentence Exercises – Sentence Worksheet - December 23, 2023
Reported Speech (Indirect Speech)
Exercises on reported speech.
If we report what another person has said, we usually do not use the speaker’s exact words (direct speech), but reported (indirect) speech. Therefore, you need to learn how to transform direct speech into reported speech. The structure is a little different depending on whether you want to transform a statement, question or request.
When transforming statements, check whether you have to change:
- present tense verbs (3rd person singular)
- place and time expressions
- tenses (backshift)
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| “I speak English.” | |
| He says that he speaks English. | |
| He said that he spoke English. |
→ more on statements in reported speech
When transforming questions, check whether you have to change:
Also note that you have to:
- transform the question into an indirect question
- use the interrogative or if / whether
| Type | Example | |
|---|---|---|
| “Why don’t you speak English?” | ||
| He asked me why I didn’t speak English. | ||
| “Do you speak English?” | ||
| He asked me whether / if I spoke English. | ||
→ more on questions in reported speech
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Carol, speak English. | |
| He told Carol to speak English. |
→ more on requests in reported speech
Additional Information and Exeptions
Apart from the above mentioned basic rules, there are further aspects that you should keep in mind, for example:
- main clauses connected with and / but
- tense of the introductory clause
- reported speech for difficult tenses
- exeptions for backshift
- requests with must , should , ought to and let’s
→ more on additional information and exeptions in reported speech
Statements in Reported Speech
- no backshift – change of pronouns
- no backshift – change of pronouns and places
- with backshift
- with backshift and change of place and time expressions
Questions in Reported Speech
Requests in reported speech.
- Exercise 1 – requests (positive)
- Exercise 2 – requests (negative)
- Exercise 3 – requests (mixed)
Mixed Exercises on Reported Speech
- Exercise on reported speech with and without backshift
Grammar in Texts
- „ The Canterville Ghost “ (highlight direct speech and reported speech)

Reported Speech (Part 2) – Requests, Orders, and Questions

Read Reported Speech (Part 1) to learn how to make reported statements.
In Part 2, we will focus on requests, orders, and questions.
| “Please make 10 copies of this report.” She asked me to make 10 copies of the report.“Go to the bank.” He told me to go to the bank. | ||
| “Are you coming to the party?” He asked if I was coming to the party.“Has John seen the new movie?” She asked if John had seen the new movie. | ||
| “When was the company founded?” She asked when the company was founded.“What kind of car do you drive?” He wanted to know what kind of car I drive. |
1. Requests/orders
- “Asked me to” is used for requests.
- “Told me to” is stronger; it is used for orders/commands.
- The main verb stays in the infinitive: She asked me to make copies. He told me to go to the bank.
2. Yes/no questions
- “Asked if” and “wanted to know if” are equal.
- The main verb changes according to the rules for reported statements : “ Did you turn off the TV?” (past simple) She asked if I had turned off the TV (past perfect)
- We don’t use the auxiliary verbs “do/does/did” in the reported question.
3. Other questions
- “Asked” and “wanted to know” are equal.
- We don’t use the auxiliary verb “do” or “does” in the reported question: “Where does he work?” She wanted to know where he works .
- In questions with the verb “to be,” the word order changes in the reported question: “Where were you born?” (Question word + [to be] + subject) He asked where I was born (Question word + subject + [to be]) He asked where was I born

Reported Speech (Part 2) Quiz
Master the details of English grammar:

You might also like...

