Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates

How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved August 5, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jun 20, 2024 9:08 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write A Literature Review - A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
A literature review is much more than just another section in your research paper. It forms the very foundation of your research. It is a formal piece of writing where you analyze the existing theoretical framework, principles, and assumptions and use that as a base to shape your approach to the research question.
Curating and drafting a solid literature review section not only lends more credibility to your research paper but also makes your research tighter and better focused. But, writing literature reviews is a difficult task. It requires extensive reading, plus you have to consider market trends and technological and political changes, which tend to change in the blink of an eye.
Now streamline your literature review process with the help of SciSpace Copilot. With this AI research assistant, you can efficiently synthesize and analyze a vast amount of information, identify key themes and trends, and uncover gaps in the existing research. Get real-time explanations, summaries, and answers to your questions for the paper you're reviewing, making navigating and understanding the complex literature landscape easier.
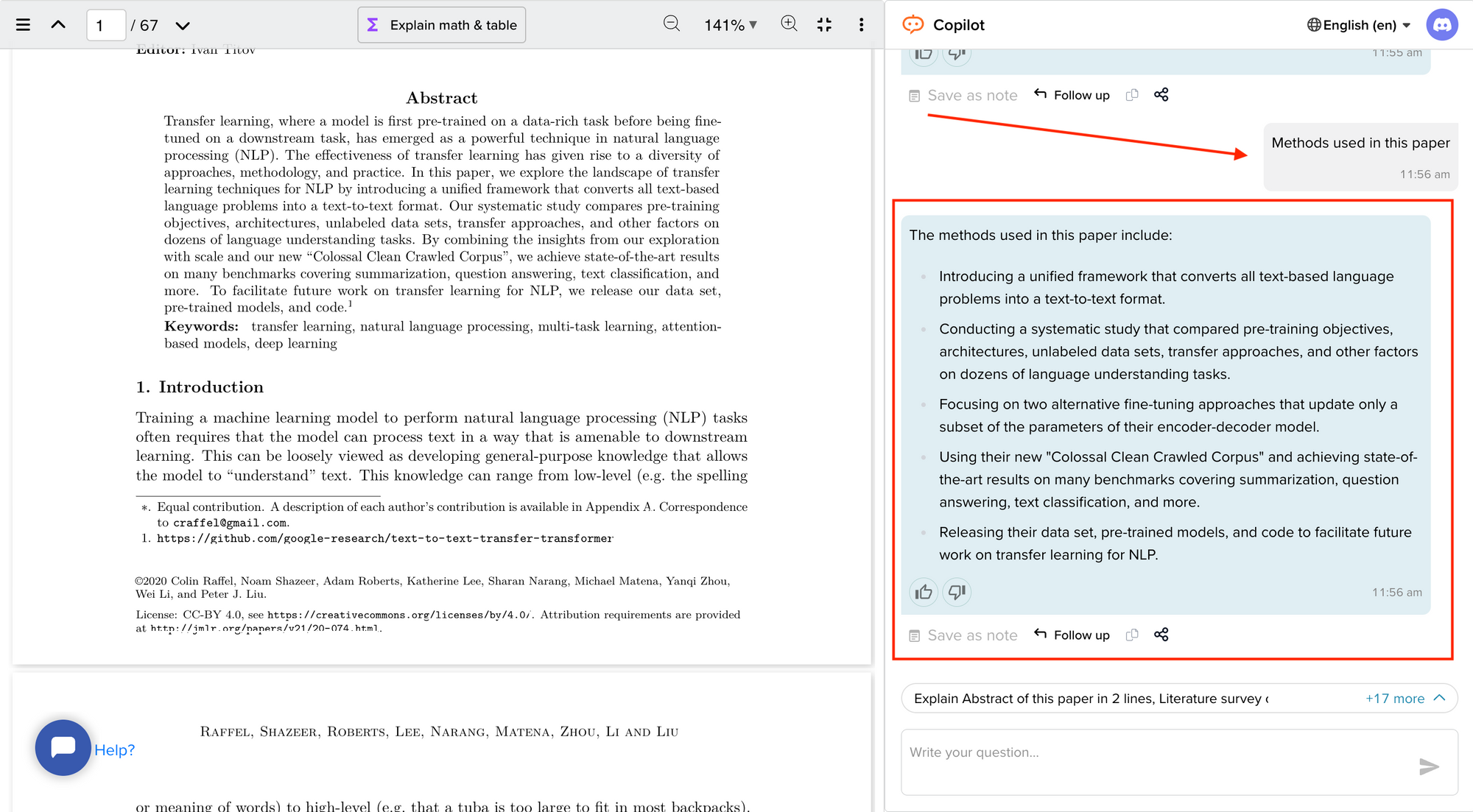
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything from the definition of a literature review, its appropriate length, various types of literature reviews, and how to write one.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a collation of survey, research, critical evaluation, and assessment of the existing literature in a preferred domain.
Eminent researcher and academic Arlene Fink, in her book Conducting Research Literature Reviews , defines it as the following:
“A literature review surveys books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated.
Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have explored while researching a particular topic, and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within a larger field of study.”
Simply put, a literature review can be defined as a critical discussion of relevant pre-existing research around your research question and carving out a definitive place for your study in the existing body of knowledge. Literature reviews can be presented in multiple ways: a section of an article, the whole research paper itself, or a chapter of your thesis.
A literature review does function as a summary of sources, but it also allows you to analyze further, interpret, and examine the stated theories, methods, viewpoints, and, of course, the gaps in the existing content.
As an author, you can discuss and interpret the research question and its various aspects and debate your adopted methods to support the claim.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is meant to help your readers understand the relevance of your research question and where it fits within the existing body of knowledge. As a researcher, you should use it to set the context, build your argument, and establish the need for your study.
What is the importance of a literature review?
The literature review is a critical part of research papers because it helps you:
- Gain an in-depth understanding of your research question and the surrounding area
- Convey that you have a thorough understanding of your research area and are up-to-date with the latest changes and advancements
- Establish how your research is connected or builds on the existing body of knowledge and how it could contribute to further research
- Elaborate on the validity and suitability of your theoretical framework and research methodology
- Identify and highlight gaps and shortcomings in the existing body of knowledge and how things need to change
- Convey to readers how your study is different or how it contributes to the research area
How long should a literature review be?
Ideally, the literature review should take up 15%-40% of the total length of your manuscript. So, if you have a 10,000-word research paper, the minimum word count could be 1500.
Your literature review format depends heavily on the kind of manuscript you are writing — an entire chapter in case of doctoral theses, a part of the introductory section in a research article, to a full-fledged review article that examines the previously published research on a topic.
Another determining factor is the type of research you are doing. The literature review section tends to be longer for secondary research projects than primary research projects.
What are the different types of literature reviews?
All literature reviews are not the same. There are a variety of possible approaches that you can take. It all depends on the type of research you are pursuing.
Here are the different types of literature reviews:
Argumentative review
It is called an argumentative review when you carefully present literature that only supports or counters a specific argument or premise to establish a viewpoint.
Integrative review
It is a type of literature review focused on building a comprehensive understanding of a topic by combining available theoretical frameworks and empirical evidence.
Methodological review
This approach delves into the ''how'' and the ''what" of the research question — you cannot look at the outcome in isolation; you should also review the methodology used.
Systematic review
This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research and collect, report, and analyze data from the studies included in the review.
Meta-analysis review
Meta-analysis uses statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects than those derived from the individual studies included within a review.
Historical review
Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, or phenomenon emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and identify future research's likely directions.
Theoretical Review
This form aims to examine the corpus of theory accumulated regarding an issue, concept, theory, and phenomenon. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories exist, the relationships between them, the degree the existing approaches have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested.
Scoping Review
The Scoping Review is often used at the beginning of an article, dissertation, or research proposal. It is conducted before the research to highlight gaps in the existing body of knowledge and explains why the project should be greenlit.
State-of-the-Art Review
The State-of-the-Art review is conducted periodically, focusing on the most recent research. It describes what is currently known, understood, or agreed upon regarding the research topic and highlights where there are still disagreements.
Can you use the first person in a literature review?
When writing literature reviews, you should avoid the usage of first-person pronouns. It means that instead of "I argue that" or "we argue that," the appropriate expression would be "this research paper argues that."
Do you need an abstract for a literature review?
Ideally, yes. It is always good to have a condensed summary that is self-contained and independent of the rest of your review. As for how to draft one, you can follow the same fundamental idea when preparing an abstract for a literature review. It should also include:
- The research topic and your motivation behind selecting it
- A one-sentence thesis statement
- An explanation of the kinds of literature featured in the review
- Summary of what you've learned
- Conclusions you drew from the literature you reviewed
- Potential implications and future scope for research
Here's an example of the abstract of a literature review
Is a literature review written in the past tense?
Yes, the literature review should ideally be written in the past tense. You should not use the present or future tense when writing one. The exceptions are when you have statements describing events that happened earlier than the literature you are reviewing or events that are currently occurring; then, you can use the past perfect or present perfect tenses.
How many sources for a literature review?
There are multiple approaches to deciding how many sources to include in a literature review section. The first approach would be to look level you are at as a researcher. For instance, a doctoral thesis might need 60+ sources. In contrast, you might only need to refer to 5-15 sources at the undergraduate level.
The second approach is based on the kind of literature review you are doing — whether it is merely a chapter of your paper or if it is a self-contained paper in itself. When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. In the second scenario, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
Quick tips on how to write a literature review
To know how to write a literature review, you must clearly understand its impact and role in establishing your work as substantive research material.
You need to follow the below-mentioned steps, to write a literature review:
- Outline the purpose behind the literature review
- Search relevant literature
- Examine and assess the relevant resources
- Discover connections by drawing deep insights from the resources
- Structure planning to write a good literature review
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review
As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications. You must be able to the answer below questions before you start:
- How many sources do I need to include?
- What kind of sources should I analyze?
- How much should I critically evaluate each source?
- Should I summarize, synthesize or offer a critique of the sources?
- Do I need to include any background information or definitions?
Additionally, you should know that the narrower your research topic is, the swifter it will be for you to restrict the number of sources to be analyzed.
2. Search relevant literature
Dig deeper into search engines to discover what has already been published around your chosen topic. Make sure you thoroughly go through appropriate reference sources like books, reports, journal articles, government docs, and web-based resources.
You must prepare a list of keywords and their different variations. You can start your search from any library’s catalog, provided you are an active member of that institution. The exact keywords can be extended to widen your research over other databases and academic search engines like:
- Google Scholar
- Microsoft Academic
- Science.gov
Besides, it is not advisable to go through every resource word by word. Alternatively, what you can do is you can start by reading the abstract and then decide whether that source is relevant to your research or not.
Additionally, you must spend surplus time assessing the quality and relevance of resources. It would help if you tried preparing a list of citations to ensure that there lies no repetition of authors, publications, or articles in the literature review.
3. Examine and assess the sources
It is nearly impossible for you to go through every detail in the research article. So rather than trying to fetch every detail, you have to analyze and decide which research sources resemble closest and appear relevant to your chosen domain.
While analyzing the sources, you should look to find out answers to questions like:
- What question or problem has the author been describing and debating?
- What is the definition of critical aspects?
- How well the theories, approach, and methodology have been explained?
- Whether the research theory used some conventional or new innovative approach?
- How relevant are the key findings of the work?
- In what ways does it relate to other sources on the same topic?
- What challenges does this research paper pose to the existing theory
- What are the possible contributions or benefits it adds to the subject domain?
Be always mindful that you refer only to credible and authentic resources. It would be best if you always take references from different publications to validate your theory.
Always keep track of important information or data you can present in your literature review right from the beginning. It will help steer your path from any threats of plagiarism and also make it easier to curate an annotated bibliography or reference section.
4. Discover connections
At this stage, you must start deciding on the argument and structure of your literature review. To accomplish this, you must discover and identify the relations and connections between various resources while drafting your abstract.
A few aspects that you should be aware of while writing a literature review include:
- Rise to prominence: Theories and methods that have gained reputation and supporters over time.
- Constant scrutiny: Concepts or theories that repeatedly went under examination.
- Contradictions and conflicts: Theories, both the supporting and the contradictory ones, for the research topic.
- Knowledge gaps: What exactly does it fail to address, and how to bridge them with further research?
- Influential resources: Significant research projects available that have been upheld as milestones or perhaps, something that can modify the current trends
Once you join the dots between various past research works, it will be easier for you to draw a conclusion and identify your contribution to the existing knowledge base.
5. Structure planning to write a good literature review
There exist different ways towards planning and executing the structure of a literature review. The format of a literature review varies and depends upon the length of the research.
Like any other research paper, the literature review format must contain three sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. The goals and objectives of the research question determine what goes inside these three sections.
Nevertheless, a good literature review can be structured according to the chronological, thematic, methodological, or theoretical framework approach.
Literature review samples
1. Standalone
2. As a section of a research paper
How SciSpace Discover makes literature review a breeze?
SciSpace Discover is a one-stop solution to do an effective literature search and get barrier-free access to scientific knowledge. It is an excellent repository where you can find millions of only peer-reviewed articles and full-text PDF files. Here’s more on how you can use it:
Find the right information
Find what you want quickly and easily with comprehensive search filters that let you narrow down papers according to PDF availability, year of publishing, document type, and affiliated institution. Moreover, you can sort the results based on the publishing date, citation count, and relevance.
Assess credibility of papers quickly
When doing the literature review, it is critical to establish the quality of your sources. They form the foundation of your research. SciSpace Discover helps you assess the quality of a source by providing an overview of its references, citations, and performance metrics.
Get the complete picture in no time
SciSpace Discover’s personalized suggestion engine helps you stay on course and get the complete picture of the topic from one place. Every time you visit an article page, it provides you links to related papers. Besides that, it helps you understand what’s trending, who are the top authors, and who are the leading publishers on a topic.
Make referring sources super easy
To ensure you don't lose track of your sources, you must start noting down your references when doing the literature review. SciSpace Discover makes this step effortless. Click the 'cite' button on an article page, and you will receive preloaded citation text in multiple styles — all you've to do is copy-paste it into your manuscript.
Final tips on how to write a literature review
A massive chunk of time and effort is required to write a good literature review. But, if you go about it systematically, you'll be able to save a ton of time and build a solid foundation for your research.
We hope this guide has helped you answer several key questions you have about writing literature reviews.
Would you like to explore SciSpace Discover and kick off your literature search right away? You can get started here .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. how to start a literature review.
• What questions do you want to answer?
• What sources do you need to answer these questions?
• What information do these sources contain?
• How can you use this information to answer your questions?
2. What to include in a literature review?
• A brief background of the problem or issue
• What has previously been done to address the problem or issue
• A description of what you will do in your project
• How this study will contribute to research on the subject
3. Why literature review is important?
The literature review is an important part of any research project because it allows the writer to look at previous studies on a topic and determine existing gaps in the literature, as well as what has already been done. It will also help them to choose the most appropriate method for their own study.
4. How to cite a literature review in APA format?
To cite a literature review in APA style, you need to provide the author's name, the title of the article, and the year of publication. For example: Patel, A. B., & Stokes, G. S. (2012). The relationship between personality and intelligence: A meta-analysis of longitudinal research. Personality and Individual Differences, 53(1), 16-21
5. What are the components of a literature review?
• A brief introduction to the topic, including its background and context. The introduction should also include a rationale for why the study is being conducted and what it will accomplish.
• A description of the methodologies used in the study. This can include information about data collection methods, sample size, and statistical analyses.
• A presentation of the findings in an organized format that helps readers follow along with the author's conclusions.
6. What are common errors in writing literature review?
• Not spending enough time to critically evaluate the relevance of resources, observations and conclusions.
• Totally relying on secondary data while ignoring primary data.
• Letting your personal bias seep into your interpretation of existing literature.
• No detailed explanation of the procedure to discover and identify an appropriate literature review.
7. What are the 5 C's of writing literature review?
• Cite - the sources you utilized and referenced in your research.
• Compare - existing arguments, hypotheses, methodologies, and conclusions found in the knowledge base.
• Contrast - the arguments, topics, methodologies, approaches, and disputes that may be found in the literature.
• Critique - the literature and describe the ideas and opinions you find more convincing and why.
• Connect - the various studies you reviewed in your research.
8. How many sources should a literature review have?
When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. if it is a self-contained paper in itself, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
9. Can literature review have diagrams?
• To represent an abstract idea or concept
• To explain the steps of a process or procedure
• To help readers understand the relationships between different concepts
10. How old should sources be in a literature review?
Sources for a literature review should be as current as possible or not older than ten years. The only exception to this rule is if you are reviewing a historical topic and need to use older sources.
11. What are the types of literature review?
• Argumentative review
• Integrative review
• Methodological review
• Systematic review
• Meta-analysis review
• Historical review
• Theoretical review
• Scoping review
• State-of-the-Art review
12. Is a literature review mandatory?
Yes. Literature review is a mandatory part of any research project. It is a critical step in the process that allows you to establish the scope of your research, and provide a background for the rest of your work.
But before you go,
- Six Online Tools for Easy Literature Review
- Evaluating literature review: systematic vs. scoping reviews
- Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review
- Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
The Sheridan Libraries
- Write a Literature Review
- Sheridan Libraries
- Evaluate This link opens in a new window
What Will You Do Differently?
Please help your librarians by filling out this two-minute survey of today's class session..
Professor, this one's for you .
Introduction
Literature reviews take time. here is some general information to know before you start. .
- VIDEO -- This video is a great overview of the entire process. (2020; North Carolina State University Libraries) --The transcript is included --This is for everyone; ignore the mention of "graduate students" --9.5 minutes, and every second is important
- OVERVIEW -- Read this page from Purdue's OWL. It's not long, and gives some tips to fill in what you just learned from the video.
- NOT A RESEARCH ARTICLE -- A literature review follows a different style, format, and structure from a research article.
| Reports on the work of others. | Reports on original research. | |
| To examine and evaluate previous literature. | To test a hypothesis and/or make an argument. May include a short literature review to introduce the subject. |
- Next: Evaluate >>
- Last Updated: Jul 30, 2024 1:42 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.jhu.edu/lit-review
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar

