

What Does a Business Planning Manager Do?
Find out what a Business Planning Manager does, how to get this job, salary information, and what it takes to succeed as a Business Planning Manager.

The Business Planning Manager plays a strategic role in steering the company’s direction through comprehensive market analysis, forecasting, and resource allocation. This position involves synthesizing complex data into actionable strategies that align with the company’s long-term goals and financial objectives. By closely monitoring industry trends and evaluating business performance, the Business Planning Manager ensures that the organization remains agile and responsive to changing market demands. Collaboration with various departments to develop and implement plans that enhance operational efficiency and profitability is also a significant aspect of the role. Through a balanced approach to risk management and opportunity identification, the Business Planning Manager supports the company in maintaining a competitive edge and achieving sustainable growth.
Business Planning Manager Job Duties
- Develop and implement comprehensive business plans to facilitate achievement by planning cost-effective operations and market development activities.
- Analyze and forecast financial, economic, and other data to provide accurate and timely information for strategic and operational decisions.
- Coordinate cross-functional teams to develop business strategies and objectives, ensuring alignment with corporate goals.
- Evaluate competitive market strategies through analysis of related product, market, or share trends.
- Identify and drive initiatives to improve operational efficiency, including process improvements, cost reduction, and systems enhancements.
- Facilitate communication and collaboration among departments to ensure that business planning and strategies are aligned with company-wide goals.
- Oversee the preparation of operational and risk reports for management analysis.
- Spearhead the development of new business opportunities, including expansion, mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships.
Business Planning Manager Salary & Outlook
Factors affecting a Business Planning Manager’s salary include industry sector, company size, years of experience, and specific skills in strategic planning, financial modeling, and market analysis. Performance outcomes and the ability to influence business growth also significantly impact compensation.
- Median Annual Salary: $110,250 ($53/hour)
- Top 10% Annual Salary: $152,000 ($73.08/hour)
The employment of business planning managers is expected to grow faster than average over the next decade.
This growth is driven by the increasing complexity of global markets, the need for strategic planning in competitive environments, and the demand for innovation in product and service development. Business Planning Managers are pivotal in navigating these challenges, making their role more critical than ever.
Business Planning Manager Job Requirements
Education: A Business Planning Manager typically holds a Bachelor’s Degree in Business Administration, Finance, or a related field. Coursework often includes strategic management, financial analysis, market research, and organizational behavior. Advanced degrees like an MBA can enhance prospects, focusing on leadership, advanced strategic planning, and international business. Specialized courses in data analysis, project management, and economics are also beneficial, equipping candidates with the necessary skills to excel in developing and implementing business strategies.
Experience: Business Planning Managers typically come from diverse experience backgrounds, with a significant portion having substantial experience in strategic planning, financial analysis, and project management. Many have progressed through roles that required increasing responsibility in business strategy and operations. On-the-job training is common, often through mentorship or rotational programs within a company, allowing for hands-on experience in different business units. Training programs focusing on leadership, data analysis, and market research are also valuable, equipping candidates with the skills to lead cross-functional teams and drive business growth. Successful candidates often demonstrate a blend of practical experience in business planning and strategic initiatives, coupled with formal training programs that enhance their analytical and leadership capabilities.
Certifications & Licenses: Certifications and licenses are not typically required for the role of Business Planning Manager.
Business Planning Manager Skills
Strategic Forecasting: Leveraging data-driven insights, a Business Planning Manager predicts market trends to develop strategies that align with organizational goals. This involves synthesizing diverse information sources to anticipate challenges and opportunities, keeping the company agile and competitive.
Market Analysis: Through the meticulous examination of trends, customer behaviors, and competitor activities, Business Planning Managers can forecast market demands and pinpoint opportunities or threats. This skill hinges on thorough data collection and interpretation to inform strategic decisions.
Financial Modeling: Business Planning Managers create detailed, predictive models of a company’s financial future to forecast revenue, assess risk, and efficiently allocate resources. This requires a solid grasp of accounting principles, spreadsheet software proficiency, and the ability to interpret market trends for data-driven strategic planning.
Risk Management: By identifying potential threats and developing strategies to mitigate them, Business Planning Managers protect the organization’s interests and ensure its long-term sustainability. Analyzing market trends, financial forecasts, and operational vulnerabilities is crucial for preemptively addressing challenges.
Stakeholder Engagement: Building and maintaining strong relationships with investors, partners, and internal teams is critical for aligning business strategies and meeting project milestones. This skill ensures smoother project execution and fosters an environment of trust and mutual respect.
Performance Optimization: Data-driven insights and lean methodologies are used to streamline operations, reduce waste, and boost business efficiency. Analyzing performance metrics, identifying bottlenecks, and implementing strategic interventions are key for sustained organizational improvement.
Business Planning Manager Work Environment
A Business Planning Manager typically operates within a structured office environment, where the workspace is designed to foster both concentration and collaboration. The setup usually includes personal computers, advanced planning software, and access to data analytics tools, essential for strategic decision-making and forecasting.
Work hours might extend beyond the traditional 9-to-5, especially during critical planning phases, though many organizations offer flexibility to accommodate work-life balance. The dress code tends to align with corporate standards, leaning towards business casual or formal, depending on the company’s culture and external meeting requirements.
The role demands frequent interaction with team members, stakeholders, and departments, necessitating strong communication channels and a cooperative atmosphere. Travel may be required for industry events or company-wide meetings, adding variety to the routine.
Professional development opportunities are often available, encouraging continuous learning and advancement in strategic planning methodologies and leadership skills. This role thrives in a setting that values analytical thinking, adaptability, and collaborative problem-solving.
Advancement Prospects
A Business Planning Manager can ascend to higher strategic roles within an organization, such as Director of Strategy or Chief Operations Officer (COO), by demonstrating exceptional analytical, leadership, and decision-making skills. Success in this career path hinges on the ability to drive business growth and efficiency through innovative planning and execution.
To achieve these advancements, a Business Planning Manager should focus on spearheading high-impact projects and initiatives that align with the company’s long-term goals. Gaining experience in cross-functional team leadership and developing a deep understanding of the industry’s competitive landscape are crucial.
Building a track record of successful business plans and strategies that have significantly contributed to the company’s profitability and market position will set a solid foundation for moving into top executive roles. Engaging in high-level decision-making processes and demonstrating a keen insight into market trends and business opportunities are essential steps toward career progression in this field.
What Does a Rental Car Manager Do?
What does a radiology coordinator do, you may also be interested in..., 10 community engagement skills and how to improve them, what does a resident care director do, what does an insurance accountant do, what does a bim coordinator do.
What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 28, 2024
Years ago, I had an idea to launch a line of region-specific board games. I knew there was a market for games that celebrated local culture and heritage. I was so excited about the concept and couldn't wait to get started.

But my idea never took off. Why? Because I didn‘t have a plan. I lacked direction, missed opportunities, and ultimately, the venture never got off the ground.

And that’s exactly why a business plan is important. It cements your vision, gives you clarity, and outlines your next step.
In this post, I‘ll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you’d need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.
Table of Contents
What is a business plan?
What is a business plan used for.
- Business Plan Template [Download Now]
Purposes of a Business Plan
What does a business plan need to include, types of business plans.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
A business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, and financial projections. It provides a detailed description of the business, including its products or services, target market, competitive landscape, and marketing and sales strategies. The plan also includes a financial section that forecasts revenue, expenses, and cash flow, as well as a funding request if the business is seeking investment.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

23 of My Favorite Free Marketing Newsletters
![business planner role The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/free-flowchart-template-1-20240716-6679104-1.webp)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

18 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![business planner role 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-1-20240625-3861486-1.webp)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![business planner role How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]
20 Free & Paid Small Business Tools for Any Budget

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2024

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- Career Blog
Planner: Job Description, Salary, and Skills for 2024

As the backbone of any project, a Planner plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth flow of operations from start to finish. A Planner has the responsibility of laying out the framework that guides a project’s progression from initiation to completion. In the broadest sense, a Planner is responsible for the identification and segregation of different tasks that make up a project, setting milestones and deadlines, and monitoring progress to an ultimate goal. The Planner plays a vital role in ensuring that a project is completed efficiently and on time, while staying within budget constraints.
To put it in simpler terms, a Planner is responsible for coordinating resources, timelines, and budgets to ensure a project is successful. They have the bird’s eye view on the entire project and are usually involved right from the start when the project is being conceptualized.
Primary responsibilities of a Planner include:
1. Develop Project Plans
One of the primary responsibilities of a Planner is to create plans that outline the steps and resources required for a project. This includes forming a documented roadmap and timeline to follow, which helps to ensure that the project progresses smoothly and on schedule.
2. Budget Management
Budget management is also an essential part of a Planner’s responsibility, and they must ensure that the project stays within the financial limitations set out. They keep a close eye on the cost of resources and materials needed and adjust budgets accordingly.
3. Team Management
A Planner has to manage teams of people working on different phases of a project, making sure the teams have the right resources at the right time. They communicate goals, deadlines, and help resolve any conflicts as well.

4. Risk Management
A Planner identifies any foreseeable risks and obstacles that may impact the project’s timeline or budget. They prepare contingency plans, provide risk analysis, and have measures in place to address any issues that may arise.
As a Planner, attention to detail, time management, and communication skills are key elements for achieving success. It’s also essential to be able to work in a team, handle pressure, and be adaptable, as projects could change or take unexpected turns.
Now that you understand the key responsibilities of a Planner, let’s delve deeper into what makes this job exciting and what it takes to qualify as a Planner.
Job Description
For individuals who are interested in a career in urban planning, it is essential to have an understanding of the job description, duties, and qualifications necessary to become a planner. In this section, we will take a closer look at the job description of a planner, as well as the required skills and qualifications, and education and training requirements.
Overview of the Job Description of a Planner
Planners are responsible for developing, implementing, and evaluating plans and programs related to land use, community development, and environmental issues. They work with local government officials, community groups, and key stakeholders to develop strategies that help create sustainable, livable neighborhoods and cities.
Duties and Responsibilities of a Planner
Planners are responsible for a wide range of duties and responsibilities, including:
- Conducting research and gathering data on community needs, environmental issues, and other relevant factors
- Analyzing data and creating reports to inform decision-making processes
- Working with local government officials to develop and implement zoning and land use policies
- Collaborating with other stakeholders to develop comprehensive plans for community development and redevelopment
- Evaluating the effectiveness of existing plans and programs and recommending changes as needed
Required Skills and Qualifications
To be successful in this role, planners are required to have a strong foundation in the following areas:
- Communication skills: Planners must have excellent verbal and written communication skills in order to work effectively with a range of stakeholders including government officials, community groups, and the public.
- Analytical skills: Planners must be able to gather and analyze complex data to inform decision-making processes.
- Problem-solving skills: Planners are often tasked with finding creative solutions to complex problems related to community development and sustainability.
- Project management skills: Planners must be able to manage projects from start to finish, often working within tight time frames and budgets.
- Knowledge of planning software: Familiarity with planning software is important for planners to effectively analyze data and create reports.
Education and Training Requirements
Most employers require planners to have a bachelor’s or master’s degree in urban planning, geography, or a related field. Some planners may also have a degree in architecture, engineering, or public administration. In addition to formal education, planners may also have training or certification through professional organizations such as the American Planning Association.
Planners play a critical role in shaping the physical and social landscape of our communities and cities. They are responsible for developing and implementing plans that create sustainable, livable neighborhoods and cities. To be successful in this field, planners must have strong communication, analytical, and problem-solving skills, as well as relevant education and training.
As an urban or regional planner, you can expect to earn a competitive salary that reflects your expertise and experience. Here, we’ll explore how much planners can earn, factors that influence salary, and average salaries for different levels of experience.
How much Planners can earn
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual salary for urban and regional planners in the United States was $76,240 as of May 2020. However, depending on their expertise, experience and location, planners can earn more or less than this amount.
Planners working in municipalities and government agencies typically earn less than those working in the private sector. The BLS states that the median annual wage for planners employed in local government was $75,600 and $72,830 for those employed in state government. In contrast, those working in architectural or engineering firms can earn upwards of $90,000 per year.

