
The Savvy Scientist
Experiences of a London PhD student and beyond

PhD Salary UK: How Much Do PhD Students Get Paid Compared to Graduates?

Considering whether to stay in university as a PhD student or to leave and get a job? If so, you may be wondering “How much do PhD student get paid?” and “How does a UK PhD salary compare to a graduate salary?” .
In this post I delve into the details and reveal that the difference in take home pay between a UK PhD stipend and a grad position can actually be much lower than it first appears!
If you’re looking to know how much a PhD could boost your career and salary after finishing your doctoral degree I’d suggest checking out my post: Is a PhD Worth It ? See details here for how much people earn in academia after getting their PhD .
I also have a complementary post covering my monthly expenses as a PhD student. You may also wish to check out my guide to the application process , PhD FAQs and article on how I got a PhD scholarship .
February 2024 : This post has been updated to include figures for the 2023/24 academic year.
Do PhD students get paid in the UK? If so, how much do PhD students get paid?
Before we delve into the details let’s first cover whether PhD students get paid in the UK. Generally, yes, most PhD students get what is called a PhD stipend to support themselves during their PhD. Importantly, a PhD stipend (in the UK at least) is tax free .
It is worth noting though that not all PhD projects automatically include funding. Funding may also not be applicable for every applicant. For example sometimes it may only be available to home students i.e. those from the UK.
Therefore some students may resort to self funding their PhD. In STEM subjects self funding a PhD is pretty rare and often only happens because of limitations in funding eligibility. I’ve personally worked with a mix of funded and self-funded (often by parents) PhD students, though most are certainly funded by grants and scholarships.
If your project doesn’t already include funding, for most people I strongly advise trying to find funding rather than considering self funding. For more information on this check out my post on PhD Funding in the UK.
2023/24 UK PhD Salary
- PhD salary outside of London: In 2023/24 most new PhD students in the UK will receive a PhD stipend worth at least £18,622 per year .
- PhD salary in London : In 2023/24 most new PhD students in London will receive an increased stipend to account for cost of living , which is typically around £20,622 per year .
Notice that the PhD stipend for outside of London is at least £18,622 per year. I’ve seen several advertised at the London rate. There are also some available at an even higher rate. For example I know of CDTs in Bristol paying more like £24,000 tax-free.
Your PhD stipend will usually provide funding for 3.5 years, although it can occasionally be for 3 or 4 years.
These values are for most PhD studentships including those awarded by all UK research councils following the UKRI guidelines .
Certain scholarship schemes pay upwards of £25,000 per year, such as the £25,150 (2024/25 rate) President’s PhD Scholarships at Imperial. For details on how to get such a scholarship, check out this article where I go over how I got awarded my own PhD scholarship.
The Marie Skłodowska-Curie Innovative Training Network (ITN) runs all across the EU. As well as nice training and exchange opportunities it pays a staggering stipend of approx £40,000 – £45,000 . The grant level is reviewed each year and increases if you have family dependents. I personally wish I’d known about it earlier and highly recommend anyone interested puts a reminder in their diary for when the next call opens!
Is a UK PhD stipend taxable?
Here is what PhD stipends look like compared to some fairly typical starting grad salaries in the UK:

At first glance a PhD stipend doesn’t stack up well against the higher wages of a graduate salary which can sometimes be twice this amount or more. But crucially PhD stipends for students are tax free !
There are a few other financial perks that come with being a student so I was intrigued to find out how the two salaries really compared. The results may surprise you!
Below is a high level overview and I’ll delve into each of the numbers in depth later in the post.

Grad salary vs PhD salary starting numbers
As mentioned earlier, in 2023/24 a typical PhD stipend outside of London is at least £18,622 . Within London this will typically increase slightly to account for cost of living to around £20,622 . These rates rise every year for new students, but do not rise for each year of the PhD. So for new students considering starting in 2024/25 a UK PhD salary will likely be around £19,100 outside of London.
For the sake of simplifying the comparison I averaged the 2023/24 PhD stipend to £19,622 for all PhD students studying in the UK.
A fairly typical grad salary, for someone qualified enough to be considering a science PhD, is around £30,000 . Of course this is an average salary so needs to be taken with a pinch of salt. As the number can vary dramatically it may be considered too low by some, but I think it’s a good benchmark accounting for different regions of the UK.
I’ve included higher and lower graduate salaries too in the summary charts for this post.