Credit: Getty
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
WENTING ZHAO: Be focused and avoid jargon
Assistant professor of chemical and biomedical engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore.
When I was a research student, review writing improved my understanding of the history of my field. I also learnt about unmet challenges in the field that triggered ideas.
For example, while writing my first review 1 as a PhD student, I was frustrated by how poorly we understood how cells actively sense, interact with and adapt to nanoparticles used in drug delivery. This experience motivated me to study how the surface properties of nanoparticles can be modified to enhance biological sensing. When I transitioned to my postdoctoral research, this question led me to discover the role of cell-membrane curvature, which led to publications and my current research focus. I wouldn’t have started in this area without writing that review.

Collection: Careers toolkit
A common problem for students writing their first reviews is being overly ambitious. When I wrote mine, I imagined producing a comprehensive summary of every single type of nanomaterial used in biological applications. It ended up becoming a colossal piece of work, with too many papers discussed and without a clear way to categorize them. We published the work in the end, but decided to limit the discussion strictly to nanoparticles for biological sensing, rather than covering how different nanomaterials are used in biology.
My advice to students is to accept that a review is unlike a textbook: it should offer a more focused discussion, and it’s OK to skip some topics so that you do not distract your readers. Students should also consider editorial deadlines, especially for invited reviews: make sure that the review’s scope is not so extensive that it delays the writing.
A good review should also avoid jargon and explain the basic concepts for someone who is new to the field. Although I trained as an engineer, I’m interested in biology, and my research is about developing nanomaterials to manipulate proteins at the cell membrane and how this can affect ageing and cancer. As an ‘outsider’, the reviews that I find most useful for these biological topics are those that speak to me in accessible scientific language.

Bozhi Tian likes to get a variety of perspectives into a review. Credit: Aleksander Prominski
BOZHI TIAN: Have a process and develop your style
Associate professor of chemistry, University of Chicago, Illinois.
In my lab, we start by asking: what is the purpose of this review? My reasons for writing one can include the chance to contribute insights to the scientific community and identify opportunities for my research. I also see review writing as a way to train early-career researchers in soft skills such as project management and leadership. This is especially true for lead authors, because they will learn to work with their co-authors to integrate the various sections into a piece with smooth transitions and no overlaps.
After we have identified the need and purpose of a review article, I will form a team from the researchers in my lab. I try to include students with different areas of expertise, because it is useful to get a variety of perspectives. For example, in the review ‘An atlas of nano-enabled neural interfaces’ 2 , we had authors with backgrounds in biophysics, neuroengineering, neurobiology and materials sciences focusing on different sections of the review.
After this, I will discuss an outline with my team. We go through multiple iterations to make sure that we have scanned the literature sufficiently and do not repeat discussions that have appeared in other reviews. It is also important that the outline is not decided by me alone: students often have fresh ideas that they can bring to the table. Once this is done, we proceed with the writing.
I often remind my students to imagine themselves as ‘artists of science’ and encourage them to develop how they write and present information. Adding more words isn’t always the best way: for example, I enjoy using tables to summarize research progress and suggest future research trajectories. I’ve also considered including short videos in our review papers to highlight key aspects of the work. I think this can increase readership and accessibility because these videos can be easily shared on social-media platforms.
ANKITA ANIRBAN: Timeliness and figures make a huge difference
Editor, Nature Reviews Physics .
One of my roles as a journal editor is to evaluate proposals for reviews. The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic.
It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the most interesting reviews instead provide a discussion about disagreements in the field.

Careers Collection: Publishing
Scientists often centre the story of their primary research papers around their figures — but when it comes to reviews, figures often take a secondary role. In my opinion, review figures are more important than most people think. One of my favourite review-style articles 3 presents a plot bringing together data from multiple research papers (many of which directly contradict each other). This is then used to identify broad trends and suggest underlying mechanisms that could explain all of the different conclusions.
An important role of a review article is to introduce researchers to a field. For this, schematic figures can be useful to illustrate the science being discussed, in much the same way as the first slide of a talk should. That is why, at Nature Reviews, we have in-house illustrators to assist authors. However, simplicity is key, and even without support from professional illustrators, researchers can still make use of many free drawing tools to enhance the value of their review figures.

Yoojin Choi recommends that researchers be open to critiques when writing reviews. Credit: Yoojin Choi
YOOJIN CHOI: Stay updated and be open to suggestions
Research assistant professor, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon.
I started writing the review ‘Biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials using microbial cells and bacteriophages’ 4 as a PhD student in 2018. It took me one year to write the first draft because I was working on the review alongside my PhD research and mostly on my own, with support from my adviser. It took a further year to complete the processes of peer review, revision and publication. During this time, many new papers and even competing reviews were published. To provide the most up-to-date and original review, I had to stay abreast of the literature. In my case, I made use of Google Scholar, which I set to send me daily updates of relevant literature based on key words.
Through my review-writing process, I also learnt to be more open to critiques to enhance the value and increase the readership of my work. Initially, my review was focused only on using microbial cells such as bacteria to produce nanomaterials, which was the subject of my PhD research. Bacteria such as these are known as biofactories: that is, organisms that produce biological material which can be modified to produce useful materials, such as magnetic nanoparticles for drug-delivery purposes.
Synchronized editing: the future of collaborative writing
However, when the first peer-review report came back, all three reviewers suggested expanding the review to cover another type of biofactory: bacteriophages. These are essentially viruses that infect bacteria, and they can also produce nanomaterials.
The feedback eventually led me to include a discussion of the differences between the various biofactories (bacteriophages, bacteria, fungi and microalgae) and their advantages and disadvantages. This turned out to be a great addition because it made the review more comprehensive.
Writing the review also led me to an idea about using nanomaterial-modified microorganisms to produce chemicals, which I’m still researching now.
PAULA MARTIN-GONZALEZ: Make good use of technology
PhD student, University of Cambridge, UK.
Just before the coronavirus lockdown, my PhD adviser and I decided to write a literature review discussing the integration of medical imaging with genomics to improve ovarian cancer management.
As I was researching the review, I noticed a trend in which some papers were consistently being cited by many other papers in the field. It was clear to me that those papers must be important, but as a new member of the field of integrated cancer biology, it was difficult to immediately find and read all of these ‘seminal papers’.
That was when I decided to code a small application to make my literature research more efficient. Using my code, users can enter a query, such as ‘ovarian cancer, computer tomography, radiomics’, and the application searches for all relevant literature archived in databases such as PubMed that feature these key words.
The code then identifies the relevant papers and creates a citation graph of all the references cited in the results of the search. The software highlights papers that have many citation relationships with other papers in the search, and could therefore be called seminal papers.
My code has substantially improved how I organize papers and has informed me of key publications and discoveries in my research field: something that would have taken more time and experience in the field otherwise. After I shared my code on GitHub, I received feedback that it can be daunting for researchers who are not used to coding. Consequently, I am hoping to build a more user-friendly interface in a form of a web page, akin to PubMed or Google Scholar, where users can simply input their queries to generate citation graphs.
Tools and techniques
Most reference managers on the market offer similar capabilities when it comes to providing a Microsoft Word plug-in and producing different citation styles. But depending on your working preferences, some might be more suitable than others.
Reference managers
Attribute | EndNote | Mendeley | Zotero | Paperpile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Cost | A one-time cost of around US$340 but comes with discounts for academics; around $150 for students | Free version available | Free version available | Low and comes with academic discounts |
Level of user support | Extensive user tutorials available; dedicated help desk | Extensive user tutorials available; global network of 5,000 volunteers to advise users | Forum discussions to troubleshoot | Forum discussions to troubleshoot |
Desktop version available for offline use? | Available | Available | Available | Unavailable |
Document storage on cloud | Up to 2 GB (free version) | Up to 2 GB (free version) | Up to 300 MB (free version) | Storage linked to Google Drive |
Compatible with Google Docs? | No | No | Yes | Yes |
Supports collaborative working? | No group working | References can be shared or edited by a maximum of three other users (or more in the paid-for version) | No limit on the number of users | No limit on the number of users |
Here is a comparison of the more popular collaborative writing tools, but there are other options, including Fidus Writer, Manuscript.io, Authorea and Stencila.
Collaborative writing tools
Attribute | Manubot | Overleaf | Google Docs |
|---|---|---|---|
Cost | Free, open source | $15–30 per month, comes with academic discounts | Free, comes with a Google account |
Writing language | Type and write in Markdown* | Type and format in LaTex* | Standard word processor |
Can be used with a mobile device? | No | No | Yes |
References | Bibliographies are built using DOIs, circumventing reference managers | Citation styles can be imported from reference managers | Possible but requires additional referencing tools in a plug-in, such as Paperpile |
*Markdown and LaTex are code-based formatting languages favoured by physicists, mathematicians and computer scientists who code on a regular basis, and less popular in other disciplines such as biology and chemistry.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

Why I’ve removed journal titles from the papers on my CV
Career Column 09 AUG 24

Why we quit: how ‘toxic management’ and pandemic pressures fuelled disillusionment in higher education
Career News 08 AUG 24

Scientists are falling victim to deepfake AI video scams — here’s how to fight back
Career Feature 07 AUG 24

Our local research project put us on the global stage — here’s how you can do it, too
Comment 06 AUG 24

Hybrid conferences should be the norm — optimize them so everyone benefits
Editorial 06 AUG 24

How a space physicist is shaking up China’s research funding
News Q&A 02 AUG 24

The UK launched a metascience unit. Will other countries follow suit?
Nature Index 07 AUG 24
Postdoctoral Fellowships at West China Hospital/West China School of Medicine of Sichuan University
Open to PhD students, PhD, Post-Doc and residents.
Chengdu, Sichuan, China
West China School of Medicine/West China Hospital
Welcome Global Talents to West China Hospital/West China School of Medicine of Sichuan University
Top Talents; Leading Talents; Excellent Overseas Young Talents on National level; Overseas Young Talents
Open Faculty Position in Mathematical and Information Security
We are now seeking outstanding candidates in all areas of mathematics and information security.
Dongguan, Guangdong, China
GREAT BAY INSTITUTE FOR ADVANCED STUDY: Institute of Mathematical and Information Security
Recruitment of Talent Positions at Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University
Call for top experts and scholars in the field of science and technology.
Shenyang, Liaoning, China
Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University
The Recruitment of Fuyao University of Science and Technology
This recruitment of Fuyao University Technologyof Science andUcovers 7 departments including the 6 Schools and the Faculty of Fundamental Disciplines.
Fuzhou, Fujian (CN)
Fuzhou FuYao Institute for Advanced Study
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Reference management. Clean and simple.
Literature review

How to write a literature review in 6 steps
How do you write a good literature review? This step-by-step guide on how to write an excellent literature review covers all aspects of planning and writing literature reviews for academic papers and theses.

How to write a systematic literature review [9 steps]
How do you write a systematic literature review? What types of systematic literature reviews exist and where do you use them? Learn everything you need to know about a systematic literature review in this guide

What is a literature review? [with examples]
Not sure what a literature review is? This guide covers the definition, purpose, and format of a literature review.

What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as you go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface with the option to save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.
- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
| Annotated Bibliography | Literature Review | |
| Purpose | List of citations of books, articles, and other sources with a brief description (annotation) of each source. | Comprehensive and critical analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. |
| Focus | Summary and evaluation of each source, including its relevance, methodology, and key findings. | Provides an overview of the current state of knowledge on a particular subject and identifies gaps, trends, and patterns in existing literature. |
| Structure | Each citation is followed by a concise paragraph (annotation) that describes the source’s content, methodology, and its contribution to the topic. | The literature review is organized thematically or chronologically and involves a synthesis of the findings from different sources to build a narrative or argument. |
| Length | Typically 100-200 words | Length of literature review ranges from a few pages to several chapters |
| Independence | Each source is treated separately, with less emphasis on synthesizing the information across sources. | The writer synthesizes information from multiple sources to present a cohesive overview of the topic. |
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?

6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, the ai revolution: authors’ role in upholding academic..., the future of academia: how ai tools are..., how to write a research proposal: (with examples..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), five things authors need to know when using..., 7 best referencing tools and citation management software..., maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing....

How To Structure Your Literature Review
3 options to help structure your chapter.
By: Amy Rommelspacher (PhD) | Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | November 2020 (Updated May 2023)
Writing the literature review chapter can seem pretty daunting when you’re piecing together your dissertation or thesis. As we’ve discussed before , a good literature review needs to achieve a few very important objectives – it should:
- Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic
- Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these
- Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one)
- Inform your own methodology and research design
To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure . Get the structure of your literature review chapter wrong and you’ll struggle to achieve these objectives. Don’t worry though – in this post, we’ll look at how to structure your literature review for maximum impact (and marks!).