Factors that influence salary
There are several factors that can affect a planner’s salary, including their level of education, years of experience, geographic location, and sector of employment.
Salary tends to increase with education level, with planners who hold a master’s degree typically earning higher salaries than those with a bachelor’s degree.
The amount of experience a planner has can also significantly influence their salary. Entry-level planners with less than two years of experience can expect to earn less than those with more years of experience.
Geographic location also plays a significant role in determining a planner’s salary. Planners living and working in large cities or coastal areas typically earn more than those based in rural areas.
Lastly, the sector in which a planner works can significantly impact their salary. Planners who work in the private sector typically earn more than those working in the public sector.
Average salary for different levels of experience
As mentioned earlier, a planner’s level of experience can affect their salary. Here’s a breakdown of the average salaries for different experience levels, according to the BLS:
- Entry-level (less than 2 years of experience): $50,400
- Mid-career (2-4 years of experience): $60,540
- Experienced (5-9 years of experience): $75,130
- Late-career (10 or more years of experience): $89,320
Keep in mind that these are just average salaries, and actual salaries can vary based on the factors mentioned above.
Urban and regional planners can expect to earn competitive salaries that reflect their expertise, education, experience, and location. The salaries for planners vary depending on their area of expertise, sector, and level of expertise. Given the nature of the profession, with expected growth in urban planning jobs, it’s important to have an idea of the potential salary range for planners across different skill levels.
Planners must have a specific set of skills to thrive in their job. In this section, we will discuss the essential skills required of a planner, soft skills necessary to excel in the role, and advanced skills to differentiate oneself in the field.
Essential skills required of a Planner
Effective planners must have strong analytical skills to successfully gather, analyze, and interpret data. They should be able to think critically, evaluate situations, and make informed decisions. Good numerical and financial skills are necessary as well. This includes an understanding of budgeting, forecasting, and cost analysis. A planner must also possess excellent communication skills to convey their findings and recommendations to various stakeholders in a clear and concise manner.
Soft skills needed to excel in the role
In addition to essential technical skills, planners must also have soft skills to excel in their role. They should have strong interpersonal skills, be able to collaborate and work effectively with others. Good time management and organizational skills are necessary for this fast-paced and dynamic role. The ability to adapt and work well under pressure is essential for success in this field.
Advanced skills to differentiate oneself in the field
To stand out in a competitive planning industry, it is necessary to have advanced skills that set you apart from others. These may include proficiency in data analytics and visualization, advanced financial modeling, project management, and market research. Knowledge of emerging technologies and experience in implementing new tools to streamline processes is also crucial. Effective networking, public speaking, and leadership skills can also be valuable. Continual research, learning and development can be a unique differentiator, especially when a planner is able to gain deeper insights through immersion in innovative, multi-disciplinary environments beyond their own field.
A planner’s success depends on a combination of essential, soft and advanced skills. By continuing to develop these skills, a planner can differentiate themselves in the field, bring more value to their organization, and ultimately earn a higher salary.
Types of Planners
It takes a variety of planners in different industries to help individuals or organizations effectively manage their resources, from finances and time to people and space. Here are some examples of planners and their job descriptions and responsibilities:
Financial Planners
Financial planners help clients make informed decisions about how to invest their money and plan for their financial future. They create financial plans, provide advice on investment strategies, and review clients’ portfolios regularly to ensure they meet their goals. They must also stay up to date with changes in tax laws, financial regulations, and market trends to best guide their clients.
Event Planners
Event planners organize and manage various types of events, including weddings, trade shows, music festivals, and corporate events. They liaise with clients to determine event goals, budgets, and timelines, then coordinate with vendors, manage event logistics, and handle all aspects of event production. They must have strong communication skills, attention to detail, and the ability to work well under pressure.
Urban Planners
Urban planners help communities create and manage land use plans, zoning ordinances, transportation systems, and environmental plans. They work with government officials, local residents, and developers to ensure projects meet community needs and goals. They must consider factors such as sustainability, accessibility, and economic feasibility when designing plans and recommending policies.
Production Planners
Production planners ensure manufacturing facilities run efficiently by creating production plans, maintaining inventory levels, and scheduling operations. They analyze data, predict demand, and optimize production processes. They must collaborate with various departments, including engineering, operations, and finance, to ensure timely delivery of products and minimize waste.
Academic Planners
Academic planners assist in student success by providing academic advisement, coordinating schedules, registering students for classes, and providing orientation for new enrollees. They must have an excellent knowledge of university policies, procedures and standards, and the different programs the school offers. They also have to be great communicators and good at dealing with people in high-pressure situations.
Planners play a vital role in ensuring effective and efficient management across various industries. Whether it’s financial planning, event production, community development or manufacturing, each type of planner is responsible for facilitating order and managing a range of responsibilities to reach established goals.
Industries That Need Planners
Planners are essential in various industries as they bring in their expertise to help organizations achieve their goals. Listed below are some of the industries that rely on the expertise of planners:
Public Sector
Private sector.
In the public sector, planners play a vital role in ensuring that the local community’s needs are met. They are responsible for developing comprehensive plans that guide land use, transportation, and economic development, among others. Planners in the public sector also work collaboratively with elected officials, community leaders, and other professionals to make sure that their plans are executed and policies are enforced.
One of the crucial tasks of planners in the public sector is to manage the growing demand for affordable housing, nearby transportation, and accessible amenities. They work to improve the quality of life in communities, providing equitable access to services and facilities.
In the private sector, planners contribute to the success of the organization by improving operational efficiency, managing resources and employees, and using data-driven approaches to make informed decisions. They provide insights into real estate development, land use, and zoning regulations that help businesses prosper.
Private sector planners also work in the development of private infrastructure, such as stadiums, office buildings, and housing developments. They are responsible for ensuring that these projects follow local, state, and federal regulations, as well as environmental and health standards.
Planners in the nonprofit sector have a unique set of responsibilities, as they work towards fulfilling the organization’s mission while serving their communities. They often have limited resources and rely on volunteers, so their planning is critical for a successful outcome.
Nonprofit planners develop strategic plans that align with the organization’s goals and priorities while collaborating with stakeholders, policymakers, and community members. They identify funding sources and grants for community development and implement programs that improve the quality of life and address social issues.
Planners are essential in various industries, whether it’s in the public sector, private sector, or nonprofit. Their responsibility is to ensure that organizations make informed decisions that lead to positive outcomes, which creates a better world for all of us.
Job Outlook
As a Planner, the employment outlook is promising. With the increasing need for organizations to plan and strategize how they use their resources, Planners are becoming more valuable in various industries.
In the coming years, several factors will influence the job market for Planners. First, the rapid pace of technological advancements means that organizations must continually adapt to new tools and systems. This will require skilled Planners who can effectively integrate new technologies into planning processes. Second, the growing concern for sustainability and ethical practices will require Planners to incorporate eco-friendly and socially responsible policies into their plans. This shift will create new opportunities for Planners with expertise in sustainable development and ethical practices.
Moreover, the growth opportunities for Planners are not limited to a specific industry. Every sector requires professionals who can analyze data, forecast trends, and create strategies for business growth. Therefore, Planners can find work in various fields, including government agencies, health care, education, transportation, and manufacturing.
In the government, Planners can work for local, state or federal agencies to develop policies and allocate resources that benefit the community. Similarly, in healthcare, Planners can work to optimize resource utilization, develop effective patient care plans, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
In the education sector, Planners can use data analysis and planning tools to ensure the success of educational programs and student advancement. They can also develop financial plans that increase the value of schools and universities.
In transportation, Planners can use their skills to reduce congestion, increase accessibility, and minimize the carbon footprint of transportation systems. In the manufacturing industry, Planners can optimize resource allocation, develop efficient supply chains and improve organizational efficiency.
The employment outlook for Planners is positive, with expected job growth projected in the coming years. Moreover, the adaptability of Planners means that they can work in various industries and find employment opportunities in multiple sectors, from government agencies to manufacturing firms. Finally, to be successful Planners, professionals must stay informed of the changing needs of their industries and develop adaptive skill sets that are relevant to the ever-evolving nature of their profession.
Pros and Cons of the Job
Being a Planner can be both rewarding and challenging. In this section, we will discuss the advantages of being a Planner as well as the challenges faced by Planners and how to overcome them.
Advantages of being a Planner
Job Satisfaction: One of the biggest advantages of being a Planner is job satisfaction. Planners have the opportunity to create positive change in their communities by developing and implementing plans that improve the quality of life for residents.
Variety of Work: Planners get to work on a variety of projects, which keeps their work interesting and diverse. From developing zoning regulations to designing public spaces, Planners get to use their skills in a wide range of areas.
Positive Work-Life Balance: Many planning positions offer flexible work schedules that provide a good balance between work and personal life. This is a great advantage to those who value a healthy work-life balance.
Career Growth: The field of planning offers plenty of opportunities for career growth and development. Planners can specialize in areas such as transportation planning or environmental planning, and can advance to leadership positions within their organizations.
Challenges faced by Planners and how to overcome them
Navigating Politics: One of the biggest challenges faced by Planners is navigating the world of politics. Often, Planners are tasked with developing plans that are politically sensitive or controversial. To overcome this challenge, Planners need to develop strong communication and negotiation skills, and be able to work collaboratively with stakeholders to find solutions that benefit everyone.
Managing Conflicting Priorities: Planners often have to balance competing priorities from various departments, organizations, or groups. This can be a challenging task, but Planners can overcome it by developing effective project management skills, keeping their priorities clear, and maintaining open communication with stakeholders.
Staying Current: The field of planning is constantly evolving, and Planners need to keep up with the latest trends and technologies to remain effective in their jobs. To overcome this challenge, Planners should make a habit of attending conferences, networking with other professionals, and staying up to date with industry publications.
Building Consensus: Another challenge faced by Planners is building consensus among stakeholders who have differing opinions or goals. To overcome this challenge, Planners need to be good listeners, skilled facilitators, and adept at finding common ground. Planners should focus on building relationships with stakeholders, fostering trust, and working collaboratively to achieve shared goals.
Being a Planner has many advantages, from job satisfaction to career growth. However, there are also challenges that come with the job, including navigating politics, managing conflicting priorities, staying current, and building consensus. With effective communication, negotiation, project management, and facilitation skills, Planners can overcome these challenges and continue to make a positive impact in their communities.
How to Become a Planner
If you’re interested in becoming a Planner, there are specific steps you can take to prepare yourself for this career path. In this section, we’ll provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to become a Planner, job search strategies for aspiring Planners, and common mistakes to avoid when applying for Planner roles.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Become a Planner
Pursue a degree in Urban Planning, Geography, Environmental Science or other related fields: A Bachelor’s or Master’s degree in any of these fields will provide a solid foundation for a career in Planning.
Gain experience: Get some work experience in the field of Planning, whether through an internship, volunteering, or entry-level jobs. This will give you a better understanding of the field and help you gain the skills and knowledge needed to be a successful Planner.
Build your skills: In addition to academic qualifications and practical experience, it is also essential to develop a diverse range of skills that are relevant to the Planning profession. These may include analytical, critical thinking, communication, interpersonal, and project management skills.
Seek professional certification: Several organizations offer certifications that can help you stand out to potential employers as a qualified Planner. These include the American Planning Association’s (APA) AICP certification and the National Institute for Certification in Engineering Technologies (NICET) certification.
Apply for Planner positions: Once you’ve gained the necessary qualifications, skills, and certifications, you can start applying for Planner roles in various organizations, including government agencies, consulting firms, and non-profit organizations.
Job Search Strategies for Aspiring Planners
Get involved in networking: Attend industry events, join professional organizations, and connect with other Planners on social media platforms to build your professional network.
Research potential employers: Identify organizations that align with your goals and interests in Planning, and research their values, projects, and culture to see if they are a good fit for you.
Tailor your resume and cover letter: Customize your application materials for the Planner position you’re applying for to stand out to hiring managers.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Applying for Planner Roles
Forgetting to proofread: Check your application materials for typos and grammatical errors. A clean and polished application shows attention to detail and professionalism.
Not doing research: Not researching the organization and the position you’re applying for can make you appear disinterested or unprepared during interviews.
Focusing solely on technical skills: While technical skills are crucial for a career in Planning, hiring managers also value soft skills such as communication and teamwork. Make sure to highlight both sets of skills on your application materials and during interviews.
By following these steps and job search strategies while avoiding common mistakes, you can increase your chances of becoming a successful Planner.
Certifications and Advancements
As a Planner, obtaining relevant certifications and advanced qualifications is crucial to stand out in today’s competitive job market. Certifications not only enhance a Planner’s credibility but also demonstrate a commitment to ongoing professional development.
Importance of Certifications for Planners
Certifications provide a comprehensive understanding of the principles, tools, and techniques used in planning, which helps Planners make informed decisions and provide effective services to clients. Employers are increasingly recognizing the value of certified Planners, and many job listings now require applicants to hold a relevant certification.
Some of the most recognized certifications for Planners include:
Certified Planner : Offered by the American Institute of Certified Planners (AICP), this certification is the most widely recognized and respected credential in the planning profession. AICP-credentialed Planners have demonstrated a mastery of the principles and practices of planning and are committed to ethical conduct and professional excellence.
LEED Accredited Professional : This certification by the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) demonstrates expertise in sustainable building and design practices. Planners with this certification can help clients develop environmentally responsible projects and initiatives.
Project Management Professional (PMP) : Offered by the Project Management Institute (PMI), this certification demonstrates expertise in planning, executing, and delivering projects on time, within budget, and with high quality.
Advanced Qualifications to Help Planners Stand Out
In addition to certifications, Planners can pursue advanced qualifications that deepen their expertise in specific areas of planning. These qualifications may include:
Master of Urban Planning (MUP) : A graduate degree in urban planning that provides a theoretical and practical understanding of urban and regional development, transportation planning, community engagement, and environmental planning.
Professional Certificate in Sustainable Urban Development : This certificate program offered by Columbia University provides a comprehensive understanding of the principles and practices of sustainable urban development.
Certified Economic Developer (CEcD) : This certification by the International Economic Development Council (IEDC) demonstrates expertise in economic development strategies, marketing, and community revitalization.
Additional Training Options for Planners to Consider
Alongside certifications and advanced qualifications, there are various training options that Planners can consider to enhance their skills and knowledge. These may include:
Attending conferences : Conferences provide opportunities for Planners to learn about emerging trends, network with industry professionals, and gain insights into best practices.
Taking online courses : Online courses offer the flexibility to learn at one’s own pace and can cover topics ranging from GIS mapping to community engagement strategies.
Participating in community initiatives : Participating in community initiatives can help Planners understand the needs and challenges of the communities they serve, while also giving back to the community.
Example of a Day in the Life of a Planner
As a planner, your daily routine is never set in stone. You will spend most of your time coordinating with various stakeholders, researching and analyzing data, and strategizing for upcoming events or campaigns. Here is a typical day in the life of a planner:
Morning Routine (8:00 AM – 10:00 AM)
Most planners start their day by checking emails and scheduling meetings with clients or colleagues. They may also use this time to review their to-do list for the day and prioritize tasks based on urgency and importance.
After that, the planner may begin conducting research and gathering data on various aspects of the project, such as target audience demographics, market trends, and industry best practices.
Afternoon Routine (12:00 PM – 2:00 PM)
After lunch, the planner may start analyzing the data they gathered in the morning, using it to create strategies for the project. They may work on creating timelines, budgets, and other relevant documents.
The planner may also spend this time coordinating with various stakeholders, such as vendors, contractors, and team members, to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that the project is moving forward as planned.
Evening Routine (4:00 PM – 6:00 PM)
As the workday winds down, the planner may use this time to review their progress and prepare for the next day. This could involve revising their to-do list, checking in with team members, or wrapping up any loose ends.
Some planners may also attend networking events or meetings in the evening to expand their professional network and stay up-to-date on industry trends.
Insights from Current Planners
According to current planners, the daily routine can vary significantly depending on the specific project, employer, and industry. However, there are a few common themes that many planners share:
Communication is key: Planners spend a significant amount of time communicating with clients, team members, and vendors to ensure the project runs smoothly.
Research is essential: Planners must conduct in-depth research and analyze data to develop effective strategies for the project.
Adaptability is crucial: Plans can change at a moment’s notice, and planners must be able to adapt quickly to keep the project on track.
Attention to detail is a must: One small mistake can have significant consequences, so planners must pay close attention to all aspects of the project.
Being a planner requires a wide range of skills and abilities, from communication and research to adaptability and attention to detail. However, for those who enjoy working in a fast-paced environment and making a real impact on the success of a project, being a planner can be an incredibly rewarding career path.
Related Articles
- Freelance Artist Resume: Examples and Best Practices
- The Best Resume Fonts: How to Make Your Resume Stand Out
- Building Your Dental Hygienist Resume for 2023
- Notary Signing Agent Resume: Winning Examples for 2023
- Nutrition Assistant: Job Description, Salary, and Skills
Rate this article
1 / 5. Reviews: 1