Salary Gap: £10,378
On the face of it the PhD student would be earning £10,378 less per year: around 35% lower! This is enough of a difference to put off a lot of potential PhD candidates who’ve likely spent the last few years building up student loans.
But unlike normal wages, PhD stipends are tax free so maybe things aren’t as bleak for PhD students as it seems? Let’s explore how they really compare.
Income Tax & National Insurance Contributions

The 2023/24 Personal Income Allowance is £12,570. This means that you can earn up to this amount and not pay any income tax. Earnings from £12,571 up to £50,270 fall into the basic rate bracket of 20% tax.
PhD Student Salary: PhD stipends are tax free and incur no income tax or national insurance contributions. Remaining stipend: £19,622
Professional Salary: On £30,000 you’d pay £ 3486 in income tax and NI contributions of £2004 . Remaining wage: £24,510
Salary Gap: £4888 Income tax and national insurance contributions have immediately almost halved the difference in take-home pay from £10,378 down to £4888!
Student Loan Repayment

PhD Student Salary: Even with a PhD stipend you are officially an unwaged student so you won’t make student loan repayments as a PhD student. Remaining stipend: £19,622 [see footnote 1]
Professional Salary: The amount you may have to pay for student loan repayments depends upon when you started your undergraduate course. If you started your undergraduate course since 2012 you pay student loan repayments on earnings above £27,295. Meaning on a salary of £30,000 you’d pay £243 a year on student loan repayments. If you began your undergraduate course before 2012, repayments start on salaries above £22,015 and would be £541 a year . Most of you likely completed your undergrad degree recently so we’ll go with the more recent, lower, repayments. Remaining wage: £24,267
Salary Gap: £4645
Council Tax

PhD Student Salary: Another cost that students are exempt from is council tax. Though be careful if you share a house with non-students since council tax must then be paid on the property. [2] Remaining stipend: £19,622
Professional Salary: Council tax varies greatly between council boroughs, and depends on the property you live in. For example in Cardiff I lived in a one bed flat and the annual council tax was £1050 per year. During my PhD in London council tax for a lovely three bed house in Clapham it was £1000! Now that I live in Bristol it is over £2000 per year for a three bed house. I’ll go to the liberty of saying on average it would be £1150 per year and would be divided between two people: -£575 each. Total: £23,692
Salary Gap: £4070
Private Pension Contributions
PhD Student Salary: Although universities pay a PhD stipend to students, you are not a member of staff and hence do not make private pension contributions. Remaining stipend: £19,622
Professional Salary: Legislation has been phasing in making contribution to private pensions mandatory. The upside is that employers match your contribution up to varying percentages: sometimes up to about 10% of your salary. Additionally there are tax benefits to contributing so overall you could see it as boosting your salary looking at the longer term view. [3]
I believe there are troubling times ahead for 20-somethings and personally am not relying on a state pension existing by the time we all reach retirement age. Therefore I wholeheartedly recommend making a decently sized contribution at least up to the same amount that your employer matches. For the purposes of this comparison I won’t deduct anything for private pension since it’s not really being deducted so I’ll call this one a draw. Total: £23,692
Student Discount
Ah the obvious one! Student discount may have been the first thing you thought of when you saw this article, but I’m not going to include it in this analysis.
A student card does allow a significant amount to be saved, not only on luxuries such as entry to attractions and deals in shops but also travel. For example in London, an 18+ student oystercard gets you 30% off travelcards. For a monthly zones 1-3 ticket this would save about £50 a month: over £600 a year!
The reason I’ve not included it? How much you use student discount depends on your circumstances and lifestyle and I wanted to keep the analysis widely applicable. Also, there are ways around needing to pay for travel at all: I started cycling to university every day in London .
Curveball: the £12,570 Tax-Free Personal Income Allowance
So far the recent grad is still earning an additional £4842 per year: almost a third more than the PhD student. Owing to the fact that PhD students are exempt from income tax, national insurance contributions, council tax and student loan repayments the gap in earnings has shrunk considerably.
One last calculation I wanted to try was to consider the scenario of a student earning some additional money on the side. It is a common thing to make extra money with teaching assistant, tutoring and consultancy opportunities. In fact I think every PhD student I know does at least a little. There are of course non-academic routes to make additional money too.
I have written a post about some of the ways that I make extra money , many of which are in fact available to non-students. Do be careful to check that this is acceptable at your institution. My favourite way to make extra money is matched betting which is tax-free for everybody. You can find my complete guide to matched betting here .
Tax-free side-hustle
Currently you can earn £12,570 tax free in the UK . Given that the PhD stipend itself is tax free, unlike an equivalent worker you wouldn’t pay any tax on extra earnings up to this threshold. This might sound insignificant but it’s not.
Admittedly, unless you’re very entrepreneurial, it is unlikely that you would make use of the whole tax-free opportunity. But earning several thousand pounds per year on top of the stipend is certainly common.
As pointed out by a reader, John, in the comments below: a consideration should be that that some universities limit how much paid work you can do per month. Even so, there are lots of ways to make money and your time as a student could even be a great time to start your own business .
I’ve been paid more than £25 an hour doing pretty simple work for the university , so these earnings can mount up quickly.
To illustrate the extra earning potential afforded to PhD students, let’s consider the most extreme case where the tax-free earnings are maximised.
Since 2017 there has been a £1000 tax-free trading allowance for workers in the UK , meaning even those in a normal taxable job can earn £1000 on top of their salary from side-hustle jobs. Therefore the grad will pay additional taxes on £11,570 instead of £12,570.