But wait – is this the right time?
Deciding on the structure of your literature review should come towards the end of the literature review process – after you have collected and digested the literature, but before you start writing the chapter.
In other words, you need to first develop a rich understanding of the literature before you even attempt to map out a structure. There’s no use trying to develop a structure before you’ve fully wrapped your head around the existing research.
Equally importantly, you need to have a structure in place before you start writing , or your literature review will most likely end up a rambling, disjointed mess.
Importantly, don’t feel that once you’ve defined a structure you can’t iterate on it. It’s perfectly natural to adjust as you engage in the writing process. As we’ve discussed before , writing is a way of developing your thinking, so it’s quite common for your thinking to change – and therefore, for your chapter structure to change – as you write.
Need a helping hand?
Like any other chapter in your thesis or dissertation, your literature review needs to have a clear, logical structure. At a minimum, it should have three essential components – an introduction , a body and a conclusion .
Let’s take a closer look at each of these.
1: The Introduction Section
Just like any good introduction, the introduction section of your literature review should introduce the purpose and layout (organisation) of the chapter. In other words, your introduction needs to give the reader a taste of what’s to come, and how you’re going to lay that out. Essentially, you should provide the reader with a high-level roadmap of your chapter to give them a taste of the journey that lies ahead.
Here’s an example of the layout visualised in a literature review introduction:
Your introduction should also outline your topic (including any tricky terminology or jargon) and provide an explanation of the scope of your literature review – in other words, what you will and won’t be covering (the delimitations ). This helps ringfence your review and achieve a clear focus . The clearer and narrower your focus, the deeper you can dive into the topic (which is typically where the magic lies).
Depending on the nature of your project, you could also present your stance or point of view at this stage. In other words, after grappling with the literature you’ll have an opinion about what the trends and concerns are in the field as well as what’s lacking. The introduction section can then present these ideas so that it is clear to examiners that you’re aware of how your research connects with existing knowledge .

2: The Body Section
The body of your literature review is the centre of your work. This is where you’ll present, analyse, evaluate and synthesise the existing research. In other words, this is where you’re going to earn (or lose) the most marks. Therefore, it’s important to carefully think about how you will organise your discussion to present it in a clear way.
The body of your literature review should do just as the description of this chapter suggests. It should “review” the literature – in other words, identify, analyse, and synthesise it. So, when thinking about structuring your literature review, you need to think about which structural approach will provide the best “review” for your specific type of research and objectives (we’ll get to this shortly).
There are (broadly speaking) three options for organising your literature review.

Option 1: Chronological (according to date)
Organising the literature chronologically is one of the simplest ways to structure your literature review. You start with what was published first and work your way through the literature until you reach the work published most recently. Pretty straightforward.
The benefit of this option is that it makes it easy to discuss the developments and debates in the field as they emerged over time. Organising your literature chronologically also allows you to highlight how specific articles or pieces of work might have changed the course of the field – in other words, which research has had the most impact . Therefore, this approach is very useful when your research is aimed at understanding how the topic has unfolded over time and is often used by scholars in the field of history. That said, this approach can be utilised by anyone that wants to explore change over time .

For example , if a student of politics is investigating how the understanding of democracy has evolved over time, they could use the chronological approach to provide a narrative that demonstrates how this understanding has changed through the ages.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself to help you structure your literature review chronologically.
- What is the earliest literature published relating to this topic?
- How has the field changed over time? Why?
- What are the most recent discoveries/theories?
In some ways, chronology plays a part whichever way you decide to structure your literature review, because you will always, to a certain extent, be analysing how the literature has developed. However, with the chronological approach, the emphasis is very firmly on how the discussion has evolved over time , as opposed to how all the literature links together (which we’ll discuss next ).
Option 2: Thematic (grouped by theme)
The thematic approach to structuring a literature review means organising your literature by theme or category – for example, by independent variables (i.e. factors that have an impact on a specific outcome).
As you’ve been collecting and synthesising literature , you’ll likely have started seeing some themes or patterns emerging. You can then use these themes or patterns as a structure for your body discussion. The thematic approach is the most common approach and is useful for structuring literature reviews in most fields.
For example, if you were researching which factors contributed towards people trusting an organisation, you might find themes such as consumers’ perceptions of an organisation’s competence, benevolence and integrity. Structuring your literature review thematically would mean structuring your literature review’s body section to discuss each of these themes, one section at a time.

Here are some questions to ask yourself when structuring your literature review by themes:
- Are there any patterns that have come to light in the literature?
- What are the central themes and categories used by the researchers?
- Do I have enough evidence of these themes?
PS – you can see an example of a thematically structured literature review in our literature review sample walkthrough video here.
Option 3: Methodological
The methodological option is a way of structuring your literature review by the research methodologies used . In other words, organising your discussion based on the angle from which each piece of research was approached – for example, qualitative , quantitative or mixed methodologies.
Structuring your literature review by methodology can be useful if you are drawing research from a variety of disciplines and are critiquing different methodologies. The point of this approach is to question how existing research has been conducted, as opposed to what the conclusions and/or findings the research were.

For example, a sociologist might centre their research around critiquing specific fieldwork practices. Their literature review will then be a summary of the fieldwork methodologies used by different studies.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself when structuring your literature review according to methodology:
- Which methodologies have been utilised in this field?
- Which methodology is the most popular (and why)?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the various methodologies?
- How can the existing methodologies inform my own methodology?
3: The Conclusion Section
Once you’ve completed the body section of your literature review using one of the structural approaches we discussed above, you’ll need to “wrap up” your literature review and pull all the pieces together to set the direction for the rest of your dissertation or thesis.
The conclusion is where you’ll present the key findings of your literature review. In this section, you should emphasise the research that is especially important to your research questions and highlight the gaps that exist in the literature. Based on this, you need to make it clear what you will add to the literature – in other words, justify your own research by showing how it will help fill one or more of the gaps you just identified.
Last but not least, if it’s your intention to develop a conceptual framework for your dissertation or thesis, the conclusion section is a good place to present this.

Example: Thematically Structured Review
In the video below, we unpack a literature review chapter so that you can see an example of a thematically structure review in practice.
Let’s Recap
In this article, we’ve discussed how to structure your literature review for maximum impact. Here’s a quick recap of what you need to keep in mind when deciding on your literature review structure:
- Just like other chapters, your literature review needs a clear introduction , body and conclusion .
- The introduction section should provide an overview of what you will discuss in your literature review.
- The body section of your literature review can be organised by chronology , theme or methodology . The right structural approach depends on what you’re trying to achieve with your research.
- The conclusion section should draw together the key findings of your literature review and link them to your research questions.
If you’re ready to get started, be sure to download our free literature review template to fast-track your chapter outline.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
28 Comments
Great work. This is exactly what I was looking for and helps a lot together with your previous post on literature review. One last thing is missing: a link to a great literature chapter of an journal article (maybe with comments of the different sections in this review chapter). Do you know any great literature review chapters?
I agree with you Marin… A great piece
I agree with Marin. This would be quite helpful if you annotate a nicely structured literature from previously published research articles.
Awesome article for my research.
I thank you immensely for this wonderful guide
It is indeed thought and supportive work for the futurist researcher and students
Very educative and good time to get guide. Thank you
Great work, very insightful. Thank you.
Thanks for this wonderful presentation. My question is that do I put all the variables into a single conceptual framework or each hypothesis will have it own conceptual framework?
Thank you very much, very helpful
This is very educative and precise . Thank you very much for dropping this kind of write up .
Pheeww, so damn helpful, thank you for this informative piece.
I’m doing a research project topic ; stool analysis for parasitic worm (enteric) worm, how do I structure it, thanks.
comprehensive explanation. Help us by pasting the URL of some good “literature review” for better understanding.
great piece. thanks for the awesome explanation. it is really worth sharing. I have a little question, if anyone can help me out, which of the options in the body of literature can be best fit if you are writing an architectural thesis that deals with design?
I am doing a research on nanofluids how can l structure it?
Beautifully clear.nThank you!
Lucid! Thankyou!
Brilliant work, well understood, many thanks
I like how this was so clear with simple language 😊😊 thank you so much 😊 for these information 😊
Insightful. I was struggling to come up with a sensible literature review but this has been really helpful. Thank you!
You have given thought-provoking information about the review of the literature.
Thank you. It has made my own research better and to impart your work to students I teach
I learnt a lot from this teaching. It’s a great piece.
I am doing research on EFL teacher motivation for his/her job. How Can I structure it? Is there any detailed template, additional to this?
You are so cool! I do not think I’ve read through something like this before. So nice to find somebody with some genuine thoughts on this issue. Seriously.. thank you for starting this up. This site is one thing that is required on the internet, someone with a little originality!
I’m asked to do conceptual, theoretical and empirical literature, and i just don’t know how to structure it
Asking questions are actually fastidious thing if you are not understanding anything fully, but this article presents good understanding yet.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Libraries | Research Guides
Literature reviews, what is a literature review, learning more about how to do a literature review.
- Planning the Review
- The Research Question
- Choosing Where to Search
- Organizing the Review
- Writing the Review
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the literature you have read.
- Sage Research Methods Core This link opens in a new window SAGE Research Methods supports research at all levels by providing material to guide users through every step of the research process. SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from across the social sciences, including the largest collection of qualitative methods books available online from any scholarly publisher. – Publisher
- Next: Planning the Review >>
- Last Updated: Jul 8, 2024 11:22 AM
- URL: https://libguides.northwestern.edu/literaturereviews
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.9(7); 2013 Jul

Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
Marco pautasso.
1 Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France
2 Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,

The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.

Write a Literature Review
1. narrow your topic and select papers accordingly, 2. search for literature, 3. read the selected articles thoroughly and evaluate them, 4. organize the selected papers by looking for patterns and by developing subtopics, 5. develop a thesis or purpose statement, 6. write the paper, 7. review your work.
- Resources for Gathering and Reading the Literature
- Resources for Writing and Revising
- Other Useful Resources
Ask Us: Chat, email, visit or call

Get Assistance
The library offers a range of helpful services. All of our appointments are free of charge and confidential.
- Book an appointment
Consider your specific area of study. Think about what interests you and what interests other researchers in your field.
Talk to your professor, brainstorm, and read lecture notes and recent issues of periodicals in the field.
Limit your scope to a smaller topic area (ie. focusing on France's role in WWII instead of focusing on WWII in general).
- Four Steps to Narrow Your Research Topic (Video) This 3-minute video provides instructions on how to narrow the focus of your research topic.
- Developing a Research Question + Worksheet Use this worksheet to develop, assess, and refine your research questions. There is also a downloadable PDF version.
Define your source selection criteria (ie. articles published between a specific date range, focusing on a specific geographic region, or using a specific methodology).
Using keywords, search a library database.
Reference lists of recent articles and reviews can lead to other useful papers.
Include any studies contrary to your point of view.
Evaluate and synthesize the studies' findings and conclusions.
Note the following:
- Assumptions some or most researchers seem to make
- Methodologies, testing procedures, subjects, material tested researchers use
- Experts in the field: names/labs that are frequently referenced
- Conflicting theories, results, methodologies
- Popularity of theories and how this has/has not changed over time
- Findings that are common/contested
- Important trends in the research
- The most influential theories
Tip: If your literature review is extensive, find a large table surface, and on it place post-it notes or filing cards to organize all your findings into categories.
- Move them around if you decide that (a) they fit better under different headings, or (b) you need to establish new topic headings.
- Develop headings/subheadings that reflect the major themes and patterns you detected
Write a one or two sentence statement summarizing the conclusion you have reached about the major trends and developments you see in the research that has been conducted on your subject.
- Templates for Writing Thesis Statements This template provides a two-step guide for writing thesis statements. There is also a downloadable PDF version.
- 5 Types of Thesis Statements Learn about five different types of thesis statements to help you choose the best type for your research. There is also a downloadable PDF version.
- 5 Questions to Strengthen Your Thesis Statement Follow these five steps to strengthen your thesis statements. There is also a downloadable PDF version.
Follow the organizational structure you developed above, including the headings and subheadings you constructed.
Make certain that each section links logically to the one before and after.
Structure your sections by themes or subtopics, not by individual theorists or researchers.
- Tip: If you find that each paragraph begins with a researcher's name, it might indicate that, instead of evaluating and comparing the research literature from an analytical point of view, you have simply described what research has been done.
Prioritize analysis over description.
- For example, look at the following two passages and note that Student A merely describes the literature, whereas Student B takes a more analytical and evaluative approach by comparing and contrasting. You can also see that this evaluative approach is well signaled by linguistic markers indicating logical connections (words such as "however," "moreover") and phrases such as "substantiates the claim that," which indicate supporting evidence and Student B's ability to synthesize knowledge.
Student A: Smith (2000) concludes that personal privacy in their living quarters is the most important factor in nursing home residents' perception of their autonomy. He suggests that the physical environment in the more public spaces of the building did not have much impact on their perceptions. Neither the layout of the building nor the activities available seem to make much difference. Jones and Johnstone make the claim that the need to control one's environment is a fundamental need of life (2001), and suggest that the approach of most institutions, which is to provide total care, may be as bad as no care at all. If people have no choices or think that they have none, they become depressed.
Student B: After studying residents and staff from two intermediate care facilities in Calgary, Alberta, Smith (2000) came to the conclusion that except for the amount of personal privacy available to residents, the physical environment of these institutions had minimal if any effect on their perceptions of control (autonomy). However, French (1998) and Haroon (2000) found that availability of private areas is not the only aspect of the physical environment that determines residents' autonomy. Haroon interviewed 115 residents from 32 different nursing homes known to have different levels of autonomy (2000). It was found that physical structures, such as standardized furniture, heating that could not be individually regulated, and no possession of a house key for residents limited their feelings of independence. Moreover, Hope (2002), who interviewed 225 residents from various nursing homes, substantiates the claim that characteristics of the institutional environment such as the extent of resources in the facility, as well as its location, are features which residents have indicated as being of great importance to their independence.
- How to Integrate Critical Voice into Your Literature Review (Video)
- Look at the topic sentences of each paragraph. If you were to read only these sentences, would you find that your paper presented a clear position, logically developed, from beginning to end? The topic sentences of each paragraph should indicate the main points of your literature review.
- Make an outline of each section of the paper and decide whether you need to add information, to delete irrelevant information, or to re-structure sections.
- Read your work out loud. That way you will be better able to identify where you need punctuation marks to signal pauses or divisions within sentences, where you have made grammatical errors, or where your sentences are unclear.
- Since the purpose of a literature review is to demonstrate that the writer is familiar with the important professional literature on the chosen subject, check to make certain that you have covered all of the important, up-to-date, and pertinent texts. In the sciences and some of the social sciences it is important that your literature be quite recent; this is not so important in the humanities.
- Make certain that all of the citations and references are correct and that you are referencing in the appropriate style for your discipline. If you are uncertain which style to use, ask your professor.
- Check to make sure that you have not plagiarized either by failing to cite a source of information, or by using words quoted directly from a source. (Usually if you take three or more words directly from another source, you should put those words within quotation marks, and cite the page.)
- Text should be written in a clear and concise academic style; it should not be descriptive in nature or use the language of everyday speech.
- There should be no grammatical or spelling errors.
- Sentences should flow smoothly and logically.
- << Previous: Start Here
- Next: Resources for Gathering and Reading the Literature >>
- Last Updated: Jan 8, 2024 2:25 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uoguelph.ca/LiteratureReview
Suggest an edit to this guide
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