More from ResumeHead

Resume Builder
- Resume Experts
- Search Jobs
- Search for Talent
- Employer Branding
- Outplacement
Business Planner Job Description
Business planner duties & responsibilities.
To write an effective business planner job description, begin by listing detailed duties, responsibilities and expectations. We have included business planner job description templates that you can modify and use.
Sample responsibilities for this position include:
Business Planner Qualifications
Qualifications for a job description may include education, certification, and experience.
Licensing or Certifications for Business Planner
List any licenses or certifications required by the position: APICS, PMP, HSEEP, CBCP, AGILE, CPIM, DRII, BCI, CSCP, SAP
Education for Business Planner
Typically a job would require a certain level of education.
Employers hiring for the business planner job most commonly would prefer for their future employee to have a relevant degree such as Bachelor's and University Degree in Business, Finance, MBA, Business/Administration, Education, Marketing, Accounting, Economics, Engineering, Management
Skills for Business Planner
Desired skills for business planner include:
Desired experience for business planner includes:
Business Planner Examples
- Microsoft Word (.docx) .DOCX
- PDF Document (.pdf) .PDF
- Image File (.png) .PNG
- Support vendor setup and management for US-based vendors o Coordinate & prepare all journal entries for global marketing team
- Communicate internal budget management timelines to team, including monthly budget process reminders
- Purchase order submission & management, including updating milestones, closing POs, parked invoice and expense reports Enable entire team with clear financial process, reporting, and insights that drive accountability and better marketing investment decisions Develop and execute vendor management strategy for Bing Ads Marketing
- Hit vendor efficiency targets of USD$750K annually through vendor efficiency strategy execution
- Serve as SPOC for the daily management of vendor relationships to reduce friction and monitor deliverable quality Deliver annual vendor budget and subsequent modifications with goal of reducing costs and/or improving efficiencies
- Run quarterly review to ensure a clear and accurate picture of the relationship is shared with stakeholders and a process exists for resolving issues
- Represent Windows Business Planning in commercial cross-company business planning forums, licensing field events
- Partner closely with BI team to address ad hoc analytics needs (define problem, scope solution, review analysis, synthesize and share results back to team
- Working with the team, develop and drive a standard way to measure games marketing ROI across traditional marketing campaigns in events and eSports
- Help craft business requirement documents and licensing requirements necessary to implement Windows OEM offerings in close partnership with OEM Division, operations, legal
- Capable of influencing and driving better decision making through a closed loop planning process in concert across multiple stakeholders
- Lean demand pull, Flexibility
- BS or Business Degree
- Background in technical / electronic / industrial master scheduling, forecasting or procurement
- Self-starter with strong analytical and financial skills
- Excellent problem structuring, identification, and resolution
- Analyze figures, validate parameters and provide time, cost, and materials etc for new or existing projects or services
- Support business cases, provide pricing proposals and assist with RFP responses, when necessary
- Advise on cost related issues and propose more cost efficient options where possible
- Translate analytic insights into concrete, actionable recommendations
- May coordinate the activities of clerk and/or other non-exempt employee(s)
- May evaluate the performance of non-exempt employees(s), based on pre-established performance parameters
- Support of Leadership on internal (Market Visits, Business Plans, Monthly Business Unit Review), external presentations for Clients and prospects
- Plan & manage special events, meetings, and initiatives and create related presentations materials
- NGA planning in support of NGA Operations Center (NOC), Enterprise Service Center (ESC), and cyber exercises associated with NGA, IC Security Coordination Center (IC SCC) and US Cyber Command (USCC) or Combatant Command (COCOM) high-priority plans
- Develop deep insights into users and the market landscape around monetization on connected devices (PC, Tablets, Phones, IoT )
- Bachelor’s degree in Business, Sales, Fashion, Marketing or a related field
- 4 + years of experience in Buying, Planning, &/or Allocation planning for a multi-store retailer
- Understanding of gross margin profitability planning
- Outstanding analytical skills - focus on data
- Flexible, goal-oriented problem solving approach
- Draw from and leverage a well-developed set of methodologies, analytical tools, and experiences to drive risk assessment
- Assist business units in the update of their business continuity plans
- Assist in business incident management process, including distribution of status message at the direction of management
- Work with the Disaster Recovery team to ensure the technology plans address the business recovery as outlined in the business continuity plans
- Work with application teams to understand the recoverability status of applications
- Coordinate contingency testing schedules at assigned recovery sites and participate in the recovery tests
- Provide support to Business Continuity Manager for annual Disaster Recovery Exercise, including scheduling of business unit meetings and gathering of business unit test scripts
- Schedule and support functional tabletop and automated notification tests
- Assist Business Continuity Manager in the update of the Business Impact Analysis (BIA), working with the business production owners
- Assist during an actual business continuity event, crisis management event, or other incident
- Partner with Operations to drive production builds, inventory buffer review stock rotations and scrap lists
- Experience in Media Planning in a broadcast television or media agency is advantageous, although not essential
- Education - degree level or equivalent, ideally in a numerate discipline
- Working proficiency in Arabic, Turkish or Greek is advantageous, but not essential
- CBCP certification preferred, but not required
- 2-3 years private sector business continuity experience preferred
- Salesforce or similar database experience preferred
- Leading the sales forecast monthly meeting
- Achieve fill-rate target and material availability targets per Market
- Achieve Gross inventory target
- Minimize excess and obsolete inventories and help meet operating expense targets
- Utilize the PDCA approachin establishing a plan and reviewing performance
- Maintain and update the project management framework and disciplines necessary to support portfolio development
- Record amount of time spent on project work and estimates to complete to evaluate project status and budget
- Works with department head to create account specific proposals and project planning based upon terms and expectations being negotiated
- Support organizational planning to address disasters, interruptions of business functions and enterprise resilience
- Interpret government regulations and applicable directives, and advises government management on the best course of action to meet program goals, objectives and compliance with program mandates
- Strong analytical and problem solving skills in terms of both research methodologies statistical methods
- The ideal candidate will have 5+ years of experience post BA/S in finance, business planning and/or strategy
- The ability to multitask and handle multiple requests with multiple degrees of priority simultaneously
- Knowledge of retail and merchandising metrics is a plus but not required
- 1 year of experience in a quantitative, analytical role at a top-tier organization is preferred
- Provides ongoing guidance for business continuation strategies to reach desired control level, , regulatory and legal requirements, customer SLA's
- Results focused – delivery to targets and budgets
- Demonstrate a level of Initiative and ability to manage own workload effectively
- Initiative – Show an eagerness to explore new ideas
- Provide a high level of analytical rigour to aid decision making
- Develop a broad personal network across the business establishing effective relationships with a range of stakeholders
- Utilise strong organisational skills to deliver projects to timescale
- Assist in building monthly open to buy & open to spend by region, by category plans
- Partner with DTC Planning Director to develop preseason financial sales plan targets by analyzing historical and current trends while identifying risks and opportunities
- Partner with Planning leads & Merchant team to create top line and divisional sales, inventory and gross margin goals
- Risk Management – Identify and Categorize outage exposures that could cause a business interruption, then design safeguard against a disaster event
- Demonstrated end to end perspective in technology business environments
- Manages the processing of customer orders
- Works with outside processors to coordinate production to meet customer delivery dates
- Works with internal shipping department to coordinate the movement of material to the outside processors
- Receives and responds to Commercial inquiries
Related Job Descriptions
Create a Resume in Minutes with Professional Resume Templates
I am an Employer
I am a candidate.
DEI in 2024 is a more polarized topic than in 2020 – Check out our recent survey and get the insights Download the report
- HR Toolkit |
- HR Templates |
- Job descriptions |
- Administrative job descriptions |
Strategic Planner job description
A Strategic Planner is responsible for shaping business strategy, developing plans, analyzing data, and aligning goals to achieve the company’s objectives. Strong strategic thinking, analytical skills, and market research experience are essential.

Nikoletta holds an MSc in HR management and has written extensively about all things HR and recruiting.
Refreshed on
June 9, 2023
Reviewed by
Eftychia Karavelaki
Senior Recruitment Manager
This Strategic Planner job description template is optimized for posting to online job boards or careers pages and easy to customize for your company.
What is a Strategic Planner?
A Strategic Planner is a professional who is responsible for shaping the overall business strategy of a company, developing strategic plans, and assessing company performance to achieve business objectives.
What does a Strategic Planner do?
A Strategic Planner develops and implements plans to materialize the company’s strategy, conducts research and data analysis to inform business decisions, and aligns department goals with the overall strategy. They also monitor industry trends, provide insights into organizational changes, and support senior executives in making effective decisions.
Strategic Planner responsibilities include:
- Shaping the company’s overall business strategy
- Developing strategic plans and assessing company performance
- Conducting research and data analysis to inform business decisions

Want to generate a unique job description?
Looking for a job.
We are seeking a Strategic Planner to shape our company’s direction and create plans to achieve our business objectives.
You will play a crucial role in maintaining our competitive edge and effectively allocating resources.
Strategic thinking is a vital skill required for this position, along with strong analytical and organizational abilities.
Your contributions will be instrumental in guiding our company through changes, fostering growth, and ensuring long-term success.
As a Strategic Planner, you will have the opportunity to make a significant impact on our company’s strategic decisions and drive our business forward.
Join our team and be a key player in shaping our future.
Responsibilities
- Understand and shape the company’s strategy and mission
- Develop plans to materialize strategy and analyze business proposals
- Research competition to identify threats and opportunities
- Assess the company’s operational and strategic performance
- Align processes, resources-planning and department goals with overall strategy
- Provide support and insight into significant organizational changes (e.g. shift in strategic focus, mergers and acquisitions)
- Educate senior executives in making effective decisions
- Construct forecasts and analytical models
- Monitor and analyze industry trends and market changes
Requirements and skills
- Proven experience as a Strategic Planner or Business Consultant
- Understanding of market research and data analysis
- Knowledge of business operations and procedures
- Demonstrable strategic thinking abilities
- Analytical mind with problem-solving aptitude
- Organizational and leadership skills
- Excellent communication skills
- BSc/BA in Business Administration, Marketing, Finance or a related field; MSc/MA/MBA is a plus

Post this Strategic Planner job to over 200 job boards at once.
Frequently asked questions, related job descriptions.
- Business Consultant job description
- Brand Strategist job description
- CFO job description
Related Interview Questions
- Analytical interview questions and answers
- CFO interview questions and answers
- Strategic-thinking interview questions and answers
Related Topics
- 21 HR tools designed for growing companies
- How to create a great candidate experience
- Search engine optimized job descriptions: dos and don'ts
Available in
Jump to section, share on mastodon.
Business Planner Responsibilities and Duties
Develop, document and implement business plans, processes and procedures.
Develop presentations for management and stakeholders on business operations and developments.
Support business planning functions for new and existing strategic partnerships and alliances.
Assist in development of business plan to achieve operational goals.
Perform business and financial analysis across organization.
Identify project issues and develop resolutions to meet productivity and quality.
Identify risks and develop mitigation plans.
Identify new opportunities to add business value.
Table of Contents
What is a business plan, the advantages of having a business plan, the types of business plans, the key elements of a business plan, best business plan software, common challenges of writing a business plan, become an expert business planner, business planning: it’s importance, types and key elements.