British vs. American English Spelling

100 Superlatives: List & Examples

24 Examples of Adjective + Preposition Combinations

Hi, I’m Shayna. I create courses helping English as a Second Language learners become more fluent in just a few minutes a day – so they can speak English naturally and confidently in work and daily life.
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Reported speech: indirect speech
Indirect speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech , the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
direct | indirect | reported clause | |
statement | ) I was tired. | -clause | |
question | . . | clause clause clause | |
command | . | -infinitive clause |
Indirect speech: reporting statements
Indirect reports of statements consist of a reporting clause and a that -clause. We often omit that , especially in informal situations:
The pilot commented that the weather had been extremely bad as the plane came in to land. (The pilot’s words were: ‘The weather was extremely bad as the plane came in to land.’ )
I told my wife I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday. ( that -clause without that ) (or I told my wife that I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday .)
Indirect speech: reporting questions
Reporting yes-no questions and alternative questions.
Indirect reports of yes-no questions and questions with or consist of a reporting clause and a reported clause introduced by if or whether . If is more common than whether . The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She asked if [S] [V] I was Scottish. (original yes-no question: ‘Are you Scottish?’ )
The waiter asked whether [S] we [V] wanted a table near the window. (original yes-no question: ‘Do you want a table near the window? )
He asked me if [S] [V] I had come by train or by bus. (original alternative question: ‘Did you come by train or by bus?’ )
Questions: yes-no questions ( Are you feeling cold? )
Reporting wh -questions
Indirect reports of wh -questions consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a wh -word ( who, what, when, where, why, how ). We don’t use a question mark:
He asked me what I wanted.
Not: He asked me what I wanted?
The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She wanted to know who [S] we [V] had invited to the party.
Not: … who had we invited …
Who , whom and what
In indirect questions with who, whom and what , the wh- word may be the subject or the object of the reported clause:
I asked them who came to meet them at the airport. ( who is the subject of came ; original question: ‘Who came to meet you at the airport?’ )
He wondered what the repairs would cost. ( what is the object of cost ; original question: ‘What will the repairs cost?’ )
She asked us what [S] we [V] were doing . (original question: ‘What are you doing?’ )
Not: She asked us what were we doing?
When , where , why and how
We also use statement word order (subject + verb) with when , where, why and how :
I asked her when [S] it [V] had happened (original question: ‘When did it happen?’ ).
Not: I asked her when had it happened?
I asked her where [S] the bus station [V] was . (original question: ‘Where is the bus station?’ )
Not: I asked her where was the bus station?
The teacher asked them how [S] they [V] wanted to do the activity . (original question: ‘How do you want to do the activity?’ )
Not: The teacher asked them how did they want to do the activity?
Questions: wh- questions
Indirect speech: reporting commands
Indirect reports of commands consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a to -infinitive:
The General ordered the troops to advance . (original command: ‘Advance!’ )
The chairperson told him to sit down and to stop interrupting . (original command: ‘Sit down and stop interrupting!’ )
We also use a to -infinitive clause in indirect reports with other verbs that mean wanting or getting people to do something, for example, advise, encourage, warn :
They advised me to wait till the following day. (original statement: ‘You should wait till the following day.’ )
The guard warned us not to enter the area. (original statement: ‘You must not enter the area.’ )
Verbs followed by a to -infinitive
Indirect speech: present simple reporting verb
We can use the reporting verb in the present simple in indirect speech if the original words are still true or relevant at the time of reporting, or if the report is of something someone often says or repeats:
Sheila says they’re closing the motorway tomorrow for repairs.
Henry tells me he’s thinking of getting married next year.
Rupert says dogs shouldn’t be allowed on the beach. (Rupert probably often repeats this statement.)
Newspaper headlines
We often use the present simple in newspaper headlines. It makes the reported speech more dramatic:
JUDGE TELLS REPORTER TO LEAVE COURTROOM
PRIME MINISTER SAYS FAMILIES ARE TOP PRIORITY IN TAX REFORM
Present simple ( I work )
Reported speech
Reported speech: direct speech
Indirect speech: past continuous reporting verb
In indirect speech, we can use the past continuous form of the reporting verb (usually say or tell ). This happens mostly in conversation, when the speaker wants to focus on the content of the report, usually because it is interesting news or important information, or because it is a new topic in the conversation:
Rory was telling me the big cinema in James Street is going to close down. Is that true?
Alex was saying that book sales have gone up a lot this year thanks to the Internet.
‘Backshift’ refers to the changes we make to the original verbs in indirect speech because time has passed between the moment of speaking and the time of the report.
direct speech | indirect speech |
| not very happy at work.’ | not very happy at work. |
| going home.’ | going home. |
| be late.’ | be late. |
| been working,’ she said. | . |
| to make her so angry?’ he asked. | to make her so angry. |
In these examples, the present ( am ) has become the past ( was ), the future ( will ) has become the future-in-the-past ( would ) and the past ( happened ) has become the past perfect ( had happened ). The tenses have ‘shifted’ or ‘moved back’ in time.
direct | indirect | |
present simple | → | past simple |
present continuous | → | past continuous |
present perfect simple | → | past perfect simple |
present perfect continuous | → | past perfect continuous |
past simple | → | past perfect simple |
past continuous | → | past perfect continuous |
future (will) | → | future-in-the-past (would) |
past perfect | ↔ | past perfect (no change) |
The past perfect does not shift back; it stays the same:
Direct speech | Indirect speech |
| already left. |
Modal verbs
Some, but not all, modal verbs ‘shift back’ in time and change in indirect speech.
direct speech | indirect speech | change | |
| be there,’ he promised. | be there. | becomes |
| need more money.’ I open it?’ she asked. | need more money. open it. | usually becomes in reported questions, becomes |
| see you at 2.30,’ he added. | see me at 2.30. | becomes |
| be back later,’ she said. wait in the hallway,’ he said. | be back later. wait in the hallway. | (possibility) becomes (permission) becomes |
| pay by 30th April.’ be awful to live in such a noisy place,’ she said. | pay by 30th April. be awful to live in such a noisy place. | (obligation) usually becomes (speculation) does not change |
| sell it for about 2,000 euros,’ he said. | sell it for about 2,000 euros. | no change |
| go there immediately,’ she said. | go there immediately. | no change |
| buy it if I had the money,’ he said. | buy it if he had the money. | no change |
| snow tonight,’ he warned. | snow that night. | no change |
| come till six o’clock,’ he said. | come till six o’clock. | no change |
We can use a perfect form with have + - ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past:
He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: ‘The noise might be the postman delivering letters.’ )
He said he would have helped us if we’d needed a volunteer. (original statement: ‘I’ll help you if you need a volunteer’ or ‘I’d help you if you needed a volunteer.’ )
Used to and ought to do not change in indirect speech:
She said she used to live in Oxford. (original statement: ‘I used to live in Oxford.’ )
The guard warned us that we ought to leave immediately. (original statement: ‘You ought to leave immediately.’ )
No backshift
We don’t need to change the tense in indirect speech if what a person said is still true or relevant or has not happened yet. This often happens when someone talks about the future, or when someone uses the present simple, present continuous or present perfect in their original words:
He told me his brother works for an Italian company. (It is still true that his brother works for an Italian company.)
She said she ’s getting married next year. (For the speakers, the time at the moment of speaking is ‘this year’.)
He said he ’s finished painting the door. (He probably said it just a short time ago.)
She promised she ’ll help us. (The promise applies to the future.)
Indirect speech: changes to pronouns
Changes to personal pronouns in indirect reports depend on whether the person reporting the speech and the person(s) who said the original words are the same or different.
direct | indirect | |
| don’t want to shock people,’ Tom said. | said he didn’t want to shock people. | different speakers ( changes to ) |
| ’ll look after Toby,’ I said. | said I would look after Toby. | same speaker (no change) |
| need to be here at nine o’clock,’ George told Beatrice. | told Beatrice she needed to be there at nine o’clock. | different speakers ( changes to ) |
| hope you will join us tonight,’ I said to James. | told James I hoped he would join us that night. | same speaker (no change to ; changes to ) |
Indirect speech: changes to adverbs and demonstratives
We often change demonstratives ( this, that ) and adverbs of time and place ( now, here, today , etc.) because indirect speech happens at a later time than the original speech, and perhaps in a different place.
direct speech | indirect speech |
| .’ | the next/following day. |
| this moment in time.’ | . |
| .” | . |
| ,’ the boy protested. | . |
Typical changes to demonstratives, adverbs and adverbial expressions
direct | indirect | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect speech: typical errors
The word order in indirect reports of wh- questions is the same as statement word order (subject + verb), not question word order:
She always asks me where [S] [V] I am going .
Not: She always asks me where am I going .
We don’t use a question mark when reporting wh- questions:
I asked him what he was doing.
Not: I asked him what he was doing?