Writing Literature Reviews
- Literature Review Steps
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Research Question Format
- Managing Your Sources
- Library Resources
A literature review is a vital component of scientific research, serving as the foundation upon which new discoveries are built. Whether you are a budding scientist embarking on your first research project or an experienced researcher looking to refine your literature review skills, this guide is designed to be your compass through the intricate landscape of scientific literature.
In the ever-evolving world of science, staying current and informed is key to producing valuable and impactful research. A well-executed literature review is your ticket to understanding the existing body of knowledge, identifying gaps, and contributing to the advancement of your field.
So What is a Literature Review?
University of Houston Libraries. (2019, October 19). How to Write a Literature Review [Video]. Youtube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6keepo3Kqcs
What is a Literature Review in The Sciences?
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing research; it's a dynamic process of exploration, analysis, and synthesis. It involves systematically examining published works, such as scientific articles, books, and reports, to comprehend the state of knowledge on a specific topic. Your literature review should not only showcase what is known but also critically evaluate the quality of the evidence and identify areas where further research is needed.
Why is it Important?
Knowledge Foundation: A literature review lays the groundwork for your research by providing context and helping you understand the history and evolution of your topic.
Identification of Gaps: By analyzing existing literature, you can pinpoint gaps in current knowledge and formulate research questions that contribute to your field.
Research Design: It aids in shaping your research methodology, helping you choose the most appropriate methods and tools based on previous studies.
Critical Thinking: A literature review requires you to evaluate and synthesize diverse sources, honing your critical thinking skills and enhancing your ability to assess the reliability of research findings.
- Next: Literature Review Steps >>
Conduct a literature review
What is a literature review.
A literature review is a summary of the published work in a field of study. This can be a section of a larger paper or article, or can be the focus of an entire paper. Literature reviews show that you have examined the breadth of knowledge and can justify your thesis or research questions. They are also valuable tools for other researchers who need to find a summary of that field of knowledge.
Unlike an annotated bibliography, which is a list of sources with short descriptions, a literature review synthesizes sources into a summary that has a thesis or statement of purpose—stated or implied—at its core.
How do I write a literature review?
Step 1: define your research scope.
- What is the specific research question that your literature review helps to define?
- Are there a maximum or minimum number of sources that your review should include?
Ask us if you have questions about refining your topic, search methods, writing tips, or citation management.
Step 2: Identify the literature
Start by searching broadly. Literature for your review will typically be acquired through scholarly books, journal articles, and/or dissertations. Develop an understanding of what is out there, what terms are accurate and helpful, etc., and keep track of all of it with citation management tools . If you need help figuring out key terms and where to search, ask us .
Use citation searching to track how scholars interact with, and build upon, previous research:
- Mine the references cited section of each relevant source for additional key sources
- Use Google Scholar or Scopus to find other sources that have cited a particular work
Step 3: Critically analyze the literature
Key to your literature review is a critical analysis of the literature collected around your topic. The analysis will explore relationships, major themes, and any critical gaps in the research expressed in the work. Read and summarize each source with an eye toward analyzing authority, currency, coverage, methodology, and relationship to other works. The University of Toronto's Writing Center provides a comprehensive list of questions you can use to analyze your sources.
Step 4: Categorize your resources
Divide the available resources that pertain to your research into categories reflecting their roles in addressing your research question. Possible ways to categorize resources include organization by:
- methodology
- theoretical/philosophical approach
Regardless of the division, each category should be accompanied by thorough discussions and explanations of strengths and weaknesses, value to the overall survey, and comparisons with similar sources. You may have enough resources when:
- You've used multiple databases and other resources (web portals, repositories, etc.) to get a variety of perspectives on the research topic.
- The same citations are showing up in a variety of databases.
Additional resources
Undergraduate student resources.
- Literature Review Handout (University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill)
- Learn how to write a review of literature (University of Wisconsin-Madison)
Graduate student and faculty resources
- Information Research Strategies (University of Arizona)
- Literature Reviews: An Overview for Graduate Students (NC State University)
- Oliver, P. (2012). Succeeding with Your Literature Review: A Handbook for Students [ebook]
- Machi, L. A. & McEvoy, B. T. (2016). The Literature Review: Six Steps to Success [ebook]
- Graustein, J. S. (2012). How to Write an Exceptional Thesis or Dissertation: A Step-by-Step Guide from Proposal to Successful Defense [ebook]
- Thomas, R. M. & Brubaker, D. L. (2008). Theses and Dissertations: A Guide to Planning, Research, and Writing
- Research Guides
- University Libraries
- Advanced Research Topics
Common Paper Types
- Literature Review
- Scoping Review
- Systematic Review
- Author Profile
Understanding Literature Reviews
I. Getting Started with a Workshop Video (Highly recommended!)
- Searching for Literature Reviews: Before You Write, You Have to Find https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9la5ytz9MmM
A lecture by the Writing Center, TAMU.
II. What is a Literature Review?
- Generally, the purpose of a review is to analyze critically a segment of a published body of knowledge through summary, classification, and comparison of prior research studies, reviews of literature, and theoretical articles. <http://writing.wisc.edu/Handbook/ReviewofLiterature.html>
- A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis. A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information. It might give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations. Or it might trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates. And depending on the situation, the literature review may evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant. < http://writingcenter.unc.edu/resources/handouts-demos/specific-writing-assignments/literature-reviews >
- A literature review is a body of text that aims to review the critical points of current knowledge including substantive findings as well as theoretical and methodological contributions to a particular topic...Its ultimate goal is to bring the reader up to date with current literature on a topic and forms the basis for another goal, such as future research that may be needed in the area. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Literature_review>
III. What Major Steps Literature Reviews Require?
- 1. Develop a review protocol. Protocols define the scope of studies that will be reviewed, the process through which studies will be identified, and the outcomes that will be examined. Protocols also specify the time period during which relevant studies will have been conducted, the outcomes to be examined in the review, and keyword strategies for the literature search. 2. Identify relevant studies, often through a systematic search of the literature. 3. Screen studies for relevance and the adequacy of study design, implementation, and reporting. 4. Retrieve and summarize information on the intervention studied, the study characteristics, and the study findings. 5. Combine findings within studies and across studies when relevant. < http://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/pdf/reference_resources/wwc_procedures_v2_1_standards_handbook.pdf>
- The basic stages in a typical research project are: i) identify your topic of interest, ii) perform a literature review, iii) generate related questions, iv) state your unsolved problem or hypothesis, v) find or develop a solution, and vi) document your results.
- The four stages required: Problem formulation—which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? Literature search—finding materials relevant to the subject being explored Data evaluation—determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic Analysis and interpretation—discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature < http://library.ucsc.edu/help/howto/write-a-literature-review#components >
IV. What Basic Elements Comprise a Literature Review?
- An overview of the subject, issue or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review
- Division of works under review into categories (e.g. those in support of a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative theses entirely)
- Explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research
< http://library.ucsc.edu/help/howto/write-a-literature-review#components > V. Which Citation Tool Are You Going to Use to Manage the Search Results?
- Choose your citation tool before conducing your literature reviews. If you decide to use RefWorks , the information can be found at http://tamu.libguides.com/refworks .
VII. Other Useful Guides
- Literature Reviews (University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill)
- The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It
- How to Write a Literature Review (UCSC)
- Learn how to write a review of literature (WISC)
- Reviewing the Literature
- Next: Scoping Review >>
- Last Updated: Aug 5, 2024 7:43 AM
- URL: https://tamu.libguides.com/c.php?g=1415100
How to Write a Literature Review
- What Is a Literature Review
- What Is the Literature
Writing the Review
Why Are You Writing This?
There are two primary points to remember as you are writing your literature review:
- Stand-alone review: provide an overview and analysis of the current state of research on a topic or question
- Research proposal: explicate the current issues and questions concerning a topic to demonstrate how your proposed research will contribute to the field
- Research report: provide the context to which your work is a contribution.
- Write as you read, and revise as you read more. Rather than wait until you have read everything you are planning to review, start writing as soon as you start reading. You will need to reorganize and revise it all later, but writing a summary of an article when you read it helps you to think more carefully about the article. Having drafts and annotations to work with will also make writing the full review easier since you will not have to rely completely on your memory or have to keep thumbing back through all the articles. Your draft does not need to be in finished, or even presentable, form. The first draft is for you, so you can tell yourself what you are thinking. Later you can rewrite it for others to tell them what you think.
General Steps for Writing a Literature Review
Here is a general outline of steps to write a thematically organized literature review. Remember, though, that there are many ways to approach a literature review, depending on its purpose.
- Stage one: annotated bibliography. As you read articles, books, etc, on your topic, write a brief critical synopsis of each. After going through your reading list, you will have an abstract or annotation of each source you read. Later annotations are likely to include more references to other works since you will have your previous readings to compare, but at this point the important goal is to get accurate critical summaries of each individual work.
- Stage two: thematic organization. Find common themes in the works you read, and organize the works into categories. Typically, each work you include in your review can fit into one category or sub-theme of your main theme, but sometimes a work can fit in more than one. (If each work you read can fit into all the categories you list, you probably need to rethink your organization.) Write some brief paragraphs outlining your categories, how in general the works in each category relate to each other, and how the categories relate to each other and to your overall theme.
- Stage three: more reading. Based on the knowledge you have gained in your reading, you should have a better understanding of the topic and of the literature related to it. Perhaps you have discovered specific researchers who are important to the field, or research methodologies you were not aware of. Look for more literature by those authors, on those methodologies, etc. Also, you may be able to set aside some less relevant areas or articles which you pursued initially. Integrate the new readings into your literature review draft. Reorganize themes and read more as appropriate.
- Stage four: write individual sections. For each thematic section, use your draft annotations (it is a good idea to reread the articles and revise annotations, especially the ones you read initially) to write a section which discusses the articles relevant to that theme. Focus your writing on the theme of that section, showing how the articles relate to each other and to the theme, rather than focusing your writing on each individual article. Use the articles as evidence to support your critique of the theme rather than using the theme as an angle to discuss each article individually.
- Stage five: integrate sections. Now that you have the thematic sections, tie them together with an introduction, conclusion, and some additions and revisions in the sections to show how they relate to each other and to your overall theme.
Specific Points to Include
More specifically, here are some points to address when writing about specific works you are reviewing. In dealing with a paper or an argument or theory, you need to assess it (clearly understand and state the claim) and analyze it (evaluate its reliability, usefulness, validity). Look for the following points as you assess and analyze papers, arguments, etc. You do not need to state them all explicitly, but keep them in mind as you write your review:
- Be specific and be succinct. Briefly state specific findings listed in an article, specific methodologies used in a study, or other important points. Literature reviews are not the place for long quotes or in-depth analysis of each point.
- Be selective. You are trying to boil down a lot of information into a small space. Mention just the most important points (i.e. those most relevant to the review's focus) in each work you review.
- Is it a current article? How old is it? Have its claims, evidence, or arguments been superceded by more recent work? If it is not current, is it important for historical background?
- What specific claims are made? Are they stated clearly?
- What evidence, and what type (experimental, statistical, anecdotal, etc) is offered? Is the evidence relevant? sufficient?
- What arguments are given? What assumptions are made, and are they warranted?
- What is the source of the evidence or other information? The author's own experiments, surveys, etc? Historical records? Government documents? How reliable are the sources?
- Does the author take into account contrary or conflicting evidence and arguments? How does the author address disagreements with other researchers?
- What specific conclusions are drawn? Are they warranted by the evidence?
- How does this article, argument, theory, etc, relate to other work?
These, however, are just the points that should be addressed when writing about a specific work. It is not an outline of how to organize your writing. Your overall theme and categories within that theme should organize your writing, and the above points should be integrated into that organization. That is, rather than write something like:
Smith (2019) claims that blah, and provides evidence x to support it, and says it is probably because of blip. But Smith seems to have neglected factor b. Jones (2021) showed that blah by doing y, which, Jones claims, means it is likely because of blot. But that methodology does not exclude other possibilities. Johnson (2022) hypothesizes blah might be because of some other cause.
list the themes and then say how each article relates to that theme. For example:
Researchers agree that blah (Smith 2019, Jones 2021, Johnson 2022), but they do not agree on why. Smith claims it is probably due to blip, but Jones, by doing y, tries to show it is likely because of blot. Jones' methodology, however, does not exclude other possibilities. Johnson hypothesizes ...
- << Previous: What Is the Literature
- Last Updated: Jan 11, 2024 9:48 AM
- URL: https://libguides.wesleyan.edu/litreview
- Process: Literature Reviews
- Literature Review
- Managing Sources
Ask a Librarian

Does your assignment or publication require that you write a literature review? This guide is intended to help you understand what a literature is, why it is worth doing, and some quick tips composing one.
Understanding Literature Reviews
What is a literature review .
Typically, a literature review is a written discussion that examines publications about a particular subject area or topic. Depending on disciplines, publications, or authors a literature review may be:
A summary of sources An organized presentation of sources A synthesis or interpretation of sources An evaluative analysis of sources
A Literature Review may be part of a process or a product. It may be:
A part of your research process A part of your final research publication An independent publication
Why do a literature review?
The Literature Review will place your research in context. It will help you and your readers:
Locate patterns, relationships, connections, agreements, disagreements, & gaps in understanding Identify methodological and theoretical foundations Identify landmark and exemplary works Situate your voice in a broader conversation with other writers, thinkers, and scholars
The Literature Review will aid your research process. It will help you to:
Establish your knowledge Understand what has been said Define your questions Establish a relevant methodology Refine your voice Situate your voice in the conversation
What does a literature review look like?
The Literature Review structure and organization may include sections such as:
An introduction or overview A body or organizational sub-divisions A conclusion or an explanation of significance
The body of a literature review may be organized in several ways, including:
Chronologically: organized by date of publication Methodologically: organized by type of research method used Thematically: organized by concept, trend, or theme Ideologically: organized by belief, ideology, or school of thought

- Find a focus
- Find models
- Review your target publication
- Track citations
- Read critically
- Manage your citations
- Ask friends, faculty, and librarians
Additional Sources
- Reviewing the literature. Project Planner.
- Literature Review: By UNC Writing Center
- PhD on Track
- CU Graduate Students Thesis & Dissertation Guidance
- CU Honors Thesis Guidance

- Next: Managing Sources >>
- University of Colorado Boulder Libraries
- Research Guides
- Research Strategies
- Last Updated: Jun 20, 2024 3:23 PM
- URL: https://libguides.colorado.edu/strategies/litreview
- © Regents of the University of Colorado

Literature Reviews
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- Peer Review
- Citation/Style Guides
Reference & Instruction Librarian