Every year, thousands of new businesses see the light of the day. One look at the World Bank's Entrepreneurship Survey and database shows the mind-boggling rate of new business registrations. However, sadly, only a tiny percentage of them have a chance of survival.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, about 20% of small businesses fail in their first year, about 50% in their fifth year.
Research from the University of Tennessee found that 44% of businesses fail within the first three years. Among those that operate within specific sectors, like information (which includes most tech firms), 63% shut shop within three years.
Several other statistics expose the abysmal rates of business failure. But why are so many businesses bound to fail? Most studies mention "lack of business planning" as one of the reasons.
This isn’t surprising at all.
Running a business without a plan is like riding a motorcycle up a craggy cliff blindfolded. Yet, way too many firms ( a whopping 67%) don't have a formal business plan in place.
It doesn't matter if you're a startup with a great idea or a business with an excellent product. You can only go so far without a roadmap — a business plan. Only, a business plan is so much more than just a roadmap. A solid plan allows a business to weather market challenges and pivot quickly in the face of crisis, like the one global businesses are struggling with right now, in the post-pandemic world.
But before you can go ahead and develop a great business plan, you need to know the basics. In this article, we'll discuss the fundamentals of business planning to help you plan effectively for 2021.
Now before we begin with the details of business planning, let us understand what it is.
No two businesses have an identical business plan, even if they operate within the same industry. So one business plan can look entirely different from another one. Still, for the sake of simplicity, a business plan can be defined as a guide for a company to operate and achieve its goals.
More specifically, it's a document in writing that outlines the goals, objectives, and purpose of a business while laying out the blueprint for its day-to-day operations and key functions such as marketing, finance, and expansion.
A good business plan can be a game-changer for startups that are looking to raise funds to grow and scale. It convinces prospective investors that the venture will be profitable and provides a realistic outlook on how much profit is on the cards and by when it will be attained.
However, it's not only new businesses that greatly benefit from a business plan. Well-established companies and large conglomerates also need to tweak their business plans to adapt to new business environments and unpredictable market changes.
Before getting into learning more about business planning, let us learn the advantages of having one.
Since a detailed business plan offers a birds-eye view of the entire framework of an establishment, it has several benefits that make it an important part of any organization. Here are few ways a business plan can offer significant competitive edge.
- Sets objectives and benchmarks: Proper planning helps a business set realistic objectives and assign stipulated time for those goals to be met. This results in long-term profitability. It also lets a company set benchmarks and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) necessary to reach its goals.
- Maximizes resource allocation: A good business plan helps to effectively organize and allocate the company’s resources. It provides an understanding of the result of actions, such as, opening new offices, recruiting fresh staff, change in production, and so on. It also helps the business estimate the financial impact of such actions.
- Enhances viability: A plan greatly contributes towards turning concepts into reality. Though business plans vary from company to company, the blueprints of successful companies often serve as an excellent guide for nascent-stage start-ups and new entrepreneurs. It also helps existing firms to market, advertise, and promote new products and services into the market.
- Aids in decision making: Running a business involves a lot of decision making: where to pitch, where to locate, what to sell, what to charge — the list goes on. A well thought-out business plan provides an organization the ability to anticipate the curveballs that the future could throw at them. It allows them to come up with answers and solutions to these issues well in advance.
- Fix past mistakes: When businesses create plans keeping in mind the flaws and failures of the past and what worked for them and what didn’t, it can help them save time, money, and resources. Such plans that reflects the lessons learnt from the past offers businesses an opportunity to avoid future pitfalls.
- Attracts investors: A business plan gives investors an in-depth idea about the objectives, structure, and validity of a firm. It helps to secure their confidence and encourages them to invest.
Now let's look at the various types involved in business planning.
Become a Business and Leadership Professional
- Top 10 skills in demand Business Analysis As A Skill In 2020
- 14% Growth in Jobs Of Business Analysis Profile By 2028
Business Analyst
- Industry-recognized certifications from IBM and Simplilearn
- Masterclasses from IBM experts
Post Graduate Program in Business Analysis
- Get mentored and network with industry experts from Amazon, Microsoft, and Google
- Access Harvard Business Publishing case studies of Pearson, CarMax, EvCard, etc
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Assistant Consultant at Tata Consultancy Services , Tata Consultancy Services
My experience with Simplilearn has been great till now. They have good materials to start with, and a wide range of courses. I have signed up for two courses with Simplilearn over the past 6 months, Data Scientist and Agile and Scrum. My experience with both is good. One unique feature I liked about Simplilearn is that they give pre-requisites that you should complete, before a live class, so that you go there fully prepared. Secondly, there support staff is superb. I believe there are two teams, to cater to the Indian and US time zones. Simplilearn gives you the most methodical and easy way to up-skill yourself. Also, when you compare the data analytics courses across the market that offer web-based tutorials, Simplilearn, scores over the rest in my opinion. Great job, Simplilearn!
I was keenly looking for a change in my domain from business consultancy to IT(Business Analytics). This Post Graduate Program in Business Analysis course helped me achieve the same. I am proficient in business analysis now and am looking for job profiles that suit my skill set.
Business plans are formulated according to the needs of a business. It can be a simple one-page document or an elaborate 40-page affair, or anything in between. While there’s no rule set in stone as to what exactly a business plan can or can’t contain, there are a few common types of business plan that nearly all businesses in existence use.
Here’s an overview of a few fundamental types of business plans.
- Start-up plan: As the name suggests, this is a documentation of the plans, structure, and objections of a new business establishments. It describes the products and services that are to be produced by the firm, the staff management, and market analysis of their production. Often, a detailed finance spreadsheet is also attached to this document for investors to determine the viability of the new business set-up.
- Feasibility plan: A feasibility plan evaluates the prospective customers of the products or services that are to be produced by a company. It also estimates the possibility of a profit or a loss of a venture. It helps to forecast how well a product will sell at the market, the duration it will require to yield results, and the profit margin that it will secure on investments.
- Expansion Plan: This kind of plan is primarily framed when a company decided to expand in terms of production or structure. It lays down the fundamental steps and guidelines with regards to internal or external growth. It helps the firm to analyze the activities like resource allocation for increased production, financial investments, employment of extra staff, and much more.
- Operations Plan: An operational plan is also called an annual plan. This details the day-to-day activities and strategies that a business needs to follow in order to materialize its targets. It outlines the roles and responsibilities of the managing body, the various departments, and the company’s employees for the holistic success of the firm.
- Strategic Plan: This document caters to the internal strategies of the company and is a part of the foundational grounds of the establishments. It can be accurately drafted with the help of a SWOT analysis through which the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats can be categorized and evaluated so that to develop means for optimizing profits.
There is some preliminary work that’s required before you actually sit down to write a plan for your business. Knowing what goes into a business plan is one of them.
Here are the key elements of a good business plan:
- Executive Summary: An executive summary gives a clear picture of the strategies and goals of your business right at the outset. Though its value is often understated, it can be extremely helpful in creating the readers’ first impression of your business. As such, it could define the opinions of customers and investors from the get-go.
- Business Description: A thorough business description removes room for any ambiguity from your processes. An excellent business description will explain the size and structure of the firm as well as its position in the market. It also describes the kind of products and services that the company offers. It even states as to whether the company is old and established or new and aspiring. Most importantly, it highlights the USP of the products or services as compared to your competitors in the market.
- Market Analysis: A systematic market analysis helps to determine the current position of a business and analyzes its scope for future expansions. This can help in evaluating investments, promotions, marketing, and distribution of products. In-depth market understanding also helps a business combat competition and make plans for long-term success.
- Operations and Management: Much like a statement of purpose, this allows an enterprise to explain its uniqueness to its readers and customers. It showcases the ways in which the firm can deliver greater and superior products at cheaper rates and in relatively less time.
- Financial Plan: This is the most important element of a business plan and is primarily addressed to investors and sponsors. It requires a firm to reveal its financial policies and market analysis. At times, a 5-year financial report is also required to be included to show past performances and profits. The financial plan draws out the current business strategies, future projections, and the total estimated worth of the firm.
The importance of business planning is it simplifies the planning of your company's finances to present this information to a bank or investors. Here are the best business plan software providers available right now:
- Business Sorter
The importance of business planning cannot be emphasized enough, but it can be challenging to write a business plan. Here are a few issues to consider before you start your business planning:
- Create a business plan to determine your company's direction, obtain financing, and attract investors.
- Identifying financial, demographic, and achievable goals is a common challenge when writing a business plan.
- Some entrepreneurs struggle to write a business plan that is concise, interesting, and informative enough to demonstrate the viability of their business idea.
- You can streamline your business planning process by conducting research, speaking with experts and peers, and working with a business consultant.
Whether you’re running your own business or in-charge of ensuring strategic performance and growth for your employer or clients, knowing the ins and outs of business planning can set you up for success.
Be it the launch of a new and exciting product or an expansion of operations, business planning is the necessity of all large and small companies. Which is why the need for professionals with superior business planning skills will never die out. In fact, their demand is on the rise with global firms putting emphasis on business analysis and planning to cope with cut-throat competition and market uncertainties.
While some are natural-born planners, most people have to work to develop this important skill. Plus, business planning requires you to understand the fundamentals of business management and be familiar with business analysis techniques . It also requires you to have a working knowledge of data visualization, project management, and monitoring tools commonly used by businesses today.
Simpliearn’s Executive Certificate Program in General Management will help you develop and hone the required skills to become an extraordinary business planner. This comprehensive general management program by IIM Indore can serve as a career catalyst, equipping professionals with a competitive edge in the ever-evolving business environment.
What Is Meant by Business Planning?
Business planning is developing a company's mission or goals and defining the strategies you will use to achieve those goals or tasks. The process can be extensive, encompassing all aspects of the operation, or it can be concrete, focusing on specific functions within the overall corporate structure.
What Are the 4 Types of Business Plans?
The following are the four types of business plans:
Operational Planning
This type of planning typically describes the company's day-to-day operations. Single-use plans are developed for events and activities that occur only once (such as a single marketing campaign). Ongoing plans include problem-solving policies, rules for specific regulations, and procedures for a step-by-step process for achieving particular goals.
Strategic Planning
Strategic plans are all about why things must occur. A high-level overview of the entire business is included in strategic planning. It is the organization's foundation and will dictate long-term decisions.
Tactical Planning
Tactical plans are about what will happen. Strategic planning is aided by tactical planning. It outlines the tactics the organization intends to employ to achieve the goals outlined in the strategic plan.
Contingency Planning
When something unexpected occurs or something needs to be changed, contingency plans are created. In situations where a change is required, contingency planning can be beneficial.
What Are the 7 Steps of a Business Plan?
The following are the seven steps required for a business plan:
Conduct Research
If your company is to run a viable business plan and attract investors, your information must be of the highest quality.
Have a Goal
The goal must be unambiguous. You will waste your time if you don't know why you're writing a business plan. Knowing also implies having a target audience for when the plan is expected to get completed.
Create a Company Profile
Some refer to it as a company profile, while others refer to it as a snapshot. It's designed to be mentally quick and digestible because it needs to stick in the reader's mind quickly since more information is provided later in the plan.
Describe the Company in Detail
Explain the company's current situation, both good and bad. Details should also include patents, licenses, copyrights, and unique strengths that no one else has.
Create a marketing plan ahead of time.
A strategic marketing plan is required because it outlines how your product or service will be communicated, delivered, and sold to customers.
Be Willing to Change Your Plan for the Sake of Your Audience
Another standard error is that people only write one business plan. Startups have several versions, just as candidates have numerous resumes for various potential employers.
Incorporate Your Motivation
Your motivation must be a compelling reason for people to believe your company will succeed in all circumstances. A mission should drive a business, not just selling, to make money. That mission is defined by your motivation as specified in your business plan.
What Are the Basic Steps in Business Planning?
These are the basic steps in business planning:
Summary and Objectives
Briefly describe your company, its objectives, and your plan to keep it running.
Services and Products
Add specifics to your detailed description of the product or service you intend to offer. Where, why, and how much you plan to sell your product or service and any special offers.
Conduct research on your industry and the ideal customers to whom you want to sell. Identify the issues you want to solve for your customers.
Operations are the process of running your business, including the people, skills, and experience required to make it successful.
How are you going to reach your target audience? How you intend to sell to them may include positioning, pricing, promotion, and distribution.
Consider funding costs, operating expenses, and projected income. Include your financial objectives and a breakdown of what it takes to make your company profitable. With proper business planning through the help of support, system, and mentorship, it is easy to start a business.
Our Business And Leadership Courses Duration And Fees
Business And Leadership Courses typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
| Program Name | Duration | Fees |
|---|---|---|
| Cohort Starts: | 5 months | $ 2,500 |
| Cohort Starts: | 6 Months | $ 3,499 |
| Cohort Starts: | 8 Months | $ 5,000 |
| Cohort Starts: | 5 months | $ 4,500 |
| 11 Months | $ 1,449 |
Get Free Certifications with free video courses
Business and Leadership
Business Analysis Basics
Data Science & Business Analytics
Business Intelligence Fundamentals
Learn from Industry Experts with free Masterclasses
How to Think Like a Product Manager to Boost User Engagement on Netflix
Career Information Session: Find Out How to Become a Business Analyst with IIT Roorkee
Industry Trends: Unleash the AI Gateway for Advancing Your UI/UX Design Career in 2024
Recommended Reads
Business Intelligence Career Guide: Your Complete Guide to Becoming a Business Analyst
Corporate Succession Planning: How to Create Leaders According to the Business Need
Top Business Analyst Skills
Business Analytics Basics: A Beginner’s Guide
Financial Planning for Businesses Across the Globe
How to Become a Business Analyst
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated July 29, 2024

Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
Related Articles

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Get the Job
- Resumes and CVs
- Applications
- Cover Letters
- Professional References
Professional Licenses and Exams
- Get a Promotion
- Negotiation
- Professional Ethics
- Professionalism
- Dealing with Coworkers
- Dealing with Bosses
Communication Skills
Managing the office, disabilities, harassment and discrimination, unemployment.
- Career Paths
- Compare Careers
- Switching Careers
- Training and Certifications
- Start a Company
- Internships and Apprenticeships
- Entry Level Jobs
- College Degrees
Growth Trends for Related Jobs
Business planner job description.

Preparing for disaster helps reduce the impact that unforeseen events have on an organization. The best plans prevent disruption from taking place by identifying important people, processes and equipment that keep a business running. Business planners focus on developing procedures that protect organizations from catastrophe and return operations to normal as quickly as possible.
Education and Skills
The majority of business planners have a bachelor's degree or a post-baccalaureate certificate before applying for this job. The minimum requirement for most business planners is a bachelor's degree in a related field, such as emergency management, business and public administration. Business planners need critical-thinking skills and the ability to make important decisions under stressful circumstances that require a rapid response. You also need excellent communication and collaboration skills and strong leadership abilities.
Professional Development
The Business Continuity Planners Association gives you access to resources and connections difficult to find elsewhere. The Business Continuity Institute has a certification training program that teaches best practices for business planners, preparing them to earn a certificate from the institute by passing a BCI examination. Earning certification and continually developing skills and connections through professional business continuity organizations increases your chance for advancement in the face of declining demand for business planners. Previous experience in emergency management with police and firefighters sets you apart for advancement in the eyes of potential employers.
Business Planner Duties
As a business planner, you collaborate with your peers to determine the best course of action in the event that a disaster or an unfortunate occurrence threatens the normal operations of your organization. This requires that you help colleagues develop recovery plans that enhance their ability to return to full capacity. Another important business planner duty minimizes the disruption of operations when calamity strikes by developing improved processes that are more resilient to upheaval.
Additional Duties and Responsibilities
Business planners help analyze the impact of disruptions and identify the most important issues when surviving threats. They develop and document plans for efficient recovery from disaster and coordinate training exercises to help prepare the best response from vital colleagues. Preparing business continuity reports for senior management ensures that all critical functions have a backup plan. Business planners also create procedures that protect and backup vital hardware such as data servers and communication systems.
Related Articles
Job description for an internal control officer →.