PhD Student Salary: An enterprising student maxing out the tax-free allowance could earn £12,570 a year and pay no national insurance either, leaving additional take-home pay of £12,570 . With a PhD stipend of £17,062 the student would in total earn £32,192 for the year. They’d keep 100% of those extra earnings.
Again, yes it is unlikely that someone would really earn this much on the side but it is common to make at least several thousand throughout the year.
Professional Salary: As a grad on £30,000 per year in your main job, to have an equivalent side-hustle earning £12,570, in total you’d pay tax on £41,570. Income tax would be £5800: £2314 higher than on their base salary of £30,000. NI contributions would be £3335: £1331 higher. Plus student loan repayments would be £1284: £1041 higher. Student loan repayments really start increasing considerably when you’re earning more. These additional taxes and costs total deductions of £4686, leaving the professional with extra take-home pay of £7884 . Including their day-job the total they’d be left with is £31,576 .
For this extra £12,570 of work, the student would pocket 100% of it and the professional would keep £7884 ( 63% ). Looking at the pre-tax difference in their earnings: at face value the student would be earning £32,192 and the grad £41,570: a difference of £9378. Yet once taxes are considered the final result is two people with remarkably similar take-home pays: a difference of £616 in favour of the student!
Check it out:

Under these circumstances the student would in fact take home £616 more per year than the professional! I used the maximum tax-free allowance to highlight the point and yes it’s unlikely that many students will fully utilise it. Yet the point stands that any additional earnings are much better retained by PhD students.
If someone was running a fully-fledged business on the side then the difference becomes even bigger as the grad salary approaches the next tax bracket for earnings of £50,271 and above, at which point the rate of income tax doubles.
There are very few legal ways of making money which are tax-exempt for everyone. One of these rare cases is also my favourite way to make money on the side: matched betting. Intrigued? I’ve written a huge guide to it here . In this rare instance none of the grad’s extra earnings get eroded by tax.
Grad salary vs PhD student salary conclusion
Starting from a difference of £10,378 in salary, taxes and other outgoings have knocked £6308 off the graduate’s wage. This brings the difference in earnings down to £4070. This equates to £339 per month. More than nothing, but not a huge difference. And this doesn’t include any extra earnings on the side which the student can do a much better job of retaining.
Surprised how small the difference is? I certainly was whilst I was writing this.
Here is a chart for comparing a wider range of salaries:
This analysis doesn’t take in to account the extra earning power that gaining a PhD could bring, nor the potential lifestyle benefits of being a student such as autonomy and flexible working hours which it could be argued level the playing field even further. Plus the opportunities afforded to PhD students, which everyone should seize. And yes, student discount if you use it.
Furthermore if you consider the opportunity to make an additional £12k+ per year before incurring tax any difference in earnings can become close to negligible!
I hope that this post has helped explain that the wage gap between UK PhD stipends and grad salaries is not as dramatic it first seems. Perhaps it’s even encouraged you to consider a PhD. If so I’ve written posts to help with your application and an article on how to improve your chances of securing a PhD scholarship . Also if you’re curious you can read about life as a PhD student along with profiles of PhD students around the world .
If you’d like personalised help with your PhD application I am now starting to offer a small number of one-to-one sessions. Please contact me to find out more or click here to book a call.
What do you think about this comparison between a UK PhD stipend and grad salary? Do you think there are any additional factors that I have overlooked? Please share your thoughts in the comments below and if you’ve enjoyed this post you can subscribe to hear about more content:
[1] Some people might say that by continuing studying you’re simply delaying your student loan repayment. Considering most people don’t pay it off in the 30 odd years until any outstanding balance is wiped I think it’s fair to say that this doesn’t ring true.
[2] No council tax is paid on a property if all occupants are students. If you live with one professional they can claim the single occupancy discount of 25% but with two or more professionals the full council tax amount must be paid. If you share in a mixed group it is up to you how you divide it within the group. Ironically given the spirit of this post, last year I voluntarily did pay an equal (third) share of council tax given that my partner was moving to London specifically to live with me…
[3] If you go on to work for a university after your PhD you’ll be enrolled in the USS pension scheme where you’ll usually pay in 9% of your salary and your employer pays in 19%: yes, nineteen! For comparison most often the best private companies may match contributions up to 10%. Pension contributions are often removed from your pay packet before taxes. This effectively leaves you with a smaller salary and hence pay less taxes and national insurance contributions. Between this and your employer’s contributions overall your salary could be “boosted” by quite a bit, around 20% in the USS example, if you consider the pension as part of your long-term salary.
All calculations were carried out using the tax calculator on Martin’s Money Saving Expert. A fantastic website for all things personal finance.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
Related Posts