What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is not:
- just a summary of the sources
- a grouping of broad, unrelated sources
- a compilation of everything that has been written on a particular topic
- literature criticism (think English) or a book review.
So, what is it then?
A literature review :
- Surveys all of the scholarship that has been written about a particular topic (your research question).
- Provides a description , summary , and evaluation of each scholarly work.
- Synthesizes and organizes the previous research by comparing and contrasting the findings or methodology of those previous writings.
"A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. Occasionally, you will be asked to write one as a separate assignment, ..., but more often, it is part of the introduction to an essay, research report, or thesis. In writing the literature review, you aim to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic and their strengths and weaknesses. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available or a set of summaries."
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings that are related directly to your research question. That is, it represents the literature that provides background information on your topic and shows a correspondence between those writings and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand-alone work or the introduction to a more extensive research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
Where Can I Find a Lit Review?
The Literature Review portion of a scholarly article is usually close to the beginning. It often follows the introduction , or may be combined with the introduction. The writer may discuss his or her research question first, or may choose to explain it while surveying previous literature.
If you are lucky, there will be a section heading that includes " literature review ". If not, look for the section of the article with the most citations or footnotes .
- Next: Steps for Conducting a Lit Review >>
- Last Updated: Aug 10, 2024 12:21 PM
- URL: https://westlibrary.txwes.edu/literaturereview
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write a Literature Review for a Research Paper
Last Updated: April 16, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Annaliese Dunne . Annaliese Dunne is a Middle School English Teacher. With over 10 years of teaching experience, her areas of expertise include writing and grammar instruction, as well as teaching reading comprehension. She is also an experienced freelance writer. She received her Bachelor's degree in English. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 38,394 times.
You’re all set to write your first research paper in college, and then your professor says that you need to write a literature review for the paper. If you’ve never even heard of one of these before, don’t panic! It’s a very common assignment and all students have to write their first one eventually. A literature, or lit, review is basically a statement on where the field that you’re studying currently stands. It requires researching key publications within a field and presenting those arguments in a concise, clear section of your paper. It takes some time and research, but once you know what you’re doing, you can tackle the lit review and get on with the rest of your paper.
Evaluating Your Sources

- Your library search engine is the best source for recent or classic work. If your topic is the effect of racism on hiring, try searching keywords like “employment,” “discrimination,” “racism,” and “United States.”
- The librarians in your library are there to help, so don’t hesitate to ask if you need any assistance finding work to read.
- Remember that newer publications aren’t necessarily better than older ones. But it’s important to find new work so your review is up-to-date.
- You could also check the bibliographies in the work you're already using or ask your professor for reading suggestions if you need more ideas. [2] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source

- Try to state each argument as simply as possible. Sum up the author’s point in a sentence, if you can.
- In most cases, you won’t have to read the entire work to understand the author’s argument. Some state their arguments at the beginning very clearly. Only read enough so you can identify that argument so you don’t make too much work for yourself.

- One way you could evaluate a source on employment discrimination is by looking at the evidence. One source might use mostly newspaper articles for evidence, which aren’t always reliable. Another might use statistical data and government studies, which are usually more reliable, and therefore this source is more convincing.
- The evidence that the author uses should also be easy to find, and they should provide clear citations and links if possible. If you can't track down the sources the author is using, then their argument is suspect. [5] X Research source

- If you’re researching music in 20th-century Europe, for example, a musician might say that they had a huge impact on the scene. The fact that this person was a musician at the time could make their opinion biased.
- Remember that all people have bias, so a biased work isn't necessarily useless. But it's something to note in your lit review to show that you've evaluated all your sources carefully.
- Personal bias is another important part of evaluating sources.

- It’s best to take notes while you’re reading and jot down each author’s argument, sources, bias, and your own thoughts on the work. This keeps all of your information in a nice, compact place.

- Sticking with the employment discrimination topic, you might come across some authors who say this is a big problem, and others who don’t think it’s so severe. You might also see some authors acknowledging discrimination but attributing it to different causes.
Organizing Your Review

- If you need help organizing your thoughts, you could always start with a bullet-point list. This is great to get started. However, you'll need to polish this into an actual essay.
- Generally the lit review doesn't need a different format from the rest of the paper, so don't change anything unless your professor tells you to.

- Use section headings like "Introduction" and "Literature Review" to keep yourself organized. You can leave these in if your professor tells you it's okay.
- Some professors may give you a specific outline to base your review or paper around. Always follow their instructions so you get full credit.

- Try to make some larger statements as you write chronologically. You could say, “Prior to the 1950s, scholars didn’t take employment discrimination seriously. In the 1960s and 1970s, new work emerged arguing that it was a major problem that millions of people experience.” This helps move your reader along.
- If you can, tie a chronological lit review to larger historical developments. For example, you could note that the Civil Rights Movement in the 1960s led scholars to analyze discrimination more closely.

- A thematic approach might work better for medical or scientific topics, since there is often a lot of disagreement going on at the same time within these fields. Your topic could be different approaches to the treatment of cancer, with a section on each proposed treatment regimen.
- You could still work chronologically within a thematic organization. When you move on to a new theme, for example, start with the author who first introduced that concept or conclusion.

- There are also systematic reviews, or article-length literature reviews that analyze all the relevant work in a topic. Journals periodically publish pieces like this. These can be great resources for more sources and ideas.
Writing the Review

- Your research might show you that most writers agree that employment discrimination is a problem, but aren’t united on what the causes are. Your opening statement could be, “Scholars are in widespread agreement that African-Americans face discrimination on the job. However, they are divided on the causes. The most common explanations they give are racism among hiring managers, a lack of educational opportunity, and structural disadvantages that produce less past work experience.”
- Your statement doesn’t have to show agreement. It’s perfectly fine to say something like “Child psychologists are currently divided on how homework influences grade-schoolers’ development. Some see it as a crucial intellectual exercise, while others criticize it as busywork that has no real benefit.”

- If you're organizing your essay chronologically, you could break down paragraphs by decade. The first paragraph could explain how authors discussed a problem in the 1960s, then your second one moves to the 1970s, and so on.
- This also works if you're proceeding thematically. You could have a paragraph about authors who support one conclusion and another about authors who disagree.

- Remember to show how each work fits in your main narrative as well. If it’s not clear why a work fits the theme you’ve placed it in, you might lose credit.
- Quotes are always good to demonstrate a point, but make sure you don’t overuse them. 1 or 2 quotes per work is plenty. Stick with your own words for the analysis.

- You could say, “This author overall concludes that racism is not a major component of employment discrimination. This might be true on the job, but it ignores systemic racism, which could lead to disparate outcomes for those who experience it.”
- Be fair when you’re criticizing authors. They’ve probably researched the topic, and though you don’t agree with their conclusions, it’s not fair to act like they don’t know what they’re talking about.

- You can make suggestions no matter what the review shows. If the field is divided, you could say “We clearly need more research to solve these disagreements.” If a field is united, you could say “Perhaps some more diverse voices or perspectives could complicate this field and drive it in new directions.”
- If this lit review is part of a larger research paper, then conclude by stating how your research solves some of these problems.

- For a 10-20-page paper, the lit review can be a few pages. Try not to go over 2-3 unless your professor tells you to.
- In an MA thesis or PhD dissertation, the lit review might make up a whole chapter of over 20 pages.
Expert Q&A

- Always make sure you follow your professor’s directions for writing a literature review. Some may tell you how many sources to use or what types of sources are acceptable. Always stick with these guidelines. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- Cite everything while you write! It’s easy to get caught up and forget to cite during a lit review, so always double check to make sure you referenced everything. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- If you have any questions at all, it's best to ask your professor for guidance. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about writing, check out our in-depth interview with Annaliese Dunne .
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/literature-reviews/
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/literaturereview
- ↑ https://library.concordia.ca/help/writing/literature-review.php
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/evaluatesources
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/conducting_research/writing_a_literature_review.html
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/reviewofliterature/
- ↑ http://www.philau.edu/learning/INC/pdf/Writing%20a%20Literature%20Review%20SLA%20%20Arch.pdf
- ↑ https://libguides.uwf.edu/c.php?g=215199&p=1420568
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

The Cowles Library website will be unavailable on Tuesday, Aug. 6th from 1:00 p.m.- 5:00 p.m. due to a scheduled migration to a new platform. You can reach our list of Research Databases at https://library.drake.edu/az/databases
- Research, Study, Learning
- Archives & Special Collections

- Cowles Library
In This Section:
- Find Journal Articles
- Find Articles in Related Disciplines
- Find Streaming Video
Conducting a Literature Review
- Organizations, Associations, Societies
- For Faculty
What is a Literature Review?
Description.
A literature review, also called a review article or review of literature, surveys the existing research on a topic. The term "literature" in this context refers to published research or scholarship in a particular discipline, rather than "fiction" (like American Literature) or an individual work of literature. In general, literature reviews are most common in the sciences and social sciences.
Literature reviews may be written as standalone works, or as part of a scholarly article or research paper. In either case, the purpose of the review is to summarize and synthesize the key scholarly work that has already been done on the topic at hand. The literature review may also include some analysis and interpretation. A literature review is not a summary of every piece of scholarly research on a topic.
Why are literature reviews useful?
Literature reviews can be very helpful for newer researchers or those unfamiliar with a field by synthesizing the existing research on a given topic, providing the reader with connections and relationships among previous scholarship. Reviews can also be useful to veteran researchers by identifying potentials gaps in the research or steering future research questions toward unexplored areas. If a literature review is part of a scholarly article, it should include an explanation of how the current article adds to the conversation. (From: https://library.drake.edu/englit/criticism)
How is a literature review different from a research article?
Research articles: "are empirical articles that describe one or several related studies on a specific, quantitative, testable research question....they are typically organized into four text sections: Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion." Source: https://psych.uw.edu/storage/writing_center/litrev.pdf)
Steps for Writing a Literature Review
1. Identify and define the topic that you will be reviewing.
The topic, which is commonly a research question (or problem) of some kind, needs to be identified and defined as clearly as possible. You need to have an idea of what you will be reviewing in order to effectively search for references and to write a coherent summary of the research on it. At this stage it can be helpful to write down a description of the research question, area, or topic that you will be reviewing, as well as to identify any keywords that you will be using to search for relevant research.
2. Conduct a Literature Search
Use a range of keywords to search databases such as PsycINFO and any others that may contain relevant articles. You should focus on peer-reviewed, scholarly articles . In SuperSearch and most databases, you may find it helpful to select the Advanced Search mode and include "literature review" or "review of the literature" in addition to your other search terms. Published books may also be helpful, but keep in mind that peer-reviewed articles are widely considered to be the “gold standard” of scientific research. Read through titles and abstracts, select and obtain articles (that is, download, copy, or print them out), and save your searches as needed. Most of the databases you will need are linked to from the Cowles Library Psychology Research guide .
3. Read through the research that you have found and take notes.
Absorb as much information as you can. Read through the articles and books that you have found, and as you do, take notes. The notes should include anything that will be helpful in advancing your own thinking about the topic and in helping you write the literature review (such as key points, ideas, or even page numbers that index key information). Some references may turn out to be more helpful than others; you may notice patterns or striking contrasts between different sources; and some sources may refer to yet other sources of potential interest. This is often the most time-consuming part of the review process. However, it is also where you get to learn about the topic in great detail. You may want to use a Citation Manager to help you keep track of the citations you have found.
4. Organize your notes and thoughts; create an outline.
At this stage, you are close to writing the review itself. However, it is often helpful to first reflect on all the reading that you have done. What patterns stand out? Do the different sources converge on a consensus? Or not? What unresolved questions still remain? You should look over your notes (it may also be helpful to reorganize them), and as you do, to think about how you will present this research in your literature review. Are you going to summarize or critically evaluate? Are you going to use a chronological or other type of organizational structure? It can also be helpful to create an outline of how your literature review will be structured.
5. Write the literature review itself and edit and revise as needed.
The final stage involves writing. When writing, keep in mind that literature reviews are generally characterized by a summary style in which prior research is described sufficiently to explain critical findings but does not include a high level of detail (if readers want to learn about all the specific details of a study, then they can look up the references that you cite and read the original articles themselves). However, the degree of emphasis that is given to individual studies may vary (more or less detail may be warranted depending on how critical or unique a given study was). After you have written a first draft, you should read it carefully and then edit and revise as needed. You may need to repeat this process more than once. It may be helpful to have another person read through your draft(s) and provide feedback.
6. Incorporate the literature review into your research paper draft. (note: this step is only if you are using the literature review to write a research paper. Many times the literature review is an end unto itself).
After the literature review is complete, you should incorporate it into your research paper (if you are writing the review as one component of a larger paper). Depending on the stage at which your paper is at, this may involve merging your literature review into a partially complete Introduction section, writing the rest of the paper around the literature review, or other processes.
These steps were taken from: https://psychology.ucsd.edu/undergraduate-program/undergraduate-resources/academic-writing-resources/writing-research-papers/writing-lit-review.html#6.-Incorporate-the-literature-r
- << Previous: Find Streaming Video
- Next: Organizations, Associations, Societies >>
- Last Updated: Aug 8, 2024 11:43 AM
Borrow & Request
Use materials placed on reserve by your instructors
Borrow books directly from other Iowa academic library partners
Borrow material from libraries around the world
Ask the library to purchase books or other research materials
Collections
Drake history and Iowa political papers
Online access to unique items from the University Archives
Books, eBooks, and videos we highlight throughout the year
Research Support
Handpicked by experts for your area of study
Schedule a one-on-one session with a librarian
A guide to the research process
Librarians who specialize in your area of study
Find, organize, and use your citations
Writing Center, Speaking Center, and other Tutoring
Tools & resources to help develop your study skills
Teaching Support
What we teach and how we can help in your courses
Connect with a librarian
Put material on reserve for your courses
Help with course material adoptions and textbook alternatives
Explore, adopt, adapt, and create open educational resources
Resources to help you publish your research
Collections & Exhibits
Research & teaching, records management, about the archives.
What we do and why
Hours, directions, and guidelines for your Archives visit
Reach, follow, and support the Archives
Guides, tutorials, and library expertise to help you succeed as a scholar
Borrowing materials, finding a study space, locating services
Library services and support directed toward Drake Online and other off-campus students
Provide feedback or resolve a problem with the library
Faculty & Staff
Resources and information literacy expertise to support your teaching
Ask a Question
Cowles Library faculty and staff profiles
What's happening at Cowles Library
Student employment at Cowles Library
Where we are and when we're open
Services for Drake alumni and visitors
Library Spaces
Navigate the library
Check availability and reserve a room
Technology in the library
Mission & Planning
Cowles Library mission and vision
Policies governing use of library resources, space, and services
Library support for diversity, equity, inclusion, and social justice