MIS Specialist Job Description →

Crisis Management Job Description →

Job Description of a Business Specialist →

Demand Planner Job Description →

Business Controller Job Description →

- O*Net Online: Business Continuity Planners
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics: Occupational Outlook Handbook: How to Become an Emergency Management Director
- Business Continuity Planners Association: About BCPA
- Business Continuity Institute: BCI Certification Training
- Data Center Assistance Group: Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Job Descriptions
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics: Occupational Outlook Handbook: Emergency Management Directors
Kent Tukeli has been writing for business and media organizations since 2007, including Valnet Inc., Top Affiliate Publishing and Mirvish Productions. He honed his skills at the University of Toronto, earning a Bachelor of Arts in English literature.
demaerre/iStock/GettyImages
- Job Descriptions
- Law Enforcement Job Descriptions
- Administrative Job Descriptions
- Healthcare Job Descriptions
- Sales Job Descriptions
- Fashion Job Descriptions
- Education Job Descriptions
- Salary Insights
- Journalism Salaries
- Healthcare Salaries
- Military Salaries
- Engineering Salaries
- Teaching Salaries
- Accessibility
- Privacy Notice
- Cookie Notice
- Copyright Policy
- Contact Us
- Find a Job
- Manage Preferences
- California Notice of Collection
- Terms of Use
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that outlines a company's goals and the strategies to achieve them. It's valuable for both startups and established companies. For startups, a well-crafted business plan is crucial for attracting potential lenders and investors. Established businesses use business plans to stay on track and aligned with their growth objectives. This article will explain the key components of an effective business plan and guidance on how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document detailing a company's business activities and strategies for achieving its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to launch their venture and to attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan helps keep the executive team focused on short- and long-term objectives.
- There's no single required format for a business plan, but certain key elements are essential for most companies.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place before beginning operations. Banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before considering making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a company doesn't need additional funding, having a business plan helps it stay focused on its goals. Research from the University of Oregon shows that businesses with a plan are significantly more likely to secure funding than those without one. Moreover, companies with a business plan grow 30% faster than those that don't plan. According to a Harvard Business Review article, entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than those who don't.
A business plan should ideally be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect achieved goals or changes in direction. An established business moving in a new direction might even create an entirely new plan.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. It allows for careful consideration of ideas before significant investment, highlights potential obstacles to success, and provides a tool for seeking objective feedback from trusted outsiders. A business plan may also help ensure that a company’s executive team remains aligned on strategic action items and priorities.
While business plans vary widely, even among competitors in the same industry, they often share basic elements detailed below.
A well-crafted business plan is essential for attracting investors and guiding a company's strategic growth. It should address market needs and investor requirements and provide clear financial projections.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, gathering the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document is best. Any additional crucial elements, such as patent applications, can be referenced in the main document and included as appendices.
Common elements in many business plans include:
- Executive summary : This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services : Describe the products and services the company offers or plans to introduce. Include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique consumer benefits. Mention production and manufacturing processes, relevant patents , proprietary technology , and research and development (R&D) information.
- Market analysis : Explain the current state of the industry and the competition. Detail where the company fits in, the types of customers it plans to target, and how it plans to capture market share from competitors.
- Marketing strategy : Outline the company's plans to attract and retain customers, including anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. Describe the distribution channels that will be used to deliver products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections : Established businesses should include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. This section may also include any funding requests.
Investors want to see a clear exit strategy, expected returns, and a timeline for cashing out. It's likely a good idea to provide five-year profitability forecasts and realistic financial estimates.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can vary in format, often categorized into traditional and lean startup plans. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These are detailed and lengthy, requiring more effort to create but offering comprehensive information that can be persuasive to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These are concise, sometimes just one page, and focus on key elements. While they save time, companies should be ready to provide additional details if requested by investors or lenders.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan isn't a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections. Markets and the economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All this calls for building flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How Often Should a Business Plan Be Updated?
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on its nature. Updating your business plan is crucial due to changes in external factors (market trends, competition, and regulations) and internal developments (like employee growth and new products). While a well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary, a new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is ideal for quickly explaining a business, especially for new companies that don't have much information yet. Key sections may include a value proposition , major activities and advantages, resources (staff, intellectual property, and capital), partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
A well-crafted business plan is crucial for any company, whether it's a startup looking for investment or an established business wanting to stay on course. It outlines goals and strategies, boosting a company's chances of securing funding and achieving growth.
As your business and the market change, update your business plan regularly. This keeps it relevant and aligned with your current goals and conditions. Think of your business plan as a living document that evolves with your company, not something carved in stone.
University of Oregon Department of Economics. " Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Business Planning Using Palo Alto's Business Plan Pro ." Eason Ding & Tim Hursey.
Bplans. " Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes ."
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
Harvard Business Review. " How to Write a Winning Business Plan ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
SCORE. " When and Why Should You Review Your Business Plan? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/marketing-plan-ff4bce0e2c52493f909e631039c8f4ca.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
What is a staffing manager?