Word of the Day
long weekend
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
Saturday and Sunday with at least one extra day added, either Friday or Monday.

It’s not really my thing (How to say you don’t like something)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
To add ${headword} to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.

Reported speech
Reported questions
Reported questions.
When we report what people say, we usually change the tense of the verbs to reflect that we are reporting – not giving direct speech. This pattern is followed when we report questions and there are also other important changes between direct questions and reported questions.
Reported questions are one form of reported speech.
| direct question | reported question |
|---|---|
| She said: "Are you cold?" | She asked me if I was cold. |
| He said: "Where's my pen?" | He asked where his pen was. |
We usually introduce reported questions with the verb "ask":
- He asked (me) if / whether ... (YES/NO questions)
- He asked (me) why / when / where / what / how ... (question-word questions)
As with reported statements, we may need to change pronouns and tense (backshift) as well as time and place in reported questions.
But we also need to change the word order . After we report a question, it is no longer a question (and in writing there is no question mark). The word order is like that of a normal statement (subject-verb-object).
Reported YES/NO questions
We introduce reported YES/NO questions with ask + if :
| direct question | She said, | |
|---|---|---|
| reported question | She asked | . |
Note that in the above example the reported question has no auxiliary "do". But there is pronoun change and backshift.
Note that we sometimes use "whether" instead of "if". The meaning is the same. "Whether" is a little more formal and more usual in writing:
- They asked us if we wanted lunch.
- They asked us whether we wanted lunch.
Reported question-word questions
We introduce reported question-word questions with ask + question word :
| direct question | He said, | "Where | do you live?" |
|---|---|---|---|
| reported question | He asked me | where | I lived. |
Remember that there are basically three types of question:
- YES/NO questions: Do you want tea?
- Question Word questions: Where did you drink tea?
- Choice questions: Do you prefer tea or coffee?
Reported choice questions have the same structure as Reported YES/NO questions. Questions with the verb BE always have a different structure: Was the tea cold? Where is my tea? You can see all these differences in the examples below.
Look at these example sentences:
| direct question | reported question | |
|---|---|---|
| YES/NO questions | I said: "Can I help you?" | I asked if I could help her. |
| She said to us: "Did you feel cold?" | She asked if we had felt cold. | |
| He said: "Are your hands cold?" | He asked whether my hands were cold. | |
| question-word questions | He said: "Where are you going?" | He asked me where I was going. |
| He said: "Why didn't you say something?" | He asked me why I hadn't said anything. | |
| He said: "When will they come?" | He asked when they would come. | |
| He said: "Who has seen Avatar?" | He asked me who had seen Avatar. | |
| He said: "How much might it cost?" | He asked me how much it might cost. | |
| She said to me: "Where is the station?" | She asked me where the station was. | |
| choice questions | He asked, "Do you want tea or coffee?" | He asked whether I wanted tea or coffee. |
| He said, "Is the car new or second-hand?" | He asked whether the car was new or second-hand. |
Course Curriculum
- Changing time and place in reported speech 20 mins
- Direct and indirect speech 15 mins
- Tense changes in reported speech 20 mins
- Reported questions 20 mins
- Reporting verbs 20 mins
- Reporting orders and requests 15 mins
- Reporting hopes, intentions and promises 20 mins
100 Reported Speech Examples: How To Change Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of communicating what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. For example, if your friend said, “ I am going to the store ,” in reported speech, you might convey this as, “ My friend said he was going to the store. ” Reported speech is common in both spoken and written language, especially in storytelling, news reporting, and everyday conversations.
Reported speech can be quite challenging for English language learners because in order to change direct speech into reported speech, one must change the perspective and tense of what was said by the original speaker or writer. In this guide, we will explain in detail how to change direct speech into indirect speech and provide lots of examples of reported speech to help you understand. Here are the key aspects of converting direct speech into reported speech.
Reported Speech: Changing Pronouns
Pronouns are usually changed to match the perspective of the person reporting the speech. For example, “I” in direct speech may become “he” or “she” in reported speech, depending on the context. Here are some example sentences:
Reported Speech: Reporting Verbs
Reported speech: tense shifts.
When converting direct speech into reported speech, the verb tense is often shifted back one step in time. This is known as the “backshift” of tenses. It’s essential to adjust the tense to reflect the time elapsed between the original speech and the reporting. Here are some examples to illustrate how different tenses in direct speech are transformed in reported speech:
Reported Speech: Changing Time and Place References
Reported speech: question format.
When converting questions from direct speech into reported speech, the format changes significantly. Unlike statements, questions require rephrasing into a statement format and often involve the use of introductory verbs like ‘asked’ or ‘inquired’. Here are some examples to demonstrate how questions in direct speech are converted into statements in reported speech:
Reported Speech: Omitting Quotation Marks
Reported speech quiz.
Questions in Reported Speech
Learn through the article!
Pass a language test
Check the results
Subscribe to reach fluency!

Questions in reported speech are a common feature of the English language. This reference will guide you through the basics of reported speech questions, including what they are, how to use them, and common mistakes to avoid.
What are reported questions?
Reported questions, also known as indirect questions, are questions that are reported or repeated by someone else. They are used to convey what someone else has asked, and they are often used in formal and informal settings. Reported questions are different from direct questions, which are the questions that we ask directly.
For example, a direct question would be "What time is the meeting?" A reported question would be "She asked what time the meeting was." In the second sentence, the question is reported indirectly, and the tense is changed to reflect the past tense.
The basics of reported speech questions
When reporting questions, we usually use a reporting verb, such as "asked," "enquired," or "wondered." The reporting verb is followed by the question itself, which is often a statement that begins with "if" or "whether."
For example, "He asked if you were coming to the party." In this sentence, the reporting verb is "asked," and the question itself is "if you were coming to the party."
When reporting questions, we also need to consider the tense, word order, and pronouns. The tense is usually changed to reflect the past tense. The word order is often changed to reflect a statement instead of a question, and the pronouns are changed to reflect the speaker or the person being spoken about.

Examples of reported speech questions
Here are some examples of reported speech questions:
- Direct question : "What time is it?"
- Reported question : "He asked what time it was."
- Direct question: "Are you coming to the party?"
- Reported question : "She wondered if you were coming to the party."
- Direct question : "Why did you do that?"
- Reported question : "He asked why you had done that."
- Direct question : "Where are you going?"
- Reported question : "She enquired where you were going."
Changes in tense and pronouns when reporting questions
When reporting questions, we need to change the tense to reflect the past tense . For example, if the direct question is in the present tense , we need to change it to the past tense when reporting it.
We also need to change the pronouns to reflect the speaker or the person being spoken about. For example, if the direct question is "Are you coming to the party?" and the person being spoken about is John, we need to change it to "She asked if John was coming to the party."
Common reporting verbs used with questions
Here are some common reporting verbs that are used with questions:
- wanted to know
Note that the choice of reporting verb depends on the context and the tone of the conversation.
Reported speech questions vs. direct questions
Reported speech questions are different from direct questions in several ways. Direct questions are the questions that we ask directly, whereas reported questions are questions that are reported or repeated by someone else.
Direct questions typically start with a question word, such as "what," "where," "when," "who," "why," or "how." Reported questions, on the other hand, often start with "if" or "whether."
In direct questions, the subject usually comes before the verb . In reported questions, the subject usually comes after the verb.
Common mistakes
Things to avoid when using reported speech questions:
- Forgetting to change the tense to reflect the past tense.
- Using the wrong reporting verb for the context or tone of the conversation.
- Forgetting to change the pronouns to reflect the speaker or the person being spoken about.
- Using a direct question instead of a reported question.
Reported speech questions are an important aspect of English grammar that enables us to report what someone else has said. When reporting questions, we need to use a reporting verb, change the tense, word order, and pronouns, and consider the context and tone of the conversation.
By following the guidelines outlined in this reference, you should get it right every time. Check out more handy English lessons below!
Make your next step to fluency with Promova