How To Get A Fully Funded PhD Scholarship
14th February 2023 30th January 2024

How to Find PhD Funding in the UK
2nd January 2018 30th January 2024
17 Comments on “PhD Salary UK: How Much Do PhD Students Get Paid Compared to Graduates?”
It’s probably worth factoring in that most HEIs limit PhD students to a maximum I’m of 10hours pw of external work. By my rough estimate, the student would have to earn £25 an hour to make the money you’ve described here. The side hustle, should probably be halved to reflect a more typical salary. Still a fair whack though.
Hi John, yes that’s a good point and I’ll update the post to reflect this. In my experience £25/hour is realistic, at least here at Imperial, though I appreciate it would rarely get fully utilised. Thanks again
Hello Jeff! I am a Sustainability Consultant from India, looking at PhD opportunities in UK. It would be great if we can connect and discuss a bit about your experience and journey. Looking forward!
Hey Akhyata! Great, yes let’s have a chat. I’ve emailed you to arrange it. Best wishes, Jeff
Hi Jeff! I love your article, I’m a pharmacist juggling the idea of a PhD. I would love to take up on your offer to connect.
Hey Kai! Great, I’ll email you now to arrange it.
Hi Jeff, I am a law grad very interested in further study and pursuing a PhD.
I would love the chance to chat to you further about this article and your experience!
Thanks in advance
Hey Clara, Yeah no worries. I’ll send you an email now to discuss.
Hi Jeff, I’m putting together a PhD proposal at the moment and would really appreciate your input on a few things about the process when you have some free time. Cheers, Ben
Hi Ben, sure no problem, I’m happy to try and help. Let’s discuss over email.
Hi Jeff, Thank you for taking the time to write the articles you do. On this particular article, you have saved us all quite a lot of time. With such a minimal difference even without an additional income, it makes a lot of sense, especially with an increase when you graduate.
Those from the UK can take a £24k loan from the Gov (as if they didn’t have enough debt already). Still, it could enable a student to focus more on academia, speeding up the process and increasing the quality of work.
Apologies Jeff, the stipend and student loan are not available at the same time.
Thanks very much for your comments Tyrone. I’m pleased you find the website useful!
If you can get funding, I agree that there isn’t much of a reason to not do a PhD.
I must admit I’ve never looked much at postgraduate loans, in part because I encourage everyone doing a PhD (in STEM at least) to pursue funding. We’re doing PhDs which can help wider society and it doesn’t make sense for people to have to sacrifice even more by adding extra debt if they can avoid it. Interesting to hear that you can’t take out a loan if you have a stipend, thanks for letting me know.
Perhaps of interest to you, there is a post going live tomorrow which should put the length of a PhD in context of someone’s whole career. In short it doesn’t sacrifice much of a career but of course but make a very useful addition!
If there are any other topics you want to see covered please do let me know.
Best wishes.
Tax Free is not a perk. If you are not paying tax in the UK you cannot contribute to your pension. This may not seem important now, but it will later. This is especially important for mature students who can really lose out if there is a break in their NI contributions.