If you sell professional services or work in project mode, resource planning is part of your daily routine.
Managing it properly is an important performance issue. For this reason, a resource planning manager is likely to support your project teams in improving the resource distribution .
What is the role of the staffing manager?
The staffing manager, or resource planning manager, is responsible for strategic planning of resource capacity . He or she is in a position to allocate the best profiles to a project's tasks and sub-tasks, so as to meet the 3 key criteria for success:
- cost constraints,
- time constraints,
- quality requirements.
Talent acquisition and management: a major challenge
To carry out their mission successfully, all good resource planning managers need to have sufficient technical and business knowledge to understand project resource requirements.
During the talent sourcing analytical skills are also required for optimal resource planning, notably through analysis of past projects.
This responsibility is aligned with a company's strategic objectives, since this matching of skills and employees in the short and long term leads to greater efficiency.
Resource planning manager and recruiter: what are the differences?
While both play a central role in resource management, staffing managers and recruiters are involved at different levels.
The resource planning manager works on a broader, more strategic scope, in order to plan projects to meet customer needs.
The recruiter has a more operational role, and is responsible for the process of recruiting candidates to meet identified resource requirements - for for example by the resource planning manager.
These two missions are naturally intertwined, which is why it's possible that the resource planning manager's hat is worn by the HR department, the BU director, or even project managers in certain structures.
But the resource planning manager is a profession in its own right, and one that is becoming increasingly important as the size of the company grows.
How does the staffing manager contribute to company growth?
The staffing manager implements best practices in resource planning to improve business efficiency.
The workforce optimization work orchestrated by the staffing manager can be considered as performance management in its own right. Resource planning has a direct impact on customer satisfaction, by guaranteeing :
- quality production through a careful selection of skills;
- timely delivery thanks to the assignment of sufficiently experienced profiles.
Using the Stafiz tool, you can manage your resource planning with complete short-, medium- and long-term visibility on resource planning!
Stay one step ahead, and plan your projects from the pre-sales stage.
- When a job is won, the profiles pre-staffed via the time reserved for jobs are automatically integrated into the schedule.
- In the event of failure, the resource planning forecast is deleted, and your staff's availabilities are updated.
Staff your teams with Stafiz
Thanks to improved organizational efficiency you'll be able to accept more customer requests, and grow your business.
How can resource planning software make resource planning manager's job easier?
Resource planning manager's techniques for optimizing recruitment processes.
Anticipating recruitment needs is a key challenge for resource planning.
A shortage of talent or skills can lead to periods of understaffing, and increase the risk of overload for your employees. A sustainable business needs to ensure a certain degree of continuity. Shortages also mean under-performance in sales: without the right talent, you can't get projects off the ground on time and satisfy your customers.
The resource requirements are more easily identified by the resource planning manager if his tool offers him complete visibility of manpower availability .
He can then decide on the best course of action: training, subcontracting or recruitment.
Stafiz enables you to anticipate these needs by monitoring projects that have been won and those that are about to be won:
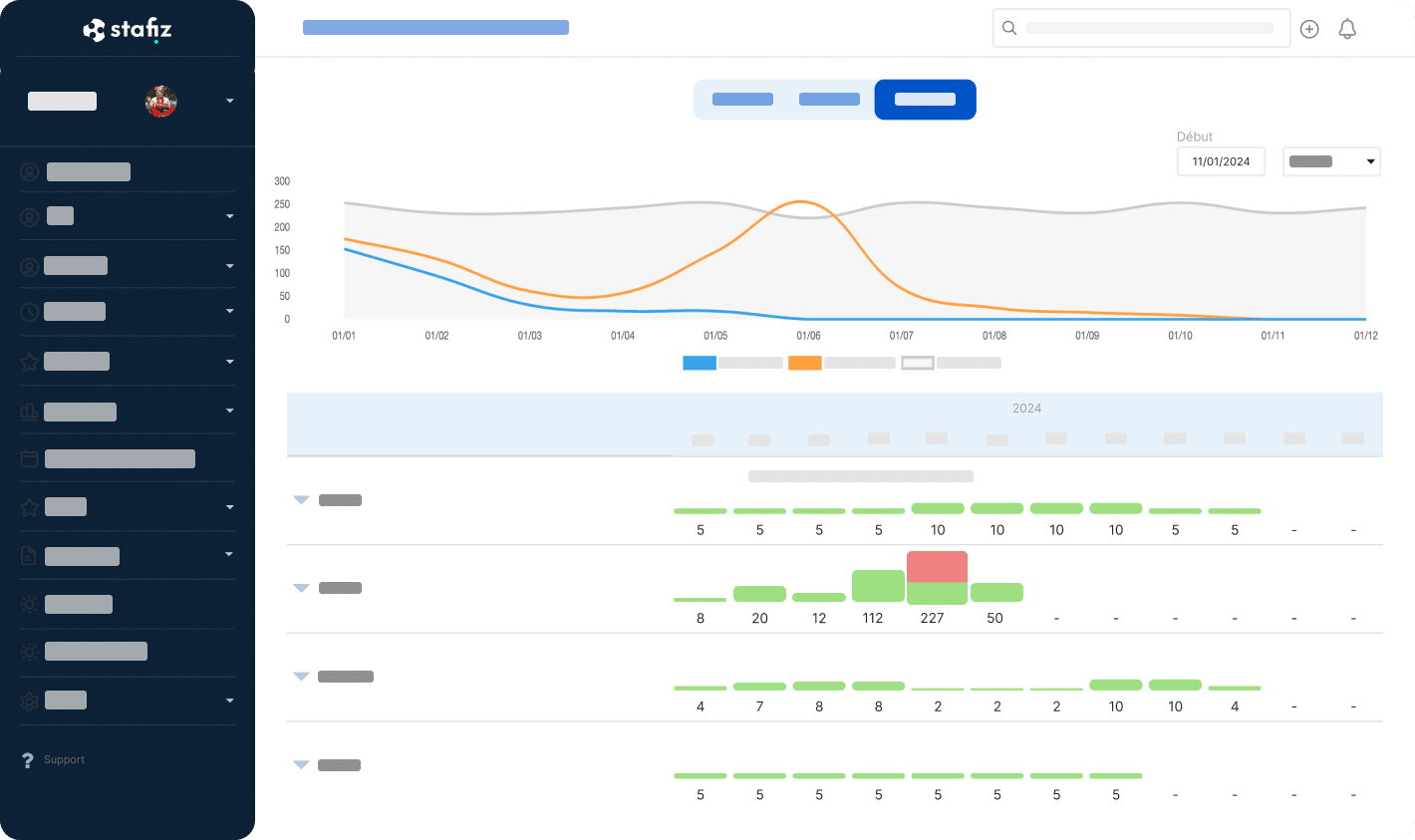
Stafiz CRM lets you manage and anticipate opportunities. The Stafiz API connects your CRM.
Learn more about integrations
How do you source talent and keep your talent pool up to date?
Centralizing resource requirements is essential for efficient management of resource planning.
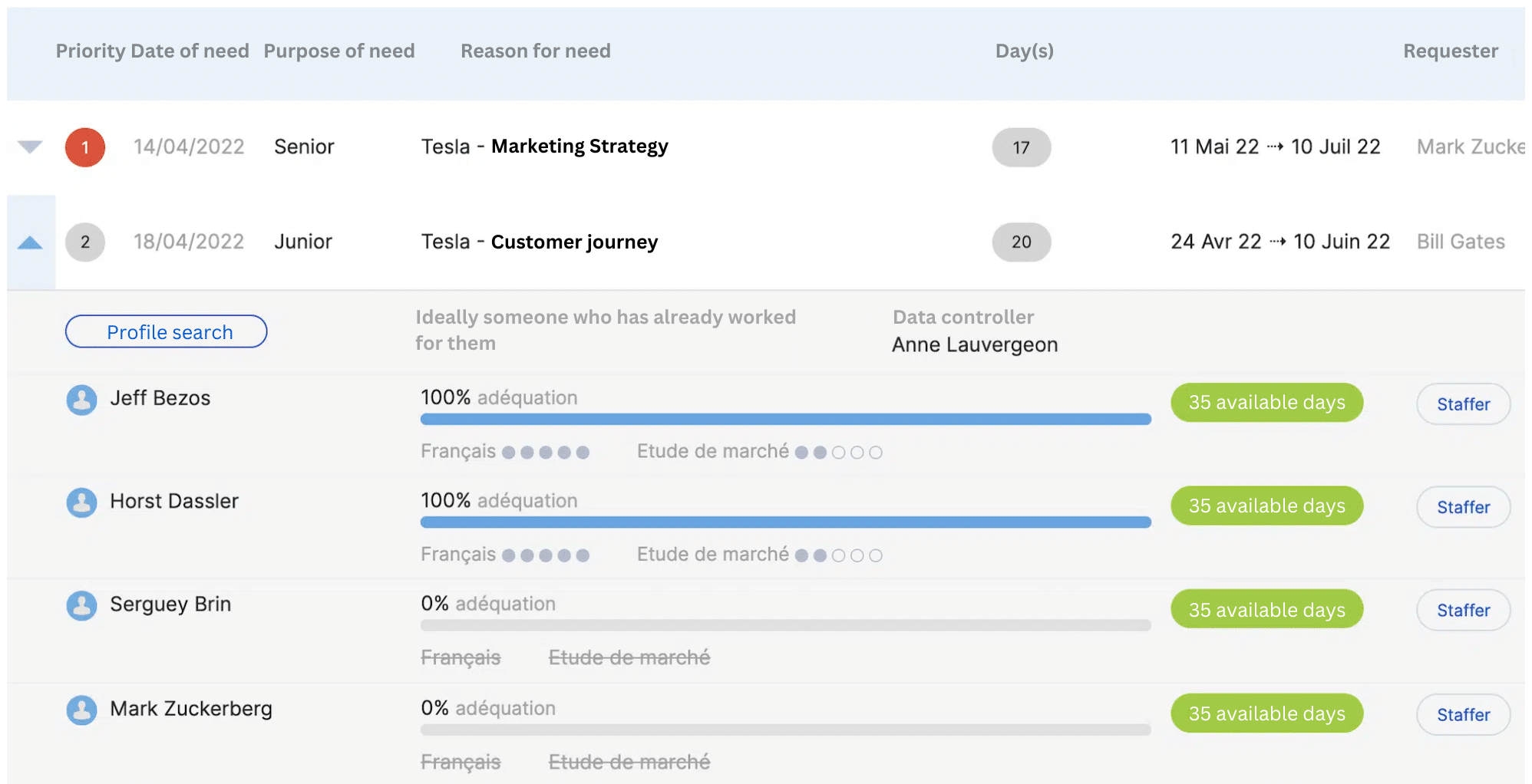
This approach enables you to take stock of your current resource capacity but also to select the profiles and teams to assign to each current or future project.
In particular, Stafiz offers a powerful skills management engine to facilitate your search for profiles to allocate.
Short on time for manual profile entry?
Transfer your employees' CVs and let Stafiz work its magic! OCR technology lets you search and read PDFs directly from the source. Time saving guaranteed!
The data in the pool is then used by the algorithm to search for profiles during the resource planning .
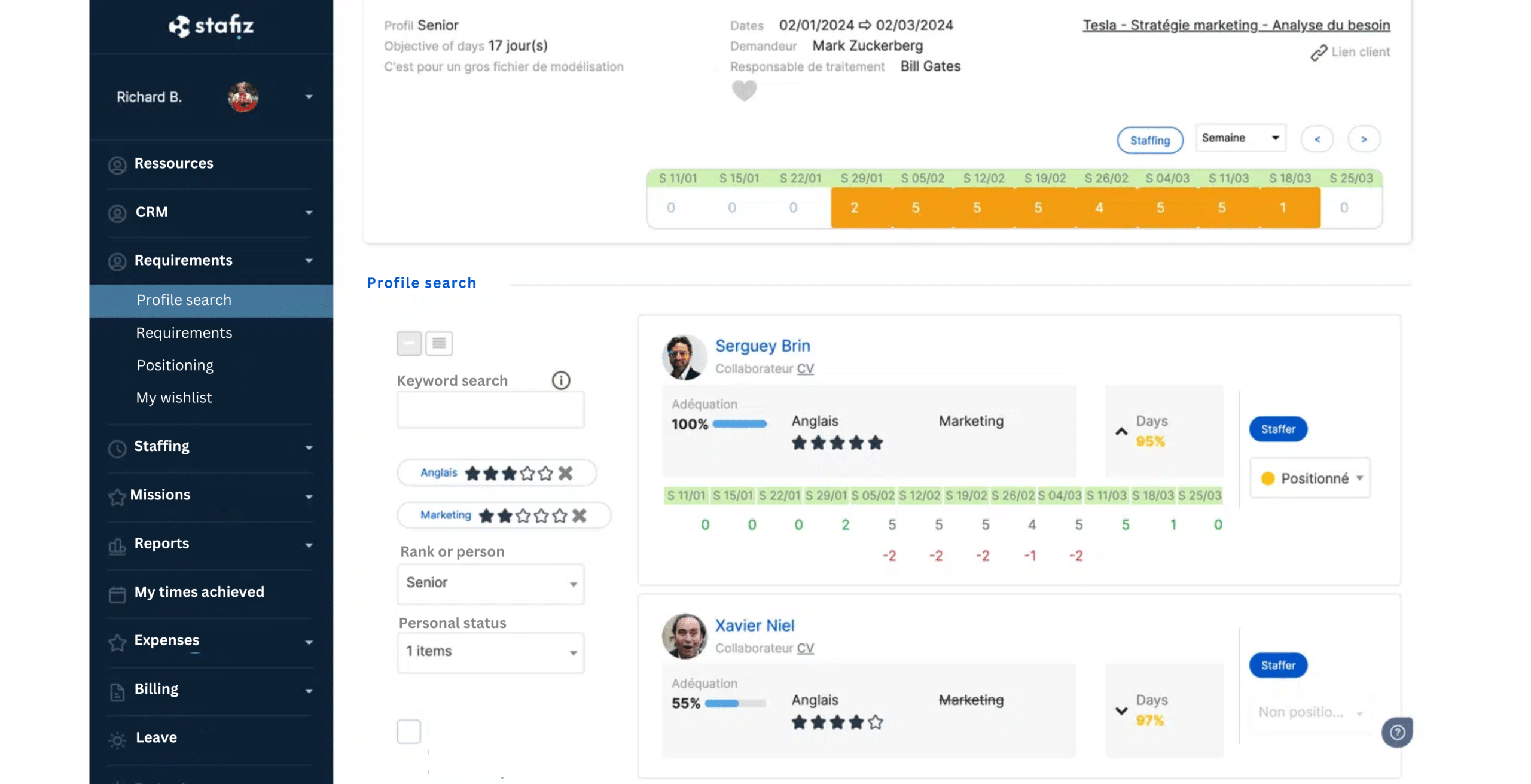
Enter your keywords, select the right usage level, and take advantage of the Smart Matching Stafiz for optimal resource allocation in just a few clicks.
Find out more about resource planning
How do you maintain an efficient, balanced load distribution?
Are you managing your load planning with Excel and lacking real-time and forecast visibility?
Do you find it difficult to visualize and anticipate your occupancy rates, overloads or underloads (or even "gaps" in the schedule or periods between contracts)? Do you find it difficult to study utilization rate ?
Stafiz lets you anticipate.
The load load distribution obvious to you? With just a few clicks, you can readjust your workload by adding or subtracting time from one employee and allocating it to another.
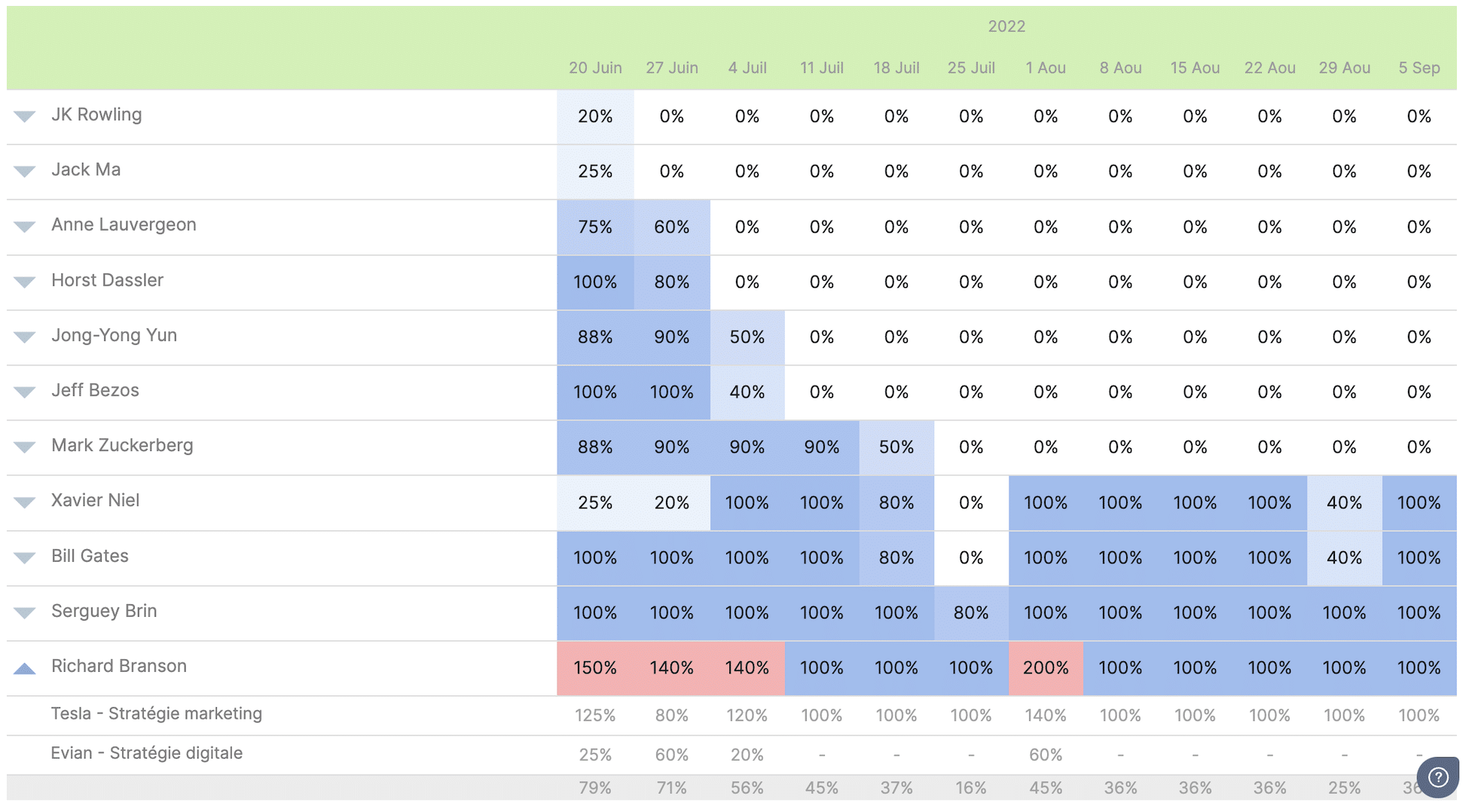
This vision enables you to optimize your utilization rate , so as to keep your teams mobilized on profit-generating projects.
To go one step further, with time tracking , you can monitor the actual occupancy of projects.
Staffing managers' methods for engaging teams
Resource planning software is proving to be a real springboard for employee engagement and satisfaction .
Firstly, sharing the same level of information between project stakeholders provides greater transparency concerning the overall progress.
Secondly, a collaborative solution with notification functionalities such as Stafiz helps to empower employees with greater autonomy and flexibility.
But the best way to engage your employees is to make a point of taking their preferences into account!
We know that despite all your good intentions, the reality on the ground can make the task complicated.
To overcome this problem, Stafiz offers employees the opportunity to indicate on their profile their preferences for a particular type of mission, sector or skill to be mobilized during a project.
This data inks the information, which is sometimes discussed at annual meetings, and makes it possible to establish a genuine monitoring process and facilitate its application.
If you give your collaborators access to the various projects they have won or are about to win in Stafiz, they can keep up to date on upcoming activity and notify managers of their interest on the needs screen.
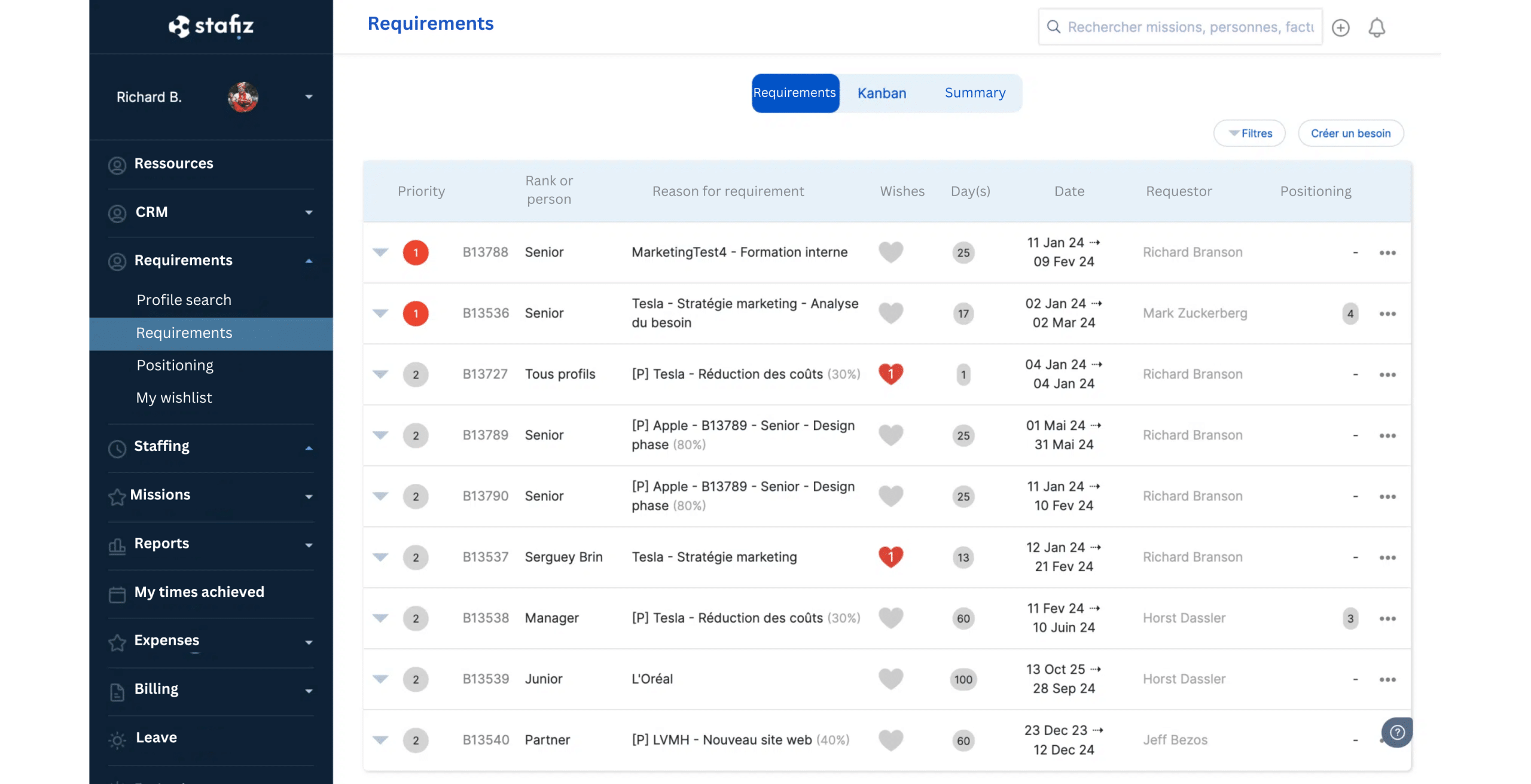
Why is Stafiz the best technological assistant for resource planning ?
Designed specifically to meet the resource management and planning needs of professional service companies, Stafiz will simplify your day-to-day management.
Promoting collaboration between HR and project teams
The data collected by the staffingl solution on individual employee performance complements the annual appraisal interviews by implementing a employee follow-up .
This reflects a more objective reality, thanks to the precise data collected throughout the project.
Taking financial imperatives into account in the management of the resource planning
By integrating both resource planning and financial planning data, Stafiz is able to forecast costs and benefits based on resource planning. This means you can adjust your workload to reduce expenses and increase margins!
The scenario builder even offers you different scenarios for optimizing your resource allocation according to your objectives: optimizing margins, occupancy rates...