More helpful articles:
Indirect Questions
Perfect english grammar.

| Present simple with 'be' | Is he Spanish? | Can you tell me if he is Spanish? |
| Present continuous | Is the restaurant closing now? | Can you tell me if the restaurant is closing now? |
| Past simple with 'be' | Was he late for the meeting? | Can you tell me if he was late for the meeting? |
| Past continuous | Were you watching TV at 3pm? | Can you tell me if you were watching TV at 3pm? |
| Present perfect | Has Lucy been to Mexico? | Can you tell me if Lucy has been to Mexico? |
| Present perfect continuous | Has she been living here long? | Can you tell me if she has been living here long? |
| Past perfect | Had she found this job when she moved here? | Can you tell me if she had found this job when she moved here? |
| Past perfect continuous | Had she been living here long when she met you? | Can you tell me if she had been living here long when she met you? |
| Future simple with 'will' | Will she start her new job next week? | Can you tell me if she will start her new job next week? |
| Future simple with 'going to' | Is it going to rain later? | Can you tell me if it is going to rain later? |
| Future continuous | Will Lisa be meeting the boss later? | Can you tell me if Lisa will be meeting the boss later? |
| Future perfect | Will he have finished the report by tonight? | Can you tell me if he will have finished the report by tonight? |
| Future perfect continuous | Will he have been studying French for twenty years when he retires? | Can you tell me if he will have been studying French for twenty years when he retires? |
| Modal verbs | Should we start now? | Can you tell me if we should start now? |
| Present simple with any verb except 'be' | Does David live in London? | Can you tell me if David lives in London? |
| Past simple with any verb except 'be' | Did Amanda call John yesterday? | Can you tell me if Amanda called John yesterday? |
| Present simple with 'be' | Why is he unhappy? | Can you tell me why he is unhappy? |
| Present continuous | When is the restaurant closing? | Can you tell me when the restaurant is closing? |
| Past simple with 'be' | Why was he late for the meeting? | Can you tell me why he was late for the meeting? |
| Past continuous | What were you doing at 3pm? | Can you tell me what you were doing at 3pm? |
| Present perfect | Where has Lucy been? | Can you tell me where Lucy has been? |
| Present perfect continuous | How long has she been living here? | Can you tell me how long she has been living here? |
| Past perfect | Why had she quit her job before she moved here? | Can you tell me why she had quit her job before she moved here? |
| Past perfect continuous | How long had she been living here when she met you? | Can you tell me how long she had been living here when she met you? |
| Future simple with 'will' | When will she start her new job? | Can you tell me when she will start her new job? |
| Future simple with 'going to' | When is it going to rain? | Can you tell me when it is going to rain? |
| Future continuous | What time will Lisa be meeting the boss? | Can you tell me what time Lisa will be meeting the boss? |
| Future perfect | When will he have finished the report? | Can you tell me when he will have finished the report? |
| Future perfect continuous | How long will he have been studying French when he retires? | Can you tell me how long he will have been studying French when he retires? |
| Modal verbs | What should we do now? | Can you tell me what we should do now? |
| Present simple with any verb except 'be' | Where does David live? | Can you tell me where David lives? |
| Past simple with any verb except 'be' | Why did Amanda call John yesterday? | Can you tell me why Amanda called John yesterday? |

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Craft a Memorable Message, According to Science
- Charan Ranganath