- 2507 University Avenue
- Des Moines, IA 50311
- (515) 271-2111
Trouble finding something? Try searching , or check out the Get Help page.
- Open access
- Published: 08 August 2024
Research evidence communication for policy-makers: a rapid scoping review on frameworks, guidance and tools, and barriers and facilitators
- Jorge Otávio Maia Barreto ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7648-0472 1 ,
- Roberta Crevelário de Melo 1 , 2 ,
- Letícia Aparecida Lopes Bezerra da Silva 1 , 2 ,
- Bruna Carolina de Araújo 1 , 2 ,
- Cintia de Freitas Oliveira 2 ,
- Tereza Setsuko Toma 2 ,
- Maritsa Carla de Bortoli 2 ,
- Peter Nichols Demaio 3 , 4 &
- Tanja Kuchenmüller 5
Health Research Policy and Systems volume 22 , Article number: 99 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
76 Accesses
Metrics details
Communication is a multifaceted process, ranging from linear, one-way approaches, such as transmitting a simple message, to continuous exchanges and feedback loops among stakeholders. In particular the COVID-19 pandemic underscored the critical need for timely, effective and credible evidence communication to increase awareness, levels of trust, and evidence uptake in policy and practice. However, whether to improve policy responses in crises or address more commonplace societal challenges, comprehensive guidance on evidence communication to decision-makers in health policies and systems remains limited. Our objective was to identify and systematize the global evidence on frameworks, guidance and tools supporting effective communication of research evidence to facilitate knowledge translation and evidence-informed policy-making processes, while also addressing barriers and facilitators.
We conducted a rapid scoping review following the Joanna Briggs Manual. Literature searches were performed across eight indexed databases and two sources of grey literature, without language or time restrictions. The methodological quality of included studies was assessed, and a narrative-interpretative synthesis was applied to present the findings.
We identified 16 documents presenting either complete frameworks or framework components, including guidance and tools, aimed at supporting evidence communication for policy development. These frameworks outlined strategies, theoretical models, barriers and facilitators, as well as insights into policy-makers’ perspectives, communication needs, and preferences. Three primary evidence communication strategies, comprising eleven sub-strategies, emerged: “Health information packaging”, “Targeting and tailoring messages to the audience”, and “Combined communication strategies”. Based on the documented barriers and facilitators at micro, meso and macro levels, critical factors for successful communication of evidence to policy-makers were identified.
Conclusions
Effective communication is indispensable for facilitating knowledge translation and evidence-informed policy-making. Nonetheless gaps persist in frameworks designed to enhance research communication to policy-makers, particularly regarding the effectiveness of multiple communication strategies. To advance in this field, the development of comprehensive frameworks incorporating implementation strategies is warranted. Additionally, barriers and facilitators to implementing effective communication must be recognized and addressed taking diverse contexts into consideration.
Registration https://zenodo.org/record/5578550
Peer Review reports
The COVID-19 pandemic has shown that managing global health emergencies requires a robust evidence ecosystem. This ecosystem must not only produce evidence but also ensure its dissemination and use, enabling decision-makers at all levels of health systems to consider it in a timely manner, in their deliberations and in dialogue with society. The challenges of getting evidence in a timely, systematic and transparent way into decision-making processes for COVID-19 demonstrated failures in communicating results effectively and contextualizing the findings appropriately for local implementation contexts [ 1 ].
To address future challenges in using scientific evidence in government decision-making, enhancing dissemination and communication processes are essential.
In the context of health policy and systems, evidence-informed policy-making (EIPM) is a systematic and transparent process that integrates the research evidence on priority policy issues, into context-sensitive decision-making processes to drive change and achieve impact on health policy and systems [ 2 ]. EIPM is built on processes of translating evidence for practical application, known as Knowledge Translation (KT), which is defined as “the exchange, synthesis, and effective communication of reliable and relevant research results, with focus on promoting interaction among the producers and users of research, removing the barriers to research use, and tailoring information to different target audiences so that effective interventions are used more widely” [ 3 ]. Thus, effective KT requires different competencies, including those related to communication between researchers, policy-makers, and other stakeholders to address barriers to reach mutual understanding, and to improve research use and uptake [ 3 ].
EIPM requires policy-makers to have access to encompassing, relevant, and trustworthy evidence that is easy to understand and apply [ 4 ] and considers their communication needs, preferences [ 5 ], and political decision-making environment [ 6 ]. Barriers to reducing the research-to-policy gap include ineffective communication, and a lack of policy-maker skills to use research evidence [ 7 , 8 ]. Additionally, policy-makers often rely on personal experience, selectively chosen evidence, public opinion, consultation feedback, or due to political and contextual pressures [ 6 ]. To improve the uptake of research in policy decision-making processes, evidence should be structured and packaged in a way that is actionable and relevant for policy-makers, including information on competing interests and other sources of information [ 9 ]. Consequently, effective communication between researchers and policy-makers may require more complex and long-term strategies to set up links and promote exchanges between these groups, as well as specific frameworks and tools to help guide the communication of evidence.
Major EIPM initiatives building on lessons learned from COVID-19 such as The Global Commission on Evidence [ 10 ] and the World Health Organization’s (WHO) “Together on the road to evidence-informed decision-making for health in the post-pandemic era: a call for action” [ 11 ], have recently stressed the importance of effective communication in promoting the uptake of research evidence in decision-making. For example, the Global Commission on Evidence report recommends that evidence groups prepare “derivative products” to communicate evidence tailored to their target audiences, including informational needs, and adopt formats that help understanding of key messages and delving deeper if interested [ 10 ]. Likewise, WHO’s call for action included recommendations for governments and intergovernmental organizations to build national and international capacity to translate, communicate, and support the use of evidence in decision-making [ 11 ].
This scoping review aimed to identify and classify the global evidence on frameworks, guidance and structured tools that support the communication of research evidence to policy-makers. The review focused on better addressing their needs, preferences, perspectives, as well as overcoming barriers and leveraging facilitators in research communication.
Study design and protocol
We conducted a rapid scoping review [ 13 ] according to the Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewer’s Manual [ 14 ] and the PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews [ 15 ]. A prospective protocol is available [ 16 ].
Research questions and eligibility criteria
PCC acronym: Population (P): policymakers; Concept (C): Preferences, perceptions, needs, guidance, tools and frameworks to support effective communication of research evidence; Context (C): Evidence-informed policy-making (EIPM); were used to define two research questions: (1) What are the available frameworks, including guidance and structured tools, to support the evidence communication to policy-makers? and (2) What are the barriers and facilitators, including policy-makers' perspectives, needs, and preferences, regarding evidence communication?
Given the various definitions of policy-makers exist, we included studies identified as having the authority to make decisions about health policies and programs at any level. This includes both individual decision-makers and collective bodies such as councils and participatory structures. We excluded studies involving other stakeholders, such as health professionals, civil society members, or health services users. We also excluded studies with participants whose decision-making power was limited to medical or clinical matters.
We selected documents that presented frameworks, guidance, and structured tools to support effective communication of research evidence to policy-makers. This included those that were part of a larger framework, such as a broader knowledge translation framework. For this study, we used a broad concept of ‘framework’, defining it as any systematization of theoretical or practical elements based on existing theories, including assumptions and any other components of theoretical foundation and practical application. Our focus was on how these structures incorporated policy-makers' perspectives, needs and preferences, while identifying the barriers or facilitators to these communication processes.
Considering the objective of this review, authors defined "framework” as any systematization of elements to support the communication of evidence to decision-makers. Thus, frameworks can be comprehensive or focus on a specific part of the communication process.
Furthermore, for the purpose of this review, we defined “guidance” as any structured set of recommendations on how to carry out evidence communication, including the identification of barriers / facilitators, as well as strategies for addressing these barriers. We defined “structured tool” as any mechanism, process, or support resource designed to aid in communicating evidence.
For this scoping review, we recognize that the communication of evidence is a complex, multifaceted process, influenced by contextual factors. Therefore, we included frameworks, guidance, or structured tools applied to health policy and systems decision-making contexts across various levels of jurisdiction, ranging from local to global, and organization levels, spanning from micro, meso to macro level.
Study designs
The review included primary and secondary research, qualitative and quantitative approaches).
We imposed no restrictions on the country from which data was collected or on the level at which decisions were made. We included studies referencing other social policy sectors, provided they also addressed a health policy or health systems issue. However, studies solely focused on sectors such as education or economics, were excluded if no clear connection to health policy was evident. Additionally, we excluded documents that lacked clear descriptions of the policy-making context.
Time and language
There were no restrictions on the date of publication or language.
Information sources and search strategies
The searches were conducted on 23 October 2021, in eight electronic databases: PubMed, Virtual Health Library Regional Portal, Embase, Cochrane Library, Health Systems Evidence, Social Systems Evidence, Epistemonikos, and Scopus. Grey literature was searched on Opengrey and Google Scholar. The search strategies were adapted for each database. Appendix 1 provides the search strategies in detail. In addition to the searches, EIPM experts, external to the research group, were consulted, and they suggested additional documents of relevance to this review.
Two pairs of reviewers (BCA, CFO, LALBS and RCM) independently screened titles and abstracts, using Rayyan [ 17 ]. Disagreements were resolved by consensus, and when needed, a third reviewer (MCB or TST) was consulted. Full-text documents were assessed by one reviewer and checked by another (BCA, CFO, LALBS and RCM).
Data extraction and categorization
We used a data extraction form developed by our team to extract the characteristics of the studies and relevant information according to predefined categories outlined in the protocol. One reviewer conducted the data extraction, with validation performed by another member of the team (BCA, CFO, LALBS or RCM). Instances where data were unavailable were documented as “not reported”. The characteristics and categories extracted included: study identification (lead author, year of publication, study design); aim/s or objective/s; studies’ focus; study participants and settings (countries where the research was undertaken, types of participants, healthcare setting/s in which the study was carried out); results/findings (message presentation, communication channels, evidence communication framework, guidance or tools, policy-makers perspectives, needs and preferences, conclusion, limitations, and research gaps). Regarding the policy-makers’ perspectives, needs, and preferences about research communication, the data were analyzed and coded into similarity categories (barriers, facilitators, and future actions).
We used the categories outlined by Blessing et al. [ 18 ] to organize our findings based on the information gathered during data extraction. These categories encompass evidence communication strategies aimed at presenting information in a user-friendly format, tailored to diverse audiences, incorporating various means of delivering the information. Blessing et al. identified four broad categories for these strategies: packaging tools, application tools, dissemination and communication tools, and linkage and exchange tools. Additionally, we coded information about the format and means of communication according to these categories, accounting for diverse mechanisms or communication modalities aimed facilitating the assimilation of health information by policy makers.
Methodological appraisal of the included studies
The quality of the studies was assessed using The Joanna Briggs Institute critical appraisal tools ( https://jbi.global/critical-appraisal-tools ), considering the methodological design of each study.
Literature search
Our searches identified 8037 records. After 1977 duplicates were removed, we screened 6060 records, of which 6015 were excluded because they did not meet the eligibility criteria. The experts consulted suggested fourteen additional documents for consideration. Only 16 documents met all the eligibility criteria (primary and secondary qualitative or quantitative studies; policymakers preferences, perceptions or needs; guidance, tools and frameworks to support effective communication for evidence-informed policy-making) and were included in this scoping review [ 5 , 8 , 12 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 ] (Fig. 1 ). The list of excluded studies with the reasons for exclusion is provided in Appendix 2.