White paper: Increase your project margins
Free download
During the project, this analysis continues with the analysis of time and cost deviations in line with operational and financial performance .
It is then possible to compare actual results with forecasts in real time.
Once the project has been completed, the history is kept so that you can evaluate your production according to the chosen criteria:
- phase progress ;
- production teams.
This makes it easier to identify the reasons for any delays or bottlenecks. An exercise that will benefit you when planning future projects !
The resource planning manager's mission is one of great responsibility.
Whether operating in a small structure - where this duty falls to an employee with a dual function or in a large organization where it's more difficult to know every employee and all the technical specifics imputed to customer needs with parsimony a tool resource planning is needed to facilitate the tasks of finding profiles, allocating resources and respecting budgets.
Other articles might interest you

9 common mistakes in money management resource planning
How to calculate a workload plan?
GUIDE: How to set up management of resource planning effective ?
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Auto Racing
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Cisco cuts thousands of jobs, 7% of workforce, as it shifts focus to AI, cybersecurity
FILE - The Cisco logo appears on a screen at the Nasdaq MarketSite on Oct. 3, 2018 in New York’s Times Square. (AP Photo/Richard Drew, File)
- Copy Link copied
Cisco Systems is planning to lay off 7% of its employees, its second round of job cuts this year , as the company shifts its focus to more rapidly growing areas in technology, such as artificial intelligence and cybersecurity.
The company based in San Jose, California, did not specify the number of jobs it is cutting. It had 84,900 employees as of July 2023. Based on that figure, the number of jobs cut would be about 5,900. In February, Cisco announced it would cut about 4,000 jobs.
The networking equipment maker said in June that it would invest $1 billion in tech startups like Cohere, Mistral and Scale to develop reliable AI products. It recently also announced a partnership with Nvidia to develop infrastructure for AI systems.
Cisco’s layoffs come just two weeks after chipmaker Intel Corp. announced it would cut about 15,000 jobs as it tries to turn its business around to compete with more successful rivals like Nvidia and AMD. Intel’s quarterly earnings report disappointed investors and its stock took a nosedive following the announcement. In contrast, Cisco’s shares were up about 6% after-hours on Wednesday.
In a foray into cybersecurity, Cisco launched a cybersecurity readiness index back in March to help businesses measure their resiliency against attacks.
Cisco Systems Inc. said Wednesday it earned $2.16 billion, or 54 cents per share, in its fiscal fourth quarter that ended on July 27, down 45% from $3.96 billion, or 97 cents per share, in the same period a year ago. Excluding special items, its adjusted earnings were 87 cents per share in the latest quarter.
Revenue fell 10% to $13.64 billion from $15.2 billion.
Analysts, on average, were expecting adjusted earnings of 85 cents per share on revenue of $13.54 billion, according to a poll by FactSet.
For the current quarter, Cisco is forecasting adjusted earnings of 86 cents to 88 cents per share on revenue of $13.65 billion to $13.85 billion. Analysts are expecting earnings of 85 cents per share on revenue of $13.74 billion.
Edward Jones analyst David Heger said Cisco is starting to see demand recover after it slowed over the past few quarters, noting that product orders were up 6% even when excluding those from its recent acquisition of cybersecurity firm Splunk .
He added that “the restructuring will help offset the earnings impact from interest expenses associated with financing the Splunk acquisition and will rationalize combined workforces.”

Philadelphia Phillies
Business analyst.
- Share via Email
- Share via Facebook
- Share via X
- Share via LinkedIn
- Learn the day-to-day operations and functions of internal business units that are regular stakeholders of the BA team and develop practices that integrate data literacy in that context.
- Assist in maintaining and growing the department’s offerings of predictive and prescriptive analytics with a focus on artificial intelligence as it relates to data to accelerate methods that add business value.
- Using data to drive revenue, solve business challenges, and optimize business outcomes will be key aspects of this role.
- Perform advanced data analysis on large datasets to prescribe data driven actions relative to business operations.
- Collaborate as part of the Business Analytics team on a variety of analytical projects that span the landscape of the organization.
- Provide a fresh, unique look at current business practices and identify potential areas of growth.
- Create new data-driven initiatives.
- Assist in the operational aspect of supporting BA functions during Phillies events.
- Other duties and projects as assigned.
- Bachelor’s Degree in Business Analytics, Statistics, Mathematics, Economics, Artificial Intelligence or a related field. Advanced Degree preferred.
- 0-2 years of relevant work experience preferred.
- Proficiency in SQL, Python, and R is a requirement.
- Strong ability to work well with co-workers in a team environment and work cross-functionally both inside and outside the department.
- Experience with Microsoft Azure, SAP, and Google Cloud Platform is a plus.
- Excellent written and oral communication skills.
- Demonstrate ability to exercise sound decision-making skills.
- Ability to mentor and teach other staff members.
- Ability to multi-task and meet strict deadlines in a fast-paced environment.
- Must be able to work flexible hours to include holidays, weekends, and evenings as needed.
Job Questions:
What is your desired salary range?
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Tom Brady on the Art of Leading Teammates
- Nitin Nohria

When our society talks about leaders, we focus on formal roles, such as the CEO. This view undervalues the role of informal leaders—team members who influence outcomes by the tone they set, how they conduct themselves, and how they interact with their peers. Their job title doesn’t include the word “manager,” but they play an outsize role in how teams perform.
In this article, NFL great Tom Brady and Nitin Nohria, of Harvard Business School, present a set of principles that people in any realm can apply to help teams successfully work together toward common goals.
The NFL great explains how he motivated himself and fellow players.
When our society talks about success, we tend to focus on individual success. We obsess about who is the “greatest of all time,” who is most responsible for a win, or what players or coaches a team might add next season to become even better.
- Tom Brady achieved great success in his 23-year NFL career, winning seven world championships. He is also an entrepreneur, a New York Times best-selling author, and a business adviser.
- Nitin Nohria is the George F. Baker Jr. and Distinguished Service University Professor. He served as the 10th dean of Harvard Business School, from 2010 to 2020.
Partner Center
As Canada braces for rail stoppage, truckers scramble to meet demand
- Medium Text

- Canadian National Railway and Canadian Pacific Kansas City plan to halt operations on Thursday
- Trucking sector sees increased demand it struggles to meet
- 85% of U.S.-Canada cross-border road freight handled by Canadian carriers
- Higher trucking demand leads to rising costs and longer lead times
- CN and CPKC begin phased network shutdowns
Sign up here.
Reporting by Anna Mehler Paperny, additional reporting by Promit Mukherjee; Editing by Rod Nickel
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. , opens new tab

Thomson Reuters
Toronto-based correspondent covering among other topics migration and health.

Nivedita Balu is a correspondent for Reuters based in Toronto, where she reports on Canadian banks and financial services. She previously covered U.S. tech, media and telecom companies, and consumer and retail companies in Bengaluru.

Domino's Australia franchise slumps 7% as high costs take larger slice of profit
Shares in Australia-based Domino's Pizza Enterprises Ltd slumped more than 7% on Wednesday, after the franchise operator flagged a weak start to fiscal 2025, as rising costs and frugal consumers weighed on profitability.

Explore Jobs
- Jobs Near Me
- Remote Jobs
- Full Time Jobs
- Part Time Jobs
- Entry Level Jobs
- Work From Home Jobs
Find Specific Jobs
- $15 Per Hour Jobs
- $20 Per Hour Jobs
- Hiring Immediately Jobs
- High School Jobs
- H1b Visa Jobs
Explore Careers
- Business And Financial
- Architecture And Engineering
- Computer And Mathematical
Explore Professions
What They Do
- Certifications
- Demographics
Best Companies
- Health Care
- Fortune 500
Explore Companies
- CEO And Executies
- Resume Builder
- Career Advice
- Explore Majors
- Questions And Answers
- Interview Questions
What does a Business Planning Manager do?
A business planning manager is responsible for overseeing the business management process and ensuring that the staff meets productivity goals and targets. Business planning managers recruit and train new staff, handle budgets for projects, and identify opportunities that would increase more revenue resources and profits for the business. They also coordinate with clients for updates and adjust business plans as needed. A business planning manager must have excellent communication and leadership skills to manage teams and achieve long-term objectives.
- Responsibilities
- Skills And Traits
- Comparisions
- Types of Business Planning Manager

Business planning manager responsibilities
Business planning managers play a crucial role in ensuring that a company's products and services meet customer expectations in an ever-changing market. They manage processes that produce or support the firm's products, requiring the ability to analyze data to make informed decisions, drive continuous improvement, and solve problems through critical thinking. Dr. Kim Roberts , Professor of Operations Management, emphasizes this, stating, "Business professionals lead organizations by focused efforts that revolve around products/services, processes, and people."
Resume snippets for business planning managers often highlight responsibilities such as demand planning various product lines, managing customer service division policy deployment and ISO 9000 preparation and audits, and achieving 80% demand forecast accuracy through the implementation of dashboard metrics, KPIs, and competitive market analytics. These tasks demonstrate the ability to manage processes, analyze data, and make informed decisions that drive continuous improvement.
Here are examples of responsibilities from real business planning manager resumes:
- Lead central team summarizing and prioritizing all DOD opportunities, enabling more efficient and effective resource allocation across several program departments.
- Create and implement new product BOM's.
- Verify WIP movement transactions are complete and with the latest BOM changes.
- Provide management with managerial reporting, variances explanations, and KPIs for decision making.
- Perform discounted cash flow and ROI analysis to plan and approve capital equipment investments.
- Create and execute a global staffing scorecard to measure hiring process focusing on ROI to ensure essential staffing.
- Provide specialized CRM consulting, strategy development and systems integration services to help clients leverage technology to build effective customer relationships.
- Generate statistical forecast models using Manugistics and NEFOR (proprietary forecasting tool).
- Maintain and document forecasting and reporting procedures used in forecasting software (Manugistics).
Business planning manager skills and personality traits
We calculated that 19 % of Business Planning Managers are proficient in Business Planning , Competitive Analysis , and Direct Reports . They’re also known for soft skills such as Creativity , Interpersonal skills , and Organizational skills .
We break down the percentage of Business Planning Managers that have these skills listed on their resume here:
Create, communicate and coordinate quarterly adjustments to the annual plan as dictated by Corporate Business Planning and operational requirements.
Developed a market research and competitive analysis strategy that successfully differentiated the Ford product offering that increased sales and revenues.
Created, approved, and processed compensation transactions for senior executives and their direct reports.
Provided training to project management audience to promote efficient and standardized project management processes.
Develop metrics, performance measures and reports that support the business objectives and results.
Analyzed market trends, price cliffs, and competitor behavior to ensure pricing strategy drove profitable growth.
Most business planning managers use their skills in "business planning," "competitive analysis," and "direct reports" to do their jobs. You can find more detail on essential business planning manager responsibilities here:
Creativity. To carry out their duties, the most important skill for a business planning manager to have is creativity. Their role and responsibilities require that "advertising, promotions, and marketing managers must be able to generate new and imaginative ideas." Business planning managers often use creativity in their day-to-day job, as shown by this real resume: "managed 6 business planners in multiple countries coordinating all scheduling, delivery, and inventory activities for $250m+ product line. "
Interpersonal skills. Another essential skill to perform business planning manager duties is interpersonal skills. Business planning managers responsibilities require that "managers must deal with a range of people in different roles, both inside and outside the organization." Business planning managers also use interpersonal skills in their role according to a real resume snippet: "trained new employees in business practices, new business development, and interpersonal communication. "
Organizational skills. business planning managers are also known for organizational skills, which are critical to their duties. You can see how this skill relates to business planning manager responsibilities, because "advertising, promotions, and marketing managers must manage their time and budget efficiently while directing and motivating staff members." A business planning manager resume example shows how organizational skills is used in the workplace: "influence strong organizational effectiveness including effective project management, cross-functional leadership, corporate training and organizational development. "
Analytical skills. business planning manager responsibilities often require "analytical skills." The duties that rely on this skill are shown by the fact that "advertising, promotions, and marketing managers must be able to analyze industry trends to determine the most promising strategies for their organization." This resume example shows what business planning managers do with analytical skills on a typical day: "performed project and product profitability analysis for all product lines of the organization. "
Communication skills. A commonly-found skill in business planning manager job descriptions, "communication skills" is essential to what business planning managers do. Business planning manager responsibilities rely on this skill because "managers must be able to communicate effectively with a broad-based team made up of other managers or staff members during the advertising, promotions, and marketing process." You can also see how business planning manager duties rely on communication skills in this resume example: "directed business planning and internal communication activity for the $1.6b global transportation industry. "
Most common business planning manager skills
The three companies that hire the most business planning managers are:
- Ernst & Young 56 business planning managers jobs
- Oracle 48 business planning managers jobs
- Samsung Electronics Device Solutions (Semiconductor & Display) 15 business planning managers jobs
Choose from 10+ customizable business planning manager resume templates