Thanks for your comment Marie.
The point is that normal tax-paying jobs don’t actually pay quite as much more than PhD stipends once you consider tax. I agree that over the long term avoiding paying taxes is neither a good idea because of things like pensions, nor is it socially ethical. But I don’t think there is any harm in taking 3-4 years out for a PhD:
You have to pay NI for a minimum of only 10 years to qualify for some level of state pension in the UK. After this the pension received simply increases linearly with the number of years of contributions, up to a max of 35 years. With retirement age edging up to 70 that gives at least 45 years between undergrad and retirement so most people will comfortably qualify (for now) for the full state pension. I’d argue that there is ample time to earn some tax free money as a PhD student without having to worry about making enough NI contributions. You can even voluntarily pay NI to gain additional qualifying years on your record. More generally I’d suggest also to not rely on receiving the state pension, I’m not personally betting on there even being a state pension by my own retirement (nor do I want to retire at 70+) so it’s always a good idea to build up your own private pension and savings too!
Hi Jeff, I was looking for funded PhD projects in the Marie Curie network and found a few on the EURAXESS website, but they all require a Master’s degree to apply. I was wondering if there is something I am missing or if you know where to find PhD funding opportunities in the Marie Curie network with only a bachelor’s degree. Thank you.
Hi Alex, thanks for your comment. I must admit I’m not an expert on all of the different Marie Curie funding routes available. If you’ve already done an extensive search then it sounds like yes they all may require a Master’s. By the way, when I first wrote this post I believed that all PhDs funded by UK research councils (UKRI) were at the very specific levels as mentioned in the post. However, I now know that there are some exceptions. For example, the Interactive AI CDT here at Bristol pays a stipend of £22,106: quite a bit higher than the standard non-London rate. CDTs such as this one include a foundation year and not everyone has a Master’s, so it may be worth considering schemes such as this. Best wishes, Jeff.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
Do You Get Paid for a PhD?
- Leon Menezes
- July 31, 2024

For many students who don’t have the luxury of never worrying about money, one of the main considerations when weighing up if a PhD is the right move is how they will support themselves as they pursue their doctoral title. However, gone are the days when the prestigious academic accolade is only available to the upper classes. Several financial options are available for PhD students in the UK, including tax-free stipends and scholarships and seeking employment opportunities around their part-time or full-time studies.
It is crucial for prospective PhD students to fully understand the financial landscape while contemplating taking a monumental step in their academic career. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of each available option and provide prospective PhD students with guidance towards fully-funded options, which make academia accessible and viable to all.