Four ways to make your point in a way that sticks.
Numerous researches have shown that we forget much of what we experience in a day. Knowing this, how do you create messages so there is a better chance of people remembering them? The author uses concepts from memory science to help you craft messages — whether it’s a presentation, an email, or a speech — that will be likely to stick. One way to craft a memorable message is to chunk it up. Explicitly tie together the points that you want to convey under the umbrella of a central idea. With this approach, your listener can stitch the pieces together in a meaningful way and build a rich memory for that material. Or, when communicating about a complex topic, you can make your message memorable with a concrete example instead of something vague. Remember to provide callbacks as recalling something that we previously learned can make it stronger and easier to access when we will need it. Lastly, spark their curiosity. The key to memorable communication lies not in conveying the answer, but in establishing a compelling question.
Imagine sitting in a meeting where someone is giving a presentation. You’re somewhat interested in the topic, and the speaker seems to be doing a good job. The meeting ends, and 30 minutes later, you try to recall what was discussed. You can remember that the coffee was weak, the room was too cold, and the speaker was wearing a pink tie … but you can’t remember what he was talking about.
- Dr. Charan Ranganath is a professor at the Center for Neuroscience and Department of Psychology and the director of the Dynamic Memory Lab at the University of California, Davis, and the author of the book Why We Remember: Unlocking Memory’s Power to Hold On to What Matters (Penguin Random House).
Partner Center
Reported questions in English
Reported questions.
If you use a question in Reported Speech, follow the steps described on our page Reported Speech – Summary (changing of the person, backshift of tenses, shifting of expressions of time/place).
In Reported speech the question becomes a statement. Mind the word order: subject – verb
1. The introductory sentence in Reported Questions
1.1. the introductory sentence is in the simple present.
If the introductory sentence is in the Simple Present, there is no backshift of tenses.
- Direct Speech → Susan, “ Do es Mary work in an office?”
- Reported Speech → Susan asks if/whether Mary work s in an office.
The introductory sentence: Susan asks ... → is in the Simple Present . There is no backshift of tenses. The auxiliary do is dropped in the Reported speech.
1.2. The introductory sentence in the Simple Past
If the introductory sentence is in the Simple Past, there is usually backshift of tenses.
- Reported Speech → Susan asked if/whether Mary work ed in an office.
The introductory sentence: Susan asked ... → is in the Simple Past . There is backshift of tenses.
1.3. Types of introductory sentences
The word ask in introductory sentences in Reported Questions can be substituted with other words, e.g.
- want to know
2. Questions with and without question words
Questions can be formed with or without question words.
If there is a question without a question word in Direct Speech, use whether or if in Reported Speech .
- Peter, “Do you play football?” → Peter asked me whether (if) I play ed football.
If there is a question with a question word in Direct Speech, use this question word in Reported Speech .
- Peter, “ When do you play football?” → Peter asked me when I play ed football.
- You are here:
- Grammar Explanations
- Reported Speech
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election results
- Google trends
- AP & Elections
- U.S. Open Tennis
- Paralympic Games
- College football
- Auto Racing
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
RFK Jr. suspends his presidential bid and backs Donald Trump before appearing with him at his rally
Robert F. Kennedy said Friday he is suspending his independent presidential bid and is backing Donald Trump. Kennedy said his internal polls had showed that his presence in the race would hurt Trump and help Democratic nominee Kamala Harris.
- Copy Link copied
▶ Follow the AP’s live coverage and analysis from the 2024 Democratic National Convention.
PHOENIX (AP) — Robert F. Kennedy Jr. suspended his independent campaign for the White House and endorsed Donald Trump on Friday, a late-stage shakeup of the race that could give the former president a modest boost from Kennedy’s supporters.
Hours later, Kennedy joined Trump onstage at an Arizona rally, where the crowd burst into “Bobby!” cheers.
Kennedy said his internal polls had shown that his presence in the race would hurt Trump and help Democratic nominee Kamala Harris, though recent public polls don’t provide a clear indication that he is having an outsize impact on support for either major-party candidate.
Kennedy cited free speech, the war in Ukraine and “a war on our children” as among the reasons he would try to remove his name from the ballot in battleground states.
“These are the principal causes that persuaded me to leave the Democratic Party and run as an independent, and now to throw my support to President Trump,” Kennedy said at his event in Phoenix.
However, he made clear that he wasn’t formally ending his bid and said his supporters could continue to back him in the majority of states where they are unlikely to sway the outcome. Kennedy took steps to withdraw his candidacy in at least two states late this week, Arizona and Pennsylvania, but election officials in the battlegrounds of Michigan, Nevada and Wisconsin said it would be too late for him to take his name off the ballot even if he wants to do so.
Kennedy said his actions followed conversations with Trump over the past few weeks. He cast their alliance as “a unity party,” an arrangement that would “allow us to disagree publicly and privately and seriously.” Kennedy suggested Trump offered him a job if he returns to the White House, but neither he nor Trump offered details.
Kennedy’s running mate, Nicole Shanahan, this week entertained the idea that Kennedy could join Trump’s administration as secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services.
The announcement ended days of speculation and landed with heaps of confusion and contradictions from Kennedy’s aides and allies, an emblematic cap for a quixotic campaign.