Compare different business planning managers
Business planning manager vs. manager, strategy.
A strategy manager is an individual who reviews a company's objectives for growth and works with executives to formulate actionable plans to achieve these objectives. To make comprehensive recommendations, strategy managers must conduct data analysis of the organization as well as the overall industry. They must provide assessments of market trends and identify business threats and opportunities. Strategy managers should also work with department heads to develop individual team goals and break them down into actionable steps for the employees to complete.
There are some key differences in the responsibilities of each position. For example, business planning manager responsibilities require skills like "business planning," "continuous improvement," "supply chain planning," and "business performance." Meanwhile a typical manager, strategy has skills in areas such as "portfolio," "client facing," "digital marketing," and "strategic thinking." This difference in skills reveals the differences in what each career does.
Business planning manager vs. Product manager
A product manager is responsible for ensuring product development, providing the best marketing strategies, and effectively handling the sales and marketing team. Product managers' duties include monitoring the market trends and conditions, identifying business opportunities and plan initiatives, and collaborating the product launch process with the appropriate departments. A product manager is also responsible for generating ideas on improving product features, determining timetables and reasonable pricing, and analyzing product sales. A product manager must have excellent strategic and decision-making skills to contribute to its growth and profitability.
Each career also uses different skills, according to real business planning manager resumes. While business planning manager responsibilities can utilize skills like "business planning," "business objectives," "financial analysis," and "data analysis," product managers use skills like "product management," "qa," "product strategy," and "user stories."
Business planning manager vs. Market manager
A marketing manager is an executive who manages a brand or product's promotion positioning. Marketing managers analyze the trends in the industry and the demand for certain products and services. Typically, they attract more customers to purchase products and/or services and raise brand awareness through marketing campaigns. They research, identify, examine, and evaluate product demand. Also, they review advertising materials like print ads to boost the marketing strategy of the company and strengthen its campaign.
The required skills of the two careers differ considerably. For example, business planning managers are more likely to have skills like "business planning," "business objectives," "financial analysis," and "data analysis." But a market manager is more likely to have skills like "customer service," "strong analytical," "excellent interpersonal," and "human resources."
Business planning manager vs. Manager finance planning and analysis
A manager finance planning and analysis oversees the daily operations of a company's financial planning department. They typically have administrative duties such as setting goals and guidelines, establishing timelines and budgets, delegating tasks among teams and staff, and reviewing financial reports regularly. They also perform research and assessments, gather and analyze financial data from different departments, coordinate staff, and solve issues and concerns when any arise. Additionally, as a manager, they must lead and empower staff to reach goals while implementing company policies and regulations.
Even though a few skill sets overlap between business planning managers and managers finance planning and analysis, there are some differences that are important to note. For one, a business planning manager might have more use for skills like "business planning," "competitive analysis," "project management," and "business objectives." Meanwhile, some responsibilities of managers finance planning and analysis require skills like "customer service," "visualization," "financial operations," and "financial reports. "
Types of business planning manager
- Business Development Manager
- Business Manager
Product Manager
- Business Operations Manager
- Business Unit Manager
- Business Leader
Updated June 25, 2024
Editorial Staff
The Zippia Research Team has spent countless hours reviewing resumes, job postings, and government data to determine what goes into getting a job in each phase of life. Professional writers and data scientists comprise the Zippia Research Team.
What Similar Roles Do
- What a Brand Manager Does
- What a Business Development And Marketing Manager Does
- What a Business Development Manager Does
- What a Business Director Does
- What a Business Leader Does
- What a Business Manager Does
- What a Business Operations Manager Does
- What a Business Partner Does
- What a Business Unit Manager Does
- What a Manager Finance Planning And Analysis Does
- What a Manager, Strategy Does
- What a Market Manager Does
- What a Media Manager Does
- What a Planning Director Does
- What a Planning Manager Does
Business Planning Manager Related Careers
- Brand Manager
- Business Development And Marketing Manager
- Business Director
- Business Partner
- Manager Finance Planning And Analysis
- Manager, Strategy
- Market Manager
- Media Manager
- Planning Director
- Planning Manager
Business Planning Manager Related Jobs
Resume for related jobs.
- Brand Manager Resume
- Business Development And Marketing Manager Resume
- Business Development Manager Resume
- Business Director Resume
- Business Leader Resume
- Business Manager Resume
- Business Operations Manager Resume
- Business Partner Resume
- Business Unit Manager Resume
- Manager Finance Planning And Analysis Resume
- Manager, Strategy Resume
- Market Manager Resume
- Media Manager Resume
- Planning Director Resume
- Planning Manager Resume
- Zippia Careers
- Executive Management Industry
- Business Planning Manager
- What Does A Business Planning Manager Do
Browse executive management jobs
Advertisement
Supported by
News analysis
Harris and Trump Offer a Clear Contrast on the Economy
Both candidates embrace expansions of government power to steer economic outcomes — but in vastly different areas.
- Share full article

By Jim Tankersley
Jim Tankersley has covered economic policy in presidential elections since 2004.
Vice President Kamala Harris and former President Donald J. Trump flew to North Carolina this week to deliver what were billed as major speeches on the economy. Neither laid out a comprehensive policy plan — not Ms. Harris in her half-hour focus on housing, groceries and prescription drugs, nor Mr. Trump in 80 minutes of sprinkling various proposals among musings about dangerous immigrants.
But in their own ways, both candidates sent voters clear and important messages about their economic visions. Each embraced a vision of a powerful federal government, using its muscle to intervene in markets in pursuit of a stronger and more prosperous economy.
They just disagreed, almost entirely, on when and how that power should be used.
In Raleigh on Friday, Ms. Harris began to put her own stamp on the brand of progressive economics that has come to dominate Democratic politics over the last decade. That economic thinking embraces the idea that the federal government must act aggressively to foster competition and correct distortions in private markets.
The approach seeks large tax increases on corporations and high earners, to fund assistance for low-income and middle-class workers who are struggling to build wealth for themselves and their children. At the same time, it provides big tax breaks to companies engaged in what Ms. Harris and other progressives see as delivering great economic benefit — like manufacturing technologies needed to fight global warming , or building affordable housing.
That philosophy animated the policy agenda that Ms. Harris unveiled on Friday. She pledged to send up to $25,000 in down-payment assistance to every first-time home buyer over four years, while directing $40 billion to construction companies that build starter homes. She said she would permanently reinstate an expanded child tax credit that President Biden temporarily established with his 2021 stimulus law, while offering even more assistance to parents of newborns.
She called for a federal ban on corporate price gouging on groceries and for new federal enforcement tools to punish companies that unfairly push up food prices. “My plan will include new penalties for opportunistic companies that exploit crises and break the rules,” she said, adding: “We will help the food industry become more competitive, because I believe competition is the lifeblood of our economy.”
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Business planners take a primary role in the strategic planning process for clients or organizations. They plan, develop, and implement strategies for all facets of business operations, including budgeting, administration, production, personnel, sales, and logistics. They have a strong focus on long-term growth and identify tactics and ...
Depending on the type of Business Planner role you're pursuing, you may want to explore certification in certified business continuity professional. 4. Advance in Your Business Planner Career Following entry-level, there are several Business Planner career path levels to advance into. It can take 2 years as an entry-level Business Planner to ...
A business planner specializes in developing and implementing business plans and procedures. Their job entails conducting extensive research and analyses to identify key business participants, determine the strengths and weaknesses of existing operations, and find new business opportunities. They also perform risk assessments, address potential ...
Published Feb 20, 2024. The Business Planning Manager plays a strategic role in steering the company's direction through comprehensive market analysis, forecasting, and resource allocation. This position involves synthesizing complex data into actionable strategies that align with the company's long-term goals and financial objectives.
To join our growing team, please review the list of responsibilities and qualifications. Responsibilities for business planning. Provide business case, ROI and payback analysis (e.g., total cost of ownership, lease vs. Manage the processing and scheduling of customer orders. Scheduling and procurement of materials.
It typically takes 6-8 years to become a business planner: Years 1-5: Obtaining a Master's degree in a relevant field, such as business administration, finance, or economics. Year 6-7: Accumulating the necessary work experience, typically 1-2 years, in roles that involve budgeting, forecasting, and strategic planning.
A business plan provides a detailed roadmap for your company's future. It outlines your objectives, strategies, and the specific actions you need to achieve your goals. When you define your path forward, a business plan helps you stay focused and on track, even when you face challenges or distractions.
As the backbone of any project, a Planner plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth flow of operations from start to finish. A Planner has the responsibility of laying out the framework that guides a project's progression from initiation to completion. In the broadest sense, a Planner is responsible for the identification and segregation of different tasks that make up a project, setting ...
Responsibilities for business planner. Provides ongoing guidance for business continuation strategies to reach desired control level, , regulatory and legal requirements, customer SLA's. Results focused - delivery to targets and budgets. Demonstrate a level of Initiative and ability to manage own workload effectively.
Business planners take a primary role in the strategic planning process for clients or organizations. They plan, develop, and implement strategies for all facets of business operations, including budgeting, administration, production, personnel, sales, and logistics. They have a strong focus on long-term growth and identify tactics and ...
A Strategic Planner develops and implements plans to materialize the company's strategy, conducts research and data analysis to inform business decisions, and aligns department goals with the overall strategy. They also monitor industry trends, provide insights into organizational changes, and support senior executives in making effective ...
Develop, document and implement business plans, processes and procedures. Develop presentations for management and stakeholders on business operations and developments. Support business planning functions for new and existing strategic partnerships and alliances. Address operational and cost related issues in business planning projects.
Here are the key elements of a good business plan: Executive Summary: An executive summary gives a clear picture of the strategies and goals of your business right at the outset. Though its value is often understated, it can be extremely helpful in creating the readers' first impression of your business.
Develop manufacturing concepts and strategies to support business objectives. Oversee and supervise the development of architectural documents, elevations, sections, details, etc. Answer planning, zoning and development process questions from citizens, developers and other agencies. Develop and document new job practices, techniques and standards.
They conduct research, design, and advanced programs. Some of them focus on a few roles, such as planning transportation, while some will most likely work at different planning types throughout their profession. They develop a plan through data analysis, determine the project's goals or the community, and form a specific vision.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Business Continuity Planner. University of California, Riverside. Riverside, CA 92521. ( University area) $73,600 - $133,200 a year. Full-time. We base salary offers on a variety of considerations, such as education, licensure and certifications, experience, and other business and organizational needs. Posted 30+ days ago ·.
Business Planner Job Description. Preparing for disaster helps reduce the impact that unforeseen events have on an organization. The best plans prevent disruption from taking place by identifying important people, processes and equipment that keep a business running. Business planners focus on developing procedures that protect organizations ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Thanks to improved organizational efficiency you'll be able to accept more customer requests, and grow your business. How can resource planning software make resource planning manager's job easier? resource planning manager's techniques for optimizing recruitment processes. Anticipating recruitment needs is a key challenge for resource planning.
The manager plays a lead role in developing and implementing comprehensive, long-term strategic plans, delegating roles and tasks, and establishing metrics for evaluating results. Business planning managers typically have a minimum of a bachelor's degree, although it is an advantage to have an advanced degree such as an MBA.
Cisco Systems is planning to lay off 7% of its employees, its second round of job cuts this year, as the company shifts its focus to more rapidly growing areas in technology, such as artificial intelligence and cybersecurity.. The company based in San Jose, California, did not specify the number of jobs it is cutting.
The Business Analytics (BA) strategic plan includes maximizing the value of owned and acquired data as a business asset that enables measurable and positive financial returns while combining operational business data to form powerful insights that support decision-making at all levels of the organization. This position is responsible for ...
Business Planner job description example 1. Pernod Ricard USA business planner job description. Job PurposeBusiness planning and communication of business priorities for the field sales teams Manage and maintain the D-Star control tower by validating and pushing weekly priorities to enable field sales teams Collect, optimize, reconcile and ...
Their job title doesn't include the word "manager," but they play an outsize role in how teams perform. In this article, NFL great Tom Brady and Nitin Nohria, of Harvard Business School ...
Canadian National Railway and Canadian Pacific Kansas City plan to halt operations on Thursday Trucking sector sees increased demand it struggles to meet 85% of U.S.-Canada cross-border road ...
Business planning manager responsibilities rely on this skill because "managers must be able to communicate effectively with a broad-based team made up of other managers or staff members during the advertising, promotions, and marketing process." You can also see how business planning manager duties rely on communication skills in this resume ...
Neither laid out a comprehensive policy plan — not Ms. Harris in her half-hour focus on housing, groceries and prescription drugs, nor Mr. Trump in 80 minutes of sprinkling various proposals ...
Business Economy Economic Policy Personal Finance Work Technology ... praised Harris for returning to help Jamaica but disputed that the 2012 plan played much of a role in the country's economic ...