Study selection flow diagram, adapted from PRISMA 2020[ 31 ]
Characteristics of the included studies
The included studies were published from 2002 to 2021. Study designs included: systematic reviews [ 8 , 19 , 21 , 27 , 29 ]; a scoping review [ 18 ]; an overview of systematic reviews [ 12 ]; a qualitative review combined with a survey [ 28 ]; a qualitative study [ 22 ]; a quality assurance exercise [ 30 ]; a fundamental qualitative descriptive design [ 5 ]; a qualitative exploratory study [ 24 ]; a mixed qualitative methods case study [ 26 ]; and a technical report that includes a systematic review of reviews (overview) and a scoping review [ 20 ]. Two studies did not inform their own methodological designs, but for the purpose of evaluating the methodological quality, we categorized them as one non-systematic literature review [ 23 ] and one qualitative study [ 25 ].
The primary studies, including those reported in the selected reviews, were carried out in: low- and middle-income countries (LMIC) [ 20 ], high-income countries [ 20 , 21 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 29 , 30 ], and a mix of both LMIC and high-income countries [ 12 ]. Six publications did not provide any information on the countries in which the primary studies were conducted [ 5 , 8 , 18 , 19 , 22 , 28 ].
Among the studies included in this scoping review, thirteen of them described the roles and responsibilities of individuals identified as policy-makers [ 5 , 12 , 18 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 29 , 30 ], seven of which presented a specific definition [ 12 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 26 , 27 ]. Thirteen studies were conducted in healthcare settings [ 5 , 8 , 12 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 30 ], six of which also involved other sectors [ 8 , 20 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 28 ]. Two studies did not specify the settings [ 18 , 29 ], but health messages were communicated to policy-makers.
Additional characteristics of the included studies are presented in Table 1 and detailed in Appendix 3.
Methodological assessment of included studies
We assessed the methodological quality of the included studies. Five systematic reviews [ 8 , 18 , 21 , 27 , 29 ], one overview of systematic reviews [ 12 ], one scoping review [ 19 ], and one report that combined an overview and systematic review of reviews (overview) with a scoping review [ 20 ] were evaluated with the JBI Checklist for Systematic Reviews, but they did not provide information on quality assessment of primary studies or on strategies to minimize data extraction errors. Five of seven studies evaluated with the JBI Checklist for Qualitative Research did not report on influence of researchers in conducting the research [ 5 , 24 , 26 , 28 , 30 ]. One study [ 23 ] evaluated with the scale for the quality assessment of narrative review articles (SANRA) had a score of 8/12, due to the lack of a detailed description of the searches, and the lack of presentation of the designs of the included studies [ 23 ]. Details of the methodological quality assessment are provided in the Appendixes 4.1 to 4.3.
Categorization of findings on evidence communication strategies
We found four studies that presented comprehensive frameworks to guide the evidence communication to policy-makers [ 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 ].
From the perspective of Blessing et al. [ 18 ] and Funk et al. [ 19 ], relevant mechanisms for knowledge translation require structured communication processes, including:
push efforts—providing knowledge to users in appropriate formats;
push methods—information producers use research data and health information to create various products;
pull efforts—enabling policy-makers to identify relevant information;
pull methods—policy-makers commissioning a summary of evidence based on exact specifications;
pull efforts by end-users—e.g., through knowledge brokering;
linkage and exchange efforts—to build relationships between producers and users of health information;
integrated methods—a knowledge translation platform institutionalized in an organization or in the health system [ 18 , 19 ].
To analyze the findings of studies that did not include comprehensive frameworks, but communication strategies or tools that were part of other integrated frameworks, we used a combination of the categories proposed by Blessing et al. [ 18 ], Funk et al. [ 19 ], Langer et al. [ 20 ] and McCormack [ 21 ], covering a wider range of categories that may overlap, but with slightly different nomenclatures. Thus, the findings of this section are categorized into an eclectic framework that aggregates categories from these four studies (Table 2 ).
It is important to note that Langer et al. [ 20 ] and McCormack et al. [ 21 ] presented “communication” and “dissemination” strategies separately, however for the purpose of this review, we considered these strategies together as communication processes involving evidence and decision-makers. The strategies for evidence communication are presented in Appendix 5.
We categorized communication strategies or tools into four groups: Health information packaging tools; Targeting and tailoring the messages; Strategies to improve reach of evidence; and Combined communication strategies (Table 3 ).
The strategies “Health information packaging tools” are composed of synthesis tools [ 5 , 12 , 18 , 19 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 28 , 29 , 30 ], visualization tools [ 12 , 18 , 19 , 23 ], and narratives [ 12 , 20 , 23 ]. The strategies “Targeting and tailoring the messages to the audience” refers to Targeting the message [ 5 , 12 , 18 , 20 , 21 , 26 , 29 , 30 ] and Tailoring the message [ 21 ]. The “Strategies to improve reach of evidence” include: electronic tools for communication [ 5 , 12 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 25 , 28 , 29 ], automated electronic dissemination of information [ 5 , 12 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 28 ], online and social media [ 12 , 20 , 29 ], mass media [ 8 , 12 , 29 ], person-to-person communication [ 5 , 12 , 18 , 19 , 23 , 26 , 28 , 29 , 30 ], linkage and exchange tools [ 12 , 18 , 20 , 28 , 29 ], enhance recipients' ability to use and apply evidence (regardless of delivery mode) [ 12 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 29 ], and combined strategies [ 12 , 20 , 21 ].
Most strategies were reported in only one study; however, the findings related to “Targeting the message” as brief forms for the presentation of evidence were the most cited, with different nomenclatures, such as: evidence summaries ( n = 7) and policy briefs ( n = 6). In addition, there was a higher frequency of findings of synthesis tools, a category composed of systematic reviews ( n = 4) and public health program reports ( n = 3).
Among the findings about the “Strategies to improve reach of evidence”, the most frequently found were Conferences ( n = 4), Newsletters ( n = 2), E-mails ( n = 2), Websites ( n = 2), and Deliberative dialogues ( n = 2). In addition, Information linkage and exchange tools were reported in five studies [ 12 , 18 , 20 , 28 , 29 ], including focusing on individual knowledge brokers ( n = 3), evidence champions or brokers ( n = 2), and networks ( n = 2). Enhance recipients' ability to use and apply evidence (regardless of delivery mode) was most frequently observed in two categories: workshops ( n = 2) and Interventions designed to motivate target audiences to use and apply evidence (e.g., knowledge brokering) ( n = 2).
Combined communication strategies refer to messages that can be implemented together and at the same time [ 12 , 20 , 21 ].
Barriers and facilitators on evidence communication to policy-makers
Perceptions of policy-makers were reported in 13 studies [ 8 , 12 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 ], aggregated into factors that can hinder (barriers) or facilitate (facilitators) the communication of research evidence.
Barriers were divided into eight thematic categories, applicable to the three levels of an organization (micro, meso and macro level) according to RNAO [ 32 ]. The lack of access to information ( n = 8), as well as of the relevance of the information ( n = 8) were mentioned the most frequently. Facilitators were also divided into eight thematic categories, highlighting the format/content of the materials ( n = 7), and relationship between researchers and policy-makers ( n = 5). The small numbers of studies could be misleading in terms of frequency counter. Thus, our analysis of these elements considers the frequency with which they appeared across studies. The Table 4 presents the barriers and facilitators found for each of the influencing factors identified at the micro-, meso-, and macro-levels. More details are available in Appendix 6.
Many influencing factors (barriers and facilitators) reported in the studies appear at the micro level, which corresponds to the individual level, addressing policy-makers’ attitudes, beliefs, and knowledge. At this level, the following was pointed out as barriers: (1) the format for presenting evidence [ 8 , 12 , 22 , 23 , 25 , 26 , 30 ], for example excessive information or inadequate language; (2) difficulty in accessing evidence [ 8 , 12 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 26 , 27 , 30 ], which may be due to an untimely delivery; (3) lack of relevant or good quality research [ 8 , 12 , 22 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 ] that often does not respond to the decision-maker’s needs; (4) lack of ability to deal with evidence, mainly due to lack of training to understand the data [ 8 , 12 , 26 ]; and (5) low collaboration between researchers and policy-makers in the research partnership or alignment between interests [ 12 , 27 , 30 ].
Still at the micro level, facilitators included: (1) format and content of materials [ 8 , 12 , 20 , 21 , 23 , 25 , 27 ], since the message needs to be simple, well-written, clear, concise, easy to read, transparent, and well-organized; (2) relevance of the information produced for policy-makers [ 23 , 25 , 27 ], especially the credibility of research and its applicability to the local context; (3) personalized and specific products for the target audience [ 8 , 20 , 23 , 25 , 29 ], such as the option of printed or online materials; easy access to information [ 8 , 20 , 25 , 27 ] with availability of electronic repositories for the materials produced, and guarantee of internet access for dissemination of content; and (4) relationship between researchers and policy-makers [ 8 , 22 , 27 , 29 , 30 ], which allows, for example, a pre-established dialogue and increased trust between the parties, and the understanding of policy-makers about research results.
The meso level includes aspects of leadership, culture, and available resources within the organization. At this level, the following was identified as barriers: (1) the lack of institutionalization/culture for the use of scientific evidence [ 12 , 29 , 30 ], since policy-makers are not sensitized to use evidence or are unaware of the need to use them in decision-making; and (2) the lack of material/human resources [ 12 , 25 , 27 ], especially internet access, printed materials, as well as specialists to carry out searches for evidence.
The identified facilitators at meso level were: (1) diversity of communication channels [ 23 , 24 ], which can have multiple approaches and be customized to sensitize policy-makers; (2) participation of knowledge brokers [ 21 ] (professionals capable of bringing quality, relevant and effective information to policy-makers); (3) encouraging the production of evidence and knowledge translation plans [ 8 , 20 , 27 ] to assist the communication process; and (4) engagement of policy-makers in research, and in conducting studies and prioritizing the themes to be investigated, based on the needs of health systems.
The macro level encompasses the system, where the extent to which aspects of change are aligned with existing policies and government standards is verified. The barrier identified at this level was political or organizational instability that can be seen in situations such as turnover of managers, sectoral reform processes, or political interests [ 27 ]. No facilitators were reported by the studies.
Future perspectives on evidence communication to policy-makers
In order to systematize the strategies to improve evidence communication to policy-makers, we organized our findings into five categories, linked to the influencing factors presented in the earlier section. The categories and number of studies that referred to each set of strategies were: Format/Content of materials/Delivery mode ( n = 6); Relationship between researchers and policy-makers ( n = 4); Relevance of information ( n = 3); Institutionalization/Culture for the use of scientific evidence ( n = 2); and Access to evidence ( n = 1).
Similarly, information on strategies to improve evidence communication to policy-makers was more frequent at the micro level. The included studies did not report macro-level perspectives (Table 5 ). Details of each category are available in Appendix 7.
Strategies to improve evidence communication to policy-makers at micro level included: (1) format and content of materials and the delivery mode [ 5 , 22 , 23 , 25 , 28 , 30 ]; (2) useful recommendations for the presentation of evidence; relevant information; (3) delivery time for the response to the decision-maker; (4) the need for executive summaries of evidence; relationship between researchers and policy-makers [ 22 , 26 , 29 , 30 ]; (5) involving researchers in policy discussions; fostering mutual trust; (6) more efficient formats of interpersonal contact; and (7) relevant evidence [ 5 , 25 , 26 ], demand-driven and needs-based needs as well as actionable evidence [ 25 ] with recommendations for making evidence available in a timely manner.
At the meso level, the identified strategies included: (1) the institutionalization of and culture for the use of scientific evidence [ 28 , 30 ]; (2) encouraging funders to invest in effective evidence communication; and (3) providing alignment between researchers, implementers and policy-makers.
In this rapid scoping review, evidence communication for policy-makers was seen as an innovative approach that leverages specific frameworks to support the communication of evidence to policy makers. Frameworks and their strategies, including tools and techniques for evidence communication were reported, including how to package and synthesize information, and the means to deliver these results to policy-makers. These strategies cater to the needs and preferences of policy-makers, which were analyzed in this scoping review as barriers and facilitators in evidence communication for policy.
This rapid scoping review addressed two important and comprehensive questions to support the discussion on ways to improve the evidence communication to policy-makers, and to support advances in communication processes related to knowledge translation for EIPM. To our knowledge, this is the first study that focuses on a comprehensive view of evidence communication frameworks, guidance, and tools for health policy, while there are knowledge translation frameworks that refer to communication as an integral part, it does not present a comprehensive framework to improve this specific process.
Evidence communication frameworks
Although communication frameworks to foster the use of evidence are extremely important, this scoping review showed that evidence on this topic is scarce. Only four studies were identified in this review which presented complete communication frameworks [ 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 ], one of which addresses individual-level decision-makers with a clinical focus [ 21 ], which we decided to include in this review as we considered it relevant.
The results of this scoping review reinforce and are reinforced by the results of other previous synthesis studies, in particular those dedicated to systematizing a wide variety of approaches and communication strategies, including KT and communication frameworks, such as the study by Chapman et al. [ 12 ].
We also found various strategies (also called “tools” and “techniques” in the included studies) to support evidence communication. While important, these were in the majority of cases not part of structured, integrated frameworks focusing on improving evidence communication for policy.
This scoping review confirmed that effective communication is a complex process going beyond sending messages or making information available. Communication can be understood as the establishment of links between participants in the information exchange process, where communication barriers need to actively addressed and minimized, and participants are willing to interpolate as senders and receivers of relevant and useful messages, in recurrent communication feedback processes.
The findings of this scoping review showed that at times, it is difficult to separate communication from other processes inherent to decision-making such as deliberative processes that are based on dialogues about evidence, if they are built on communication mechanisms. While communication is embedded in and an inherent part of knowledge translation processes, due attention has not been paid to the strategies to more effectively communicate evidence between researchers, evidence intermediaries and policy-makers.
Categorization of evidence communication strategies
The three groups of communication strategies can be adapted to different contexts, at distinct levels of jurisdiction in policy organizations and health systems. Regarding evidence packaging, evidence syntheses is an important means that the frameworks [ 5 , 12 , 18 , 19 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 28 , 29 , 30 ]. Chapman and colleagues [ 12 ] pointed out that evidence syntheses such as evidence briefs for policy proved to be easier to understand, however, there was no difference in effect when compared to systematic reviews in relation to the use, understanding, belief or perceived usefulness of the evidence. Consequently, there is a need to advance knowledge about the impact of communication formats, and to better define the role that evidence synthesis and systematic reviews can play in a complex communication process.
To effectively communicate, targeting and tailoring messages to the audience seems essential. The highest proportion of studies addressing targeting the message, especially of systematic reviews, [ 5 , 12 , 20 , 30 ] showed this to be a valued strategy. However, the content of systematic reviews may not be the type of message or information most appreciated by policy-makers, and the use of alternative ways to present them may provide better results [ 12 ].
As Chapman and colleagues have already demonstrated [ 12 ], combined strategies with multiple interventions to communicate evidence is the strategy for which we found the least amount of evidence, compared e.g. with tailored and targeted messages. This shows that there is still a knowledge gap to be filled, given that the evidence on multicomponent communication strategies is insufficient to make definitive judgements on their effectiveness [ 12 ]. Nevertheless, a structured framework on communicating evidence to policy-makers should include a set of strategies that can be combined according to the needs and opportunity of a specific context.
Importantly, when the communication strategy involves stakeholders, motivation and commitment are strengthened. For example, in the context of the use of communication for support formulation and implementation of programs and projects, in the perspective of economic development, meetings are an opportunity to involve participants in a project, and when they are engaged in supporting it, they will do all they can to take it forward [ 33 ].
Focus on specific audiences is another strategy that integrated frameworks to support the communication of evidence to policy-makers. These can be divided into Audience segmentation [ 20 ], process of dividing audiences into smaller groups that are homogeneous with respect to critical attributes (e.g., demographics, behavior, ideology), and Improve reach of evidence [ 5 , 8 , 12 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 23 , 25 , 26 , 28 , 29 , 30 ]. Ashcraft et al. [ 29 ] showed that communication efforts are more effective when start early and ongoing engagement with policymakers throughout the research process in order to maximize interest and applicability, researchers seek outside support for their work, consider contextual factors (policy-makers’ own personal beliefs and experiences and the prevailing political ideology of a given context), are timely, relevant and accessible. Other studies showed that the use of multiple strategies increases awareness and encourages the use of evidence for decision-making [ 18 , 23 ] including for policy [ 19 ].
Strategies related to information linkage and exchange [ 12 , 18 , 20 , 28 , 29 ] and person-to-person communication [ 5 , 12 , 18 , 19 , 26 , 28 , 29 , 30 ] showed the contribution of individual or group interaction with a focus on knowledge intermediaries. The interaction of policy-makers with researchers to discuss research results and their implications for practice, including the opportunity to debate implementation strategies, has a profound influence on the use of research evidence as improving recipients’ understanding and hence ability to use and apply evidence (regardless of delivery mode) [ 12 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 29 ].
The categorization of evidence communication strategies based on Langer et al. [ 20 ] and McCormack et al. [ 21 ] showed a lack of knowledge about implementation strategies for evidence communication, including interventions that could forecast and test future scenarios, which were not found among the included studies.
Barriers and facilitators on evidence communication
The evidence communication frameworks and strategies found in this scoping review cater for policy-makers' perspectives, needs and preferences. Lasting and trusted relationships between researchers and policy-makers, and the use of adequate channels, language and materials were identified to be a key facilitator. As an example, Dobbins et al. [ 25 ] pointed out that policy-makers want to choose and control the information they receive in terms of detail (i.e., abstract, full document) and how the information should be delivered (i.e., electronic, hard copy, Internet). Another study reported the interest and value that policymakers placed on accessing information and interacting directly with researchers, and how this helped to increase willingness to use research evidence in policy [ 30 ]. Chapman et al. [ 12 ], however, pointed out that implementation of this interaction with researchers did not show a significant effect.
As for the macro-level barriers and facilitators little to no evidence was found.
The diverse and multifaceted nature of communication can influence the communication strategies, their formats and means of implementation for different sectors of public policy, which poses a challenge for developmental communication specialists due to the need for the clarity of information that is shared. The broader function of communication is to create confidence between stakeholders, evaluate the situation, explore options, and seek ample consensus that leads to sustainable change [ 33 ].