Shortly before his speech in Phoenix, his campaign had said in a Pennsylvania court filing that he would be endorsing Trump for president. However, a spokesperson for Kennedy said the court filing had been made in error and the lawyer who wrote it said he’d correct it. Kennedy took the stage moments later, aired his grievances with the Democratic Party, the news media and political institutions, and extolled Trump. He spoke for nearly 20 minutes before he said explicitly that he was endorsing Trump.
Kennedy later joined Trump onstage at a rally co-hosted by Turning Point Action in Glendale, where Trump’s campaign had teased he would be joined by “a special guest.”
Kennedy was greeted by thundering applause as he took the stage to the Foo Fighters and a pyrotechnics display after being introduced by Trump as “a man who has been an incredible champion for so many of these values that we all share.”
“We are both in this to do what’s right for the country,” Trump said, later commending Kennedy for having “raised critical issues that have been too long ignored in this country.”
What to know about the 2024 Election
- Today’s news: Follow live updates from the campaign trail from the AP.
- We want to hear from you: Are you a nonwhite evangelical planning to vote for Harris? Tell us why you’re supporting her and if you’re campaigning for her.
- Ground Game: Sign up for AP’s weekly politics newsletter to get it in your inbox every Monday.
- AP’s Role: The Associated Press is the most trusted source of information on election night, with a history of accuracy dating to 1848. Learn more.
With Kennedy standing nearby, Trump invoked his slain uncle and father, John F. Kennedy and Robert F. Kennedy, saying he knows “that they are looking down right now and they are very, very proud.”
He said that, if he wins this fall, he will establish a new independent presidential commission on assassination attempts that will release all remaining documents related to John F. Kennedy’s assassination.
And he repeated his pledge to establish a panel — “working with Bobby” — to investigate the increase in chronic health conditions and childhood diseases, including autoimmune disorders, autism, obesity and infertility.
A year ago, some would have thought it inconceivable that a member of arguably the most storied family in Democratic politics would work with Trump to keep a Democrat out of the White House. Even in recent months, Kennedy has accused Trump of betraying his followers, while Trump has criticized Kennedy as “the most radical left candidate in the race.”
Five of Kennedy’s family members issued a statement Friday calling his support for Trump “a sad ending to a sad story” and reiterating their support for Harris.
“Our brother Bobby’s decision to endorse Trump today is a betrayal of the values that our father and our family hold most dear,” read the statement, which his sister Kerry Kennedy posted on X .
Kennedy Jr. acknowledged his decision to endorse Trump had caused tension with his family. He is married to actor Cheryl Hines, who wrote on X that she deeply respects her husband’s decision to drop out but did not address the Trump endorsement.
“This decision is agonizing for me because of the difficulties it causes my wife and my children and my friends,” Kennedy said. “But I have the certainty that this is what I’m meant to do. And that certainty gives me internal peace, even in storms.”
In a statement, Harris campaign chair Jen O’Malley Dillon reached out to Kennedy’s supporters who are “tired of Donald Trump and looking for a new way forward” and said that Harris wanted to earn their backing.
At Kennedy’s Phoenix event, 38-year-old Casey Westerman said she trusted Kennedy’s judgment and had planned to vote for him, but would support Trump if Kennedy endorsed him.
“My decision would really be based on who he thinks is best suited to run this country,” said Westerman, who wore a “Kennedy 2024” trucker hat and voted for Trump in the last two presidential elections.
Kennedy first entered the 2024 presidential race as a Democrat but left the party last fall to run as an independent. He built an unusually strong base for a third-party bid, fueled in part by anti-establishment voters and vaccine skeptics who have followed his anti-vaccine work since the COVID-19 pandemic. But he has since faced strained campaign finances and mounting legal challenges.
At Trump’s event in Las Vegas, Alida Roberts, 49, said Kennedy’s endorsement of Trump spoke volumes about the current state of the Democratic Party.
“It says that he doesn’t trust what’s going on, that it’s not the party he grew up in,” Roberts said.
Roberts, who voted twice for Trump, said she was relieved and excited by the endorsement because she’d been “teeter-tottering” between the two candidates.
Recent polls put Kennedy’s support in the mid-single digits, and it’s unclear if he’d get even that in a general election.
There’s some evidence that Kennedy’s staying in the race would hurt Trump more than Harris. According to a July AP-NORC poll, Republicans were significantly more likely than Democrats to have a favorable view of Kennedy. And those with a positive impression of Kennedy were significantly more likely to also have a favorable view of Trump (52%) than Harris (37%).
Associated Press writers Jill Colvin and Ali Swenson in New York, Rio Yamat in Las Vegas, Marc Levy in Harrisburg, Pa., Meg Kinnard in Chicago and Linley Sanders in Washington contributed to this report.
___ The Associated Press receives support from several private foundations to enhance its explanatory coverage of elections and democracy. See more about AP’s democracy initiative here . The AP is solely responsible for all content.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Reported questions are one form of reported speech. direct question. reported question. She said: "Are you cold?" She asked me if I was cold. He said: "Where's my pen?" He asked where his pen was. We usually introduce reported questions with the verb "ask": He asked (me) if / whether ...
To make questions in reported speech, you need to use an introductory phrase such as "asked" or "wondered" followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here are the steps to make questions in reported speech:
We make the question form of the present simple of be by inverting (changing the position of)the subject and verb. So, we need to change them back before putting the verb into the past simple. ... In fact, we make this into reported speech in the same way as a request. We just use 'tell' instead of 'ask': Reported speech: She told me to sit ...