The Complex Landscape of PhD Funding
The funding scenario for PhD programmes in the UK is multifaceted. While some PhD programs come with funding, others do not, leaving students to seek financial support independently. The availability of funding can depend on various factors, including the field of study, the university, and the student’s nationality.
For instance, funding for STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) subjects is often more readily available compared to humanities and social sciences. Additionally, UK and EU students typically have more funding opportunities compared to international students from outside the EU. Via websites such as Postgraduate Studentships , it is easy to find fully-funded PhD programs in a variety of fields. Alternatively, prospective PhD students can directly search for funded PhD programs at the universities of their choice.
For students who are unsuccessful with their scholarship or studentship applications, there are also alternative avenues to explore, such as taking out a PhD loan, exploring the possibilities of employer sponsorship, and even crowdfunding your PhD study.
Stipends: A Primary Source of PhD Support
Stipends are a common form of financial support for PhD students in the UK. These are usually tax-free payments made to students to cover their living expenses while they focus on their studies. The nature of these stipends can vary – some are attached to teaching assistantships or research assistantships, where students are expected to contribute to teaching or research work in their department. This not only provides financial support but also valuable professional experience, which can improve the career prospects of PhD graduates.
Stipend Amounts and Living Costs
For the academic year 2022/2023, PhD stipends in the UK were set at £16,062 for students outside of London and £18,062 for those within London, reflecting the higher cost of living in the capital. These stipends are typically paid over 3.5 years, the standard duration for a full-time PhD programme. However, some institutions may choose to pay the annual stipend for three or four years.
Students should be aware that the cost of living can vary significantly across different parts of the UK, and these stipends may not fully cover all expenses, particularly in more expensive cities. Surprisingly, when the most and least affordable university towns and cities in the UK were ranked in 2023, London came behind Edinburgh and Glasgow. Meanwhile, the most affordable cities included Bournemouth, Cardiff, and Lincoln.
Scholarships: A More Generous Funding Option
Scholarships are another key source of funding for PhD students. These are often more substantial than stipends, with many exceeding £21,000. Scholarships can be provided by universities, external organisations, or industry partners and are usually awarded based on academic excellence, research potential, or specific criteria set by the funding body.
For example, the UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) offers doctoral training partnerships and studentships that provide generous funding and are highly sought after. For more information on PhD scholarships and to find scholarships which may be suited to you, consult the Find a PhD database. At the time of writing, the database contained over 7,000 PhD projects and scholarships in the UK.
Employment Opportunities for PhD Students
Despite the availability of stipends and scholarships, some PhD students may find it necessary to seek part-time employment to support themselves financially. The key is to find flexible work that can be balanced with the demanding schedule of a PhD programme.
Options such as freelance work, private tutoring, remote data entry, or part-time roles in a field related to their studies can be ideal. If finding work related to your field of study is difficult or the prospect feels too demanding, there’s no shame in seeking less mentally strenuous and taxing options or creating an income which aligns with other passions and interests.
Universities often provide career services that can help students find suitable part-time work. Furthermore, there are several websites dedicated to helping students find suitable part-time work, such as Jobs.ac.uk.
Additional Financial Perks for PhD Students
PhD students in the UK are eligible for various financial benefits that can help ease the burden of living expenses. These include council tax exemptions, which can lead to significant savings, especially in urban areas with higher council tax rates. Additionally, students can avail of various discounts on travel, retail, and entertainment, often through schemes like the NUS (National Union of Students) card. In the grand scheme of things, these savings and exemptions may not add up to much, but while you are crunching the numbers and assessing the viability of pursuing a PhD, it is certainly something to consider.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, while the financial aspect of pursuing a PhD in the UK can seem daunting, numerous options are available to support students through their academic journey. Students can navigate this landscape with careful planning and resourcefulness, from stipends and scholarships to part-time employment.
It’s important for prospective PhD students to thoroughly research and understand the financial support available to them, ensuring they can focus on their academic pursuits without the financial stress of contemplating how they will make ends meet. With the right approach, the financial challenges of a PhD can be managed effectively, paving the way for a successful and rewarding academic career which compensates for years of reduced income.
You might also like

The Best London Boroughs for Home Study
Students have much to consider when viewing and moving into their student accommodation. As well as the feel of the home, it is important to

Undergraduate degree vs postgraduate degree: key differences
Going to university and choosing the right educational path are likely going to be some of the most important decisions in your life. This means

Do You Get Paid for a PhD? For many students who don’t have the luxury of never worrying about money, one of the main considerations
Enquire with us
We are here to help and to make your journey to UWS London as smooth as possible. Please use the relevant button below to enquiry about a course you would like to apply, or to clarify any questions you may have about us and our admission’s process. After you submit your enquiry, one of our advisers will get back to you as soon as possible.