Global and national initiatives can make strong use of evidence communication to promote evidence-informed policy-making, such as the Evidence-Informed Policy Network (EVIPNet), launched in 2005 by the World Health Organization, whose members produce evidence syntheses and support decision-making processes to help interaction between researchers and policy-makers, and to promote the incorporation of evidence into health policies and programs. In the field of health technology assessment, there are also global collaborative networks such as The International Network of Agencies for Health Technology Assessment (INAHTA), as well as regional and national networks. The Cochrane Collaboration is also recognized as a network that supplies high-quality information through systematic reviews to guide healthcare decision-making. However, this form of access to information was rarely mentioned in the included studies. In addition, guides and checklists, such as Checklist and Guidance for Disseminating Findings from Cochrane Intervention Reviews [ 34 ] and Guidelines Policy Influence Plan [ 35 ], may be strategies adopted by researchers to communicate and disseminate evidence to improve the understanding and use of evidence in policy. Given this scenario, it is essential that initiatives such as those described above are ready to facilitate, support and encourage the best communication of evidence.
Limitations
This rapid scoping review has limitations. First, the fact of using studies involving the health sector as an inclusion criterion will have limited relevant information on communication. Second, the searches were undertaken to find only evidence communication frameworks, guidance and tools. A search for studies on knowledge translation, where evidence communication elements can be embedded, could have retrieved more results of interest. Third, although there was no language limitation in the searches, only studies in English were selected, and selection bias could be considered. As this was a rapid review, we must recognize that methodological shortcuts can lead to the loss of some relevant information, but we argue that the risk of other biases has been minimized by our systematic and transparent methods. Fourth, as this is a rapid scoping review, only the title/abstract screening was conducted in duplicate and independently. Fifth, some included studies did not report their methodological design, and we attributed a design classification, based on the described methods, and this may have affected the assessment of the methodological quality of the included studies.
Communication is essential for knowledge translation and evidence-informed policy-making. More evidence on effectiveness of communication strategies remains needed to advance research evidence communication to policy-makers and stablish comprehensive frameworks that can be more useful than single strategies.
Thus, there is a clear need to increase efforts and investments in identifying and applying suitable strategies for establishing effective evidence communication to policy-makers, in particular on comprehensive communication frameworks as part of knowledge translation processes. Research is also needed on communication for policy that should be piloted to have a more rigorous tool and, at the same time, contribute to knowledge generation on what works. It should be taken into consideration that the group of policy-makers is heterogenous, hence the importance of building long-lasting relationships with researchers and other stakeholders to increase mutual understanding and so that relevant information is available at the time of decision-making.
Availability of data and materials
Available in the supplementary material.
La Bella E, Allen C, Lirussi F. Communication vs evidence: What hinders the outreach of science during an infodemic? A narrative review. Integr Med Res. 2021;10(4): 100731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imr.2021.100731 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Scarlett J, Köhler K, Reinap M, Ciobanu A, Tirdea M, Koikov V, et al. CASE STUDY AND LESSONS LEARNT. Evidence-informed Policy Network (EVIPNet) Europe: success stories in knowledge translation. Public Health Panorama. 2018;4(2):161–69. https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1232219/retrieve .
World Health Organization. World report on knowledge for better health: strengthening health systems. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2004. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/43058 .
Oxman AD, Glenton C, Flottorp S, Lewin S, Rosenbaum S, Fretheim A. Development of a checklist for people communicating evidence-based information about the effects of healthcare interventions: a mixed methods study. BMJ Open. 2020;10(7): e036348. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2019-036348 .
Dobbins M, Jack S, Thomas H, Kothari A. Public health decision-makers’ informational needs and preferences for receiving research evidence. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2007;4(3):156–63. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1741-6787.2007.00089.x .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Cairney P, Kwiatkowski R. How to communicate effectively with policymakers: combine insights from psychology and policy studies. Palgrave Commun. 2017;3:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-017-0046-8 .
Article Google Scholar
Oliver K, Innvar S, Lorenc T, Woodman J, Thomas J. A systematic review of barriers to and facilitators of the use of evidence by policymakers. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014;14:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-14-2 .
Oliver K, Cairney P. The dos and don’ts of influencing policy: a systematic review of advice to academics. Palgrave Commun. 2019;5:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-019-0232-y .
Topp L, Mair D, Smillie L, Cairney P. Knowledge management for policy impact: the case of the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre. Palgrave Commun. 2018;4:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-018-0143-3 .
McMaster Health Forum. Global Commission on Evidence to Address Societal Challenges. The Evidence Commission report: a wake-up call and path forward for decision makers, evidence intermediaries, and impact-oriented evidence producers. 2022. https://www.mcmasterforum.org/docs/default-source/evidence-commission/evidence-commission-report.pdf .
World Health Organization. Together on the road to evidence-informed decision-making for health in the ‘post-pandemic era: a call for action. 2021. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/together-on-the-road-to-evidence-informed-decision-making-for-health-in-the-post-pandemic-era-a-draft-call-for-action .
Chapman E, Pantoja T, Kuchenmüller T, Sharma T, Terry RF. Assessing the impact of knowledge communication and dissemination strategies targeted at health policymakers and managers: an overview of systematic reviews. Heal Res Policy Syst. 2021;19(1):140. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-021-00780-4 .
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2007;8(1):19–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/1364557032000119616 .
Joanna Briggs Institute. Critical Appraisal Tools. 2021. https://jbi.global/critical-appraisal-tools .
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169:467–73. https://doi.org/10.7326/M18-0850 .
Barreto JOM, Toma TS, Bortoli MC, Araújo BC, Freitas CO, Silva LALB, et al. Research communication guidance, tools, and frameworks: a rapid scoping review. 2021. https://zenodo.org/record/5578550 .
Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, Elmagarmid A. Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016;5:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0384-4 .
Blessing V, Davé A, Varnai P. Evidence on mechanisms and tools for use of health information for decision-making. 2017. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/326289 .
Funk T, Sharma T, Chapman E, Kuchenmüller T. Translating health information into policy-making: a pragmatic framework. Health Policy. 2022;126(1):16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthpol.2021.10.001 .
Langer L, Tripney J, Gough D. The Science of Using Science: Researching the Use of Research Evidence in Decision-Making. London: EPPI-Centre, Social Science Research Unit, UCL Institute of Education, University College London. 2016. https://eppi.ioe.ac.uk/cms/Default.aspx?tabid=3504 .
McCormack L, Sheridan S, Lewis M, Boudewyns V, Melvin CL, Kistler C, et al. Communication and Dissemination Strategies to Facilitate the Use of Health-Related Evidence. 2013. https://effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov/sites/default/files/pdf/medical-evidence-communication_research.pdf .
Meisel ZF, Mitchell J, Polsky D, Boualam N, McGeoch E, Weiner J, et al. Strengthening partnerships between substance use researchers and policymakers to take advantage of a window of opportunity. Subst Abus Treat Prev Policy. 2019;14:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13011-019-0199-0 .
Purtle J, Nelson KL, Bruns EJ, Hoagwood KE. Dissemination strategies to accelerate the policy impact of children’s mental health services research. Psychiatr Serv. 2020;71(11):1170–8. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.201900527 .
Schmidt AM, Ranney LM, Goldstein AO. Communicating program outcomes to encourage policymaker support for evidence-based state tobacco control. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014;11(12):12562–74. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph111212562 .
Dobbins M, Decorby K, Twiddy T. A knowledge transfer strategy for public health decision makers. Worldviews Evid-Based Nurs. 2004;1(2):120–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1741-6787.2004.t01-1-04009.x .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Wye L, Brangan E, Cameron A, Gabbay J, Klein JH, Pope C. Evidence based policy making and the ‘art’ of commissioning—how English healthcare commissioners access and use information and academic research in ‘real life’ decision-making: an empirical qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2015;15:430. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-015-1091-x .
Innvaer S, Vist G, Trommald M, Oxman A. Health policy-makers’ perceptions of their use of evidence: a systematic review. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2002;7(4):239–44. https://doi.org/10.1258/135581902320432778 .
Lavis JN, Robertson D, Woodside JM, McLeod CB, Abelson J. How can research organizations more effectively transfer research knowledge to decision makers? Milbank Q. 2003;81(2):221–48. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-0009.t01-1-00052 .
Ashcraft LE, Quinn DA, Brownson RC. Strategies for effective dissemination of research to United States policymakers: a systematic review. Implement Sci. 2020;15(1):89. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-020-01046-3 .
Campbell DM, Redman S, Jorm L, Cooke M, Zwi AB, Rychetnik L. Increasing the use of evidence in health policy: practice and views of policymakers and researchers. Aust N Z Health Policy. 2009;6:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8462-6-21 .
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71 .
RNAO. Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario. Examples of common barriers and facilitators. Leading Change Toolkit™ RNAO. Ontario. 2022. https://rnao.ca/leading-change-toolkit/examples-of-common-barriers-and-facilitators .
Mefalopulos P. Development communication sourcebook: Broadening the boundaries of communication. World Bank Publications, 2008. https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/752011468314090450/pdf/446360Dev0Comm1ns0handbook01PUBLIC1.pdf .
Cochrane. Checklist and Guidance for disseminating findings from Cochrane intervention reviews. 2020. https://training.cochrane.org/online-learning/knowledge-translation/how-share-cochrane-evidence/dissemination-essentials-checklist .
International Initiative for Impact Evaluation. Guidelines POLICY INFLUENCE PLAN. https://www.conafe.gob.mx/transparencia1/libro-blanco/2-anexos-edu-inicial/anexo99/MX%20-%20OW3-1079%20-Policy%20Influence%20Plan%20-%20Revised%202011-06-13%20(2).pdf .
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Mabel Figueiró for supporting the development of search strategies for this review.
The authors alone are responsible for the views expressed in this publication and they do not necessarily represent the views, decisions or policies of the institutions with which they are affiliated.
This rapid scoping review was commissioned by the Evidence to Policy and Impact, Research for Health—Science Division—World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland (Consultant Contract No. 202759444/2021).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Oswaldo Cruz Foundation, Fiocruz, Brasília, Brazil
Jorge Otávio Maia Barreto, Roberta Crevelário de Melo, Letícia Aparecida Lopes Bezerra da Silva & Bruna Carolina de Araújo
Health Institute, São Paulo, Brazil
Roberta Crevelário de Melo, Letícia Aparecida Lopes Bezerra da Silva, Bruna Carolina de Araújo, Cintia de Freitas Oliveira, Tereza Setsuko Toma & Maritsa Carla de Bortoli
McMaster Health Forum, Hamilton, Canada
Peter Nichols Demaio
Department of Health, Aging and Society, McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada
Evidence to Policy and Impact, Research for Health, Science Division, World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
Tanja Kuchenmüller
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JOMB, MCB, TST, PND and TK led the protocol development. JOMB, MCB and TST performed an exploratory search to define the search terms. BCA, CFO, LALBS and RCM performed the screening and selection, data extraction and quality assessment of the included studies. MCB and TST helped resolve differences in selection and checked data extraction and study evaluations. BCA, CFO, LALBS, MCB, RCM and TST analyzed the data, and drafted the manuscript. JOMB coordinated the work as a whole. PND and TK contributed critical review and substantial input on drafts prepared by JOMB, MCB, TST, BCA, CFO, LALBS and RCM. All authors revised and approved the protocol and the draft paper.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jorge Otávio Maia Barreto .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
Authors declare that they have no known financial conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the views expressed in this article and they do not necessarily represent the views, decisions, or policies of the institutions with which they are affiliated.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Barreto, J.O.M., de Melo, R.C., da Silva, L.A.L.B. et al. Research evidence communication for policy-makers: a rapid scoping review on frameworks, guidance and tools, and barriers and facilitators. Health Res Policy Sys 22 , 99 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-024-01169-9
Download citation
Received : 26 January 2023
Accepted : 23 June 2024
Published : 08 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-024-01169-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Evidence-informed policy
- Knowledge translation
- Research communication
- Policy-makers
Health Research Policy and Systems
ISSN: 1478-4505
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Learn how to collect, summarize, synthesize, and analyze key sources on a topic in a literature review. Find out the purposes, conventions, and structures of lit reviews in different disciplines and situations.
3. Evaluate and select literature. 4. Analyze the literature. 5. Plan the structure of your literature review. 6. Write your literature review. Other resources to help you write a successful literature review.
A literature review is important because it: Explains the background of research on a topic. Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area. Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas. Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic. Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
Learn how to write a literature review in three steps: finding, understanding and synthesising the relevant literature for your research topic. Get tips, examples and a free template to help you structure and plan your review chapter.
Learn what a literature review is, why it is important, and how to write one for different types of research. This guide covers the definition, purpose, format, and examples of literature reviews, and how to use SciSpace Copilot to streamline your process.
Lit Review Article: Research Article: Does What? Reports on the work of others. Reports on original research. Purpose: To examine and evaluate previous literature. To test a hypothesis and/or make an argument. May include a short literature review to introduce the subject.
he simplest thing of all—structure. Everything you write has three components: a beginning, a middle and an e. d and each serves a different purpose. In practice, this means your review will have an introduction, a main body where you review the literature an. a conclusion where you tie things up.
Learn from editors and scientists who share their tips on writing reviews for scientific journals. Find out how to choose a topic, structure the review, avoid jargon, use figures and stay updated.
Learn how to write a literature review for academic papers and theses in 6 steps. Find out what a literature review is, how to do a systematic review, and see examples of different types of reviews.
Learn the purpose, structure, and tips of writing a literature review for research. See a literature review example on climate change impacts on biodiversity and how to use Paperpal to find academic papers faster.
This resource is adapted from the Graduate Writing Place's workshop "Tackling a Literature Review & Synthesizing the Work of Others." For more information about our workshops, see Graduate Writing Workshops. INTRODUCTION Compiling and synthesizing literature as a justification for one's own research is a key element of most academic work.
Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic. Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these. Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one) Inform your own methodology and research design. To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure.
Mapping the gap. The purpose of the literature review section of a manuscript is not to report what is known about your topic. The purpose is to identify what remains unknown—what academic writing scholar Janet Giltrow has called the 'knowledge deficit'—thus establishing the need for your research study [].In an earlier Writer's Craft instalment, the Problem-Gap-Hook heuristic was ...
A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the ...
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
Note the following: Findings that are common/contested; Important trends in the research; The most influential theories; Tip: If your literature review is extensive, find a large table surface, and on it place post-it notes or filing cards to organize all your findings into categories.
Your report, in addition to detailing the methods, results, etc. of your research, should show how your work relates to others' work. A literature review for a research report is often a revision of the review for a research proposal, which can be a revision of a stand-alone review. Each revision should be a fairly extensive revision.
A literature review is a vital component of scientific research, serving as the foundation upon which new discoveries are built. Whether you are a budding scientist embarking on your first research project or an experienced researcher looking to refine your literature review skills, this guide is designed to be your compass through the intricate landscape of scientific literature.
Since the literature review forms the backbone of your research, writing a clear and thorough review is essential. The steps below will help you do so: 1. Search for relevant information and findings. In research, information published on a given subject is called "literature" or "background literature.".
Step 3: Critically analyze the literature. Key to your literature review is a critical analysis of the literature collected around your topic. The analysis will explore relationships, major themes, and any critical gaps in the research expressed in the work. Read and summarize each source with an eye toward analyzing authority, currency ...
The basic stages in a typical research project are: i) identify your topic of interest, ii) perform a literature review, iii) generate related questions, iv) state your unsolved problem or hypothesis, v) find or develop a solution, and vi) document your results.
Look for more literature by those authors, on those methodologies, etc. Also, you may be able to set aside some less relevant areas or articles which you pursued initially. Integrate the new readings into your literature review draft. Reorganize themes and read more as appropriate. Stage four: write individual sections.
The Literature Review will place your research in context. It will help you and your readers: Locate patterns, relationships, connections, agreements, disagreements, & gaps in understanding. Identify methodological and theoretical foundations. Identify landmark and exemplary works. Situate your voice in a broader conversation with other writers ...
The Literature Review portion of a scholarly article is usually close to the beginning. It often follows the introduction, or may be combined with the introduction.The writer may discuss his or her research question first, or may choose to explain it while surveying previous literature.. If you are lucky, there will be a section heading that includes "literature review".
Download Article. 1. Locate the most recent work in the field. In general, a literature review should be up-to-date so your reader knows the current state of the field. Start by looking for the most recent publications in the field you're working on. Use these works to get an idea of where the field currently lies.
Description. A literature review, also called a review article or review of literature, surveys the existing research on a topic. The term "literature" in this context refers to published research or scholarship in a particular discipline, rather than "fiction" (like American Literature) or an individual work of literature.
We conducted a rapid scoping review following the Joanna Briggs Manual. Literature searches were performed across eight indexed databases and two sources of grey literature, without language or time restrictions. The methodological quality of included studies was assessed, and a narrative-interpretative synthesis was applied to present the ...
This is followed by the conceptual framework and its implications for new-age consumer decision-making and neural processes built around the data in correspondence to literature. Subsequently, we discuss the contributions to theory and practice. Lastly, we conclude with a detailed research agenda. 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
BackgroundThe intent of plain-language resources (PLRs) reporting medical research information is to advance health literacy among the general public and enable them to participate in shared decision-making (SDM). Regulatory mandates coupled with academic and industry initiatives have given rise to an increasing volume of PLRs summarizing medical research information. However, there is ...