Reported speech: He wanted to know whether I had a computer. You introduce the reported question with a different word and change the word order to that of a statement. End the sentence with a full stop. How to Report Wh and Yes/No Questions Reported Speech Questions: Yes/No Questions. To report yes/no questions, use if or whether.
For example: Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken. Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken. Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form. Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting.
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called "backshift.". Here are some examples in different verb tenses: "I want to go home.". She said she wanted to go home. "I 'm reading a good book.". She said she was reading a good book. "I ate pasta for dinner last night.".
In reported speech though, you may need to make certain changes to the grammar to make the sentence make sense. Some examples below highlight what needs to be changed. ... Reported Questions. When converting questions from direct to indirect speech, you follow rules similar to those for statements. Verbs used include inquire, ...
transform the question into an indirect question. use the interrogative or if / whether. Type. Example. with interrogative. direct speech. "Why don't you speak English?". reported speech. He asked me why I didn't speak English.
Requests/orders. "Asked me to" is used for requests. "Told me to" is stronger; it is used for orders/commands. She asked me to make copies. He told me to go to the bank. 2. Yes/no questions. "Asked if" and "wanted to know if" are equal. We don't use the auxiliary verbs "do/does/did" in the reported question.
Reported speech: indirect speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Reported Questions. When we report what people say, we usually change the tense of the verbs to reflect that we are reporting - not giving direct speech. This pattern is followed when we report questions and there are also other important changes between direct questions and reported questions. Reported questions are one form of reported speech.
Direct: "I will help you," she promised. Reported: She promised that she would help me. Direct: "You should study harder," he advised. Reported: He advised that I should study harder. Direct: "I didn't take your book," he denied. Reported: He denied taking my book. Direct: "Let's go to the cinema," she suggested.
REPORTED SPEECH | INDIRECT SPEECH | DIRECT SPEECH Hi Everyone,In today's lesson, let's look at REPORTED SPEECH (aka INDIRECT SPEECH) in detail. We'll look at...
Reported Speech → Susan said (that)* she worked in an office. Here I is changed to she. 4. Backshift of tenses. If there is backshift of tenses in Reported Speech, the tenses are shifted the following way. Direct Speech → Peter, " I work in the garden." Reported Speech → Peter said (that)* he work ed in the garden.
The basics of reported speech questions. When reporting questions, we usually use a reporting verb, such as "asked," "enquired," or "wondered." The reporting verb is followed by the question itself, which is often a statement that begins with "if" or "whether." For example, "He asked if you were coming to the party."
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message. Q2.
In this video you will learn about how to report questions. you will learn what changes to make when changing a question from a direct to an indirect questio...
https://goo.gl/jchqAb Click here and get the best resources online to master English grammar and improve your vocabulary with tons of content for FREE! ↓ Che...
However, we use indirect questions in a different way from reported questions. Indirect questions are a way of being polite. They are very, very common in English, especially when you're talking to someone you don't know. 'Yes / No' Questions To make an indirect 'yes / no' question, we use 'if' and the word order of a normal positive sentence ...
US job growth during much of the past year was significantly weaker than initially estimated, according to new data released Wednesday.
The author uses concepts from memory science to help you craft messages — whether it's a presentation, an email, or a speech — that will be likely to stick. One way to craft a memorable ...
Questions still loom. Ms. Harris's commitment to the White House budget clarifies much about how she hopes to raise revenue if she wins the election in November. But even the thick White House ...
Kennedy's speech will come days after his running mate, Nicole Shanahan, said in a podcast interview on Tuesday that the campaign is considering whether to "join forces" with Trump to ...
Wall Street analysts had projected that the department's preliminary revision would cut as many as 1 million jobs from the tallies reported between April 2023 and March 2024, when average ...
Until now, Lt. Gen. H.R. McMaster has held his fire about his stint in the Trump White House. McMaster served with distinction in key American conflicts of the past decades: the Gulf War, the Iraq ...
In Reported speech the question becomes a statement. Mind the word order: subject - verb. 1. The introductory sentence in Reported Questions. 1.1. The introductory sentence is in the Simple Present. If the introductory sentence is in the Simple Present, there is no backshift of tenses. Direct Speech → Susan, " Does Mary work in an office?".
So, make that clear. Issue The Call To Action. Not every speech may need a formal call to action, but every public utterance needs to be understood as a call for unity, a coming together to ...
This tutorial deals with the word order of yes/no questions in the reported speech.For more general information, watch the video about the basics of reported...
Mr. Durov's arrest has become a point of contention in the debate about free speech on the internet. President Emmanuel Macron of France on Monday dismissed accusations from supporters of ...
PHOENIX (AP) — Robert F. Kennedy Jr. suspended his independent campaign for the White House and endorsed Donald Trump on Friday, a late-stage shakeup of the race that could give the former president a modest boost from Kennedy's supporters. Hours later, Kennedy joined Trump onstage at an Arizona rally, where the crowd burst into "Bobby!" cheers.