- Lecturer and Professor Salaries – Explained
- After a PhD
Based on the 2018/19 HE Single Pay Spine and the typical 2019/20 university grade system, the average possible salary for university staff in the UK is: £40,761 for a Lecturer, £51,590 for a Senior Lecturer, £64,356 for an Associate Professor and £90,891 for a Professor.
Introduction
On this page, we discuss how the UK academic pay scale works, the average salaries of university lecturers and professors, and how they change with academic rank. While we’ve summarised the salaries at the top of this page, we go on to provide a full breakdown for each rank, so continue reading for the full picture.
How Salary Scales Work within UK Universities
In the United Kingdom, there is a single national pay spine that governs the salaries of university staff. The pay spine, formally known as the ‘ HE Single Pay Spine ’, is led by University and College Union ( UCU ) which negotiates salaries, pay structure and employment conditions on behalf of higher education (HE) and further education (FE) institutions.
It’s important to recognise that although the vast majority of UK universities adopt the HE Single Pay Spine, a handful of institutions do not. In such cases, staff salaries are regulated internally and may differ from those stated on this page.
Many considerations go into determining a staff member’s salary, but to summarise, staff members are assigned a grade based on their level of responsibility, experience and position (e.g. Lecturer, Senior Lecturer or Professor) and a corresponding spine value. In turn, the spine value corresponds to a pre-determined salary listed in the ‘HE Single Pay Spine’.
Note: London universities generally offer slightly higher Lecturer and Professor salaries, but this is only to offset the higher cost of living associated with working in the capital. This offset, more commonly referred to as a ‘London Allowance’, is typically in the region of £3,000 per year .
Average Salaries of University Lecturers and Professors in the UK
Based on the 2018/19 HE Single Pay Spine and the average 2019/20 grading levels adopted by three UK universities, we have determined the average salaries of research assistants, lecturers and professors as shown in the table below.
Note: Although the average salaries provide a quick, useful insight, it would be equally advantageous to know the salary range for each position, as academic salaries are relatively dynamic; the reason for this is discussed later.
Table showing average salaries and ranges for Research Assistants, Lecturers and Professors in the UK
The following image shows these salary ranges in the context of the typical progression paths observed for higher education positions within UK universities.
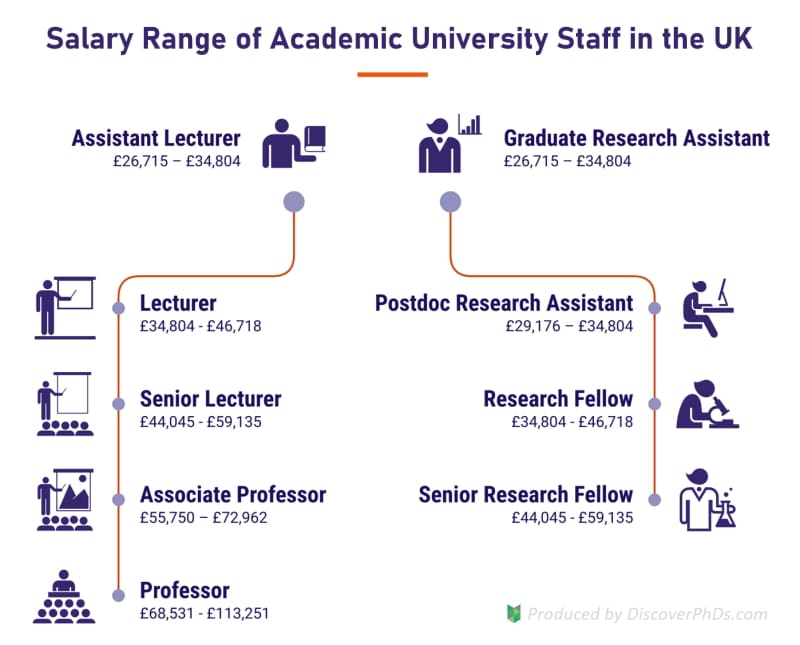
It is worth noting that while salaries can exceed £100,000 per year for positions with significant managerial responsibility, very few individuals will reach these positions. In fact, data from the Office for Students (OfS) shows that in 2017/18, only 1.5% of academic staff were paid over £100,000.
How Salary Increases Works
Salary increases within a grade.
The expectation is that each year, staff members will move up the spine scale and receive a pay increase in line with their new spine level. This will continue until the ceiling of their current grade is reached. At that point, with the exception of inflation-adjusted increases, the staff member will stop receiving wage increases until they move up a grade.
Note: The grade of a staff member reflects the level of responsibility they have, which usually coincides with their job title, i.e. whether they are a Lecturer, an Associate Professor or a Professor.
Increasing Grades
Moving up a grade is only possible when the responsibilities of a staff member increase noticeably or when they are promoted to a higher position, such as from a Senior Lecturer to an Associate Professor.
Non-Monetary Benefits
As with most professions, a university Lecturer or Professor’s job position comes with non-monetary benefits that complement their salary. These will vary between universities, and sometimes even within the same university, but can include:
- Allowances for travel or relocation,
- Discounted or fully waived access to training, university courses and on-site recreational facilities,
- Private healthcare,
UK vs US Lecturer and Professor Salaries
Unlike the United Kingdom, the United States does not have a national academic pay scale. This means that the salaries of Lectures and Professors in the US vary considerably not only between universities but also between states, institution types (public or private) and academic fields.
In addition, because the US does not have a national academic pay scale, it’s common for staff members to negotiate a pay increase when moving to a new institution. This is not generally the case in the UK as it would place staff members outside of the single pay spine.
According to ‘ The Annual Report on the Economic Status of the Profession, 2018-2019 ‘, produced by the American Association of University Professors ( AAUP ), the average university lecturer salary and average university professor salary within the United States is as per the comparison table below.
Table comparing average salaries for Lectures and Professors in the UK and the US
It should be noted that the US salaries stated above have the potential to be skewed. This is because the data provides a total sum only for the number of universities forming the data, and not for the number of staff members holding each position type.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
What Are PhD Salaries? The average cost of undertaking a PhD in the UK is approximately £20,000 per academic year for UK students and £40,000 for international students. To help offset the cost of this, many students question whether undertaking a doctorate comes with a PhD salary.
Here is a table of the most common PhD salary sources in the UK and when they're paid: PhD salary sources Salary type: Salary amount: Typical pay schedule: PhD stipend: £18,622 tax free: Quarterly or monthly: Graduate teaching assistantships (GTAs) £15-20 per hour: Weekly or monthly:
2023/24 UK PhD Salary. PhD salary outside of London: In 2023/24 most new PhD students in the UK will receive a PhD stipend worth at least £18,622 per year. PhD salary in London: In 2023/24 most new PhD students in London will receive an increased stipend to account for cost of living, which is typically around £20,622 per year.
Another factor you might think about when considering a doctorate is whether it'll improve your earning potential. Looking again at the Graduate Outcomes survey from HESA, it does seem that PhD holders are more likely to enjoy higher starting salary and overall earnings than people with a Masters degree.. As you can see in the table below, those with a PhD are more likely to earn more than ...
Avg. Salary £20k — £148k. Master of Finance (MFin) Avg. Salary £26k — £98k. Philosophiae Doctor (PhD) Avg. Salary £39k — £56k. Master of Applied Computer Science (MACS) Avg. Salary £ ...
For the academic year 2022/2023, PhD stipends in the UK were set at £16,062 for students outside of London and £18,062 for those within London, reflecting the higher cost of living in the capital. These stipends are typically paid over 3.5 years, the standard duration for a full-time PhD programme. However, some institutions may choose to pay ...
Note: The above salaries were determined using an average of the 2019/20 grade levels adopted by the University of Birmingham, the University of Bristol and the University of Exeter. Academic Title: Average Salary (per year) Salary Range (per year) Graduate Research Assistant: £30,760: £26,715 - £34,804: Associate Lecturer: £30,760: £ ...
Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), Photonics. Avg. Salary £43k Master of Computer Science (MCS) Avg. Salary £26k — £84k Graduate Certificate, Electronic & Computer Technology. Avg. Salary £44k ...
The length of a UK PhD thesis varies by subject. Dissertations in the Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences tend to be between 60,000 and 100,000 words. Dissertations in STEM subjects are shorter, as much of the information is conveyed through graphs and data tables.
The estimated salary for a Phd is £16,788 per year. This number represents the median, which is the midpoint of the ranges from our proprietary Total Pay Estimate model and based on salaries collected from our users. The "Most Likely Range" represents values that exist within the 25th and 75th percentile of all pay data available for this role.